Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Chanthaburi Coast, Thailand and Implications for the Sedimentary Dynamic Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
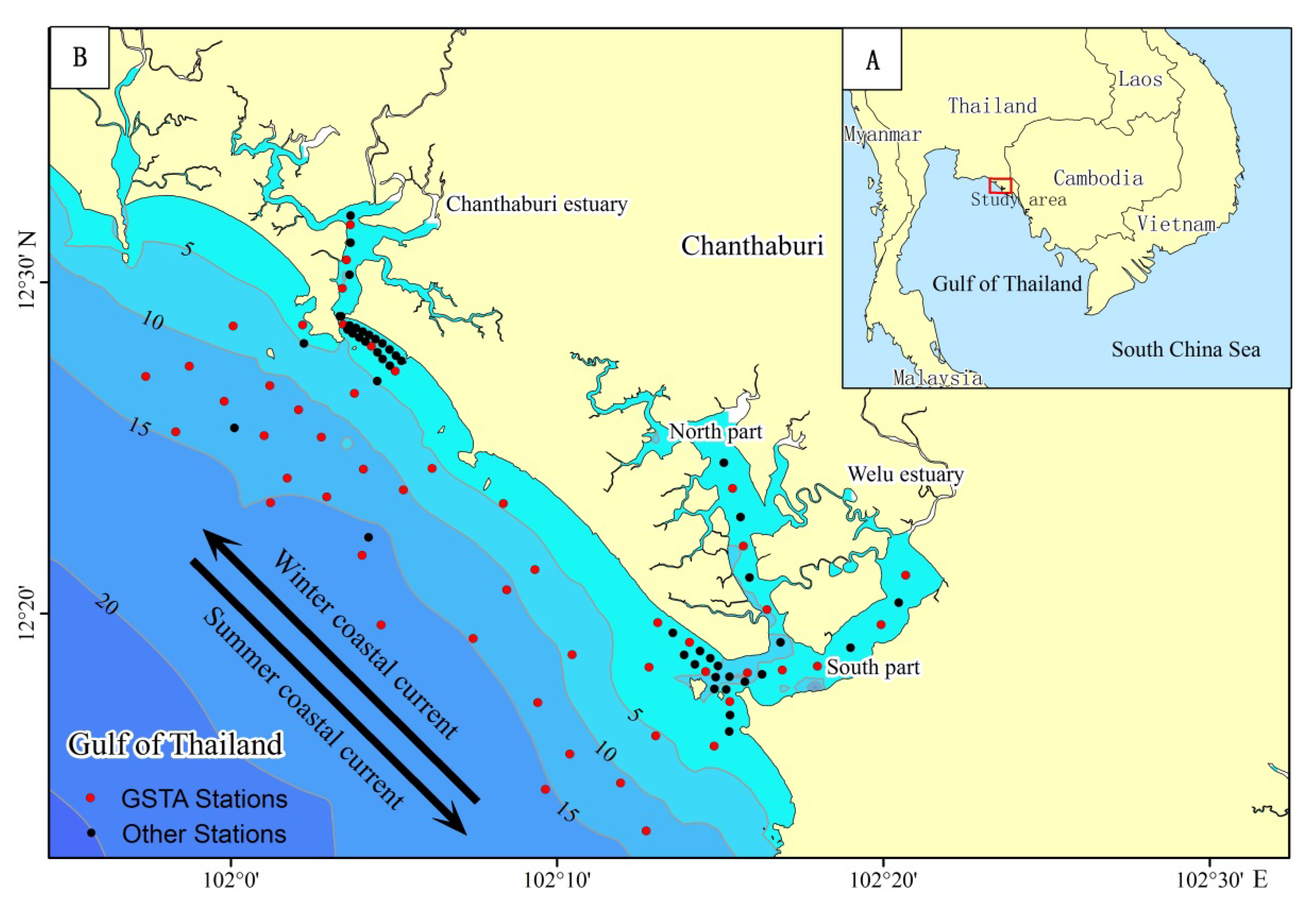
2.1. Sediment Sampling
2.2. Sediment Grain Size Measurements
2.3. Grain-Size Transport Trend Analysis
3. Results
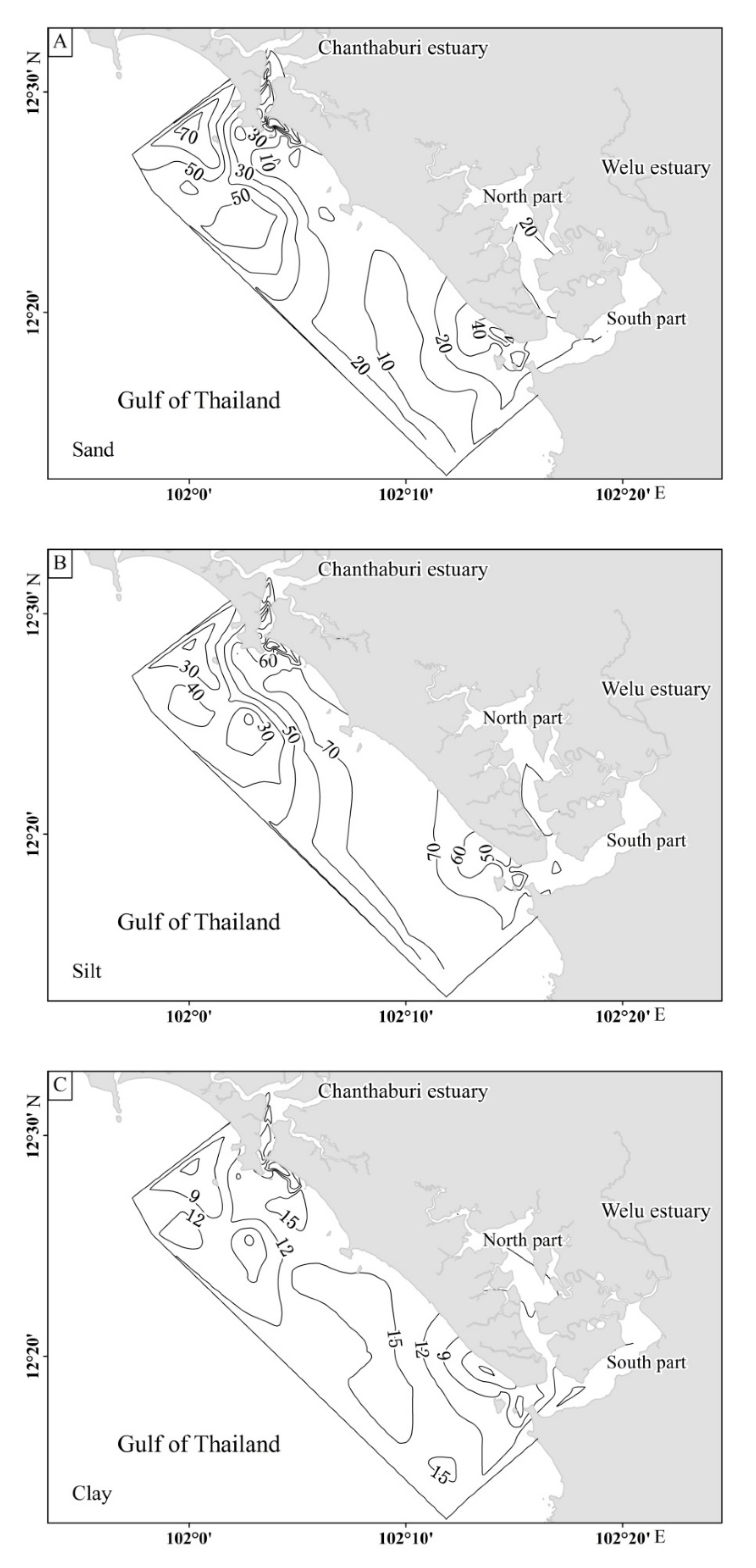
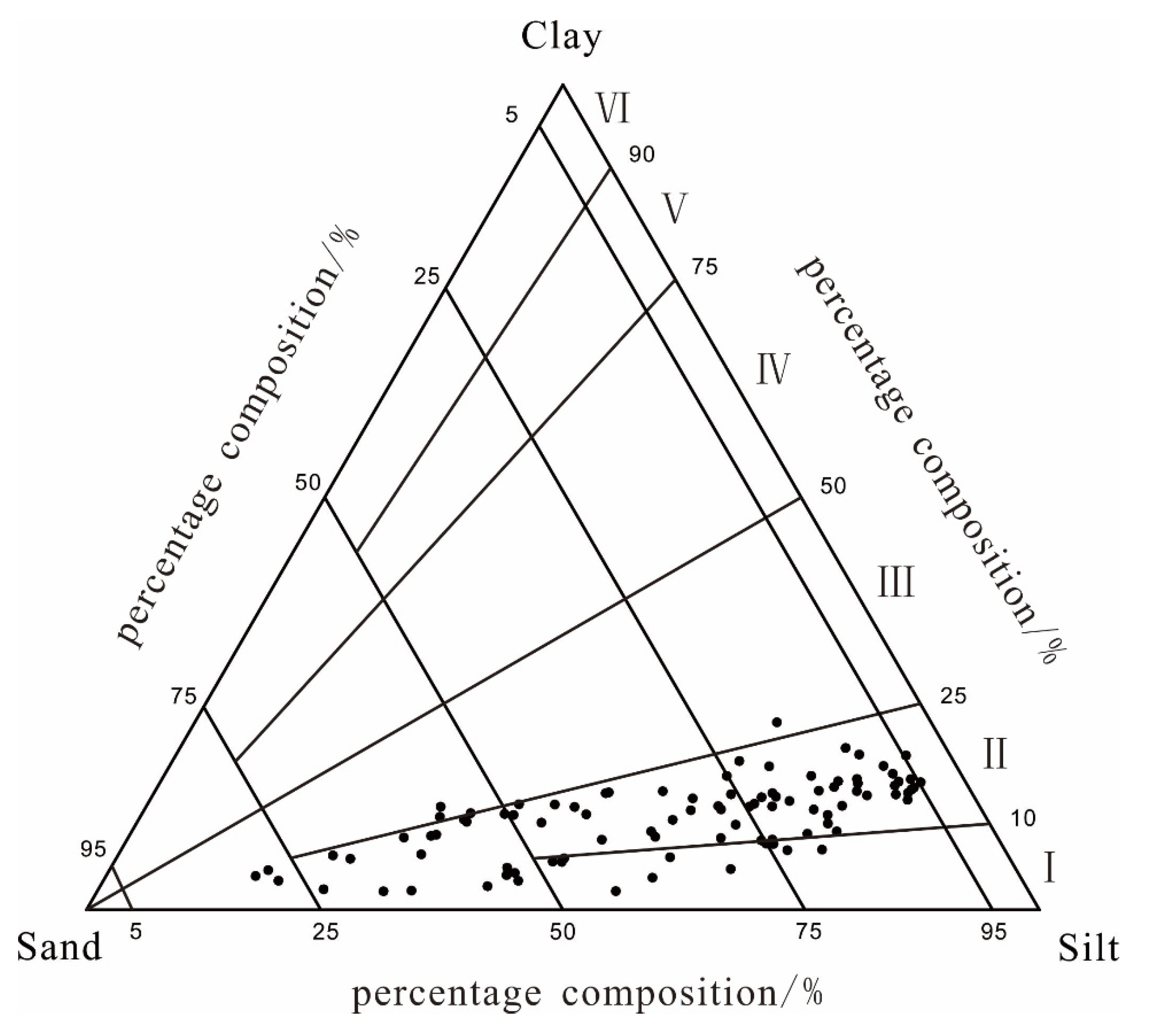
3.1. Sediment Distribution Characteristics
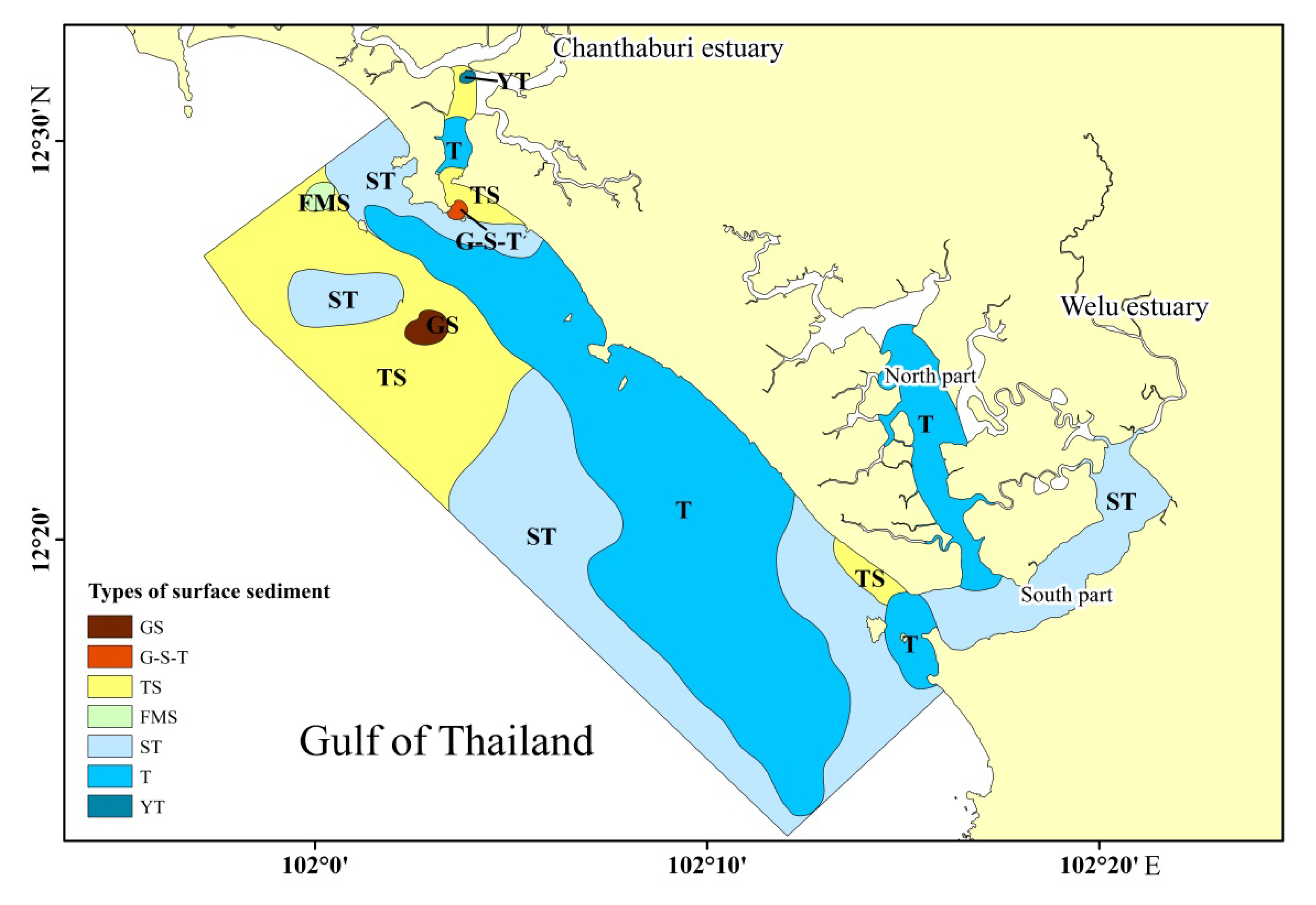
3.2. Planar Distribution Characteristics of Sedimentary Grain Groups
3.3. Analysis of Sediment Grain-Size Characteristics
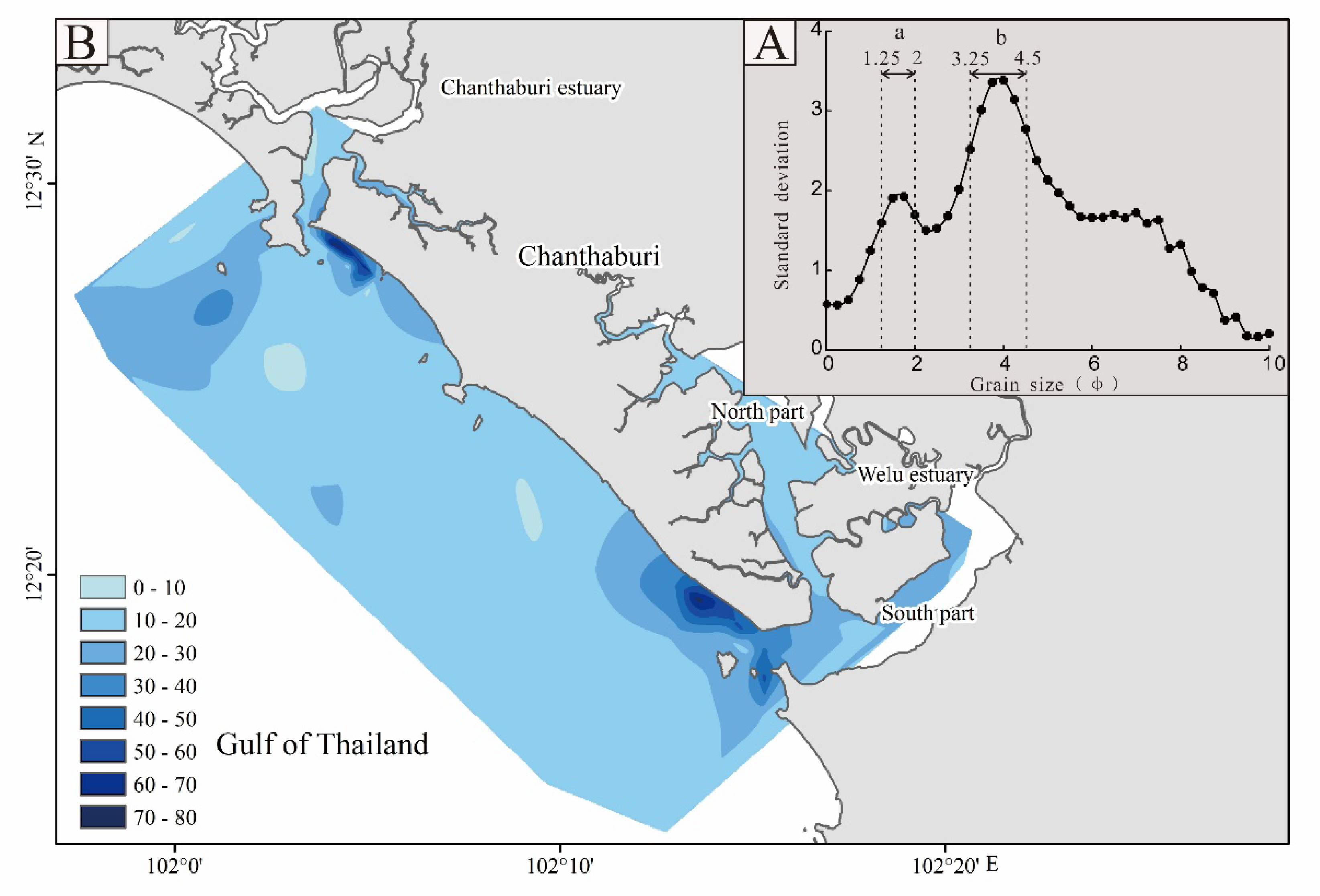
3.4. Sensitive Grain-Size Component
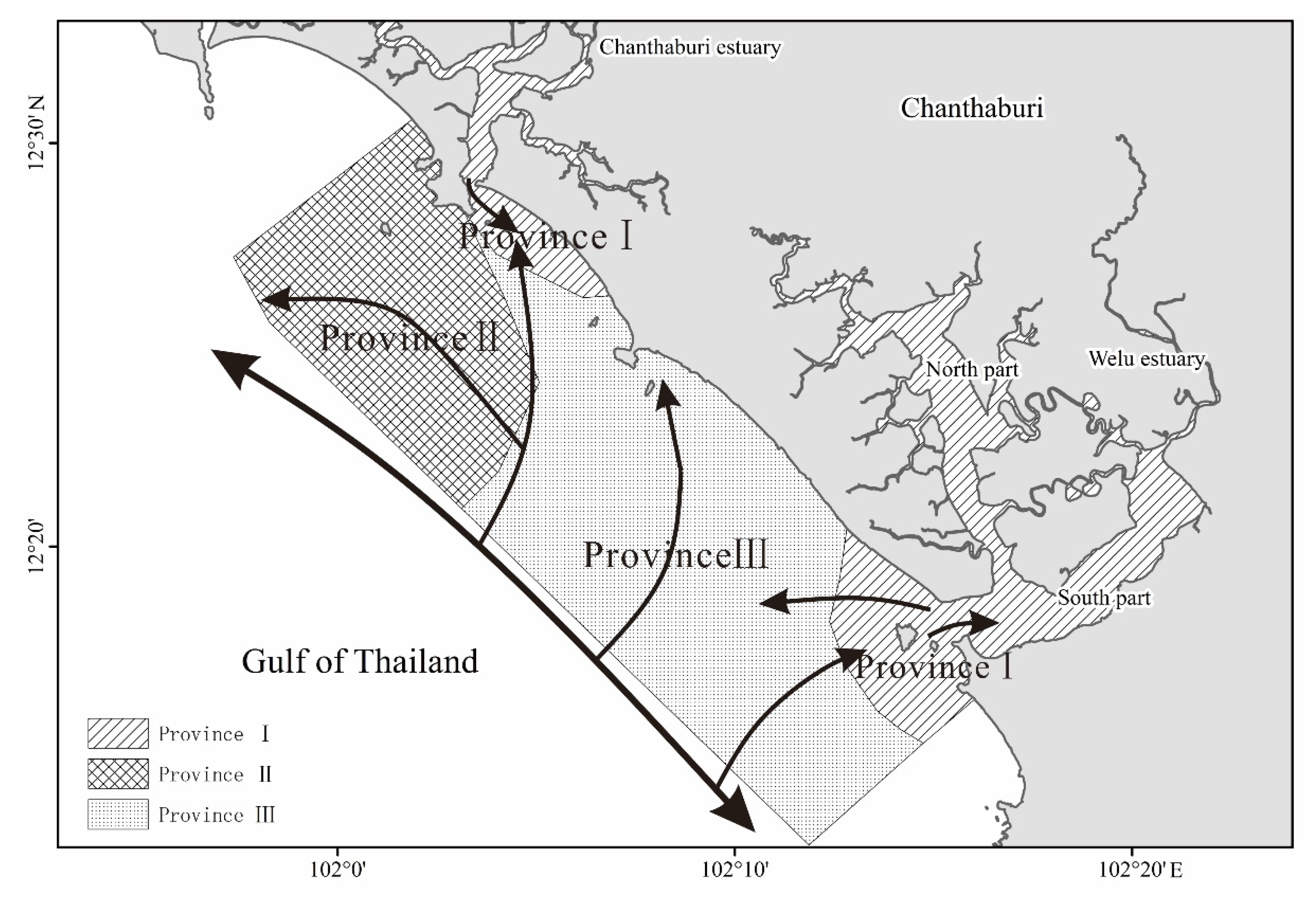
3.5. Surface Sedimentary Dynamic Division
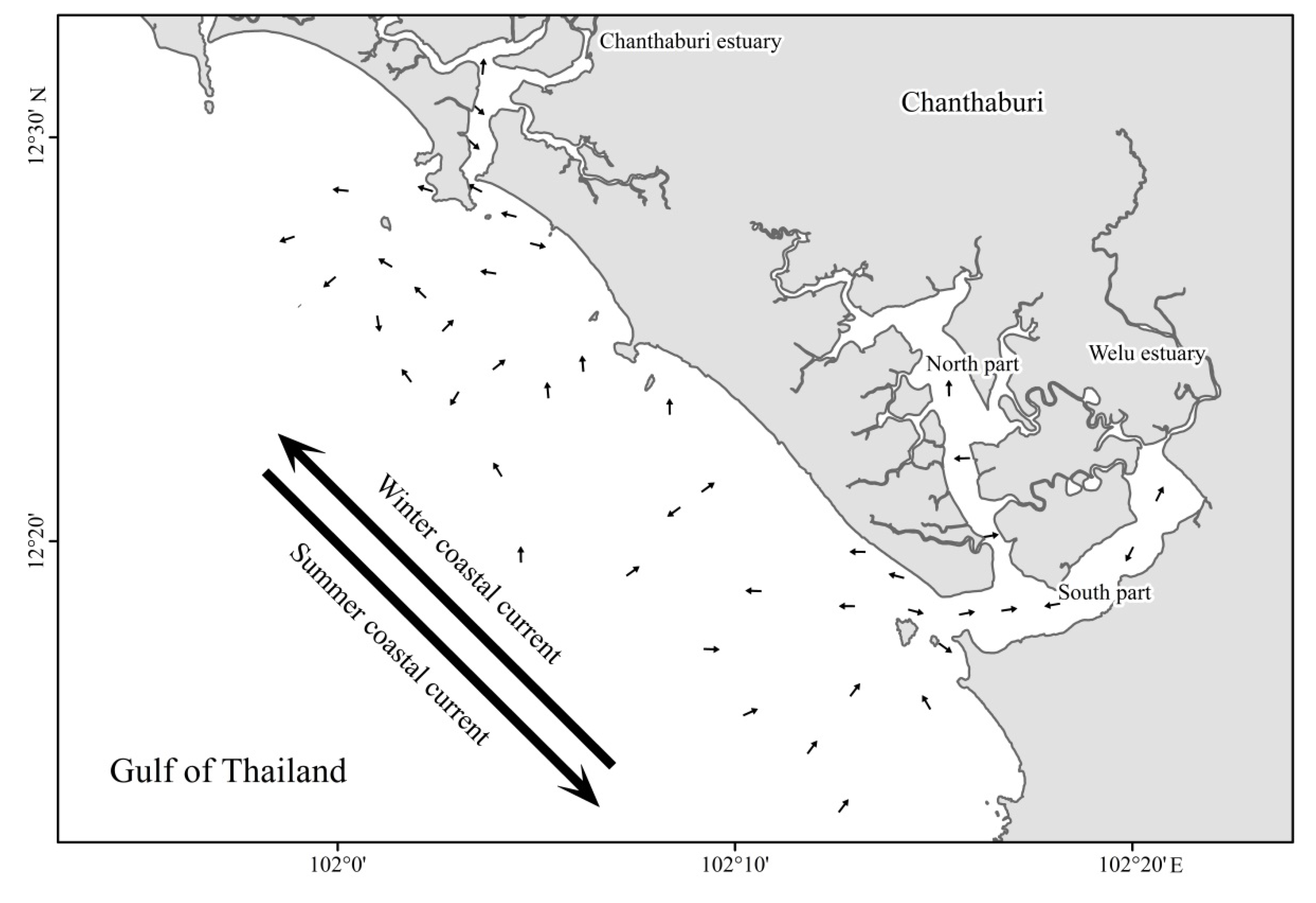
3.6. Sediment Grain-Size Trend Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Division of Sedimentary Environments and Preliminary Analysis of Sediment Provenance
4.2. Comparison with Tidal-Controlled Estuaries in the Temperate Region of Eastern China
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.; Liu, S.; Fang, X.; Qiao, S.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N. Distribution of clay minerals in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: Sources and transport patterns. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranapratheprat, A.; Luadnakrob, P.; Yanagi, T.; Morimoto, A.; Qiao, F. The modification of water column conditions in the Gulf of Thailand by the influences of the South China Sea and monsoonal winds. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 118, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Yang, G.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N. Distribution of major and trace elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: Implications to modern sedimentation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 117, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, N.; Jia, P. End member inversion of surface sediment grain size in the South Yellow Sea and its implications for dynamic sedimentary environments. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 59, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez, C.; Hassan, M.A.; Franca, M. The Origin of Fine Sediment Determines the Observations of Suspended Sediment Fluxes Under Unsteady Flow Conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5654–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, S.; Colin, C.; Trentesaux, A.; Pluquet, F.; Bertaux, J.; Blamart, T.; Buehring, C.; Wang, P. Mineralogy and Sedimentology of Pleistocene Sediment in the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144). Proc. ODP Sci. Result. 2003, 184, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, A.; Wan, S. Sensitive grain-size records of Holocene East Asian summer monsoon in sediments of northern South China Sea slope. Quat. Res. 2011, 75, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Mei, X. Dynamic control on grain-size distribution of terrigenous sediments in the western South China Sea: Implication for East Asian monsoon evolution. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, G.J. End-member modeling of compositional data: Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem. Math. Geol. 1997, 29, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, E.; Hartmann, K.; Diekmann, B.; Ijmker, J.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Opitz, S.; Stauch, G.; Wünnemann, B.; Borchers, A. An end-member algorithm for deciphering modern detrital processes from lake sediments of Lake Donggi Cona, NE Tibetan Plateau, China. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 243, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, D.B.P. The Effects of Sediment Transport on Grain-Size Distributions. J. Sediment. Res. 1985, 4, 457–470. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, P.; Hill, S.; Bowles, D. Deriving transport pathways in a sediment trend analysis (STA). Sediment. Geol. 2007, 202, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Collins, M.; Lanckneus, J.; De Moor, G.; Van Lancker, V. Grain size trends associated with net sediment transport patterns: An example from the Belgian continental shelf. Mar. Geol. 1994, 121, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S. A FORTRAN program for grain-size trend analysis to define net sediment transport pathways. Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, G.; Feo, R.; Freni, G. Sediment transport modelling based on grain size trend analysis in Augusta Harbour (Sicily). In Proceedings of the International Conference of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering 2015 (Iccmse 2015); AIP Publishing: Athens, Greece, 2015; Volume 1702, p. 180008. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Q.; Peng, C.; Yi, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, H. An improved method of sediment grain size trend analysis in the Xiaoqinghe Estuary, southwestern Laizhou Bay, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, T.J. Sediment transport processes in the Pearl River Estuary as revealed by grain-size end-member modeling and sediment trend analysis. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2017, 38, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranapratheprat, A.; Bunpapong, M. A Two-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model for the Gulf of Thailand. Ioc/westpac Fourth Int. Sci. Symp. 1998, 469, 478. [Google Scholar]
- Udden, J.A. Mechanical composition of clastic sediments. GSA Bull. 1914, 25, 655–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, B.; Yin, X.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Shu, F.; Qiao, L. Evolution of sedimentary organic matter in a small river estuary after the typhoon process: A case study of Quanzhou Bay. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 686, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Collins, M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends based upon definition of Btransport vectors. Sediment. Geol. 1992, 80, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Gao, S.; Bokuniewicz, H. Net sediment transport patterns over the Bohai Strait based on grain size trend analysis. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S. The use of grain size trends in marine sediment dynamics (in Chinese). China Sci. Found. 1998, 12, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Le Roux, J. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends, based upon definition of “transport vectors”—Comment. Sediment. Geol. 1994, 90, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, F.; Cisternas, M.; Correa, I.; Le Roux, J. Seasonal sediment transport pathways in Lirquen Harbor, Chile, as inferred from grain-size trends. Investig. Mar. 2002, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, F.P. Nomenclature Based on Sand-silt-clay Ratios. J. Sediment. Res. 1954, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Doeglas, D.J. Grain-size indices, classification and environment. Sedimentology 1968, 10, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ze-wen, L.; Zhen-dong, L.; Jun, Y.; Li-hua, Z. Characterization of grain size parameters and the provenance analysis of the surface sediment in the outer shelf of the northern South China Sea (in Chinese). Mar. Sci. 2011, 35, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, B. A revised textural classification of gravel-free muddy sediments on the basis of ternary diagrams. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Saito, Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Xiang, L.; Wen, C.; Nakashima, R. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary, East China Sea, during the last ∼13,000 years, with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2424–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Pang, Y. Sensitive grain size components and their geological implication in the inner shelf of the East China Sea (in Chinese). Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2016, 47, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Qi, H.; Wichen, I.; Apichai, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A. Distributions of diatoms in surface sediments from the Chanthaburicoast, Gulf of Thailand, and correlations with environmental factors. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 2352–4855. [Google Scholar]
- Committee, C.G.C. China Gulf Records (in Chinese); Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zordan, J.; Juez, C.; Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M. Entrainment, transport and deposition of sediment by saline gravity currents. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 115, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sikka, D.R. Synoptic Systems and Weather; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 131–201. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Sheng, J.; Ji, X.; Cao, W.; Liu, D. Investigation of three-dimensional circulation and hydrography over the Pearl River Estuary of China using a nested-grid coastal circulation model. Ocean Dyn. 2009, 59, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, M.; Mai, M. Hydrographic and sediment analyses of the Oujiang estuary (in Chinese). J. Waterw. Harbor 2008, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; You, X.-Y. Numerical simulation of suspended sediment concentration by 3D coupled wave-current model in the Oujiang River Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 137, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H. Analysis of Sand Volume and Its Change in Three Major Rivers in Fujian (in Chinese). Fujian Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 1, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W. On water level change of the south channel in the estuary of Jiulongjiang River (in Chinese). J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ. 2008, 3, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Hydrological and Sediment Characteristics of the Pearl River Estuary (in Chinese). Trop. Geogr. 1989, 3, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, L.A.; Heinke, G.; Chen, J.C.; Xue, H.; Dong, L.X.; Su, J.L. A model study of the circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and its adjacent coastal waters: 1. Simulations and comparison with observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Shi, P.; Yin, K.; Gan, J.; Qi, Y. Tides and tidal currents in the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Clay minerals of suspended sediments in Oujiang River (in Chinese). Mar. Sci. Bull. 1995, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Li, D.; Huang, C. The modern sedimentary environment and transport trends in Jiulongjiang estuary (in Chinese). Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2010, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Mai, M.; Han, Z. Analysis of Hydrodynamic and Sediment Environment in the Oujiang River Estuary (in Chinese). Water Resour. Sci. Technol. 2018, 24, 5–9. [Google Scholar]

| River | Climate Zone | Nation | Tidal Range (m) | Suspended Sediment Concentration (kg/m3) | Runoff (m3/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chanthaburi | Tropical | Thailand | 0.8–1.2 | 0.023 | - |
| Welu | Tropical | Thailand | 0.8–1.2 | 0.016 | - |
| Oujiang [38,39] | Temperate | China | >4 | 0.131 | 469.1 × 108 |
| Jiulongjiang [40,41] | Temperate | China | 4 | 0.21–0.23 | 148.05 × 108 |
| The Pearl River [42,43,44] | Temperate | China | 1–1.7 | 0.1–0.3 | 1741 × 108 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Qi, H.; Intasen, W.; Kanchanapant, A. Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Chanthaburi Coast, Thailand and Implications for the Sedimentary Dynamic Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040242
Wang C, Chen M, Qi H, Intasen W, Kanchanapant A. Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Chanthaburi Coast, Thailand and Implications for the Sedimentary Dynamic Environment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(4):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040242
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chengtao, Min Chen, Hongshuai Qi, Wichien Intasen, and Apichai Kanchanapant. 2020. "Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Chanthaburi Coast, Thailand and Implications for the Sedimentary Dynamic Environment" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 4: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040242
APA StyleWang, C., Chen, M., Qi, H., Intasen, W., & Kanchanapant, A. (2020). Grain-Size Distribution of Surface Sediments in the Chanthaburi Coast, Thailand and Implications for the Sedimentary Dynamic Environment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(4), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040242





