Sequential Geoacoustic Inversion Using an Improved Kalman Particle Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
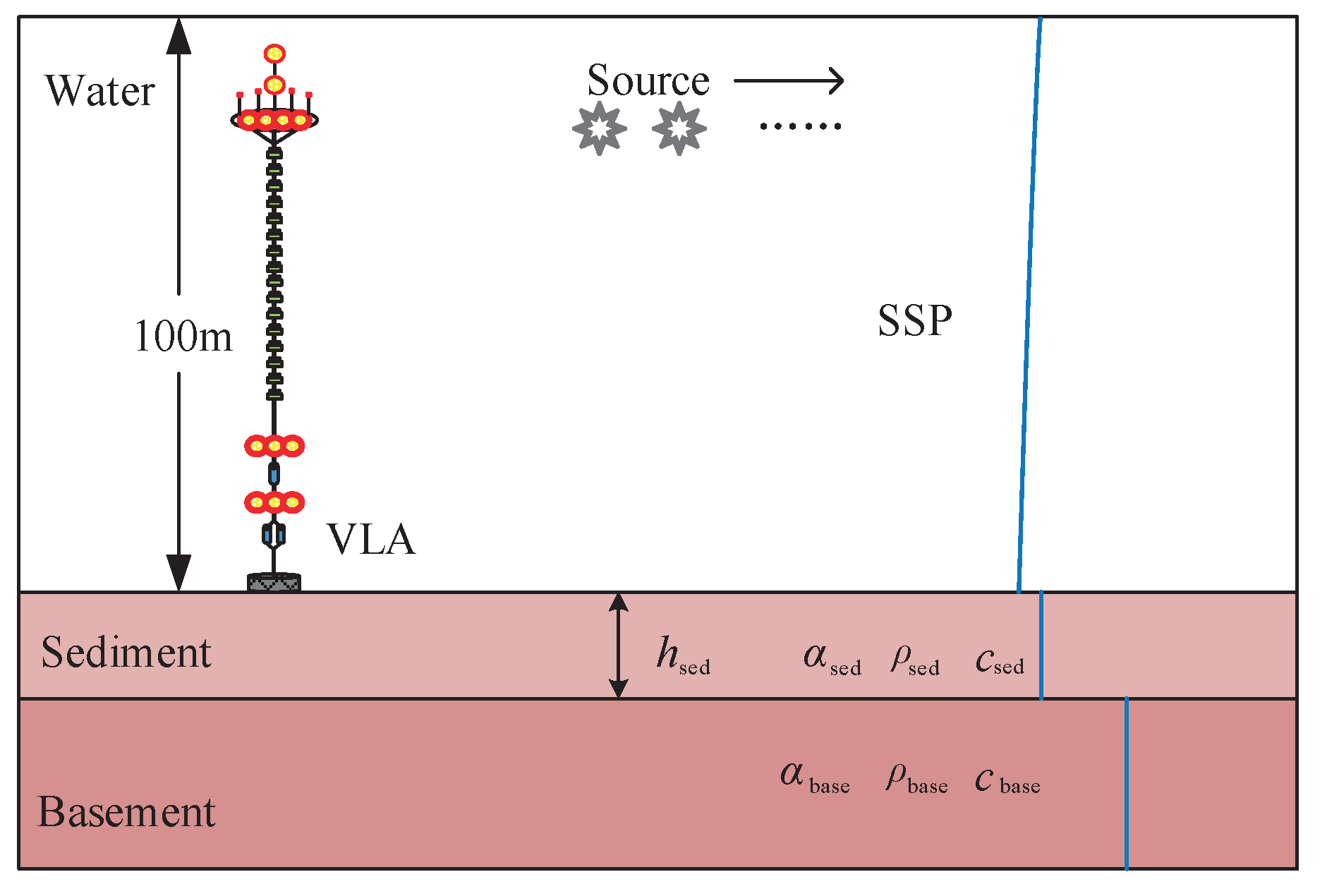
2.1. Sequential Geoacoustic Tacking Modeling
2.2. EnKPF as a Sequential Tracking Processor
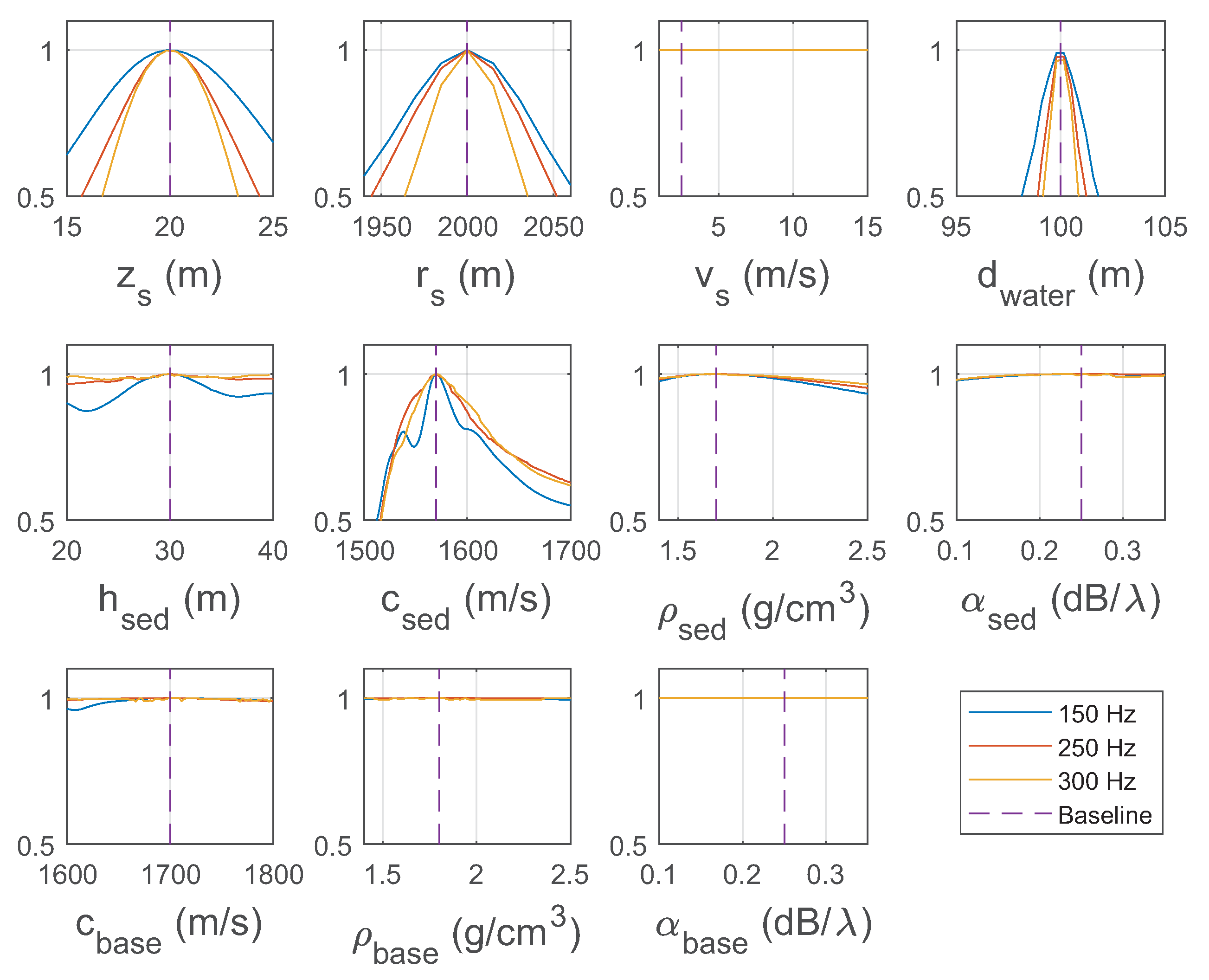
3. Simulation
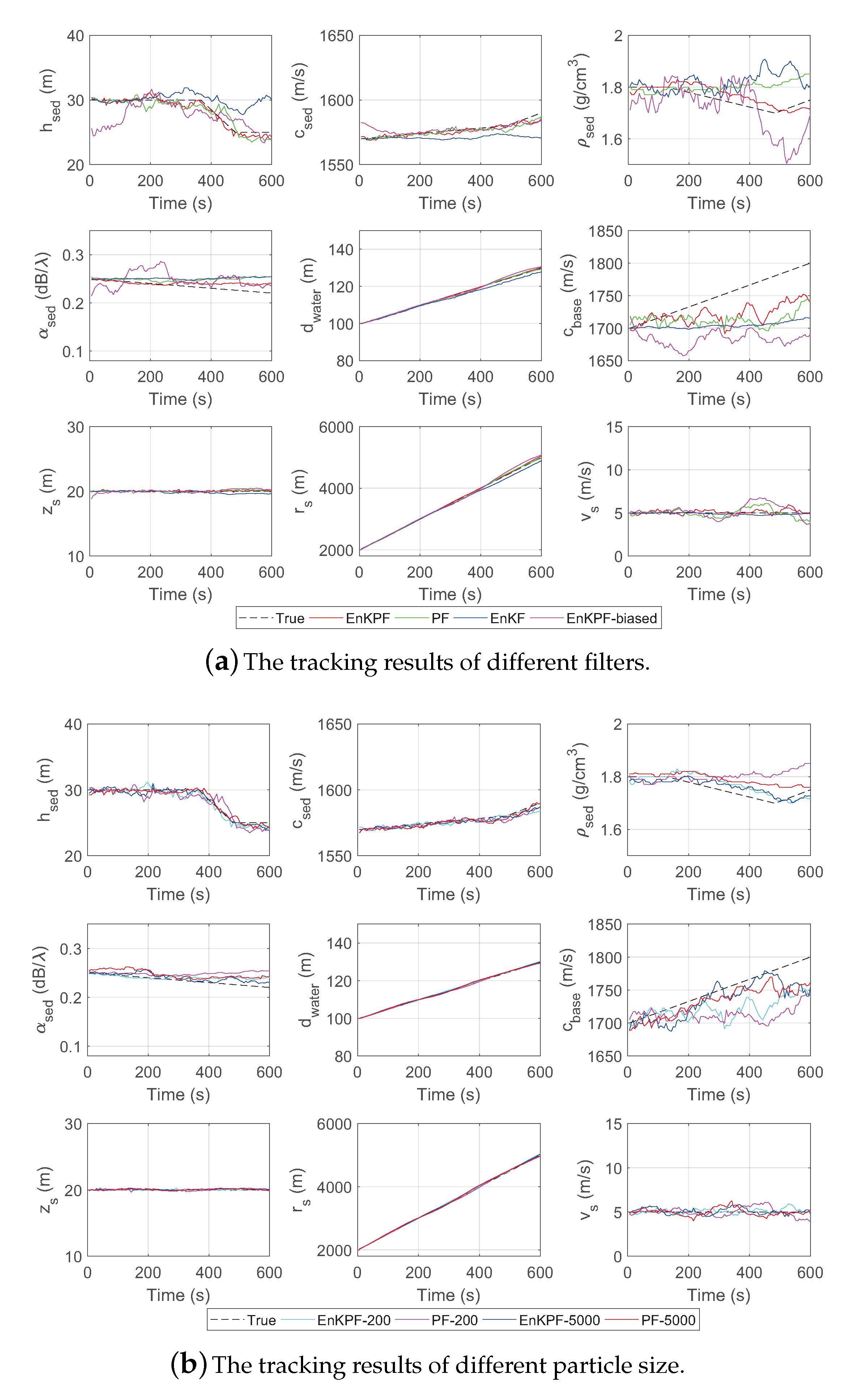
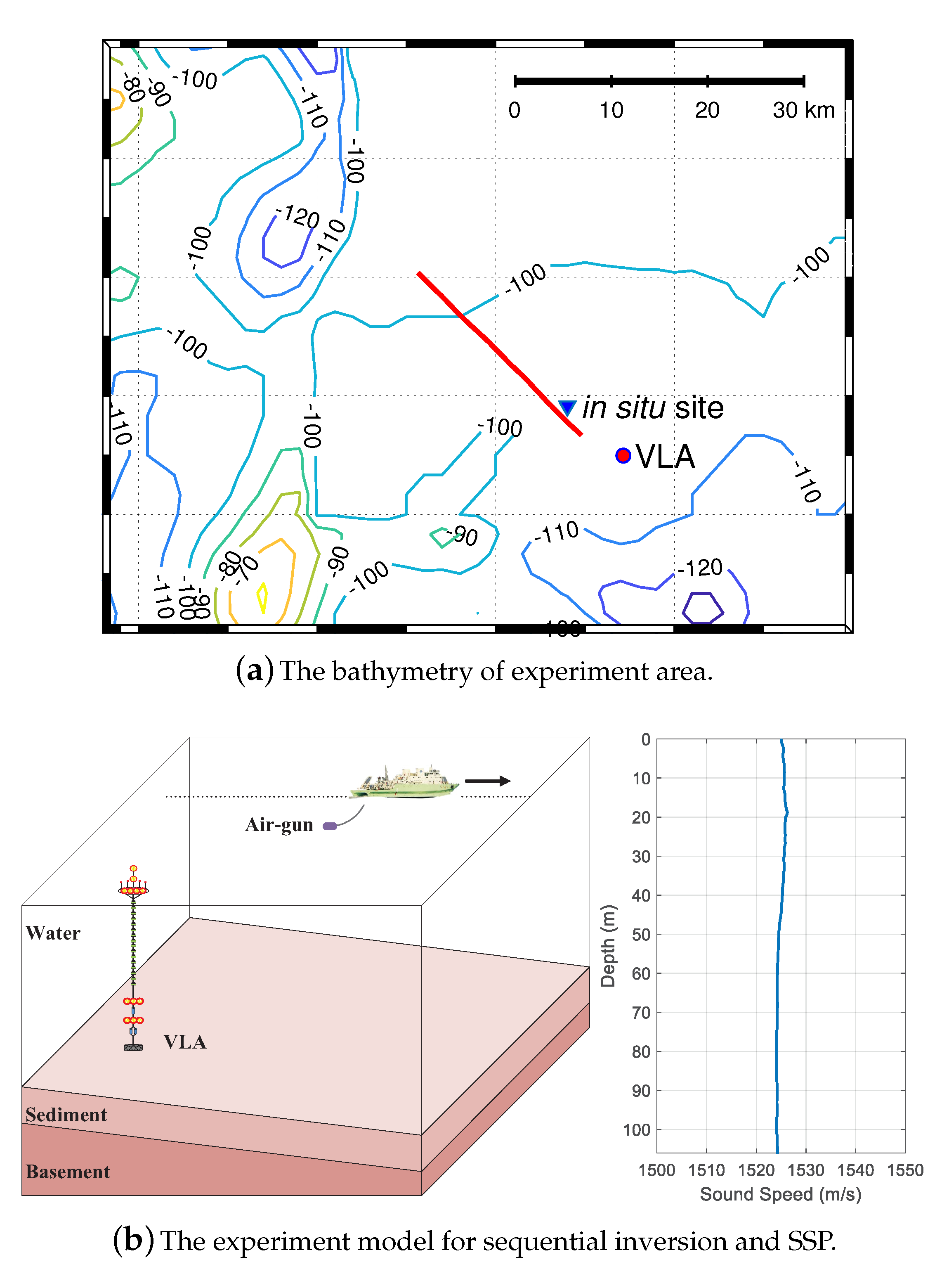
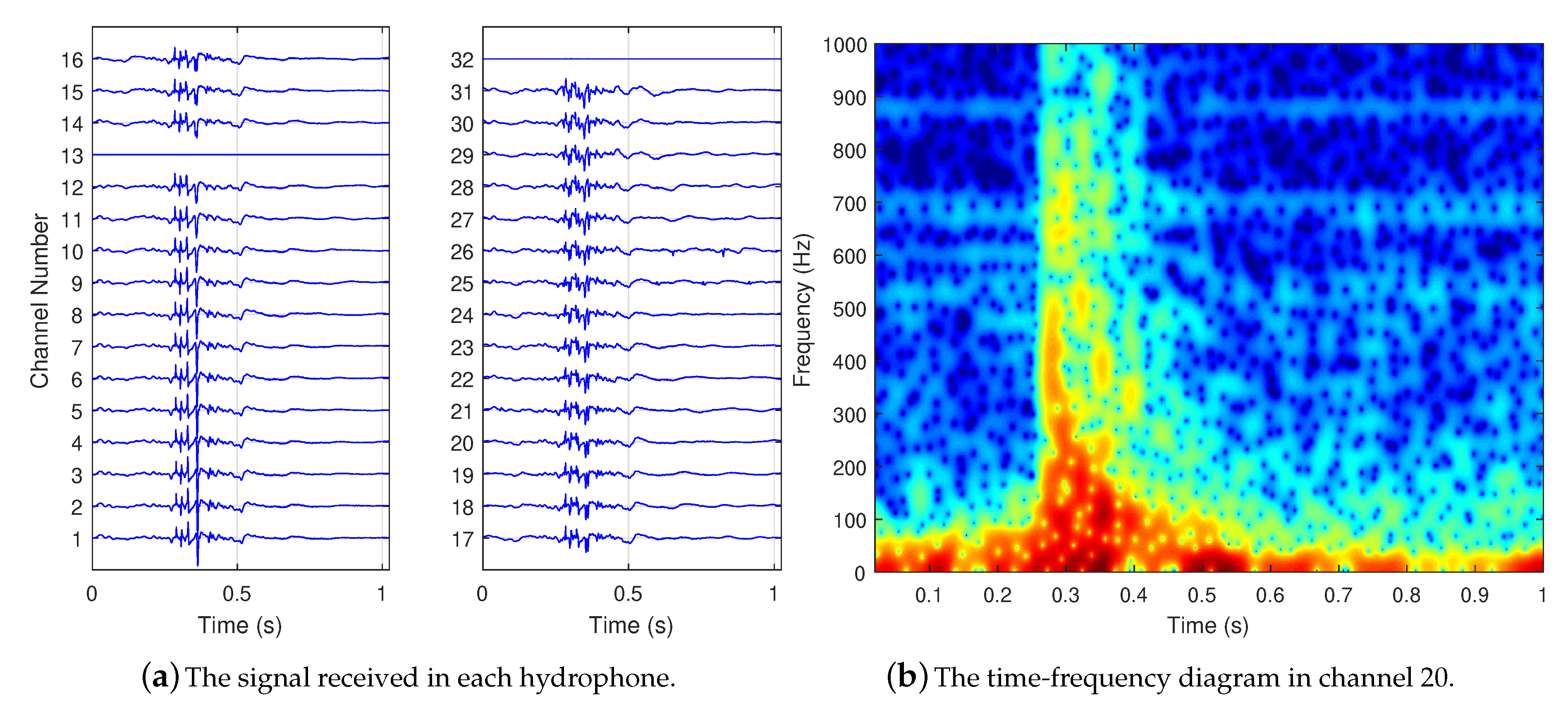
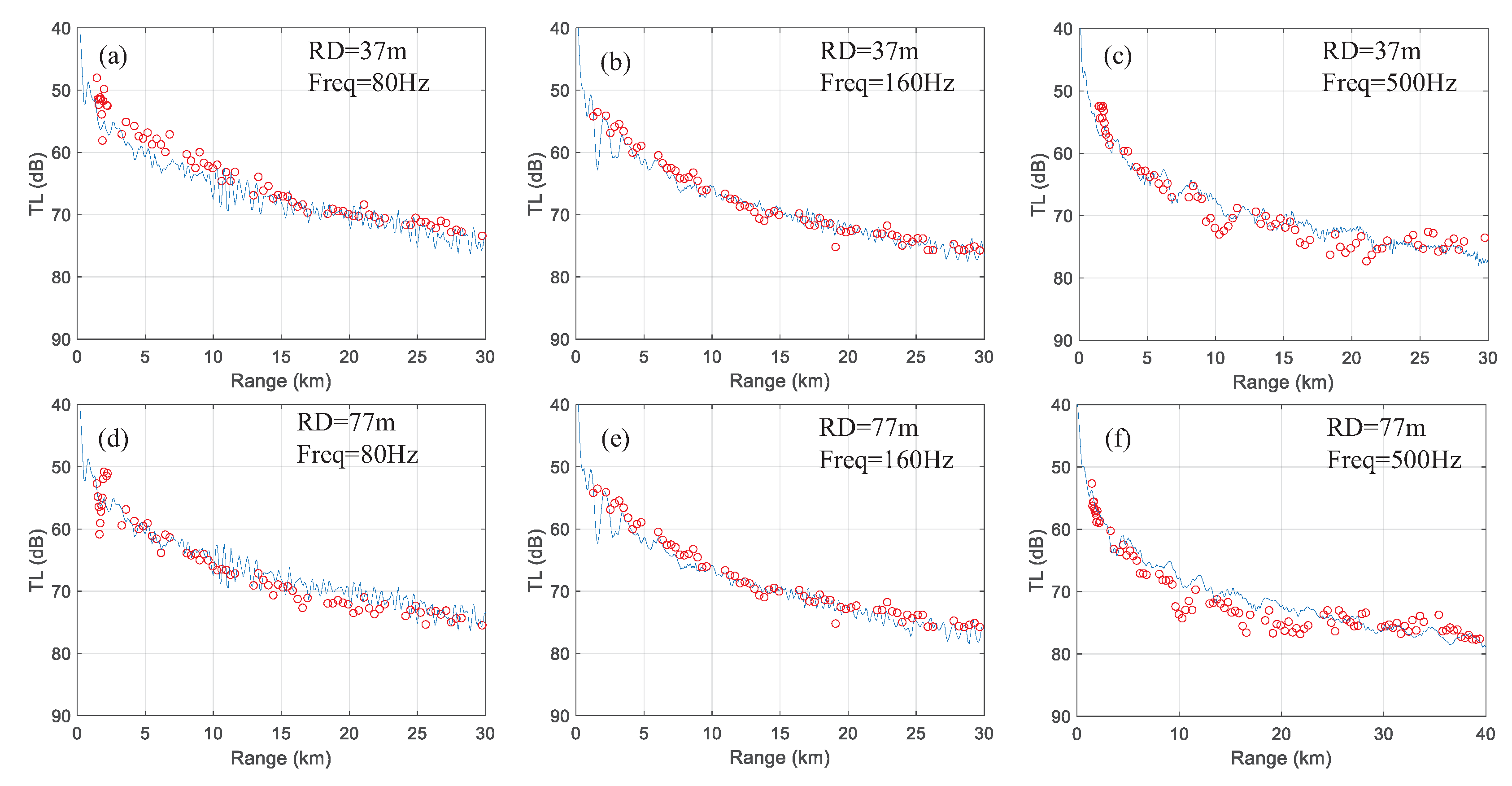
4. Experiment in Shallow Water
Experiment Data and Implementation of Filtering
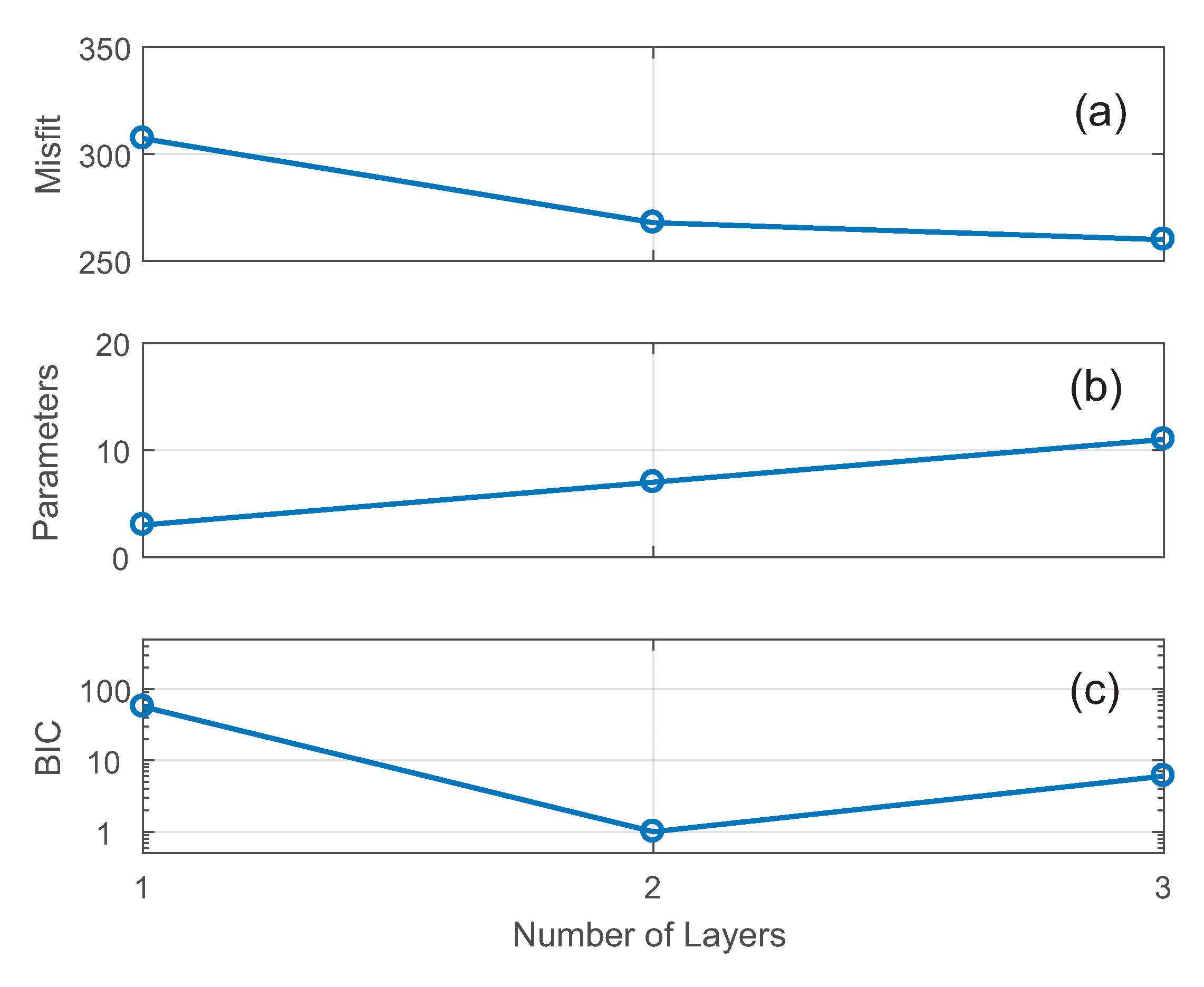
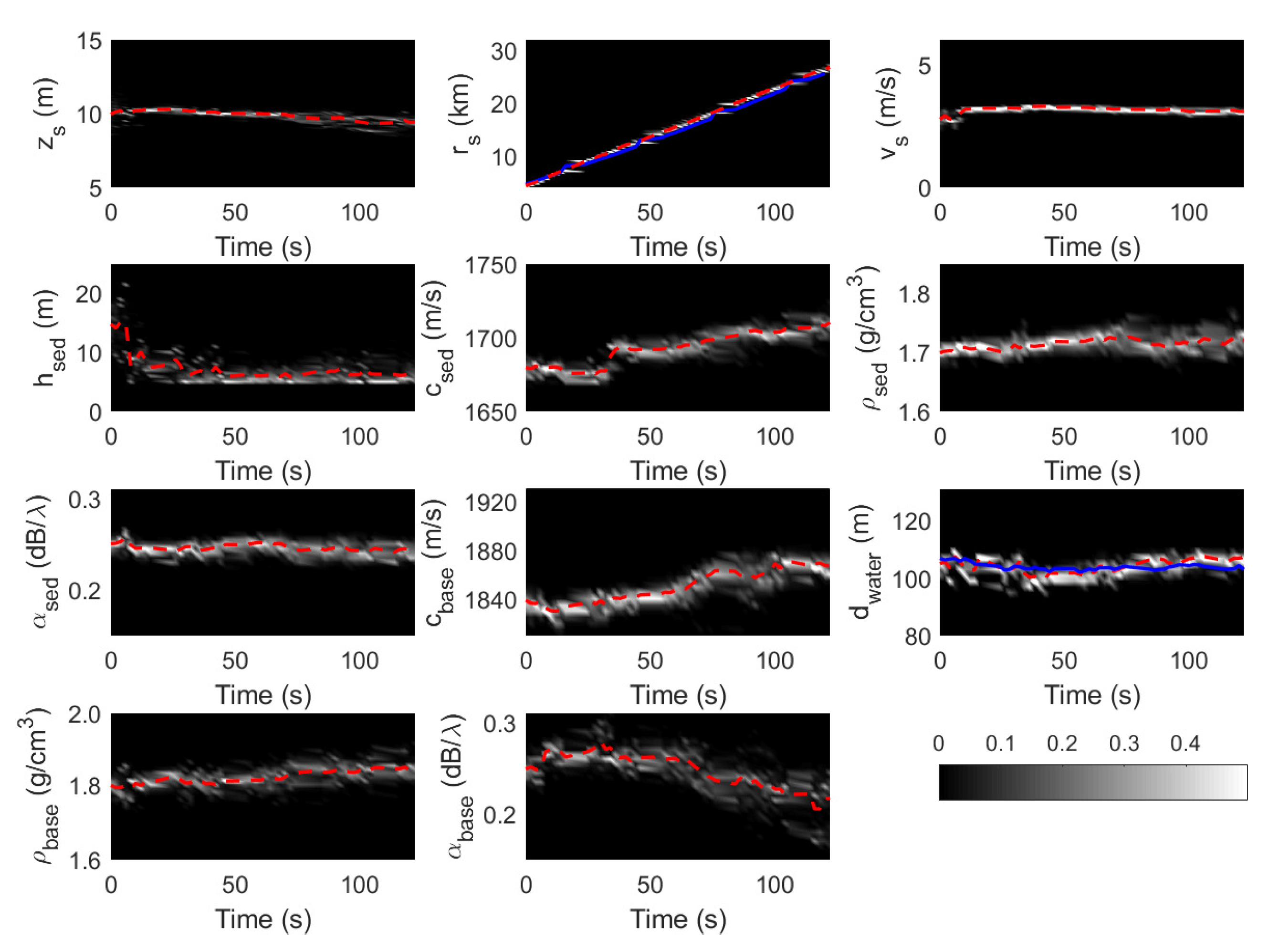
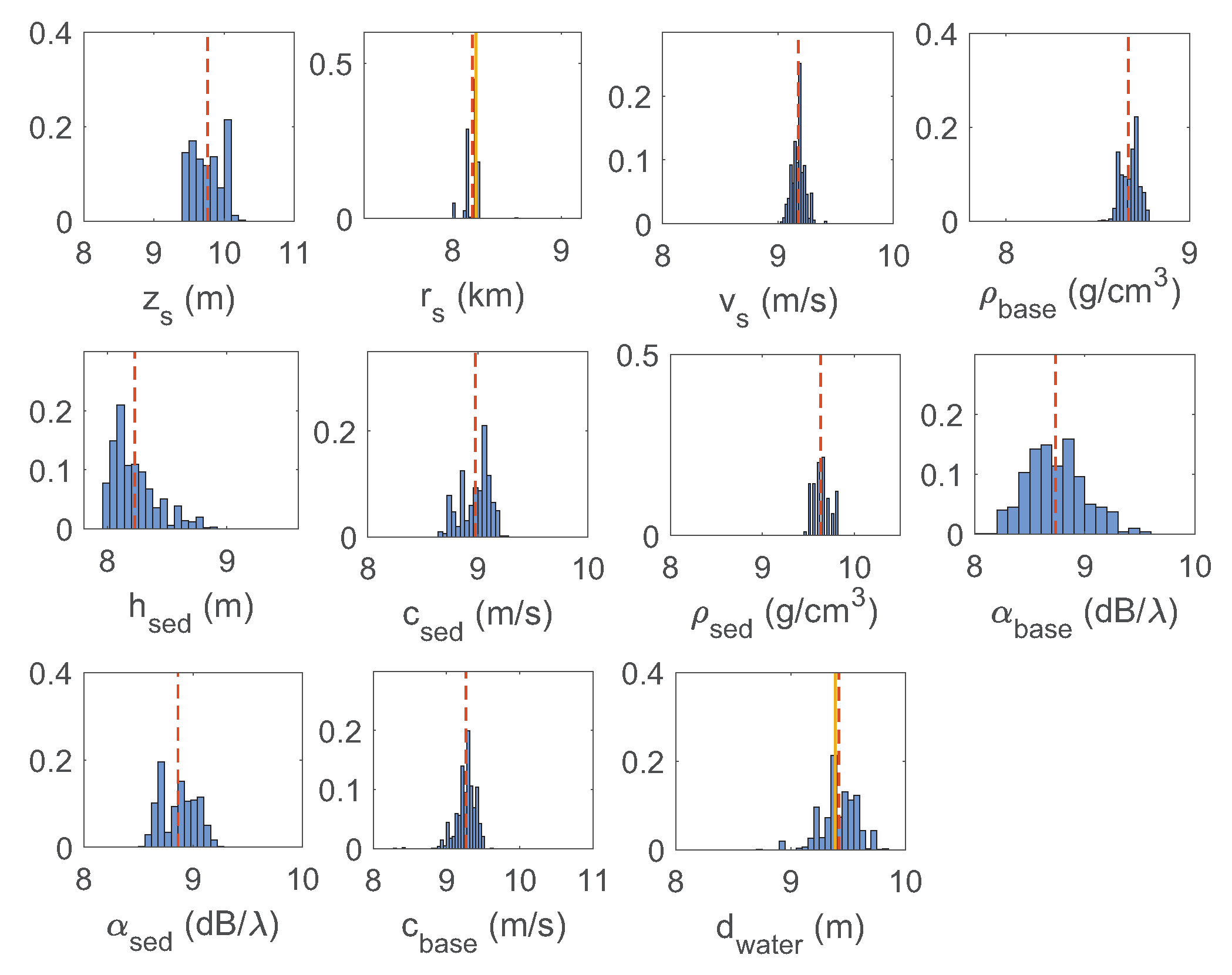
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunde, Y.; Yuanliang, M.; Chao, S.; Miller, J.H.; Potty, G.R. Multistep matched-field inversion for broad-band data from ASIAEX2001. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Uncertainty analysis in matched-field geoacoustic inversions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.F.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Effect of ocean sound speed uncertainty on matched-field geoacoustic inversion. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, EL162–EL168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yang, K.; Guo, X.; Li, H. Bistatic Bottom Reverberation in Deep Ocean: Modeling and Data Comparison. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2016, Shanghai, China, 10 April 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Chapman, N.R.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y. Sequential inversion of modal data for sound attenuation in sediment at the New Jersey Shelf. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wu, L.X.; Niu, H.Q.; Zhang, R.H. Sequential parameter estimation using modal dispersion curves in shallow water. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2018, 35, 044301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chapman, N.R.; Ma, Y. Estimating parameter uncertainties in matched field inversion by a neighborhood approximation algorithm. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstoft, P.; Mecklenbräuker, C.F. Ocean acoustic inversion with estimation of a posteriori probability distributions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosso, S.E.; Wilmut, M.J.; Lapinski, A.S. An adaptive-hybrid algorithm for geoacoustic inversion. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Chapman, N.R. Bayesian geoacoustic inversion in a dynamic shallow water environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, EL155–EL161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosso, S.E.; Dettmer, J. Bayesian matched-field geoacoustic inversion. Inverse Probl. 2011, 27, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Michalopoulou, Z.; Gerstoft, P. An Overview of Sequential Bayesian Filtering in Ocean Acoustics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 36, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, O.; Hermand, J.P.; Le Gac, J.C.; Rixen, M. Full-field tomography and Kalman tracking of the range-dependent sound speed field in a coastal water environment. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S382–S392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Moving source localization with a single hydrophone using multipath time delays in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, EL159–EL165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, E.A.; Merwe, R.V.D. The unscented Kalman filter for nonlinear estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2000 Adaptive Systems for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control Symposium (Cat. No.00EX373), Lake Louise, AB, Canada, 4 October 2000; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, G. The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean. Dyn. 