Abstract
The objective of this work is to develop a case study in order to improve the ballast water management in the Black Sea’s ports. From this perspective, the present paper provides an extensive explanation about the main issues related to the control of marine non-indigenous species introduction through ballast water discharged by ships during their operations in the ports. Thereafter, it quantifies the amount of the ballast water discharged in the major ports of the Black Sea and the amount of the invading species that could reach these ports. Although, globally speaking, the problem of ballast water management is a reality, only three of the six neighboring countries in the Black Sea basin have signed, in 2004, the ratification of the International Convention on Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments. This is also known as the Water Ballast Management Convention, and it provides regulations concerning ballast water management generated by the shipping activities through a common set of rules.
1. Introduction
Maritime transportation in the Black Sea has increased in the last years and requires suitable measures for safe navigation and environmental protection. The quality of the information regarding the prediction of sea state conditions, or of other natural phenomena that influence the maritime transport safety, is extremely important. Although the fetch for wave development is considerably smaller in the Black Sea than in open ocean, very strong storms are sometimes present, and they can generate waves comparable even to the high ocean waves [1,2,3]. The maritime operations are usually very dynamic in the coastal areas [4], near to the major ports; on the other hand, some coastal sectors are very dangerous for navigation, for example, those which are close to the mouths of the Danube River [5,6].
All vessels need to have adequate stability at sea, and the ballast is used to control it and also to maintain the appropriate draft of the boat. Ballast is defined as a form of balancing an object—it is an unwanted element, but shipping effectiveness requires its use. In the naval field, the ballast once appeared in solid form, using stones, metals, and other materials. When shipbuilding evolved to more complex forms, using metal sheets as the raw material, the liquid ballast form was introduced. This liquid ballast was quickly adopted due to the lower cost and time of the water handling of the ship’s tanks.
Ballast for a ship has multiple roles in unloading the cargo, with the most important ones listed below:
- Makes an optimal draft to correct the propeller efficiency;
- Amends the trim of the ship, reducing the operating costs;
- Reduces the structural stress resulting from the uneven distribution of masses/weights on the length of the ship;
- Improves the stability of the ship.
The ballasting/de-ballasting procedures are graphically illustrated in Figure 1. Ballasting begins when the cargo carried on board is unloaded in the port. It can be seen how the water level in the tanks increases as the cargo area is emptied. De-ballasting takes place when the ship arrives at the port where the ship must load the cargo. When the cargo is loaded aboard the ship, the water from the ballast tanks is discharged by pumps especially dedicated for this operation.
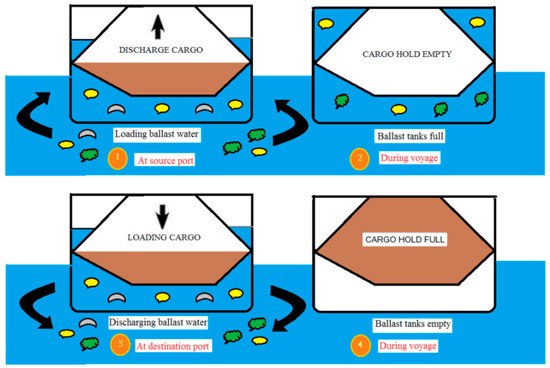
Figure 1.
Ballasting/de-ballasting procedures for a bulk carrier.
Although many countries seem to have understood the importance of limiting traffic with the globalization of the dangerous species and pathogens from one geographic area to another [7,8,9,10], the EU has not yet adopted a valid regulation for all countries [11]. What is also highlighted at the regional level, in Table 1 (data processed from [12]), is that out of the six countries bordering the Black Sea, two countries have been members of the EU since 2007. Thus, Bulgaria and Romania are countries that have not signed the convention.

Table 1.
Status of Black Sea countries for International Marine Organization (IMO) Ballast Water International Convention.
