The Role of Beach Morphology and Mid-Century Climate Change Effects on Wave Runup and Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
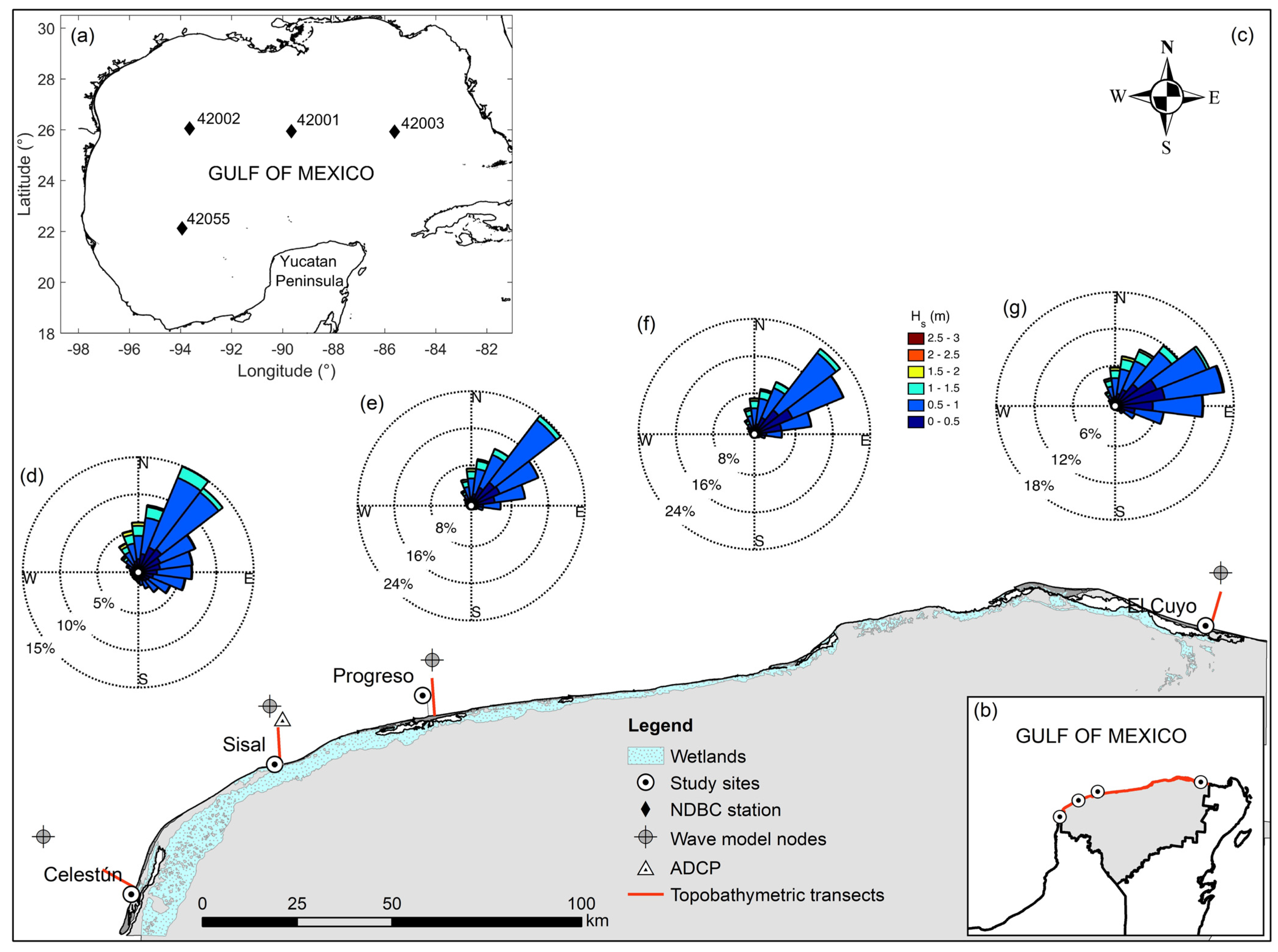
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
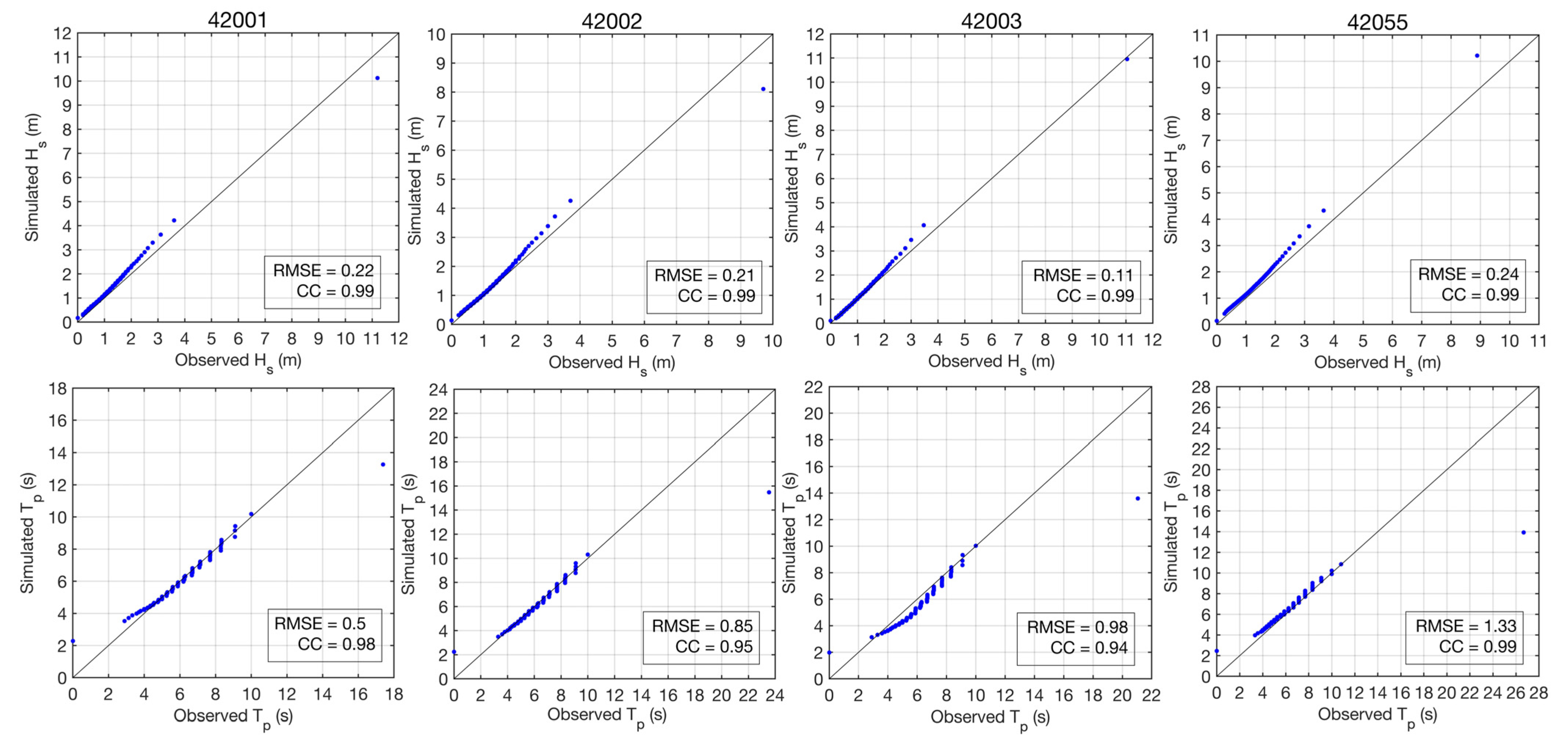
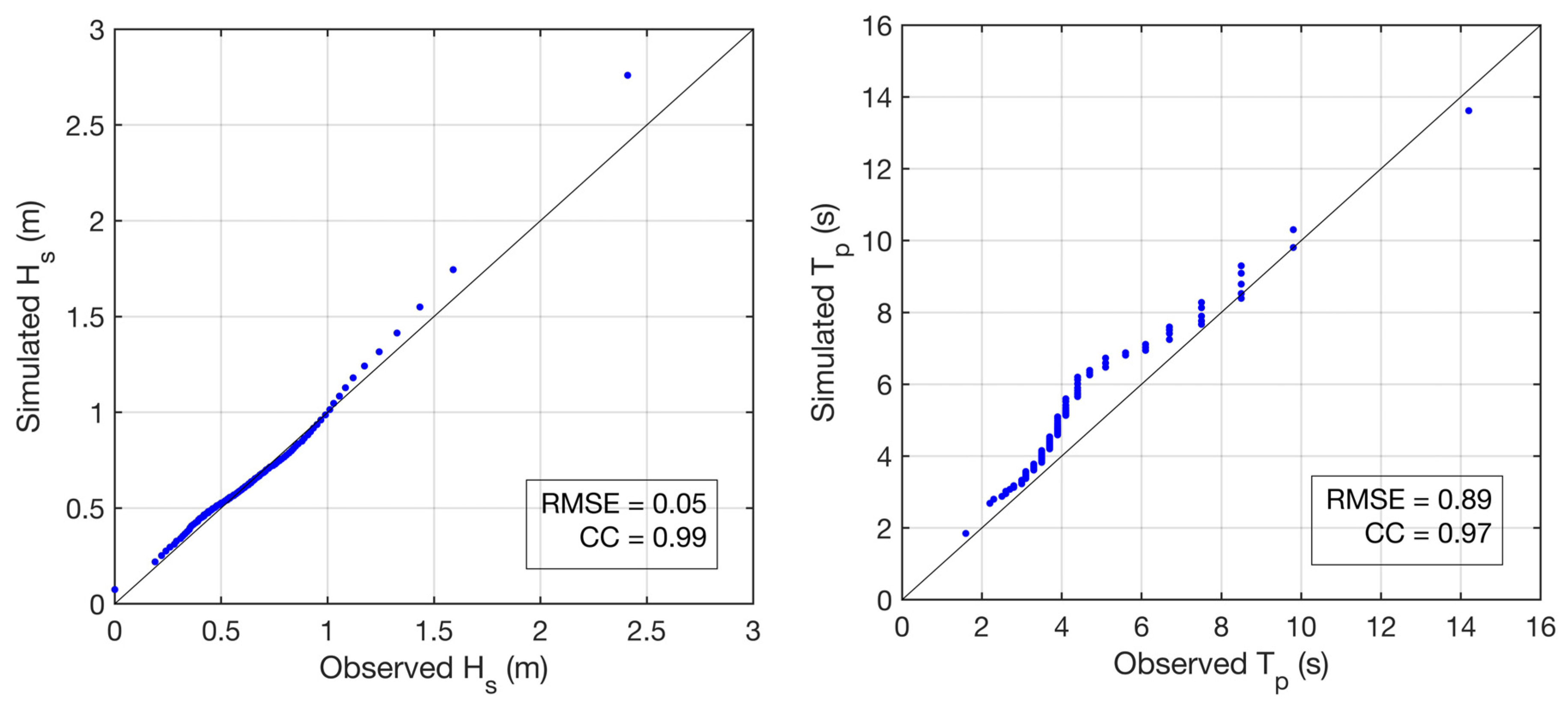
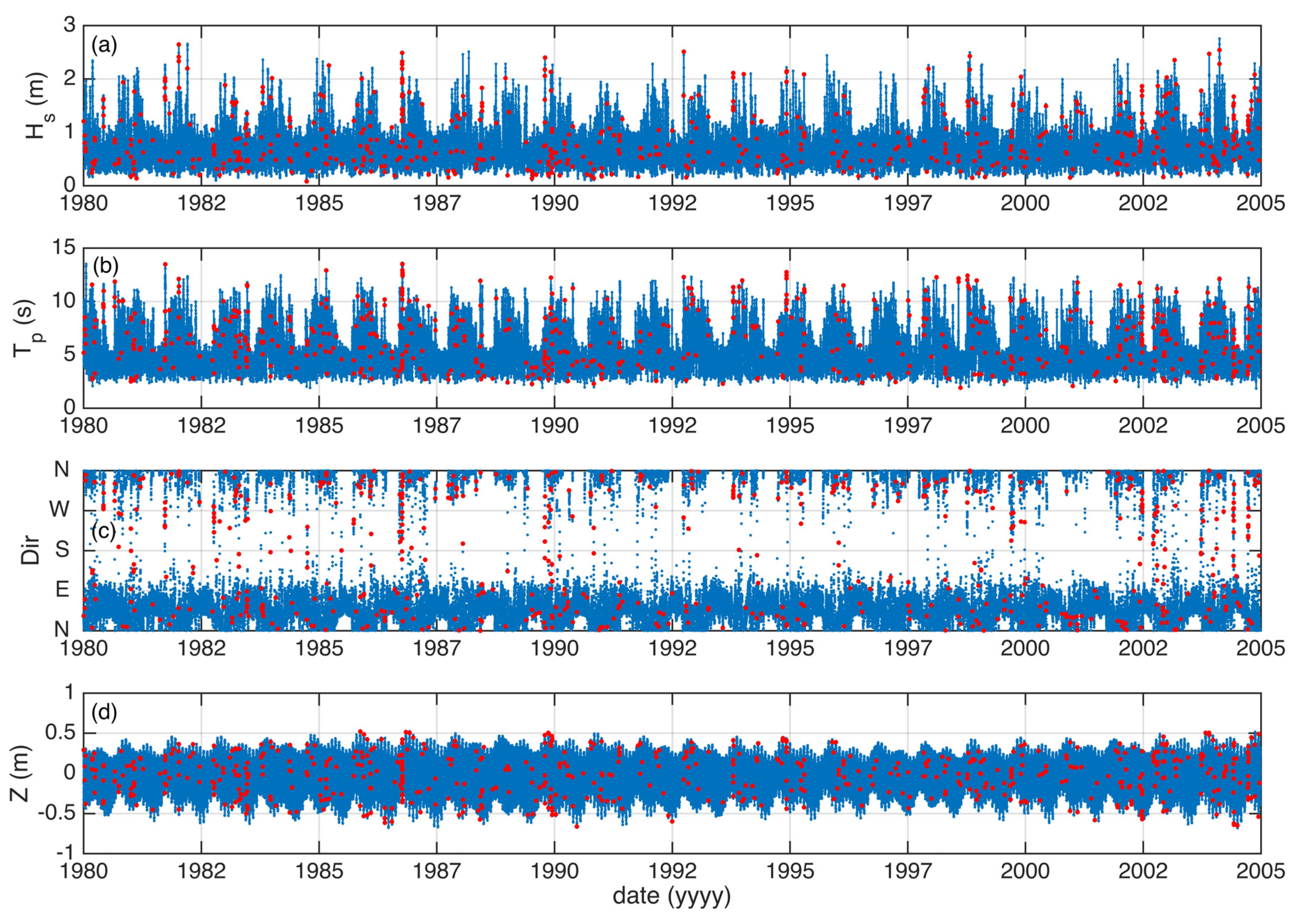
3.1. Wave Data
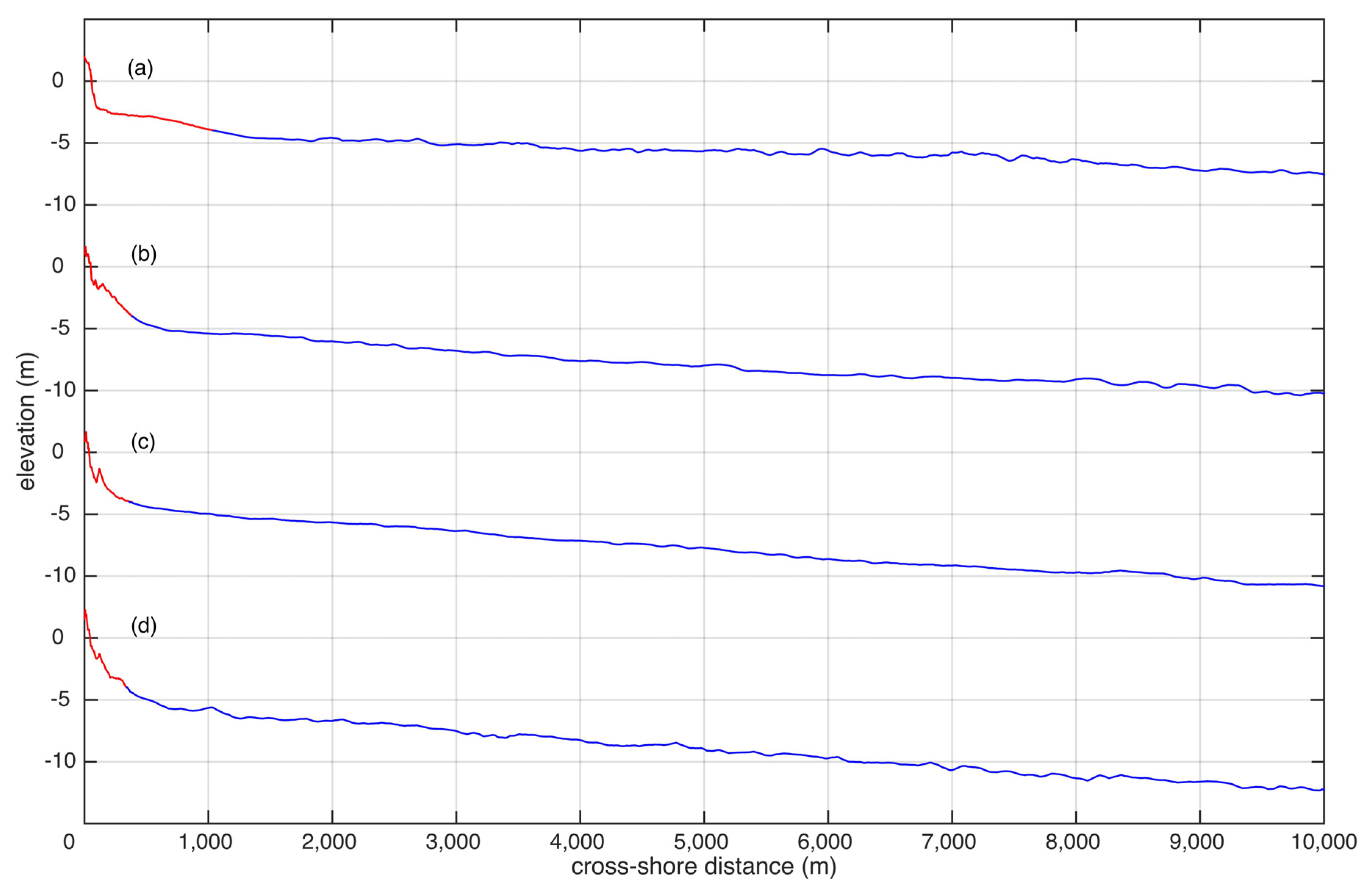
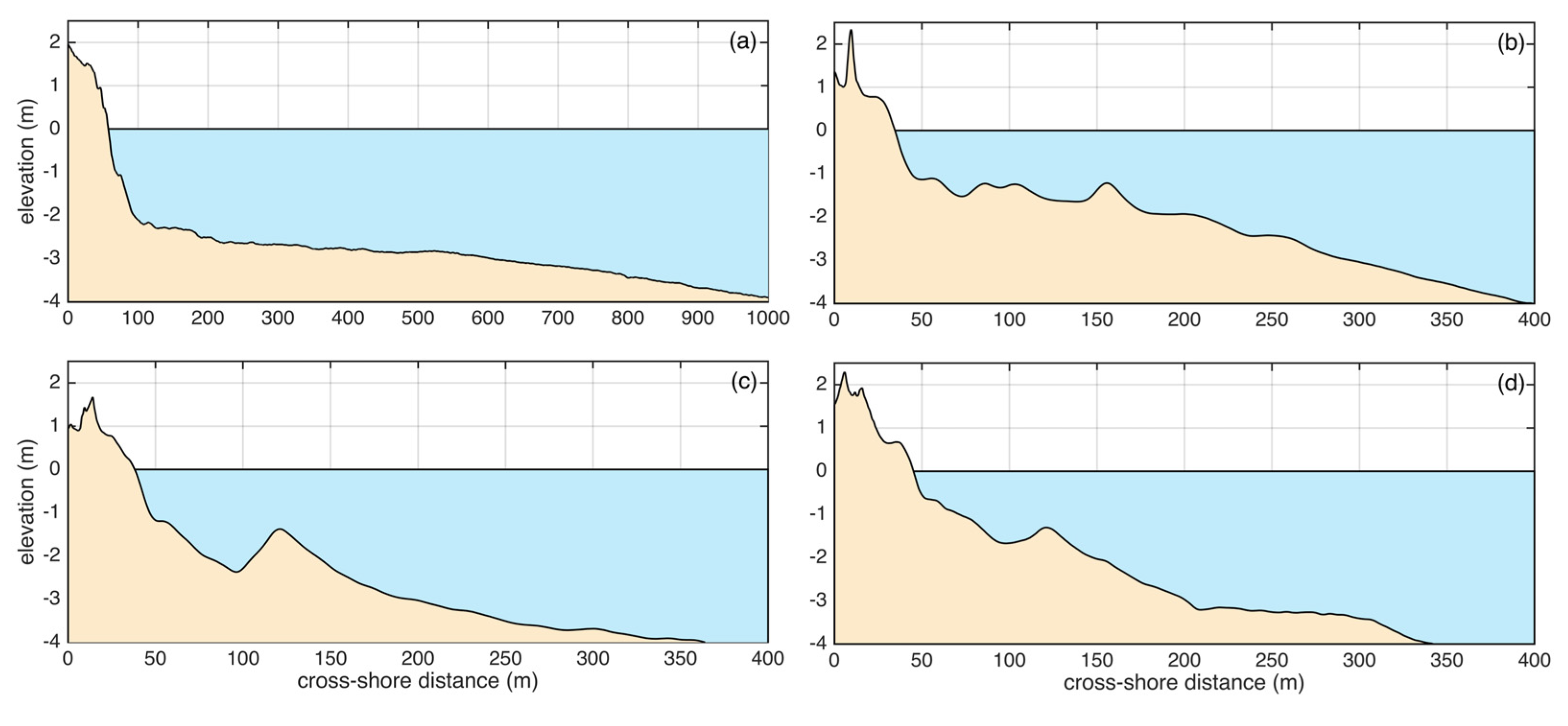
3.2. Topo-Bathymetric Measurements
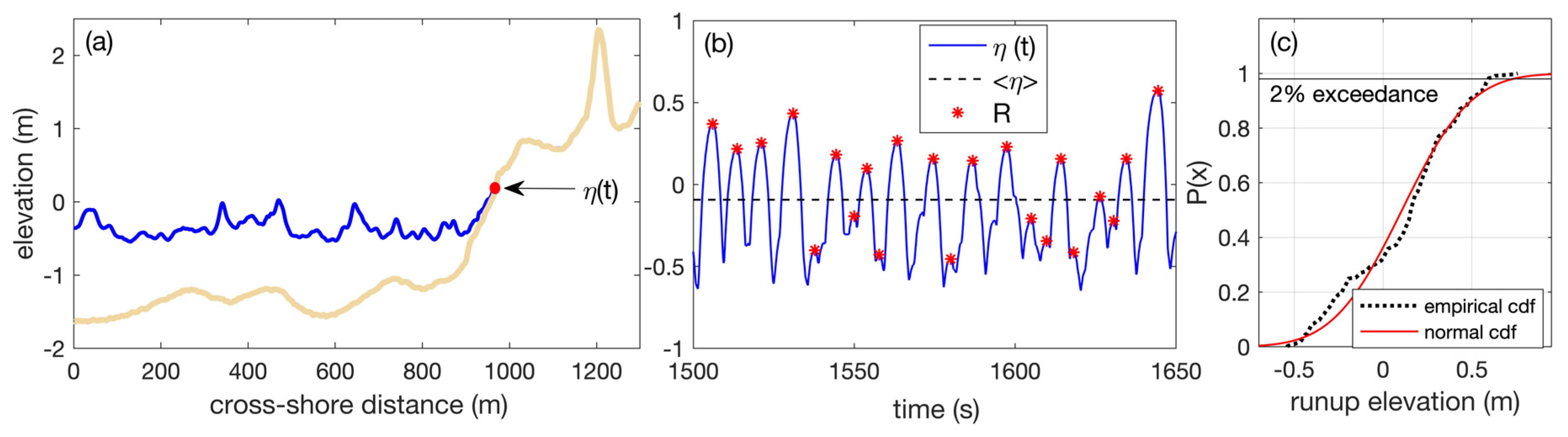
3.3. Wave Propagation and Wave Runup
3.4. Storm Impact
4. Results
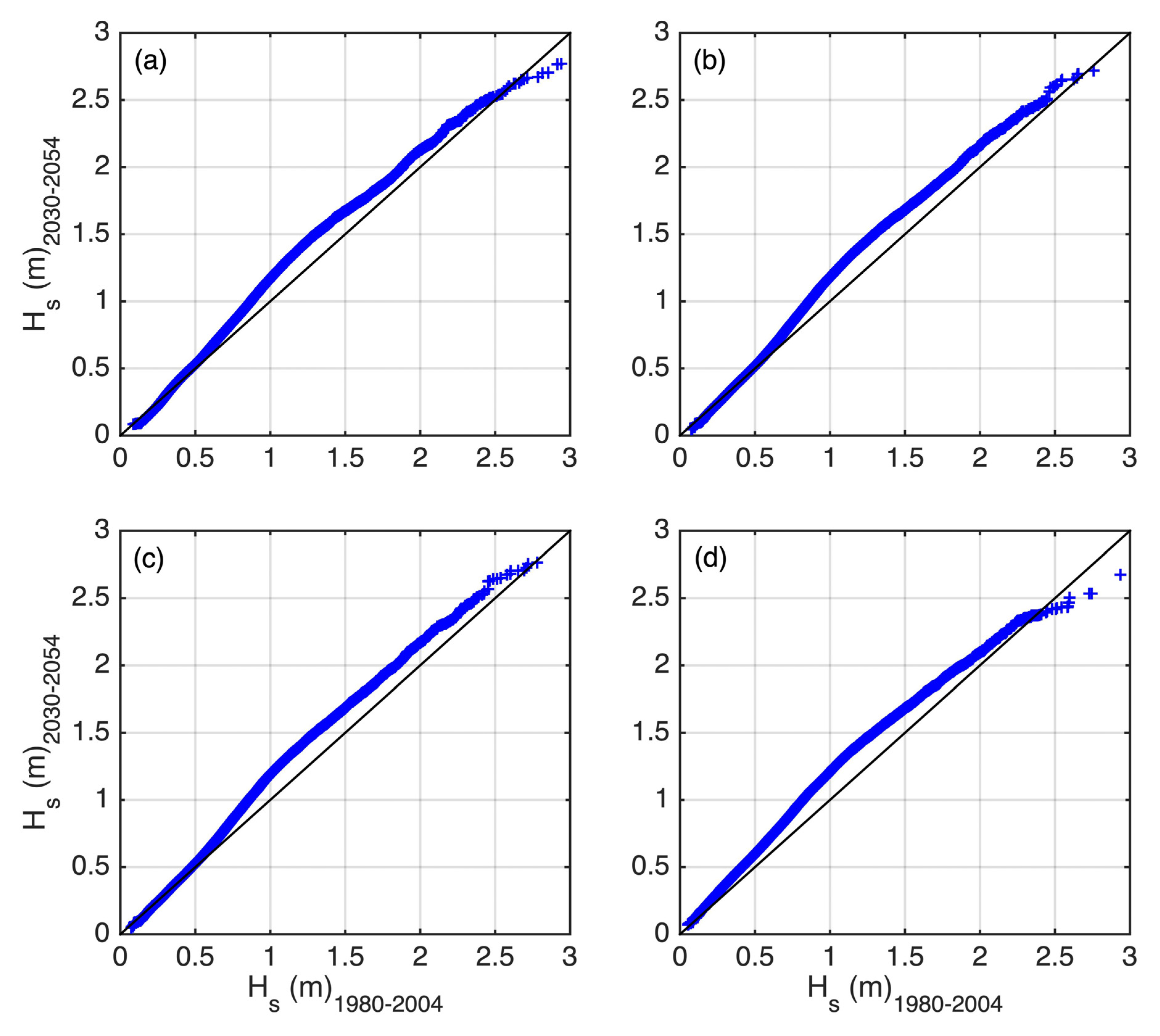
4.1. Present and Mid-Century Wave Conditions
4.2. Beach Dune Morphology
4.3. Extreme Water Levels
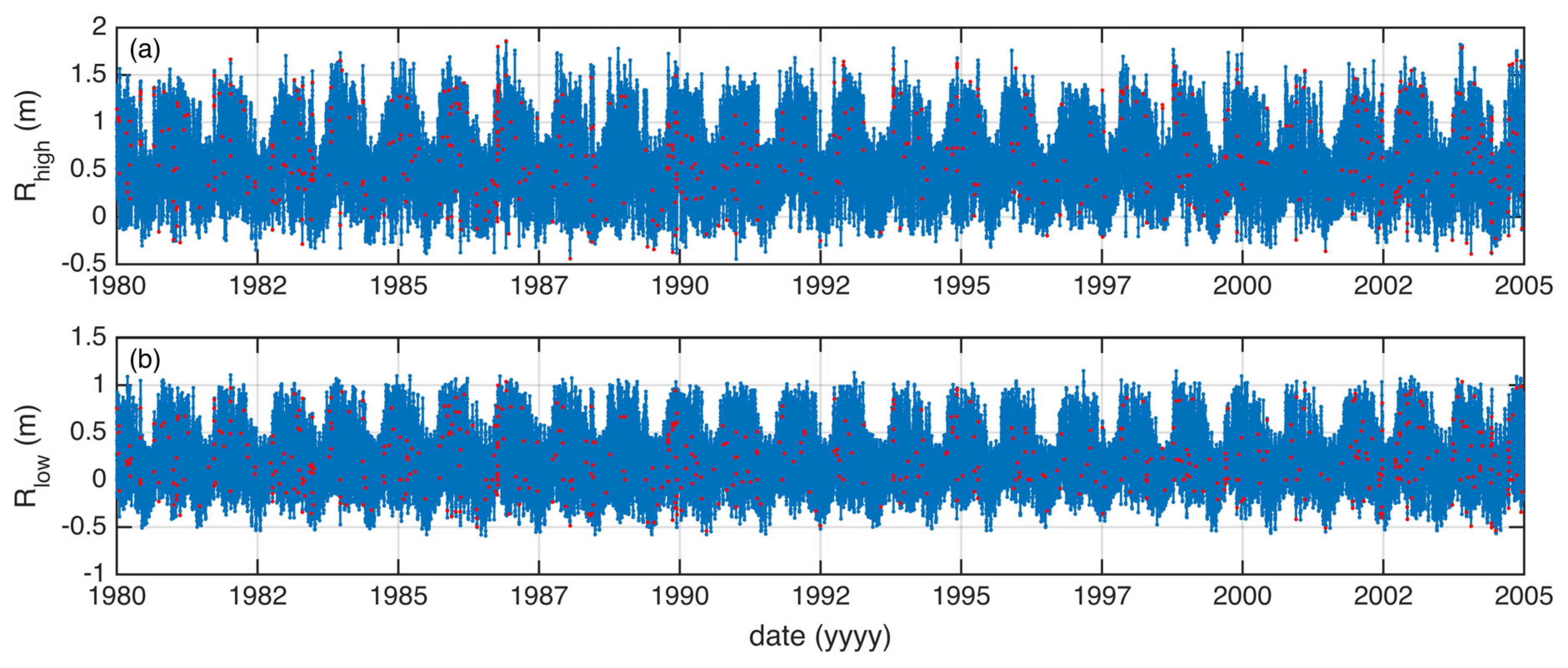
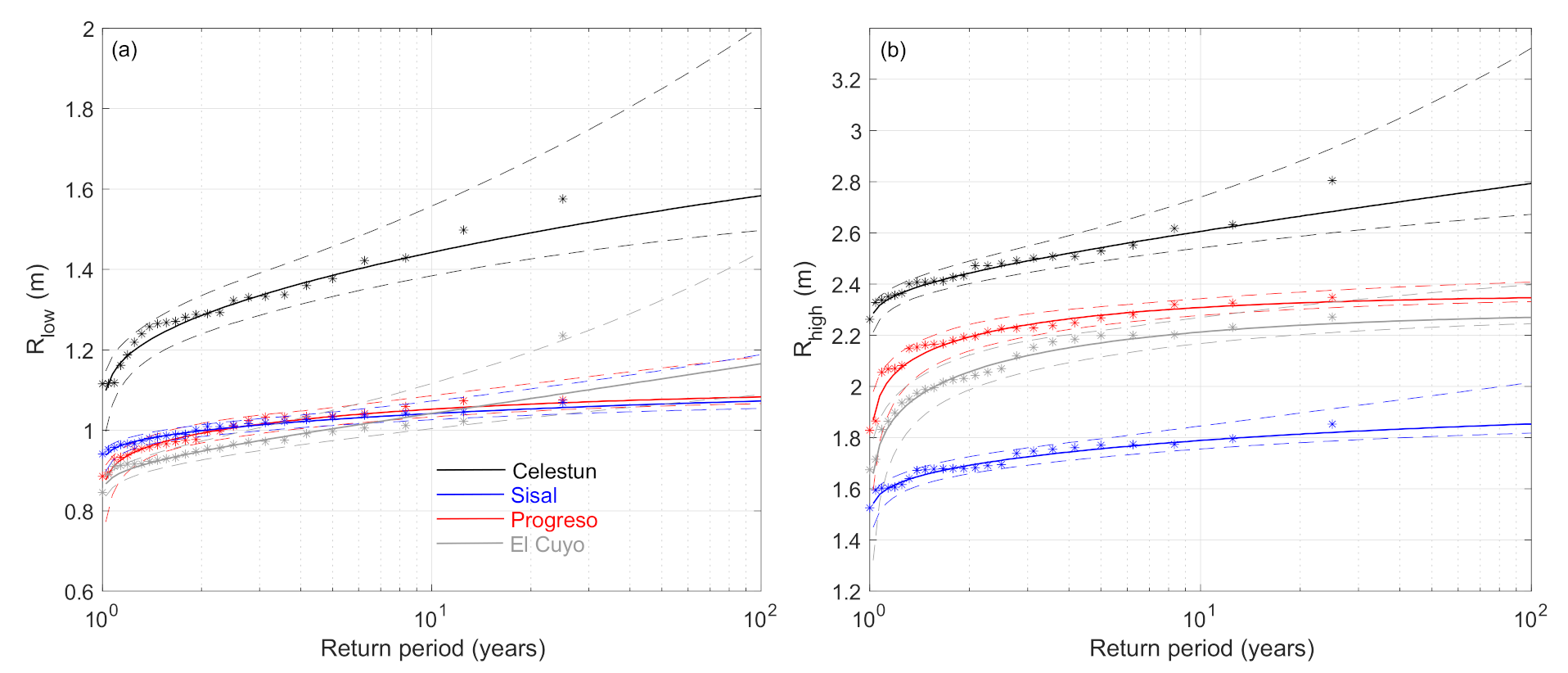
4.3.1. Extreme Water Levels: Present Conditions
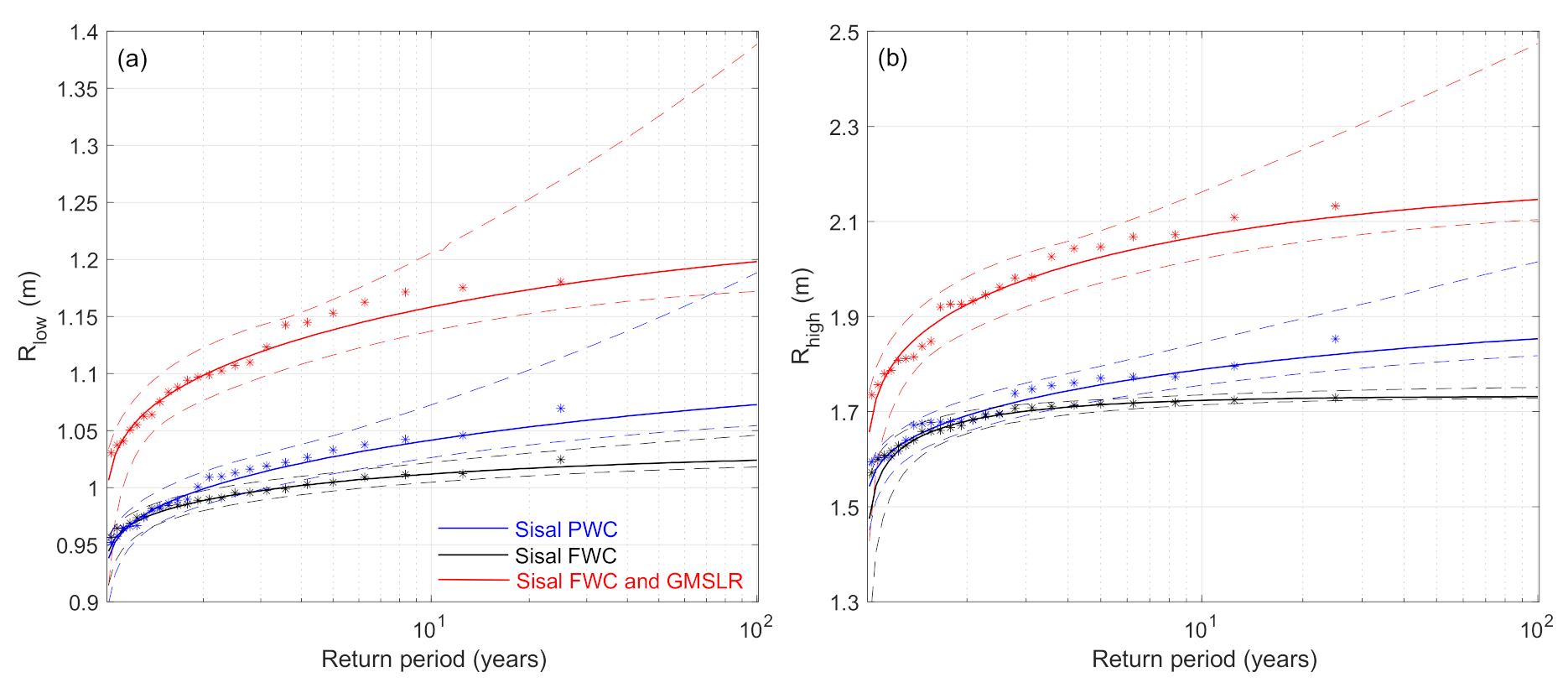
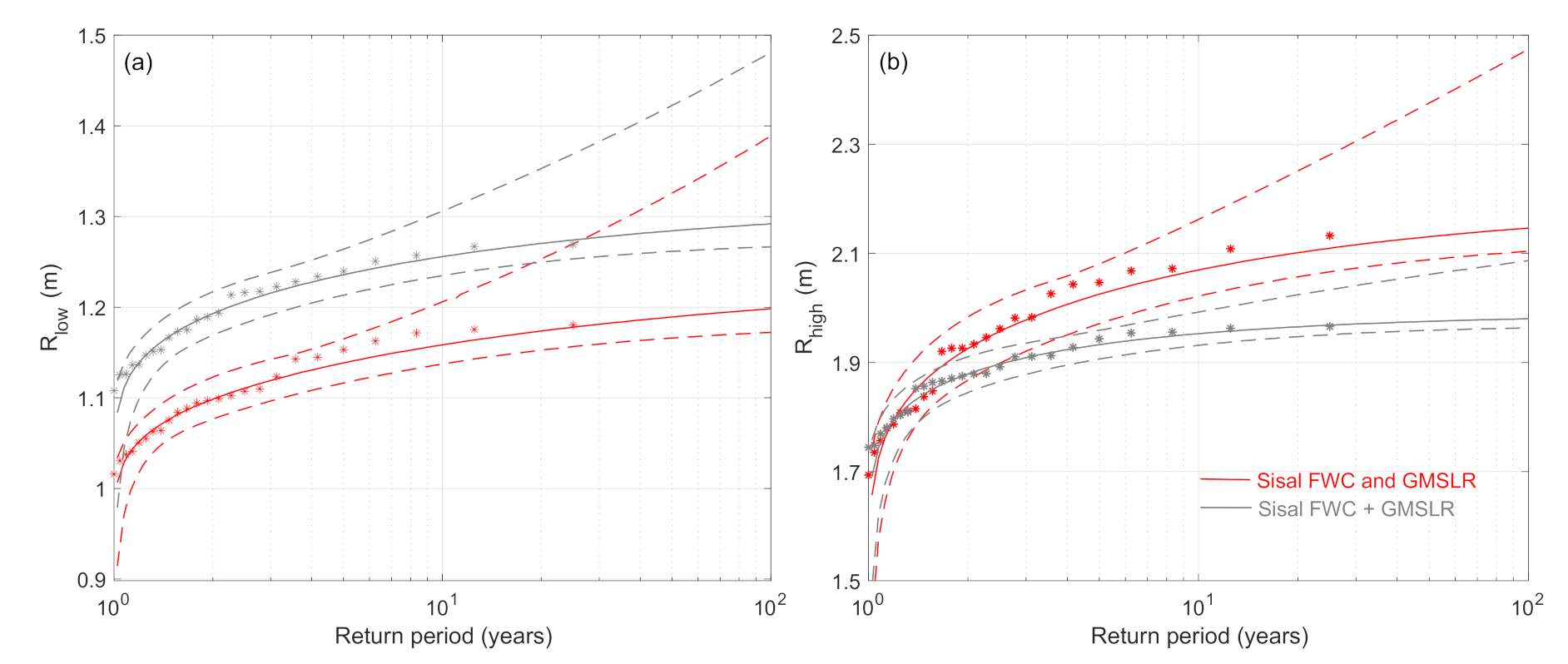
4.3.2. Extreme Water Levels: Mid-Century Conditions
4.4. Storm Impact: Present and Mid-Century Conditions
5. Discussion
5.1. The Role of Beach Morphology
5.2. The Role of Climate Change
