Near-Inertial Waves Induced by Typhoon Megi (2010) in the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
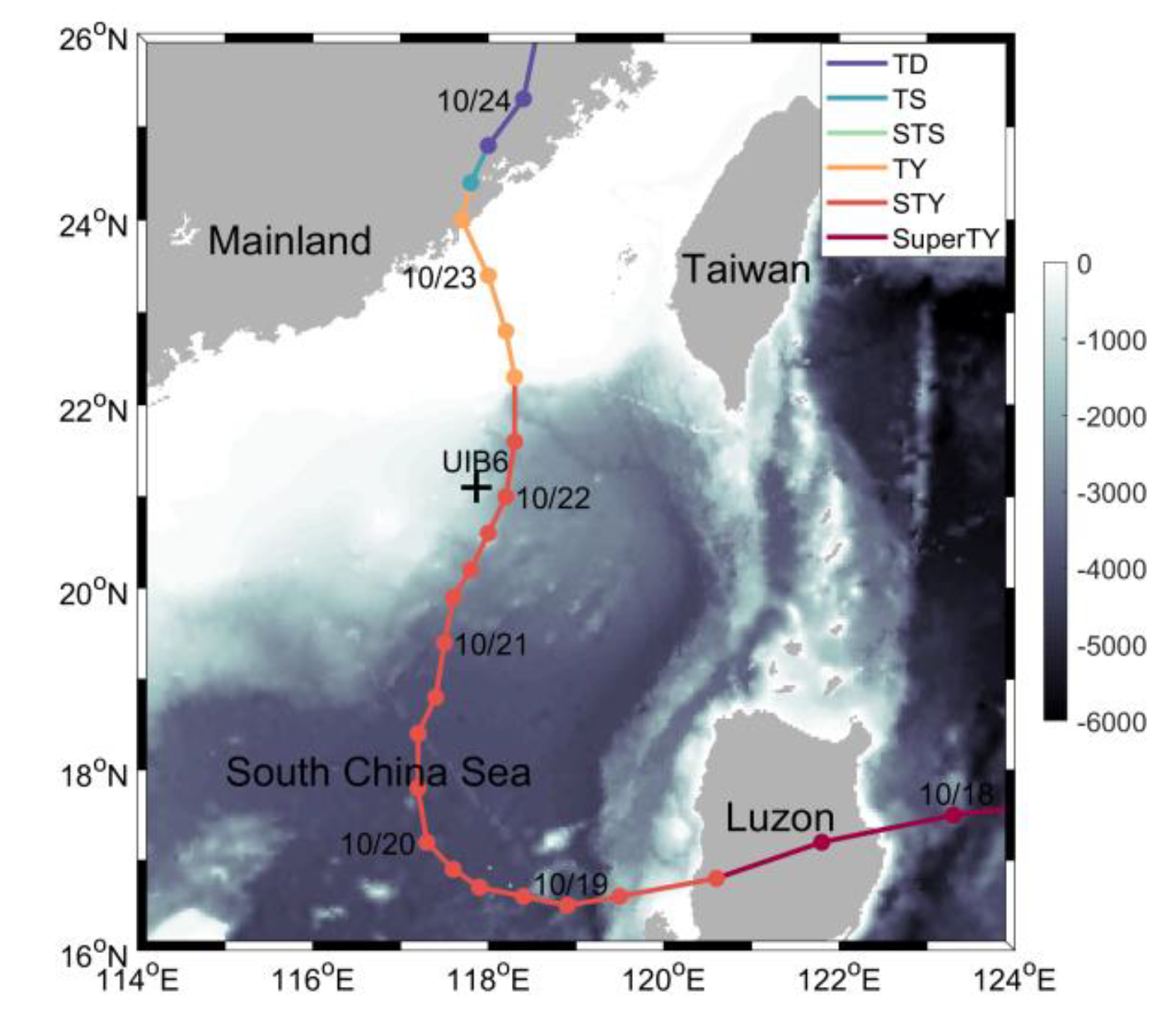
2.1. Typhoon Megi
2.2. Data
2.3. Methodology
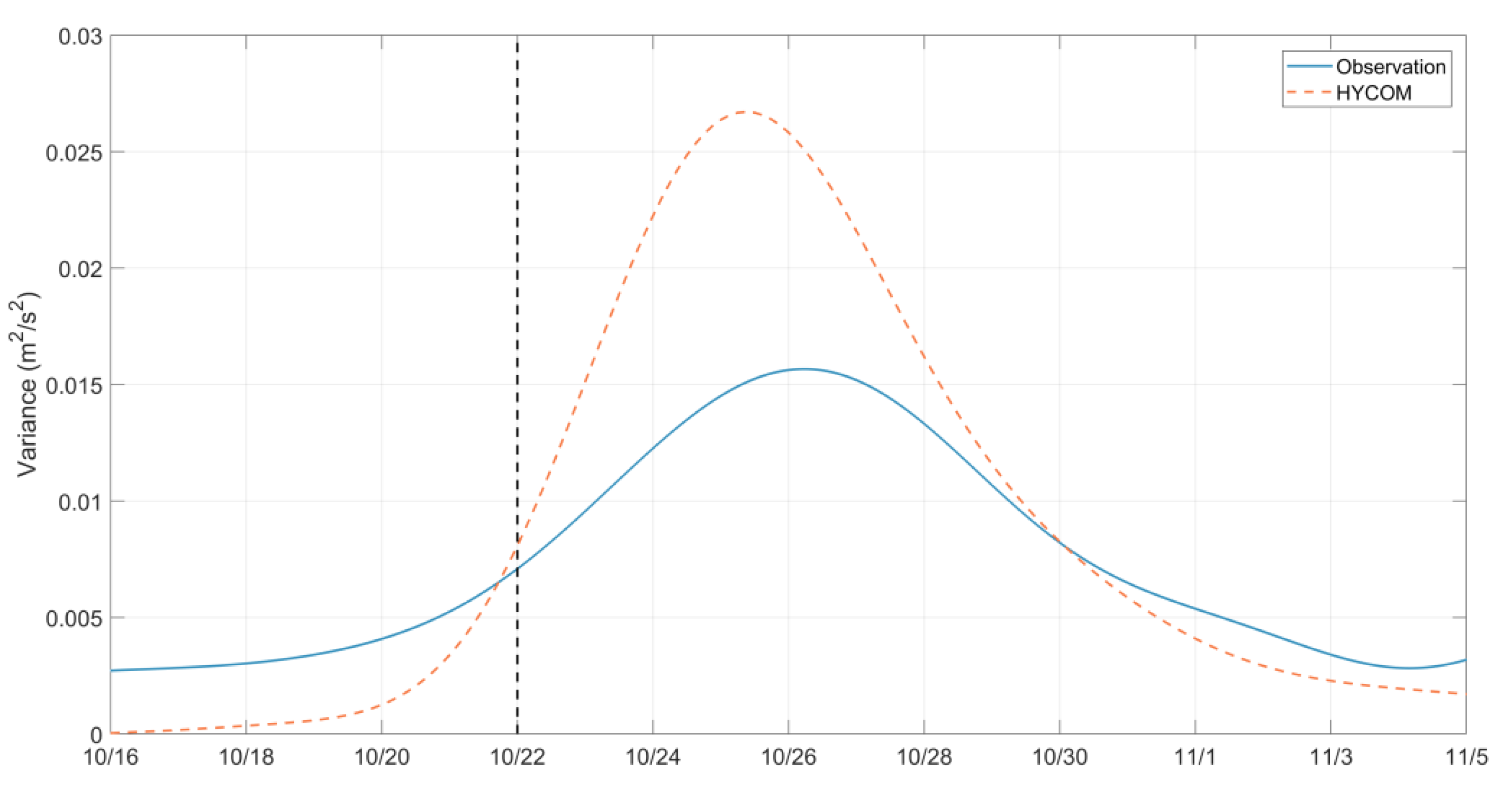
3. Comparison with In Situ Observations
4. Megi-Induced NIKE
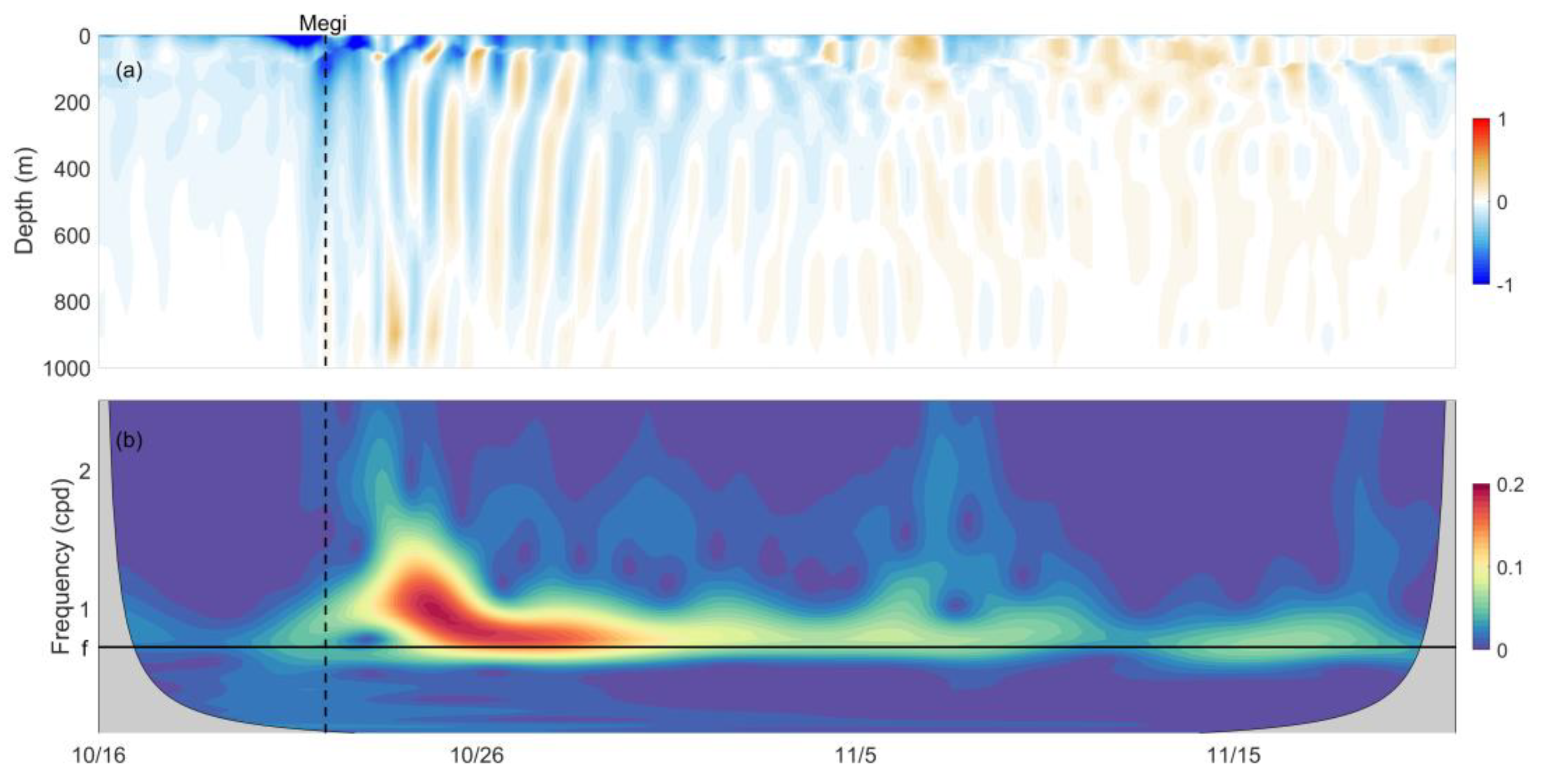
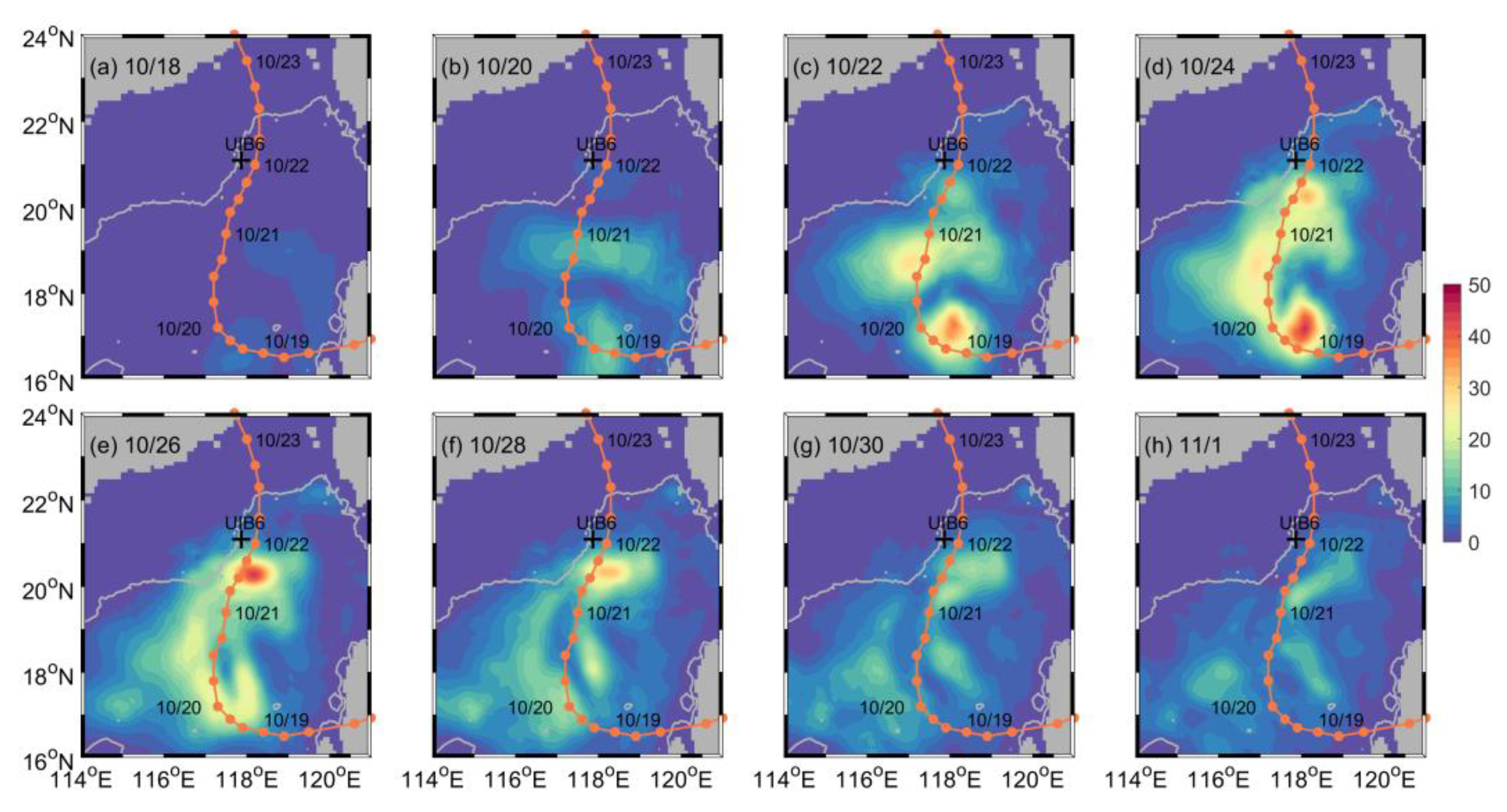
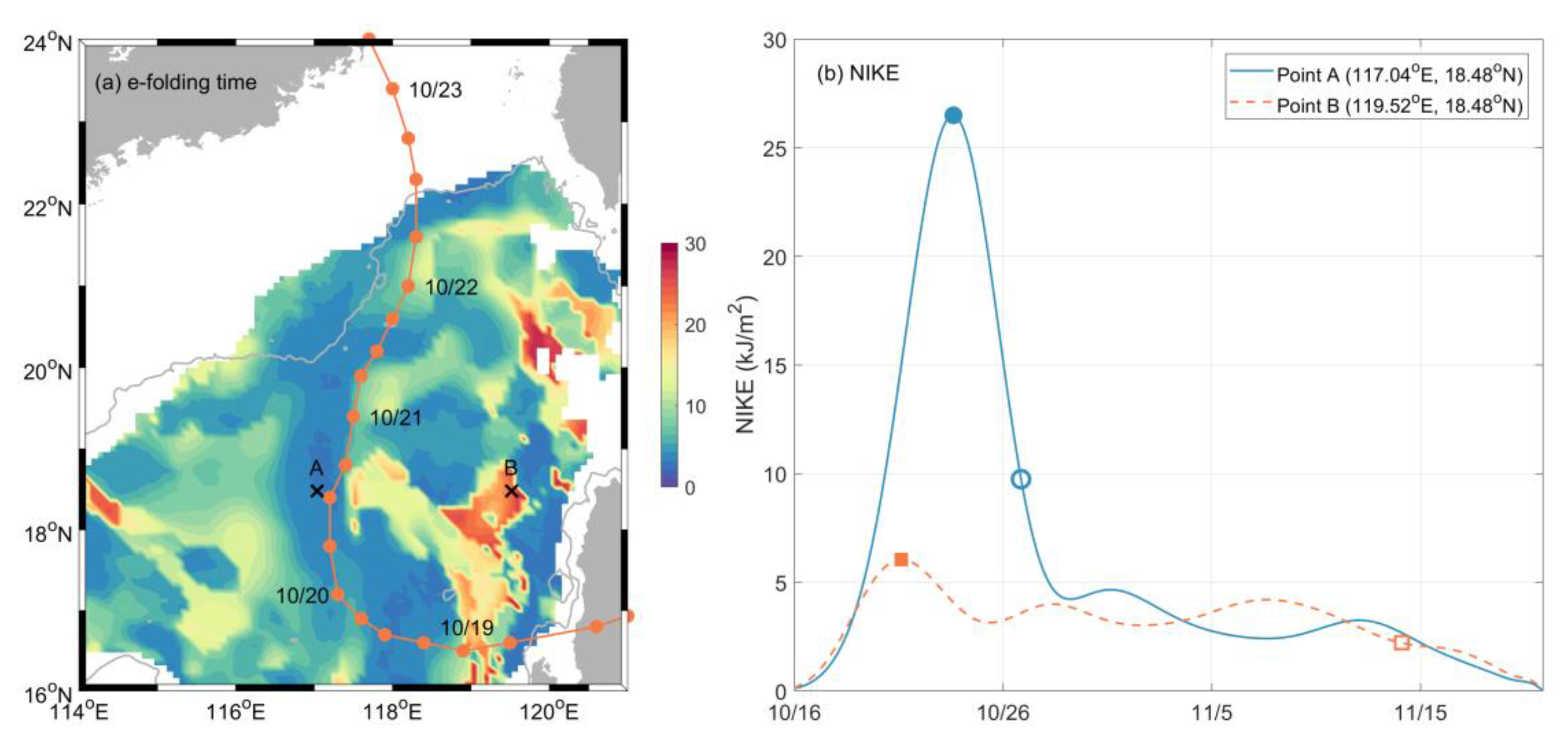
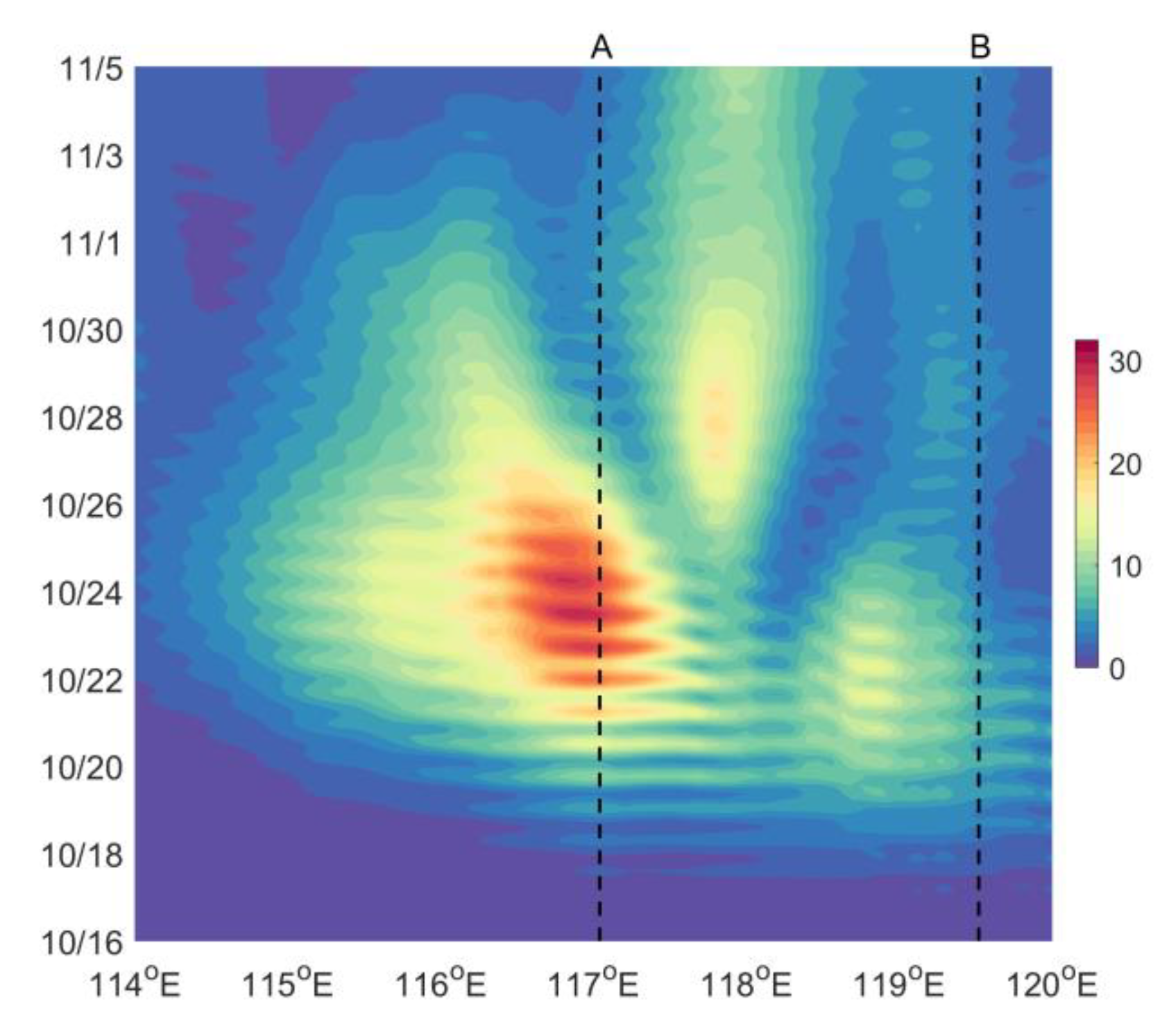
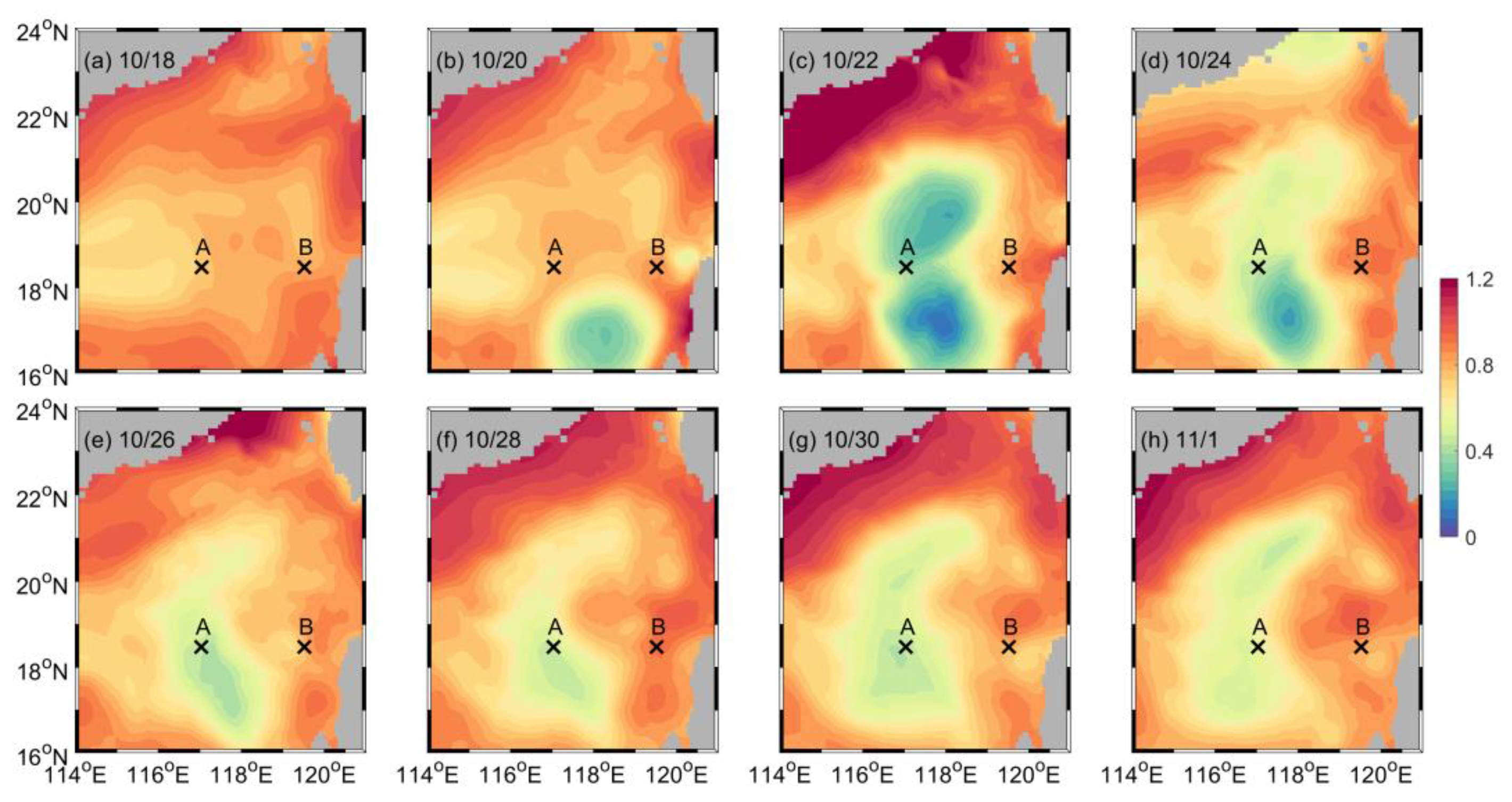
4.1. Temporal Variation and Spatial Distribution
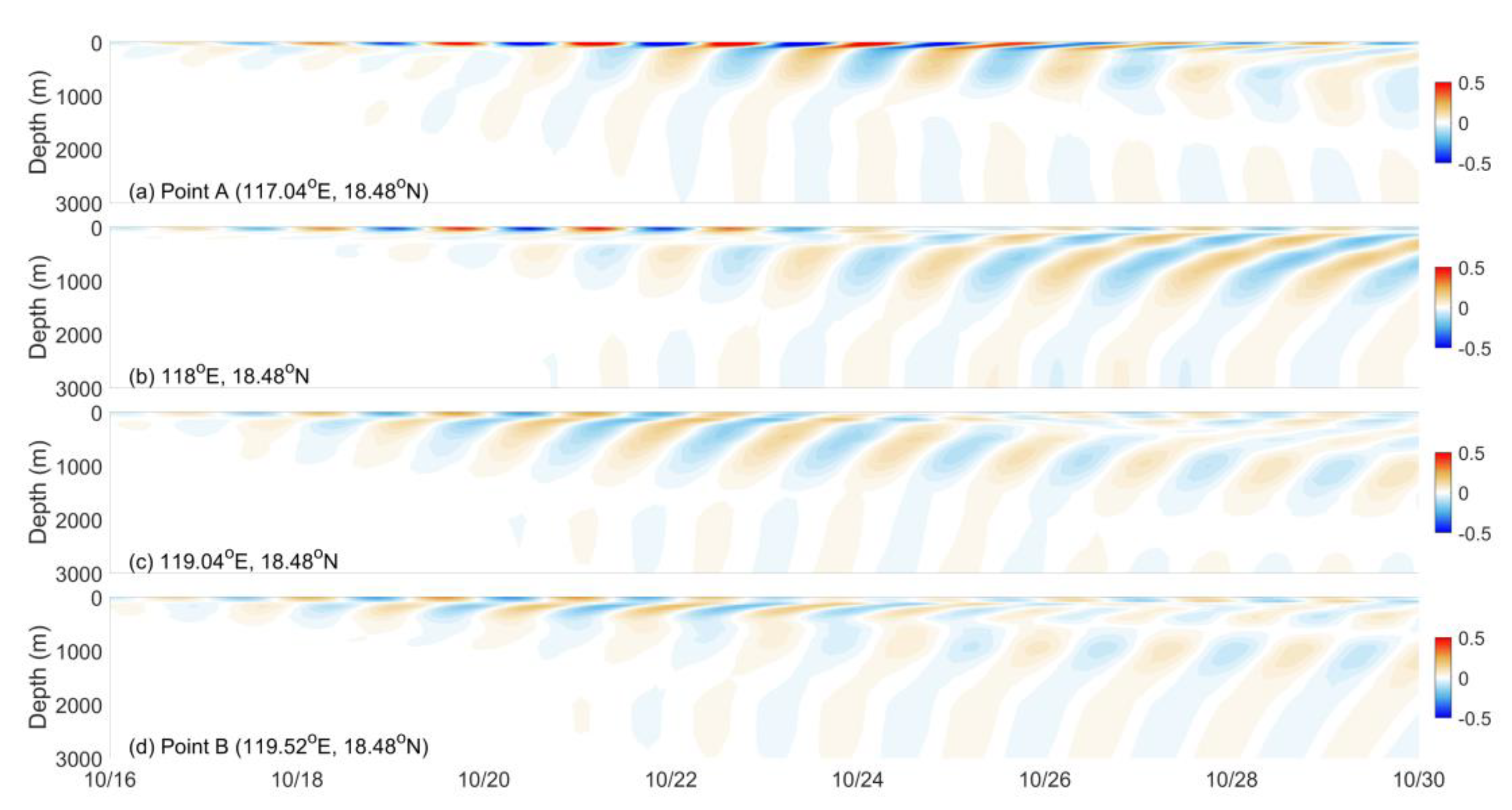
4.2. Damping
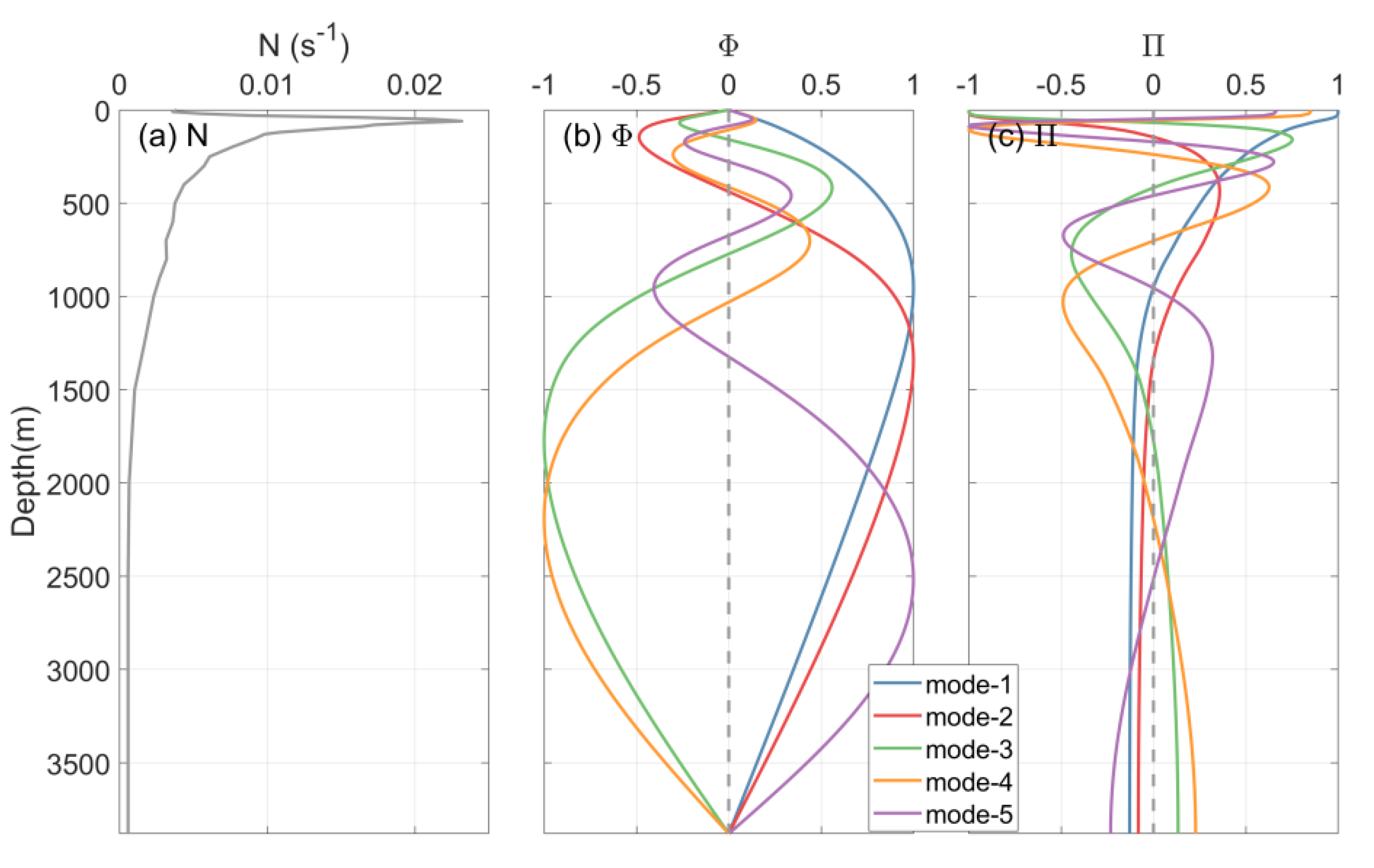
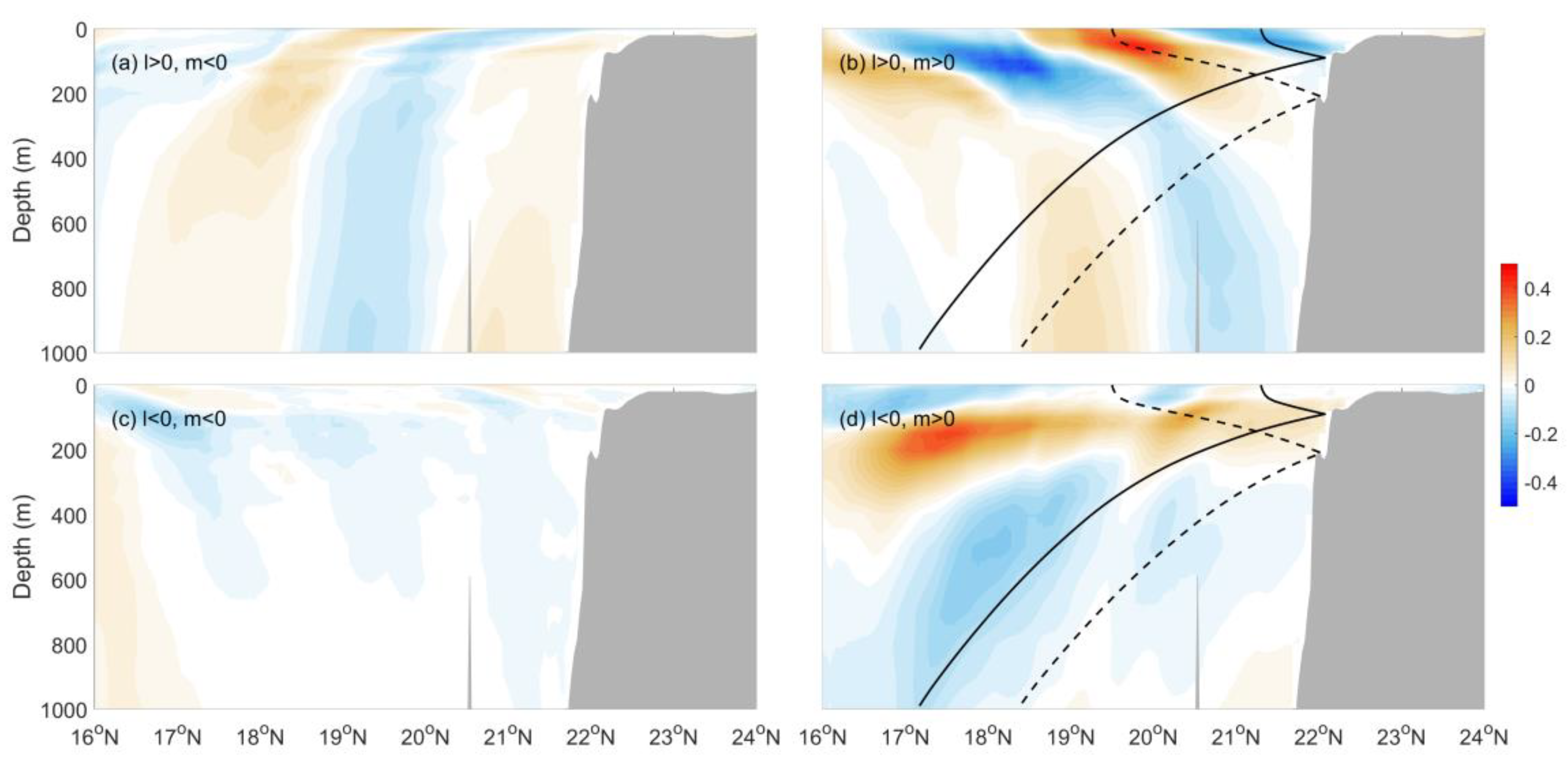
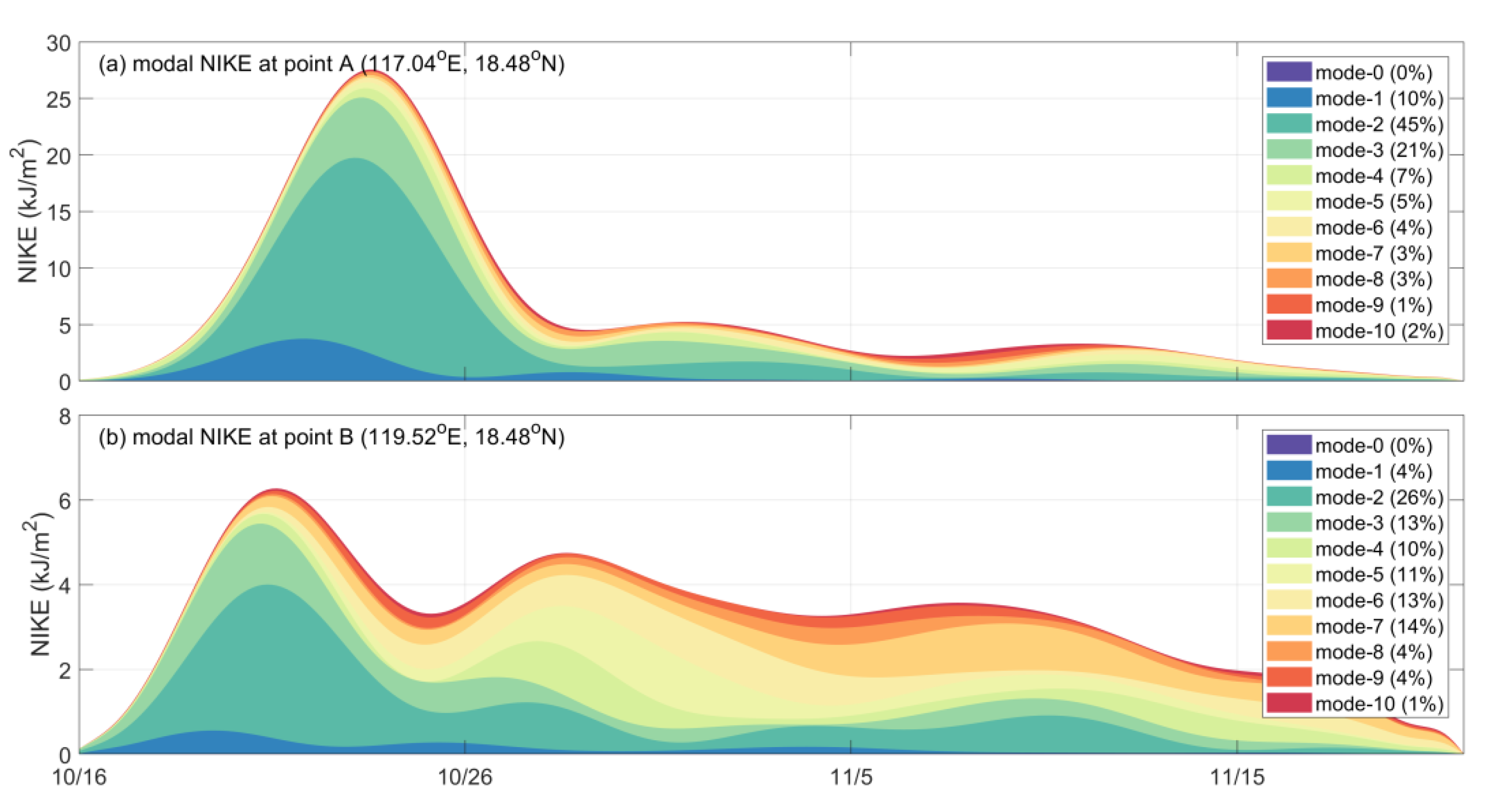
5. Modal Content
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alford, M.H.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Simmons, H.L.; Nash, J.D. Near-Inertial Internal Gravity Waves in the Ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C. Mixing with latitude. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 422, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, G.; Fringer, O.; Zaron, E. Regional Models of Internal Tides. Oceanography 2012, 25, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, B.; Tian, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, X. Latitude-dependent finescale turbulent shear generations in the Pacific trop-ical-extratropical upper ocean. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, A.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Lv, X.; Song, J. Upper ocean shear in the northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 75, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wu, L. Low-Frequency Modulation of Turbulent Diapycnal Mixing by Anticyclonic Eddies Inferred from the HOT Time Series. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, C.B.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Talley, L.D. Large-scale impacts of the mesoscale environment on mixing from wind-driven internal waves. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H. Internal Swell Generation: The Spatial Distribution of Energy Flux from the Wind to Mixed Layer Near-Inertial Motions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H. Improved global maps and 54-year history of wind-work on ocean inertial motions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Hibiya, T. Global estimates of the wind-induced energy flux to inertial motions in the surface mixed layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 64-1–64-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, N.; Hibiya, T.; Niwa, Y. Model-predicted distribution of wind-induced internal wave energy in the world’s oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C09034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Perrie, W. Estimating the energy flux from the wind to ocean inertial motions: The sensitivity to surface wind fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimac, A.; Storch, J.; Eden, C.; Haak, H. The influence of high-resolution wind stress field on the power input to near-inertial motions in the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4882–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, H.; Alford, M. Simulating the Long-Range Swell of Internal Waves Generated by Ocean Storms. Oceanography 2012, 25, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Wunsch, C. Abyssal recipes II: Energetics of tidal and wind mixing. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1998, 45, 1977–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Ray, R.D. Significant dissipation of tidal energy in the deep ocean inferred from satellite altimeter data. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 405, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Zhao, Z.; Pinkel, R.; Klymak, J.; Peacock, T. Internal waves across the Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 24601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-H.; Shang, X.-D.; Chen, G.-Y.; Sun, L. Variations of diurnal and inertial spectral peaks near the bi-diurnal critical latitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 02606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, J.A.; Alford, M.H.; Sun, O.; Pinkel, R.; Zhao, Z.; Klymak, J. Parametric Subharmonic Instability of the Internal Tide at 29° N. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikurashin, M.; Legg, S. A Mechanism for Local Dissipation of Internal Tides Generated at Rough Topography. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wunsch, C. Note on the redistribution and dissipation of tidal energy over mid-ocean ridges. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 67, 27385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, A.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Song, J. On the resonant triad interaction over mid-ocean ridges. Ocean. Model. 2021, 158, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikurashin, M.; Ferrari, R. Radiation and dissipation of internal waves generated by geostrophic gotions impinging on small-scale topography: Theory. J. PhysOceanogr. 