The Convention is not ratified in the Black Sea, although it is known that there is a precedent in this marine environment of relationships with invasive species with major ecological impact [13]. In the agenda of the last conference held in London, the session of the International Marine Organization’s Marine Environment Protection Committee (IMO MEPC) 71 also raised the problem of noxious species in the ballast water. It has been decided that, starting in September 2017, all new ships will be fitted with ballast water treatment systems. For the ships that were already in operation before September 2017, depending on the schedule of the next mandatory docking, they are required to comply with the new procedures governing the management of ballast water and its treatment.
Due to the fact that not all ships will be able to implement functional ballast water treatment systems, in order to maintain profitability, the Black Sea ports will have to invest in new facilities for the treatment of the ballast water. Having these facilities, the possibility of becoming more attractive destination points for a larger number of commercial ships will increase.
2. Incidents of Harmful Species as a Result of the Global Ballast Water Movement
The Target Areas
Invasive species are those organisms that are introduced anthropically into a new environment where they can adapt, multiply, and spread, thus damaging the natural systems of that environment, as well as its economic activities [14,15]. Regarding the Black Sea basin and the Romanian coastal environment, various studies presented the non-indigenous species that invaded this area [16,17,18,19]; a selection of these are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Selection of alien invasive species in the Black Sea.
In the 1980s, the Black Sea faced the jellyfish “Mnemiopsis leidyi”, which affected the entire trophic chain in this marine ecosystem [16]. The implications of this episode have been traced to a number of plankton-eating fish. The disappearance of the plankton has led to a chain reaction, ultimately affecting the dolphins and the sharks from the Black Sea, as well as the entire fishing economy in the neighboring countries of this affected ecosystem. The impact on the economy has been a major one. According to specialist studies, the losses to the fishing industry would have been around $200 million in 1997, only for the Black Sea. The situation in the Black Sea has improved, almost naturally, with the emergence of the new invasive species, “Beroe ovata”, a predator that feeds on other jellyfish. This was identified in the Black Sea in 1998, according to the information presented in Table 2.
The main target of the “Beroe ovata” species, in the Black Sea ecosystem, is “Mnemiopsis leidyi”. By its unpleasant appearance in this sea environment, it has led to the regulation of the trophic chain by diminishing the population of “Mnemiopsis leidyi”. The same jellyfish “Mnemiopsis leidyi”, originally from the West Atlantic area [20], migrated around the 1990s from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea, where they followed the same pattern. Thus, it has succeeded in affecting the population of the Caspian Sea species. For example, “Pusa caspica” is now threatened by extinction [21], according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list of threatened species.
The territorial expansion of the Mnemiopsis leidyi jelly seems not to have stopped. Thus, in 2006, it was identified both in the North Sea and in the Baltic Sea. Its effects on these environments are still unknown. A possible journey route of the jelly fish could be via the Black Sea-Danube-Main-Rhine navigation corridor, and also through the ballast water of ships. According to Table 2, it can be seen that a large variety of foreign species arrived in the Black Sea from various other areas of the ocean through the ballast water transported by commercial vessels. It has to be highlighted that not all these species are harmful, but their migration needs to be monitored and prevented.
Migration from the ports in the Black Sea is ensured, especially by surface currents [22,23]. These water currents create conditions for the accelerated spread of organisms from the local level to other currents that act on a very large area. Such factors create the probability of an aggressive spread of species which find a favorable breeding medium in the Black Sea. Climate changes lead to an increase in the coastal use [24]. This could elevate the vulnerability of the harbors regarding any type of problem, such as invasive species. Soft solutions could be used to tackle them. On the other hand, sea level rise could lead to a change in the amount of water discharged as ballast, which could have an impact on the number of samples of invasive species transported.
Conditions of an increase in the duration and energy of storms [25] might enhance the mortality of the jellyfish. On the other hand, it could change the patterns of the natural transportation of invasive species, as well as artificial patterns, due to the redesign of ship routes as a consequence of harsh weather [26].
Worldwide incidents with “alien species” have occurred and they are still taking place, so it is desirable to regulate the treatment of the ballast water through the International Convention on the Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments.
3. The Black Sea’s Ports
Maritime traffic in the Black Sea mainly takes place between the ports of Constanta, Odessa, Novorossiysk, Samsun, but also from and to the Mediterranean Sea, through the Bosporus Strait. The main factor that poses a threat to the Black Sea from the point of view of invasive marine life is a positive economic practice and is desired by all states in the Black Sea region, namely, goods export.
