Abstract
An asset allocation optimization model for key clients and financial products is developed and deployed on a business platform by compiling a program to a module using MATLAB to show how to integrate financial big data and fintech in a real application for a bank. Firstly, we establish a single objective linear programming model with the percent of assets in products as the decision variables, the minimum-weighted duration as the objective, and the business requirements as constraints. Then, we select non-integer linear programming as the model solver by testing two algorithm solvers with six real test cases separately, according to the solving time. Finally, we directly compile the model and the algorithm program into a module to complete the deployment into a business platform to quickly complete the transformation of data and model the actual productivity of the bank.
1. Introduction
Big data are having a profound impact on the economy, politics, culture, and people’s lives. In finance, massive economic and financial data can be continuously accumulated and precipitated. To comprehensively use and share the existing financial data, and provide support and service for banks, the height, breadth, depth, and precision of the omnidirectional data promote banking business ability; this is one of the most important research directions in the field of financial big data research [1]. With the rapid development of financial big data, fintech, represented by bank financial platforms, is undergoing a data service revolution, including personalized service, big data credit investigation, intelligent investment, risk pricing, quantitative investment, profiling tax and financial behavior, and so on [2,3,4]. Financial big data promote the development of fintech, whereas fintech is the carrier of value realization of financial big data. The two are closely related but have different connotations. However, both are based on the financial industry and share the purpose of promoting the development of the financial industry, so the two can be naturally integrated. If we regard financial big data as data and fintech as technology, then the joining point of the two can be easily found because data need to be applied through technology. Determining how to combine the two is a broad and abstract question. In this study, we aimed to analyze the fusion mode and process of the two through a specific and typical example regarding asset allocation for key clients or for designing financial products in a bank.
This asset allocation example was obtained from key client business. Although the proportions of key client business in different types of banks are somewhat different, they are crucial to the stability of the bank’s business. Key client business is characterized by a large amount of capital, stable business, and low transaction costs [5]. However, key clients generally have specific requirements for banks, such as requiring a guaranteed annualized rate of return within a certain storage time range. To meet the basic requirements of key clients, the investment department of the bank usually allocates the fund of key clients according to the income, delivery period, asset capacity, and other attributes of the assets. When the number of assets is lower, the investment personnel can manually handle the allocation of these assets. With the development of financial business, banks have increasing amounts of investable assets, so manual asset allocation efficiency is low. In addition, it is impossible to consider the capital allocation problem of multiple key clients because manual configuration prioritizes the allocation of good assets to the first clients, so it is difficult to guarantee the minimum return requirements of the key clients. Similar to the business of key clients, the business of designing financial products also involves the allocation of assets, such as financial products to be issued for internet finance [6] (Chen et al., 2019). Therefore, to facilitate unifying the description of the problem, the asset allocation of key clients and product design are unified into product design, and namely products.
As a general introduction of this problem, there are products needing to be configured, whose properties are capital amount, minimum return, investment term, etc., and their capital should be allocated to assets, each of which has capital capacity, return, a delivery date, etc. The principle of capital allocation is to make the weighted duration a minimum when the basic requirements are met. So, this is a typical programming problem, which can be solved by operations research. However, if the size of and are relatively larger, the solving time will also become longer. For a banking platform, the system response time cannot exceed a certain value. In addition, key clients have other requirements, while assets have other constraints. Therefore, considering these practical requirements, this problem becomes more complicated and deserves further study.
Some scholars studied the asset allocation of banks. Wu [7] studied the impact of capital constraint on the asset allocation of banks from the perspective of regulations. Sang et al. [8] studied the credit asset allocation model of some customers in commercial banks based on the principle of matching risk and return. Ren et al. [9] reviewed the theory and model of asset allocation. Wang et al. [10] conducted theoretical and empirical research on the relationship between asset bubbles and bank stability. Zhu et al. [11] analyzed the optimal discrete-time asset allocation under a higher-order hidden Markov model. Zhang et al. [12] studied the portfolio model of multi-risk assets with institutional transformation. Li et al. [13] developed an asset allocation model to explain how inflation experiences affect household investment and consumption through corresponding inflation expectations. Ahamed [14] investigated whether a shift toward non-interest income activities improves the profitability of Indian banks and, if so, how it varies across ownership groups and banks with different asset qualities. Ormos and Timotity [15] introduced an equilibrium asset pricing model built on the relationship between a novel risk measure, the expected downside risk (EDR), and the expected return.
Although these studies focused on asset allocation and its related fields, they are different from the objectives of this study. We focused on how to effectively use banking data to establish an asset allocation model for products, more specifically, for key clients and designing financial products.
