Role of Hepcidins from Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) in Iron-Metabolic Function and Bacterial Defense
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Strains
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Expression of Peptides in E. coli
2.4. Purification of the Peptides Using an Affinity Column
2.5. Tricine-SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis
2.6. Mass Spectroscopy Analysis and Amino Acid Sequence
2.7. Antimicrobial Activity Testing
2.8. RT-PCR
2.9. Production of Hamp1, Hamp2, and FPN1 mRNA Response to Excess Iron and Infection
2.10. Analysis of Hepcidin-Related Gene Expression
2.11. Ethical Statement
3. Results
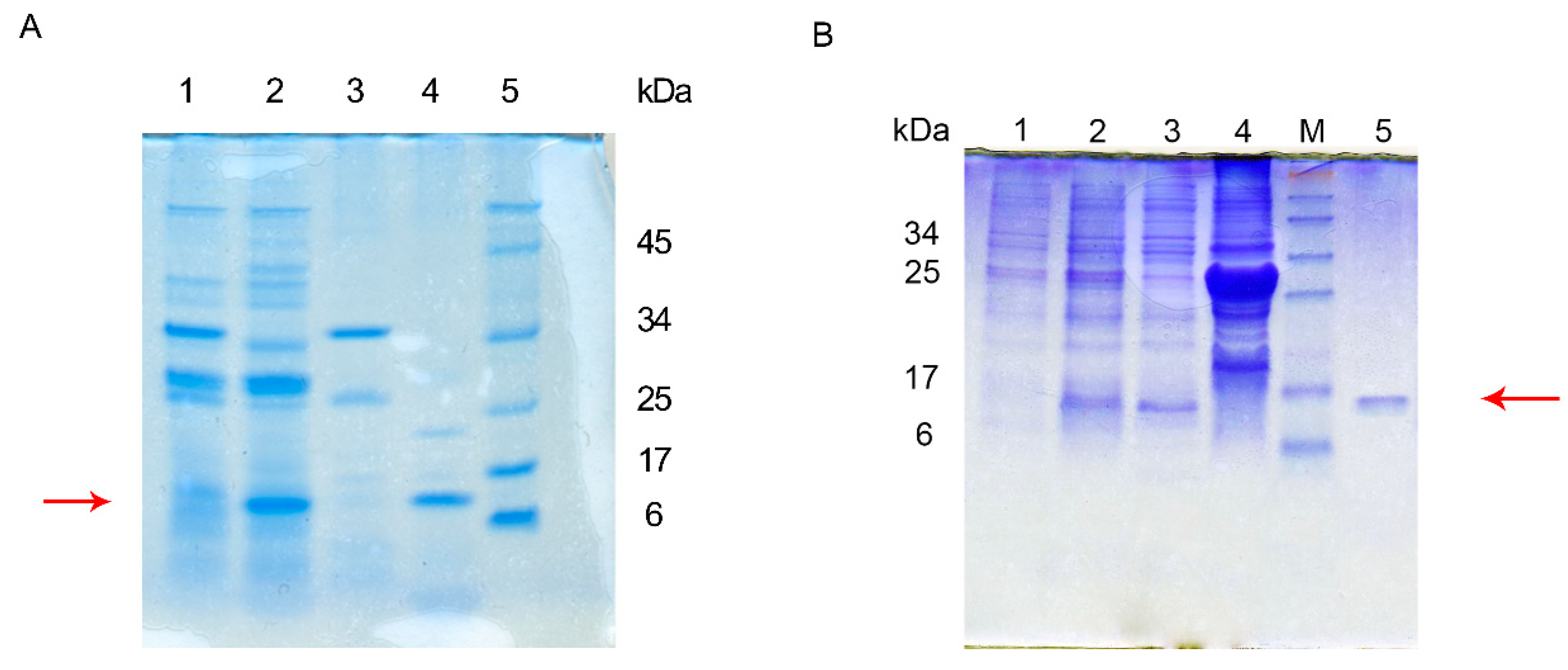
3.1. Construction of a Recombinant Peptide Expression System and Expression
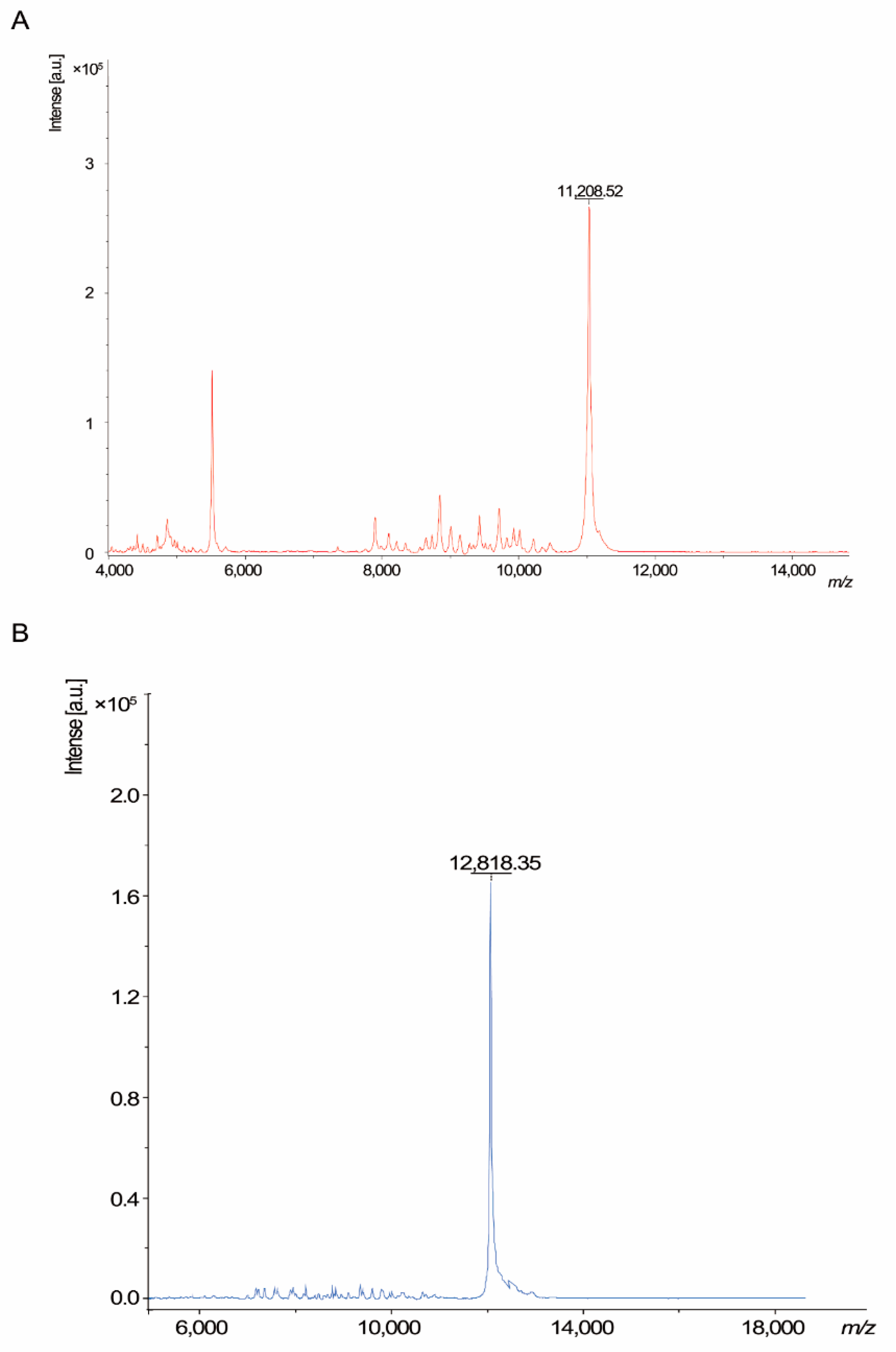
3.2. Characterization of Recombinant Peptide
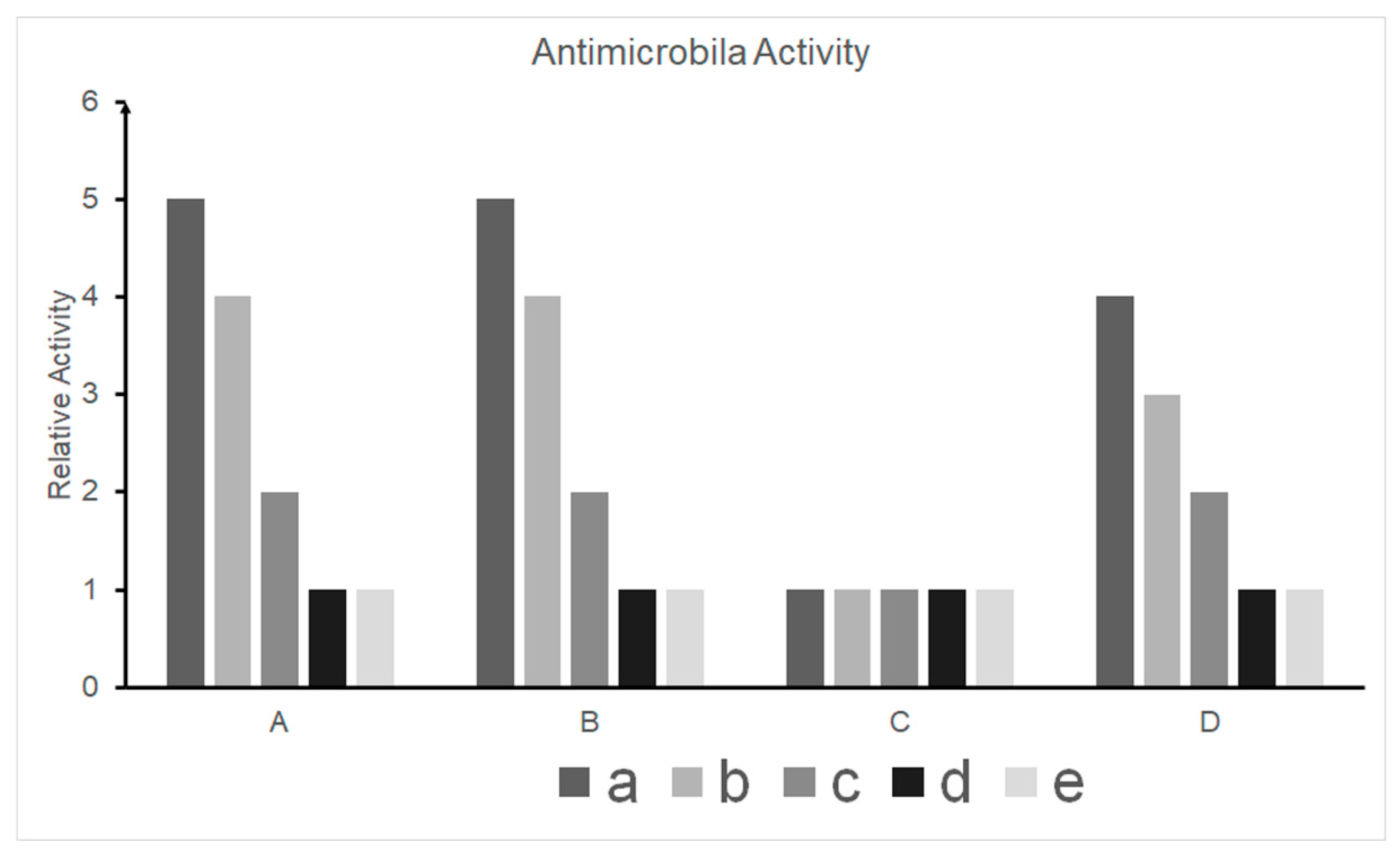
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity Test
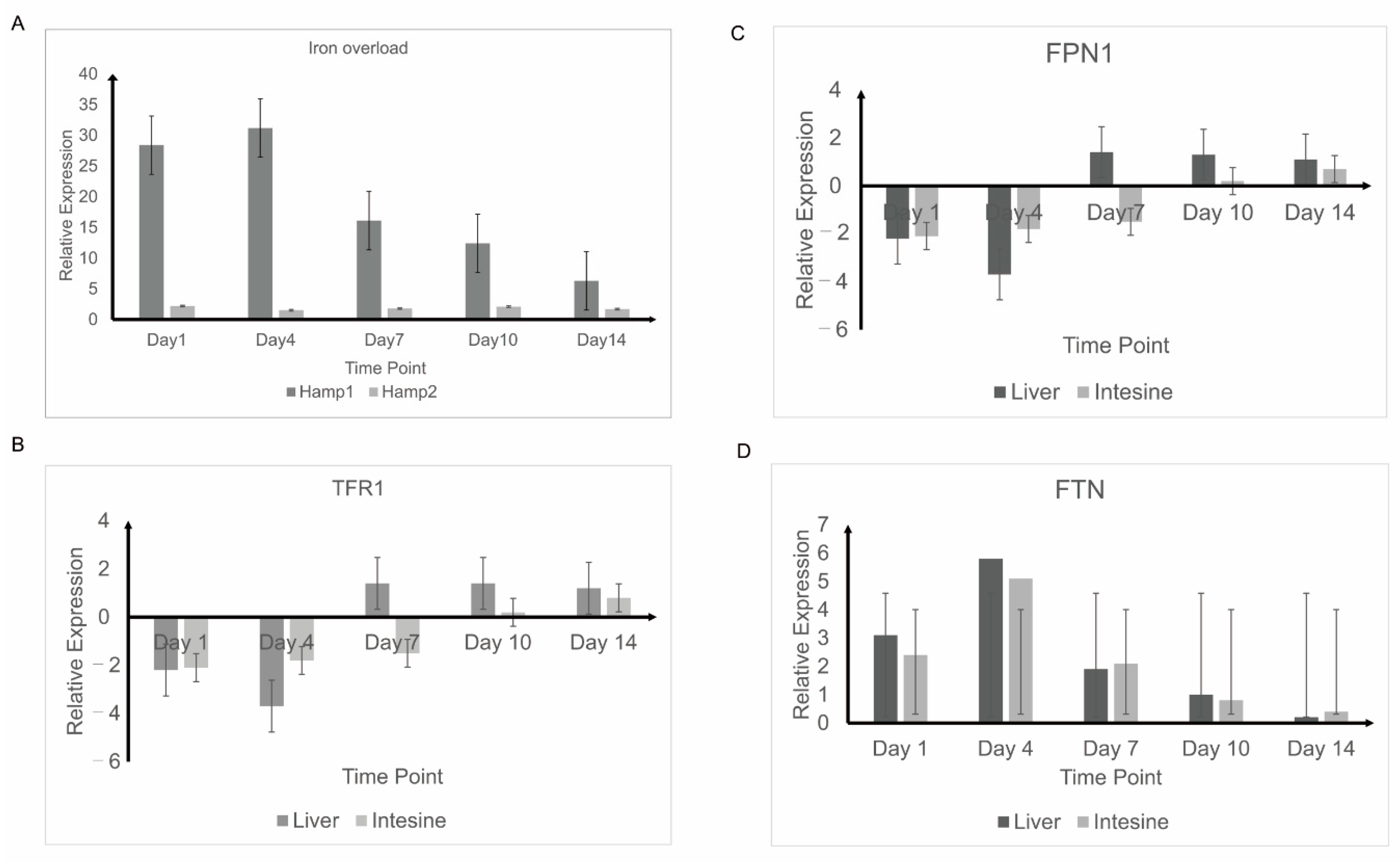
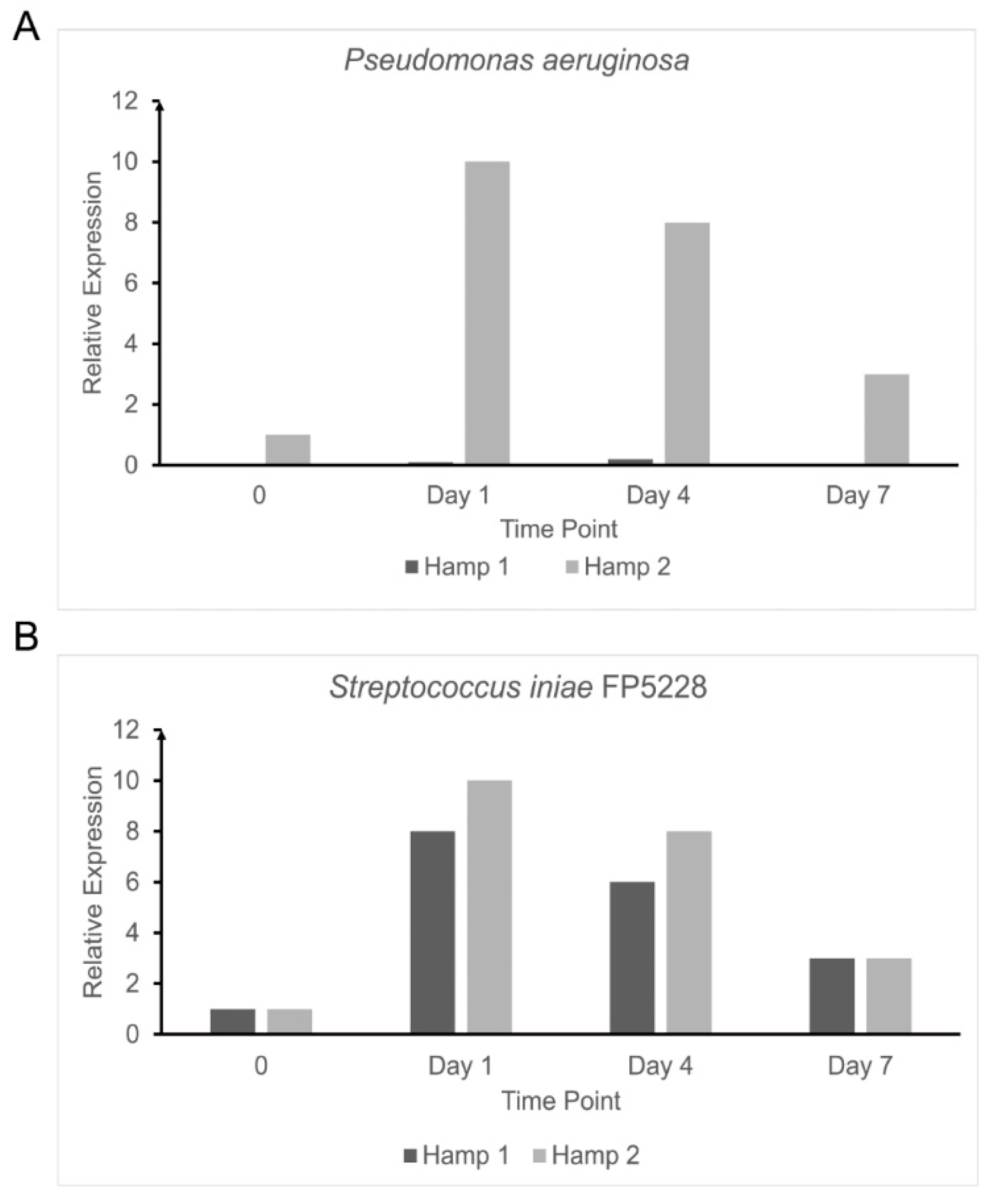
3.4. Response to Experimental Iron Overload and Infection
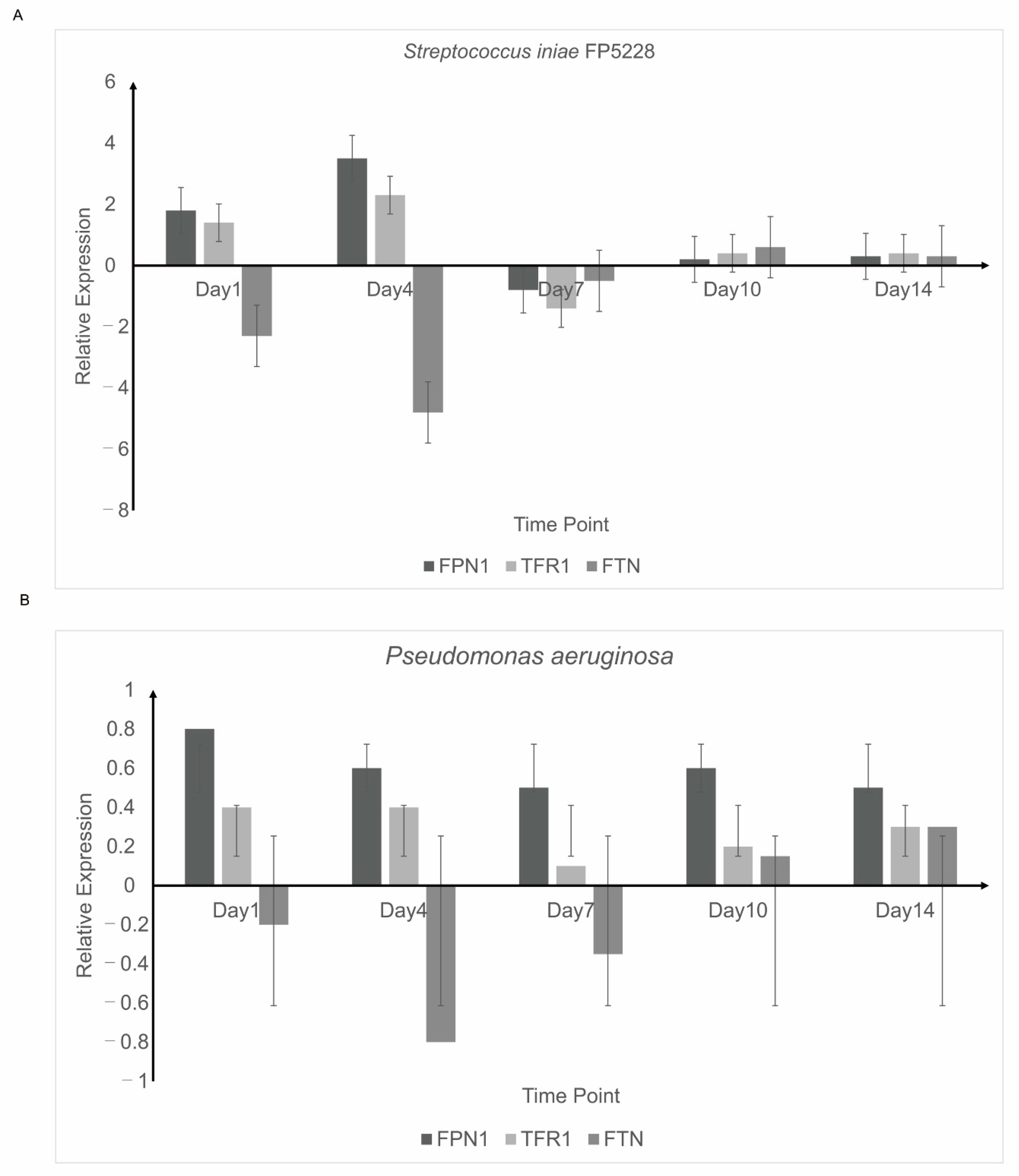
3.5. Detection of Iron Balance-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Al-Khakani, M.M.; Al-Kindi, M.A. Correlation of hepcidin level with insulin resistance and endocrine glands function in major thalassemia. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschemeyer, S.; Qiao, B.; Stefanova, D.; Valore, E.V.; Sek, A.C.; Ruwe, T.A.; Vieth, K.R.; Jung, G.; Casu, C.; Rivella, S.; et al. Structure-function analysis of ferroportin defines the binding site and an alternative mechanism of action of hepcidin. Blood 2018, 131, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xu, P.C.; Hu, S.Y.; Gao, S.; Jia, J.Y.; Yan, T.K. High serum hepcidin is associated with the occurrence of anemia in anti-myeloperoxidase antibody-associated vasculitis with normal kidney function: A cross-sectional study. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detivaud, L.; Nemeth, E.; Boudjema, K.; Turlin, B.; Troadec, M.B.; Leroyer, P.; Ropert, M.; Jacquelinet, S.; Courselaud, B.; Ganz, T.; et al. Hepcidin levels in humans are correlated with hepatic iron stores, hemoglobin levels, and hepatic function. Blood 2005, 106, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K. Function of hepcidin in iron metabolism. Jpn. J. Clin. Hematol. 