Relationship between Sea Surface Drag Coefficient and Wave State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Calculations on Sea Surface Drag Coefficient ()
2.2. Calculations on Sea Spray Momentum Flux
2.3. Sea Spray Generation Function
3. Results
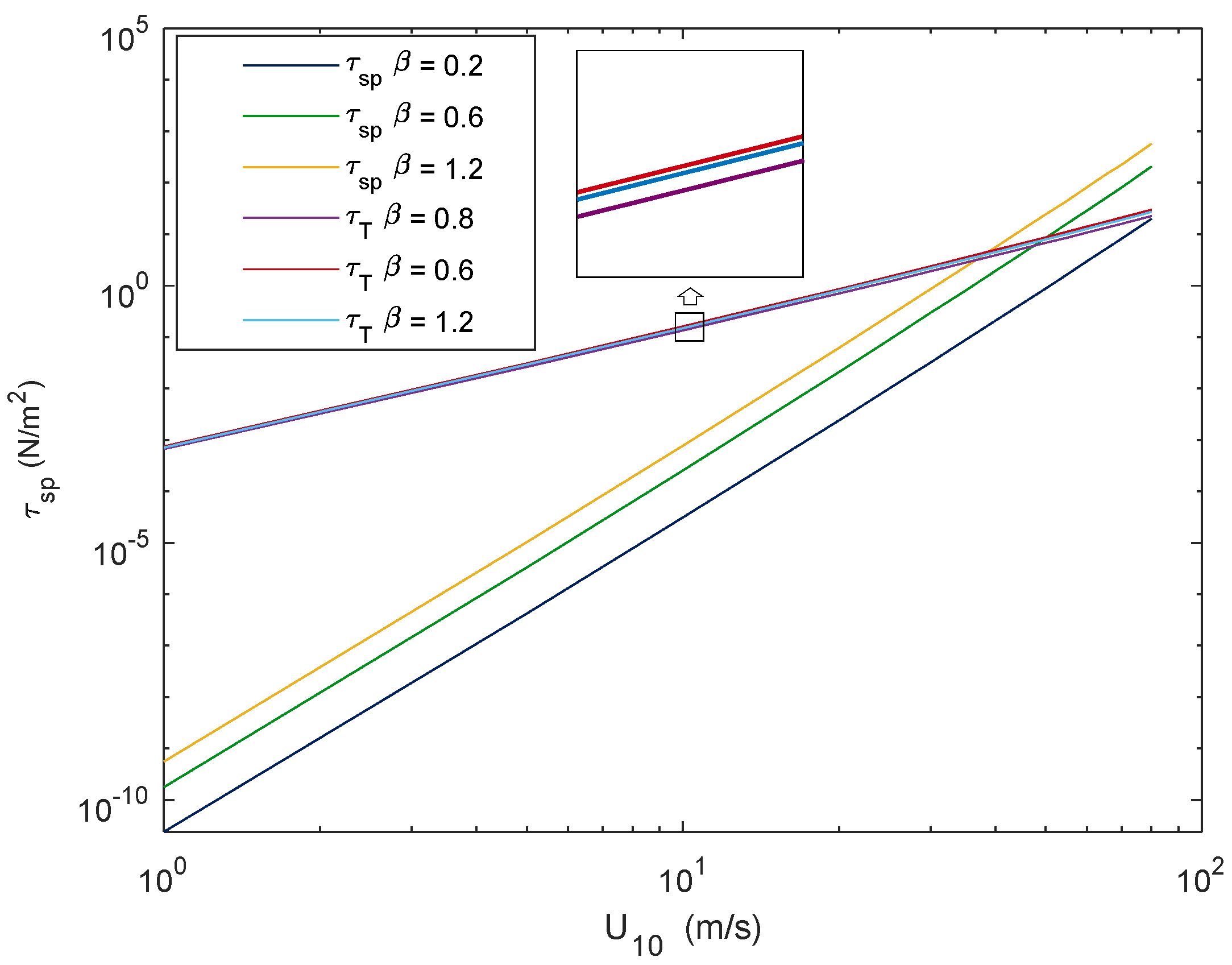
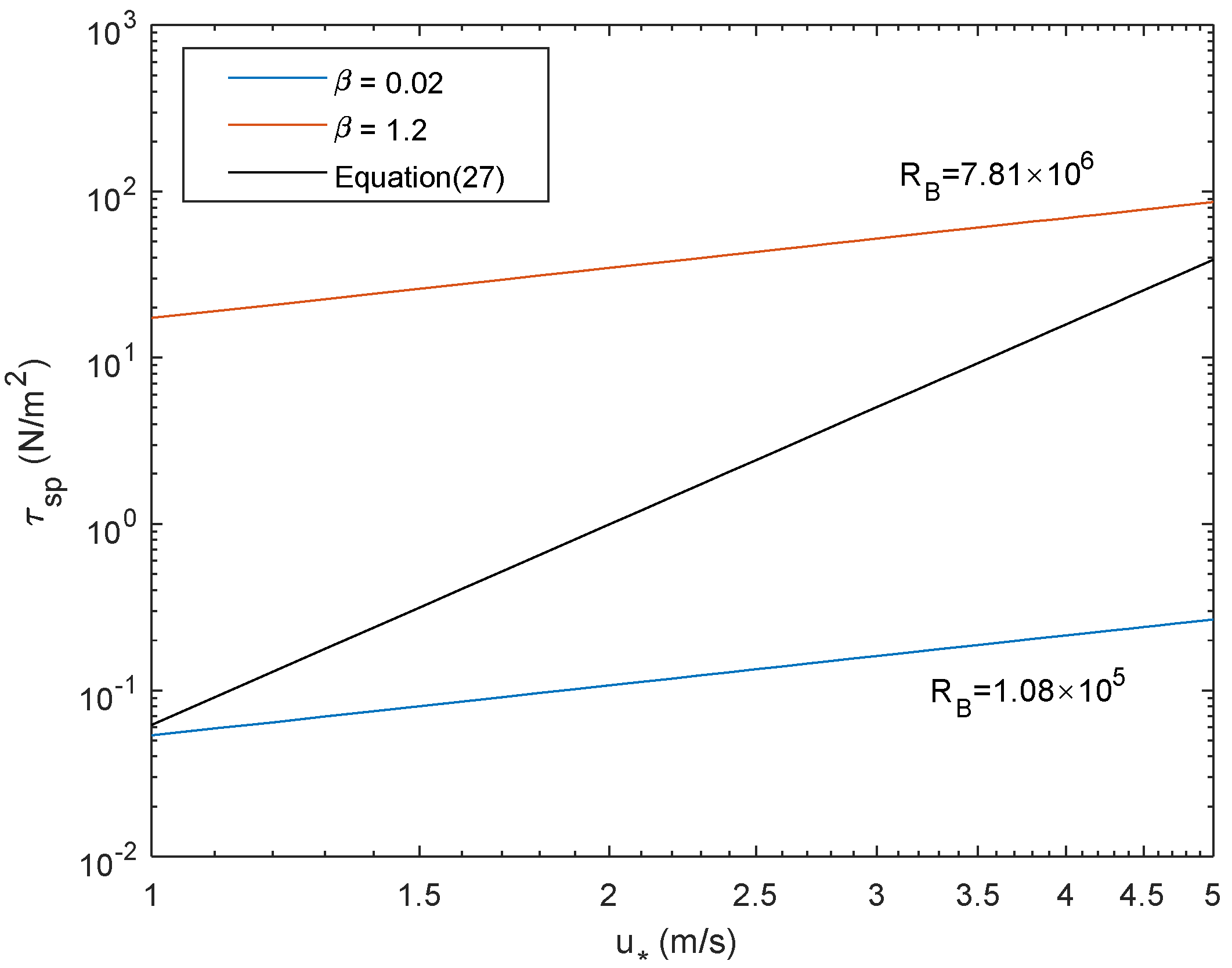
3.1. Wave State Influence on Sea Spray Momentum Flux
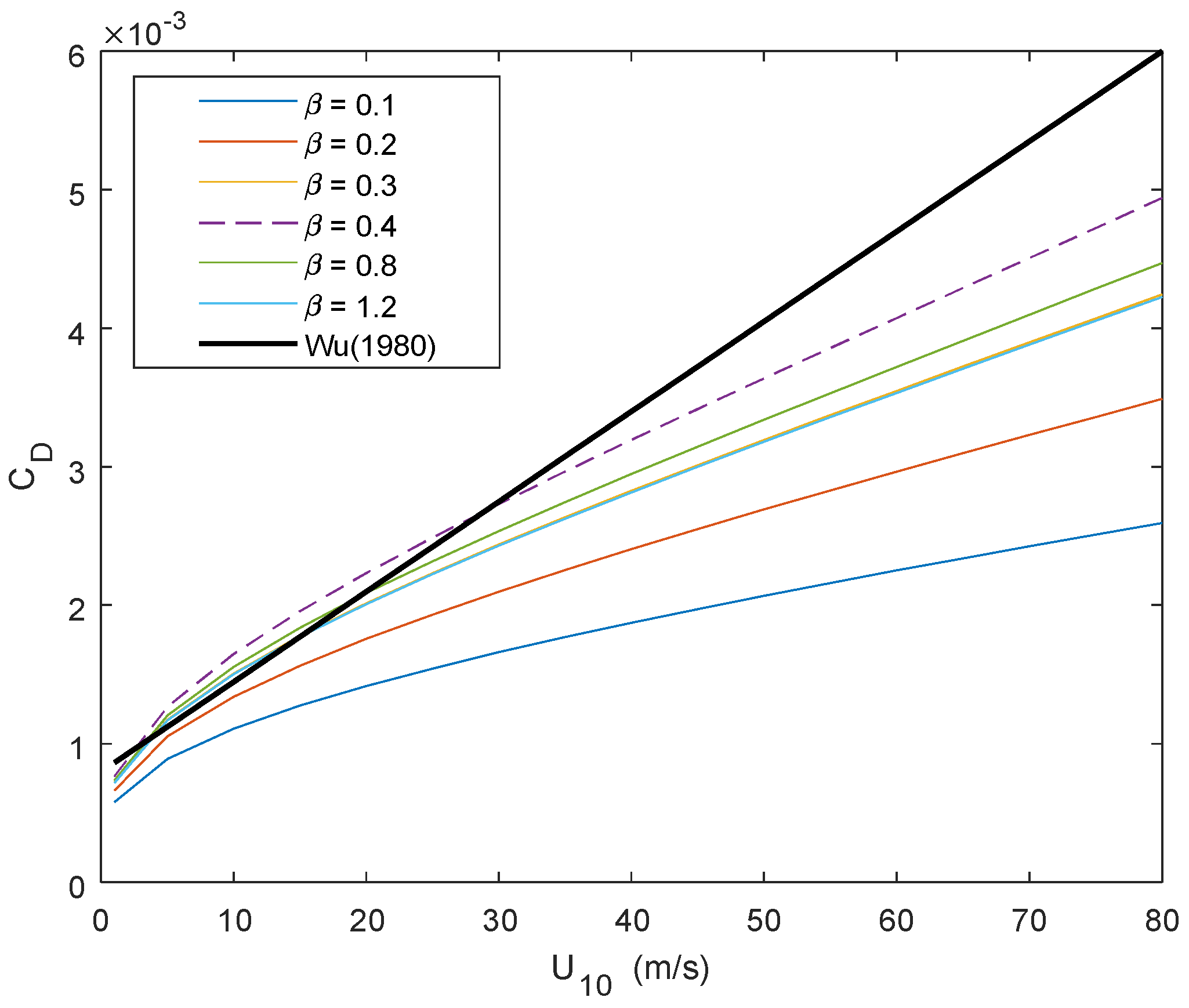
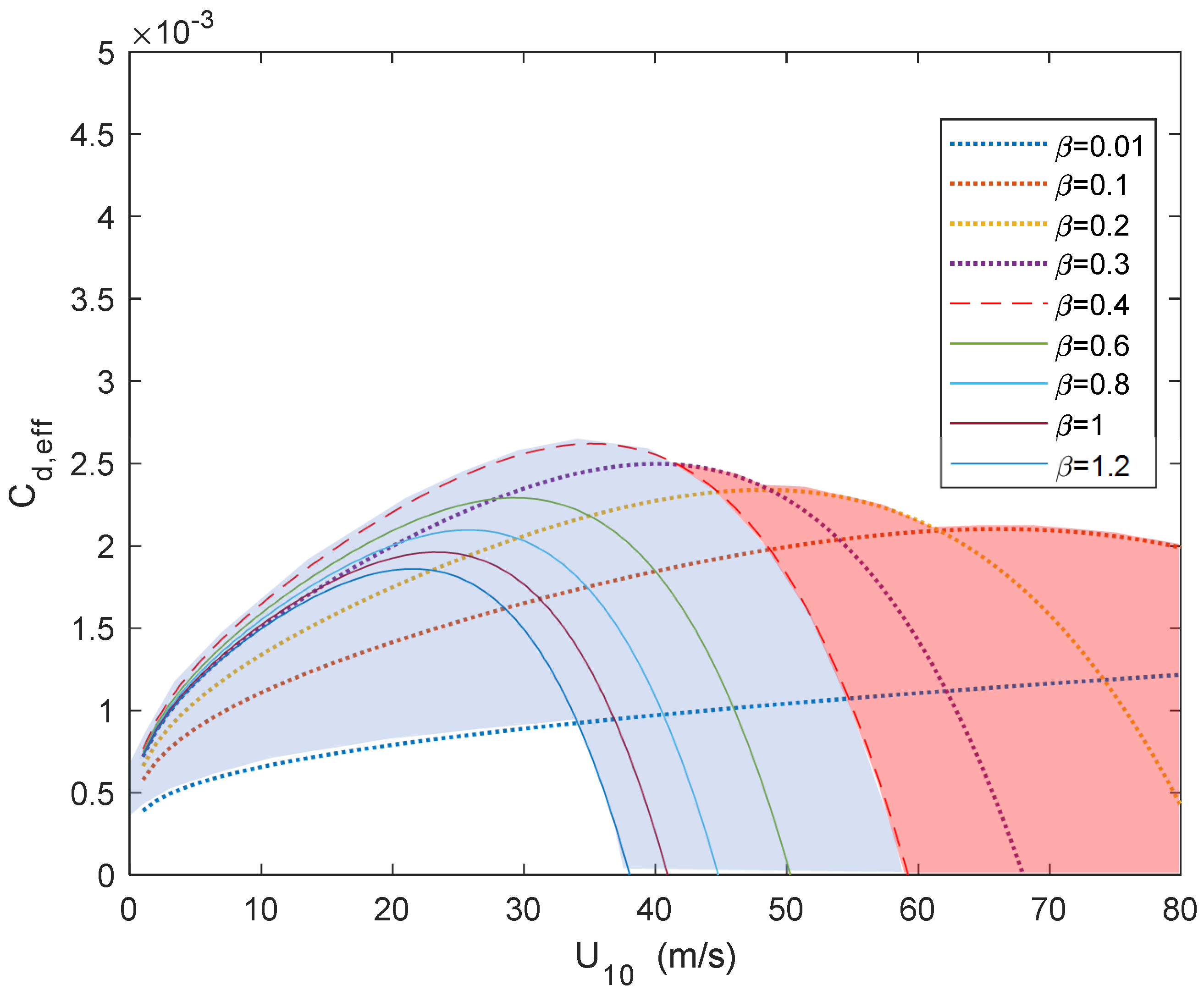
3.2. Sea Surface Drag Coefficient
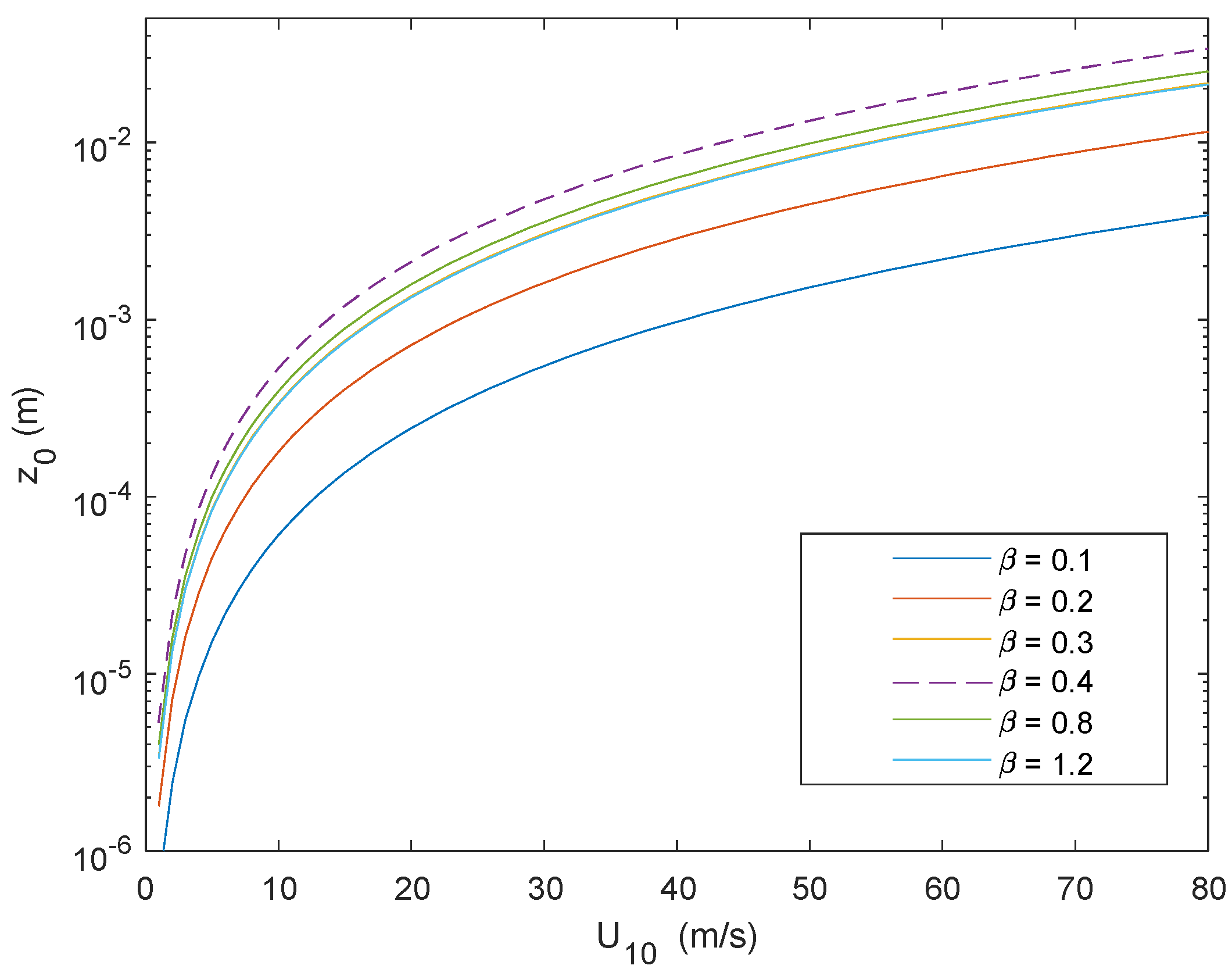
3.3. Sea Surface Roughness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charnock, H. Wind stress on a water surface. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1955, 81, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, C.; Piazzola, J.; Forget, P.; Le Calve, O.; Despiau, S. Analysis of the Variation of the Whitecap Fraction as Measured in a Coastalzone. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2004, 111, 339–360. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Xie, L. On the Linear Parameterization of Drag Coefcient over Sea Surface. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 847–2851. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, M. Dependence of Wind Stress across an Air–sea Interface on Wave States. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 75, 207–223. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Wind-stress Coefcients over Sea Surface near Neutral Conditions—A Revisit. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1980, 10, 727–740. [Google Scholar]
