The Validation of a New GSTA Case in a Dynamic Coastal Environment Using Morphodynamic Modelling and Bathymetric Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Gaining a deeper understanding of shoreline changes on Rossbeigh and Inch by examining alternative data sources including satellite imagery.
- Undertaking regular topographic surveys to document the evolution of the breach area and Rossbeigh.
- Characterising the wave climate and tidal current regime of Dingle Bay.
- Conducting seasonal bathymetry surveys to identify where sediment is being transported to.
- Investigate the applicability of novel and experimental methods on Inner Dingle Bay’s Barriers such as Grain Size Trend Analysis, Surface Wave Radar Monitoring and Sediment Dye Testing
- (1)
- Establishing tangible sediment pathways to provide another insight into the morphology of Rossbeigh.
- (2)
- Provide a case study into the accuracy and applicability of the GSTA method in inlet-ebb tidal bar scenario.
2. Background
- Finer, Better Sorted, Positively Skewed (FB+)
- Finer, Poorer Sorted, Negatively Skewed (FP−)
- Finer, Better Sorted, Negatively Skewed (FB−)
- Finer, Poorer Sorted, Positively Skewed (FP+)
- Coarser, Better Sorted, Positively Skewed (CB+)
- Coarser, Poorer Sorted, Negatively Skewed (CP−)
- Coarser, Better Sorted, Negatively Skewed (CB−)
- Coarser, Poorer Sorted, Positively Skewed (CP+)
3. Environmental Setting
4. Experimental Setup
- Zm = Depth of Disturbance
- Hb = Breaking wave height
4.1. Sediment Sieving Analysis
4.2. Numerical Model Set up
4.2.1. Model Domain and Boundary Conditions
- t = time
- x = (x, y) Cartesian co = ordinates
- v = (cx, cy, cσ, cθ) the propagation velocity of a wave group in four dimensional space
- S = the source term for energy balance equation
