Use of Multibeam and Dual-Beam Sonar Systems to Observe Cavitating Flow Produced by Ferryboats: In a Marine Renewable Energy Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
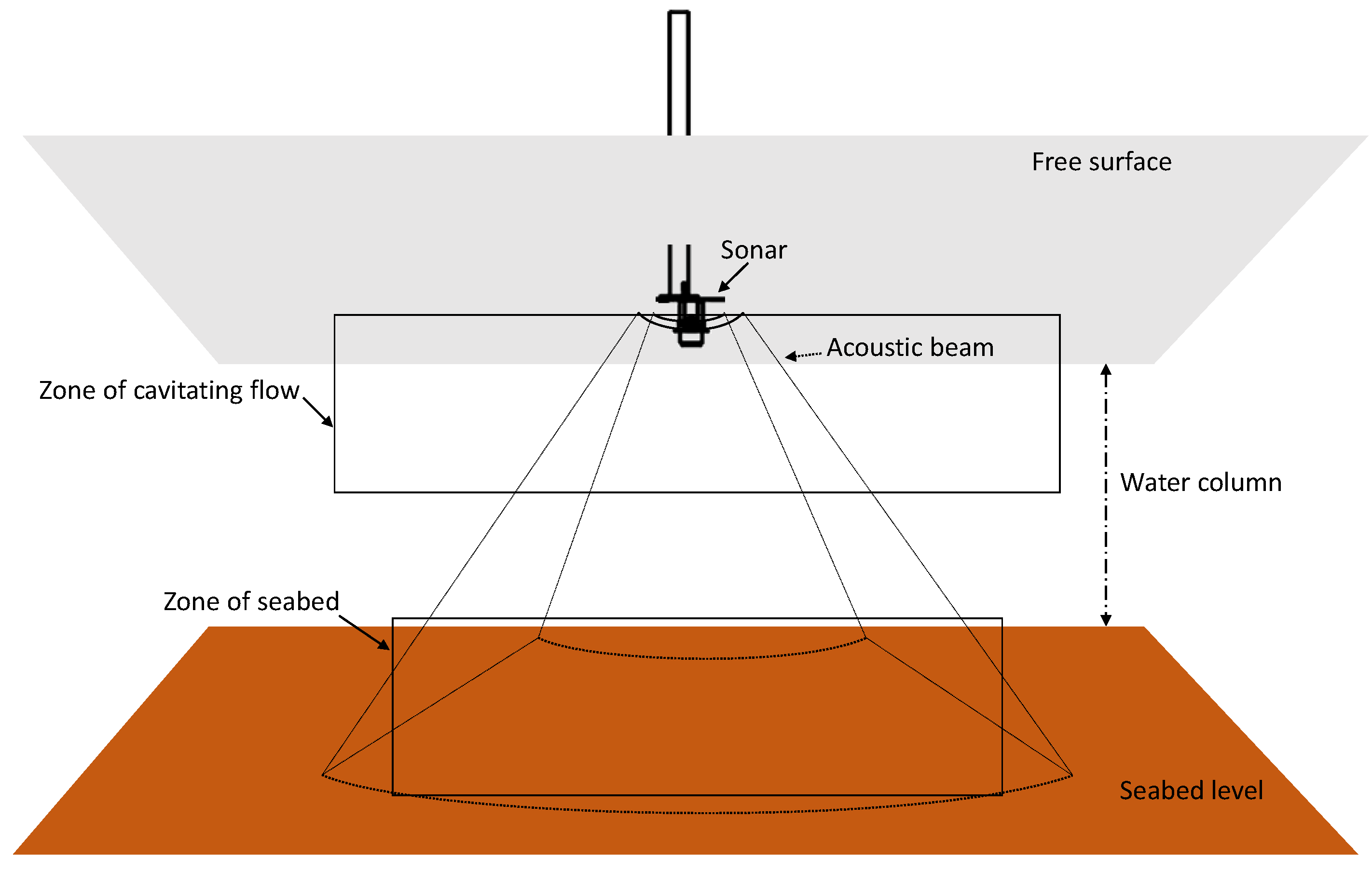
2. Cavitation and Cavitating Flow: An Overview
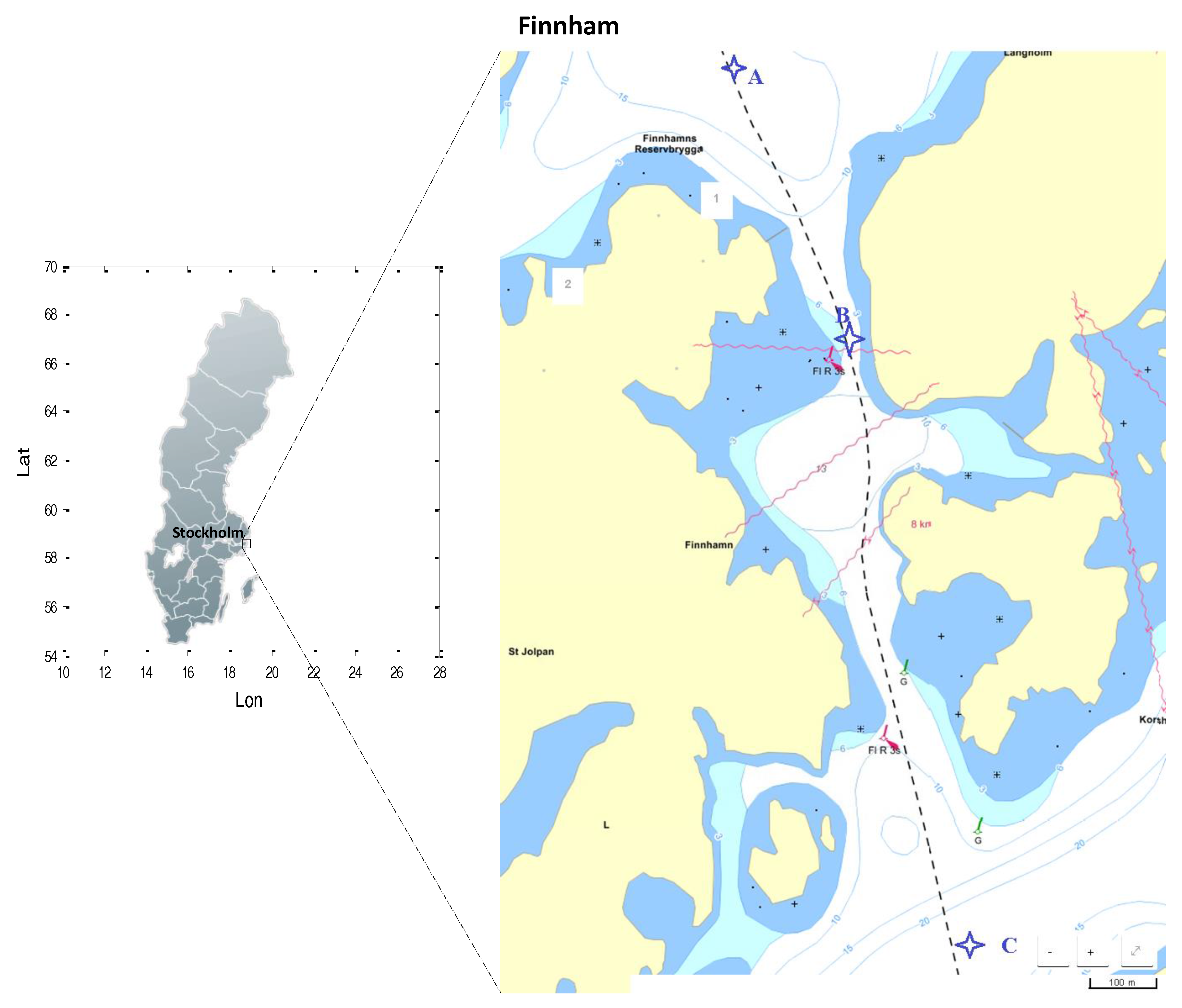