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, P.P.; Losada, I.J.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Hinkel, J.; Khattabi, A.; McInnes, K.L.; Saito, Y.; Sallenger, A. Coastal systems and low-lying areas. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 361–409. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, B.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Zimmermann, J.; Nicholls, R.J. Future Coastal Population Growth and Exposure to Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Flooding—A Global Assessment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, S.; Beck, M.W.; Reguero, B.G.; Losada, I.J.; Van Wesenbeeck, B.; Pontee, N.; Sanchirico, J.N.; Ingram, J.C.; Lange, G.-M.; Burks-Copes, K.A. The Effectiveness, Costs and Coastal Protection Benefits of Natural and Nature-Based Defences. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulp, S.A.; Strauss, B.H. New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodet, G.; Melet, A.; Ardhuin, F.; Bertin, X.; Idier, D.; Almar, R. The Contribution of Wind-Generated Waves to Coastal Sea-Level Changes. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1563–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melet, A.; Meyssignac, B.; Almar, R.; Le Cozannet, G. Under-estimated wave contribution to coastal sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, S.; Barnard, P.L.; Fletcher, C.H.; Frazer, N.; Erikson, L.; Storlazzi, C.D. Doubling of coastal flooding frequency within decades due to sea-level rise. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.A.; Sallenger, A.H. Setup and swash on a natural beach. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1985, 90, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdon, H.F.; Holman, R.A.; Howd, P.A.; Sallenger, A.H. Empirical parameterization of setup, swash, and runup. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poate, T.G.; McCall, R.T.; Masselink, G. A new parameterisation for runup on gravel beaches. Coast. Eng. 2016, 117, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodet, G.; Leckler, F.; Sous, D.; Ardhuin, F.; Filipot, J.F.; Suanez, S. Wave Runup over Steep Rocky Cliffs. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 7185–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, D.; Caulet, C.; Bandet, M.; Bernatchez, P.; Dumont, D.; Augereau, E.; Floc’H, F.; Delacourt, C. Wave runup parameterization for sandy, gravel and platform beaches in a fetch-limited, large estuarine system. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 192, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, P.G.; Coco, G.; Garnier, R.; Klein, A.H.F. On the prediction of runup, setup and swash on beaches. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 204, 103148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkkemper, J.A.