- V = is the four dimensional operator in the x, σ,θ-space
- K0 = 42
- Kswell = swell correction factor for swell waves <2 m, Kswell = Tswell/Tref
- Kgrain = particle size correction factor
- Kslope = bed slope correction factor
- Veff.L = effective longshore velocity for tidal velocity component and wave induced velocity component.
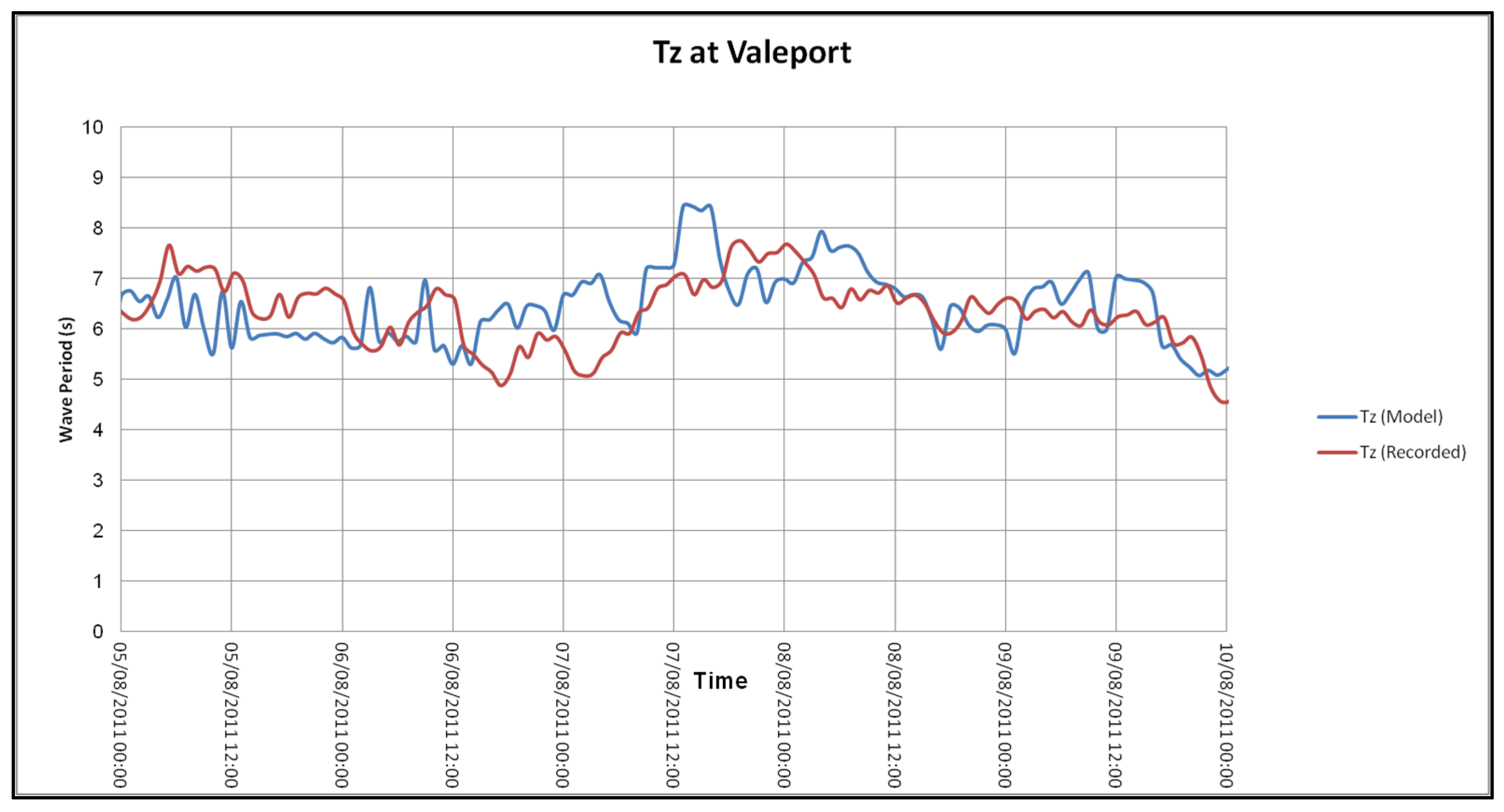
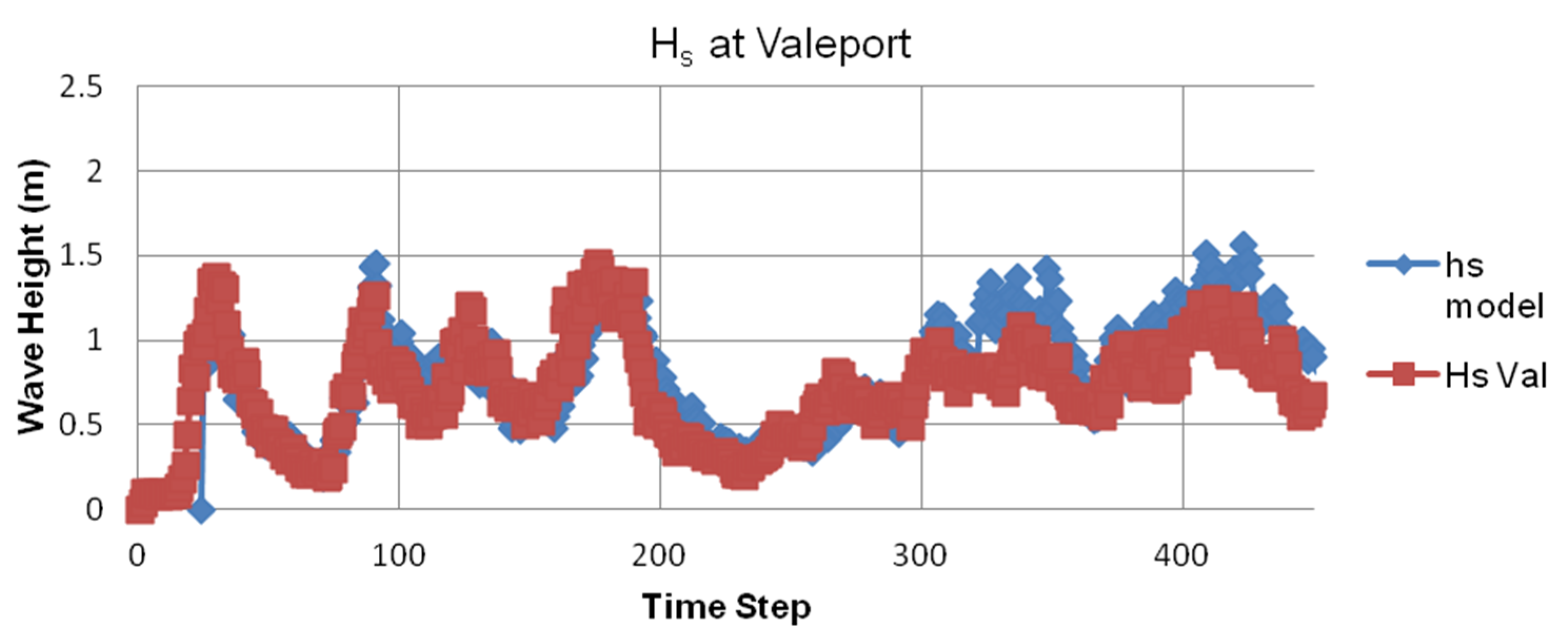
4.2.2. Model Validation
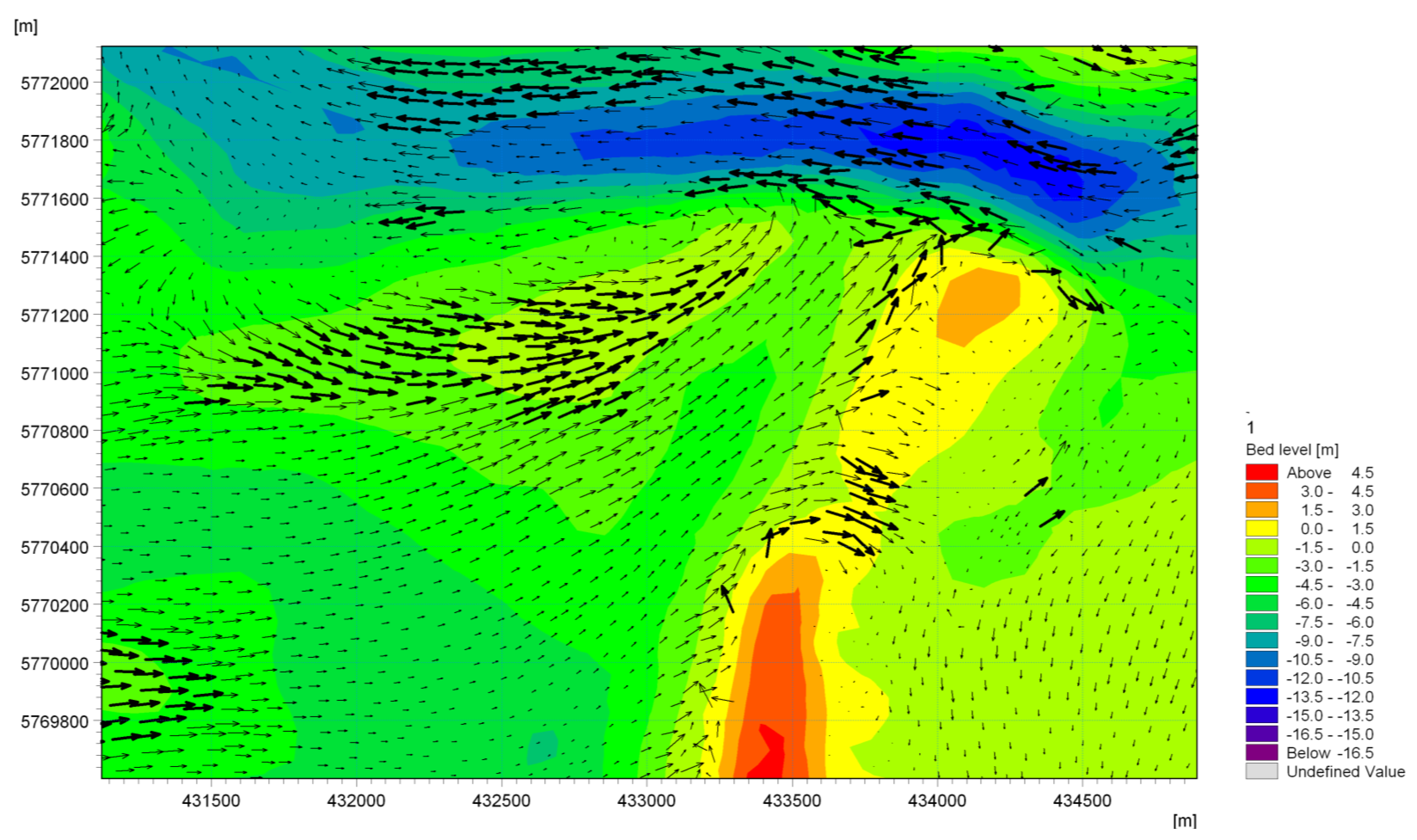
4.2.3. Sediment Transport and Morphology
5. Results and Discussion
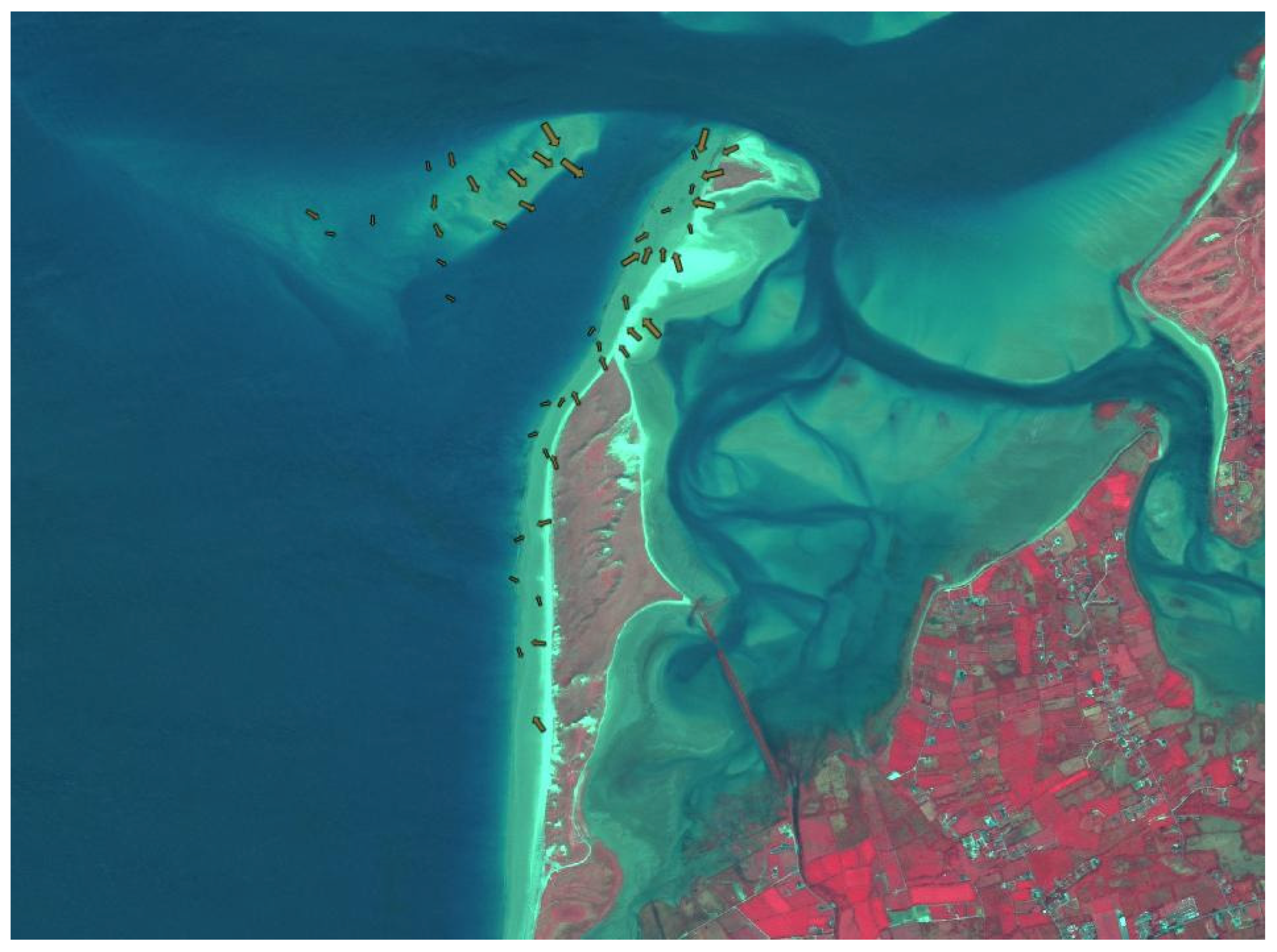
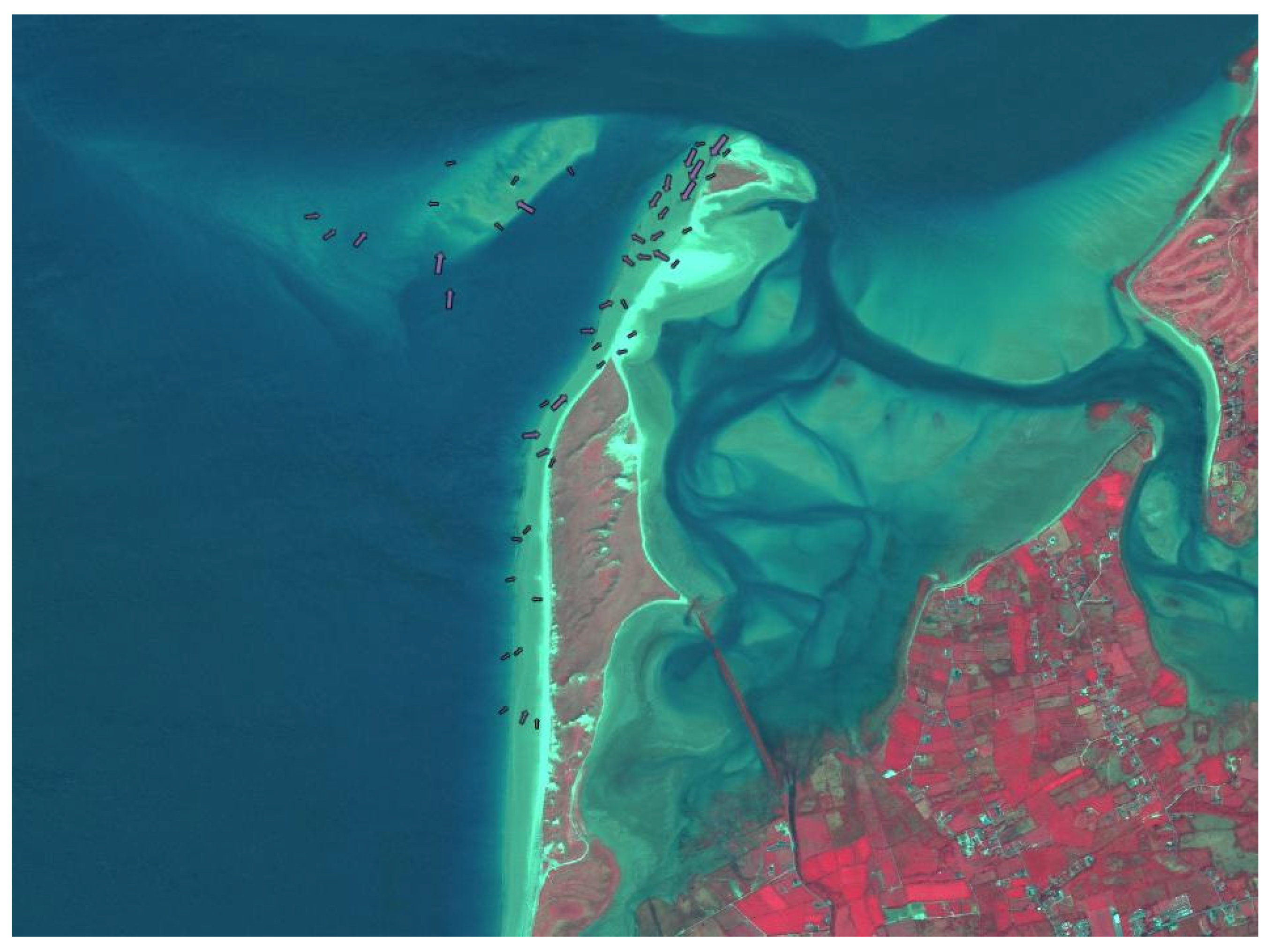
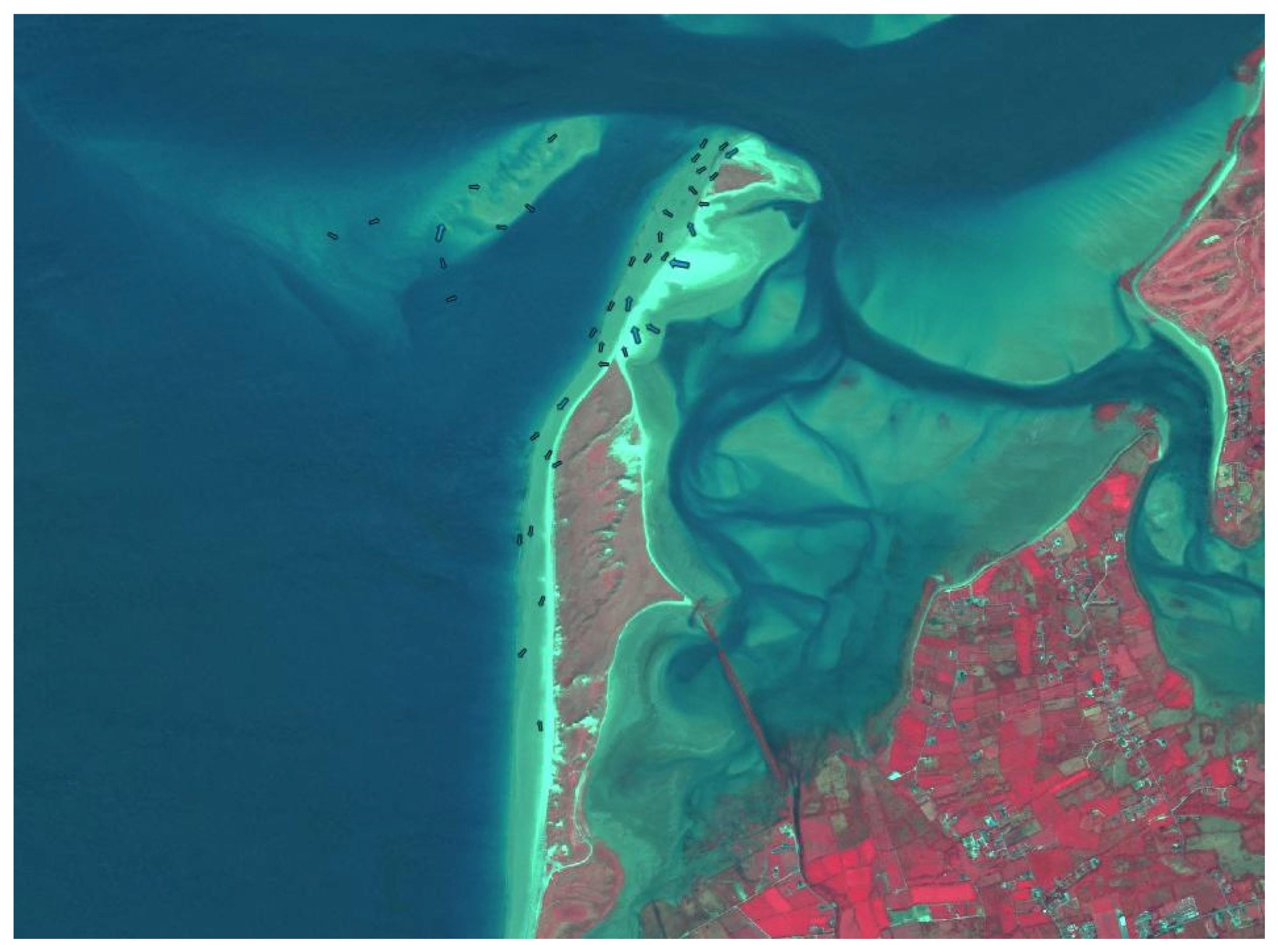
5.1. Grain Size Trend Analysis Results
5.2. Comparison with Sediment Transport Simulations
6. Further Work
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- December Ordinary Meeting Minutes; Kerry County Council: County Kerry, Ireland, 2009; p. 58.
