1. Introduction
Northern Ireland has long been one of the most religious regions of Europe, with much higher rates of religious identification and practice than elsewhere on the continent. Northern Ireland’s ‘abnormally’ high levels of religiosity have often been attributed to the impact of the Troubles (circa 1968–1998) (
Mitchell 2004;
Ganiel 2024). The violence of the Troubles was structured along ethno-national-religious lines, following the contours of sectarian social and political institutions that had been embedded in the region for centuries (
Morrow and Ganiel 2024). Scholars argued that the social dimensions of religion—so important during times of crisis—contributed to high rates of religiosity. In short, religion helped (some) people cope with trauma (
Ganiel and Yohanis 2019), and religious identification and practice became a way of identifying with one’s own ethno-national community. Indeed, rates of religious identification and practice have declined significantly since the 1998 Belfast/Good Friday Agreement, usually considered the ‘end’ of the Troubles. In the 1961 Census, 58 percent identified as either Presbyterian, Church of Ireland, or Methodist, while 35 percent identified as Catholic. By the 2021 Census, 42 percent identified as Catholic, 37 percent as Protestant/other Christian, and 19 percent as ‘no religion’/not stated (
Macourt 2024, p. 343). The apparent increase in the Catholic population has been driven by demographic change, i.e., a declining population among Protestants, rather than religious conversion. In addition, in the late 1960s, weekly religious attendance was about 95 percent among Catholics and 66 percent among Protestants (
Ganiel 2016, pp. 34–35;
Hayes and Dowds 2010). These rates are now much lower, declining precipitously among Catholics and steadily among Protestants. The Northern Ireland Life and Times survey records monthly (or more) attendance among Catholics at 77 percent in 1999, 68 percent in 2008, and 46 percent in 2019; for Protestants, the rates are 52 percent in 1998 and 2008 and 46 percent in 2019 (
Ganiel 2024, p. 326). During the COVID-19 pandemic, Protestants (40 percent) were more likely than Catholics (27 percent) to access virtual services two to three times per month or more (
Ganiel and Morris 2021, p. 5).
1Given the relatively high rates of identification and practice, there is long-standing academic debate about whether or to what extent religion matters as a contributor to conflict, with some dismissing religion as an ‘ethnic marker’ for the more important ethno-national differences of nationalism (those who seek a politically united Ireland) and unionism (those who want Northern Ireland to remain in the United Kingdom) (
McGarry and O’Leary 1995). Others argued that religious structures and ideas were important even beyond the most devout, informing the construction of wider communities and providing meaningful content for communal identities (
Mitchell 2005). Such works explored how religion mattered differently for Protestant unionists and Catholic nationalists (
Ruane and Todd 1996;
Mitchell 2006;
Morrow and Ganiel 2024). Here, the importance of evangelical Protestantism was emphasised, with some drawing the conclusion that religion
as ideas or ideology or
as a component of identity mattered more for Protestants than for Catholics (
Wright 1973;
Bruce 1986,
2007;
Ganiel 2008;
Mitchel 2003,
2024). Others emphasised that Northern Ireland’s settler colonial history had structured division along sectarian lines, favoring Protestant unionism (
Altglas 2022;
Lloyd 2021).
Throughout the Troubles, evangelical Protestantism was a large and significant sub-group (
Bruce 1986;
Mitchel 2003;
Ganiel 2008). Evangelicalism was regarded as highly politicised, in no small part due to the towering influence of the Rev. Ian Paisley. Indeed, scholarly curiosity about evangelicalism has been dominated by Paisley, who founded not only his own Christian denomination—the Free Presbyterian Church—but also a political party, the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) (
Southern 2005a;
Ganiel and Dixon 2008). Paisley got his start as an anti-ecumenical preacher in the late 1960s, forging his public persona as an opponent of the largest Protestant churches’ tentative efforts to engage with the Catholic Church. Paisley also articulated a ‘theology of political resistance’ (
Southern 2005b), inspired by the fathers of the Protestant Reformation, that justified Protestant unionist privilege and the right to fight (whether violently or non-violently was never entirely clear) to defend it (
Mac Iver 1987). Paisley was notorious for his anti-Catholic rhetoric, which tapped into a centuries-long strain of anti-Catholicism on the island (
Brewer and Higgins 1998). The 1646 Westminster Confession of Faith, which could be considered a founding document of Presbyterianism in Scotland, Ireland, and Britain, identified the pope as the anti-Christ, a designation Paisley readily accepted. He energetically articulated anti-Catholic ideas through his sermons and publications, such as the
Protestant Telegraph, published between 1966 and 1982. For Paisley, evangelicalism was at the vanguard of promoting religious and political liberty in Northern Ireland, and he frequently referred to Ulster (the historic nine-county province that includes the six counties of modern Northern Ireland) as ‘the last bastion of evangelical Protestantism in Western Europe’. Writing in the
Protestant Telegraph in 1968, he asserted (quoted in
Mac Iver 1987, p. 368):
… we are the defenders of Truth in this Province and in this island. … Ulster is the last bastion of Evangelical Protestantism in Western Europe; we must not let drop the torch of Truth at this stage of the eternal conflict between Truth and Evil.
Bruce (
1986) claimed that Paisley’s prominence and political success reflected the significance of evangelicalism for a wider, even secularizing unionist community. And while the Free Presbyterian Church remained numerically small, Paisley dominated popular perceptions of evangelicalism. In reality, evangelicalism was more diverse and complex, including an apolitical/pietist stain as well as a reforming strain that critiqued Paisley’s anti-Catholicism and mixing of religion and politics (
Jordan 2001;
Mitchel 2003;
Ganiel 2008;
Mitchell and Ganiel 2011). This is unsurprising: the international literature on evangelicalism has long recognised its diversity. Moreover, scholars have grappled with how to define evangelicalism, noting potential conflation and overlapping with categories or descriptors like fundamentalism, conservativism, or ‘born-again’ Christianity (
Mitchell and Tilley 2008). At the same time, moderate or reforming evangelicalism became very significant in mid-1980s Northern Ireland, with the formation of an organization dedicated to challenging Paisleyism and promoting peacebuilding: Evangelical Contribution on Northern Ireland (ECONI). ECONI critiqued Northern Ireland’s evangelical tradition, including its anti-Catholicism and its use of Calvinist theology to justify Protestant unionism’s historic privilege and power. ECONI produced biblically grounded resources, including training courses, a magazine (
Lion and Lamb), and other publications, to justify its new, reconciliatory vision. Qualitative studies revealed the importance of ECONI in stimulating identity change and activism among some evangelicals, concluding that because of evangelicalism’s long-standing socio-political influence, ECONI was Northern Ireland’s most important faith-based peacebuilding organization during the 1990s (
Ganiel 2008; see also
Power 2011). Further qualitative research has revealed that some members of the Presbyterian Church, Northern Ireland’s largest Protestant denomination, believed that their church should have done more to challenge Paisley (
Ganiel and Yohanis 2019, pp. 29–30). As one Presbyterian minister put it (
Ganiel and Yohanis 2019, p. 29):
We were under pressure from the Paisleyite faction who would be very quick to say ‘Traitor!’ Paisley was a great problem for our ministers. A lot of our members were influenced by Paisley. A lot of ministers would have loved to have said and done more but that Paisley threat inhibited them from saying too much, too plainly, too publicly.