Furthermore, the export of products made on long water routes exceeds the Black Sea area. The danger arises when, for the goods transported for export, the vessels used are ballasted with water from geographical areas other than the Black Sea, Figure 1. Thus, the ballasted vessels entering the Black Sea ports are required to de-ballast the water from the ballast tanks at the time of loading the goods on board. Water from geographic areas other than the Black Sea, if not treated before discharge into the port area, can bring with them pathogenic elements that can create pandemics in the marine ecosystem [27].
Demand for transport exists. This is presented in Table 3 (data processed from [28,29,30,31], where we can see the need for maritime transport services by volume of exported goods, expressed in tons. For the most important Black Sea ports, the export demand for 2016 was about 110 million tons of cargo.

Table 3.
Annual report of the tonnage exports from Black Sea’s ports.
Taking into account the fact that there are exports in this way, maritime transport comes with associated risks that the ballast water presents. This should lead to the adoption of a ballast water treatment system and its rules, even in the Black Sea, thereby reducing the risks to this natural biosystem via the ballast water brought by shipping vessels [32].
Ballast water from outside the Black Sea transported through the ballast tanks of vessels can be calculated as follows [33,34]:
A short explanation will be given next. Thus, ballast water represents the water carried in the ships’ tanks to improve stability, trim, balance, or structural tensions. Deadweight (DW) indicates the measure of a vessel’s weight-carrying capacity. This does not include the weight of the ship itself. Deadweight cargo capacity (DWCC) indicates the measure of how much pure cargo can be loaded, without provisions, lubricant, and fuels for the vessel.
Results from Equations (1)–(3) indicate that the ballast water (BW) accounts for 40% of the transported cargo (DWCC), a value known from Table 3. These results are assuming that the ships leave the port fully loaded, which is an ideal scenario for a basic calculation. In reality, not all the ships leave the harbor with cargo holds full, but because not all local exports leave the Black Sea geographical area, we work with this percentage, which will compensate somehow by moderating the differences. Thus, for the year 2016, for the four major Black Sea ports, this results in a volume of about 44 million tons of potentially hazardous ballast water. Despite this obvious evidence, Romania and Bulgaria have not taken any action in this respect, and no EU directive has been ratified regarding these aspects.
The traffic from the Bosporus Strait is a very intense one—more than 21,000 vessels (see Table 4, data processed from [35]) that pass annually to the Black Sea, from which over 30% present significant risks. In order to remain competitive at an economic level, the Black Sea ports must adopt methods to increase or maintain the maritime traffic in the region.

Table 4.
Annual reports of the ships sailing to the Black Sea through Bosporus Strait.
According to Figure 2, it is easy to understand that, by creating the port facilities, shipping will increase in these areas, or at least it will not decrease. Starting from the premise that not all shipowners will succeed or will not be able to bring their entire fleet of ships to the standards imposed by IMO, the Black Sea ports should come to their aid. Carrying out a modernization of the entire fleet, depicted in Figure 2, implies a fairly high financial availability, and most of the owners of such vessels will seek to avoid or delay as much as possible such investment.
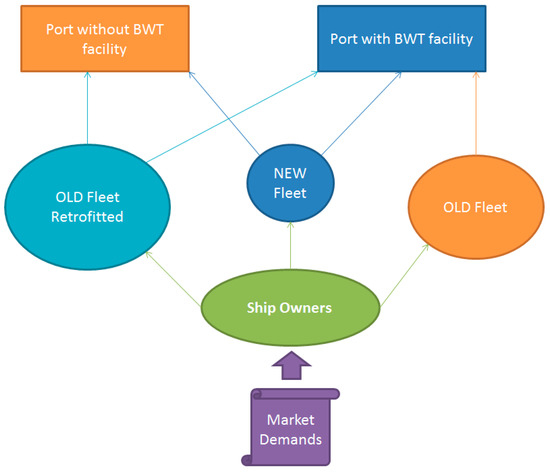
Figure 2.