- High Tides Bring Food Threat. The Kerrys Eye, 11 November 2010; 8.
- Krumbein, W.C.; Pettijohn, F.J. Manual of Sedimentary Petrography; Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York, NY, USA, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, P. An interpretation of trends in grain size measures. J. Sediment. Res. 1981, 51, 611–624. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Collins, M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends, based upon definition of “transport vectors”. Sediment. Geol. 1992, 80, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoux, J.P. An alternative approach to the identification of the end sediment transport paths based on grain size trends. Sediment. Geol. A 1994, 94, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, S.; Ballay, A. Grain-size trend analysis for the determination of non-biogenic sediment transport pathways on the Kwinte Bank (southern North Sea), in relation to sand dredging. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 51, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Poizot, E.; Méar, Y. ECSedtrend: A new software to improve sediment trend analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poizot, E.; Méar, Y. Using a GIS to enhance grain size trend analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, P. Morphodynamic Evolution of a Tidal Inlet Mid-bay Barrier System. Master’s Thesis, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vial, T. Monitoring the Morphological Response of an Embayed High Energy Beach To Storms and Atlantic Waves. Master’s Thesis, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.; Jackson, N.L.; Nordstrom, K.F. Depth of activation on a mixed sediment beach. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHI. MIKE 21: Sediment Transport and Morphological Modelling—User Guide; DHI Water and Environment: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2007; p. 388. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Principles of Coastal Morphology; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, M.; Murphy, J. Predicting and Monitoring the Evolution of a Coastal Barrier Dune System Postbreaching. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
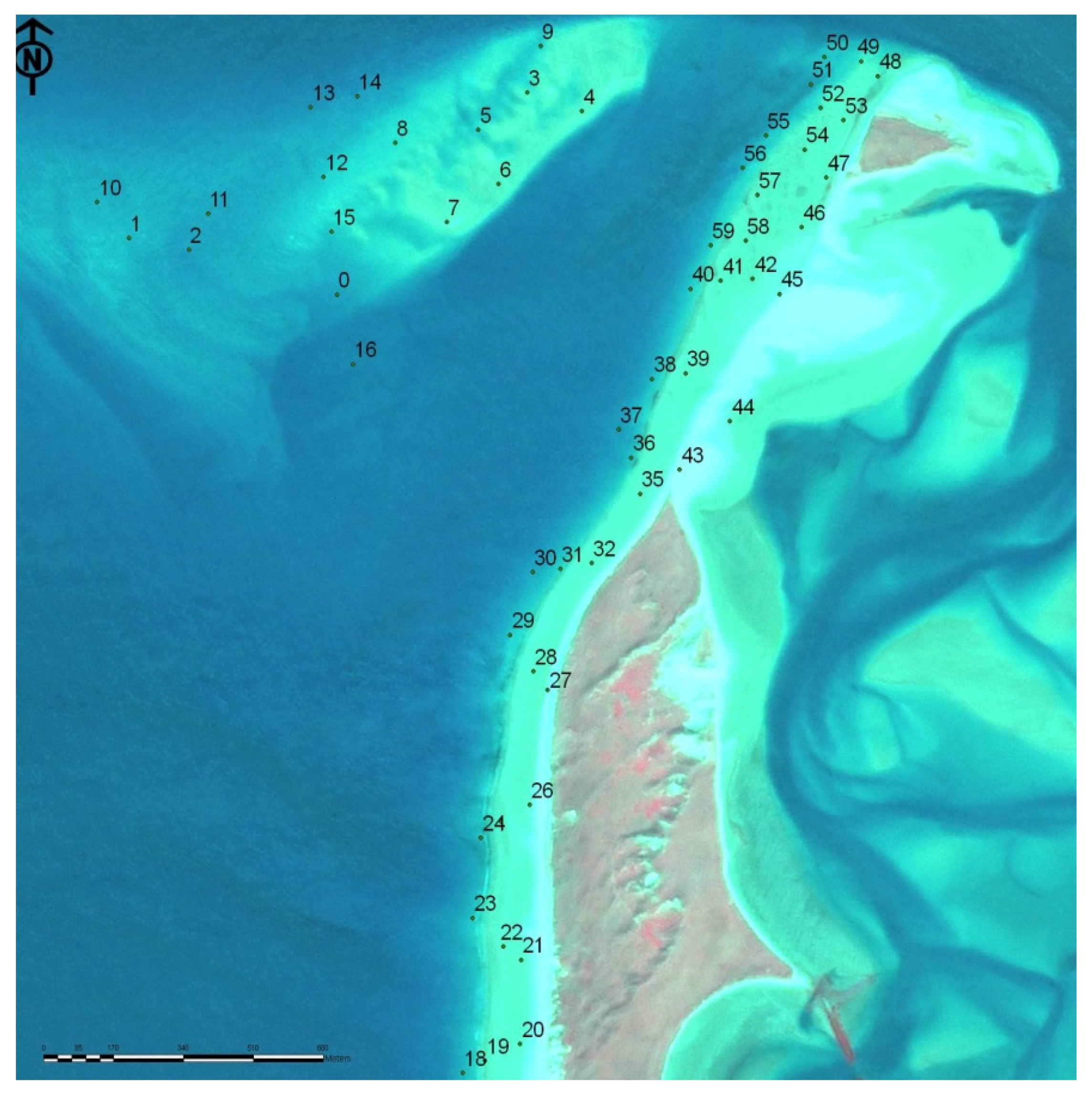
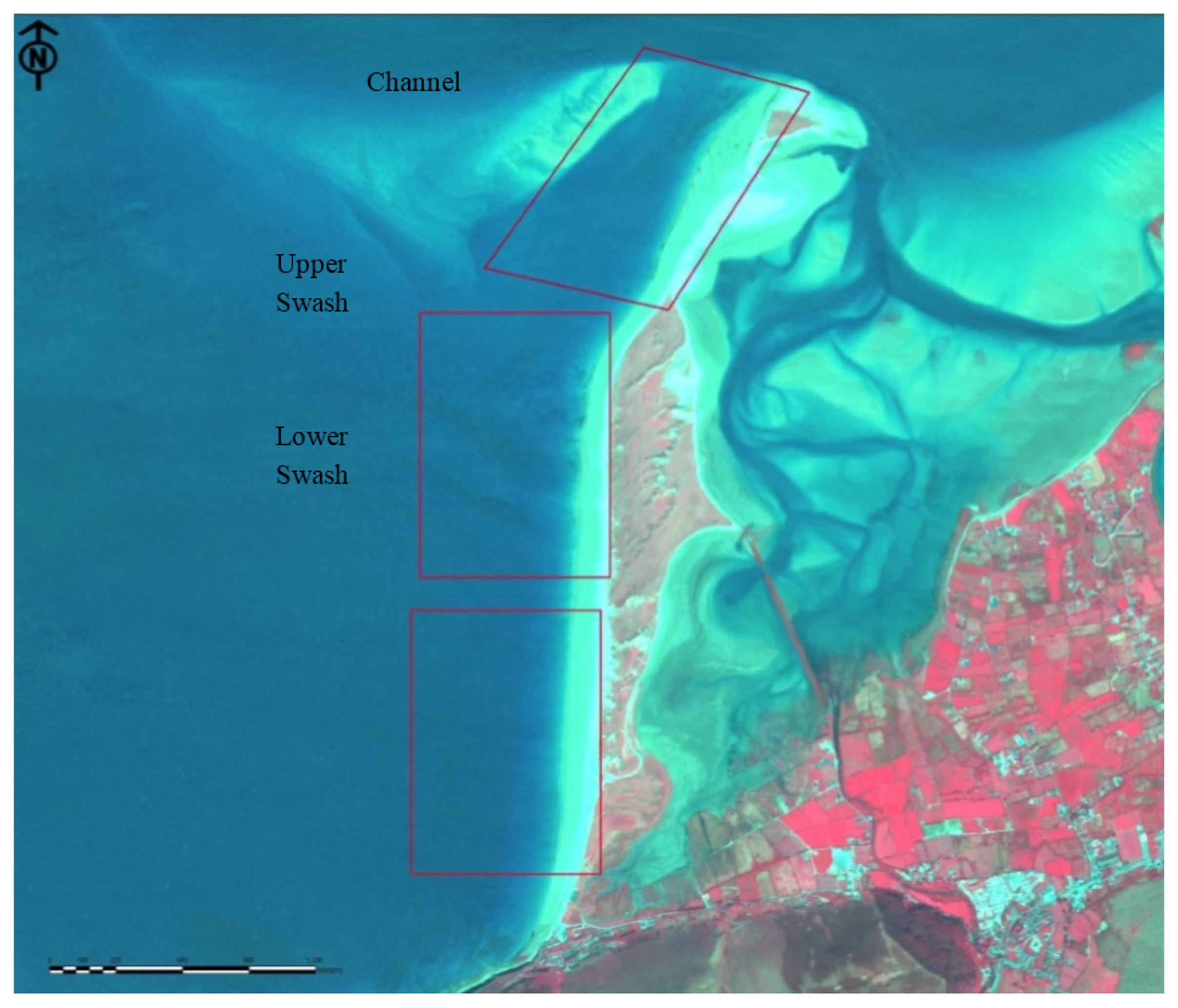
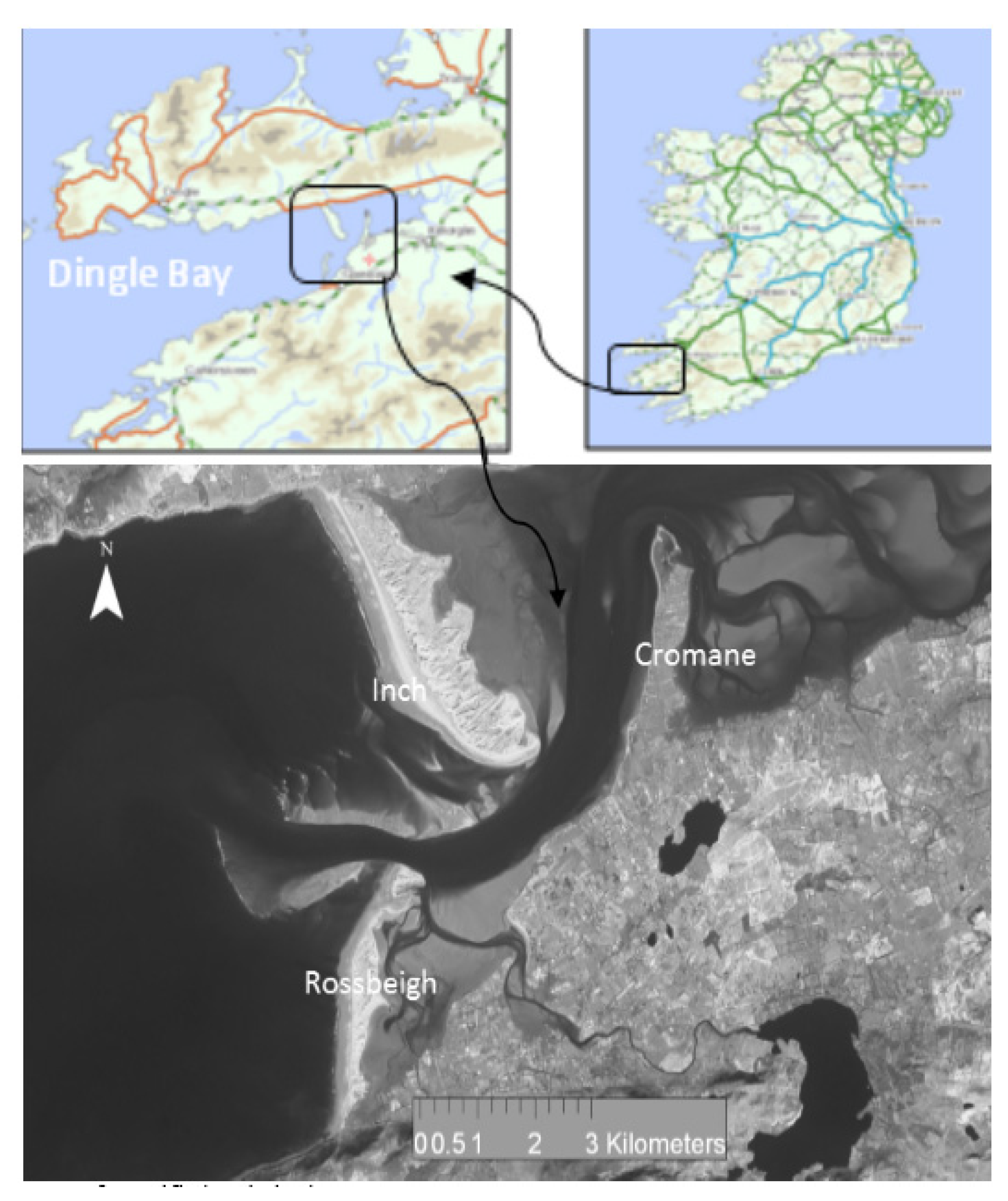

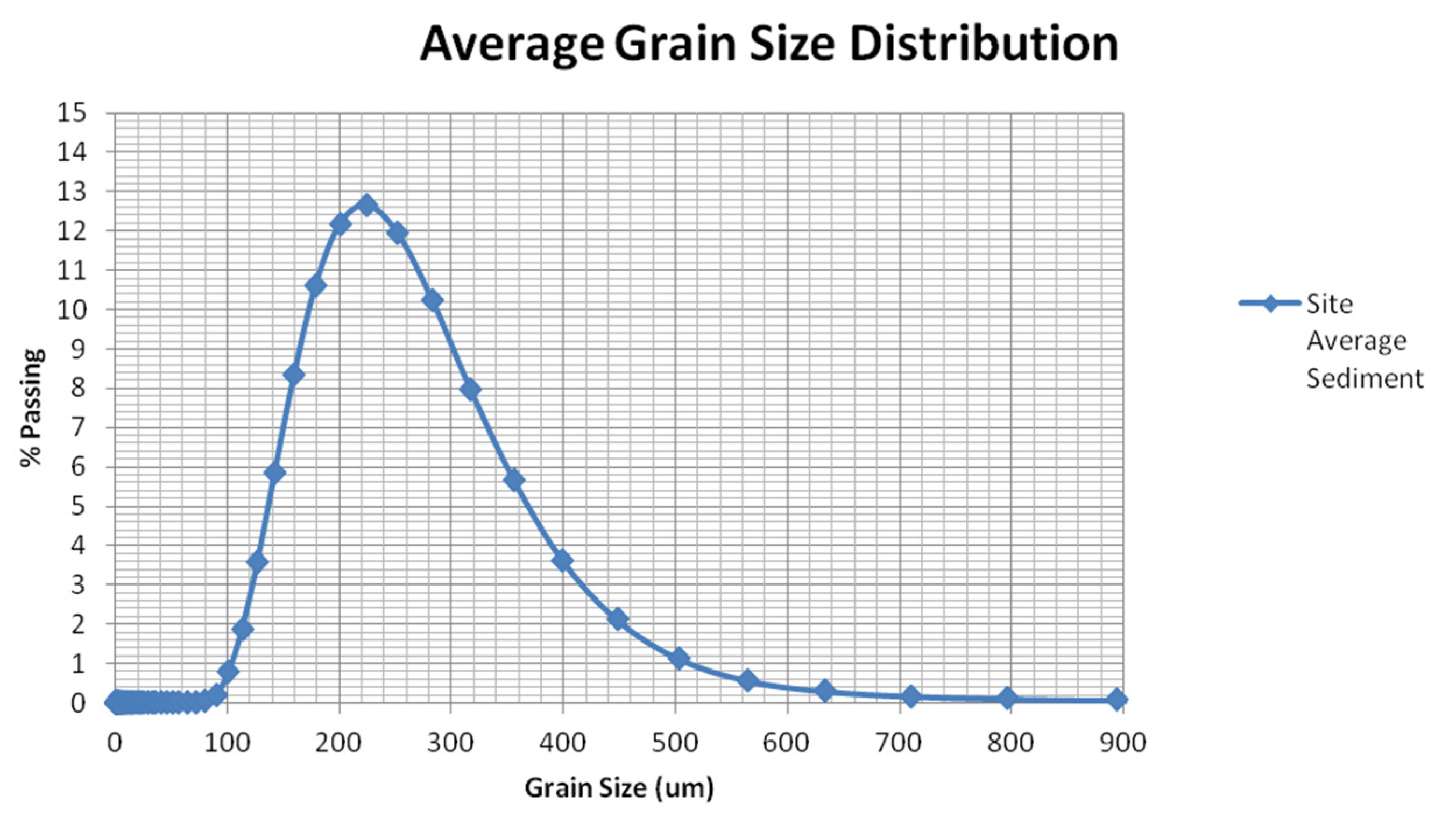
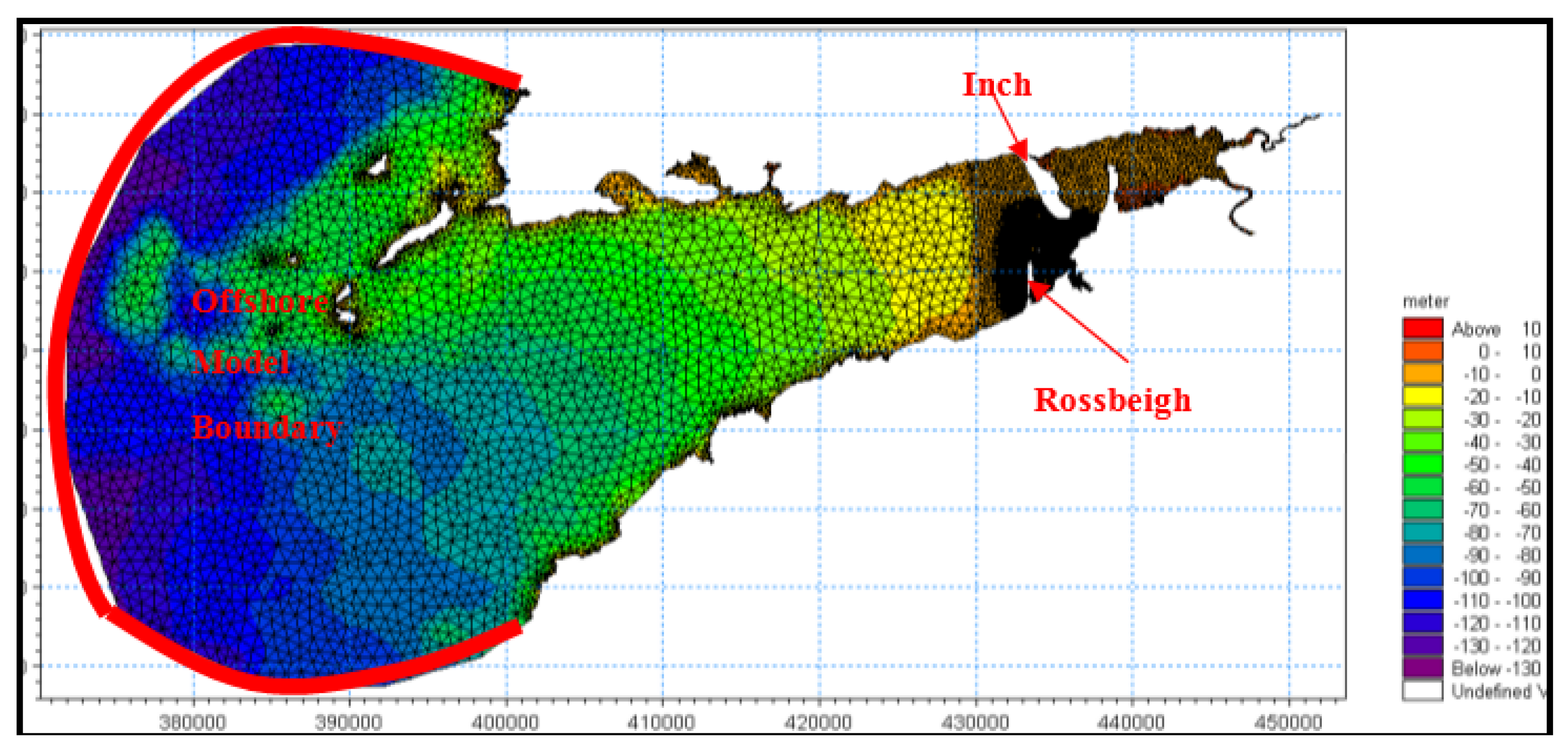
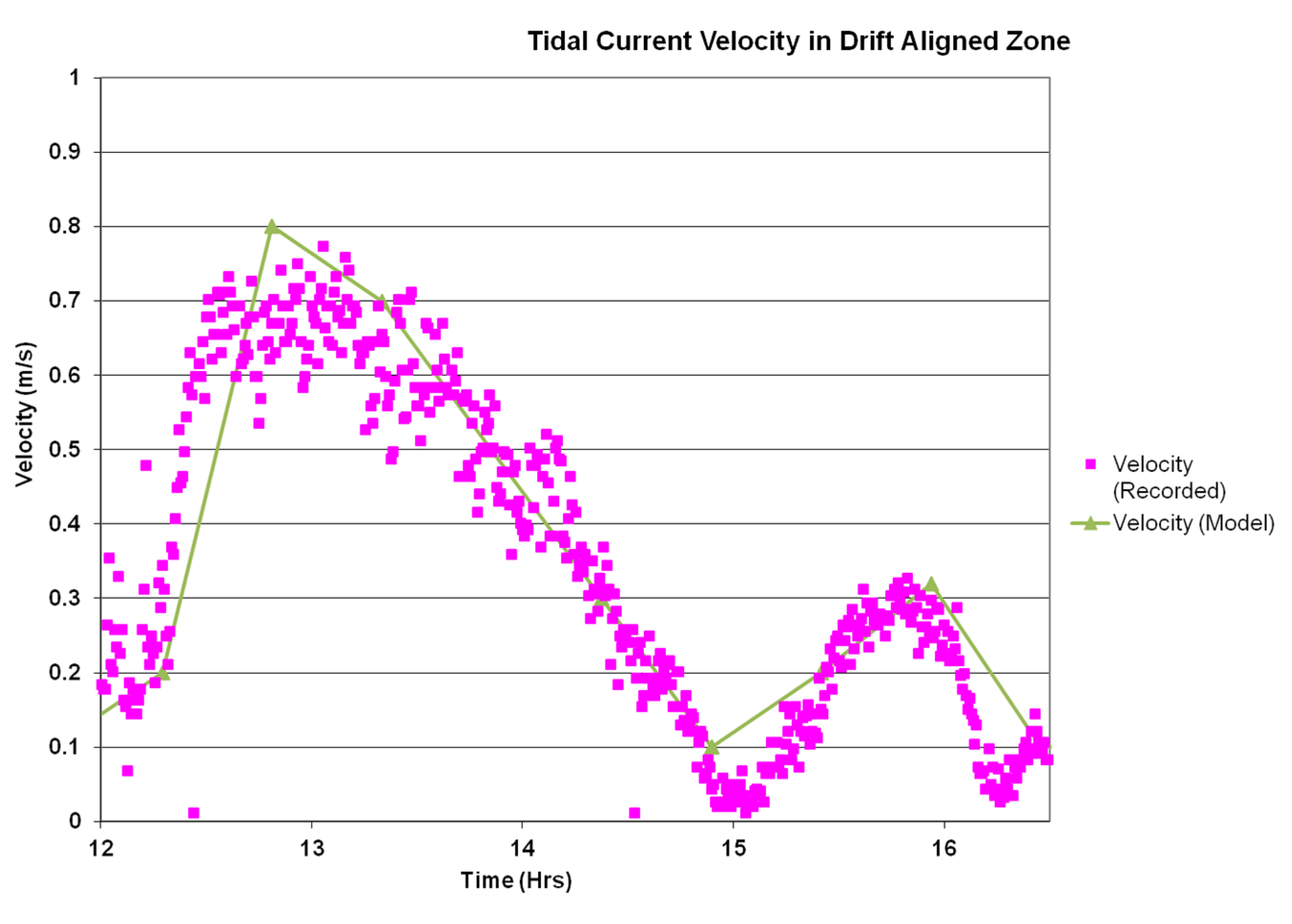


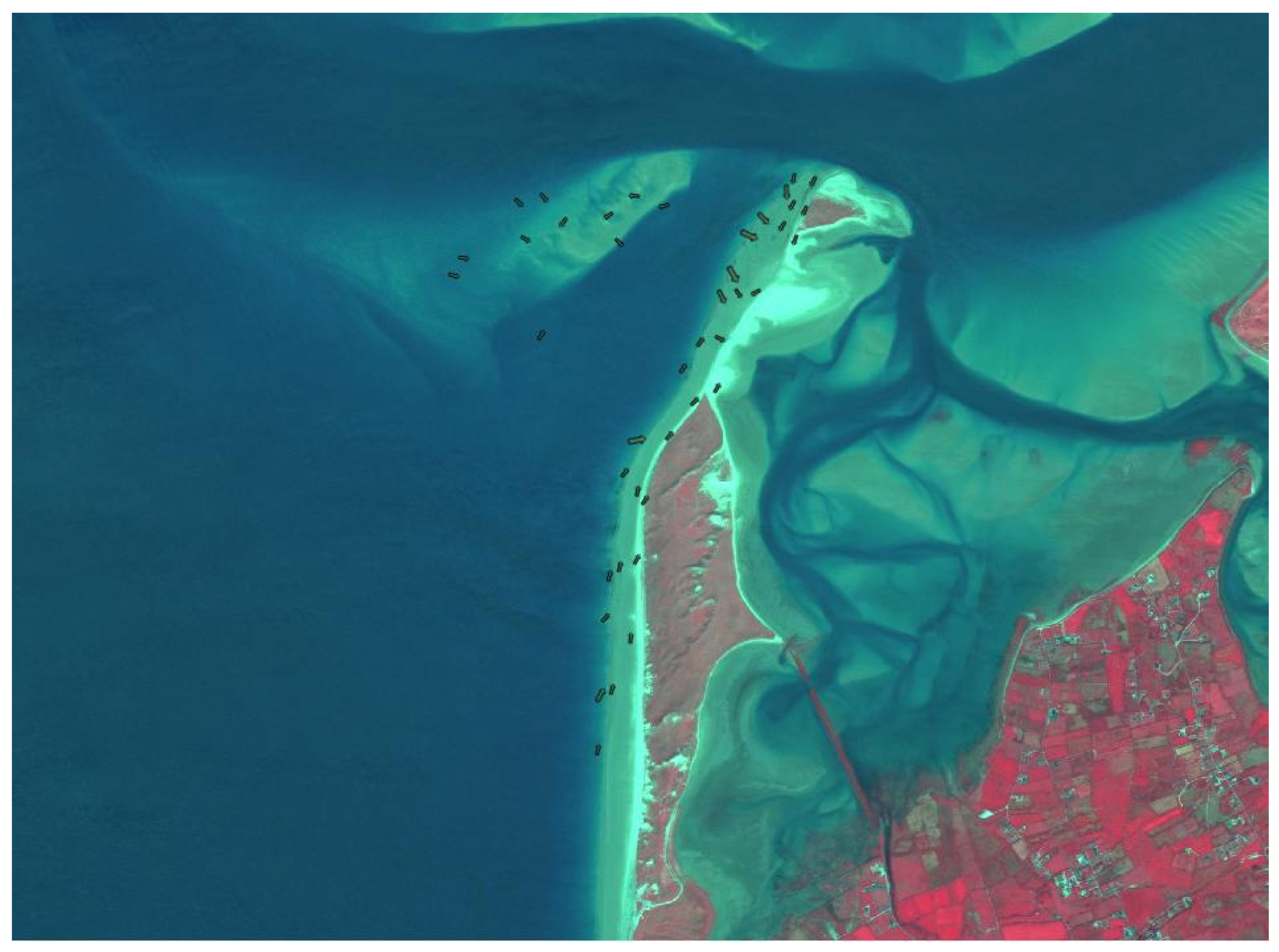


| Location | Easting | Northing | Mean | Sorting (σɸ) | Skewness (SKɸ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 464191 | 594426 | 1.861 | 0.411 | −0.028 |
| 1 | 463685 | 594556 | 1.956 | 0.406 | −0.020 |
| 2 | 463831 | 594530 | 1.906 | 0.413 | −0.033 |
| 3 | 464653 | 594893 | 2.206 | 0.407 | −0.013 |
| 4 | 464787 | 594851 | 2.022 | 0.370 | −0.013 |
| 5 | 464535 | 594807 | 2.050 | 0.369 | −0.013 |
| 6 | 464583 | 594682 | 1.959 | 0.405 | −0.023 |
| 7 | 464458 | 594593 | 2.006 | 0.367 | −0.020 |
| 8 | 464333 | 594777 | 2.020 | 0.369 | −0.008 |
| 9 | 464686 | 595001 | 2.159 | 0.365 | −0.009 |
| 10 | 463607 | 594640 | 1.994 | 0.404 | −0.015 |
| 11 | 463877 | 594614 | 2.109 | 0.382 | −0.006 |
