A Wind–Wave-Dependent Sea Spray Volume Flux Model Based on Field Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
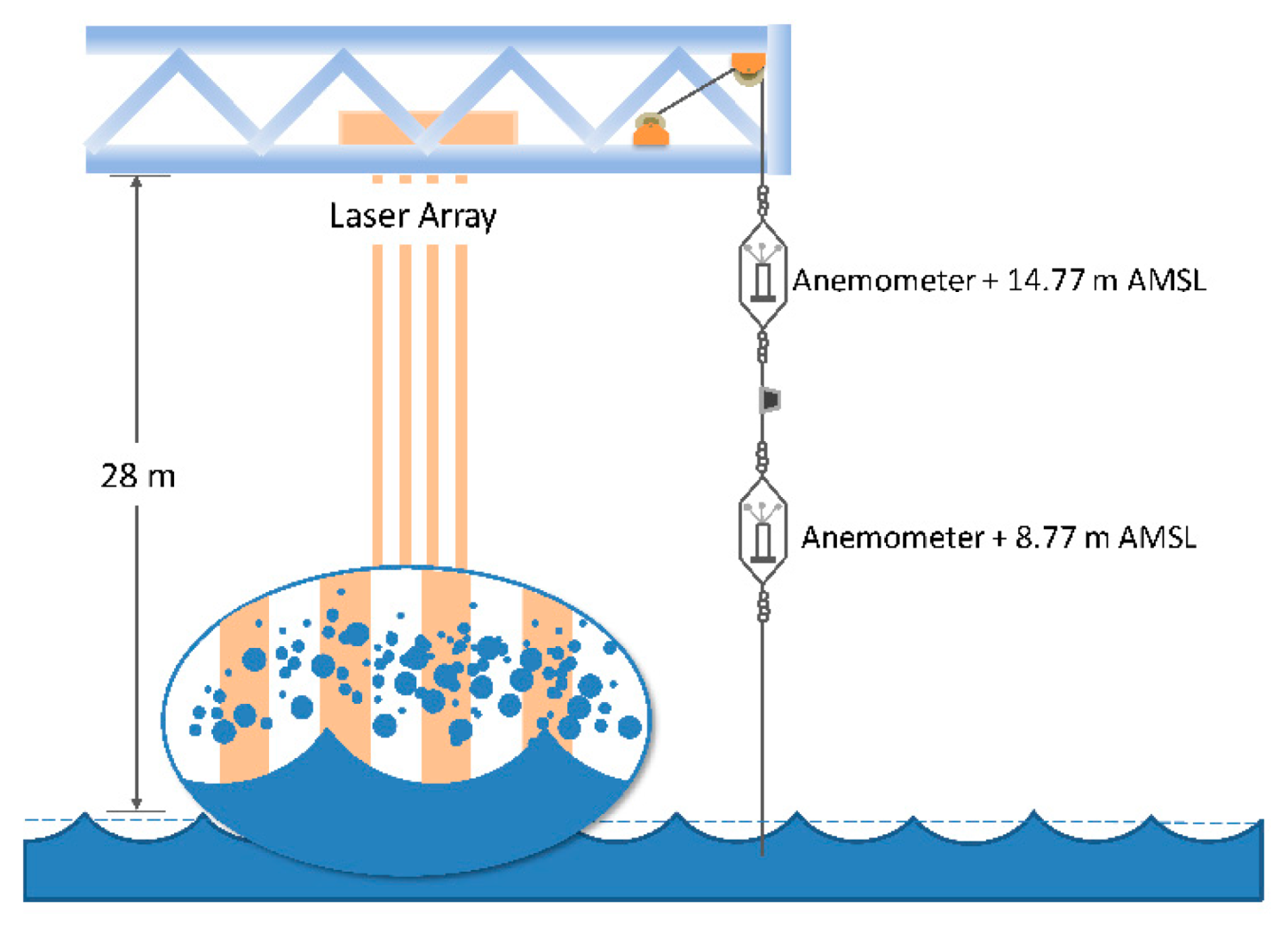
2.1. Sea Spray Volume Flux from Laser Attenuation
2.2. Experimental Data
2.2.1. Wind and Wave Observations
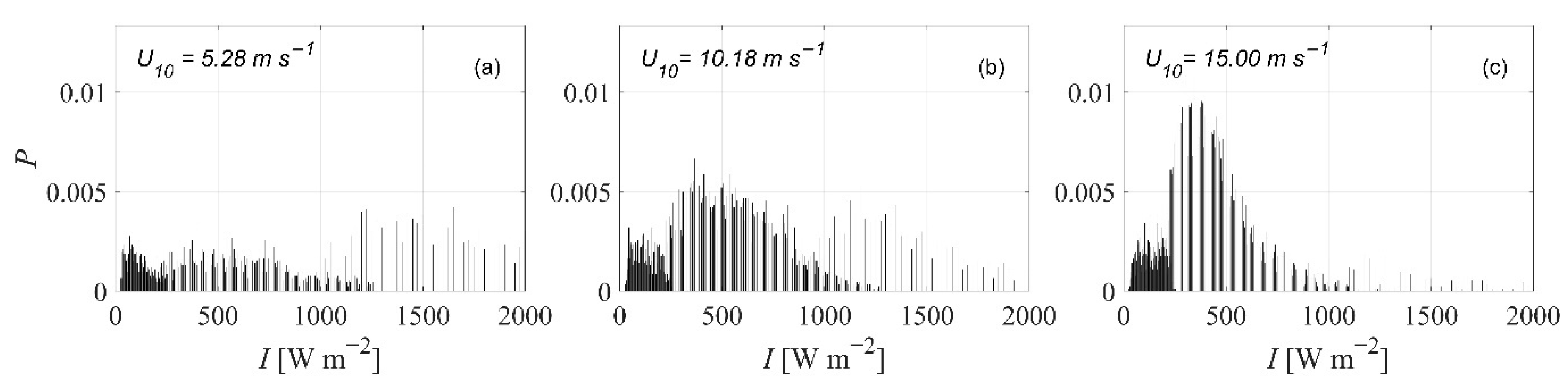
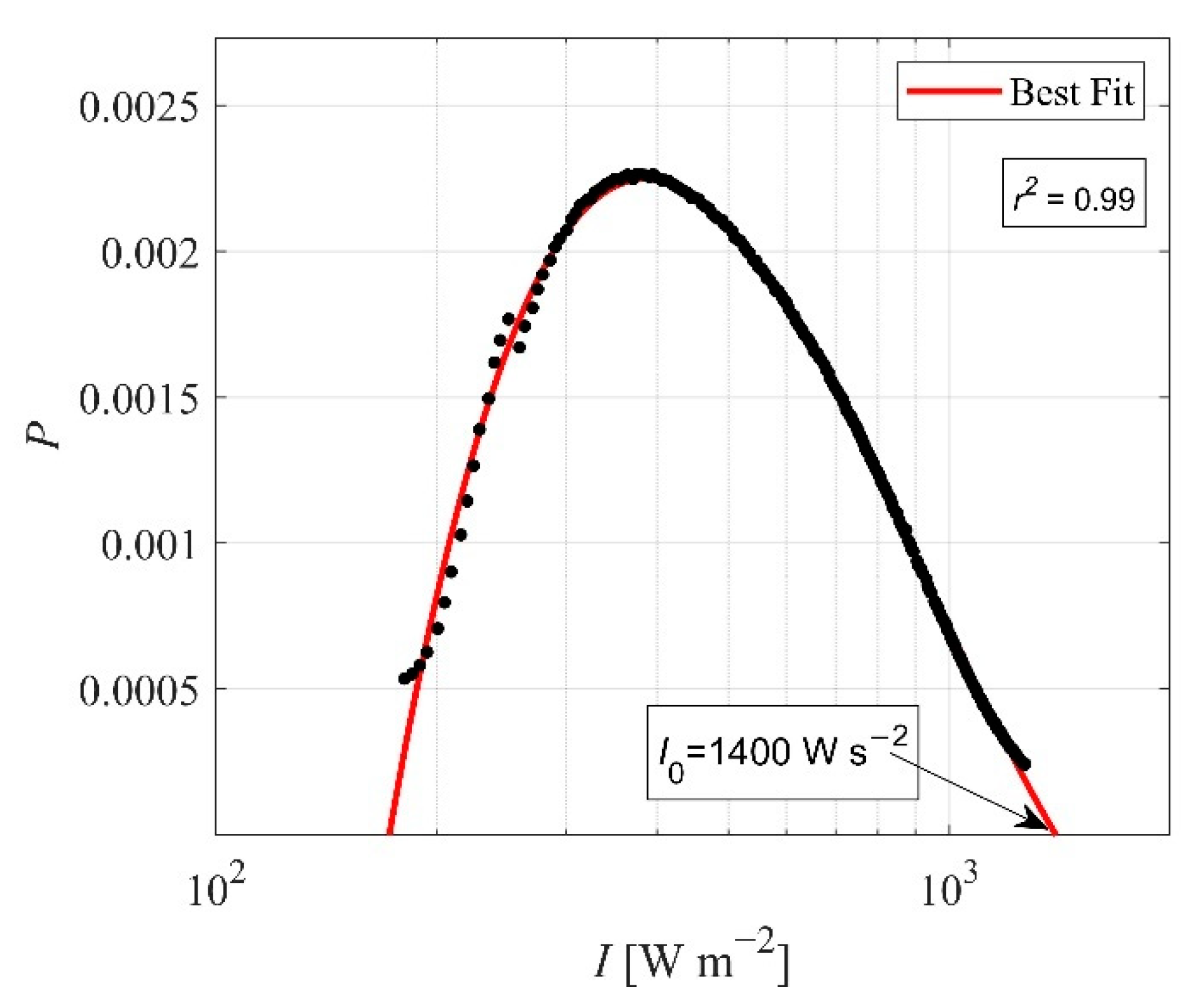
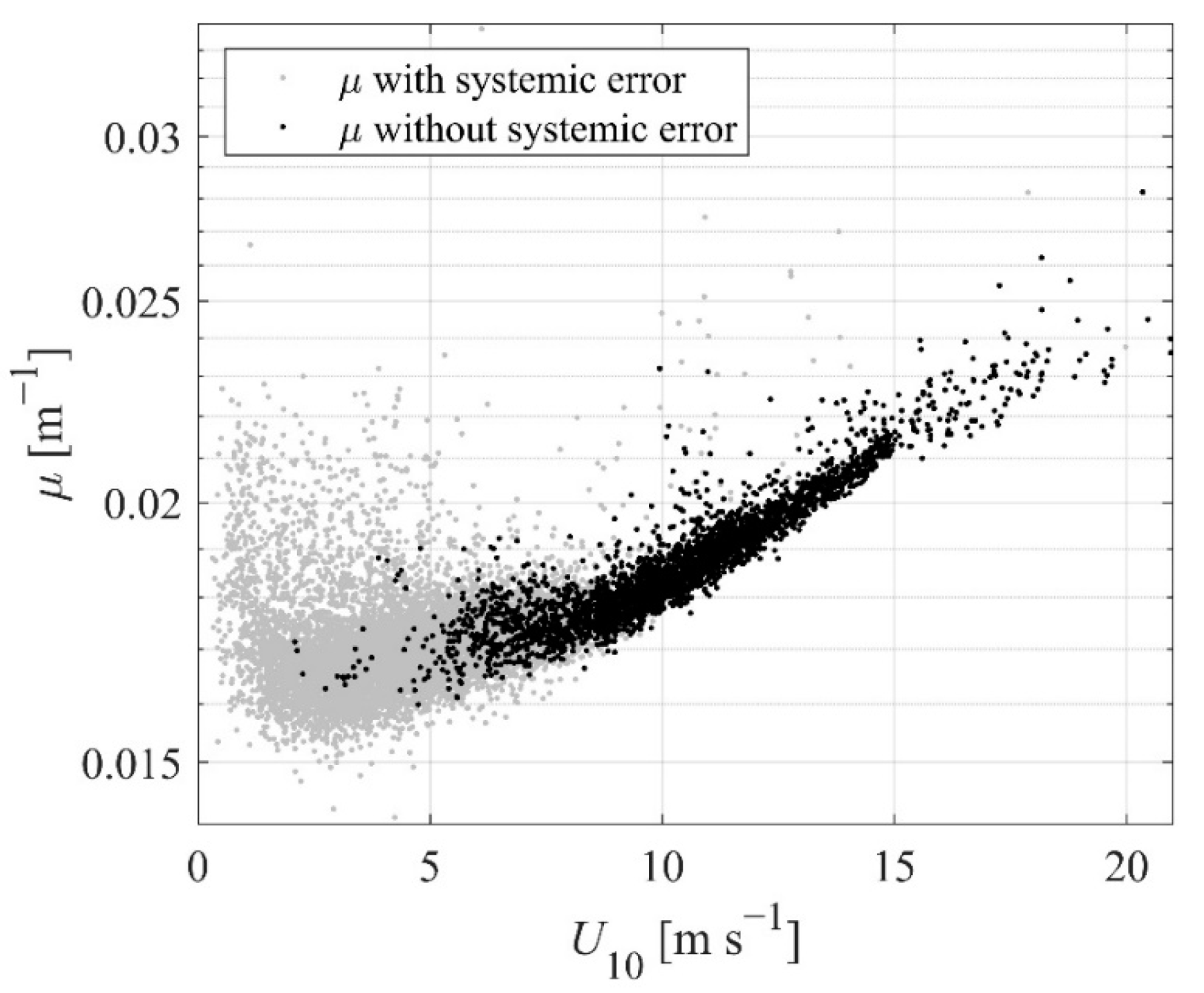
2.2.2. Laser Intensity
3. Results
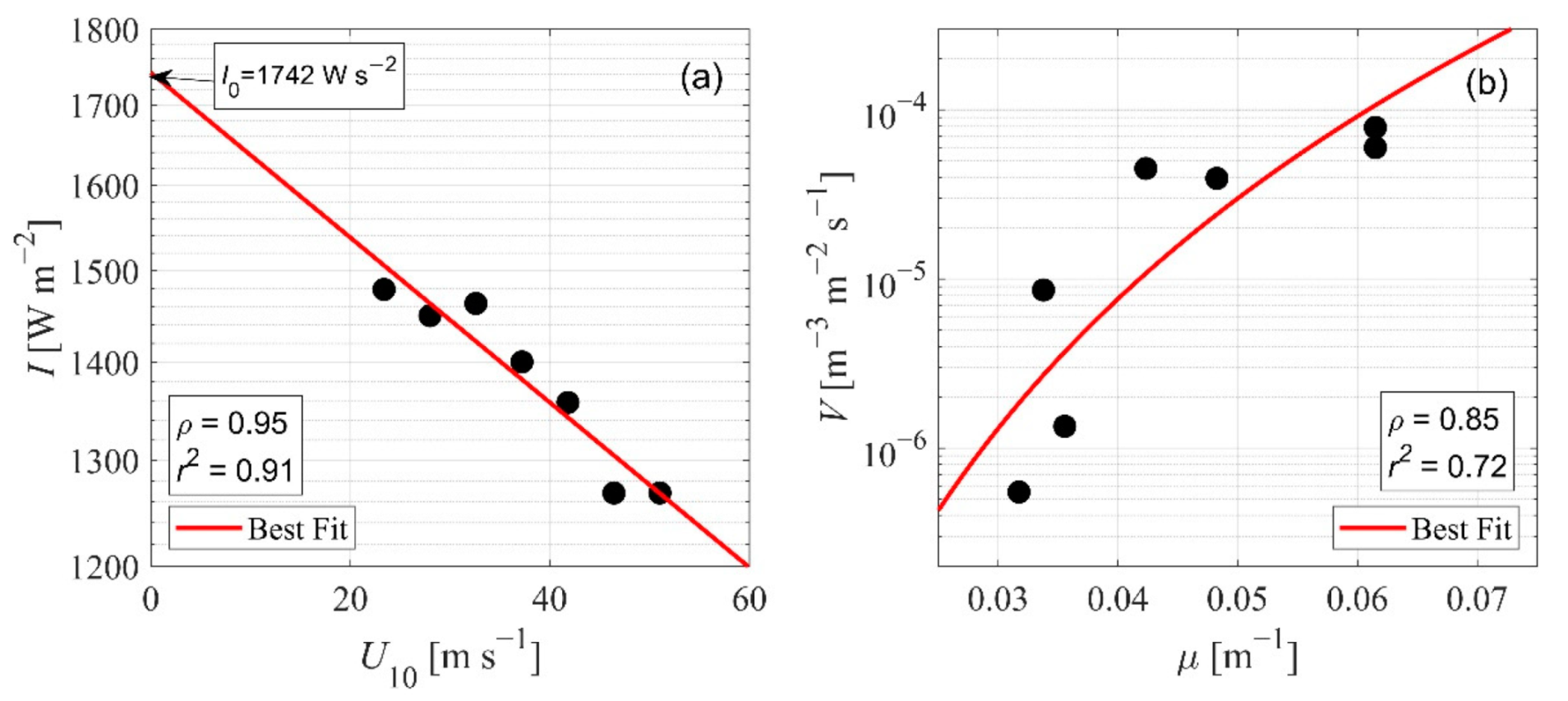
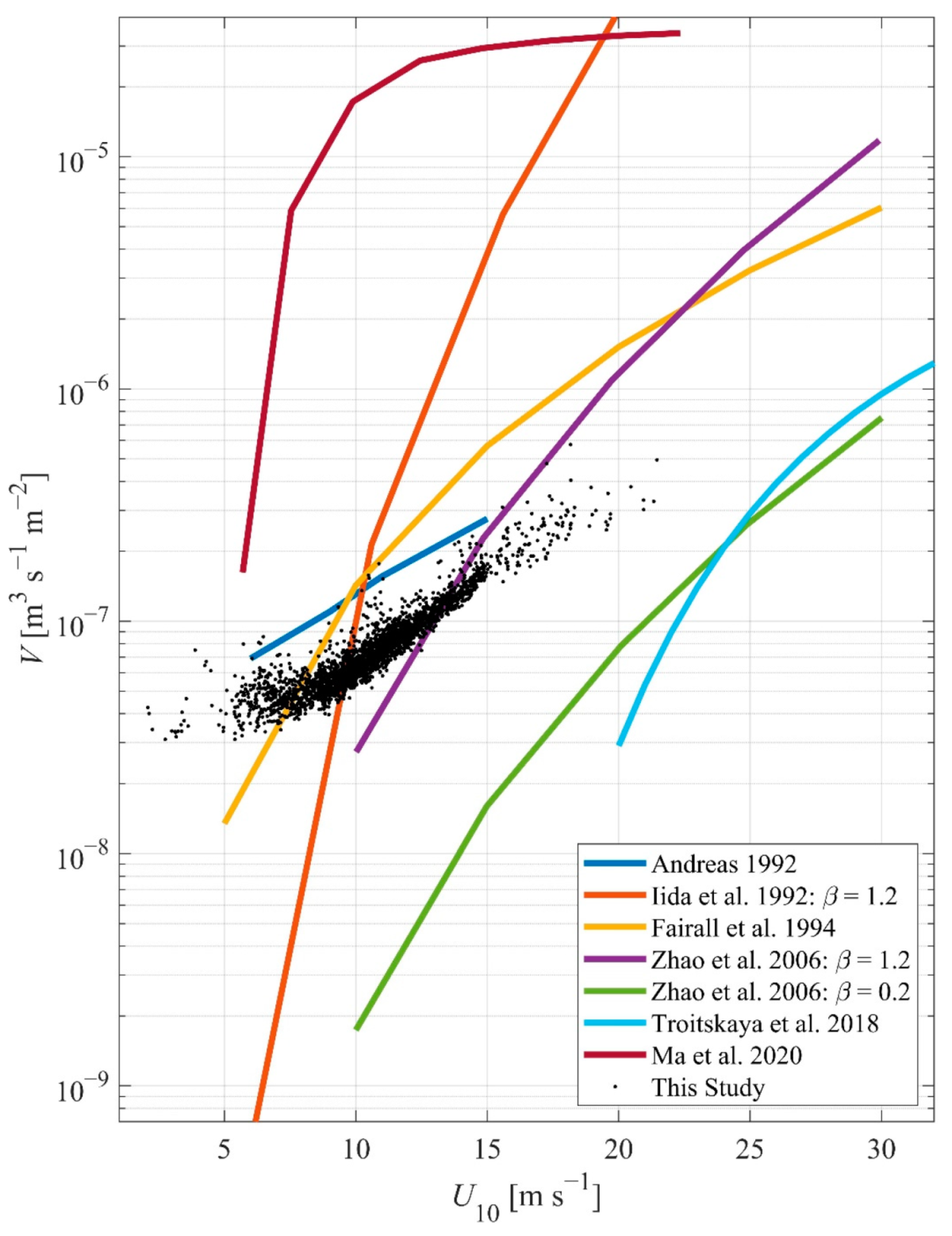
3.1. Sea Spray Volume Flux
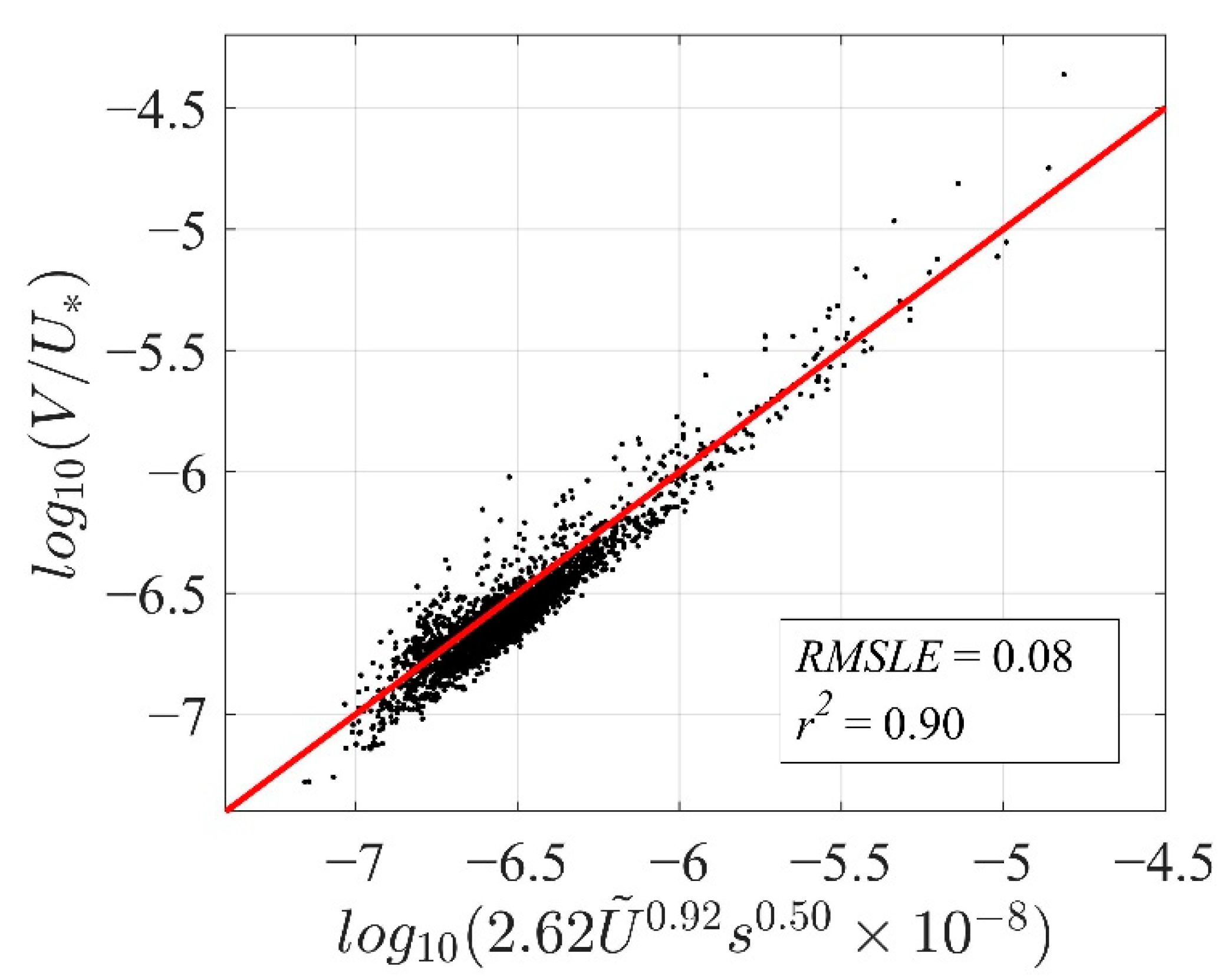
3.2. Sea Spray Volume Flux Parameterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
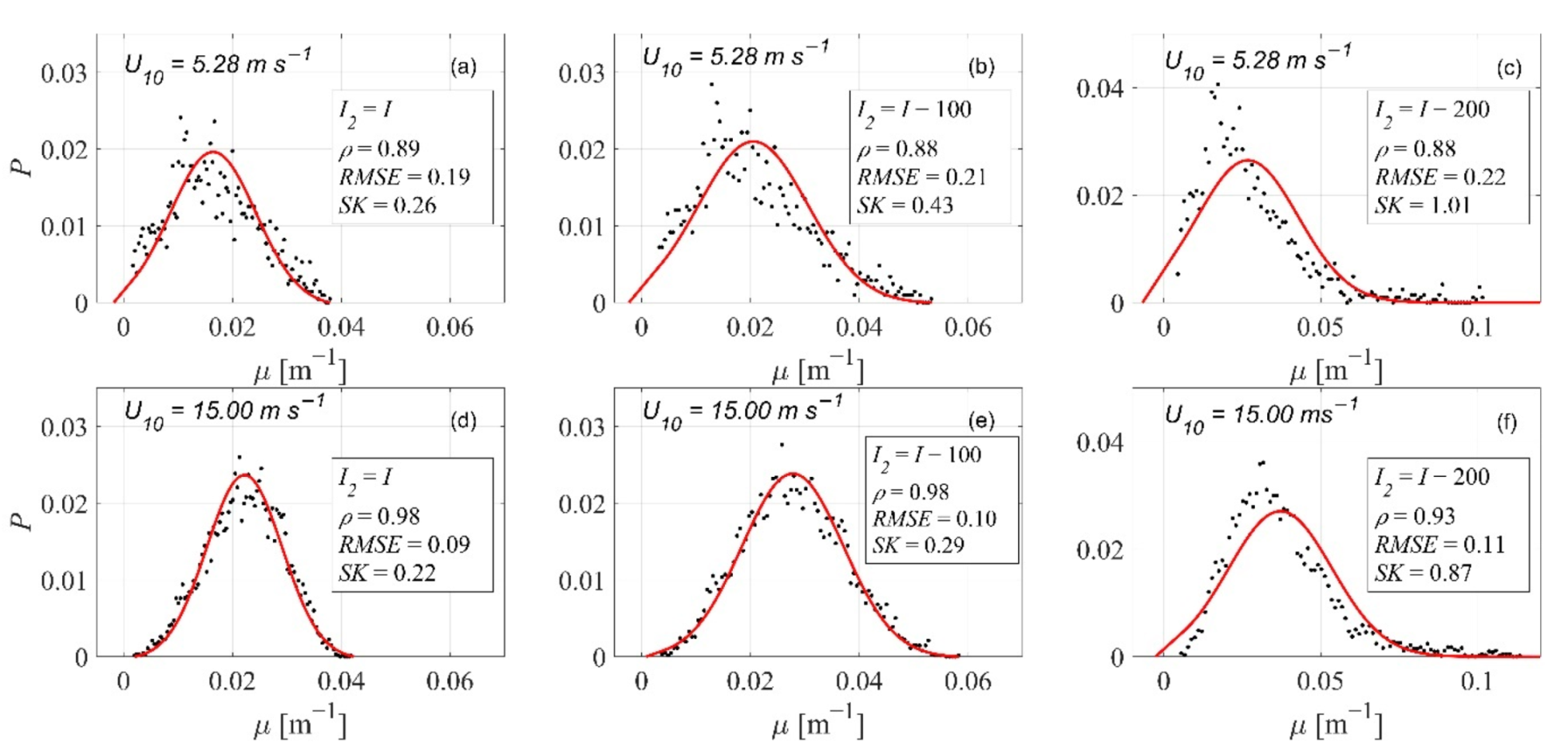
Appendix A. Statistics for Validation
References
- Veron, F. Ocean spray. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cheng, X.; Zeng, Q.; Jin, J.; Huang, J.; Feng, Y. On the upward flux of sea-spray spume droplets in high-wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5976–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, J.B.; Andreas, E.L. Modeling the role of sea spray on air-sea heat and moisture exchange. Final Rep. 1997, 6, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Fairall, C.; Kepert, J.; Holland, G. The effect of sea spray on surface energy transports over the ocean. Global Atmos. Ocean Syst. 1994, 2, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eijk, A.; Kusmierczyk-Michulec, J.; Francius, M.; Tedeschi, G.; Piazzola, J.; Merritt, D.; Fontana, J. Sea-spray aerosol particles generated in the surf zone. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 29397–29409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreas, E.L. Sea spray and the turbulent air-sea heat fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1992, 97, 11429–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Spray stress revisited. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Xie, L.; Guan, C.; Zhao, D. A coupled atmosphere–wave–ocean modeling system: Simulation of the intensity of an idealized tropical cyclone. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelan, M.A.; Haus, B.K.; Reul, N.; Plant, W.J.; Stiassnie, M.; Graber, H.C.; Brown, O.B.; Saltzman, E.S. On the limiting aerodynamic roughness of the ocean in very strong winds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veron, F.; Hopkins, C.; Harrison, E.L.; Mueller, J.A. Sea spray spume droplet production in high wind speeds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L16602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreas, E.L.; Emanuel, K.A. Effects of sea spray on tropical cyclone intensity. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreas, E.L.; Persson, P.O.G.; Hare, J.E. A bulk turbulent air–sea flux algorithm for high-wind, spray conditions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. A new sea spray generation function for wind speeds up to 32 ms−1. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorpe, S. Bubble clouds and the dynamics of the upper ocean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 118, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, W.K. The role of surface-wave breaking in air-sea interaction. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1996, 28, 279–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiel, D.E. More on the births of jet drops from bubbles bursting on seawater surfaces. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1997, 102, 5815–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, F.; Afeti, G. Film drop distributions from bubbles bursting in seawater. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1991, 96, 10681–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhuissier, H.; Villermaux, E. Bursting bubble aerosols. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 696, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, F. Flow patterns in breaking bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 5211–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E. Andreas, E. A review of spray generation function for the open ocean. In Atmosphere-Ocean Interactions Volume 1; Perrie, W., Ed.; WIT Press: Billerica, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, E.L.; Edson, J.B.; Monahan, E.C.; Rouault, M.P.; Smith, S.D. The spray contribution to net evaporation from the sea: A review of recent progress. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1995, 72, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M. Direct production of droplets from breaking wind-waves—Its observation by a multi-colored overlapping exposure photographing technique. Tellus 1981, 33, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monahan, E.C. Sea spray as a function of low elevation wind speed. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troitskaya, Y.; Kandaurov, A.; Ermakova, O.; Kozlov, D.; Sergeev, D.; Zilitinkevich, S. The “bag breakup” spume droplet generation mechanism at high winds. Part I: Spray generation function. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2018, 48, 2167–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Davidson, K.L.; Spiel, D.E. Whitecap aerosol productivity deduced from simulation tank measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1982, 87, 8898–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L. Parameterizing scalar transfer over snow and ice: A review. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.; Banner, M.; Peirson, W.; Asher, W.; Morison, R. Investigation of the physical scaling of sea spray spume droplet production. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultin, K.A.H.; Nilsson, E.D.; Krejci, R.; Mårtensson, E.M.; Ehn, M.; Hagström, Å.; de Leeuw, G. In situ laboratory sea spray production during the marine aerosol production 2006 cruise on the northeastern atlantic ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D062012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Hill, M.K.; Brooks, B.J.; Smith, M.H.; Sproson, D.A.J. Eddy covariance measurements of the sea spray aerosol flux over the open ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D07210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartery, S.; Toohey, D.; Revell, L.; Sellegri, K.; Kuma, P.; Harvey, M.; McDonald, A.J. Constraining the surface flux of sea spray particles from the southern ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, D032026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, T.; Toda, S.; Yamaguchi, H. Field investigation of impinging seawater spray on the R/V mirai using spray particle counter type sea spray meter. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Symposium on Okhotsk Sea and Polar Oceans, Hokkaido, Japan, 18–21 February 2018; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, R.; Kanitz, T.; Baars, H.; Heese, B.; Althausen, D.; Skupin, A.; Wandinger, U.; Komppula, M.