Diagram of the port’s strategy.
4. Case Study, the Port of Constanta
Ballast water treatment devices should only be forecasted for future investments, as solutions exist on the market. Only a forecast of the demands for the type of service that the port can offer to the ships arriving to be loaded with cargo should be made. Once a possible scenario for the facility demands is established, the type of the vessels’ access to these ballast water treatment devices will be established.
There is the possibility to purchase containers, which can be transported by a trailer at the quays, that require externalized treatment of the ballast water, schematically presented in Figure 3. The advantage of this method is that it is cheaper in terms of the device displacement and even functioning because it will be connected to the power resources of the port. Of course, the initial purchase price is much lower than other solutions. The disadvantage would be the time—being able to condition the cargo operations in a timely manner.
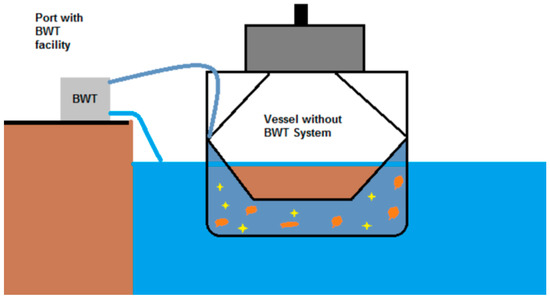
Figure 3.
Harbor’s facility—ballast water treatment (BWT) container.
The second solution may be a barge dedicated to ballast water treatment, as presented in Figure 4. The main advantage of this choice is the opportunity to save time to carry the cargo handling maneuvers in the port because the barge can accompany the ship outside the harbor. The barge can operate outside the port only in weather conditions favorable to this operation, and it is known that the Black Sea is a rough sea, at least in the winter season, and some recent studies showed that this feature will be even more accentuated in the future [29].
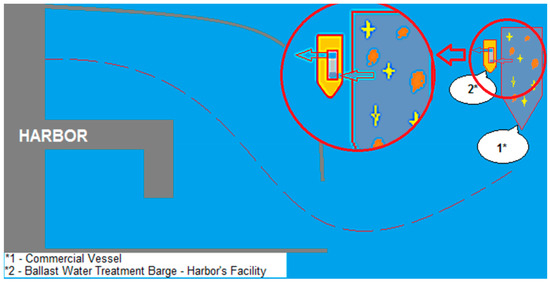
Figure 4.
Harbor’s facility—ballast water treatment barge.
The disadvantage is the relatively long time until the port can be in the possession of such a barge because it involves the construction steps of a ship: concept design, offering, design, and construction. Also, the higher costs, maintenance, operation, and acquisition may be a disadvantage in choosing this solution.
The port of Constanta, which is the most important European Black Sea port, will be considered next as a case study. According to Table 3, the total goods exported from Constanta Port represent 17.2% of the total calculated for the four major ports considered in this table. Thus, 17.2% of the ballast water (44 million tons) brought by the vessels carrying goods for export from the Black Sea reaches Constanta Port.
Annually, 7.6 million tons of the potentially hazardous ballast water is discharged into the port of Constanta (see Table 5). Approximately 15% of the ships sailing in the Black Sea were built after January 2010 [34]. However, this does not guarantee that these ships have installed or use the ballast water treatment system. This is due to the fact that the convention is not adopted in all countries. Thus, even if the vessels have ballast water treatment systems, they may not use them in order to avoid the unjustified costs.

Table 5.
Constanta harbor’s capability of ballast water treatment.
The minimum capacity foreseen for Constanta’s harbor consists of the conditional assessment of the year 2022, when IMO will enforce the ballast water norms. Under these conditions, 4.16 thousand tons of ballast water will have to be treated daily by the facilities of Constanta Port if it is desired to keep the flow of the ships at the level of this moment. This means that 173 tons of ballast water per hour must be handled in the port. Taking into account the possibility of increasing ship traffic in the port, this value should be added.