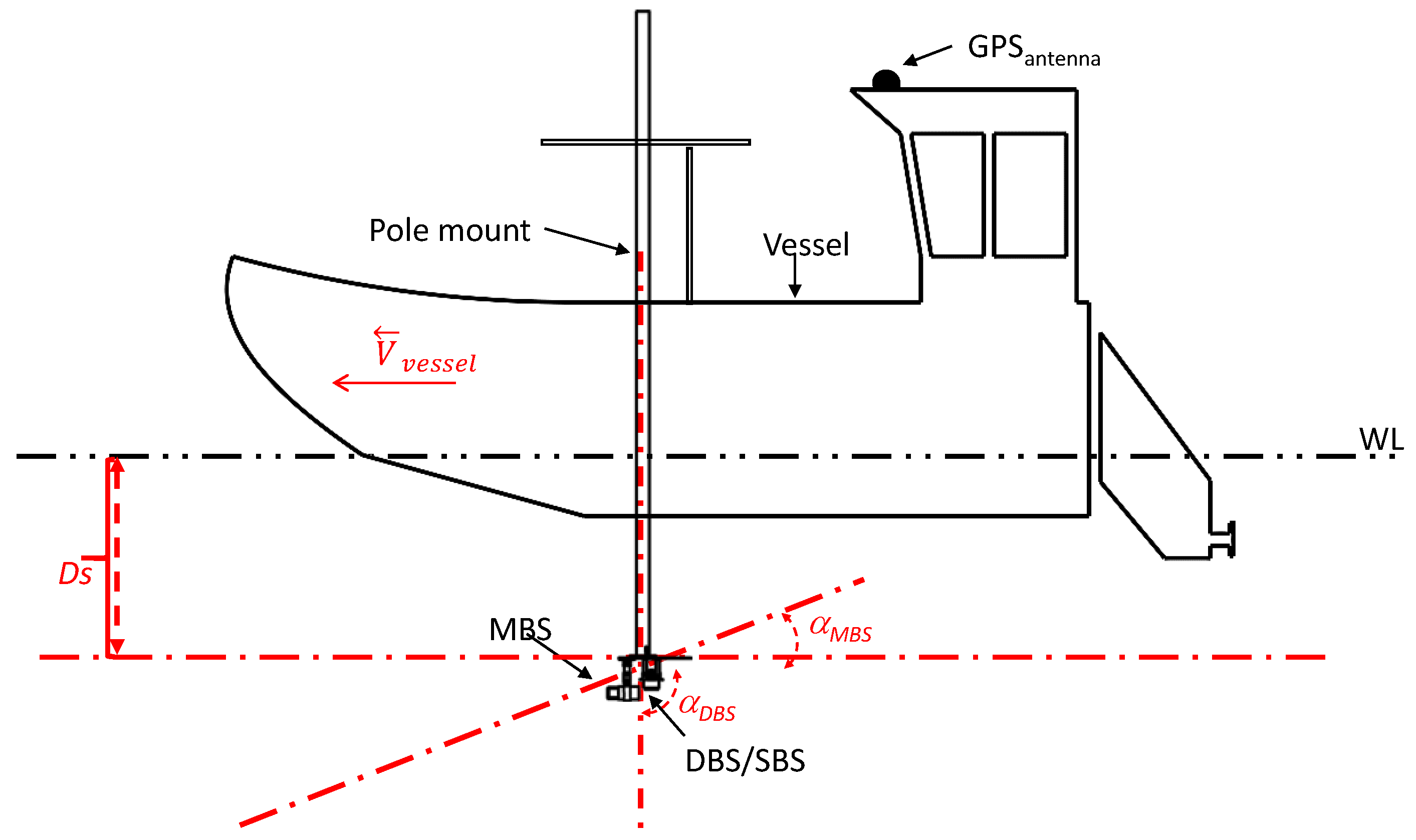
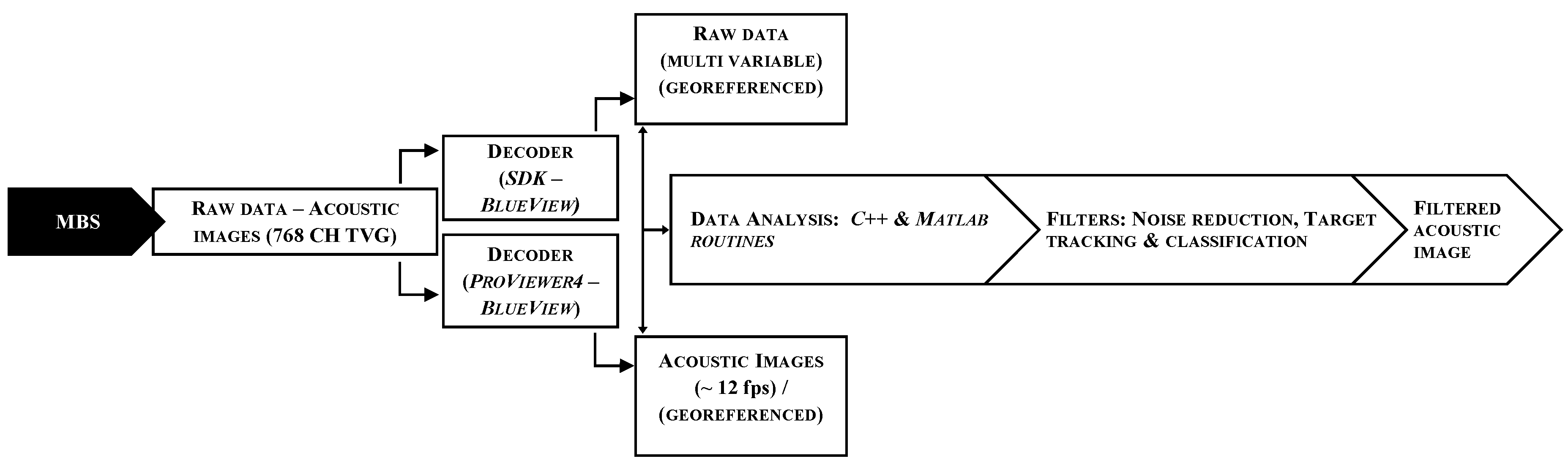
3. Methods of Observation
4. Results from Observation
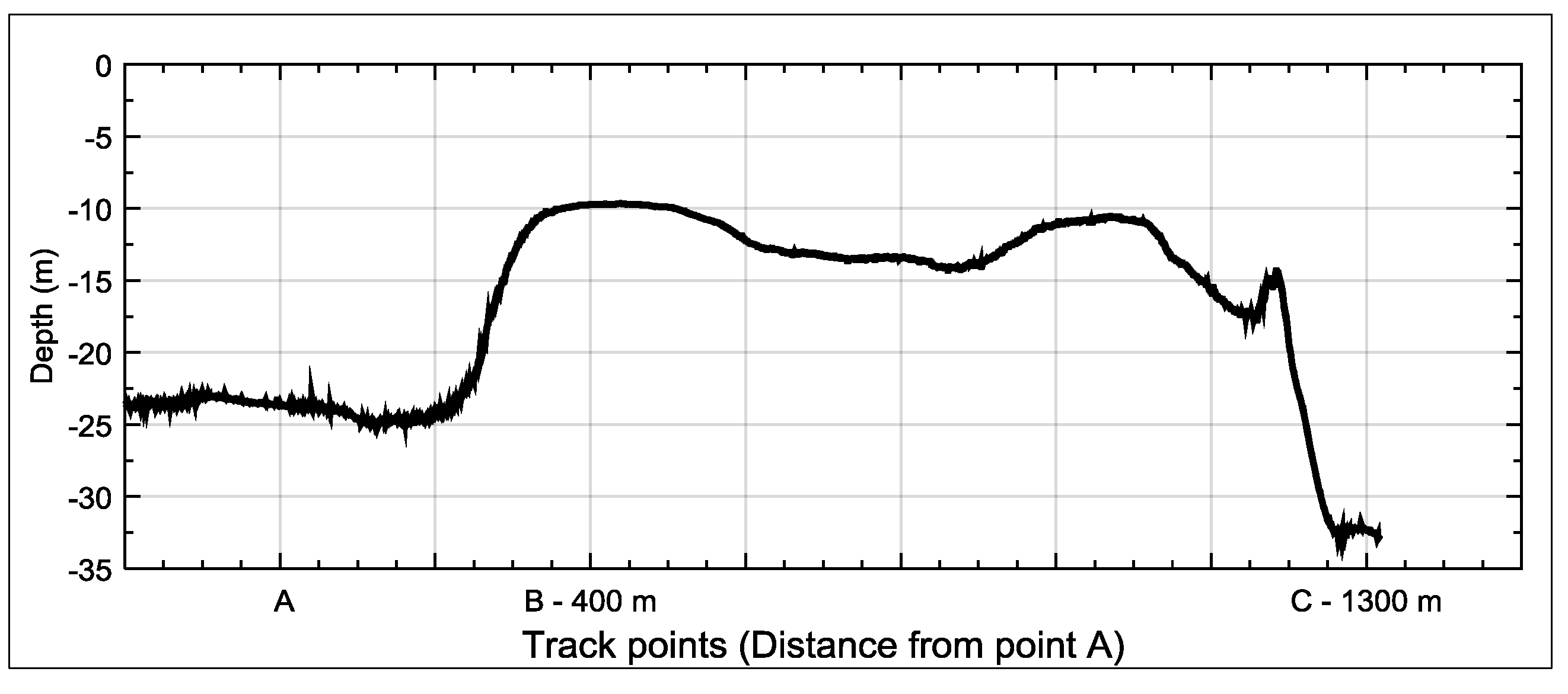