There are three main contributions in this paper. The first is establishing a linear programming model of asset allocation according to banking requirements. In this smart design, we used the equality constraints of signed functions to express the non-value range of variables. Second, a set of test examples was used to test the solvers of two different algorithms in MATLAB. According to the requirement of the solving time being less than the maximum system response time, a non-integer programming solver was selected. Third, with the MATLAB compilation function, the program of the model and algorithm was directly compiled into a module to complete its deployment on the business platform, to quickly complete the transformation of data, and to model the actual productivity of the bank. The whole process shows how to integrate financial big data and fintech to improve financial business.
Next, an example of using data to achieve optimal asset allocation through modeling is described in detail. The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 describes the data to be used in the example. Section 3 presents the detailed process of modeling, including decision variables, objective definition, and constraints. Section 4 discusses and evaluates the solvers for the model and selecting the non-integer programming solver as the final solver. Section 5 explains how to deploy the model in a business platform and outlines the whole workflow of model deployment and operation. Finally, the paper ends with a brief conclusion. All sections are organized by the logic of the regular modeling process.
2. Data
The problem was how to optimize the allocation of available assets into various products while ensuring that the products and assets meet the constraints of various attributes. By comprehensively analyzing the business requirements of products and assets, the available data attributes of products and assets were extracted from the database from the bank business platform. The original data were stored in different data warehouses or tables; through using basic database operation methods, these data were easily selected and merged into a product table and asset table, separately. The specific product attributes and the asset attributes are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively.

Table 1.
Product attributes list and description.

Table 2.
Asset attributes list and description.
3. Modeling
This is a typical optimization problem that can be solved by establishing a programming model that includes decision variables, objective, and constraints, which are discussed in the following subsections.
3.1. Decision Variables
The key variables to be determined in this problem are the percent of the assets in each product, so the decision variables can be set as , indicating the percentage of asset j in product , , where is the number of products and , where is the number of assets. All the can constitute a matrix , which is the decision variable for the model.
3.2. Optimization Objective
The goal of the problem is to minimize the weighted duration between all products and their assets allocated. So, the objective of the model can be written as
where is the duration between product and asset , (the value in row 5 of the asset table, Table 2, and the following variables for asset attributes are labeled similarly) is the due date of the asset, and (the value in row 7 of Table 1, and the following variables for product attributes are named similarly) is the due date of the product.
3.3. Constraints
3.3.1. Non-Standard Proportional Limit
For the assets allocated to each product, the proportion of non-standard assets shall neither exceed the maximum non-standard proportion of the product, nor shall it be less than the minimum non-standard proportion, which can be expressed mathematically as
where is the maximum non-standard proportion of product , is the Whether non-standard of asset , and is the minimum non-standard proportion of product .
3.3.2. Bond Proportional Limit
For the assets allocated to each product, the proportion of assets belonging to the bond type shall neither exceed the maximum bond proportion of the product, nor shall it be less than the minimum bond proportion, which can be written as
where is the bond of asset , is the maximum bond percent of product , and is the minimum bond percent of product .
3.3.3. Return Limit
For the assets allocated to each product, its weighted return cannot exceed the sum of its return and the maximum excess return, and it cannot be less than the sum of its return and the minimum excess return, which can be expressed as
where is the adjusted return rate of asset , is the return of product , is the maximum excess return product , and is the minimum excess return of product . In the database, is a decimal value, whereas and are both percentages needing to be divided by 100 before addition with .
3.3.4. Residual Asset Limit
For each asset, the total amount of asset allocated to all products shall not exceed the remaining asset of this asset, which can be expressed as
where is the size of product and is the remaining amount of asset .
3.3.5. Single Product Weighted Macaulay Duration Limit
For those assets allocated to each product, their weighted Macaulay duration cannot exceed the duration limit of the product (generally, 10 years), which can be expressed as
where is the Macaulay duration of asset and is the weighted Macaulay duration limit of all products, which is a fixed value.
3.3.6. Product Capital Allocation Proportion Limit
For each product, to increase its profitability, the ideal is 100% allocation, but considering the actual situation, it is generally difficult to achieve the ideal result. Therefore, to ensure the maximum allocation of capital, a minimum allocation percent should be set, and the total capital percent of the product cannot exceed 100, which can be expressed as
where is the minimum allocation percent limit to all products, and it is a fixed value.