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Mendoza, E.T.; Ruessink, B.G. Parameterization of wave run-up on beaches in Yucatan, Mexico: A numerical study. Coast. Dynam. 2013, 25, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, N.; Ruggiero, P. The influence of seasonal to interannual nearshore profile variability on extreme water levels: Model-ing wave runup on dissipative beaches. Coast. Eng. 2016, 115, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarella, M.; Goldstein, E.B.; De Muro, S.; Coco, G. The use of genetic programming to develop a predictor of swash excur-sion on sandy beaches. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, J.W.; Young, A.P.; Ludka, B.C.; O’Reilly, W.C.; Henderson, C.; Merrifield, M.A.; Guza, R.T. Predicting site-specific storm wave run-up. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 493–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raubenheimer, B.; Guza, R.T.; Elgar, S. Field observations of wave-driven setdown and setup. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 4629–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.A.; Coco, G.; Bryan, K.R. Numerical simulations of wave setup overbarred beach profiles: Implications for pre-dictability. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2011, 137, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, N.; Dunkin, L.M.; Irish, J.L. An empirical model for infragravity swash on barred beaches. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, C.M.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Salles, P.; López-González, J.; Mendoza, E.T. Wave Climate and Trends for the Gulf of Mexico: A 30-Yr Wave Hindcast. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, E.; Appendini, C.M.; Mendoza, E.T. Storm-wave trends in Mexican waters of the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, C.M.; Pedrozo-Acuña, A.; Meza-Padilla, R.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Cerezo-Mota, R.; López-González, J.; Ruiz-Salcines, P. On the Role of Climate Change on Wind Waves Generated by Tropical Cyclones in the Gulf of Mexico. Coast. Eng. J. 2017, 59, 1740001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, C.M.; Hernández-Lasheras, J.; Meza-Padilla, R.; Kurczyn, J.A. Effect of climate change on wind waves generated by anticyclonic cold front intrusions in the Gulf of Mexico. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 3747–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.T.; Trejo-Rangel, M.A.; Salles, P.; Appendini, C.M.; López-González, J.; Torres-Freyermuth, A. Storm characteri-zation and coastal hazards in the Yucatan Peninsula. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, W.; Salles, P.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Ruíz-Salcines, P.; Teng, Y.-C.; Appendini, C.M.; Quintero-Ibáñez, J. Spatiotem-poral Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast during Hurricanes and Central American Cold Surge Events. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, F.; Frausto, O.; Ihl, T.; Aguilar, Y. An update soil map of The Yucatan State, Mexico: Geomorphopedological approach and WRB. Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2015, 2, 303–315. [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez, C.; Mariño-Tapia, I.J.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A. Dispersion in the Yucatan coastal zone: Implications for red tide events. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Levinson, A.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Enriquez, C.; Waterhouse, A.F. Tidal variability of salinity and velocity fields related to intense point-source submarine groundwater discharges into the coastal ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, C.M.; Salles, P.; Mendoza, E.T.; López, J.; Torres-Freyermuth, A. Longshore Sediment Transport on the Northern Coast of the Yucatan Peninsula. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 285, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reding, P.J. The Central American Cold Surge: An Observational Analysis of the Deep Southward Penetration of North American Cold Fronts. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.P.; Magaña, V.; Caetano, E.; Kusunoki, S. Cold surge activity over the Gulfof Mexico in a warmer climate. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 17, 1539–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Medellín, G.; Torres-Freyermuth, A. Morphodynamics along a micro-tidal sea breeze dominated beach in the vicinity of coastal structures. Mar. Geol. 2019, 417, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, J. Los Habitantes de la Zona Costera de Yucatán: Entre la Tradición y la Modernidad. In En: El Manejo Costero en México; Universidad Autónoma de Campeche, SEMARNAT, CETYS-Universidad; Rivera, E., Ed.; Universidad de Quintana Roo: Chetumal, Mexico, 2004; pp. 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Panorama sociodemográfico de Yucatán. Censo de Población y vivienda 2010; Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía: Aguascalientes, Mexico, 2011; 234p, ISBN 978-607-494-196-8. Available online: http://coespo.yucatan.gob.mx/general/31_Panorama_Yuc.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2021).
