The Seasonal Variation of the Anomalously High Salinity at Subsurface Salinity Maximum in Northern South China Sea from Argo Data
Abstract
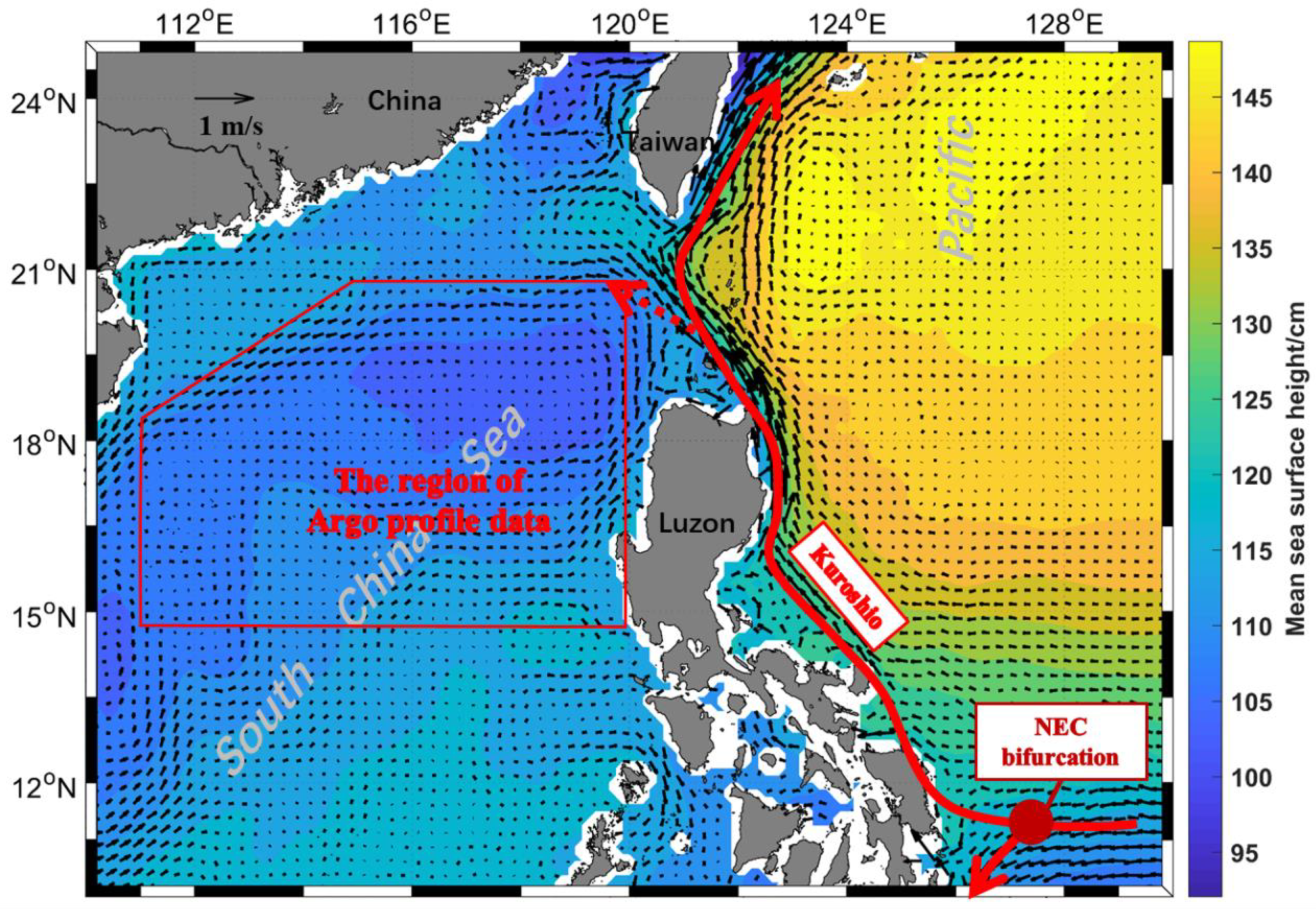
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
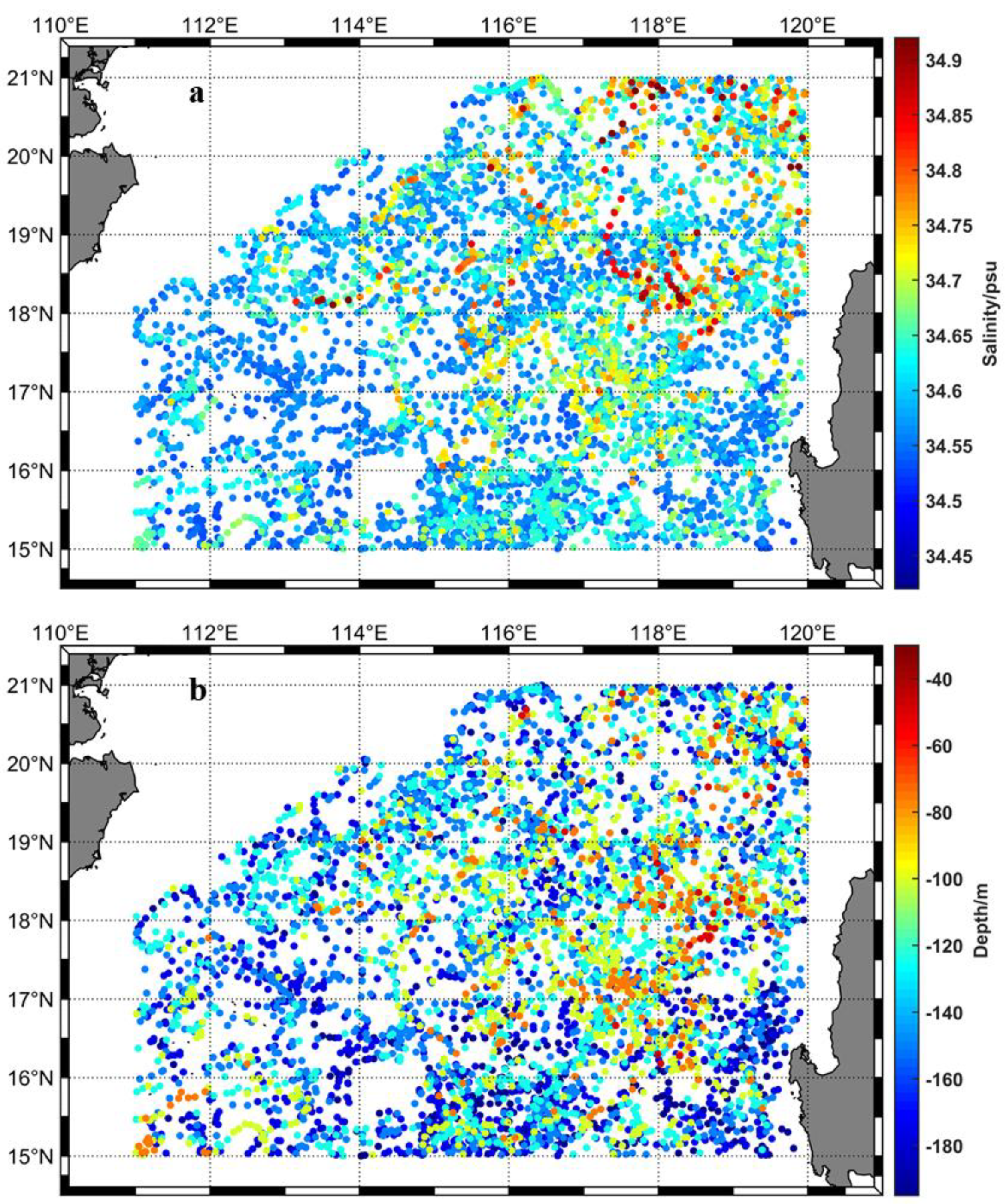
2.1. Argo Temperature and Salinity Data
2.2. Altimetry Dataset
2.3. Wind Data
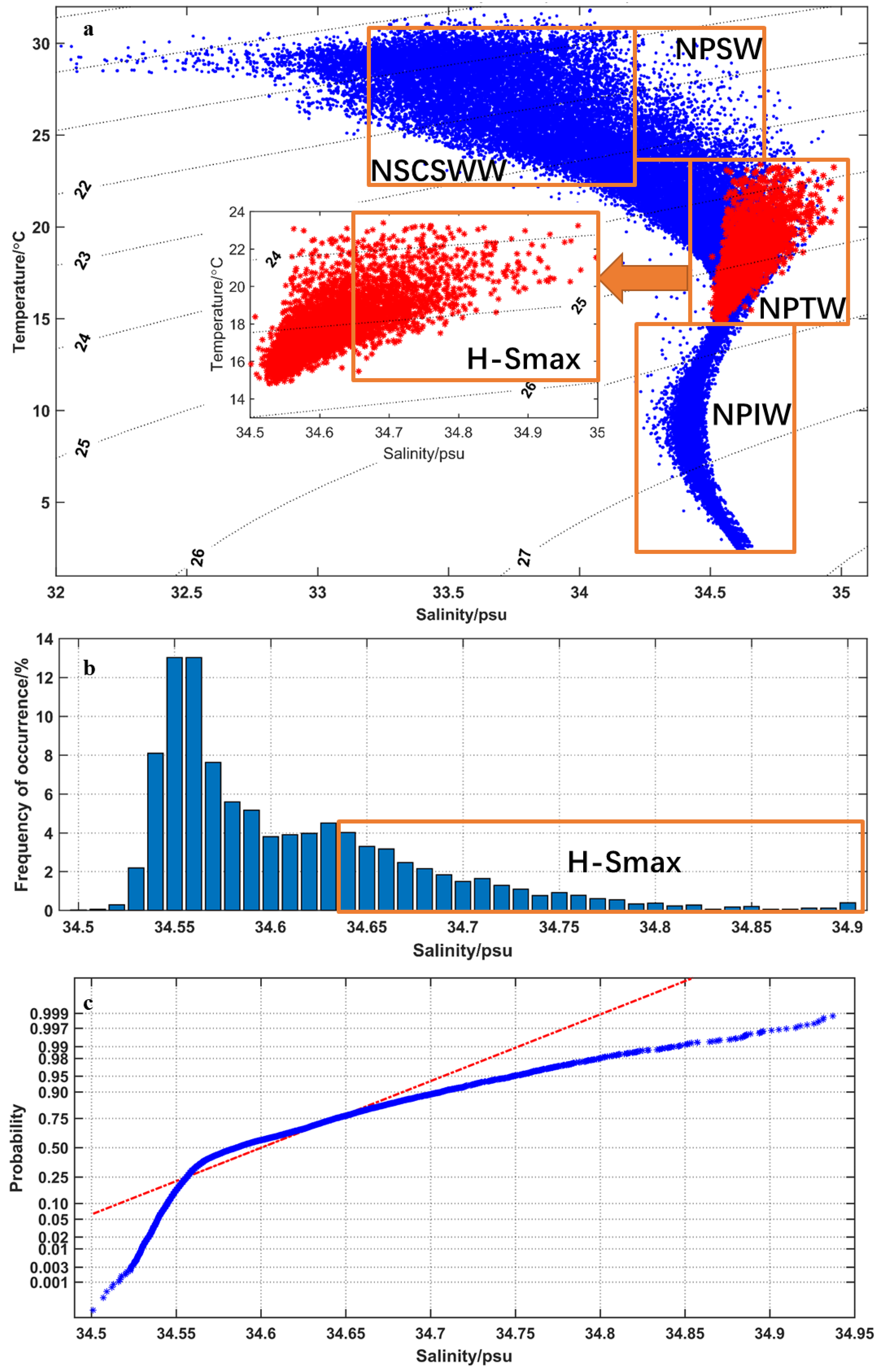
2.4. Computation and Differentiation of the Subsurface Salinity Maximum
3. Results
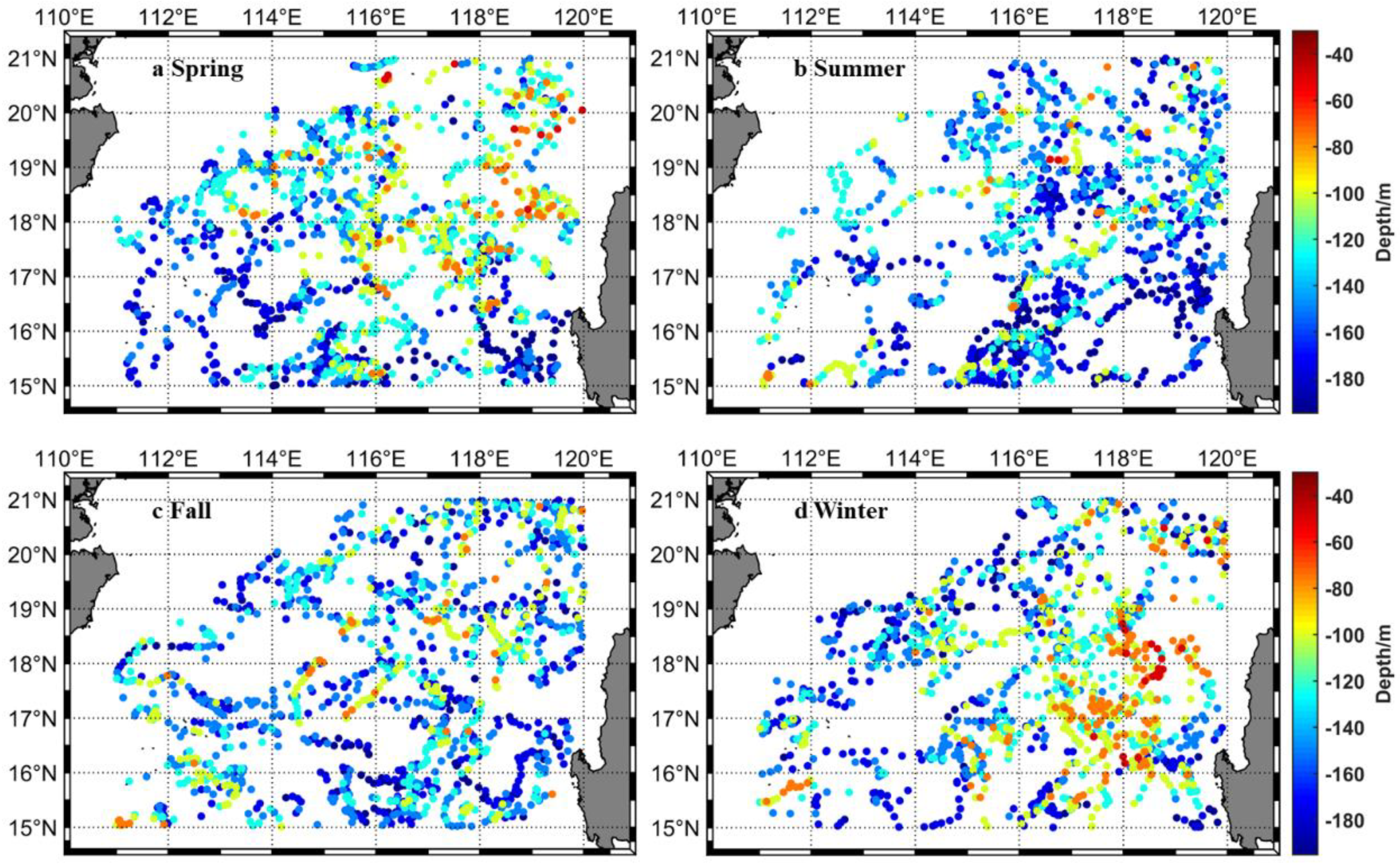
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of the Subsurface Salinity Maximum and Its Depth in the NSCS
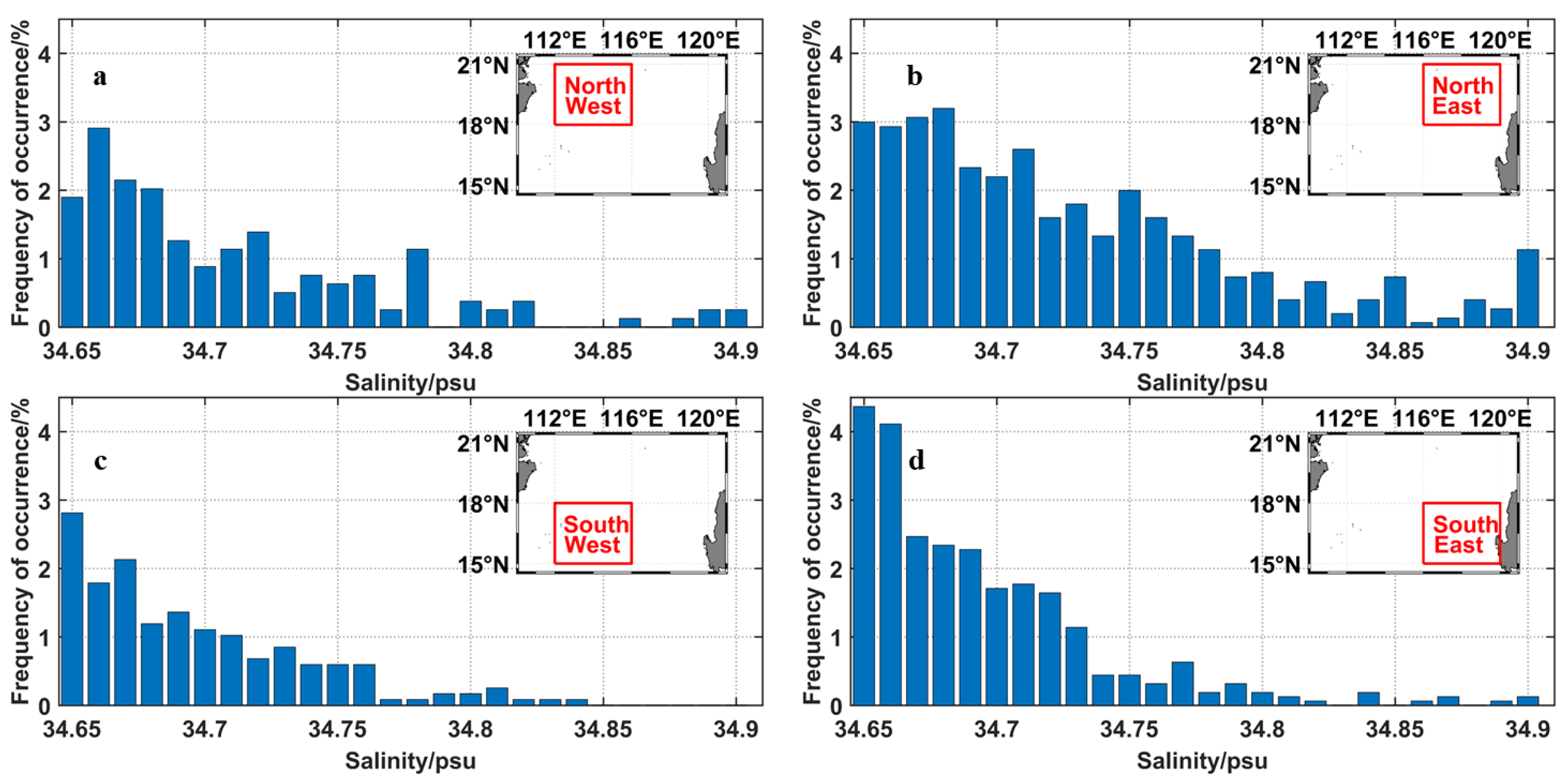
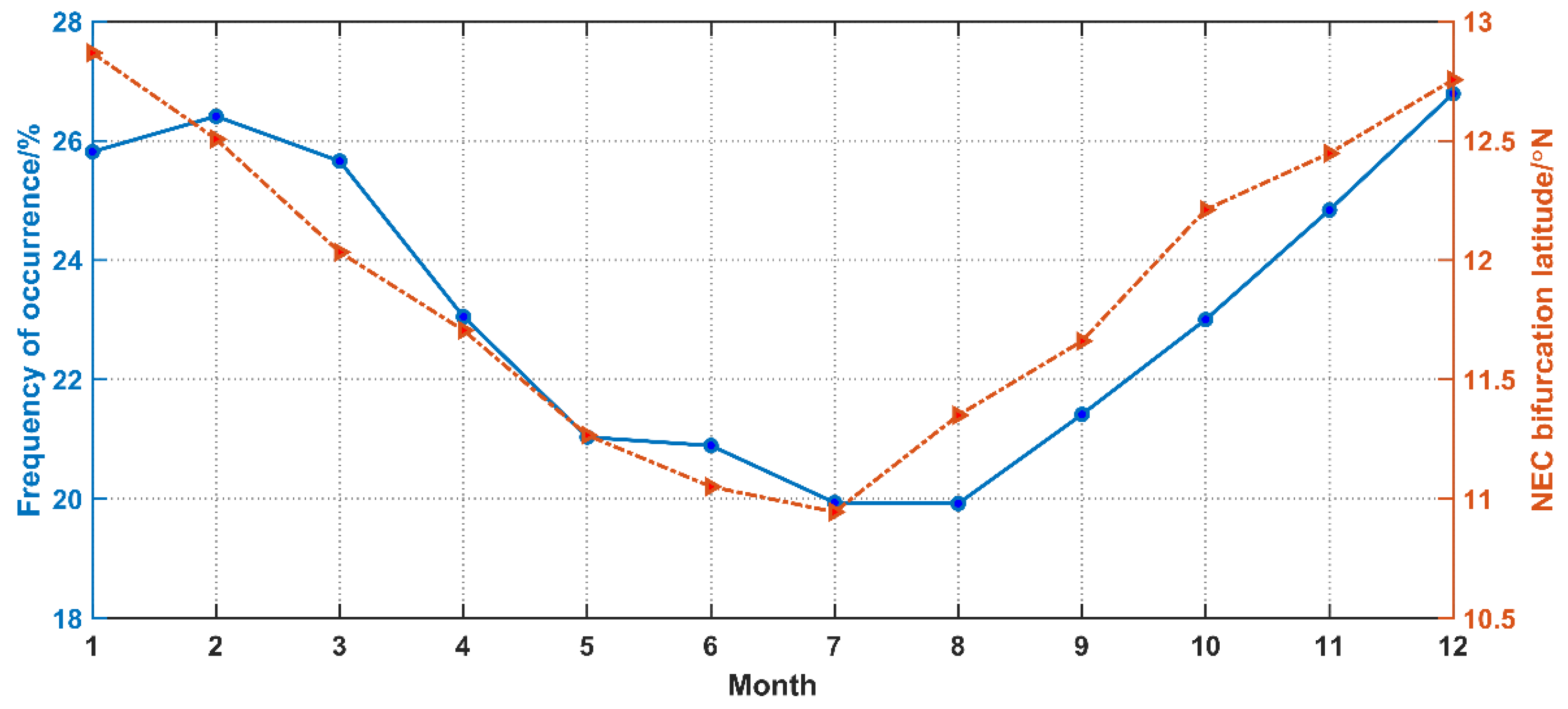
3.2. Anomalously High Subsurface Salinity
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Strength of KI on Anomalously High Subsurface Salinity
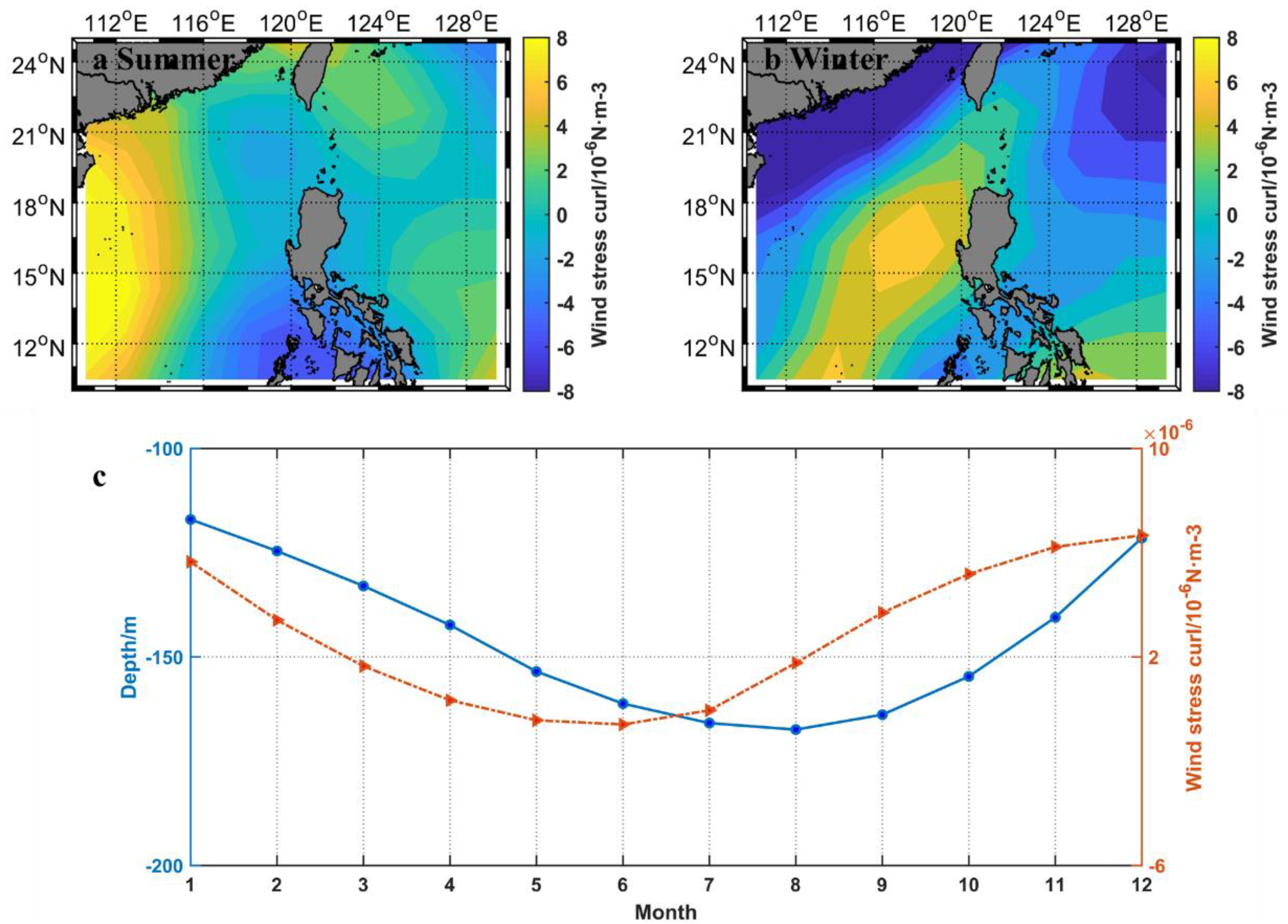
4.2. Effects of Local Wind Stress Curl on Anomalously High Subsurface Salinity
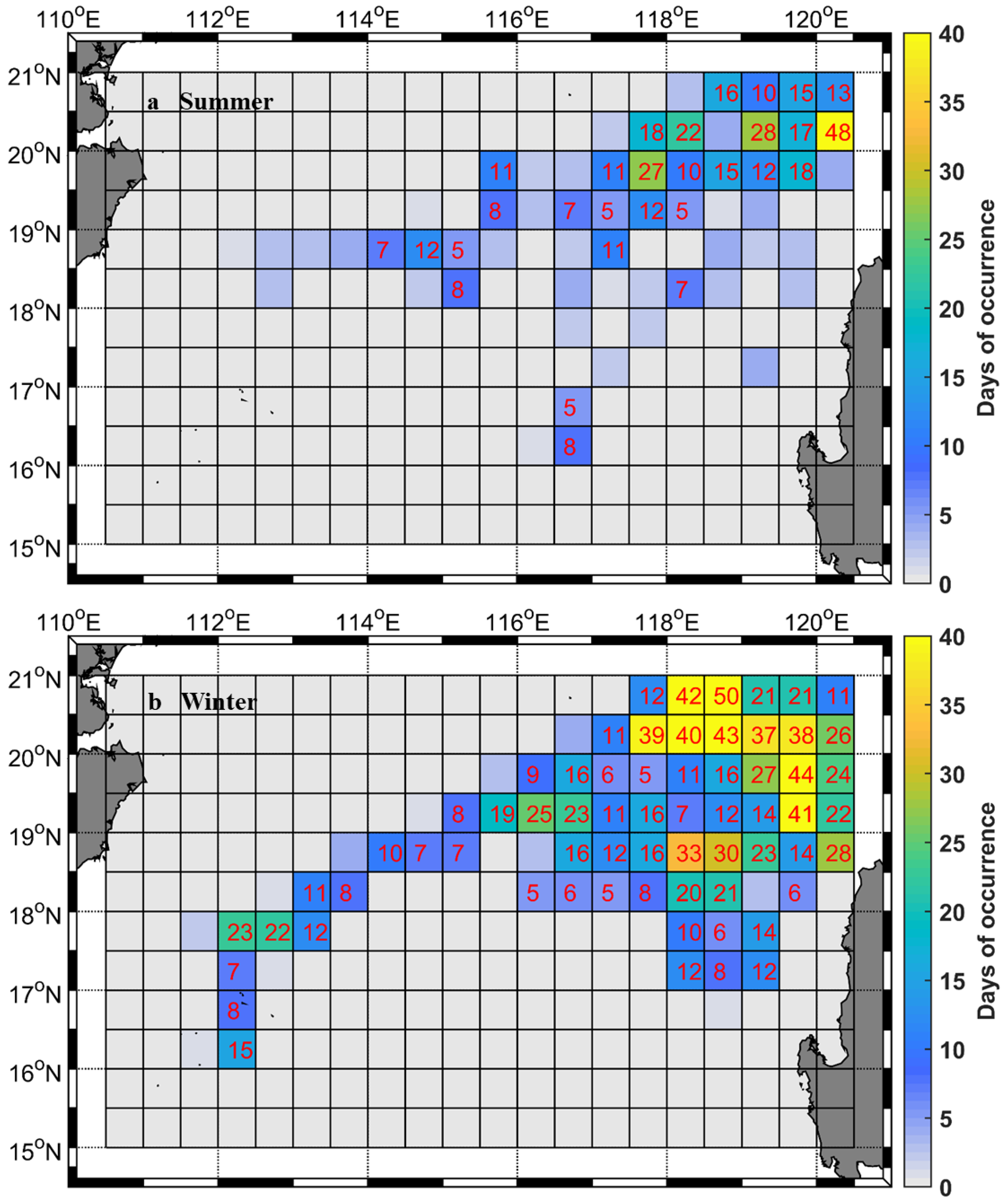
4.3. Effects of Anticyclonic Eddies Shedding from the Loop Current on Anomalously High Subsurface Salinity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helm, K.P.; Bindoff, N.L.; Church, J.A. Changes in the global hydrological-cycle inferred from ocean salinity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skliris, N.; Marsh, R.; Josey, S.A.; Good, S.A.; Liu, C.; Allan, R.P. Salinity changes in the World Ocean since 1950 in relation to changing surface freshwater fluxes. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 709–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Xue, H.; Yu, F. Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea: A review. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, Y.C. Multidecadal variations of the surface Kuroshio between 1950s and 2000s and its impacts on surrounding waters. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 1792–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qu, T. Thermohaline circulation in the deep South China Sea basin inferred from oxygen distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111, C05017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.T. The seasonal variation of the intrusion of the Philippine Sea water into the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1991, 96, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, I.F.; Wu, C.R. Variability analysis of Kuroshio intrusion through Luzon Strait using growing hierarchical self-organizing map. Ocean Dyn. 2012, 62, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; McCreary, J.P.; Yaremchuk, M.; Furue, R. Subsurface Salinity Balance in the South China Sea*. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Mitsudera, H.; Yamagata, T. Intrusion of the north Pacific waters into the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Nan, F.; Shi, M.; Zhou, L.; Guo, P. Characteristics of water exchange in the Luzon Strait during September 2006. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, M.; Wainer, I.; Signorelli, N. Investigation of the causes of historical changes in the subsurface salinity minimum of the South Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 5654–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, L. Significant salinity increase in subsurface waters of the South China Sea during 2016–2017. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, D.; Xiu, P.; Shu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J. Decadal variation and trends in subsurface salinity from 1960 to 2012 in the northern South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12181–112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Song, X.; Abraham, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, J. Examining the salinity change in the upper Pacific Ocean during the Argo period. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 6055–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y. Constructing the three-dimensional structure of an anticyclonic eddy in the South China Sea using multiple underwater gliders. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 2449–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, D.; Sun, C. Kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea with an anticyclonic eddy: Evidence from underwater glider observation. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, B.; Tian, J. Anticyclonic eddy sheddings from Kuroshio loop and the accompanying cyclonic eddy in the northeastern South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Lu, S.; Sun, C.; Cao, M. China Argo project: Progress in China Argo ocean observations and data applications. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riser, S.C.; Freeland, H.J.; Roemmich, D.; Wijffels, S.; Jayne, S.R. Fifteen years of ocean observations with the global Argo array. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximenko, N.; Niiler, P.; Centurioni, L.; Rio, M.; Melnichenko, O.; Chambers, D.; Zlotnicki, V.; Galperin, B. Mean dynamic topography of the ocean derived from satellite and drifting buoy data using three different techniques. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, M.H.; Hernandez, F. A mean dynamic topography computed over the world ocean from altimetry, in situ measurements, and a geoid model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, M.H.; Mulet, S.; Picot, N. Beyond GOCE for the ocean circulation estimate: Synergetic use of altimetry, gravimetry, and in situ data provides new insight into geostrophic and Ekman currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 8918–8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 167–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.; Pascual, A.; McWilliams, J.C. A new sea surface height–based code for oceanic mesoscale eddy tracking. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlax, M.G.; Chelton, D.B. The “Growing Method” of Eddy Identification and Tracking in Two and Three Dimensions. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woollen, J.; Yang, S.; Hnilo, J.J.; Fiorino, M.; Potter, G.L. NCEP–DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kawamura, H.; Hong, H.; Qi, Y. A review on the currents in the South China Sea: Seasonal circulation, South China Sea warm current and Kuroshio intrusion. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its influence on the coastal physical oceanography outside the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Xuan, J.; Li, F.; Yang, T.; Guo, Y. Processes controlling the distribution and cycling of dissolved manganese in the northern South China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2018, 204, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bye, J.A.; You, Y.; Bao, X.; Wu, D. The flushing and exchange of the South China Sea derived from salt and mass conservation. Deep-Sea Res. Part II-Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lim, B. A new perspective on origin of the East Sea Intermediate Water: Observations of Argo floats. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Yu, F.; Xue, H.; Zeng, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Nguyen, K.C. Freshening of the upper ocean in the South China Sea since the early 1990s. Deep-Sea Res. Part I-Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 118, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, S. Interannual-to-decadal variability in the bifurcation of the North Equatorial Current off the Philippines. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 2525–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, J.M.; Millard, R.C.; Wang, Z.; Pu, S. Observations of the Pacific North Equatorial Current Bifurcation at the Philippine Coast. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, Y.; Yamagata, T. Response of the western tropical Pacific to the Asian winter monsoon: The generation of the Mindanao Dome. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1991, 21, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tozuka, T.; Kagimoto, T.; Masumoto, Y.; Yamagata, T. Simulated Multiscale Variations in the Western Tropical Pacific: The Mindanao Dome Revisited. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 1338–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Huang, R.; Du, Y.; Qu, T. Interannual variability of the South China Sea throughflow inferred from wind data and an ocean data assimilation product. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L14605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, V.A. Hysteresis of a Western Boundary Current Leaping across a Gap. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ling, Z.; Chen, C. Winter coastal upwelling off northwest Borneo in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yaremchuk, M. Can luzon strait transport play a role in conveying the impact of ENSO to the South China Sea? J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Qiu, B. Oceanic mass transport by mesoscale eddies. Science. 2014, 345, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Xia, Y. The Seasonal Variation of the Anomalously High Salinity at Subsurface Salinity Maximum in Northern South China Sea from Argo Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020227
Shen H, Li L, Li J, He Z, Xia Y. The Seasonal Variation of the Anomalously High Salinity at Subsurface Salinity Maximum in Northern South China Sea from Argo Data. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(2):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020227
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Hui, Li Li, Jianlong Li, Zhiguo He, and Yuezhang Xia. 2021. "The Seasonal Variation of the Anomalously High Salinity at Subsurface Salinity Maximum in Northern South China Sea from Argo Data" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 2: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020227
APA StyleShen, H., Li, L., Li, J., He, Z., & Xia, Y. (2021). The Seasonal Variation of the Anomalously High Salinity at Subsurface Salinity Maximum in Northern South China Sea from Argo Data. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(2), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020227