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Amiridis, V. The automated multiwavelength Raman polarization and water-vapor lidar Polly XT: The neXT generation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1767–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhar, S.; Khawaja, H.A. Recognizing potential of LiDAR for comprehensive measurement of sea spray flux for improving the prediction of marine icing in cold conditions—A review. Ocean Eng. 2021, 223, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Park, P.; Consterdine, I. Marine aerosol concentrations and estimated fluxes over the sea. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 119, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenain, L.; Melville, W.K. Evidence of sea-state dependence of aerosol concentration in the marine atmospheric boundary layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Ortiz-Suslow, D.G.; Smith, A.W.; Haus, B.K. A Laboratory investigation of spume generation in high winds for fresh and seawater. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11297–11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Suslow, D.G.; Haus, B.K.; Mehta, S.; Laxague, N.J.M. Sea spray generation in very high winds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 3975–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.D.; Hultin, K.A.H.; Mårtensson, E.M.; Markuszewski, P.; Rosman, K.; Krejci, R. Baltic sea spray emissions: In situ eddy covariance fluxes vs. simulated tank sea spray. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Toba, Y. Dependence of whitecap coverage on wind and wind-wave properties. J. Oceanogr. 2001, 57, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Toba, Y.; Sugioka, K.-i.; Komori, S. New sea spray generation function for spume droplets. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Salisbury, D.J. A wave roughness Reynolds number parameterization of the sea spray source flux. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4415–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovadnevaite, J.; Manders, A.; De Leeuw, G.; Ceburnis, D.; Monahan, C.; Partanen, A.-I.; Korhonen, H.; O’Dowd, C. A sea spray aerosol flux parameterization encapsulating wave state. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laussac, S.; Piazzola, J.; Tedeschi, G.; Yohia, C.; Canepa, E.; Rizza, U.; Van Eijk, A.M.J. Development of a fetch dependent sea-spray source function using aerosol concentration measurements in the north-western mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 193, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, A.; Babanin, A.V.; Donelan, M.A.; Haus, B.K.; Jeong, D. Estimating sea spray volume with a laser altimeter. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Babanin, A.V.; Qiao, F. Field observations of sea spray under Tropical Cyclone Olwyn. Ocean Dyn. 2020, 70, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.; Pezoa, S.; Moran, K.; Wolfe, D. An observation of sea-spray microphysics by airborne doppler radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcic, M.; Haus, B.K. Revised Estimates of ocean surface drag in strong winds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanin, A.V.; Wake, G.G.; McConochie, J. Field observation site for air-sea interactions in tropical cyclones. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Busan, Korea, 18 October 2016; p. V003T002A002. [Google Scholar]