Paisley’s church also wielded an outsized social and political influence through the DUP, which had disproportionate numbers of Free Presbyterians among its elected officials (
Tonge et al. 2014). While the DUP was the smaller of the two main unionist parties throughout the Troubles, it overtook the Ulster Unionist Party in 2003, and Paisley himself assumed the mantle of First Minister of Northern Ireland (2007–2008). Paisley’s political pragmatism surprised many, not least Free Presbyterians. Many Free Presbyterians objected to his sharing power with Sinn Féin, long associated with the violence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA). Paisley appeared to enjoy a warm friendship with Sinn Féin Deputy First Minister Martin McGuinness, a former member of the IRA, and even said he had prayed with him. Paisley was subsequently pushed out as Moderator of the Free Presbyterian Church, a position he had held since its founding.
Almost all studies of religion in Northern Ireland are preoccupied with its role in division and conflict, so much so that scholars have produced very few insights on contemporary religious practice. But
Mitchell and Tilley’s (
2004) analysis of the 1991 Northern Irish Social Attitudes Survey and the 1998 Life and Times Survey suggests that the association of evangelicalism with political unionism is inaccurate. Referring to evangelicals as ‘the moral minority’, they argue that despite the prominence of political Paisleyism, evangelical distinctiveness is based on conservative moral values. They found ‘no relationship between evangelicalism, unionist attitudes, and DUP support’ (
Mitchell and Tilley 2004, p. 597).
Mitchell and Ganiel’s (
2011) study provides some insights into everyday evangelicalism, describing a rich subculture that structures people’s social lives and relationships and often remains oblivious to politics. Surveys of ‘highly religious’ students at Queen’s University Belfast testify to the importance of faith in young people’s lives, with substantial numbers reporting they become more religious at university (
Ganiel 2023a,
2023b). This research also reveals that students who attend the (evangelical) Christian Union (CU) are much more conservative on issues like same-sex relationships and access to abortion than their Catholic counterparts at Queen’s, or indeed evangelicals in other parts of the UK (
Ganiel 2023a, pp. 17–19). For example, 84 percent of Queen’s evangelical students believed that sex between two adults of the same sex was ‘always wrong’, compared to 18 percent of Queen’s Catholic students, 61 percent of CU students in UK universities, and 21 percent of non-CU Christian students in UK universities (
Ganiel 2023a, p. 5). The survey of UK universities was conducted more than a decade before the 2023 survey at Queen’s in 2010–11 (
Guest et al. 2013). It is likely that the views of students in UK universities have become more liberal since then, potentially making the comparison with Northern Ireland starker.
But despite the importance of Paisley, evangelicalism, and religion in Northern Ireland more generally, large-scale studies of religiosity since the 1998 Belfast/Good Friday Agreement have been minimal. As a small region of the United Kingdom (with a current population of about 1.9 million within the UK’s 68 million), Northern Ireland’s unique religious dynamics are not captured in national or European-level quantitative surveys. The UK as a whole is much more secularised than Northern Ireland; the UK’s largest ‘religious’ category is those who choose ‘no religion’ (
Woodhead 2016). Northern Ireland is also not included in surveys of religiosity focused on the Republic of Ireland. While this is understandable given the usual structure of national-level surveys, it should be noted that the Christian churches in Northern Ireland are not part of UK-wide institutions. Rather, the churches are organised on an all-Ireland basis, with the religious institutions straddling the Irish/Northern Irish border—reflecting the island’s colonial history.
Questions about religious identification and attendance are asked annually in the Life and Times Survey, which is based on a representative sample of the population. In 2004, the Life and Times included a suite of questions about religion, including beliefs about the Bible and ‘moral’ issues such as abortion, same-sex relationships, and sex before marriage. It also gave people the option to self-identify as evangelical, born-again, fundamentalist, or some combination of these categories. Twenty-one percent of Protestants and six percent of Catholics identified as evangelical, and one-third of Protestants identified with some combination of these categories (
Mitchell and Tilley 2008, p. 741).
Mitchell and Tilley’s (
2008) deeper analysis argued that the born-again designation—on its own and in combination with other categories—was the most useful for isolating a conservative Protestant sub-group. Beliefs among born-agains about moral issues (more ‘conservative’) and the Bible (more likely to believe it is literally true) differed substantially from the other groups. This means that some Protestants who self-identified as evangelical—but not born-again—held beliefs that were more similar to so-called ‘mainline’ Protestants than to their fellow evangelicals (i.e., evangelicals who also chose the born-again identification) (
Mitchell and Tilley 2008, pp. 749–50).
The new findings presented in this article are based on two landmark polls, which together provide the most comprehensive snapshot of religion in Northern Ireland in more than two decades. The polls were commissioned by the Evangelical Alliance in Northern Ireland (EANI). They were launched on 21 April 2023, and were open for three weeks. One was a representative survey of Northern Ireland, carried out by the professional polling company Savanta ComRes. The other was a self-selecting online questionnaire of Christians in Northern Ireland, which was sourced primarily through social media, email, and WhatsApp channels. This garnered 2083 responses, most of whom were Protestant evangelicals. EANI head David Smyth has stated that EANI’s motivation for conducting the polls was to help ‘the church and those in government and media to better understand evangelicals here’ (
EA 2024).
EANI is a branch of the wider UK Evangelical Alliance (EA), which was founded in 1846. The EA describes itself as ‘the oldest and largest evangelical unity movement in the UK’. It says (
EA n.d.a.):
United in mission and voice, we exist to serve and strengthen the work of the church in our communities and throughout society. Highlighting the significant opportunities and challenges facing the church today, we work together to resource Christians so that they are able to act upon their faith in Jesus, to speak up for the gospel, justice and freedom in their areas of influence.