2003, 53, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.J. Particle Filtering in Geophysical Systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 4089–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, O.; Hermand, J.; Candy, J.V. Inversion for Time-Evolving Sound-Speed Field in a Shallow Ocean by Ensemble Kalman Filtering. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 34, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, O.; Hermand, J.P. Sequential Bayesian geoacoustic inversion for mobile and compact source-receiver configuration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 2668–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; Johansen, A.M. A tutorial on particle filtering and smoothing: Fifteen years later. Handb. Nonlinear Filter. 2009, 12, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Tracking of geoacoustic parameters using Kalman and particle filters. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Geoacoustic and source tracking using particle filtering: Experimental results. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Sequential geoacoustic inversion at the continental shelfbreak. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; de Freitas, N.; Gordon, N. An Introduction to Sequential Monte Carlo Methods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, N.; Mémin, E.; Cuzol, A.; Gengembre, N. Data assimilation with the weighted ensemble Kalman filter. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2010, 62, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, M.; Künsch, H.R. Bridging the ensemble Kalman and particle filters. Biometrika 2013, 100, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, F. An Improved Particle Filter Algorithm Based on Ensemble Kalman Filter and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H. Tracking of time-evolving sound speed profiles in shallow water using an ensemble Kalman-particle filter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecklenbräuker, C.F.; Gerstoft, P. Objective functions for ocean acoustic inversion derived by likelihood methods. J. Comput. Acoust. 2000, 8, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation. IEEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, P.H.; Renhe, Z.; Miller, J.H.; Bartek, L.R.; Zhauhui, P.; Ramp, S.R.; Ji-Xun, Z.; Ching-Sang, C.; Lynch, J.F.; Simmen, J.A.; et al. Overview of results from the Asian Seas International Acoustics Experiment in the East China Sea. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Bartek, L.R.; Potty, G.R.; Dajun, T.; Jungyul, N.; Yiquan, Q. Sediments in the East China Sea. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potty, G.R.; Miller, J.H.; Dahl, P.H.; Lazauski, C.J. Geoacoustic inversion results from the ASIAEX East China Sea experiment. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B.; Reiss, E.L. A numerical method for bottom interacting ocean acoustic normal modes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Xiong, J.; Ma, S. Sequential inversion of self-noise using adaptive particle filter in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, 2487–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Unit | Initial Value | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | 100 | 0.2 | 0.35 | 80 | 145 | |
| m | 30 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 50 | |
| m/s | 1570 | 1 | 1 | 1520 | 1700 | |
| g/cm | 1.8 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.4 | 2.2 | |
| dB/ | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.08 | 0.35 | |
| m/s | 1700 | 3 | 1.5 | 1650 | 1850 | |
| m | 20 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1 | 100 | |
| m | 2000 | 20 | 0.025 | 1800 | 6000 | |
| m/s | 5 | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0 | 15 | |
| g/cm | 1.8 | - | - | - | - | |
| dB/ | 0.25 | - | - | - | - |
| Filter | (m) | (m/s) | (g/cm) | (dB/) | (m/s) | (m) | (m) | (m) | (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EnKF-200 | 1.68 | 7.68 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 60.00 | 1.83 | 0.33 | 75.21 | 0.24 |
| PF-200 | 0.89 | 2.08 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 46.54 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 21.70 | 0.51 |
| EnKPF-200 | 0.53 | 1.97 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 36.41 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 18.58 | 0.27 |
| PF-5000 | 0.40 | 1.86 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 21.30 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 15.37 | 0.25 |
| EnKPF-5000 | 0.40 | 1.83 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 21.65 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 16.48 | 0.24 |
| Parameter | Unit | Initial Value | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | 106.8 | 1.5 | 1 | 90 | 150 | |
| m | 18.6 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 20 | |
| m/s | 1668 | 5 | 2 | 1600 | 1750 | |
| g/cm | 1.70 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 1.50 | 2.00 | |
| dB/ | 0.25 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.35 | |
| m/s | 1841 | 5 | 3 | 1750 | 1950 | |
| g/cm | 1.8 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 1.60 | 2.00 | |
| dB/ | 0.25 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.35 | |
| m | 10 | 0.8 | 0.05 | 5 | 20 | |
| m | 3944 | 30 | 0.00025 | 3500 | 50,000 | |
| m/s | 2.75 | 0.2 | 0.00025 | 1 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, Q.; Yang, K. Sequential Geoacoustic Inversion Using an Improved Kalman Particle Filter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8120974
Liu H, Yang Q, Yang K. Sequential Geoacoustic Inversion Using an Improved Kalman Particle Filter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(12):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8120974
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hong, Qiulong Yang, and Kunde Yang. 2020. "Sequential Geoacoustic Inversion Using an Improved Kalman Particle Filter" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 12: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8120974
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, Q., & Yang, K. (2020). Sequential Geoacoustic Inversion Using an Improved Kalman Particle Filter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(12), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8120974




