FPGA Implementation of Crossover Module of Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Genetic Algorithm
1.2. Hardware Implementation of GA
1.3. Travelling Salesman Problem
1.4. Importance of Crossover Module in GA
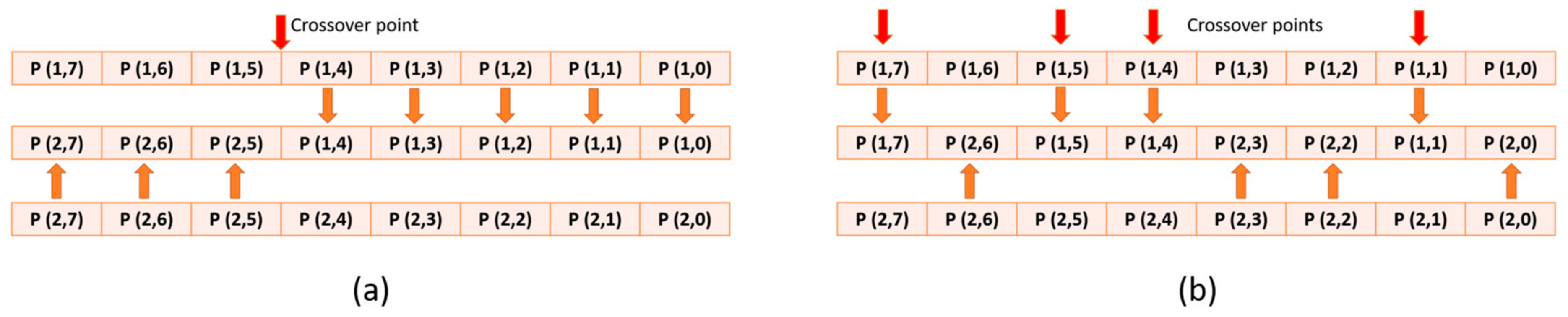
2. Crossover Technique and Related Work
2.1. Existing Work in Hardware Implementation of Crossover Module
2.2. Existing Work in Hardware Implementation of Partially-Mapped Crossover (PMX) Technique
3. Hardware Implementation
3.1. Challenges in Hardware Implementation of GA
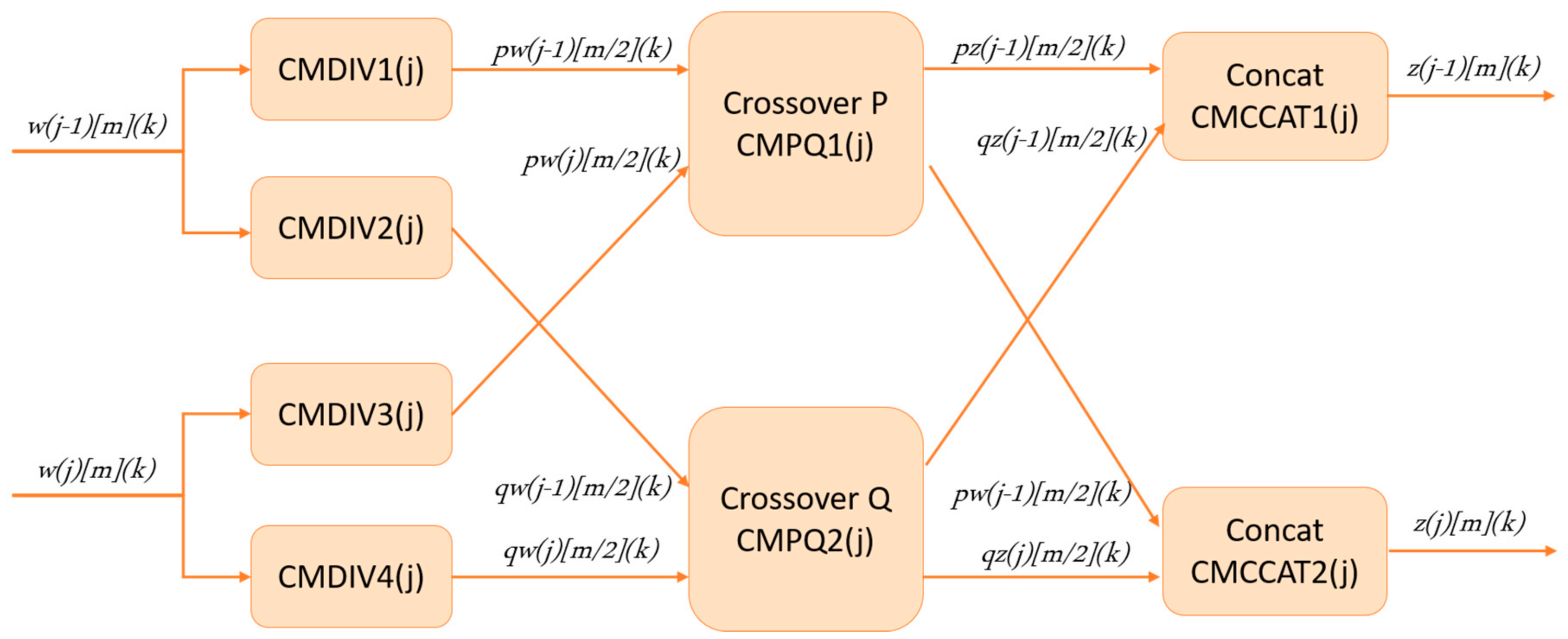
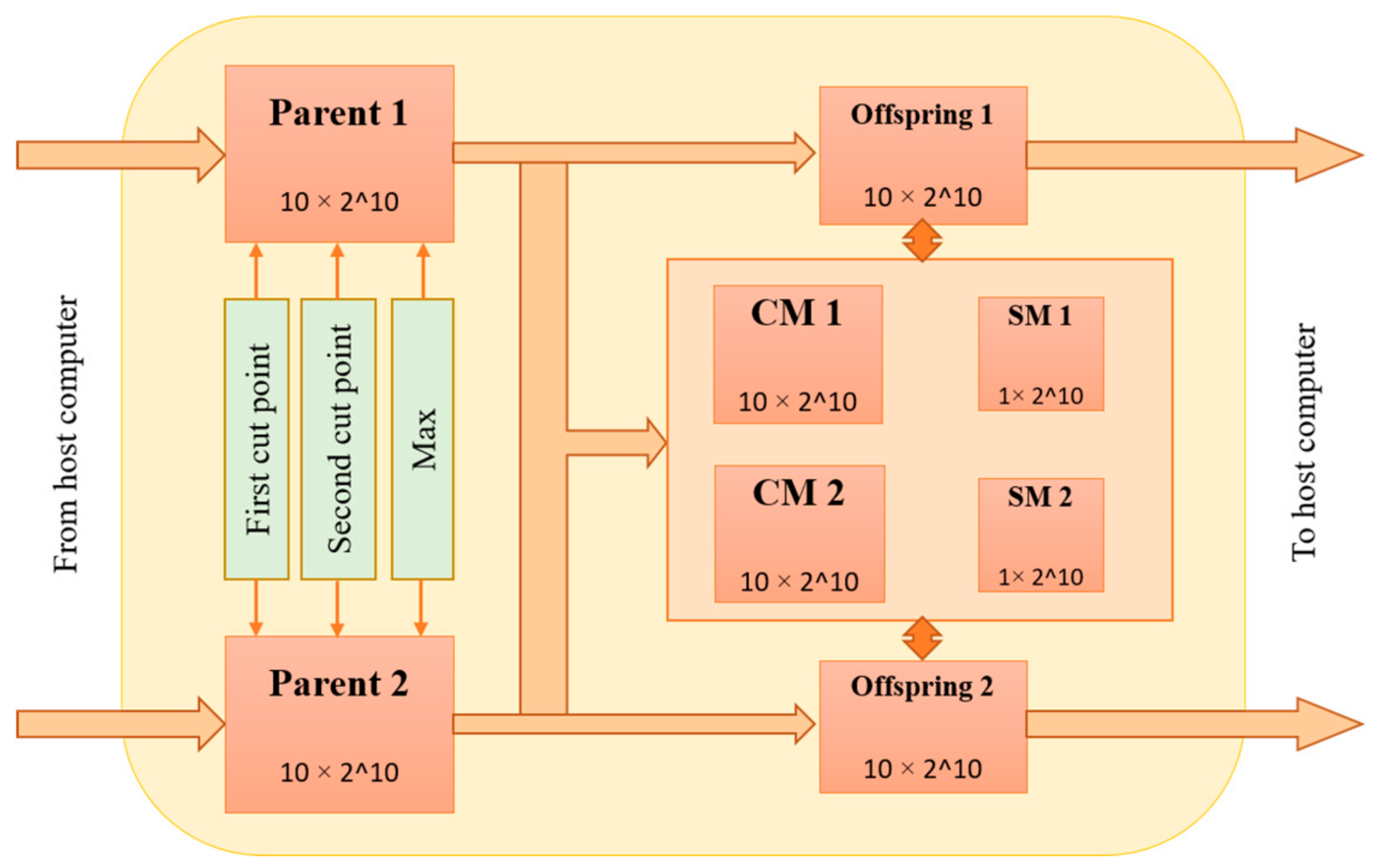
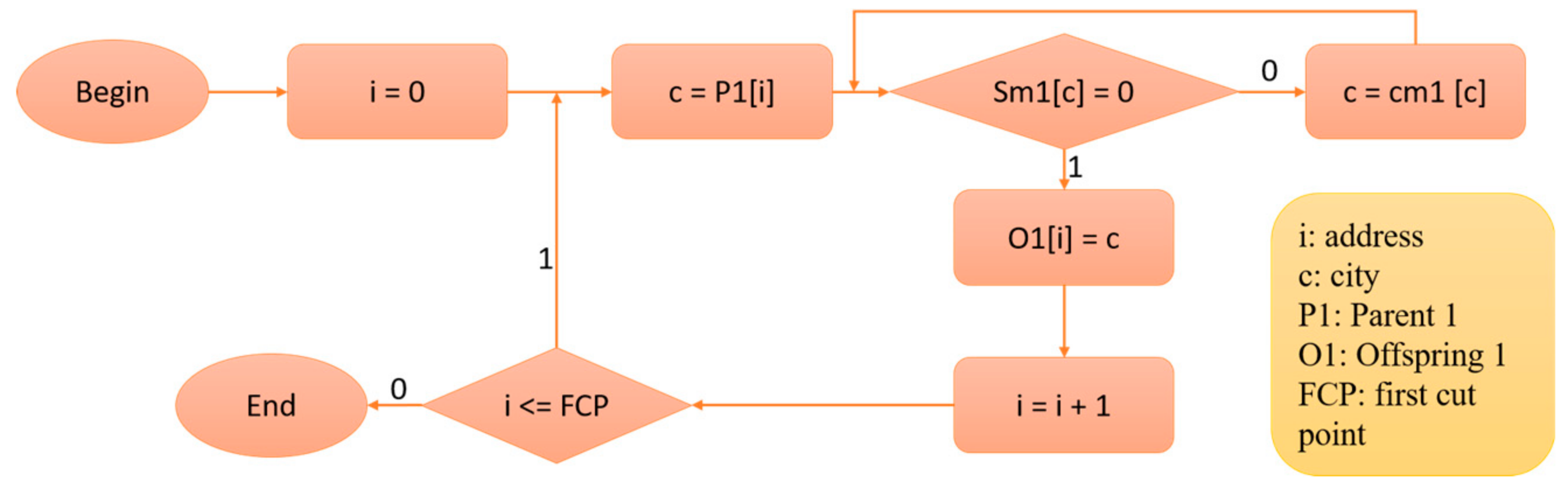
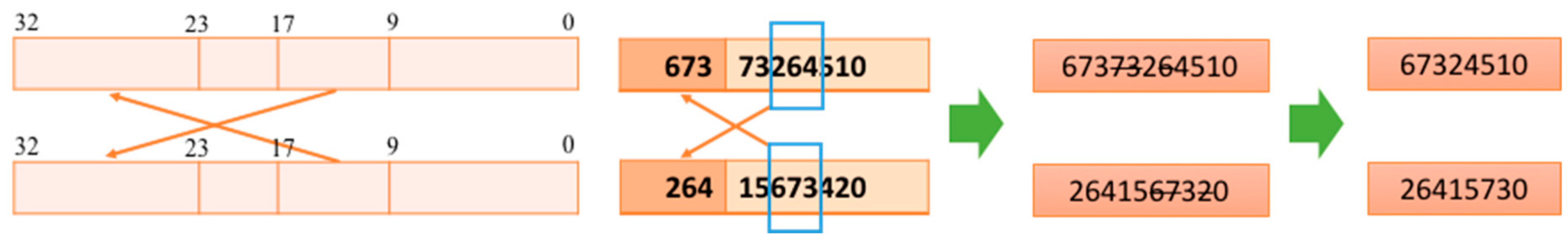
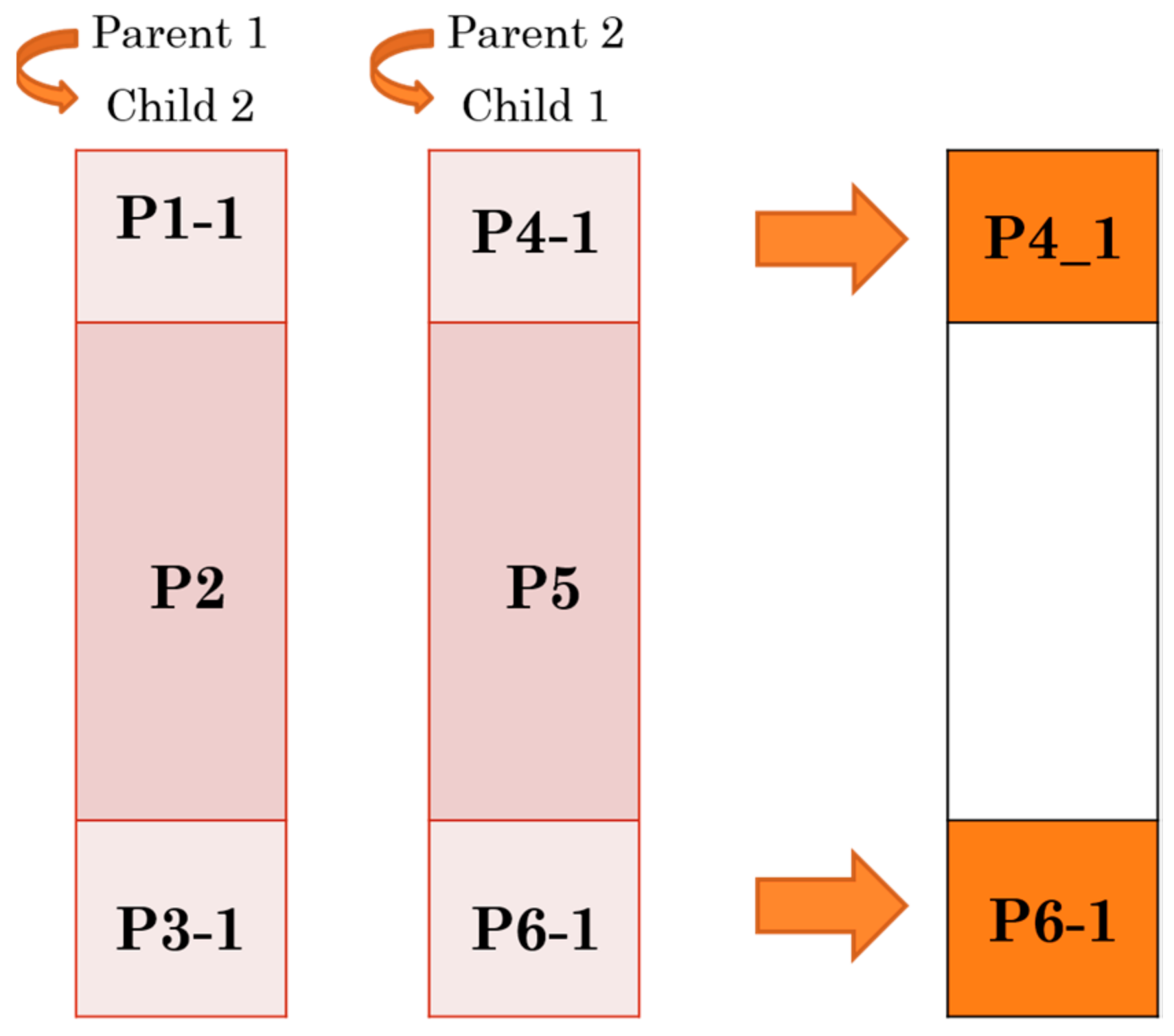