The representative survey had a sample size of 1005 and was weighted by age, sex, religion, ethnicity, and council region, providing findings that are generalizable to Northern Ireland. As far as we are aware, such a wide-ranging (27 questions) and representative survey of religion in Northern Ireland has never been carried out. The only comparable data come from the suite of questions included in the 2004 Life and Times Survey, already discussed. The 2004 Life and Times included 14 religion-related questions, in addition to its annual questions about religious identification and attendance at religious services. As such, EANI’s representative survey makes a significant contribution to our understanding of religious beliefs and practices in Northern Ireland around a quarter-century after the Belfast/Good Friday Agreement, providing insights on major gaps in knowledge.
The self-selecting questionnaire consisted of 40 questions on a range of beliefs, practices, and issues. One question asked people if they were members of the EA. Eighty-one percent said no, 11 percent said yes, and nine percent did not know. Respondents were also asked to rate their agreement with the statement, ‘In order to be a Christian, you must be “born again” and have experienced a point or process of conversion in your life’. Ninety-one percent of those who identified as evangelical strongly agreed/agreed. This resonates with
Mitchell and Tilley’s (
2008) argument that the ‘born again’ designation is especially important for understanding Northern Ireland’s distinctive ‘conservative Protestant’ sub-group. This questionnaire also included questions to probe whether people identified with the four aspects of
David Bebbington’s (
1989) classic definition of evangelicalism: the belief that (1) one must be converted or ‘born again’ to be a Christian; (2) the Bible is the inspired word of God; (3) Jesus Christ’s death on the cross was a real historical event, necessary for salvation; and (4) Christians must exercise their faith through evangelism and/or social action.
The most significant findings are identified here and analysed in detail throughout: 50 percent of the general population considers themselves practising Christians; church attendance remains high by Western standards; 38 percent of practising Catholics self-identify as evangelical; men are more likely to identify as evangelical than women; young practising Christians (18–34) are more likely to identify as evangelical than other age groups; evangelicals hold more conservative views than the general population on abortion, same-sex marriage, religious freedom, and climate change; and evangelicals hold more liberal views than the general population on welcoming asylum seekers, refugees, and newcomers. Moreover, evangelicals are broadly supportive of doing more to promote peace and reconciliation in Northern Ireland. We also develop a new four-fold typology to describe evangelicals in Northern Ireland: broad-church evangelicals, classic evangelicals, Catholic evangelicals, and ex-vangelicals (those who were once evangelical but no longer identify as such).
Taken at face value, it might appear that the data support Paisley’s notion that Northern Ireland is ‘the last bastion of evangelicalism’ in Western Europe. But that bastion is not what Paisley had in mind—it is not preoccupied with defending the faith from the perils of Catholicism. Rather, it is a bastion that now includes far more Catholics than expected. It is a bastion highly concerned with ‘moral’ issues, holding views at odds with the general population. And it is a bastion that includes most of Northern Ireland’s young, practising Christians. This suggests a future where there may be even sharper religious, social, and cultural distinctions between practising evangelical Christians (both Protestant and Catholic), decreasing numbers of non-evangelical practising Christians, and increasing numbers of people who say they have ‘no religion’ or do not practice at all.
2. Results
One of the main goals of the research was to provide insight into the religiosity of the general population of Northern Ireland. In the 2021 Census, 80 percent of the population identified as Christian (42 percent Catholic, 17 percent Presbyterian, 12 percent Church of Ireland, two percent Methodist, and seven percent other Christian denominations). But religious identification on the census does not equate to religious practice. The general population survey provides a more accurate picture of religious practice, revealing that 50 percent of the population describe themselves as practising Christians.
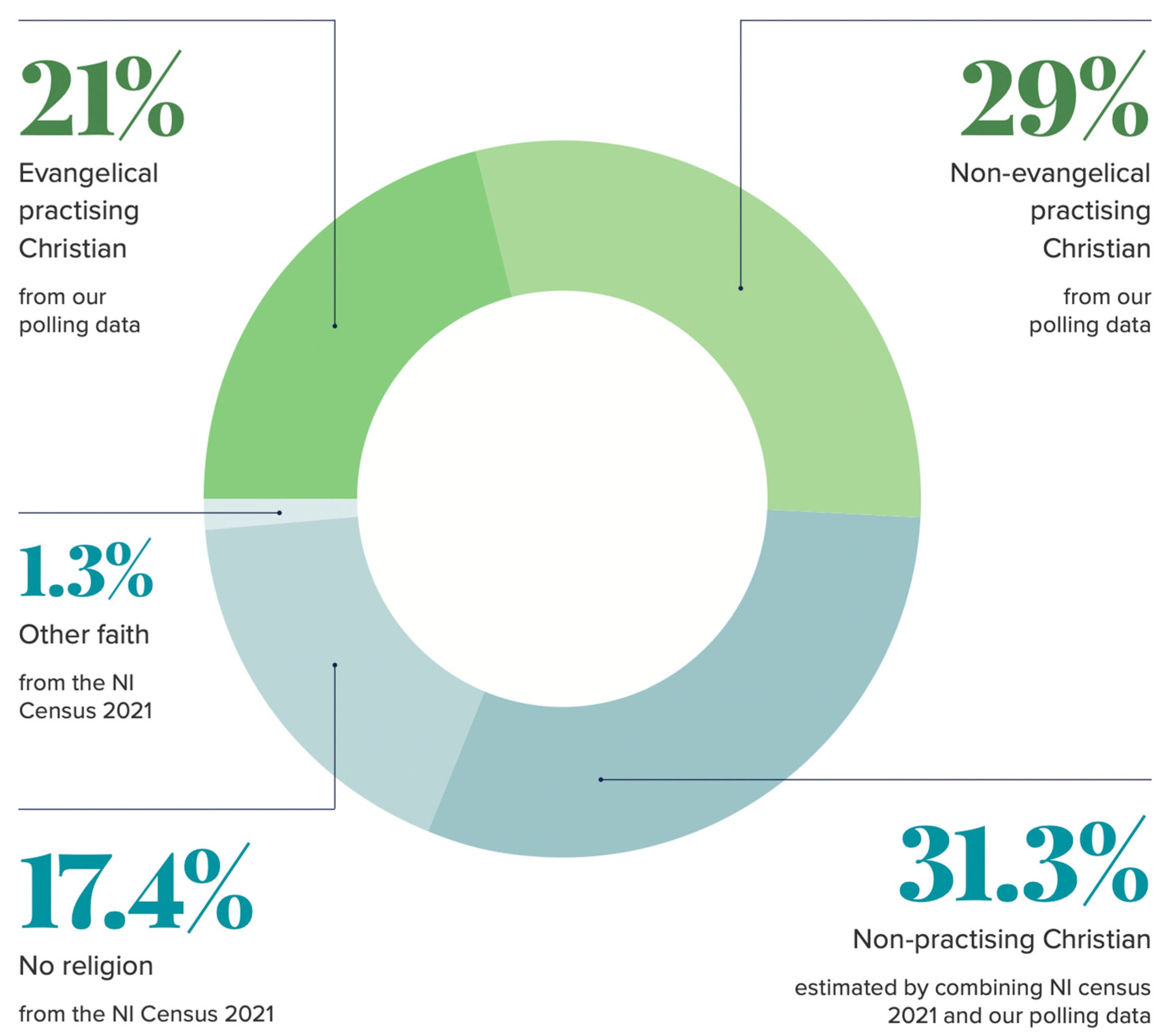
Figure 1 combines results from the general population survey and the Census, estimating that 31 percent of the population are non-practising Christians, 29 percent are non-evangelical practising Christians, 21 percent are evangelical practising Christians, 17 percent have no religion (2021 Census), and 1.3 percent identify with a religion other than Christianity (2021 Census).