2010, 40, 2025–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Alford, M.H.; Shcherbina, A.Y.; Gregg, M.C. Observations of Near-Inertial Internal Gravity Waves Radiating from a Frontal Jet. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1225–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Thurnherr, A.M. Eddy-Modulated Internal Waves and Mixing on a Midocean Ridge. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.; Black, P.; Centurioni, L.; Harr, P.; Jayne, S.; Lin, I.; Lee, C.; Morzel, J.; Mrvaljevic, R.; Niiler, P.; et al. Typhoon-Ocean Interaction in the Western North Pacific: Part 1. Oceanography 2011, 24, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Owen, J.S.; Franke, J.; Neves, L.C.; Hargreaves, D.M. Typhoon track simulations in the North West Pacific: Informing a new wind map for Vietnam. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 208, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Lizhen, W.; Jiachun, L. Estimation of extreme wind speed in SCS and NWP by a non-stationary model. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2016, 6, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cai, S. Correlation of Near-Inertial Wind Stress in Typhoon and Typhoon-Induced Oceanic Near-Inertial Kinetic Energy in the Upper South China Sea. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, C. Strong near-inertial oscillations in geostrophic shear in the northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 67, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xue, H.; Wang, D.; Xie, Q. Observed near-inertial kinetic energy in the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 4965–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Zhao, W.; Huthnance, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, J. Observed upper ocean response to typhoon Megi (2010) in the Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 3134–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Hou, Y. Near-inertial waves in the wake of 2011 Typhoon Nesat in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Hou, Y.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Shallow ocean response to tropical cyclones observed on the continental shelf of the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 3817–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, T.; Zhou, B. Upper ocean response to typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 6520–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, R.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Tang, Y.; Ke, D.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; et al. Net Modulation of Upper Ocean Thermal Structure by Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 7154–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Guo, Z.; Song, J.; Lv, X.; He, H.; Fan, W. Near-Inertial Waves and Their Underlying Mechanisms Based on the South China Sea Internal Wave Experiment (2010–2011). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 5026–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liang, C.; Liao, G.; Li, J.; Lin, F.; Jin, W.; Zhu, L. Propagation characteristics of near-inertial waves along the conti-nental shelf in the wake of the 2008 Typhoon Hagupit in the northern South China Sea. B. Mar. Sci. 2018, 94, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qi, Y.; Jing, Z. Upper ocean near-inertial response to the passage of two sequential typhoons in the north-western South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Cai, S.; Ning, D. Horizontal variations of typhoon-forced near-inertial oscillations in the south China sea simulated by a numerical model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 180, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. An Overview of the China Meteorological Administration Tropical Cyclone Database. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, M.J.; Garnier, N.B.; Dauxois, T. Reflexion and Diffraction of Internal Waves analyzed with the Hilbert Transform. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 086601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, A.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Meng, J. Estimation of the Reflection of Internal Tides on a Slope. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2020, 19, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.D.; Alford, M.H.; Kunze, E. Estimating Internal Wave Energy Fluxes in the Ocean. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1551–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Alford, M.H.; Mackinnon, J.A.; Pinkel, R. Long-Range Propagation of the Semidiurnal Internal Tide from the Ha-waiian Ridge. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 713–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.-Z.; Li, B.-T.; Lv, X.-Q. Extraction of Internal Tidal Currents and Reconstruction of Full-Depth Tidal Currents from Mooring Observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Liu, Q.; Xie, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, R. Characteristics and seasonal variability of internal tides in the southern South China Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2015, 98, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Alford, M.H.; Lien, R.-C.; Gregg, M.C.; Carter, G.S. Internal Tides and Mixing in a Submarine Canyon with Time-Varying Stratification. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 2121–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Eriksen, C.C.; Levine, M.D.; Niiler, P.; Paulson, C.A.; Meurs, P.V. Upper-ocean inertial currents forced by a strong storm. Part I: Data and comparisons with linear theory. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1995, 25, 2909–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. On the Behavior of Internal Waves in the Wakes of Storms. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 1129–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, O.M.; Pinkel, R. Energy Transfer from High-Shear, Low-Frequency Internal Waves to High-Frequency Waves near Kaena Ridge, Hawaii. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 1524–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Cao, A.; Lv, X.; Song, J. Impact of multiple tidal forcing on the simulation of the M2 internal tides in the northern South China Sea. Ocean.Dyn. 2019, 70, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F.; Sanford, T.B.; Forristall, G.Z. Forced Stage Response to a Moving Hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, D.A.; Pratson, L.F.; Ogston, A.S. The shaping of continental slopes by internal tides. Science 2020, 296, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Cao, A.; Lv, X.; Song, J. Impacts of Stratification Variation on the M2 Internal Tide Generation in Luzon Strait. Atmos. Ocean. 2020, 58, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Miao, C.; Zhao, W. Patterns of K1 and M2 internal tides and their seasonal variations in the northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D. Dynamic features of near-inertial oscillations in the Northwest Pacific derived from mooring observations from 2015 to 2018. J. Oceanol. Limn. 2020, 38, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, M.; Lamb, K.G. Focusing and vertical mode scattering of the first mode internal tide by mesoscale eddy interaction. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, A.; Guo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Song, J.; He, H.; Li, P. Near-Inertial Waves Induced by Typhoon Megi (2010) in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040440
Cao A, Guo Z, Pan Y, Song J, He H, Li P. Near-Inertial Waves Induced by Typhoon Megi (2010) in the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(4):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040440
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Anzhou, Zheng Guo, Yunhe Pan, Jinbao Song, Hailun He, and Peiliang Li. 2021. "Near-Inertial Waves Induced by Typhoon Megi (2010) in the South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 4: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040440
APA StyleCao, A., Guo, Z., Pan, Y., Song, J., He, H., & Li, P. (2021). Near-Inertial Waves Induced by Typhoon Megi (2010) in the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(4), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9040440