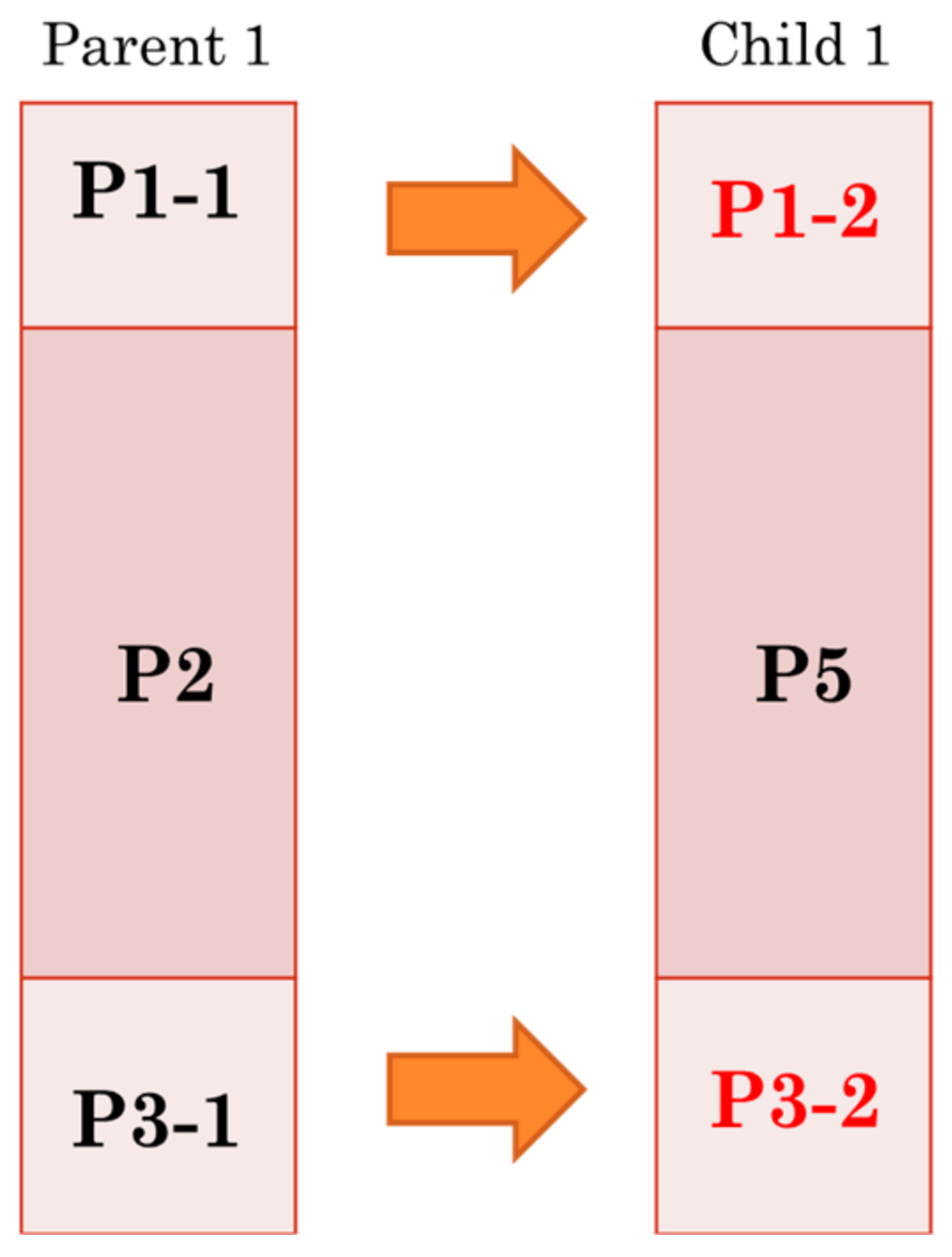
3.2. Proposed Architecture for PMX Crossover Module
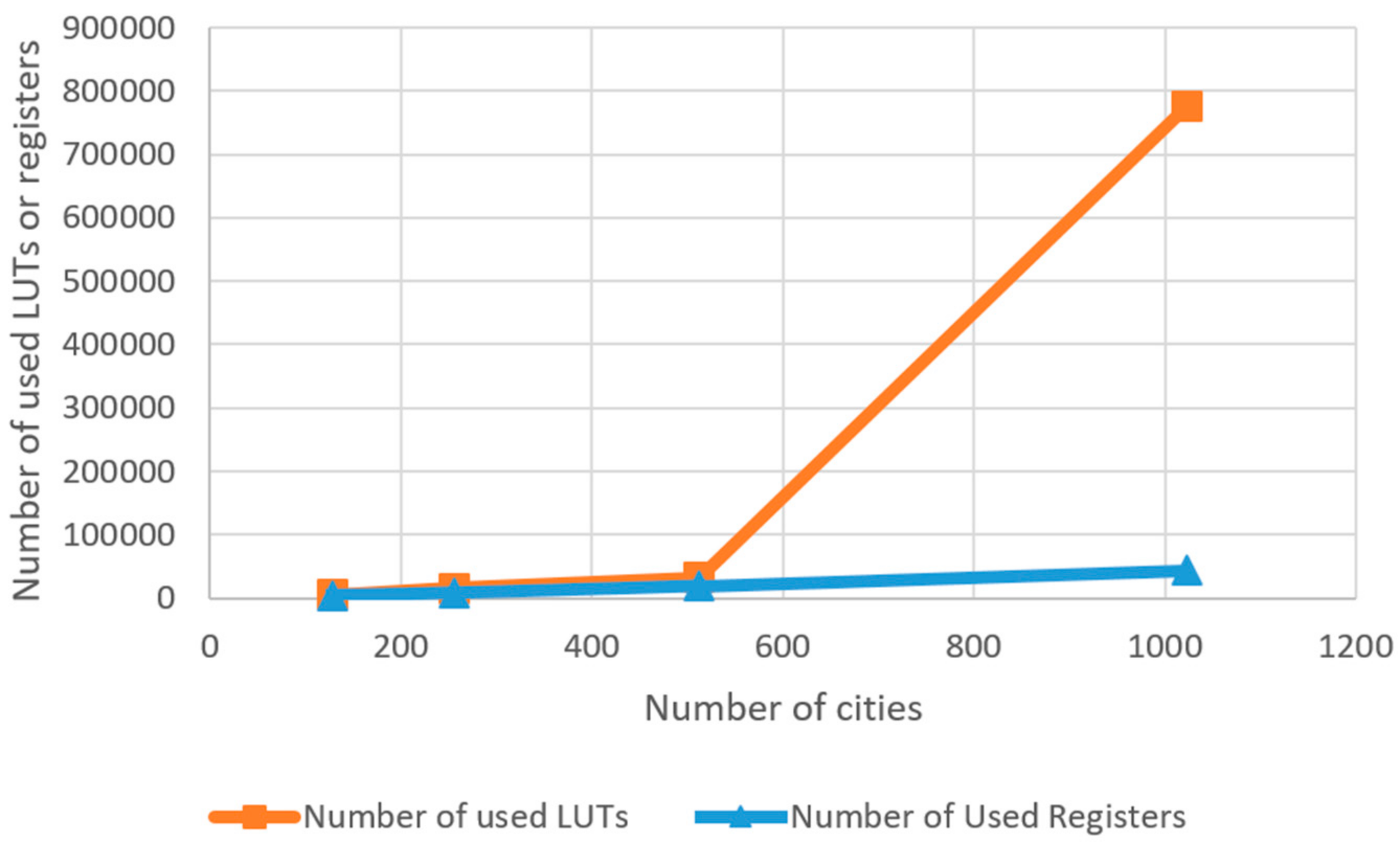
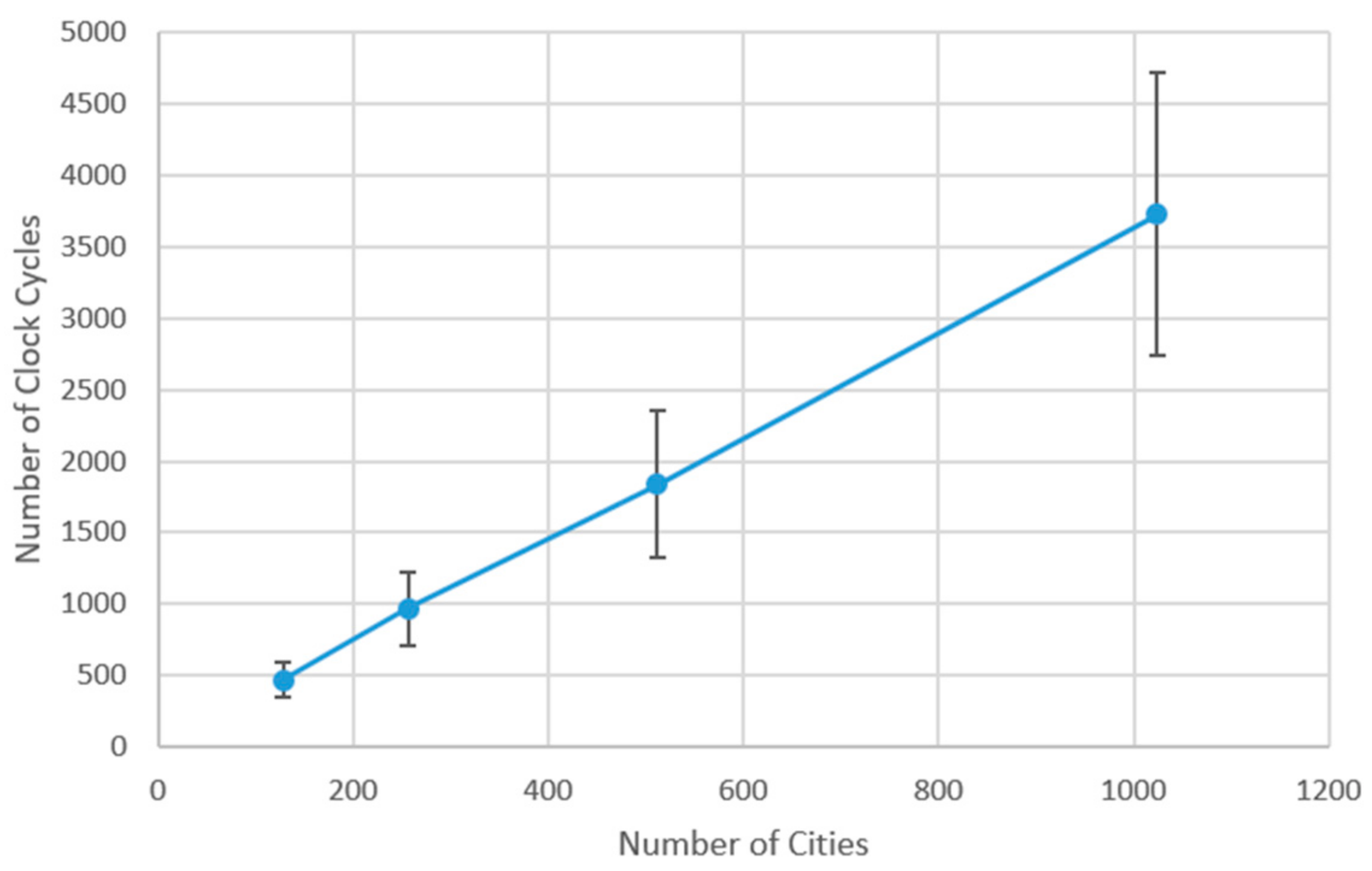
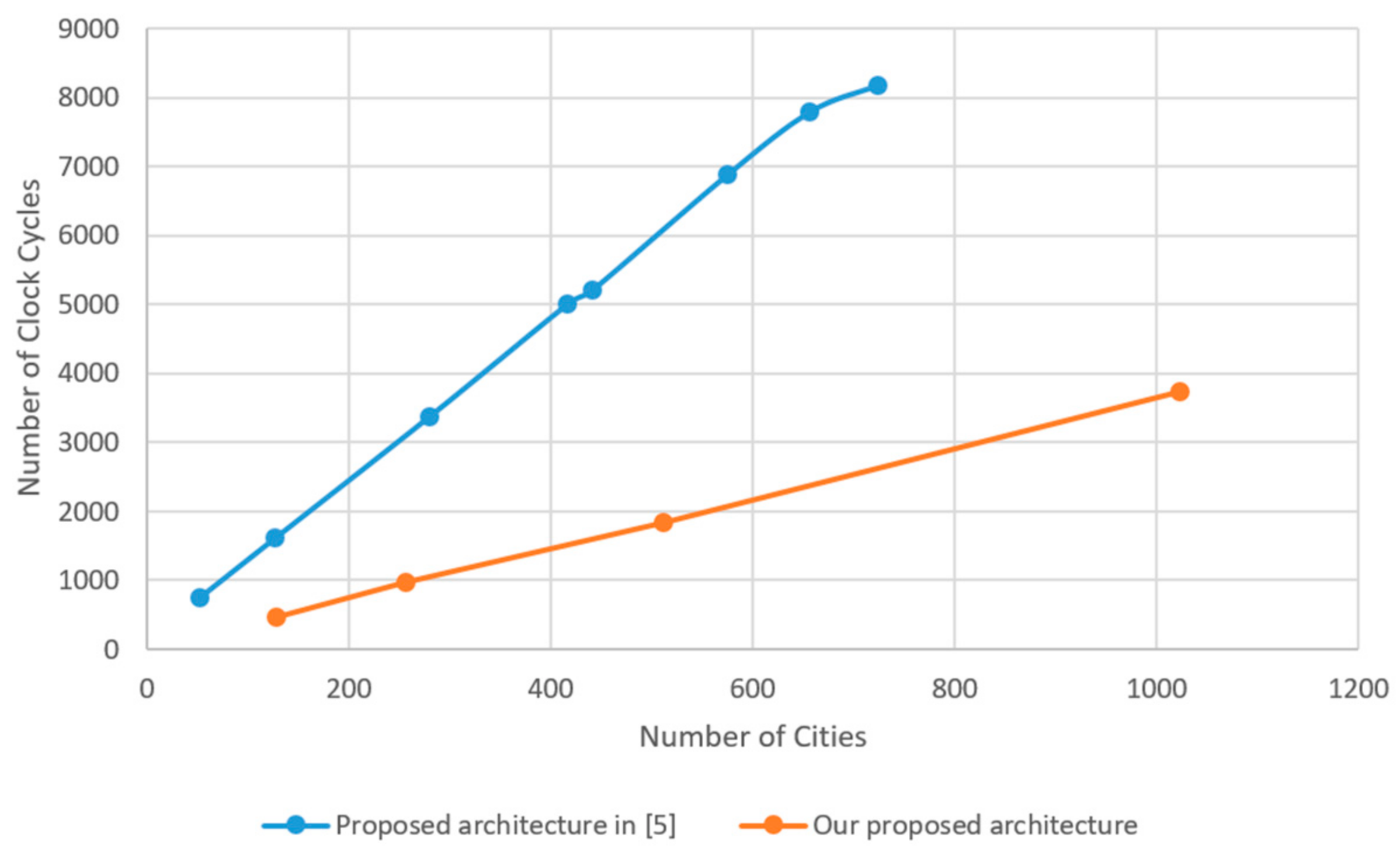
4. Experimental Results and Comparison
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallard, R.H.; Esquivel, S.C. Enhancing evolutionary algorithms through recombination and parallelism. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2001, 1. Available online: http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/bitstream/handle/10915/9423/Documento_completo.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- Applegate, D.L.; Bixby, R.E.; Chvatal, V.; Cook, W.J. The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Computational