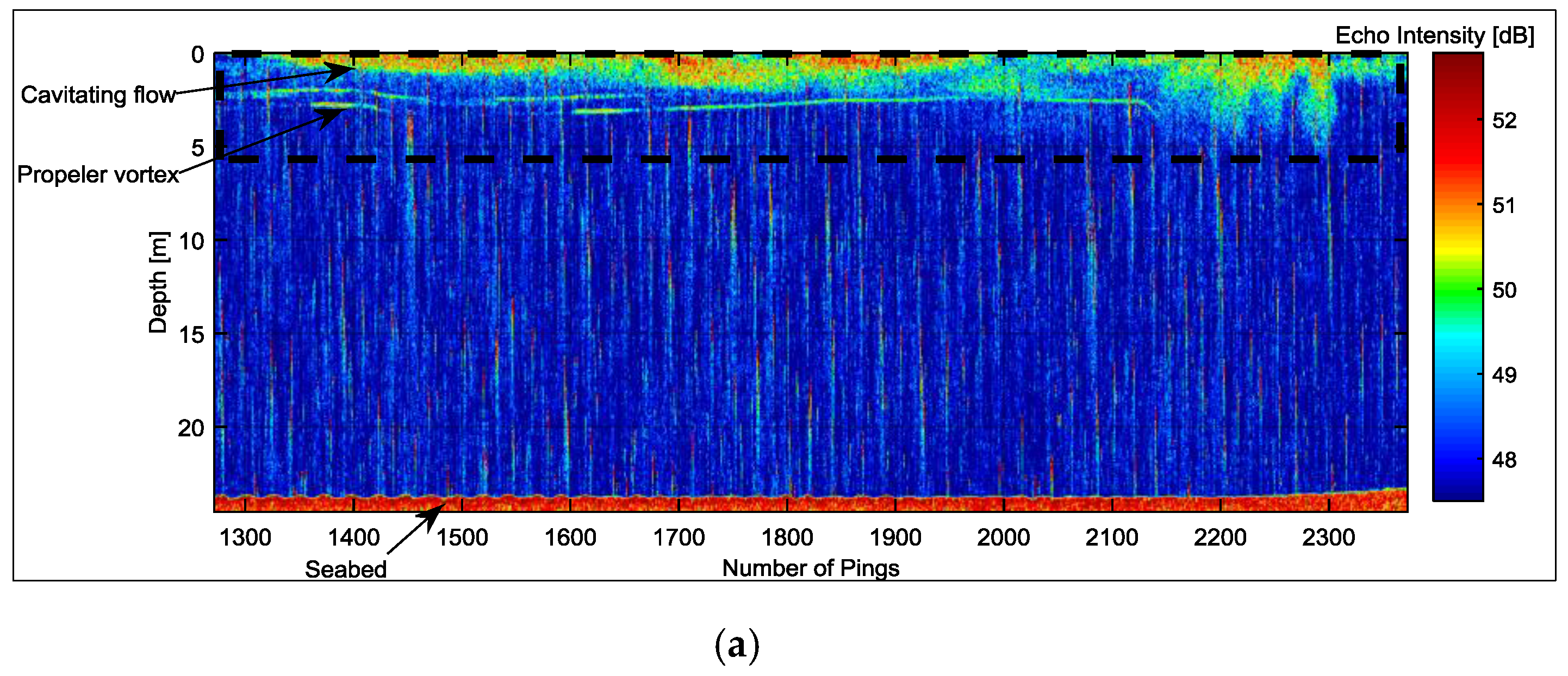
4.1. Depth Measurements
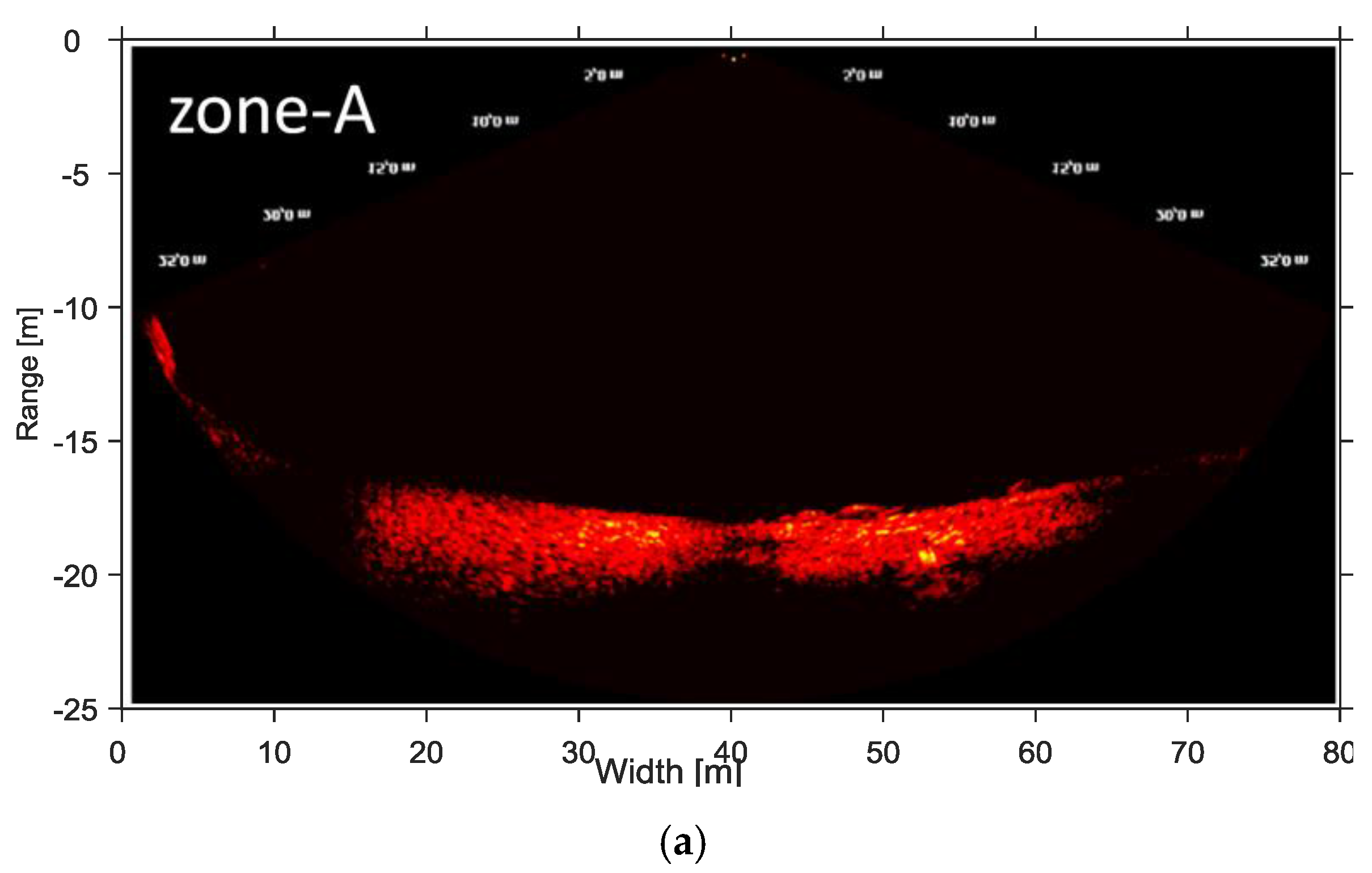
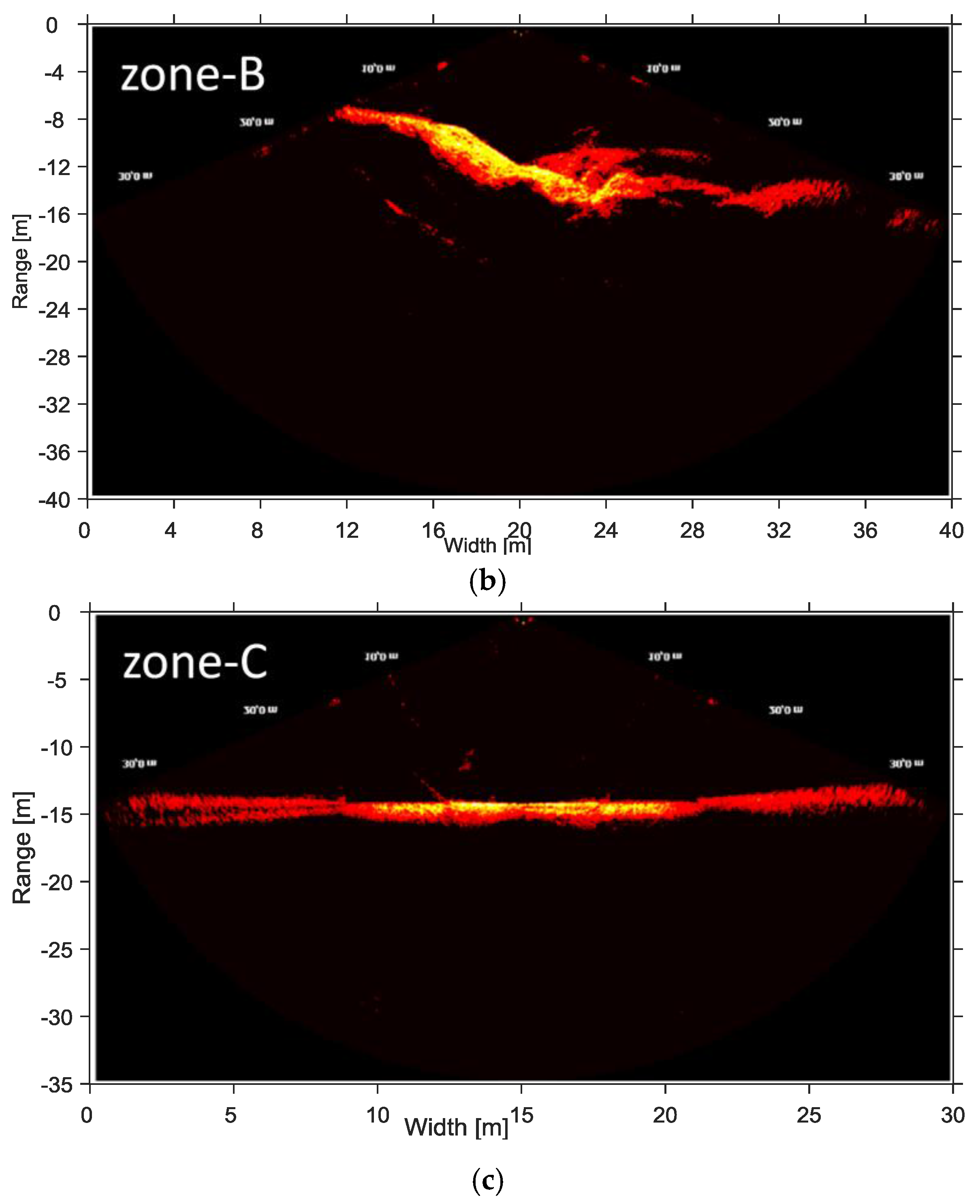