- POETCY. Programa de Ordenamiento Ecológico del Territorio Costero de Yucatán: Informe Final; Centro de Investigación y de estudios Avanzados del IPN; Unidad Mérida; Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán; Instituto Tecnológico de Conkal; Instituto Tecnológico de Mérida; Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán: Mérida, Mexico, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, O.R.; Kofoed-Hansen, H.; Rugbjerg, M.; Sørensen, L.S. A third-generation spectral wave model using an unstruc-tured finite volume technique. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Coastal Engineering ASCE, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–24 September 2004; pp. 894–906. [Google Scholar]
- Tolman, H.L. Alleviating the Garden Sprinkler Effect in wind wave models. Ocean Model. 2002, 4, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, C.M.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Oropeza, F.; Salles, P.; López, J.; Mendoza, E.T. Wave modeling performance in the Gulf of Mexico and Western Caribbean: Wind reanalyses assessment. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 39, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Geodetic Survey. Available online: https://geodesy.noaa.gov/GEOID/MEXICO97/ (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Camus, P.; Mendez, F.J.; Medina, R. A hybrid efficient method to downscale wave climate to coastal areas. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín, G.; Brinkkemper, J.A.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Appendini, C.M.; Mendoza, E.T.; Salles, P. Run-up parameteri-zation and beach vulnerability assessment on a barrier island: A downscaling approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, G.L.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Medellin, G.; Allende-Arandia, M.E.; Appendini, C.M. The role of the reef–dune system in coastal protection in Puerto Morelos (Mexico). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, A.; Cagigal, L.; Pearson, S.; Antolínez, J.A.; Storlazzi, C.; van Dongeren, A.; Camus, P.; Mendez, F.J. HyCReWW: A Hybrid Coral Reef Wave and Water level metamodel. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 127, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CICESE Predmar. Available online: http://predmar.cicese.mx/ (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, A.J., Nauels, Y., Xia, V.B., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlema, M.; Stelling, G.; Smit, P. SWASH: An operational public domain code for simulating wave fields and rapidly varied flows in coastal waters. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 992–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallenger, A.H. Storm impact scale for barrier islands. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 890–895. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, R. Scattered data interpolation: Tests of some methods. Math. Comp. 1982, 48, 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fasshauer, G.E.; Zhang, J.G. On choosing “optimal” shape parameters for RBF approximation. Numer. Algor. 2007, 45, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, A.F. The frequency distribution of the annual maximum (or minimum) values of meteorological elements. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1955, 81, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WAFO-Group. A Matlab Toolbox for Analysis of Random Waves and Loads—A Tutorial; Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stockdon, H.F.; Sallenger, A.H., Jr.; Holman, R.A.; Howd, P.A. A simple model for the spatially-variable coastal response to hurricanes. Mar. Geol. 2007, 238, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G.; van Heteren, S. Response of wave-dominated and mixed-energy barriers to storms. Mar. Geol. 2014, 352, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguero, B.G.; Losada, I.J.; Méndez, F.J. A recent increase in global wave power as a consequence of oceanic warming. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, A.D.; Lorenzo-Trueba, J. Morphodynamics of Barrier Response to Sea-Level Rise. In Barrier Dynamics and Response to Changing Climate; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch, U. Design requirement for mixed sand and gravel beach defences under scenarios of sea level rise. Coast. Eng. 2017, 124, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Site | Dlow (m) | Dhigh (m) | βf | βav |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celestun | 0.92 | 1.97 | 0.099 | 0.003 |
| Sisal | 0.84 | 2.34 | 0.124 | 0.006 |
| Progreso | 0.78 | 1.67 | 0.075 | 0.008 |
| El Cuyo | 0.66 | 2.29 | 0.118 | 0.008 |
| Study Site | Return Period (Years) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | |
| Celestun | Overwash | Overwash | Overwash | Overwash (Inundation) |
| Sisal | Collision | Collision | Collision | Collision |
| Progreso | Overwash | Overwash | Overwash | Overwash |
| El Cuyo | Collision | Collision | Collision (Overwash) | Collision (Overwash) |
| Study Site: Sisal | Return Period (Years) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | |
| PWC (1980–2004) | Collision | Collision | Collision | Collision |
| FWC (2030–2054) | Collision | Collision | Collision | Collision |
| FWC and GMSLR | Collision | Collision | Collision (Overwash) | Collision (Overwash) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medellín, G.; Mayor, M.; Appendini, C.M.; Cerezo-Mota, R.; Jiménez, J.A. The Role of Beach Morphology and Mid-Century Climate Change Effects on Wave Runup and Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050518
Medellín G, Mayor M, Appendini CM, Cerezo-Mota R, Jiménez JA. The Role of Beach Morphology and Mid-Century Climate Change Effects on Wave Runup and Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(5):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050518
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedellín, Gabriela, Martí Mayor, Christian M. Appendini, Ruth Cerezo-Mota, and José A. Jiménez. 2021. "The Role of Beach Morphology and Mid-Century Climate Change Effects on Wave Runup and Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 5: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050518
APA StyleMedellín, G., Mayor, M., Appendini, C. M., Cerezo-Mota, R., & Jiménez, J. A. (2021). The Role of Beach Morphology and Mid-Century Climate Change Effects on Wave Runup and Storm Impact on the Northern Yucatan Coast. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(5), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050518