| 12 | 464158 | 594699 | 2.051 | 0.383 | −0.013 |
| 13 | 464127 | 594860 | 2.234 | 0.368 | −0.013 |
| 14 | 464240 | 594885 | 2.229 | 0.369 | −0.019 |
| 15 | 464177 | 594571 | 2.009 | 0.365 | −0.004 |
| 16 | 464230 | 594265 | 2.011 | 0.613 | −0.600 |
| 17 | 464484.6 | 592379.5 | 2.015 | 0.607 | −0.640 |
| 18 | 464496.9 | 592623.3 | 2.006 | 0.516 | −0.148 |
| 19 | 464551.4 | 592652.2 | 2.147 | 0.410 | −0.009 |
| 20 | 464636.1 | 592690 | 1.977 | 0.492 | −0.052 |
| 21 | 464638.2 | 592885.3 | 1.310 | 0.736 | 0.040 |
| 22 | 464596 | 592915.8 | 2.070 | 0.486 | −0.044 |
| 23 | 464520.1 | 592982.3 | 1.896 | 0.537 | −0.146 |
| 24 | 464540.8 | 593167.8 | 1.832 | 0.593 | −0.282 |
| 25 | 464589.6 | 593205.3 | 2.111 | 0.406 | −0.013 |
| 26 | 464659.6 | 593243.8 | 1.920 | 0.445 | −0.011 |
| 27 | 464703.3 | 593510.7 | 1.869 | 0.483 | −0.050 |
| 28 | 464668.2 | 593553.9 | 1.855 | 0.512 | −0.066 |
| 29 | 464612.2 | 593637.6 | 1.927 | 0.515 | −0.130 |
| 30 | 464666.8 | 593782.7 | 1.847 | 0.471 | −0.041 |
| 31 | 464734.2 | 593791.2 | 2.085 | 0.441 | −0.007 |
| 32 | 464809.7 | 593804.1 | 1.744 | 0.662 | −0.256 |
| 33 | 464578.3 | 592351.6 | 2.055 | 0.450 | −0.030 |
| 34 | 464630.9 | 592321.4 | 1.912 | 0.450 | −0.015 |
| 35 | 464928.4 | 593964.5 | 1.869 | 0.445 | −0.019 |
| 36 | 464906.4 | 594048.3 | 1.829 | 0.533 | −0.139 |
| 37 | 464875.5 | 594113.2 | 1.714 | 0.559 | −0.158 |
| 38 | 464957.2 | 594230.4 | 1.900 | 0.445 | −0.019 |
| 39 | 465038.2 | 594243.7 | 1.965 | 0.447 | −0.033 |
| 40 | 465050.7 | 594439.2 | 1.883 | 0.453 | −0.037 |
| 41 | 465124.4 | 594457.5 | 1.903 | 0.481 | −0.050 |
| 42 | 465201.9 | 594462.5 | 1.897 | 0.453 | −0.012 |