- Voermans, J.J.; Rapizo, H.; Ma, H.; Qiao, F.; Babanin, A.V. Air–sea momentum fluxes during tropical cyclone olwyn. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2019, 49, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, J.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; Monbaliu, J. Spectral partitioning and identification of wind sea and swell. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Toba, Y.; Chaen, M. A new expression for the production rate of sea water droplets on the sea surface. J. Oceanogr. 1992, 48, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K. A similarity hypothesis for air–sea exchange at extreme wind speeds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Staniec, A.; Vlahos, P. Spume drops: Their potential role in air-sea gas exchange. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 9500–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Perrie, W.; Guan, C.; Dan, B.; Sun, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, D. Impact of sea spray and sea surface roughness on the upper ocean response to super typhoon haitang. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 51, 1929–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chu, P.C.; Guan, C.; Fu, H.; Chao, G.; Han, G.; Li, W. Impact of sea spray on the yellow and east China seas thermal structure during the passage of typhoon rammasun. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 7783–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Qiao, F.; Cavaleri, L.; Wang, G.; Bertotti, L.; Liu, L. Sensitivity of typhoon modeling to surface waves and rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 1702–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Narasimalu, S. The effects of sea spray and atmosphere–wave coupling on air–sea exchange during a tropical cyclone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6001–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babanin, A.V.; Rogers, W.E.; de Camargo, R.; Doble, M.; Durrant, T.; Filchuk, K.; Ewans, K.; Hemer, M.; Janssen, T.; Kelly-Gerreyn, B.; et al. Waves and Swells in High Wind and Extreme Fetches, Measurements in the Southern Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Voermans, J.J.; Ma, H.; Guan, C.; Babanin, A.V. A Wind–Wave-Dependent Sea Spray Volume Flux Model Based on Field Experiments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111168
Xu X, Voermans JJ, Ma H, Guan C, Babanin AV. A Wind–Wave-Dependent Sea Spray Volume Flux Model Based on Field Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(11):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111168
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xingkun, Joey J. Voermans, Hongyu Ma, Changlong Guan, and Alexander V. Babanin. 2021. "A Wind–Wave-Dependent Sea Spray Volume Flux Model Based on Field Experiments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 11: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111168
APA StyleXu, X., Voermans, J. J., Ma, H., Guan, C., & Babanin, A. V. (2021). A Wind–Wave-Dependent Sea Spray Volume Flux Model Based on Field Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(11), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111168