3.3.7. Assets with a Negative Duration Are Not Allocated
Assets with negative duration cannot be allocated; that is, assets whose due date is less than the due date of the product cannot be allocated. This constraint can be written as
where is the symbolic function with duration , and its specific definition can be written as
3.3.8. Public Assets Can Only Be Allocated to Public and Non-Preservation Products
Public assets can only be allocated in public and non-preservation products, which can be expressed as
where is a symbolic function defined as
where is the Whether public of asset , is the Whether public of product , and is the Whether preservation of product .
3.3.9. Preservation Products Can Only Be Configured with Preservation Assets
If the product is a preservation product, only preservation assets can be allocated to it, which means the no preservation assets can be allocated to the preservation products. This constraint can be expressed as
where is a symbolic function defined as
where is the Whether preservation of asset and is the Whether preservation of product .
Now, all the constraints for this model have been listed, and all the constraints are linear. At this point, the single objective linear programming model for the optimal asset allocation is complete. Although there are different kinds of methods to optimize the allocation of available assets, such as non-linear programming and quadratic programming, from the optimization objective and constraints, we chose a typical single objective linear programming model.
4. Solver Testing and Empirical Results
From a practical point of view for this problem, it is generally accepted that decision variables being integers are satisfied with the business requirement. So, for this model, all decision variables were first set as integers, which means all that decision variables had integer constraints. From the algorithm design view, integer programming increases solving complexity and solving time. The solving time should be less than the maximum system response time, so we needed to first test the integer programming. We also tested the non-integer programming algorithm for a comparison and to determine if we could obtain a more accurate algorithm.
4.1. Integer Programming
Then, we considered how to solve this model. Before solving the model, some test cases were prepared. Some samples were extracted from a business database, upon which six test cases with 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 products and 1000 assets were designed. According to the model, a program was written using the integer programming solver intlinprog of MATLAB (Version: R2019b, License: 1099003, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA). Then, we executed this program on these cases, and the optimal results were obtained, as shown in Figure 1. The solving time and asset number in the optimal solution are as shown in Table 3. The solving time is suitable when the product number does not exceed 6, but the solving time exceeds 600 s when the product number is to equal or more than 8, which is not accepted by the business platform. So, some more efficient algorithms and solvers needed to be tested.
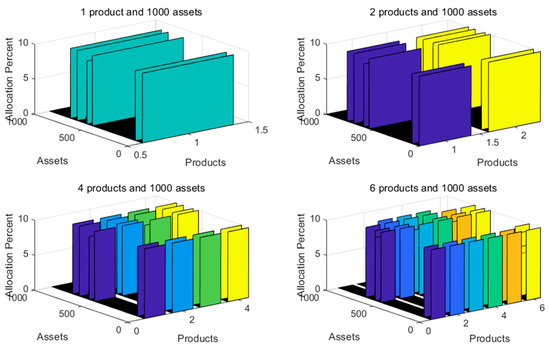
Figure 1.
Visualized results of test cases with integer programming.

Table 3.
Solving time and asset number in an optimal solution with integer programming.
Although integer programming was not a good approach for this model, from these several test cases, some interesting observations were noted. Firstly, the solving time increased as the number of products increased, which is logical as the program performs more jobs when the product number is higher. Secondly, the asset number in the optimal solution also increased as the number of products increased, which also makes sense as more assets are needed to satisfy the amount requirement when product number increases.
4.2. Non-Integer Programming
Amongst all the algorithms available for solving linear programming models, the dual simplex is relatively efficient, and it requires the decision variables to have no integer restrictions. For this problem, if there is no integer limit on the decision variables, the accuracy of the model will be higher, and the results will be more refined. Therefore, such adjustment is more beneficial to the practical application of the model. So, a new program using non-integer programming was written to solve this model with the linprog function in MATLAB (Version: R2019b, License: 1099003, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) whose default algorithm is the dual-simplex.
Then, this program was used to solve these cases. The optimal results are shown in Figure 2, and the solving time and asset number in the optimal solution are shown in Table 4. This time, the solving times for all test cases were within 1 s. Compared with integer programming, this speed is much faster and can meet the needs of business platforms.
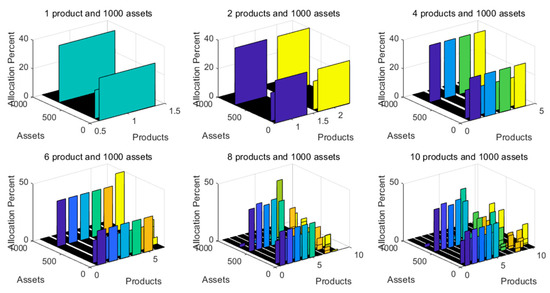
Figure 2.
Visualized results of test cases with non-integer programming.