2007, 48, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhal-Littleton, S. Cardiomyocyte hepcidin: From intracellular iron homeostasis to physiological function. Vitam. Horm. 2019, 110, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Le Tertre, M.; Ka, C.; Guellec, J.; Gourlaouen, I.; Ferec, C.; Callebaut, I.; Le Gac, G. Deciphering the molecular basis of ferroportin resistance to hepcidin: Structure/function analysis of rare slc40a1 missense mutations found in suspected hemochromatosis type 4 patients. Transfus. Clin. Biol. J. Soc. Fr. Transfus. Sang. 2017, 24, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Chung, W.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Ahn, C.; Kim, Y.S.; Sung, S.A. Serum hepcidin and iron indices affect anemia status differently according to the kidney function of non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients: Korean cohort study for outcome in patients with chronic kidney disease (know-ckd). Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, L.; Guo, L.; Feng, Y. Studying hepcidin and related pathways in osteoblasts using a mouse model with insulin receptor substrate 1loss of function. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Malyszko, J.; Kowalewski, R.; Glowinski, J.; Malyszko, J.; Koc-Zorawska, E.; Glowinska, I.; Lebkowska, U.; Gacko, M. Prospective assessment of hepcidin in relation to delayed or immediate graft function in patients undergoing kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 1506–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyszko, J.; Malyszko, J.S.; Hryszko, T.; Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M. Is hepcidin a link between anemia, inflammation and liver function in hemodialyzed patients? Am. J. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszko, J.; Malyszko, J.S.; Kozminski, P.; Mysliwiec, M. Type of renal replacement therapy and residual renal function may affect prohepcidin and hepcidin. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszko, J.; Malyszko, J.S.; Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M. Hepcidin, iron status, and renal function in chronic renal failure, kidney transplantation, and hemodialysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, E.; Tamaddoni, A.; Qujeq, D.; Nasseri, E.; Zayeri, F.; Zand, H.; Gholami, M.; Mir, S.M. An investigation of the effects of curcumin on iron overload, hepcidin level, and liver function in beta-thalassemia major patients: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res. PTR 2018, 32, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Huo, J.; Guan, Y.; Fan, D.; Xiao, X.; Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Mu, P.