| 43 | 465024.3 | 594020.2 | 1.911 | 0.404 | −0.001 |
| 44 | 465146.6 | 594132.2 | 1.876 | 0.406 | −0.012 |
| 45 | 465266.6 | 594427.5 | 1.879 | 0.409 | −0.010 |
| 46 | 465320.9 | 594581.3 | 1.762 | 0.498 | −0.015 |
| 47 | 465380.5 | 594697.2 | 1.918 | 0.409 | −0.009 |
| 48 | 465505.6 | 594932 | 1.808 | 0.451 | −0.019 |
| 49 | 465465.9 | 594966.4 | 1.781 | 0.529 | −0.256 |
| 50 | 465376.7 | 594976.2 | 1.966 | 0.427 | −0.029 |
| 51 | 465343.1 | 594912.4 | 1.844 | 0.513 | −0.101 |
| 52 | 465367 | 594857.7 | 1.728 | 0.574 | −0.120 |
| 53 | 465423 | 594829.4 | 1.915 | 0.446 | −0.022 |
| 54 | 465328.4 | 594761.7 | 1.759 | 0.505 | −0.058 |
| 55 | 465234.4 | 594793.4 | 1.803 | 0.578 | −0.366 |
| 56 | 465177.4 | 594719.7 | 1.879 | 0.587 | −0.318 |
| 57 | 465213.4 | 594656.9 | 1.787 | 0.455 | −0.042 |
| 58 | 465184.5 | 594550 | 1.680 | 0.467 | −0.044 |
| 59 | 465099.8 | 594539.7 | 2.017 | 0.475 | −0.049 |
| Dmean (µm) | ||||
| Total | Bar | Swash | Drift | |
| Max | 297 | 287 | 274 | 297 |
| Min | 210 | 220 | 210 | 220 |
| Avg | 255 | 252 | 243 | 260 |
| Sorting (σ) | ||||
| Total | Bar | Swash | Drift | |
| Max | 150 | 140 | 137 | 150 |
| Min | 57 | 57 | 60 | 68 |
| Avg | 88 | 73 | 92 | 92 |
| Skewness (SKa) | ||||
| Total | Bar | Swash | Drift | |
| Max | 4.16 | 4.09 | 4.16 | 2.89 |
| Min | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.73 | 0.71 |
| Avg | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.39 | 1.11 |
| Module | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| HD | Eddy Viscosity—Smagorinsky | 0.28 |
| Bed Resistance (Manning) | 32 m3·s−1 | |
| ST | Porosity | 0.4 |
| grain size | 0.25 | |