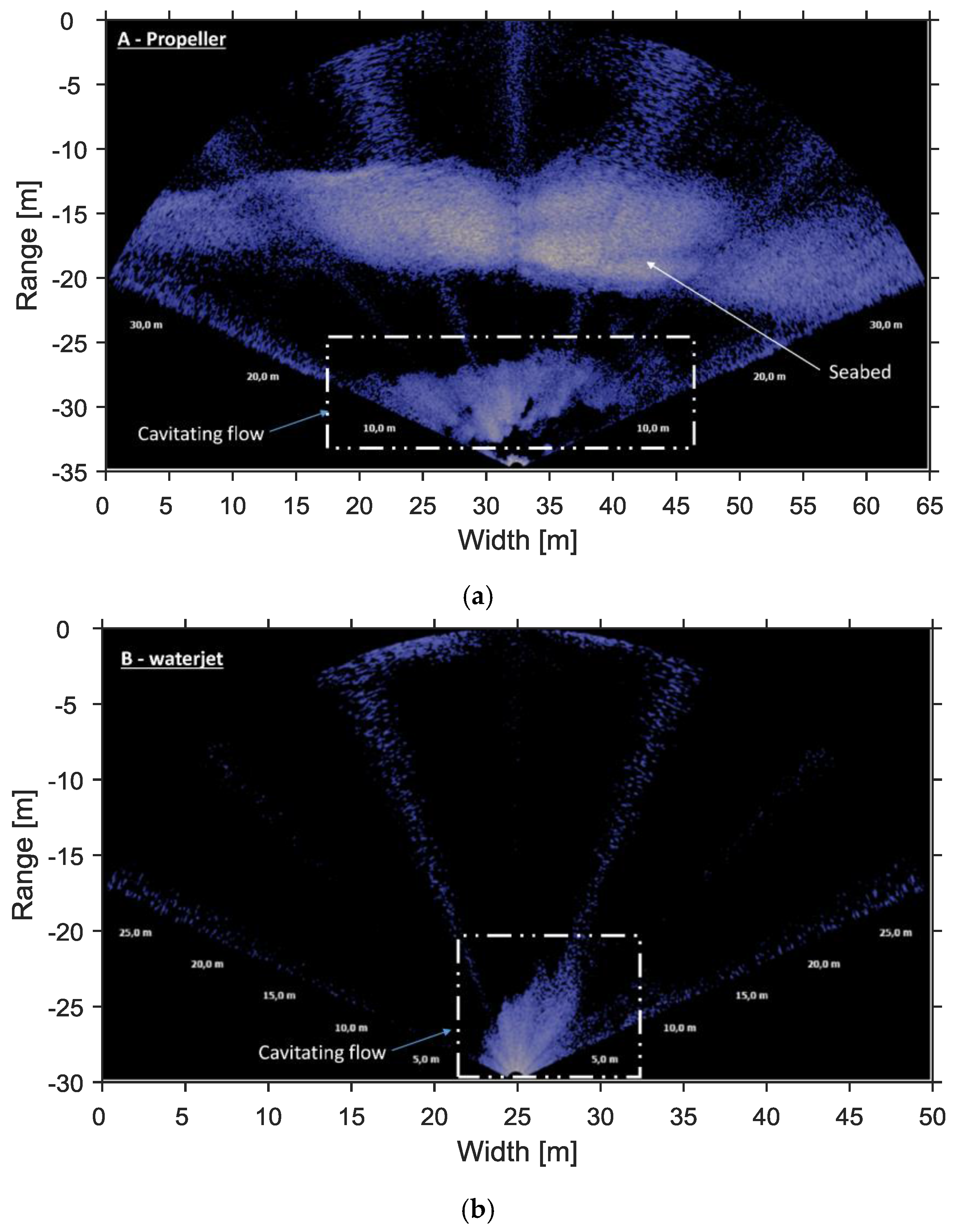
4.2. Cavitating Flow
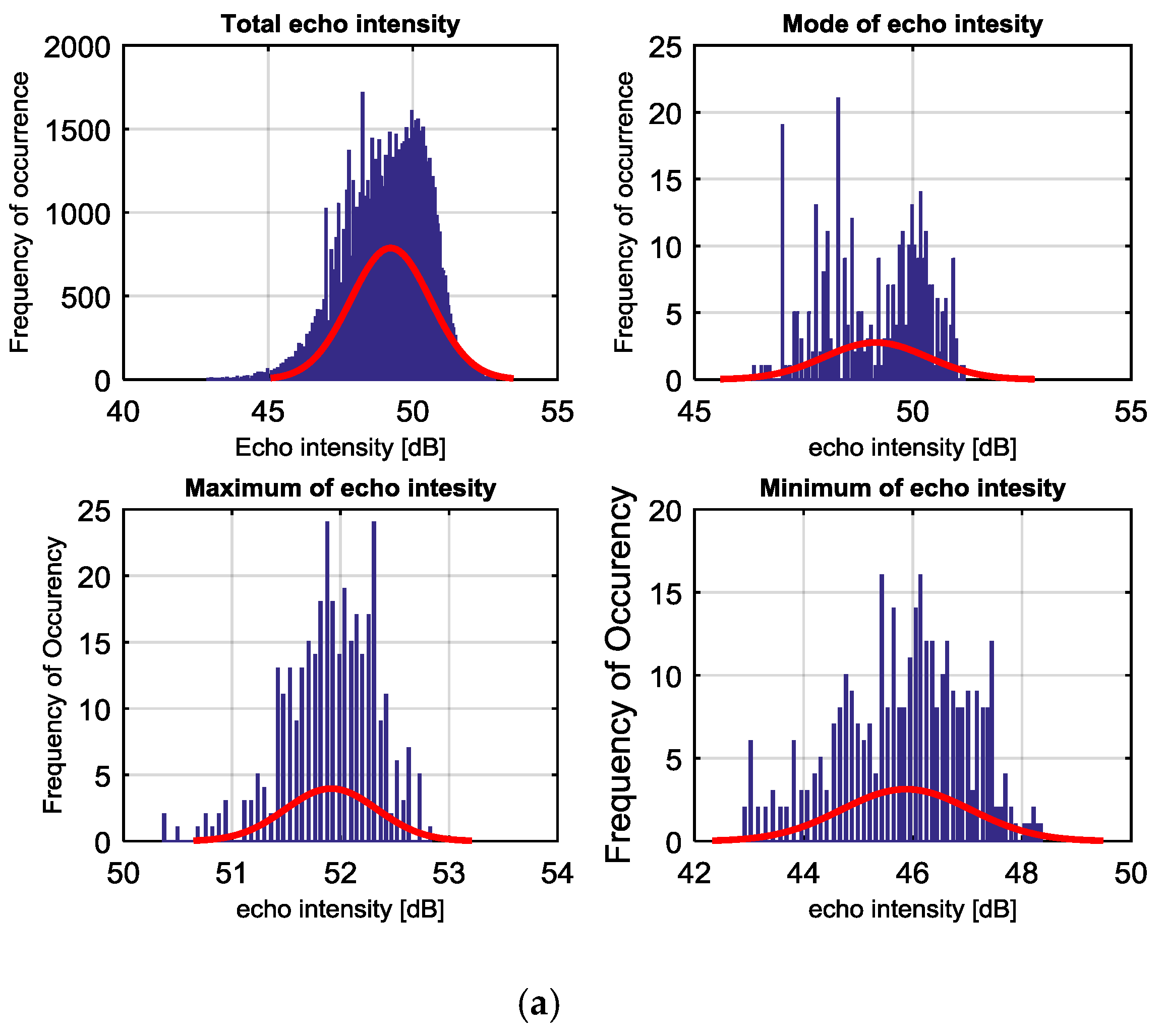
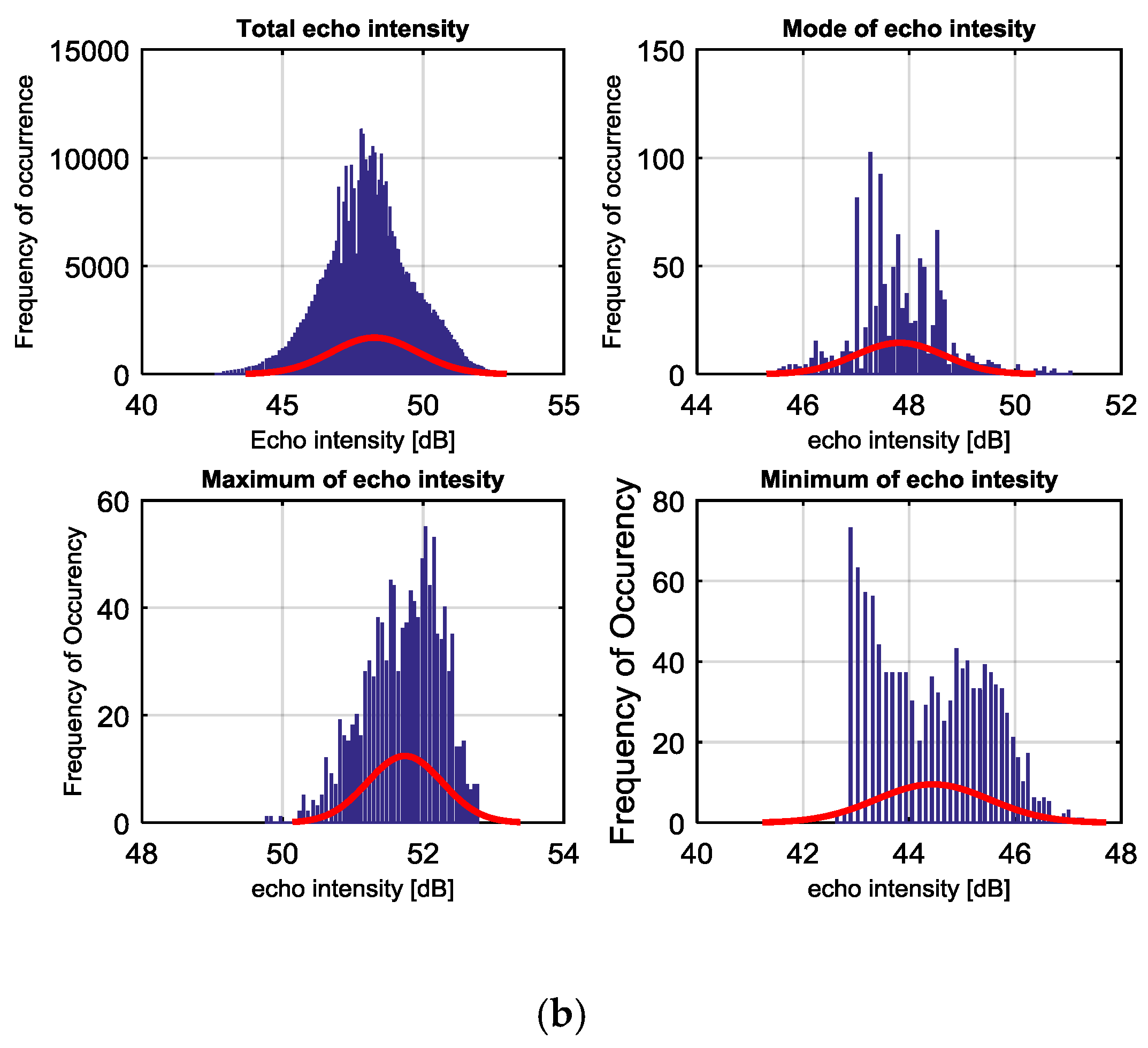
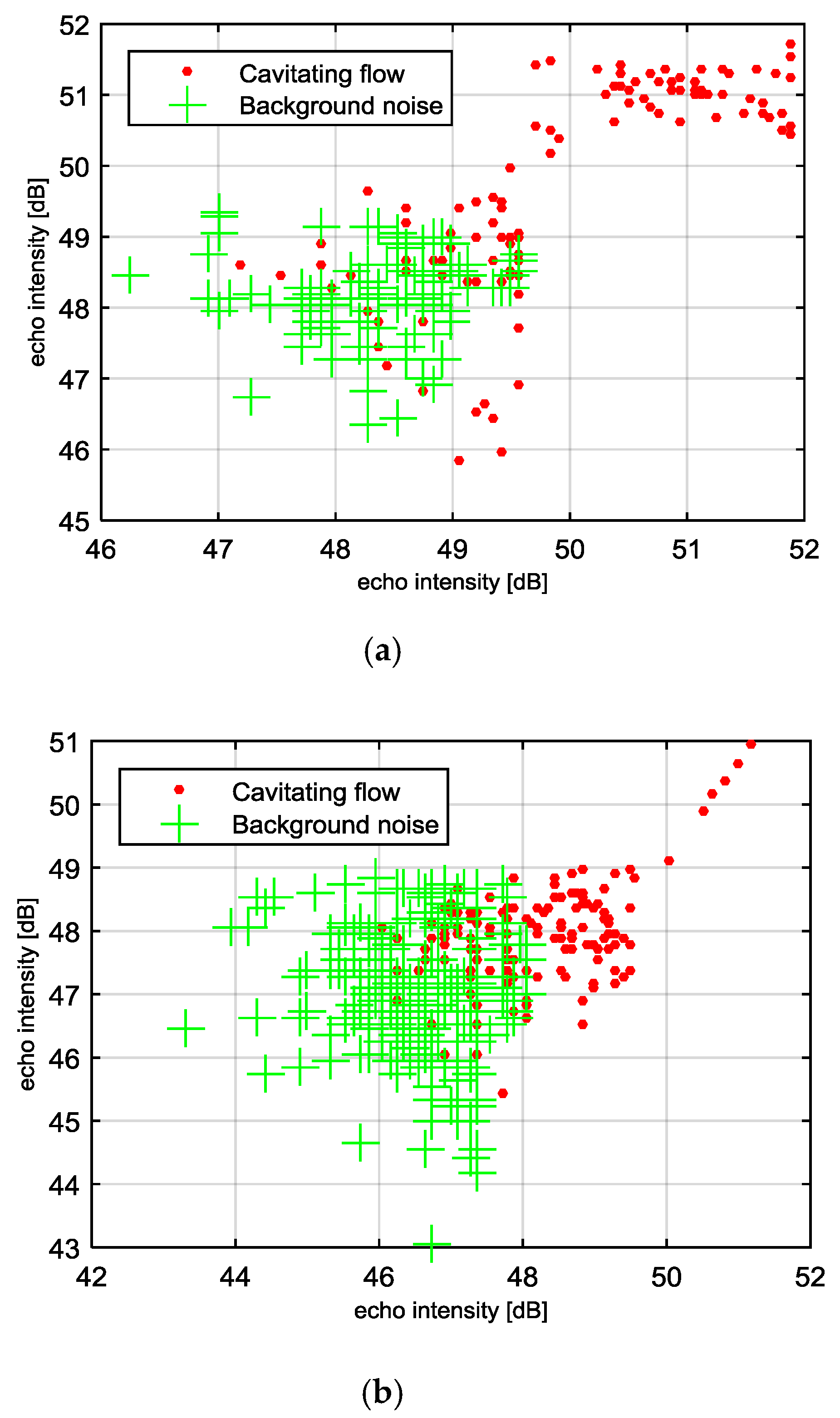
4.3. Intensity of Cavitating Flow
4.4. Discussion on Accuracy
5. Conclusions
6. Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornett, A.M. A Global Wave Energy Resource Assessment; Canadian Hydraulics Centre, National Research Council: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2014.