Considering this case, the result is that it would be enough for one container system to have a treatment capacity of 300 cm/h. Nevertheless, the recommendation would be to acquire three containers, justifying the desire to keep (or even increase) the number of the ships transiting Constanta Port. The possibility of carrying out more detailed studies according to future port management projections is also considered at this point.
5. Conclusions
According to the present study, the need to adopt policies against the unmonitored discharges of ballast water into the Black Sea basin must become a priority in the foreign policy of the six neighboring countries. The risk of a new episode similar to that of the 1980s is quite large, and serious work should be done to prevent history from repeating itself.
Furthermore, the Black Sea ports will need to address the shipowners and shipping companies with new facilities, to meet new market needs, and to take over the shipowners’ financial burden of investing in re-technology of fleets with ballast water treatment systems. This approach will enable maritime traffic which will sustain the profitability margin of the ports concerned.
The calculation pattern presented in this work can be applied to all the ports of the Black Sea, as well as others. It will help the decision-makers in ports to scale up the needs and solutions quickly for the basic design stage of implementing modern facilities for active operations of monitoring and controlling introduction of non-indigenous marine species to the Black Sea’s ecosystem. For example, the Mediterranean Sea, which is connected to the Black Sea via the Bosporus Strait, has a regional strategy addressing ship’s ballast water management and invasive species [36].
Finally, every solution adopted, following a feasibility study, should also be based on a multi-scenario forecast to facilitate technical and economic optimization.
Author Contributions
Vasile Rata processed the data and the figures, also has written the preliminary form of the manuscript. Carmen Gasparotti processed some figures and made some corrections to the preliminary form of the manuscript. Liliana Rusu has guided this research and has written the final manuscript. The final form of the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Research and Innovation, UEFISCDI grant number PN-III-P4-ID-PCE-2016-0028.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the reviewers for their suggestions and observations that helped in improving the present work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| IMO | International Marine Organization |
| BW | Ballast water |
| DW | Deadweight |
| DWCC | Deadweight Cargo Capacity |
| MEPC | Marine Environment Protection Committee |
| IUCN | International Union for Conservation of Nature |
References
- Rusu, L.; Bernardino, M.; Guedes Soares, C. Wind and wave modelling in the Black Sea. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2014, 7, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onea, F.; Raileanu, A.; Rusu, E. Analysis of extreme wind and wave conditions in the Black Sea, as reflected by the altimeter measurements. Mech. Test. Diagn. 2016, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, L.; Butunoiu, D.; Rusu, E. Analysis of the extreme storm events in the Black Sea considering the results of a ten-year wave hindcast. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2014, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, L.; Guedes Soares, C. Forecasting fishing vessel responses in coastal areas. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2014, 19, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, A.; Rusu, E. Assessment of the Navigation conditions in the coastal sector at the entrance of the Danube Delta. In Proceedings of the 12th Surveying Geology & Mining Ecology Management (SGEM) International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference, Albena, Bulgaria, 17–23 June 2012; Volume III, pp. 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, L. Application of numerical models to evaluate oil spills propagation in the coastal environment of the Black Sea. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2010, 18, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Griffiths, F.B.; Van der Wal, E.J.; Kelly, J. Cargo vessel ballast water as a vector for the transport of non-indigenous marine species. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1988, 26, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.K.; Chang, C.H.; Chou, M.L. Management strategies to prevent the introduction of non-indigenous aquatic species in response to the Ballast Water Convention in Taiwan. Mar. Policy 2014, 44, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Gollasch, S.; Leppäkoski, E. Risk assessment for exemptions from ballast water management–the Baltic Sea case study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scriven, D.R.; DiBacco, C.; Locke, A.; Therriault, T.W. Ballast water management in Canada: A historical perspective and implications for the future. Mar. Policy 2015, 59, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, S.J.; Elliott, M.; Murillas-Maza, A.; Papadopoulou, N.; Uyarra, M.C. Is existing legislation fit-for-purpose to achieve Good Environmental Status in European seas? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 111, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Maritime Organization, International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments, 2004. Available online: http://www.imo.org/en/About/Conventions/ListOfConventions (accessed on 25 August 2017).