Study, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vavouras, M.; Papadimitriou, K.; Papaefstathiou, I. High-speed FPGA-based Implementations of a Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Systems, Architectures, Modeling, and Simulation (SAMOS 2009), Samos, Greece, 20–23 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Matai, R.; Singh, S.; Mittal, M.L. Traveling Salesman Problem: An Overview of Applications, Formulations, and Solution Approaches. In Traveling Salesman Problem, Theory and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Skliarova, I.; Ferrari, A.B. FPGA-Based Implementation of Genetic Algorithm for the Traveling Salesman Problem and Its Industrial Application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems, Cairns, Australia, 17–20 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Umbarkar, A.J.; Sheth, P.D. Crossover Operations in Genetic Algorithms: A Review. ICTACT J. Soft Comput. 2015, 6, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Tati, R.; Ahmadi, S.; Hossaini, V. New Hardware Engine for Genetic Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computing, Kitakyushu, Japan, 29 August–1 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alinodehi, S.P.H.; Moshfe, S.; Zaeimian, M.S.; Khoei, A.; Hadidi, K. High-Speed General Purpose Genetic Algorithm Processor. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 46, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Funie, A.I.; Thomas, D.B.; Fu, H.; Luk, W. Parallel Genetic Algorithms on Multiple FPGAs. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2016, 43, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengxu, F.; Bin, T. FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM 2015), Guangzhou, China, 22–24 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peker, M. A Fully Customizable Hardware Implementation for General Purpose Genetic Algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 62, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, M.F.; Fernandes, M.A. High-Performance Parallel Implementation of Genetic Algorithm on FPGA. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.11555. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.11555 (accessed on 24 May 2019). [CrossRef]
- Yan-cong, Z.; Jun-hua, G.; Yong-feng, D.; Huan-ping, H. Implementation of Genetic Algorithm for TSP Based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Mianyang, China, 23–25 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Naha, R.K.; Garg, S.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Gao, L.; Xiang, Y.; Ranjan, R. Fog Computing: Survey of Trends, Architectures, Requirements, and Research Directions. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47980–48009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Condition Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Two temporary memories are not filled up |
| 2 | There is redundancy between part P2 or P5 and the other parts |
| 3 | There is no redundancy between part P2 or P5 and the other parts |
| 4 | Counter k reaches its maximum values |
| 5 | Counter k does not reach its maximum values |
| 6 | Two temporary memories filled up |
| Number of Cities | Registers | LUT | Power (W) | Max Clock Frequency (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128 | 3820 | 6487 | 3.39 | 256 |
| 256 | 8621 | 20193 | 11.91 | 247 |
| 512 | 19138 | 43312 | 21.00 | 201 |
| 1024 | 42302 | 776896 | 138.86 | unavailable |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Attarmoghaddam, N.; Li, K.F.; Kanan, A. FPGA Implementation of Crossover Module of Genetic Algorithm. Information 2019, 10, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10060184
Attarmoghaddam N, Li KF, Kanan A. FPGA Implementation of Crossover Module of Genetic Algorithm. Information. 2019; 10(6):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10060184
Chicago/Turabian StyleAttarmoghaddam, Narges, Kin Fun Li, and Awos Kanan. 2019. "FPGA Implementation of Crossover Module of Genetic Algorithm" Information 10, no. 6: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10060184
APA StyleAttarmoghaddam, N., Li, K. F., & Kanan, A. (2019). FPGA Implementation of Crossover Module of Genetic Algorithm. Information, 10(6), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10060184