- De O. Falcão, A.F. Wave energy utilization: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.; Plummer, A.; Sahinkaya, M.N. A review of wave energy converter technology. J. Power Energy 2009, 223, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enferad, E.; Nazarpour, D. Ocean’s Renewable Power and Review of Technologies: Case Study Waves. New Dev. Renew. Energy 2013, 273–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, A.; Maingot, C.; Agor, M.; Nash, L.; Dixon, K. 3D Sonar Measurements in Wakes of Ships of Opportunity. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, K.A.; Fritz, H.M.; Yang, X. Evaluating the potential for energy extraction from turbines in the gulf stream system stream system. Renew. Energy 2014, 72, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Como, S.; Meas, P.; Stergiou, K.; Williams, J. Ocean Wave Energy Harvesting. Off-Shore Overtopping Design; Technical report for Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, B.O.; Lorang, M.S.; Sherman, D.J. Estimating boat-wake-induced levee erosion using sediment suspension measurements. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2002, 128, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, A.; Gravois, U.; Tian, M. Boat-wake statistics at Jensen Beach, Florida. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2013, 139, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurennoy, D.; Parnell, K.; Soomere, T. Fast-ferry generated waves in south-west Tallinn Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 16, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Didenkulova, I.; Sheremet, A.; Torsvik, T.; Soomere, T. Characteristic properties of different vessel wake signals. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codarin, A.; Wysocki, L.E.; Ladich, F.; Picciulin, M. Effects of ambient and boat noise on hearing and communication in three fish species living in a marine protected area (Miramare, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G. Noise in the sea and its impacts on marine organisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12304–12323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soloviev, A.; Gilman, M.; Young, K.; Brusch, S.; Lehner, S. Sonar measurements in ship wakes simultaneous with TerraSAR-X overpasses. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Whitfield, A.K.; Cowley, P.D.; Järnegren, J.; Næsje, T.F. Does boat traffic cause displacement of fish in estuaries? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammar, L. Power from the Brave New Ocean: Marine Renewable Energy and Ecological Risks. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Soomere, T. Nonlinear Components of Ship Wake Waves. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2007, 60, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medwin, H.; Clay, C.S. Chapter 8—Bubbles. In Fundamentals of Acoustical Oceanography; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 287–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhao, W.G.; Shao, X.M. A pressure-based algorithm for cavitating flow computations. J. Hydrodyn. 2011, 23, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenber, P. Cavitation. In Education Development Centre Inc.; Encyclopaedia Britannica Educational Corporation: Castle Hill, Australia, 1968; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, S. Cavitation: Causes, Effects, Mitigation and Application; Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute: Hartford, CT, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Caupin, F.; Herbert, E. Cavitation in water: A review. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2006, 7, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.; Polagye, B.; Durgesh, V.; Richmond, M.C. Measurements of turbulence at two tidal energy sites in puget sound, WA. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 37, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, G.D.; Cochrane, N.A. Multibeam Acoustic Detection of Fish and Water Column Targets at High-Flow Sites. Estuar. Coast. 2014, 38, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, S.; Forslund, J.; Carpman, N.; Grabbe, M.; Yuen, K.; Apelfröjd, S.; Goude, A.; Leijon, M. The Söderfors Project: Experimental Hydrokinetic Power Station Deployment and First Results. In Proceedings of the 10th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC), Aalborg, Denmark, 2–5 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, K.; Lundin, S.; Grabbe, M.; Lalander, E.; Goude, A.; Leijon, M. The Söderfors Project: Construction of an Experimental Hydrokinetic Power Station. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Utturkar, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Shyy, W. Recent progress in modeling of cryogenic cavitation for liquid rocket propulsion. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 558–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Shyy, W. Time-dependent turbulent cavitating flow computations with interfacial transport and filter-based models. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2005, 49, 739–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senocak, I.; Shyy, W. Interfacial dynamics-based modelling of turbulent cavitating flows, part-1: Model development and steady-state computations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2004, 44, 975–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, G.; Shyy, W. Modeling of turbulent, isothermal and cryogenic cavitation under attached conditions. Acta Mech. Sin. 2010, 26, 325–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M. Numerical Investigation on the Cavitating Flow in a Waterjet Pump; Chalmers University of Technology: Goteborg, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D. Technology evolution and advances in fisheries acoustics. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2011, 19, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Traynor, J.J.; Ehrenberg, J.E. Evaluation of the dual beam acoustic fish target strength measurement method. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1979, 36, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, J.J.; Ehrenberg, J.E. Fish and standard-sphere target-strength measurements obtained with a dual-beam and split-beam echo-sounding system. Cons. Perm. Int. Explor. Mer 1990, 189, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Kmeans. Available online: https://se.mathworks.com/help/stats/kmeans.html (accessed on 29 May 2017).
- MGN 372 (M+F) Offshore Renewable Energy Installations (OREIs): Guidance to Mariners Operating in the Vicinity of UK OREIs; Maritime and Coastguard Agency: Southampton, UK, 2008; p. 14.
| 1. |

| Ferry | M/S Värmdö | M/S Cinderella I |
|---|---|---|
| Thruster | Propeller | Waterjet |
| Capacity | 340 passengers | 350 passengers |
| Length | 37.7 m | 41.8 m |
| Width | 7.5 m | 7.7 m |
| Hull depth | 1.3 m | 1.1 m |
| Maximum speed | 22 knots | 30 knots |
| Engines | 3 of D2842 LE405, 1800 kW, diesel | 2 of MTU12V396TB83, 1050 kW, diesel |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francisco, F.; Carpman, N.; Dolguntseva, I.; Sundberg, J. Use of Multibeam and Dual-Beam Sonar Systems to Observe Cavitating Flow Produced by Ferryboats: In a Marine Renewable Energy Perspective. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030030
Francisco F, Carpman N, Dolguntseva I, Sundberg J. Use of Multibeam and Dual-Beam Sonar Systems to Observe Cavitating Flow Produced by Ferryboats: In a Marine Renewable Energy Perspective. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2017; 5(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancisco, Francisco, Nicole Carpman, Irina Dolguntseva, and Jan Sundberg. 2017. "Use of Multibeam and Dual-Beam Sonar Systems to Observe Cavitating Flow Produced by Ferryboats: In a Marine Renewable Energy Perspective" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 5, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030030
APA StyleFrancisco, F., Carpman, N., Dolguntseva, I., & Sundberg, J. (2017). Use of Multibeam and Dual-Beam Sonar Systems to Observe Cavitating Flow Produced by Ferryboats: In a Marine Renewable Energy Perspective. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 5(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse5030030






