Parametrization of Seabed Liquefaction for Nonlinear Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Formulation and Verification
2.1. Formulation of Nonlinear Wave Pressure
2.2. Seabed Response Model
2.3. Boundary Condition
2.3.1. Seabed Lateral and Bottom Boundary Conditions
2.3.2. Wave–Seabed Interface Boundary Conditions
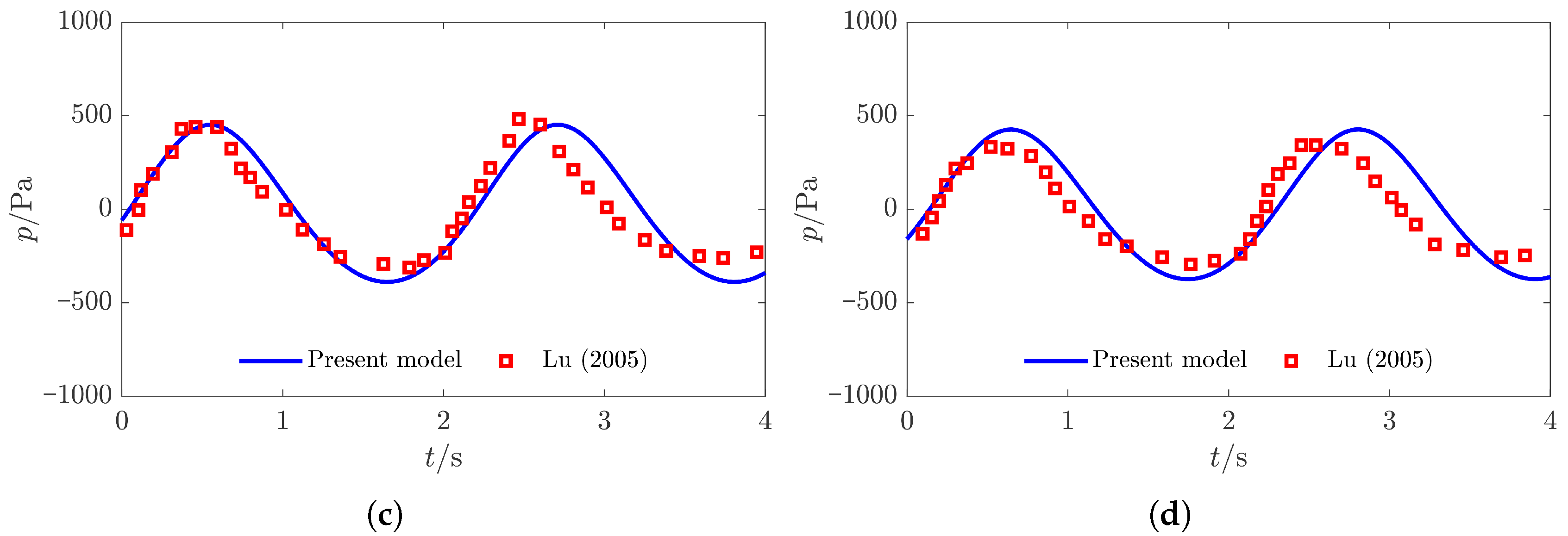
2.4. Model Verification
2.4.1. Parameter Setting
2.4.2. Vertical Distribution of Pore Water Pressure in a Sandy Seabed Under Progressive Waves
2.4.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Pore Water Pressure Under Cnoidal Wave Action
2.4.4. Vertical Distribution of Pore Pressure and Soil Stress Under Linear Wave Action
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study on Seabed Response and Instantaneous Liquefaction Under Asymmetric Wave Pressure Acceleration
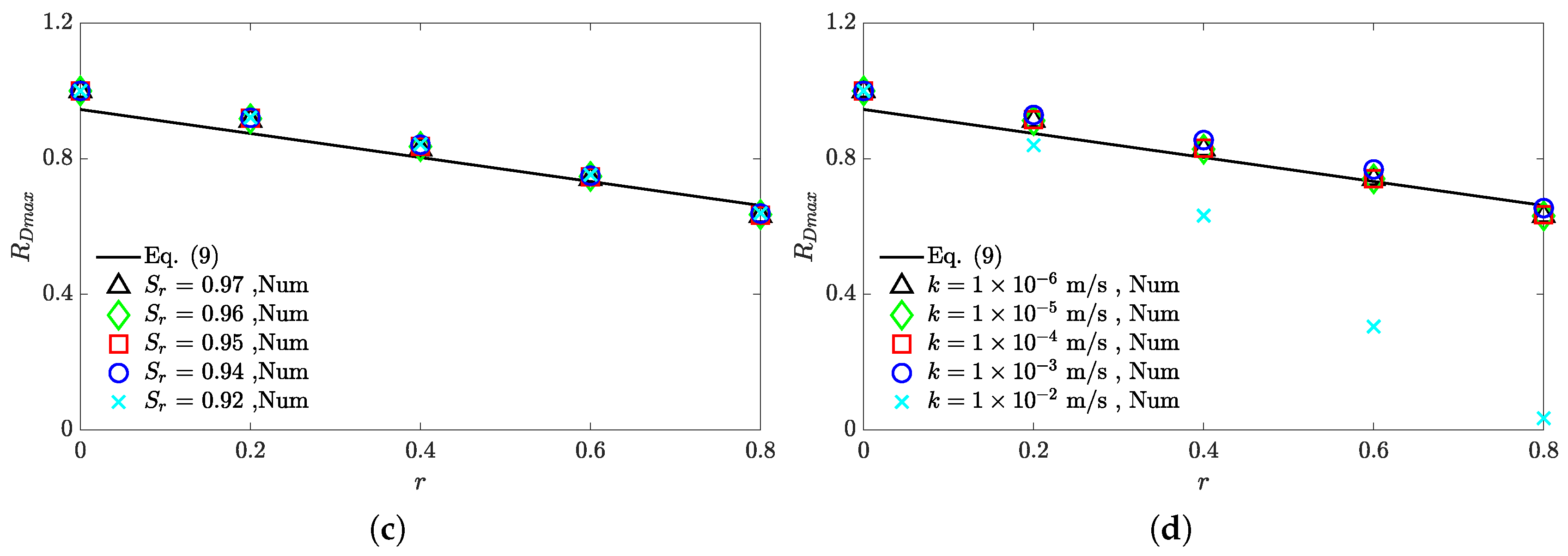
3.2. Analysis of Liquefaction Prediction Formula Applicability
Development of a Parametric Formula for Seabed Liquefaction Under Nonlinear Wave Action
3.3. Method for Computing Nonlinear Wave Parameters via Waveform Analysis
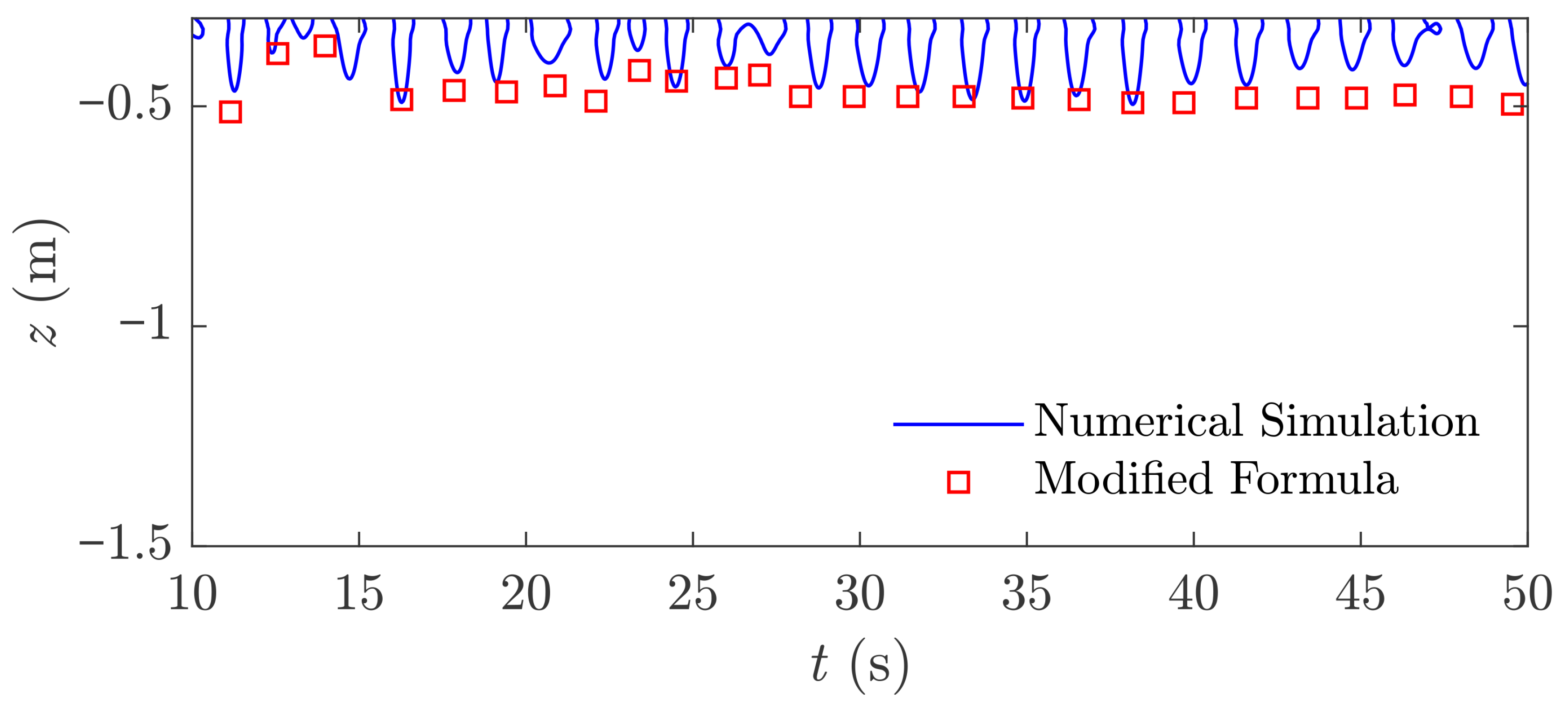
3.4. Application of the Parametrization Method to Seabed Liquefaction Problems
4. Conclusions
- Analysis based on the formula by Wang et al. [5] reveals that the predictive accuracy of their nonlinear wave-induced liquefaction formula significantly decreases when the permeability coefficient k falls within the range of ∼ m/s. By introducing a dimensionless parameter S, the formula is modified, which substantially improves the prediction accuracy of seabed liquefaction depth under specific permeability conditions.
- Through waveform analysis, nonlinear wave parameters are obtained, and a parametric method is established by integrating the liquefaction depth prediction formula. This method allows for rapid determination of the maximum liquefaction depth at each time step based on wave decomposition. Applied to a sloping seabed under practical engineering conditions, comparison with numerical results demonstrates that the modified formula performs effectively in real-world scenarios.