The general population survey confirms that religious practice remains relatively high among both Catholics and Protestants, as the annual Life and Times Survey would lead us to expect. The self-selected questionnaire, while not representative, nevertheless provides insights into the religious practices and beliefs of evangelicals who were ‘largely already within the orbit of the Evangelical Alliance and interested enough to spend 10 min completing the questions’ (
EANI 2024, p. 29). About 80 percent of these respondents expressed strong agreement that Christians should be ‘born again’.
2.1. Survey of the General Population
2.1.1. Indicators of Religiosity
The survey of the general population featured a series of questions designed to provide insights into people’s religiosity. When asked, ‘Would you consider yourself to be a practising Christian?’, 50 percent of the population responded yes, 33 percent ‘no—I never have’, and 17 percent ‘no—I used to but no longer do because [please state]’. Catholics (62 percent) were more likely to say they were practising than Protestants (46 percent). Women (51 percent) and men (50 percent) were nearly equally likely to say yes. Young people were less likely to say yes, although their rates of practice are high by international standards—41 percent of those 25–34 and 40 percent of those 18–24 (
Table 1).
The survey also confirms the staying power of evangelicalism, but with a surprising twist. Overall, 21 percent of the population said they are evangelical Christians. Among those who also said they were ‘practising Christians’, 47 percent of Protestants and a stunning 38 percent of Catholics self-identified as evangelicals. These figures suggest that evangelical Protestantism has held steady since the end of the Troubles. But the number of Catholics choosing the label has increased dramatically—recall that only six percent of Catholics self-identified as evangelical in the 2004 Life and Times. Given the long association of evangelicalism in Northern Ireland with Paisley (and thus with anti-Catholicism), this is a very significant finding that merits further research.
The survey included questions used in the UK-wide
Talking Jesus (
2022) study (conducted by EA and partners). The
Talking Jesus conception of a practising Christian includes those who attend Christian worship at least monthly and pray and read the Bible weekly. In England and Wales, six percent of the population did all three of those things. In the general population survey in Northern Ireland, nine percent of the population did all three of those things—proportionally, this is 50 percent higher than England and Wales and equal to around 171,000 people (
EANI 2024, p. 12). Moreover, in Northern Ireland, 36 percent attend Christian worship at least monthly, 35 percent pray weekly, and 13 percent read the Bible weekly.
Catholics (46 percent) are more likely than Protestants (32 percent) to attend on a monthly or more basis. Here, the figures for Protestants are lower than in more recent Life and Times surveys. Men (39 percent) are also more likely than women (33 percent) to attend on a monthly or more basis. This is somewhat surprising, as internationally, Christian women usually have higher rates of attendance than men. Church attendance is lowest among the 25–34 age group (
Table 2).
Catholics (42 percent) are also more likely than Protestants (33 percent) to pray weekly. Women (38 percent) are more likely to pray on a weekly basis than men (31 percent). On the other hand, Protestants (16 percent) are more likely than Catholics (11 percent) to read the Bible weekly, with men (14 percent) more likely to do so than women (11 percent). Again, given that internationally Christian women generally exhibit higher levels of religiosity (
Trzebiatowska and Bruce 2012), it is expected that they report praying more frequently than men, but it is somewhat unexpected that men read the Bible more often. Those older than 65 (19 percent) are more likely to read the Bible weekly than 18–24-year-olds (eight percent).
Substantial numbers of people also agreed/strongly agreed that there is a ‘role for faith’ in a number of areas, with the most popular option ‘society in general’ at 65 percent. Fifty-seven percent agreed/strongly agreed there is a role for faith in education, with 47 percent agreeing a role for faith in ‘social justice’. Smaller but still substantial minorities agreed/strongly agreed with a role for faith in ‘law’ (37 percent), ‘medicine’ (37 percent), ‘politics’ (32 percent), and business (30 percent). The general population is also fairly knowledgeable about what ‘churches in your local area’ are doing, which may indicate the continued salience of religion in social and public life. Respondents were presented with ten examples of church-based activities, a ‘none of the above’ option, and an ‘I don’t know’ option and asked if churches in their local area were engaged in any of them. Only 21 percent of people said they didn’t know what local churches were doing. Forty-nine percent knew churches that provided children and youth activities, while 45 percent knew churches providing pastoral care, such as visiting the sick and bereaved.
2.1.2. Evangelicalism
As already noted, the survey confirmed the significance of evangelicalism in Northern Ireland. It is worth repeating that among practising Christians, 47 percent of Protestants and 38 percent of Catholics chose to identify as evangelical. On the basis of previous studies, it cannot be emphasised enough how unexpected it is that so many practising Catholic Christians chose the evangelical identifier. Men (47 percent) were much more likely to identify as evangelical than women (36 percent). Among the age groups, the most evangelical of all were the youngest: 18–24-year-olds (70 percent) and 25–34-year-olds (49 percent). Given the lower levels of religiosity among these age groups discussed previously, it seems that the choice for this generation is primarily between evangelicalism and not-practising, with few non-evangelical practising Christians (
Table 3).
Younger evangelicals are also more likely to be Catholic, i.e., of evangelicals aged 18–24, 64 percent were Catholic and just 25 percent were Protestant. Of evangelicals in the 25–34 age group, 49 percent were Catholic and 46 percent were Protestant. Catholic evangelicals outnumber or are equal to Protestant evangelicals in all age brackets below 55. In contrast, 71 percent of evangelicals over 65 were Protestant, with 24 percent Catholic (
Table 4). Within Catholicism, it is people under 55 who are driving the trend towards evangelical identification.