- Large, W.G.; Pond, S. Open Ocean Momentum Fux Measurements in Moderate to Strong Winds. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 324–336. [Google Scholar]
- Geernaert, G.L.; Larsen, S.E.; Hansen, F. Measurements of the wind stress, heat flux, and turbulence intensity during storm conditions over the North Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1987, 92, 13127–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelland, M.; Taylor, P.K. Wind Stress Measurements from the Open Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1996, 26, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, P. Numerical Modeling of Wave Disturbances in the Process of Ship Movement Control. Algorithms 2018, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murashige, S.; Choi, W. A numerical study on parasitic capillary waves using unsteady conformal mapping. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 328, 234–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donelan, M.A.; Le Méhauté, B.; Hanes, D.M. Air-Sea Interaction. The Sea: Ocean Engineering Science. J. Wiley. 1990, 9, 239–292. [Google Scholar]
- Toba, Y.; Iida, N.; Kawamura, H.; Ebuchi, N.; Jones, I.S.F. Wave Dependence of Sea-Surface Wind Stress. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Sha, W. Dependence of sea surface drag coefficient on wind-wave parameters. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, Y. Local balance in the air-sea boundary processes. J. Oceanogr. 1972, 28, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.E.M. Wave-Induced Stress and the Drag of Air Flow over Sea Waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1989, 19, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Dudhia, J. On the Need to Modify the Sea Surface Roughness Formulation over Shallow Waters. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2018, 57, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel, R.A.; Viero, D.P.; Carniello, L.; Defina, A.; D’Alpaos, L. The first operations of Mo.S.E. system to prevent the flooding of Venice: Insights on the hydrodynamics of a regulated lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 261, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.A. A Mechanism for the Increase of Wind Stress (Drag) Coefficient with Wind Speed over Water Surfaces: A Parametric Model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1986, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Nystrom, R.G.; Rotunno, R.; Davis, C.A.; Zhang, F. Consistent Impacts of Surface Enthalpy and Drag Coefficient Uncertainty between an Analytical Model and Simulated Tropical Cyclone Maximum Intensity and Storm Structure. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 3059–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, I.; Ginis, I.; Hara, T. Impact of the Reduced Drag Coefficient on Ocean Wave Modeling under Hurricane Conditions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L.H.; Powell, M.; Pietrzak, J.D. Wind and waves in extreme hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 09003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donelan, M.A.; Haus, B.K.; Reul, N.; Plant, W.J.; Stiassnie, M.; Graber, H.C.; Brown, O.; Saltzman, E.S. On the limiting aerodynamic roughness of the ocean in very strong winds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagaki, N.; Komori, S.; Suzuki, N. Estimation of friction velocity from the wind-wave spectrum at extremely high wind speeds. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 35, p. 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L. Spray Stress Revisited. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, V.K. A Note on the Drag of the Sea Surface at Hurricane Winds. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2005, 115, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; DeCosmo, J. The Signature of Sea Spray in the HEXOS Turbulent Heat FluxData. Bound. Layer Meteor. 2002, 103, 303–333. [Google Scholar]
- Cavaleri, L. Wave Modeling–The State of the Art. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 75, 603–674. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Toba, Y.; Sugioka, K.-I.; Komori, S. New sea spray generation function for spume droplets. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, 02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, D.L.; Li, X.Q.; Zhong, Z. New Wave Dependent Formulae for Sea Spray Flux. J. Hydrodyn. 2009, 21, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. The Influence of wave state and sea spray on drag coefficient from low to high wind speeds. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.-H.; Zhu, J.-B.; Sun, K.; Zhou, K. An integrated turbulent simulation and parameter modeling study on sea-spray dynamics and fluxes. Ocean Eng. 2017, 130, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Toba, Y.; Chaen, M. A new expression for the production rate of sea water droplets on the sea surface. J. Oceanogr. 1992, 48, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Phillips, O.M. Wind Sea Growth and Dissipation in the Open Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 1633–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L.; Emanuel, K.A. Effects of Sea Spray on Tropical Cyclone Intensity. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, E.C.; Spiel, D.E.; Davidson, K.L. A model of Marine Aerosol Generation Via Whitecaps and Wave Disruption. In Oceanic Whitecaps and Their Role in Air-Sea Exchange Processes; Monahan, E.C., Niocaill, M.G., Eds.; Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Stramska, M. Vertical Profiles of Sea-Salt Aerosol in the Atmospheric Surface Layer: A Numerical Model. ACTA Geophys. Polonica 1987, 35, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf, D.K.; Monahan, E.C.; Spiel, D.E. Quantification