| Bank erosion slope failure | 30 Deg angle of repose | |
| SW | Spectral | Fully spectral |
| Time | Interstationary | |
| Spectral discretisation | 25 frequencies, min of 0.055 Hz | |
| Directional discretisation | 16 over 360 Deg rose | |
| Wave breaking | Gamma of 0.8 Alpha 1 | |
| White capping | 4.5—constant | |
| Directional Spreading Index | 4 |
| Location | Cut (m3) | Fill (m3) | Balance (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel | Survey | ||
| −60212 | 120106 | 59894 | |
| Model | |||
| −69210 | 114697 | 45487 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Shea, M.; Murphy, J. The Validation of a New GSTA Case in a Dynamic Coastal Environment Using Morphodynamic Modelling and Bathymetric Monitoring. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010027
O’Shea M, Murphy J. The Validation of a New GSTA Case in a Dynamic Coastal Environment Using Morphodynamic Modelling and Bathymetric Monitoring. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2016; 4(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Shea, Michael, and Jimmy Murphy. 2016. "The Validation of a New GSTA Case in a Dynamic Coastal Environment Using Morphodynamic Modelling and Bathymetric Monitoring" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 4, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010027
APA StyleO’Shea, M., & Murphy, J. (2016). The Validation of a New GSTA Case in a Dynamic Coastal Environment Using Morphodynamic Modelling and Bathymetric Monitoring. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 4(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4010027