The general population survey also asked if people had heard of the term evangelical before. Seventy-nine percent (85 percent of Protestants and 72 percent of Catholics) had. Sixty-seven percent of those who had heard the term understood it as a stream within Christianity, linked more to the Protestant churches (24 percent) than the Catholics (five percent). Those 18–24-year-olds (50 percent) were least likely to have heard of evangelicalism. This is especially interesting given evangelicalism’s apparent popularity among practising Christians in that age bracket, suggesting a disconnect between young practising evangelical Christians and their peers. Respondents were also asked to write about their impressions of evangelicals they encounter in the media and evangelicals they know personally.
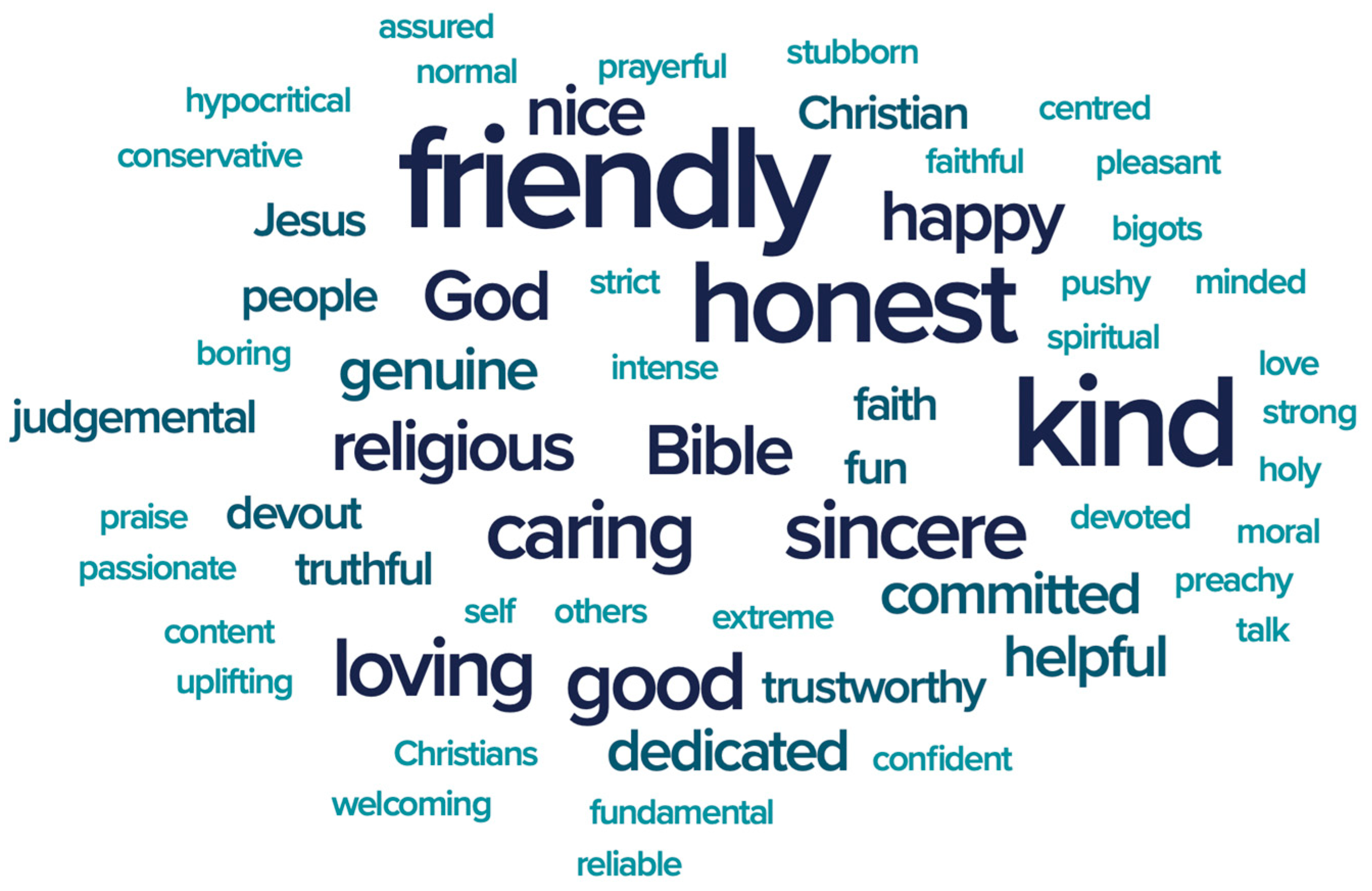
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 illustrate a great disparity between media portrayals of evangelicals and personal relationships with them. Evangelicals in the media are described as ‘religious, extreme, and loud’, while evangelicals that people know personally are depicted as ‘friendly, honest, and kind’ (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3).
The
Good News People (
EANI 2024, p. 39) report concluded that ‘relationships can override perceptions’, attributing this to the ‘social contact hypothesis’, which asserts that personal interactions can counter stereotypes.