- Gomoiu, M.T.; Alexandrov, B.; Shadrin, N.; Zaitsev, Y. The Black Sea—A recipient, donor and transit area for alien species. In Invasive Aquatic Species of Europe. Distribution, Impacts and Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 341–350. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, E. Methods for the risk assessment in maritime transportation in the Black Sea basin. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2012, 13, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, E.; Dragomir, S. The impact of anthropogenic activities on the water quality in the Danube River Basin. In Proceedings of the 13th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: Geoconference on Ecology, Economics, Education and Legislation, Albena, Bulgaria, 16–22 June 2013; Volume I, pp. 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Shiganova, T. Ponto-Caspian: Invasions. In Encyclopedia of Biological Invasions, 3rd ed.; Encyclopedia of the Natural World, No. 3; Simberloff, D., Rejmanek, M., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley/Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 549–556. ISBN 978-0-520-26421-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jernelöv, A. The Warty Comb Jelly in the Black Sea. In The Long-Term Fate of Invasive Species; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 261–278. ISBN 978-3-319-55396-2. [Google Scholar]
- Oral, M. Alien fish species in the Mediterranean–Black Sea Basin. J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2010, 16, 87–132. [Google Scholar]
- Skolka, M.; Preda, C. Alien invasive species at the Romanian Black Sea coast—Present and perspectives. Travaux du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle «Grigore Antipa» 2011, 53, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisgard, H.U.; Goldstein, J. Jellyfish and ctenophores in limfjorden (Denmark)—Mini-Review—with recent new observations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 593–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiganova, T.A. Invasion of the Black Sea by the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi and recent changes in pelagic community structure. Fish. Oceanogr. 1998, 7, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toderascu, R.; Rusu, E. Evaluation of the circulation patterns in the Black Sea using remotely sensed and in situ measurements. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black Sea Ecosystem Recovery Project. Available online: http://www.elmed-rostov.ru/Projects/TDA/Black_Sea_3_1.htm (accessed on 28 August 2017).
- Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; García-León, M.; Gràcia, V.; Devoy, R.; Stanica, A.; Gault, J. Managing costal environments under climate change: Pathways to adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 1336–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin-Ye, J.; García-León, M.; Gràcia, V.; Ortego, M.I.; Stanica, A.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A. Multivariate hybrid modelling of future wave-storms at the northwestern Black Sea. Water 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rata, V.; Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, L. The importance of the reduction of air pollution in the Black Sea basin. Mech. Test. Diagn. 2017, 2, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Onwuegbuchunam, D.E.; Ebe, T.E.; Okoroji, L.I.; Essien, A.E. An Analysis of ship-source marine pollution in Nigerian seaports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novorossiysk Grain Terminal. Annual Financial Report 2016. Available online: http://www.nzt.ru/ (accessed on 28 August 2017).
- Annual Report, Port of Constanta, 2016. Available online: http://www.portofconstantza.com (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- Turkish Chamber of Shipping, Maritime Sector Report 2016. Available online: www.denizticaretodasi.org.tr/Shared%20Documents/sektorraporu/2015_sektor_en.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2017).
- Ukrainian Sea Ports Authority. Available online: http://uspa.gov.ua/en/ (accessed on 5 September 2017).
- Pieri, G.; Cocco, M.; Salvetti, O. A marine information system for environmental monitoring: ARGO-MIS. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, G.B.; Satir, T. Ballast water problem in the Black Sea and Turkish straits. In Proceedings of the 13 International Symposium, Thessaloniki, Greece, 8–12 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- North-Western Shipping Company. Available online: http://www.nwship.com/en/ (accessed on 6 September 2017).
- Bosphorus Strait News Yearly Ship Statistics of Bosphorus Strait. Available online: http://www.bosphorusstrait.com/ (accessed on 9 September 2017).
- United Nations Environment Programme. United Nations Environment Programme. Decision IG.20/11, Regional strategy addressing ship’s ballast water management and invasive species. In Proceedings of the 17th Ordinary Meeting of the Contracting Parties to the Convention for the Protection of the Marine Enviroument and the Coastal Region of the Mediterranean and Its Protocols, Paris, France, 8–10 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).