Table 4.
Solving time and asset number in optimal solution with non-integer programming.
Figure 2 shows that only some excellent assets were allocated to products, which agrees with real business knowledge. When the product number increased, the optimal asset number also increased, which is logical given the higher number of samples compared with the results from integer programming. When solving the same test case, non-integer programming is faster than integer programming; a comparison is provided in Figure 3. Importantly, the short solving time for the non-integer programming for all test cases was below the maximal response time of the business platform, which means that this approach is suitable for real bank business platforms. Through these two groups of testing, we selected an ideal algorithm and solver for the model—non-integer programming solver.
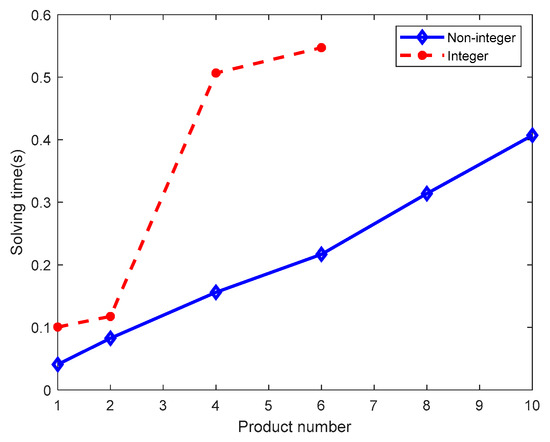
Figure 3.
Visualized results of test cases with integer programming.
4.3. An Application Example
After getting a desired solving method, a real example was executed. This example contained eight products, and its data are shown in Table 5. Part of the data of all the 1000 assets can be used as shown in Table 6. With these data as the input data, the results were obtained after executing the program. The result matrix was a sparse matrix, as only a few of the good assets were configured into products. In order to show the detailed asset allocation results, a simplified result matrix as shown in Table 7 was derived from the original result matrix by removing those rows in which all values are zeros (corresponding to those assets not been used).

Table 5.
Product data of the application example.

Table 6.
Asset data of the application example.

Table 7.
Solving results (percentages) of the application example (only used assets were kept).
In this example, the minimum allocation percent limit was set to 90 in advance. A method that could be used to evaluate the results is to sum the percentages of each column in the matrix result. The summations were easily obtained, as shown in the bottom of Table 7, from which it can be seen that all the summations are equal to or approximately equal to 90. Some summations are below 90, which was caused by the computational accuracy of the computer; thus, the results are still valid.
This example has given us a vivid full experience of how the model and program was used in practice. In practice, the program was generally to be developed into a module and then integrated into the business platform of the bank. In this way, the staff in the bank can easily use this model.
5. Model Deployment
Once the model and algorithm were proven effective, then, we considered how to deploy the model in a business platform. MATLAB programs (MathWorks, Natick, USA) can be compiled into independently running executable modules that can be directly called by other development tools (such as Java, C#, etc.) using its built-in compilation toolbox. Therefore, the MATLAB solver can be directly compiled into a module and then deployed in the business platform to quickly deploy the model. The model deployment and workflow for the bank business platform are shown in Figure 4.
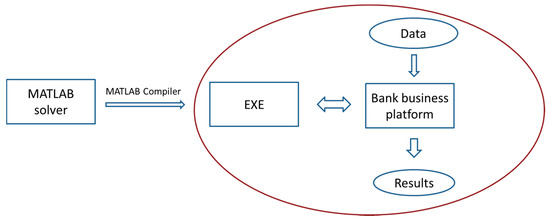
Figure 4.
Model deployment and working workflow in bank business system (EXE expresses the executable program).
Before this module, a product was manually configured. A senior analyst should spend at least 2 h finishing a combination of assets for a product. With this module, by comparison, the bank can now quickly allocate assets for key clients or for designing new products. This practice proved that this method can be successfully applied to financial big data and fintech for banks using the established mathematical model based on business platform data.
6. Conclusions
The business platforms of banks are rich in data. Determining how to use these massive data to improve the work efficiency and effect of banks and promote the improvement of the banking business is the main purpose of the application of financial big data and fintech in the financial field. There are many studies on financial big data or big data in finance and fintech, separately [16,17,18], but few studies focused on the combination of financial big data and fintech. The main goal of this study was to demonstrate how to integrate financial big data and fintech to promote the development of the financial industry through an asset allocation example. Whereas the literature on asset allocation mostly focused on theoretical research with few specific applications, we applied theoretical and technical aspects to the practical application of asset allocation.