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. An improved genome assembly for larimichthys crocea reveals hepcidin gene expansion with diversified regulation and function. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Preza, G.C.; Jung, C.L.; Kaplan, J.; Waring, A.J.; Ganz, T. The n-terminus of hepcidin is essential for its interaction with ferroportin: Structure-function study. Blood 2006, 107, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praschberger, R.; Schranz, M.; Griffiths, W.J.; Baumgartner, N.; Hermann, M.; Lomas, D.J.; Pietrangelo, A.; Cox, T.M.; Vogel, W.; Zoller, H. Impact of d181v and a69t on the function of ferroportin as an iron export pump and hepcidin receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanbabu, V.; Chen, J.Y. Antiviral function of tilapia hepcidin 1-5 and its modulation of immune-related gene expressions against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (ipnv) in chinook salmon embryo (chse)-214 cells. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.N.; Vazquez-Dorado, S.; Neves, J.V.; Wilson, J.M. Dual function of fish hepcidin: Response to experimental iron overload and bacterial infection in sea bass (dicentrarchus labrax). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weerd, N.C.; Grooteman, M.P.; Bots, M.L.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; den Hoedt, C.H.; Mazairac, A.H.; Nube, M.J.; Penne, E.L.; Gaillard, C.A.; Wetzels, J.F.; et al. Hepcidin-25 in chronic hemodialysis patients is related to residual kidney function and not to treatment with erythropoiesis stimulating agents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Zhou, C.; Shi, Y.; Lu, H.; He, X. Hepcidin as a biomarker of impaired renal function in rat models for chronic allograft nephropathy. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, C.G.; Liu, S.S.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.L. Iron-metabolic function and potential antibacterial role of hepcidin and its correlated genes (ferroportin 1 and transferrin receptor) in turbot (scophthalmus maximus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, Y.; Sadeghi, H.; Alimohammadian, M.; Andalib, A.; Moazen, F.; Rezaei, A. Expression of an innate immune element (mouse hepcidin-1) in baculovirus expression system and the comparison of its function with synthetic human hepcidin-25. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2011, 10, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Y.H.; Li, M.Y. Changes in transferrin and hepcidin genes expression in the liver of the fish pseudosciaena crocea following exposure to cadmium. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.E.; Gallant, J.W.; Liebscher, R.S.; Dacanay, A.; Tsoi, S.C. Identification and expression analysis of hepcidin-like antimicrobial peptides in bony fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xu, B. connection of hepcidin genes from two fish species and their expression in pichia pastoris. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 682–691. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, M.; Wu, M. Expression and functional analysis of hepcidin from mandarin fish (siniperca chuatsi). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.; Garrido, P.; Fernandes, J.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Costa, E.; Belo, L.; Reis, F.; Santos-Silva, A. Liver iron is a major regulator of hepcidin gene expression via bmp/smad pathway in a rat model of chronic renal failure under treatment with high rhuepo doses. Biofactors 2016, 42, 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.J.; Bo, J.; Yang, M.; Hong, H.S.; Wang, X.H.; Chen, F.Y.; Yuan, J.J. Hepcidin gene expression induced in the developmental stages of fish upon exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (bap). Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 67, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.; Garrido, P.; Fernandes, J.; Rocha, S.; Nunes, S.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Costa, E.; Belo, L.; Reis, F.; Santos-Silva, A. Liver iron regulates hepcidin expression. Studies in a rat model of chronic renal failure under recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Febs J. 2015, 282, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.J.; Cai, J.J.; Cai, L.; Qu, H.D.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Cloning and expression of a hepcidin gene from a marine fish (pseudosciaena crocea) and the antimicrobial activity of its synthetic peptide. Peptides 2009, 30, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, C.; Rossaro, L.; Ramasamooj, R.; Bowlus, C.L. Hepcidin mrna expression in human liver correlates with serum ferritin. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, A713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardenghi, S.; Casu, C.; Renaud, T.M.; Meloni, A.; Cooke, K.S.; Sasu, B.J.; Rivella, S. Investigating the role of cytokines and hepcidin in anemia of inflammation. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, E124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson-Fournier, C.; Gineste, A.; Latour, C.; Gourbeyre, O.; Meynard, D.; Aguilar-Martinez, P.; Oswald, E.; Martin, P.; Coppin, H.; Roth, M.P. Hepcidin upregulation by inflammation is not causally related to liver activation of smad1/5/8 signaling by activin b. Blood 2016, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison-Findik, D.D.; Gerjevic, L.; Eroglu, E. Inflammation-mediated activation of liver hepcidin expression is suppressed by alcohol: Role of stat3 protein. Hepatology 2009, 50, 867a. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, S.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin is the principle mediator of anemia of inflammation. Chest 2005, 128, 149s–150s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardenghi, S.; Renaud, T.M.; Meloni, A.; Ramos, P.; Casu, C.; Cooke, K.S.; Sasu, B.J.; Giardina, P.; Grady, R.W.; Rivella, S. Investigating the role of cytokines and hepcidin in anemia of inflammation. Blood 2011, 118, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, Y.; Sugiyama, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Murakami, M.; Matsui, T.; Funaba, M. Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin b. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.A.; Santana, P.A.; Guzman, F.; Marshall, S.; Mercado, L. Detection of the hepcidin prepropeptide and mature peptide in liver of rainbow trout. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadel, L.; Metzger, M.; Haymann, J.P.; Thervet, E.; Boffa, J.J.; Flamant, M. The relation of hepcidin to iron disorders, inflammation and hemoglobin in chronic kidney disease (vol 9, e99781, 2014). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e99781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroot, J.J.C.; Tjalsma, H.; Fleming, R.E.; Swinkels, D.W. Hepcidin in human iron disorders: Diagnostic implications. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 1650–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, S.; Sharp, P.; Ramesh, B.; Srai, S.K. Inhibition of iron transport across human intestinal epithelial cells by hepcidin. Blood 2004, 104, 2178–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Li, R.Q.; Cheng, G.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Bi, C.W.; Hu, C.; Yang, L.B.; et al. Role of hepcidin and iron metabolism in the onset of prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9953–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyoral, D.; Petrak, J. Hepcidin: A direct link between iron metabolism and immunity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 2005, 37, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weizer-Stern, O.; Adamsky, K.; Margalit, O.; Ashur-Fabian, O.; Givol, D.