of the Marine Aerosol Produced by Whitecaps. In Proceedings of the 7th Congress on Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction, Anaheim, CA, USA, 31 January–5 February 1988; Preprint Volume, pp. 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.L. A parameterization of sea-salt aerosol source function for sub- and super-micron particles. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Sea Spray and the Turbulent Air-Sea Heat Fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1992, 97, 11429–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. A New Sea Spray Generation Function for Wind Speeds up to 32 m s−1. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.H.; Park, P.M.; Consterdine, I.E. Marine Aerosol Concentrations and Estimated Fluxes over the Sea. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 809–824. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosz, E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Wang, D.W.; Teague, W.J. Bottom-Up Determination of Air-Sea Momentum Exchange Under a Major Tropical Cyclone. Science 2007, 315, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagaki, N.; Komori, S.; Suzuki, N.; Iwano, K.; Kuramoto, T.; Shimada, S.; Kurose, R.; Takahashi, K. Strong Correlation between the Drag Coefcient and the Shape of the Wind Sea Spectrum over a Broad Range of Wind Speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L23604. [Google Scholar]





| Laboratory Observation Data | Offshore Observation Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wave Age | Root-Mean-Square Error | Wave Age | Root-Mean-Square Error | ||
| Equation (6) | Large and Pond (1981) | Equation (6) | Large and Pond (1981) | ||
| 0.1 | 4.41 × 10−4 | 7.32 × 10−4 | 0.5 | 4.92 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−3 |
| 0.2 | 2.01 × 10−4 | 0.6 | 6.68 × 10−4 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Feng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y. Relationship between Sea Surface Drag Coefficient and Wave State. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111248
Shi J, Feng Z, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Yu Y. Relationship between Sea Surface Drag Coefficient and Wave State. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(11):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111248
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jian, Zhihao Feng, Yuan Sun, Xueyan Zhang, Wenjing Zhang, and Yi Yu. 2021. "Relationship between Sea Surface Drag Coefficient and Wave State" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 11: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111248
APA StyleShi, J., Feng, Z., Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, W., & Yu, Y. (2021). Relationship between Sea Surface Drag Coefficient and Wave State. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(11), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111248