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Jeng, D.S.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y. Recent advances of seabed liquefaction around the vicinity of marine structures. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirca, V.O.; Sumer, B.M.; Fredsøe, J. Residual liquefaction of seabed under standing waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2013, 139, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, T.; Silva, P.A.; Sancho, F.; Temperville, A. Analytical approximate wave form for asymmetric waves. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lei, Y.; Zheng, X.Y. Dynamic responses of a transversely isotropic poroelastic seabed subjected to nonlinear random waves with emphasis on liquefaction depth. Ocean Eng. 2023, 286, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.j.; Sui, T.t.; Zhang, C.; Pan, J.n. Effect of Wave Nonlinearity on the Instantaneous Seabed Liquefaction. China Ocean Eng. 2024, 38, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Koning, H.; Sellmeijer, H.; Van Hijum, E. On the response of a poro-elastic bed to water waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 87, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Jeng, D. Wave-induced soil response in an unsaturated anisotropic seabed of finite thickness. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1994, 18, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D.; Rahman, M.; Lee, T. Effects of inertia forces on wave-induced seabed response. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 1999, 9, ISOPE-99-09-4-307. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, D.S.; Cha, D. Effects of dynamic soil behavior and wave non-linearity on the wave-induced pore pressure and effective stresses in porous seabed. Ocean Eng. 2003, 30, 2065–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of elasticity and consolidation for a porous anisotropic solid. J. Appl. Phys. 1955, 26, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.; Chang, C.; Bettess, P. Drained, undrained, consolidating and dynamic behaviour assumptions in soils. Geotechnique 1980, 30, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Mase, H. Effects of inertia and gravity on seabed response to ocean waves. Model. Soil-Water-Struct. Interact. 1988, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Jeng, D.S. Response of porous seabed to nature loadings: Waves and currents. J. Eng. Mech. 2012, 138, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Jeng, D.; Wang, R.; Zhu, C. Numerical simulation of the wave-induced dynamic response of poro-elastoplastic seabed foundations and a composite breakwater. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 322–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ong, M.C.; Tang, T. A numerical toolbox for wave-induced seabed response analysis around marine structures in the OpenFOAM® framework. Ocean Eng. 2020, 195, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, Y.; Helfrich, S.C. Wave-induced pore pressures in submerged sand layer. J. Geotech. Eng. 1983, 109, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D. Porous Models for Wave-Seabed Interactions; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H. Study on Pore Water Pressure of Sandy Seabed Under Wave Action. Ph.D. Thesis, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zen, K.; Yamazaki, H. Field observation and analysis of wave-induced liquefaction in seabed. Soils Found. 1991, 31, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruessink, B.; Ramaekers, G.; Van Rijn, L. On the parameterization of the free-stream non-linear wave orbital motion in nearshore morphodynamic models. Coast. Eng. 2012, 65, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarkey, J.; Davies, A. Free-stream velocity descriptions under waves with skewness and asymmetry. