Scale-Resolving Simulations of a Circular Cylinder Subjected to Low Mach Number Turbulent Inflow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Fluid Flow Solver
2.2. Inflow Turbulence Generation
3. Test Case
3.1. Description
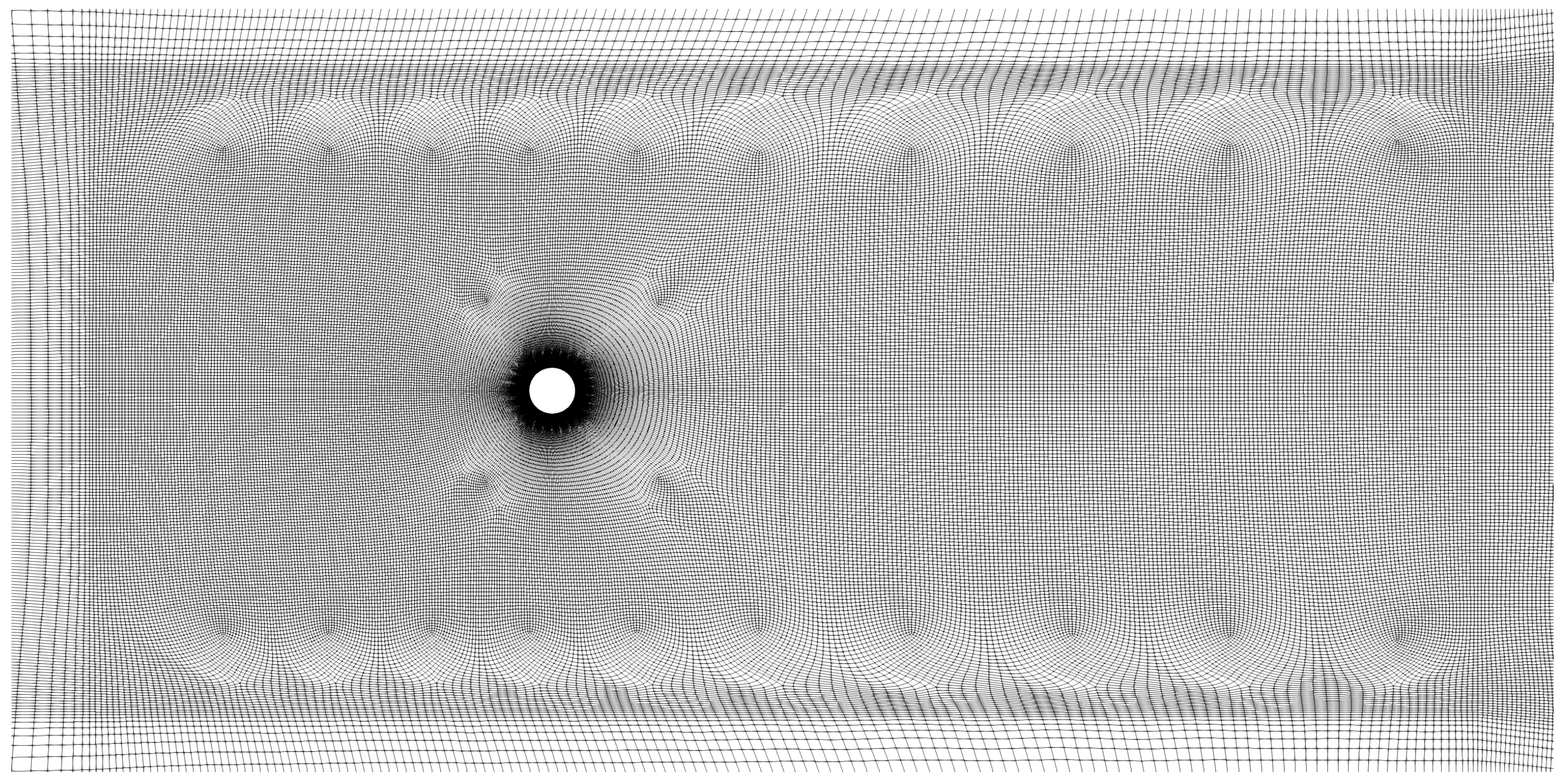
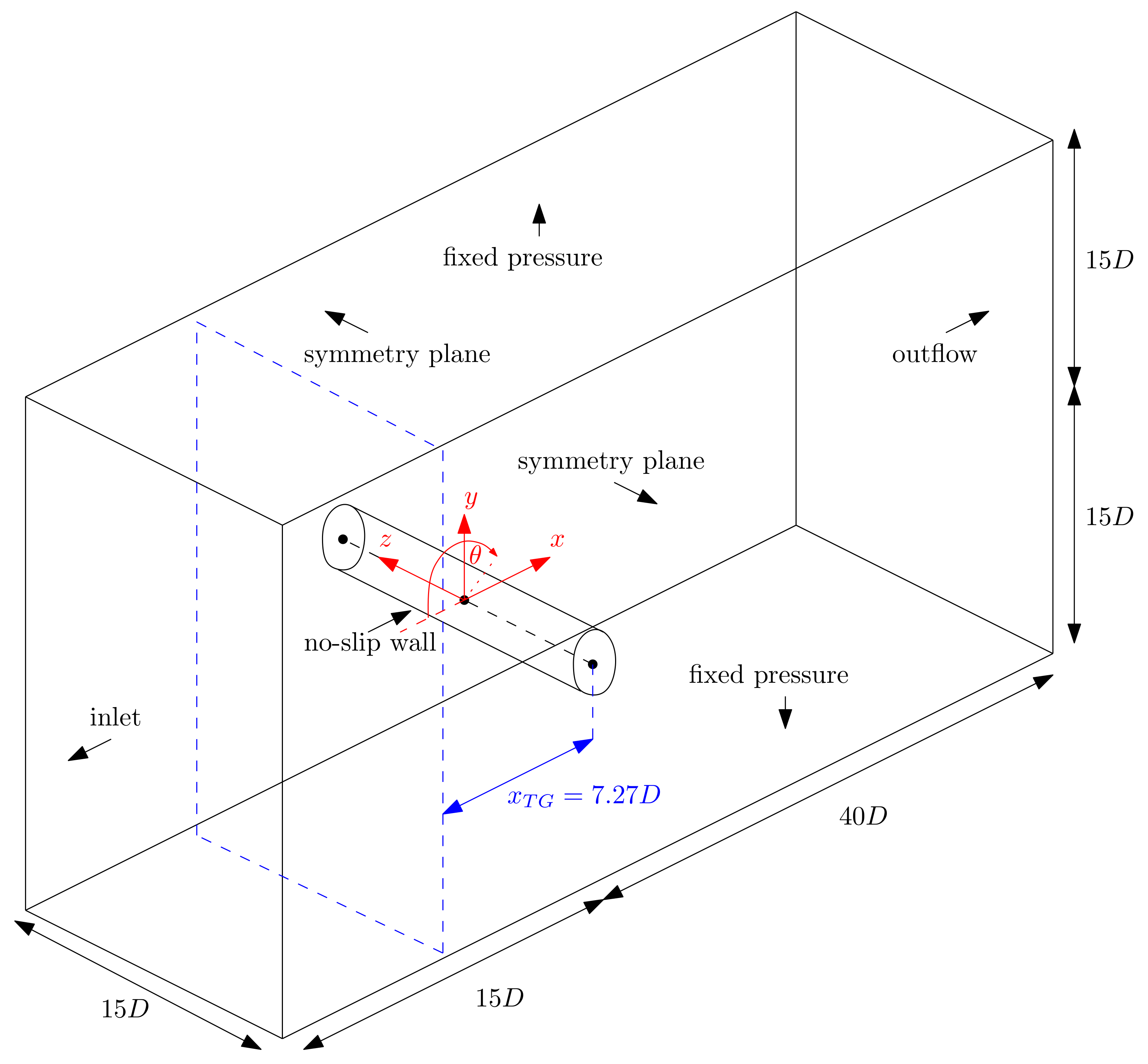
3.2. Domain and Grids
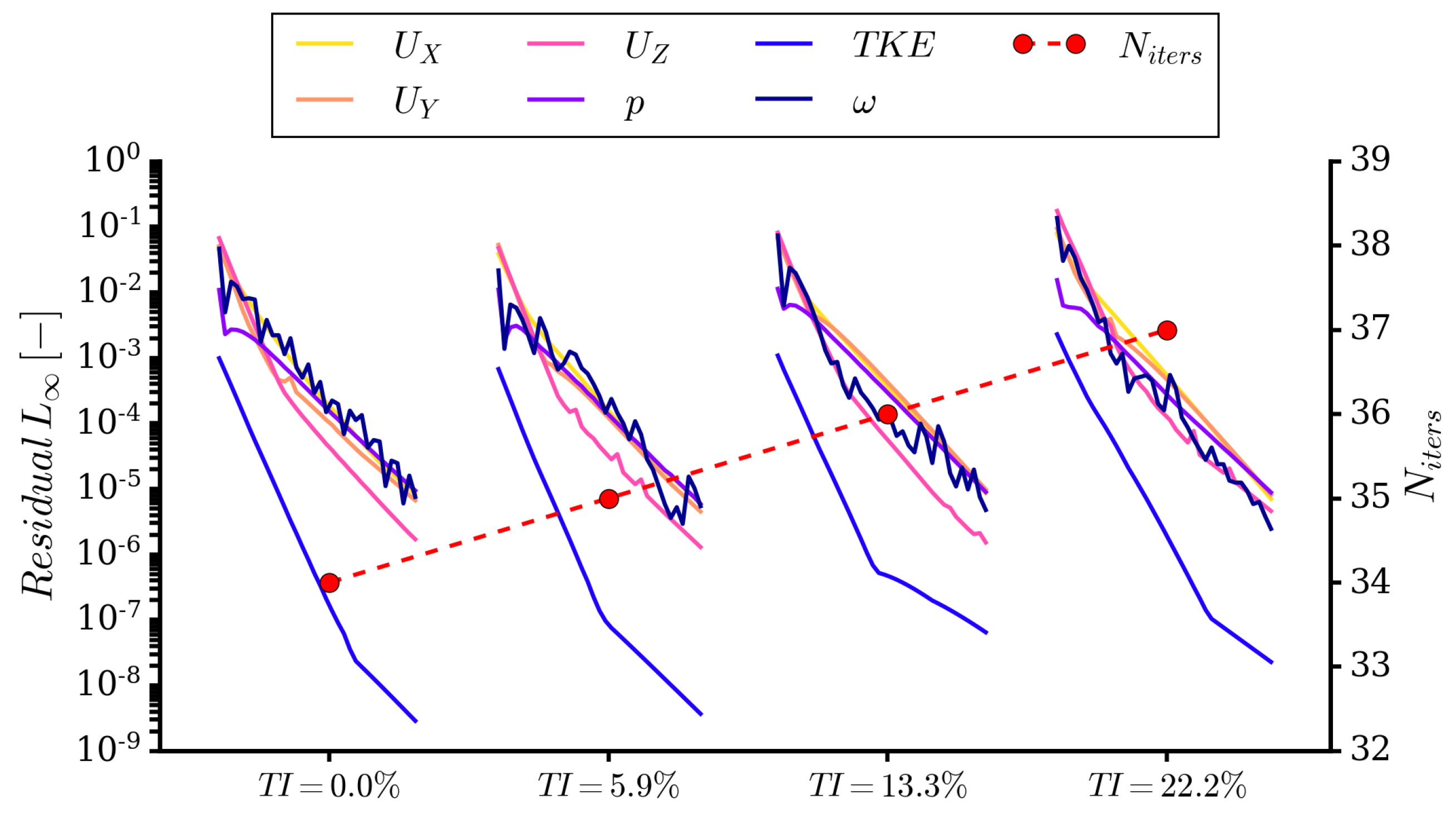
3.3. Numerical Setup
3.4. Signal Processing
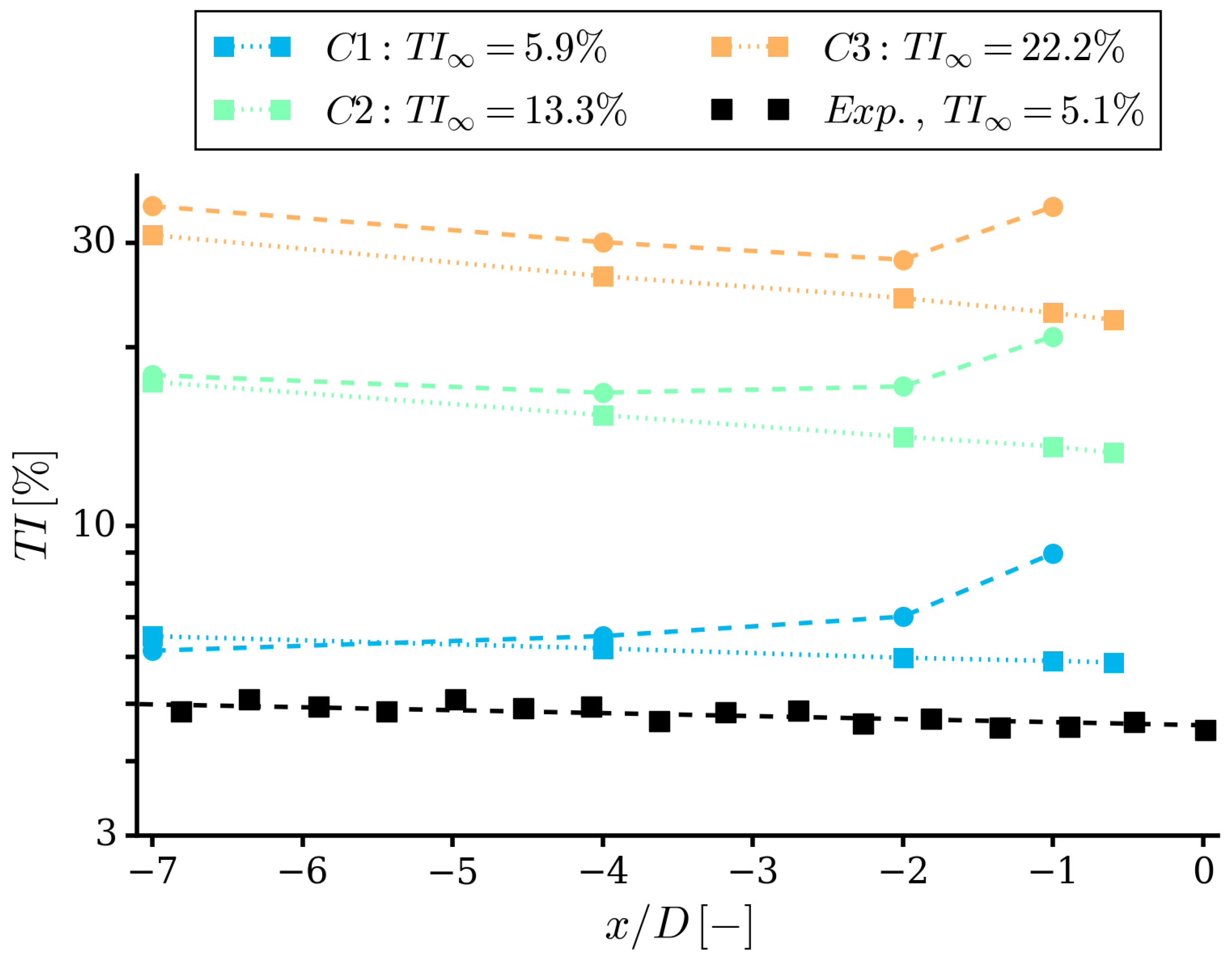
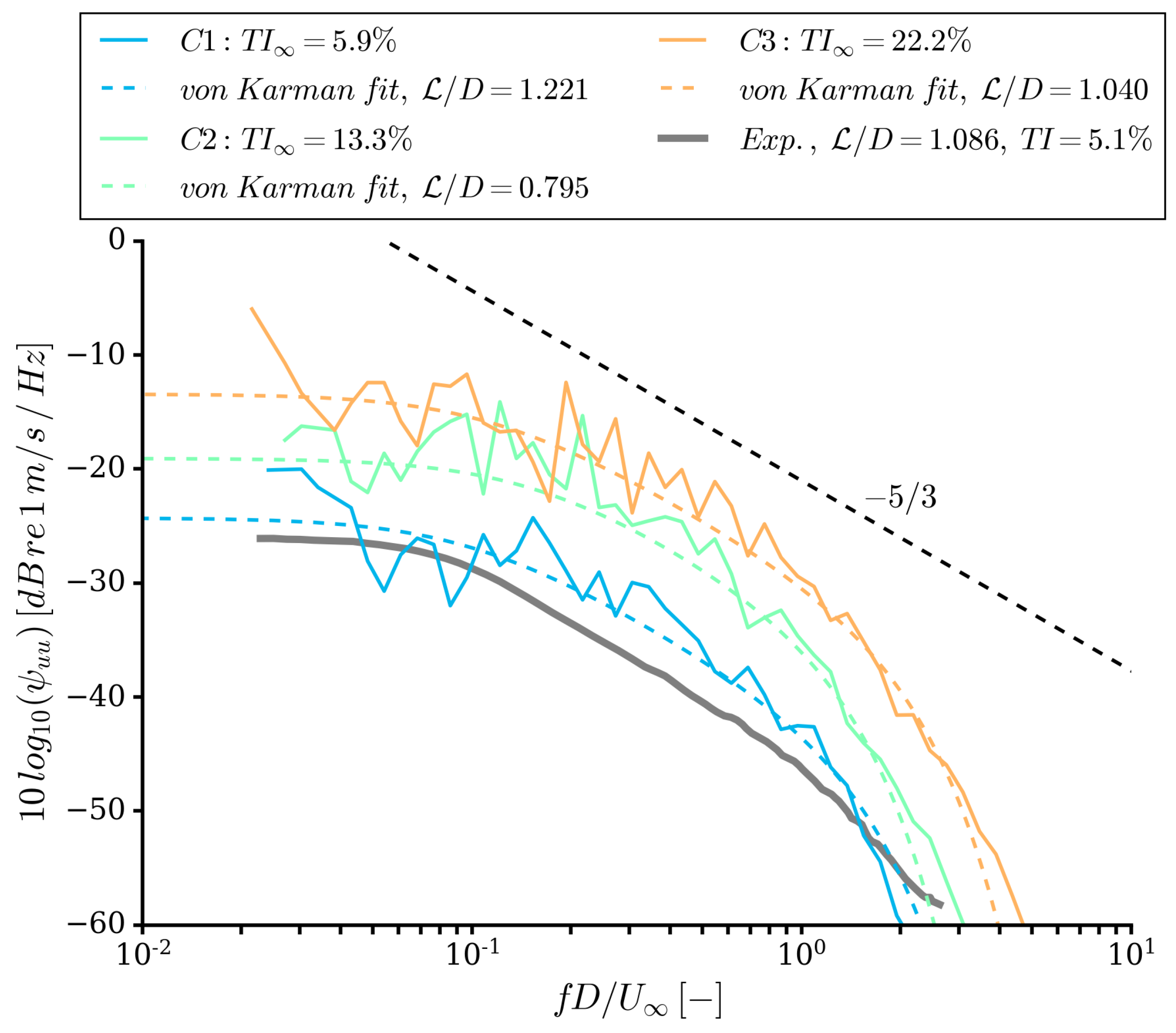
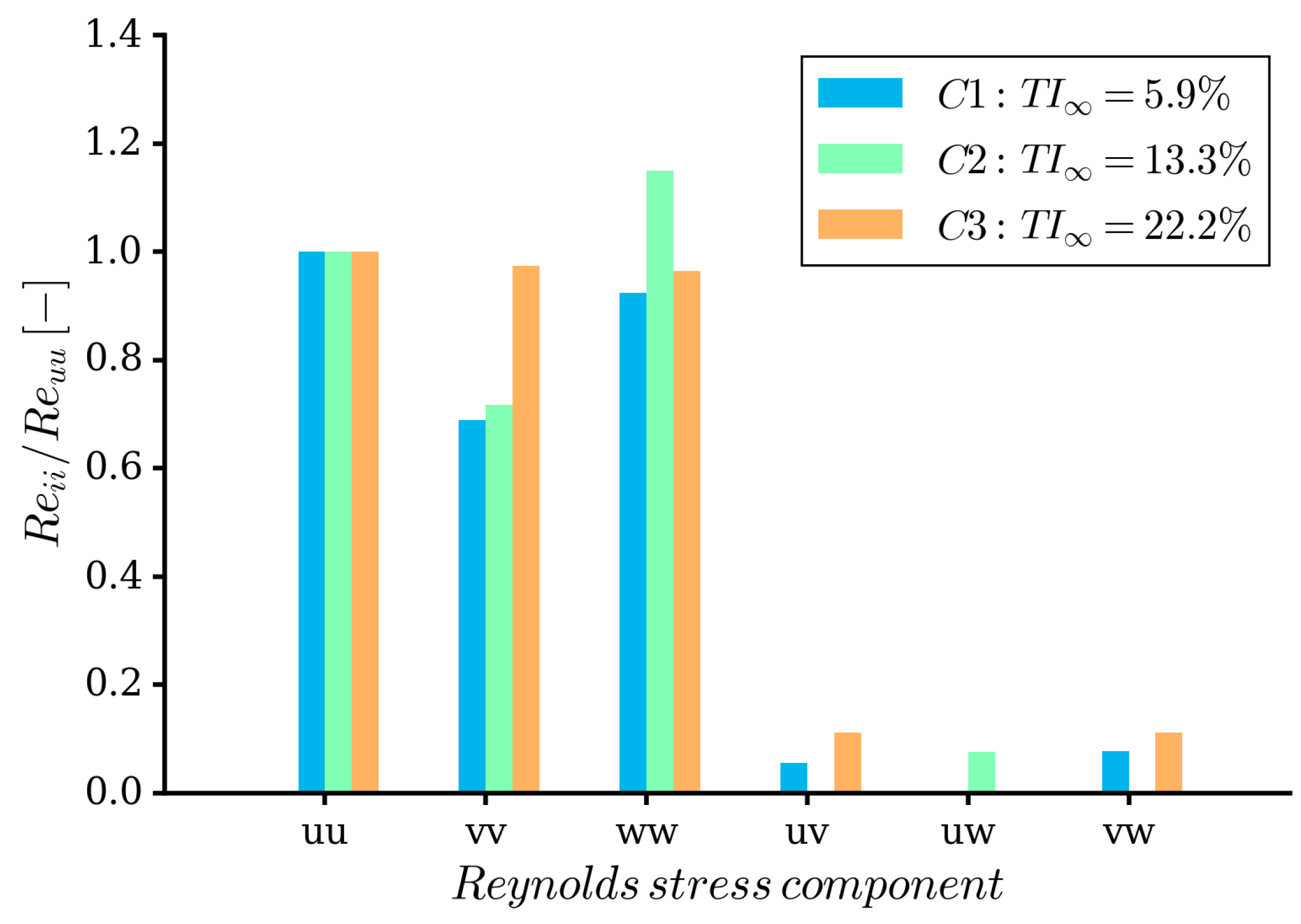
3.5. Inflow Turbulence Statistics
4. Results
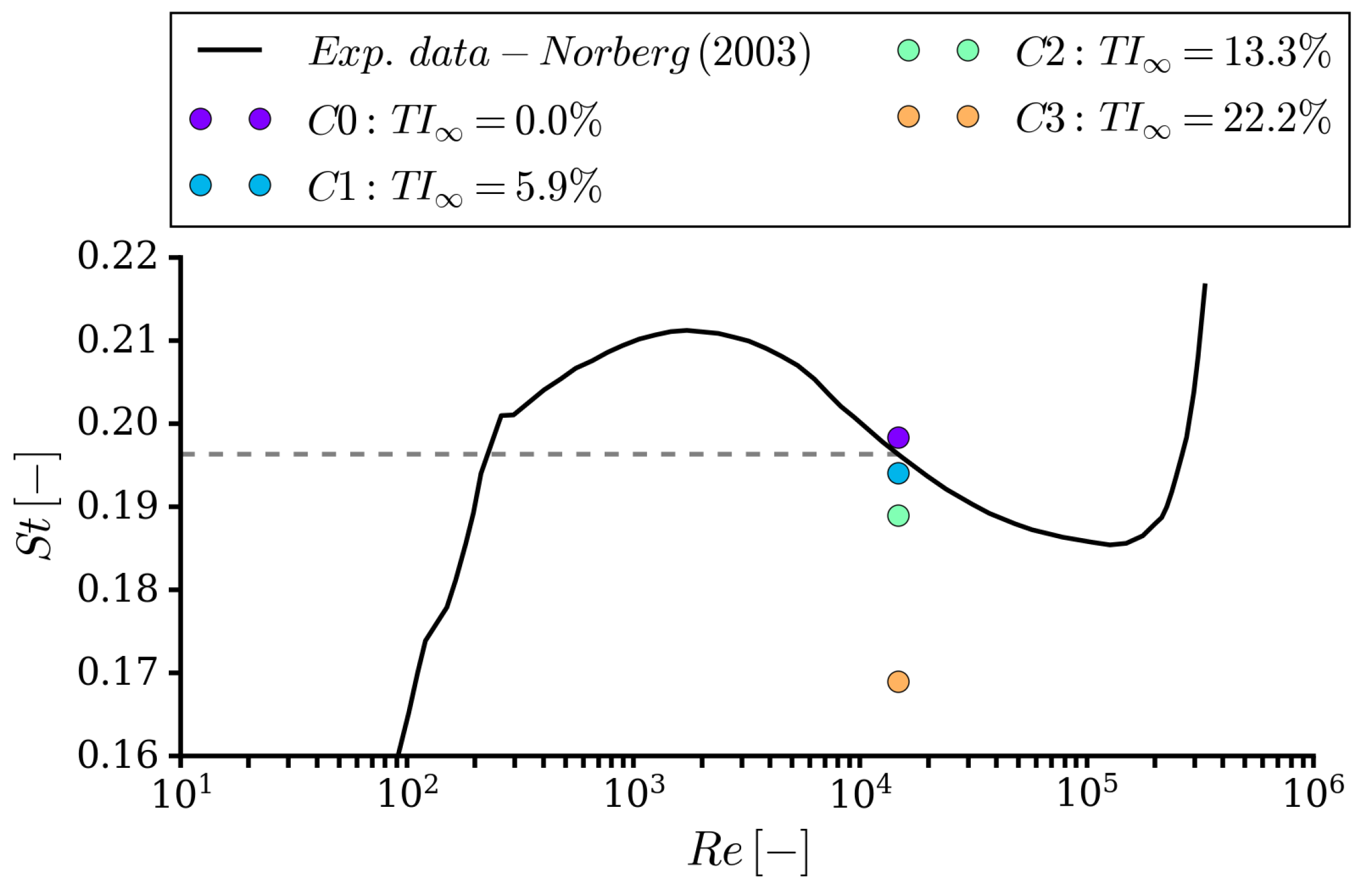
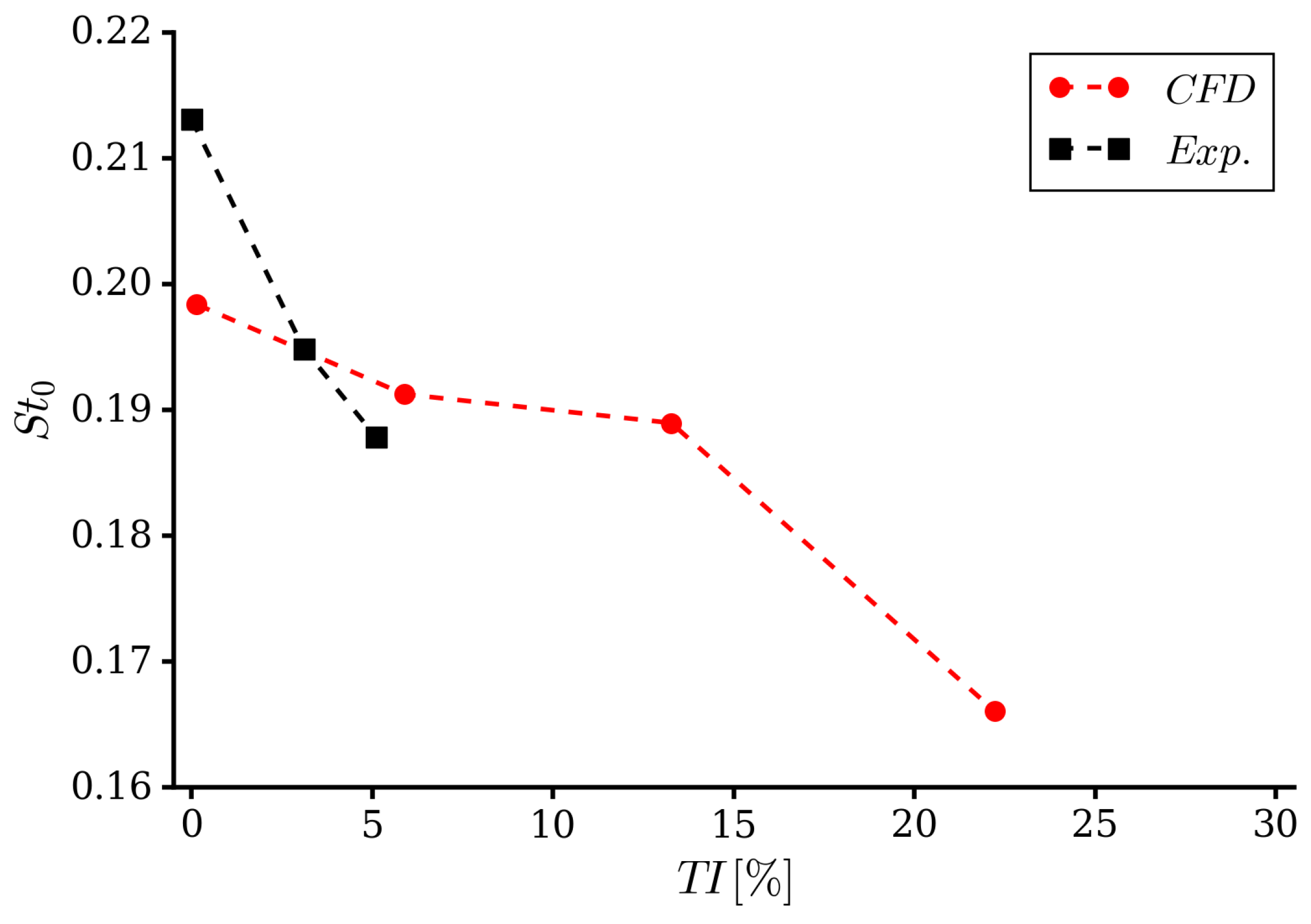
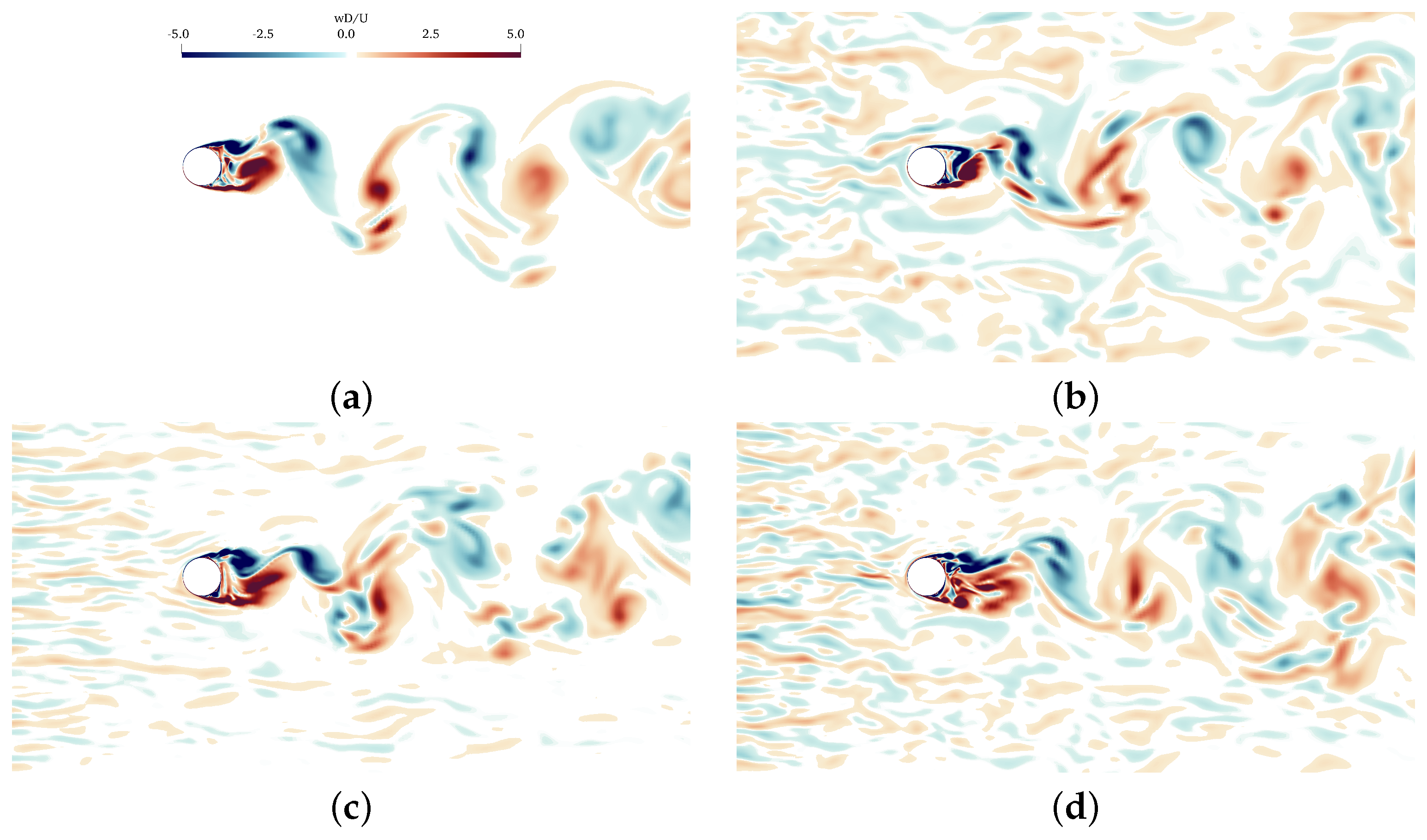
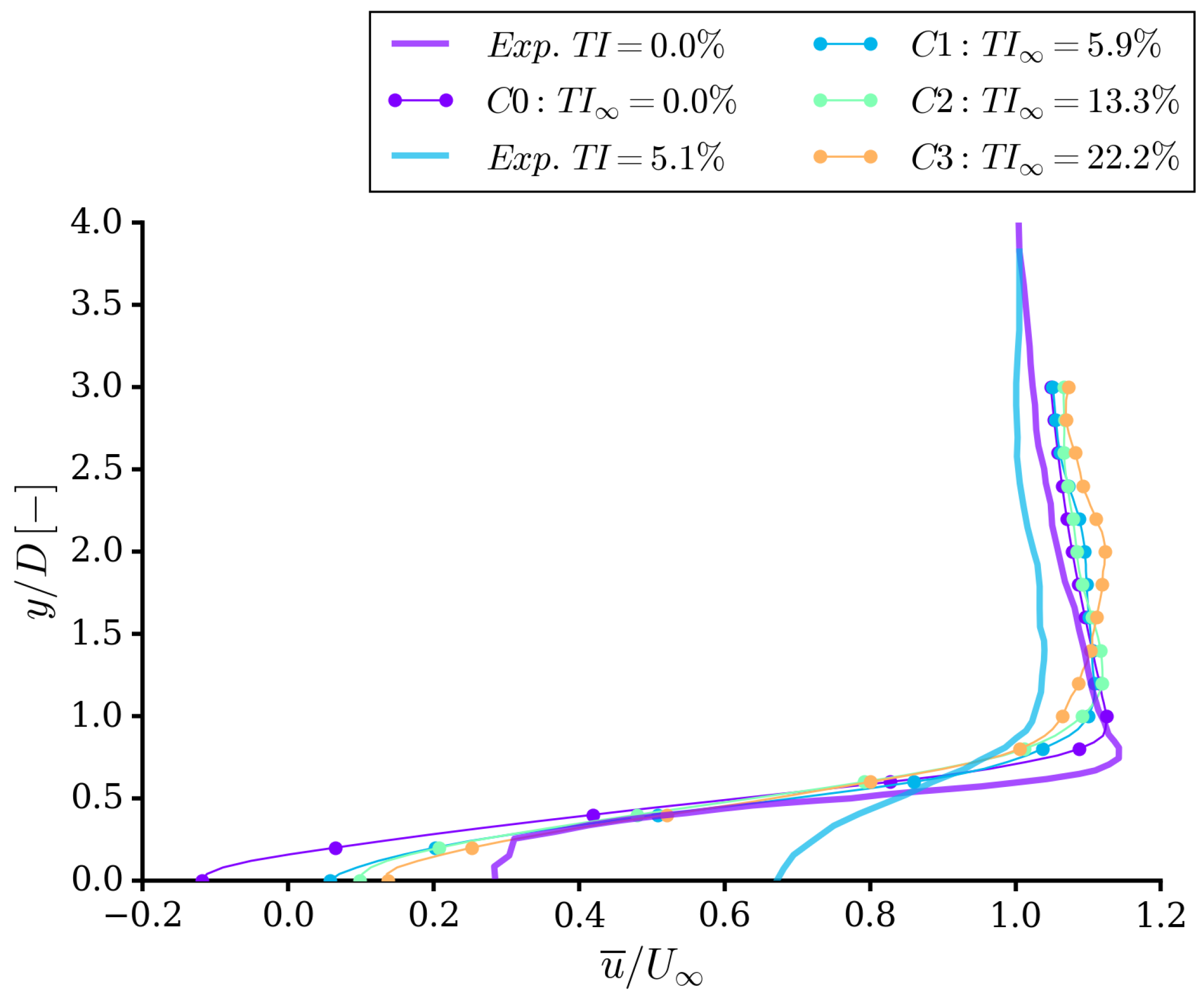
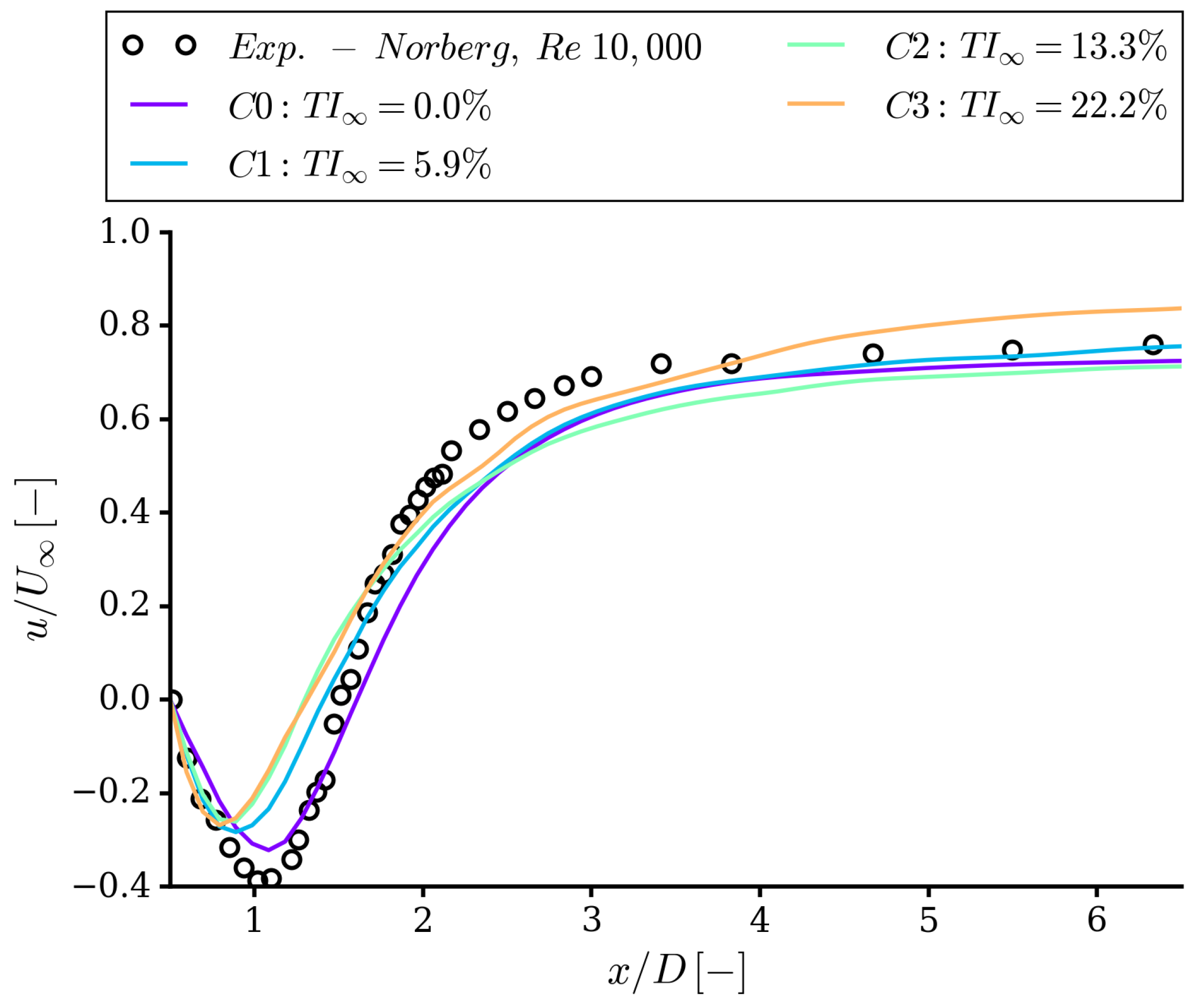
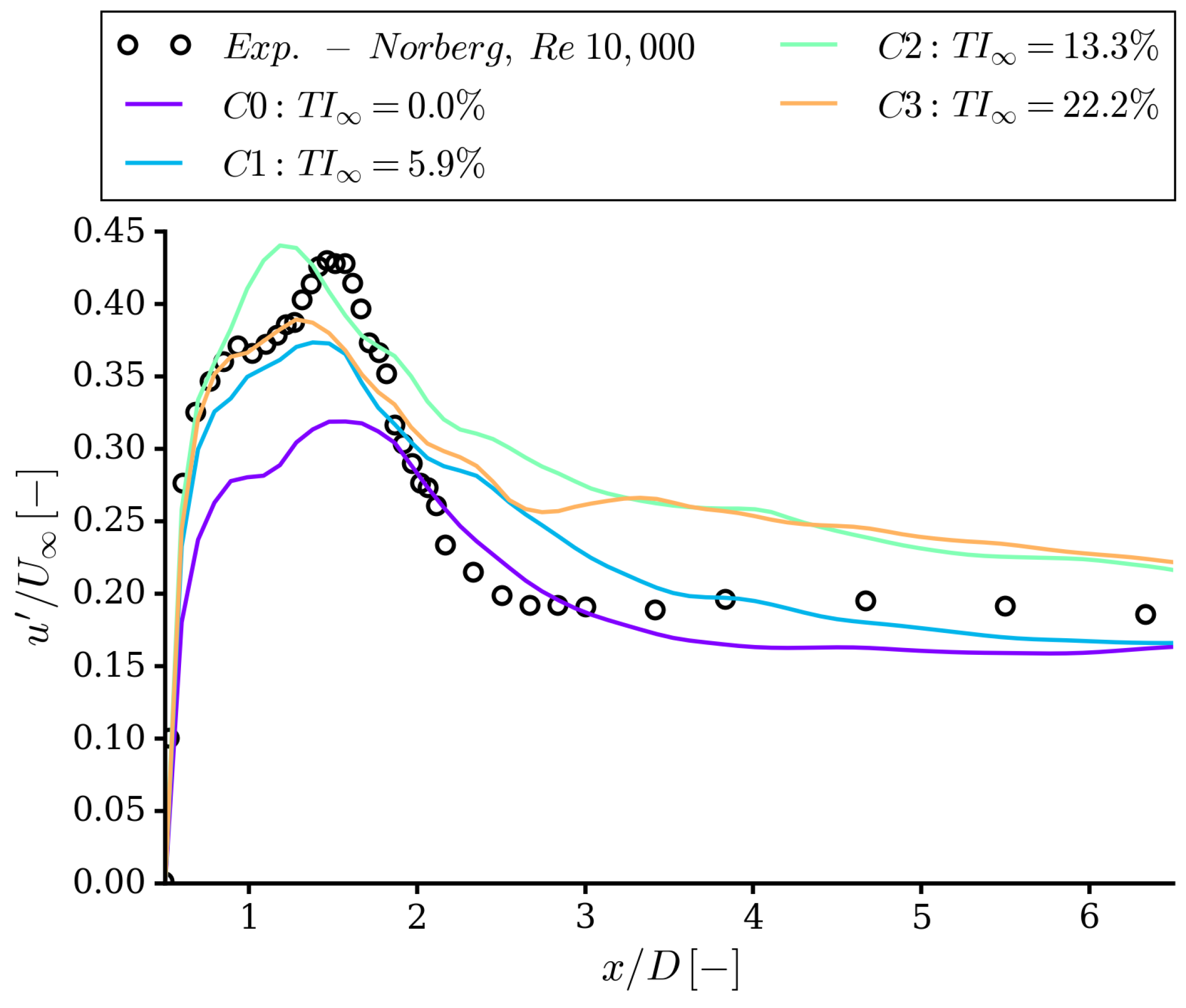
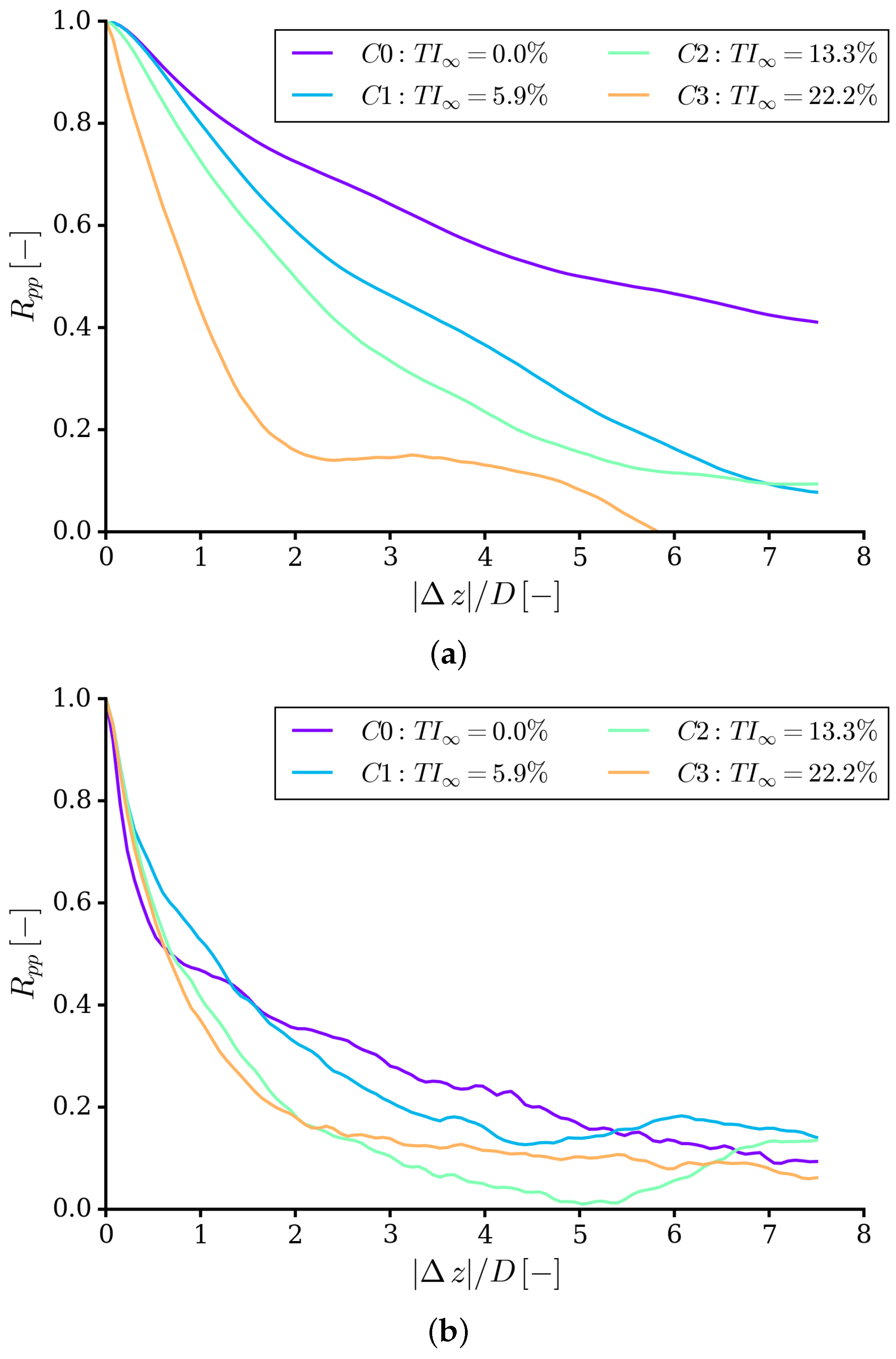
4.1. Integral Quantities and Flow Field
4.2. Surface Pressure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Churchfield, M.J.; Lee, S.; Michalakes, J.; Moriarty, P.J. A numerical study of the effects of atmospheric and wake turbulence on wind turbine dynamics. J. Turbul. 2012, 13, N14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.A.; Graham, J.M. Turbulence velocity spectra and intensities in the inflow of a turbine rotor. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 870, 870R31–870R311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornev, N.V.; Taranov, A.; Shchukin, E.; Kleinsorge, L. Development of hybrid URANS-LES methods for flow simulation in the ship stern area. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 38, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefvendahl, M.; Troëng, C. Simulation based analysis of the hydrodynamics and load fluctuations of a submarine propeller behind a fully appended submarine hull. In Proceedings of the 29th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Gothenburg, Sweden, 26–31 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Cotté, B. Wind turbine noise modeling based on Amiet’s theory: Effects of wind shear and atmospheric turbulence. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2016, 102, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanon, A.; De Gennaro, M.; Kuehnelt, H.; Giannattasio, P. Assessment of the broadband noise from an unducted axial fan including the effect of the inflow turbulence. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 429, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, F.; Brooks, T. Noise radiation from single and multiple rod configurations. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2012, 11, 291–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amiet, R.K. Acoustic radiation from an airfoil in a turbulent stream. J. Sound Vib. 1975, 41, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, R.; Satcunanathan, S.; Moreau, S.; Ragni, D.; Meinke, M.; Schröder, W.; Schram, C. On the role of turbulence distortion on leading-edge noise reduction by means of porosity. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 485, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilka, M.; Kerrian, P.; Ross, M.; Morris, S. Radiated sound from a circular cylinder in a turbulent shear layer. Int. J. Aeroacoustics 2014, 13, 511–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryami, R.; Ali, S.A.S.; Azarpeyvand, M.; Afshari, A.; Dehghan, A.A. Turbulent flow interaction with a circular cylinder. In Proceedings of the 25th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Delt, Netherlands, 20–23 May 2019; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Maryami, R.; Showkat Ali, S.A.; Azarpeyvand, M.; Afshari, A. Turbulent flow interaction with a circular cylinder. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 015105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liefvendahl, M.; Bensow, R.E. Simulation-based investigation of foil-turbulence interaction noise. In Proceedings of the 33rd Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Osaka, Japan, 31 May–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Britter, R.E.; Hunt, J.C.; Mumford, J.C. The distortion of turbulence by a circular cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 92, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Rival, D.E.; Wu, X. Sound source and pseudo-sound in the near field of a circular cylinder in subsonic conditions. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 919, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.S.; Eça, L.; Vaz, G.; Girimaji, S.S. Toward Predictive RANS and SRS Computations of Turbulent External Flows of Practical Interest. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3953–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, M.; Celik, I.; Yavuz, I. Modeling of effect of inflow turbulence data on large eddy simulation of circular cylinder flows. J. Fluids Eng. 2007, 129, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, S.; Ergin, S. Effects of temperature, salinity, and fluid type on acoustic characteristics of turbulent flow around circular cylinder. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2021, 20, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefvendahl, M.; Bensow, R.E. Simulation-based analysis of flow-generated noise from cylinders with different cross-sections. In Proceedings of the 32nd Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Hamburg, Germany, 5–10 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaz, G.; Jaouen, F.; Hoekstra, M. Free-surface viscous flow computations: Validation of URANS code FRESCO. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, Honolulu, HI, USA, 31 May–5 June 2009; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 425–437. [Google Scholar]
- Girimaji, S.; Abdol-Hamid, K. Partially averaged Navier-Stokes model for turbulence: Implementation and validation. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Germano, M. Turbulence: The filtering approach. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 238, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Vaz, G.; Eça, L.; Girimaji, S. Simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder at Re = 3900 with partially-averaged Navier-Stokes equations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 69, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulence model. Turbul. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Klapwijk, M.; Lloyd, T.; Vaz, G. On the accuracy of partially averaged Navier-Stokes resolution estimates. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 80, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapwijk, M.; Lloyd, T.; Vaz, G.; Van Terwisga, T. PANS simulations: Low versus high Reynolds number approach. In Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering (MARINE 2019), Gothenborg, Sweden, 13–15 May 2019; pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, F.; Eça, L.; Vaz, G.; Girimaji, S. On the simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder at Re=140,000. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 76, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.S.; Eca, L.; Vaz, G.; Girimaji, S.S. Challenges in Scale-Resolving Simulations of turbulent wake flows with coherent structures. J. Comput. Phys. 2018, 363, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapwijk, M.; Lloyd, T.; Vaz, G.; Van Terwisga, T. On the use of synthetic inflow turbulence for scale-resolving simulations of wetted and cavitating flows. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 228, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapwijk, M.; Lloyd, T.; Vaz, G.; Van Terwisga, T. Evaluation of scale-resolving simulations for a turbulent channel flow. Comput. Fluids 2020, 209, 104636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.T.; Castro, I. Efficient generation of inflow conditions for large eddy simulation of street-scale flows. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2008, 81, 449–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Castro, I.; Xie, Z. Divergence-free turbulence inflow conditions for large-eddy simulations with incompressible flow solvers. Comput. Fluids 2013, 84, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norberg, C. Fluctuating lift on a circular cylinder: Review and new measurements. J. Fluids Struct. 2003, 17, 57–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, U.; Balaras, E. Wall-layer models for large-eddy simulations. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2002, 34, 349–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgiadis, N.; Rizzetta, D.; Fureby, C. Large-eddy simulation: Current capabilities, recommended practices, and future research. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, P. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Paik, B.G.; Lee, S.J. PIV measurements of hull wake behind a container ship model with varying loading condition. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 36, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilmineau, E.; Deng, G.B.; Queutey, P.; Visonneau, M.; Wackers, J. Detached Eddy Simulations of the Flow Around the Japan Bulk Carrier (JBC); Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation XI; Salvetti, M.V., Armenio, V., Fröhlich, J., Geurts, B.J., Kuerten, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 579–585. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, W.K. Mechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration, Volume 2. Complex Flow-Structure Interactions, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Norberg, C.; Sunden, B. Turbulence and reynolds number effects on the flow and fluid forces on a single cylinder in cross flow. J. Fluids Struct. 1987, 1, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, C. Effects of Reynolds Number and a Low-Intensity Freestream Turbulence on the Flow around a Circular Cylinder. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University, Gothenborg, Sweden, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.C.; Lee, S.J. Flow control of circular cylinders with longitudinal grooved surfaces. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffowcs Williams, J.E.; Hawkings, D.L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1969, 264, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






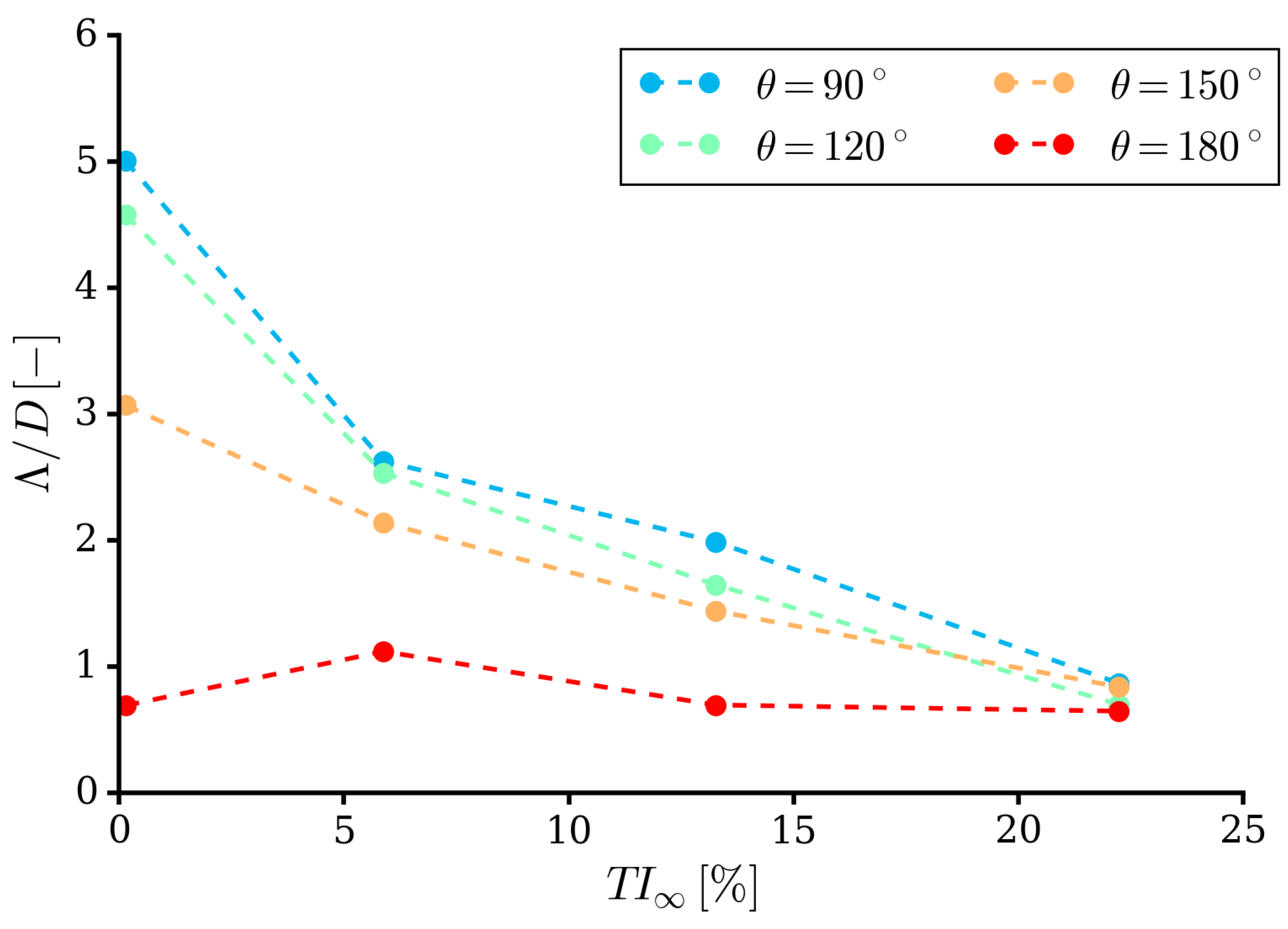
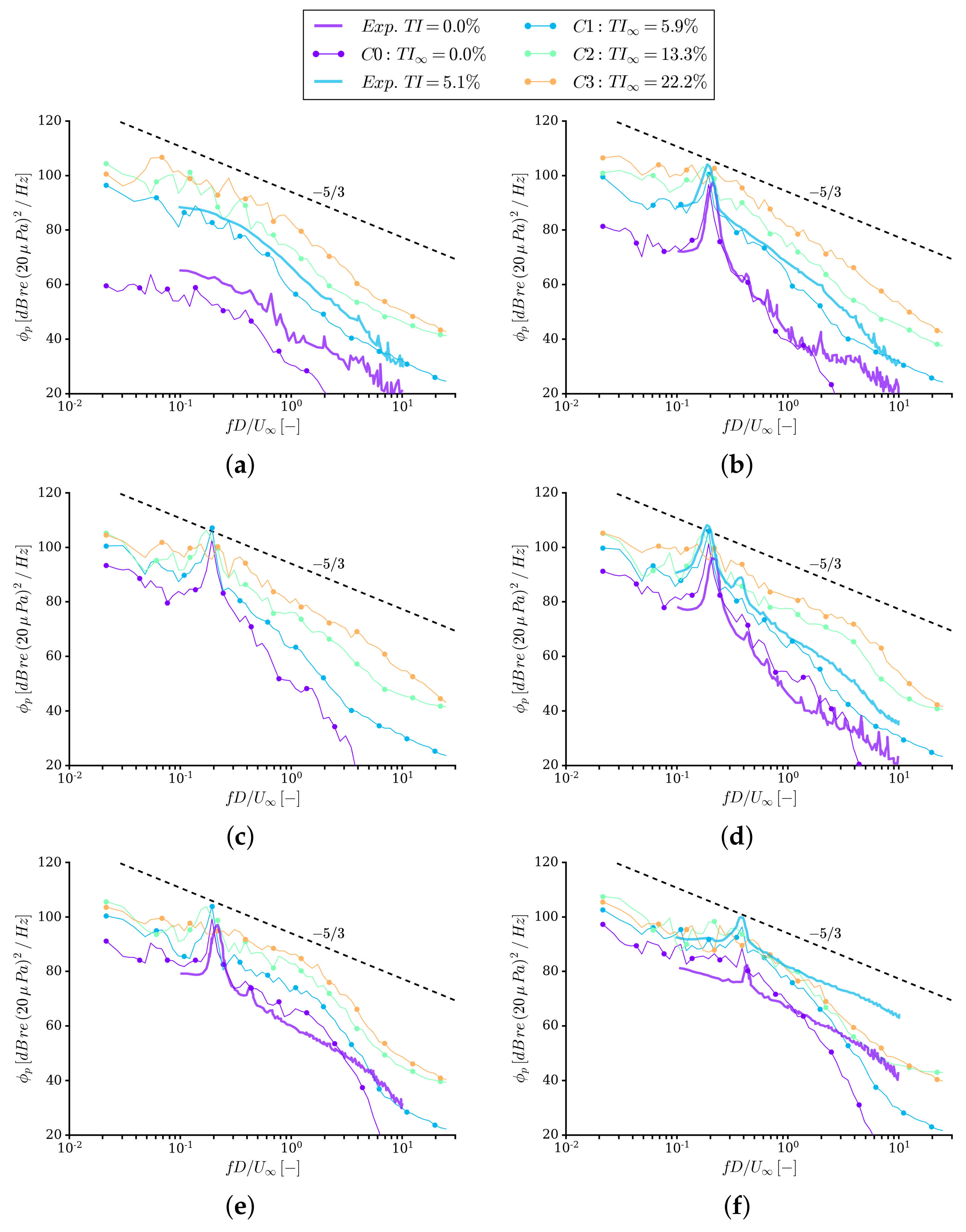
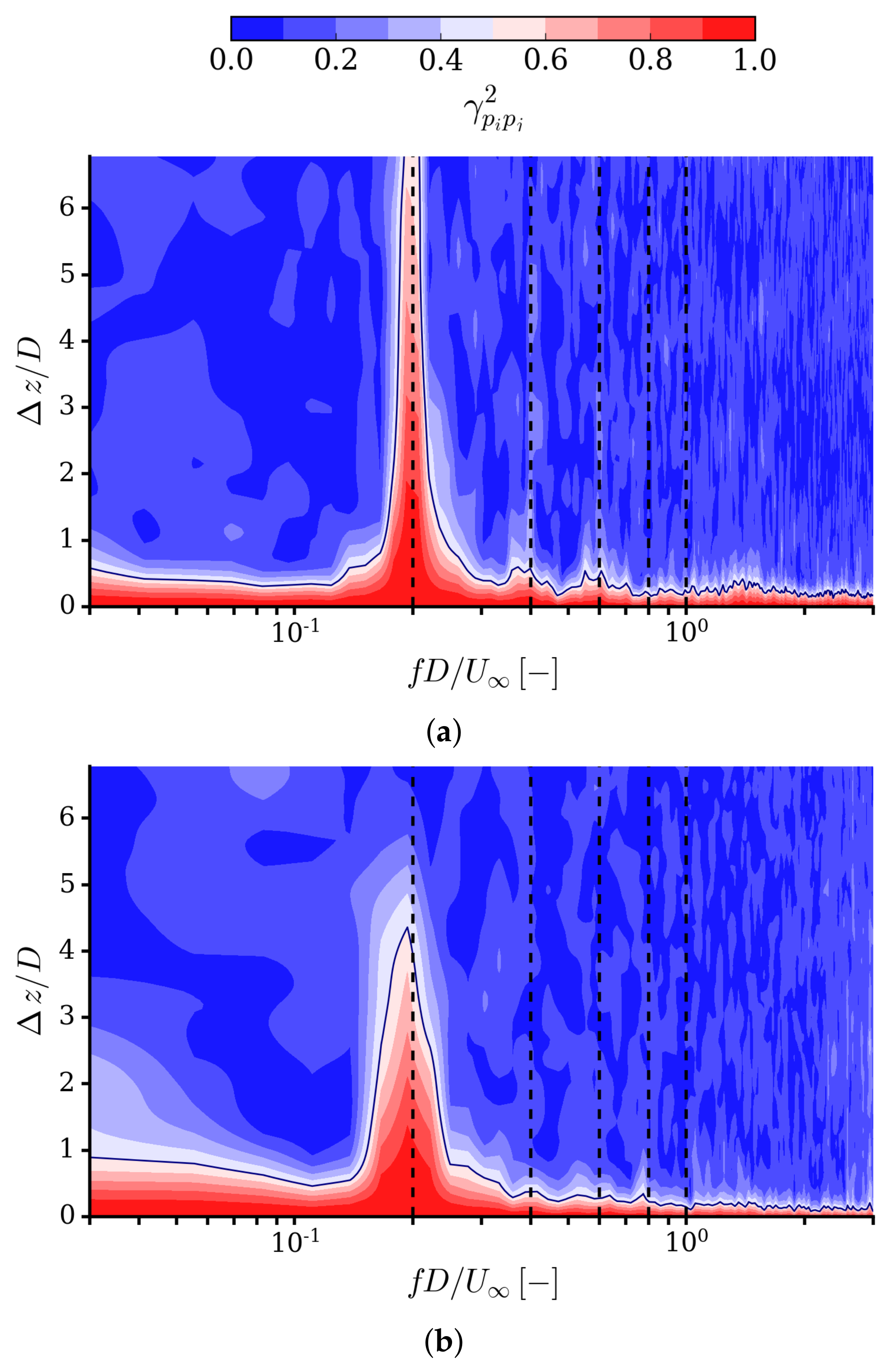
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter [m] | D | 0.022 |
| Inflow speed [m/s] | 10.07 | |
| Reynolds number | 14,700 | |
| Mach number | 0.029 | |
| Span/D (experiment) | 21 | |
| Span/D (simulation) | 15 | |
| Fluid density [kg/m] | 1.225 | |
| Turbulence intensity [%] | 5.1 | |
| Integral length scale/D | 1.086 |
| Case | [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | - | |
| 5.9 | 1.221 | |
| 13.3 | 0.795 | |
| 22.2 | 1.040 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lidtke, A.K.; Klapwijk, M.; Lloyd, T. Scale-Resolving Simulations of a Circular Cylinder Subjected to Low Mach Number Turbulent Inflow. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111274
Lidtke AK, Klapwijk M, Lloyd T. Scale-Resolving Simulations of a Circular Cylinder Subjected to Low Mach Number Turbulent Inflow. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(11):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLidtke, Artur K., Maarten Klapwijk, and Thomas Lloyd. 2021. "Scale-Resolving Simulations of a Circular Cylinder Subjected to Low Mach Number Turbulent Inflow" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 11: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111274
APA StyleLidtke, A. K., Klapwijk, M., & Lloyd, T. (2021). Scale-Resolving Simulations of a Circular Cylinder Subjected to Low Mach Number Turbulent Inflow. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(11), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111274