2.2. Self-Selecting Online Questionnaire (Evangelicals)
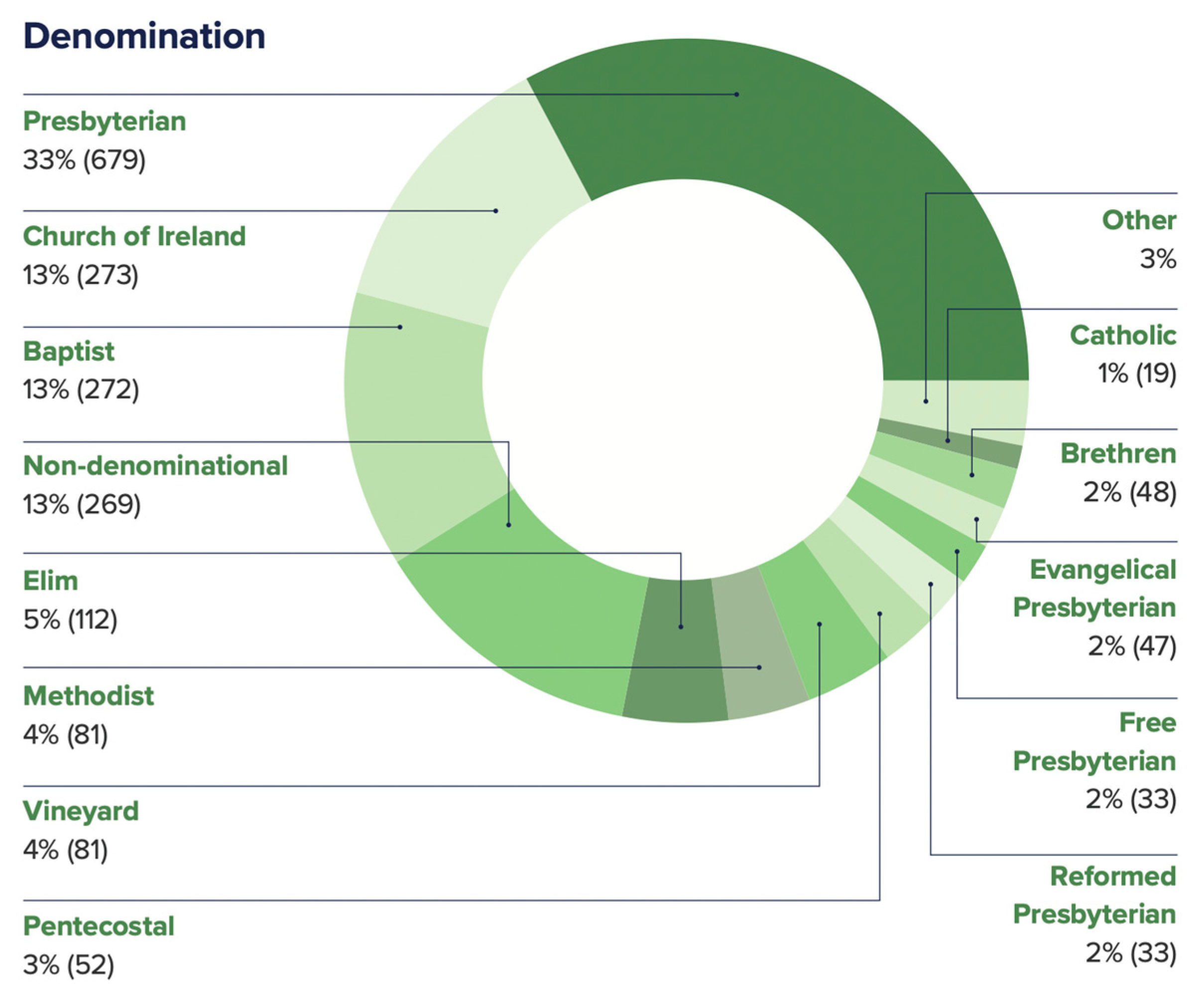
The survey of the general population was supplemented with a non-representative, self-selecting online questionnaire, which reached practising Christians through social media, WhatsApp, and email. Of the 2083 respondents, 99 percent described themselves as practising Christians, 83 percent said they were evangelical, 12 percent were practising Christians who never identified as evangelical, and five percent used to identify as evangelical but no longer do. Denominationally, the most responses were Presbyterian (33 percent), Church of Ireland (13 percent), Baptist (13 percent), and non-denominational (13 percent). Only two percent were Free Presbyterians (with a further two percent each Evangelical Presbyterian and Reformed Presbyterian—denominations with similar views to Free Presbyterians). Just one percent were Catholic (
Figure 4).
Respondents were spread fairly evenly across age groups, except for ages 18–24: 55–64 (22 percent), 35–44 (20 percent), 45–54 (19 percent), 65+ (18 percent), 25–34 (15 percent), and 18–24 (six percent—129 total responses). Fifty-two percent identified as female, 47 percent as male, and 0.4 percent ‘prefer not to say’.
The analysis that follows focuses on the 83 percent of respondents who said they were evangelical. This group exhibits extraordinarily high levels of religious practice: on a weekly basis, 96 percent pray, 95 percent attend a worship service, 92 percent read the Bible, and 55 percent volunteer for activities run by churches. The questionnaire also probed beliefs corresponding to Bebbington’s four-fold (quadrilateral) definition of evangelicalism, finding very high levels of agreement among respondents who identified as evangelical:
Ninety-nine percent believed the Bible was the word of God, with nineteen percent believing it should be taken literally, word for word. Seventy-seven percent believed it had no errors but should be read in context and, in some cases, symbolically. Just three percent believed the Bible could contain some historical or factual errors.
Eighty-four percent said the Bible was the highest authority for how they lived their lives.
Ninety-four percent believed that Christ’s death and resurrection were real historical events, with 92 percent believing Christ’s death was necessary for human reconciliation with God.
Ninety-five percent believed the church should both preach the gospel and demonstrate the good news of Jesus through its actions.
There was a further write-in question that probed, ‘To me, being an ‘evangelical Christian’ means …’. One respondent literally wrote, ‘Agree with Bebbington’s Quadrilateral’, demonstrating knowledge of academic debates about evangelicalism. While ‘Jesus’ and ‘Christ’ were the most common words written in, other responses emphasised being ‘born again’, bible-believing, sharing their faith, and having a personal relationship with Jesus. One respondent seemed to consider definitions of evangelical so commonplace as to write (emphasis ours):
Just the usual—believe in the trinity/personal relationship with God. Jesus died so we didn’t have to receive punishment for our sin and then rose again.
Other examples include:
Believing in Christ as my Saviour, having been born again.
Believing that the Bible is the infallible and inspired Word of God, that man is by nature a sinner and only faith in the work of the Lord Jesus on the cross will atone for that sin. And that you must be born again.
Participants were asked to rate their agreement on a scale of 0 to 10, with the statement, ‘In order to be a Christian you must be “born again” and have experienced a point or process of conversion in your life’. Seventy-nine percent of evangelicals strongly agreed, with a further 12 percent agreeing—a total of 91 percent.
Participants were also asked to rate their agreement on a scale of 0 to 10, with the statement, ‘I live differently to others in the culture around me because I’m a Christian’. Sixty-nine percent of evangelicals strongly agreed, while 26 percent agreed—a total of 95 percent. Part of what it means to live differently seems to be a high level of engagement in what could be considered pro-social or political activities. On at least a weekly basis, 55 percent of evangelicals volunteer for activities run by churches, 54 percent give money to their church and/or Christian mission, and 18 percent give money to development projects or humanitarian relief. On a monthly basis, 25 percent volunteer for activities run by churches, 37 percent give money to their church and/or Christian mission, and 43 percent give money to development projects or humanitarian relief.
2.3. Evangelicals vs. the General Population
Unsurprisingly, evangelicals in the self-selecting questionnaire were much more conservative than the general population in their answers to questions about same-sex relationships, abortion, religious freedom in the workplace, and climate change. Perhaps somewhat surprisingly, evangelicals held more liberal or ‘welcoming’ attitudes towards asylum seekers, refugees, and other newcomers than the general population. On the other hand, evangelicals in the self-selecting questionnaire gave answers that were much like those of the general population around questions related to peace and reconciliation in Northern Ireland, reforming the Northern Ireland Assembly, and economic policy.
Table 5 compares responses from evangelicals in the self-selected questionnaire and the general population survey. Answers where there are significant differences are presented in red type.