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G. Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism, is transcriptionally activated by p53. Brit. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.S.; Neto, L.B.D.; Biolo, A.; Goldraich, L.A.; Clausell, N. Anemia in heart failure: Iron metabolism dictates hepcidin levels in stable outpatients. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 291. [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. The antimicrobial peptide hepcidin exerts an important role in the innate immunity against bacteria in the bony fish gilthead seabream. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Park, E.M.; Nam, B.H.; Kong, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.J. Identification and molecular characterization of two hepcidin genes from black rockfish (sebastes schlegelii). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 315, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.R.; Reid, H.J.; Sharp, B.L. Modification of tricine-sds-page for online and offline analysis of phosphoproteins by icp-ms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Lu, M.; Ma, Y.; Kwag, D.G.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, Y.O.; An, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Production of disulfide bond-rich peptides by fusion expression using small transmembrane proteins of escherichia coli. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.W.; Park, E.C.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, Y.G.; Hong, Y.; Park, K.R.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, S.I. Proteomic characterization of the outer membrane vesicle of pseudomonas putida kt2440. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 4298–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardaropoli, S.; Todros, T.; Nuzzo, A.M.; Rolfo, A. Maternal serum levels and placental expression of hepcidin in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshiyama, R.; Konno, M.; Eguchi, H.; Asai, A.; Noda, T.; Koseki, J.; Asukai, K.; Ohashi, T.; Matsushita, K.; Iwagami, Y.; et al. Association of iron metabolic enzyme hepcidin expression levels with the prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8125–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Chen, F.Y.; Zhang, M.; Peng, H.; Wang, K.J. Transcriptomic analysis revealing hepcidin expression in oryzias melastigma regulated through the jak-stat signaling pathway upon exposure to bap. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 206, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillebeen, C.; Charlebois, E.; Wagner, J.; Katsarou, A.; Mui, J.; Vali, H.; Garcia-Santos, D.; Ponka, P.; Presley, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Transferrin receptor 1 controls systemic iron homeostasis by fine-tuning hepcidin expression to hepatocellular iron load. Blood 2019, 133, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Tang, F. Retinoic acid modulates iron metabolism imbalance in anemia of inflammation induced by lps via reversely regulating hepcidin and ferroportin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.N.; Ruan, H.Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhou, G.; Qian, Z.M. Aspirin increases ferroportin 1 expression by inhibiting hepcidin via the jak/stat3 pathway in interleukin 6-treated pc-12 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 662, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samba-Mondonga, M.; Calve, A.; Mallette, F.A.; Santos, M.M. Myd88 regulates the expression of smad4 and the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.A.; Clarkson, R.; Hussain, A.; Weeks, R.J.; Morison, I.M. DNA methylation of hepatic iron sensing genes and the regulation of hepcidin expression. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; You, L.H.; Ci, Y.Z.; Chang, S.; Yu, P.; Gao, G.; Chang, Y.Z. Hepcidin and iron regulatory proteins coordinately regulate ferroportin 1 expression in the brain of mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7600–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Sarath Babu, V.; Lin, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, G. Hepcidin protects grass carp (ctenopharyngodon idellus) against flavobacterium columnare infection via regulating iron distribution and immune gene expression. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 75, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; et al. Mc-lr induces dysregulation of iron homeostasis by inhibiting hepcidin expression: A preliminary study. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Huang, T.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B. Characterization, expression, and functional analysis of the hepcidin gene from brachymystax lenok. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 89, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, E.; Lu, Y.; Yan, M.; Pan, X.; Cheng, X. Increased expression of hepcidin and associated upregulation of jak/stat3 signaling in human gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2236–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, F.L.; Zhou, G.; Bao, Y.X.; Shen, Y.; Qian, Z.M. Different characteristics of hepcidin expression in il-6+/+ and il-6-/- neurons and astrocytes treated with lipopolysaccharides. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Wortham, A.M.; Enns, C.A.; Zhang, A.S. The catalytic, stem, and transmembrane portions of matriptase-2 are required for suppressing the expression of the iron-regulatory hormone hepcidin. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Application | Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Hamp1-F | Hepcidin I amplification | GGCCGGAATTCGATTGTTCTACTATTCAAGGT |
| Hamp1-R | Hepcidin I amplification | CCGGAATTCTACGTAAGCTTCAGCCTCTCT |
| Hamp2-F | Hepcidin II amplification | TCTTCTACTGTTTGTTGTATTACTAAGCCATAAGCG |
| Hamp2-R | Hepcidin II amplification | CGCTTATGGCTTAGTAATACAACAAACAGTAGAAGA |
| Hamp1RT-F | Hepcidin I RT-PCR | ATGAAGACATTCAGTGTTGCG |
| Hamp1RT-R | Hepcidin I RT-PCR | TCAGAATCTTTTTGAGCAGCA |
| Hamp2RT-F | Hepcidin II RT-PCR | ATGAAGACATTCAGTGTTGCA |
| Hamp2RT-R | Hepcidin II RT-PCR | TCATGTGCAGCACCTAATGCA |
| Beta-actin-F | control | AGGCTCAGAGCAAGAGAG |
| Beta-actin-R | control | CGGTGAGCGGACGGGTGC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Lee, C.-J.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, D.N.-J.; Nam, B.-H.; Kim, Y.-O.; An, C.-M.; Park, J.-S. Role of Hepcidins from Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) in Iron-Metabolic Function and Bacterial Defense. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070493
Ma Y, Lee C-J, Kim S-S, Kim DN-J, Nam B-H, Kim Y-O, An C-M, Park J-S. Role of Hepcidins from Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) in Iron-Metabolic Function and Bacterial Defense. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(7):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070493
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yunqi, Chang-Joo Lee, So-Sun Kim, David Nahm-Joon Kim, Bo-Hye Nam, Young-Ok Kim, Cheul-Min An, and Jang-Su Park. 2020. "Role of Hepcidins from Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) in Iron-Metabolic Function and Bacterial Defense" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 7: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070493
APA StyleMa, Y., Lee, C.-J., Kim, S.-S., Kim, D. N.-J., Nam, B.-H., Kim, Y.-O., An, C.-M., & Park, J.-S. (2020). Role of Hepcidins from Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) in Iron-Metabolic Function and Bacterial Defense. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(7), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070493