Our main goal was to establish a linear programming model using the existing product and asset data of a bank and the operational research method. Two algorithms, integer programming and non-integer programming, were tested separately on six test cases from the actual business platform, and we found that the non-integer programming algorithm was more efficient and stable. So, it was chosen as the solution of the model. We also introduced how to use the MATLAB compilation function to compile the model into a component of the business platform and quickly deploy the model on an actual business platform. We focused on finding a suitable algorithm that can quickly provide a result in various cases, mainly because from the viewpoint of bank users, the first priority of this application is its operational stability, meaning that it can quickly provide results in different situations, not only the optimal and precise solution to a general optimization question.
Through studying this example, we concluded the following four points: (1) The data accumulated by the banking platform contain large amounts of useful information; the key is determining how to use the data. Bank product configuration is a tedious task involving many computations. By using scientific modeling methods and solving algorithms, efficient and fast product configuration tools can be developed based on these data resources, thus considerably improving the business level of banks. Therefore, one application of finance big data is combining data with specific businesses, especially tedious and time-consuming businesses. (2) The asset allocation model is a classic operational research problem, but business requirements differ. As reflected in the model, the objectives and constraints of the model are different. According to the requirements of the actual business, we need to abstract the decision variables of the model, determine the objectives, and clarify the constraints. (3) In solving the model, the precision requirement on decision variables can be an integer according to the generally recognized business view, but the solution to the integer result is slower, whereas the algorithm without integer limits is more efficient and more in line with the platform response time requirement. Therefore, it is necessary to flexibly choose the algorithm according to the actual situation to solve the problem in the theoretical model as well as practical applications. (4) With the help of the mature scientific computing tool, MATLAB, the modeling, solving, and model deployment can be achieved more efficiently and conveniently, so the financial tool to be connected to the business platform can be quickly developed according to business needs, which is helpful for the development of finance big data and fintech.
The research and implementation process of the case study fully demonstrated the process of combining financial big data and fintech. The idea of studying abstract concepts through specific cases also provides reference for other relevant studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and X.L.; Data curation, J.Z.; Formal analysis, J.Z.; Investigation, J.Z. and C.Y.; Methodology, J.Z. and X.L.; Project administration, C.Y.; Resources, X.L.; Software, J.Z.; Supervision, X.L.; Validation, X.L. and C.Y.; Visualization, J.Z.; Writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; Writing—review and editing, X.L. and C.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiang, M.L.; Zhang, Y. Research on the comprehensive utilization of financial big data. China Int. Bus. 2017, 4, 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.F.; Xu, Y.Y. Research on the Development Strategy of Fintech Industry: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Financ. Theory Pract. 2019, 4, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Politou, E.; Alepis, E.; Patsakis, C. Profiling tax and financial behaviour with big data under the GDPR. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2019, 35, 306–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, O.; Çıtak, Y.E. Fintech Integration Process Suggestion for Banks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. A brief analysis of key account management in commercial banks. J. Shandong Acad. Gov. 2012, 3, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.D.; Lin, B.; He, C.Y. Internet finance characteristics, internet finance investor sentiment and the return of internet financial products. Econ. Res. 2019, 7, 78–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W. Effect of capital constraint on asset allocation behavior of commercial banks: An empirical study based on data of 175 commercial Banks. J. Financ. Res. 2011, 4, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, C.Y.; Sun, H.Q. Study on credit asset allocation model of small and medium-sized enterprise customers in commercial Banks based on the principle of matching risk and return. J. Financ. Dev. Res. 2011, 6, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.; Li, J.L. Overview of asset allocation theory and model. Prod. Res. 2007, 7, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X. Asset bubbles, banking stability and economic growth. Econ. Model. 2019, 78, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-M.; Lu, J.; Ching, W.-K.; Siu, T.K. Discrete-time optimal asset allocation under Higher-Order Hidden Markov Model. Econ. Model. 2017, 66, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Yao, H. Mean-variance portfolio selection with only risky assets under regime switching. Econ. Model. 2017, 62, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, L.; Xu, Z. Dynamic asset allocation and consumption under inflation inequality: The impacts of inflation experiences and expectations. Econ. Model. 2017, 61, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.M. Asset quality, non-interest income, and bank profitability: Evidence from Indian banks. Econ. Model. 2017, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormos, M.; Timotity, D. Generalized asset pricing: Expected Downside Risk-based equilibrium modeling. Econ. Model. 2016, 52, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kshetri, N. Big data’s role in expanding access to financial services in China. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Big data analytics for financial Market volatility forecast based on support vector machine. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, A.V. Fintech and banking: What do we know? J. Financ. Intermediation 2020, 41, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).