Self-selecting evangelicals’ sympathy towards asylum seekers, refugees, and newcomers defies the stereotype of right-wing opposition to immigration, indicating that, on this issue at least, evangelicals have more in common with the political left than would have been supposed. Evangelical enthusiasm for ‘peace and reconciliation’ could also be considered somewhat unexpected—but only if evangelicalism is reduced to a Troubles-era blend of oppositional anti-Catholicism, i.e., Paisley’s ‘last bastion’.
2.4. Types of Evangelicals
Neither poll provided a definition of evangelicalism. This meant that respondents had a great deal of freedom to interpret the term and to choose if they would identify with it. There were significant differences in religious practices and attitudes towards abortion and same-sex marriage between the general population, evangelicals in the general population survey, and evangelicals in the self-selecting questionnaire. Self-selecting evangelicals were the most distinctive from the general population (
Table 6).
The differences between evangelicals in the general population survey and evangelicals in the self-selecting questionnaire indicate that there are likely different ‘types’ of evangelicals in Northern Ireland, which merits further analysis. Indeed, earlier studies of evangelicalism have identified a range of types (
Brewer and Higgins 1998;
Jordan 2001;
Ganiel 2008); however, the data for these studies were collected around two decades ago and concerned only evangelical Protestants.
In conversation with the authors, EANI produced a new, four-fold typology for describing the evangelicals encountered through these polls: broad-church, classic, Catholic evangelicals, and ex-vangelicals (
EANI 2024, p. 29).
2.4.1. Broad-Church Evangelicals
The broad-church type encompasses the wide range of people who associate with evangelicalism across the general population. They have higher rates of church attendance, bible reading, and prayer than the general population—but not as high as classic evangelicals. They also differ from the general population on social/political issues, but again, not as much as classic evangelicals (
EANI 2024, p. 29).
We have associated broad-church evangelicals with all those who described themselves as evangelical in the general population survey. Of course, in reality, this group of survey respondents would contain classic evangelicals. Unlike the longer, self-selecting questionnaire, the general population survey did not include questions relating to Bebbington’s quadrilateral. If adherence to such beliefs is what distinguishes classic from broad-church evangelicals, we do not have the data to determine with any accuracy the mix of broad-church and classic evangelicals within the evangelical category in the general population survey. One respondent on the self-selected questionnaire even used the term broadchurch when explaining what evangelicalism meant to them. This answer recognises and honours evangelical diversity, yet insists that it should be set apart from cultural Protestantism (hence the scare quotes around Protestant):
To be an evangelical is to be part of a broad church (pun intended) of believers in Christ Jesus. Evangelical is sometimes used interchangeably with ‘Protestant’, rightly or wrongly.
However, it is likely that broad-church evangelicals include those who disagree with some aspects of classic evangelicalism (theological and/or socio-political), but still feel an affinity with evangelicalism. For some, it may be a broad cultural term that includes very little religious practice; others may practice regularly and find meaning in the evangelical category but have some reservations about the evangelical tradition.
2.4.2. Classic Evangelicals
The classic type is based on the evangelical respondents who completed the self-selected questionnaire. These evangelicals, by and large, identified with all aspects of Bebbington’s quadrilateral. They were certainly distinctive in terms of the intensity of their religious practices and their views on social issues, as already discussed extensively throughout. This group may correspond in many ways to the ‘conservative Protestants’ who also chose a ‘born again’ designation in the 2004 Life and Times (
Mitchell and Tilley 2008).
2.4.3. Catholic Evangelicals
The most surprising result of the general population survey was that 38 percent of practising Catholics chose to describe themselves as evangelical. As discussed previously, younger Catholics are driving this trend. While further research is necessary to explore this phenomenon,
EANI’s (
2024, p. 30)
Good News People reflected that, ‘Since Vatican II, there has been an increasing focus by the Catholic church on evangelization, and this has continued in ‘the new evangelization’ of Pope Francis (
Swindal 2014)’. Evangelical Catholicism has also grown in the United States (
Weigel 2014). It seems possible that Irish Catholicism has been influenced both by Francis’ example and by American trends.
Good News People (
EANI 2024, p. 30) also reported that ‘In the UK and across Ireland, there has been a recent uptick in the number of Catholic parishes running Alpha courses, and this may also have had an impact’.
Good News People asked five Catholics, including Archbishop of Armagh Eamon Martin (the head of the Catholic Church in Ireland), to share their thoughts on these results, which provide some preliminary insights. Martin said (
EANI 2024, p. 33):
The personal encounter and friendship with Jesus Christ is central to the Catholic evangelical outlook, conforming one’s life more and more with the life of Christ, who is the Way, the Truth and the Life and in whom we see the merciful face of God.
Ciara Cunningham, who describes herself as ‘from Belfast … [and] raised Catholic’, described doing a 10-week Youth Alpha course in her parish when she was 17, testifying that (
EANI 2024, p. 31):
This was where I encountered the person of Jesus which changed my life. I experienced Jesus’ love for me in a wonderfully personal way. … I received a new thirst to read the Bible and to pray using the Bible. … Since then, I sought more opportunities to grow in a personal relationship with Jesus.
In the United States, evangelical Catholics and Protestants have often united around conservative moral causes.
Good News People speculates that if the link between political unionism and Protestant evangelicalism weakens, Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland could increasingly work together in a similar way. It is also possible that evangelical Catholic-Protestant initiatives built around prayer and Bible study could develop. One such organization, ‘Evangelical Catholic Initiative’, already exists, describing itself as ‘focused on the priority of evangelism in the Catholic Church and on joining with Christians in other denominations to fulfill the Great Commission’ (
ECI n.d.).
2.4.4. Ex-Vangelicals
Ex-vangelicals are those who reported that they used to identify as evangelical but no longer do: 1.6 percent in the general population survey and 5.3 percent in the self-selecting questionnaire. In the self-selected questionnaire, 99 ex-vangelicals wrote in a response to explain why they no longer identified as evangelical. The
Good News People report (
EANI 2024, p. 34) points out that ‘while these numbers are relatively small, applying the 1.6% figure to the population would result in more ex-vangelicals in Northern Ireland than the number of people who hold any religious faith other than Christian (1.3% according to the 2021 NI census)’. Ex-vangelicals in the self-selecting questionnaire were more likely to be male (59 percent) and between the ages of 35 and 44 (36 percent).
The data do not fully capture what people do when they leave evangelicalism, which could include staying in their church, finding a different church, or leaving their faith completely. However, on a weekly basis, 69 percent of ex-vangelicals still attended church, and 71 percent read the Bible. While these numbers are higher than the general population and broad-church evangelicals, they are not as high as classic evangelicals. The self-selecting questionnaire also uncovered major differences between ex-vangelicals and classic evangelicals on several points, which provide some hints as to why ex-vangelicals may have left evangelicalism (
Table 7).
Ex-vangelical write-in responses about why they left were varied, including evangelicalism’s association with Donald Trump and right-wing politics and perceived evangelical stances on moral/social issues:
I am disgusted and embarrassed at many aspects of evangelicalism, e.g., support for Trump, treatment of those in same-sex relationships and others, treatment of female believers, sectarianism and the desire and attempts to impose so-called ‘biblical’ values on society … and the constant embracing and portrayal of Christians in our society as being persecuted for the sake of their beliefs.
Evangelical is understood as fundamentalist inside and outside the church. Thanks for that, Donald Trump.
I do not like the association with the harsh unloving ‘right’ wing of the church.
The negative associations between the word ‘evangelical’ and the ill-treatment of LGBT people. My personal views on many subjects, however, have changed over the last decade and departed significantly from modern evangelical shibboleths.
Some of these reasons for leaving evangelicalism resonate with those found in
Mitchell and Ganiel’s (
2011) qualitative research, as well as
Marti and Ganiel’s (
2014) work on emerging Christianity, which included Northern Ireland. The preoccupation with Trump, however, is new and perhaps unexpected, given the wide gulf of the Atlantic that separates Northern Ireland and the United States. Nevertheless, it is as if Trump has replaced Paisley as a byword for the perils of mixing religion and politics.
3. Discussion
In recent decades, studies of religion in Northern Ireland have been limited. Most research has focused on the role of religion in conflict or peacebuilding (
Power 2024;
Brewer et al. 2011;
Ganiel 2008) and has been qualitative in nature. The research presented here goes a long way towards furthering understanding of religion’s significance, providing foundations for future research. Crucially, the data confirm the continued salience of religion across the region, including very high levels of practice. The data confirm the existence of an evangelical ‘bastion’, albeit one that is not preoccupied with anti-Catholicism and political division. Rather, evangelicalism continues to conform to the trend that
Mitchell and Tilley (
2004, p. 598) identified more than two decades previously when they wrote: ‘the vitality of modern evangelicals in Northern Ireland may well be related to their moral conservatism and therefore does not depend on the existence of political conflict’. Indeed, Northern Ireland’s evangelical bastion now includes 38 percent of practising Catholics, an unexpected finding. There has been almost no research on evangelical Catholicism in Northern Ireland. More work is needed to understand why so many practising Catholics are identifying as evangelical, exploring the social and political significance of this. It is possible that Northern Ireland will see more joint evangelical Protestant/Catholic mobilization around ‘moral’ issues such as abortion, same sex marriage, and religious freedom. Other research could be devoted to exploring the influence of American evangelical Catholicism in Northern Ireland.
The identification of four new ‘types’ of evangelicals aids in understanding diversity within contemporary evangelicalism. Differences between broad-church and classic evangelicals are important and merit further research. A detailed theological analysis of the beliefs and practices of each evangelical type cannot be made based on this survey data. For example, the data presented here cannot tell us why broad-church evangelicals identify as evangelical despite disagreement with classic evangelicals on various theological and/or socio-political issues. Future research should explore the lasting salience of Bebbington’s quadrilateral among ‘classic’ evangelicals as well as analyse how broad-church evangelicals understand their evangelical identity, including points of theological difference with classic evangelicals. In addition, there have been no studies of ex-vangelicals in the last decade. Repeated references by ex-vangelicals to Donald Trump and right-wing American evangelicalism also merit more research, which would contribute to an international literature on the global influence of American evangelicalism/Christian nationalism. Deeper, more qualitative research is necessary to fully understand the general trends identified in the polls and to ultimately evaluate the accuracy of this fourfold typology.
The research also reveals surprising differences between men and women. Men are more likely to identify as evangelical than women—a finding that has not been apparent in previous research. While a previous study explored some of the barriers facing evangelical women (
Porter 2002), this new data may indicate a masculinization of evangelicalism or an increasing (relative) lack of enthusiasm for evangelicalism among women. There is opposition to women’s ordination within conservative evangelical ranks in the Presbyterian Church (
BBC 2023), and
Purser and O’Brien’s (
2021) analysis of ordained women in the Church of Ireland concluded that women were marginalised by interpretations of theology, patriarchal social and ecclesiastical structures, and perceptions of motherhood. While their study was not focused on evangelicalism, it may be the case that such barriers could be even stronger within evangelicalism.
Another surprising finding in this regard is that in some indicators, women were
not more religious than men—as the international literature would lead us to expect (
Trzebiatowska and Bruce 2012). Relatively less religiosity among women has previously been observed in the Republic of Ireland, but not in Northern Ireland (
Ganiel 2023b), and merits more attention. Women’s relative lack of religiosity in the predominantly Catholic Republic may be linked to the abuses and cover-ups in the Catholic Church, including the historic ill-treatment of women in Magdalene Laundries and Mother and Baby Homes. Such abuses also occurred in Northern Ireland. But unlike Northern Ireland, in the Republic of Ireland the Catholic Church’s power was facilitated by the state, making abuses potentially more deeply rooted. It is likely that in Northern Ireland, women from Catholic and evangelical Protestant backgrounds have different reasons for disengagement from religious practice, but more research is needed across the island to understand these dynamics.
Further, it is significant that among practising Christians, the most evangelical age groups were the youngest: 18–24-year-olds (70 percent) and 25–34-year-olds (49 percent). At the same time, in the general population, religious practice was lowest among these age groups. This hints at a future of potential polarization, with sharper religious, social, and cultural distinctions between practising evangelical Christians (both Protestant and Catholic), decreasing numbers of non-evangelical practising Christians, and increasing numbers of people who say they have ‘no religion’ or do not practice at all.
Finally, the general survey found no differences between evangelicals and the general population on issues of peace and reconciliation; all are broadly supportive of doing more to promote them. While Paisley-style evangelicals were once blamed for division and violence, it seems that such a claim can no longer be made. The survey did not ask if people would take it upon themselves to promote peace and reconciliation, so it is impossible to say if evangelical agreement that ‘more effort is needed’ will translate into more effort on the part of evangelicals. Post-Belfast/Good Friday Agreement peacebuilding initiatives, such as the 4 Corners Festival and the Irish Churches Peace project (concluded in 2015), have been inter-church, not explicitly evangelical—although there has been evangelical involvement. The faith-based peace sector is not as large or vibrant as it once was, and it is not clear that young Christians are engaged with peacebuilding. Evangelicals’ trademark enthusiasm would lead us to believe that they would mobilise around some issues. It remains to be seen if conservative moral issues will trump peacebuilding or if evangelicals will devote themselves to activism in both areas.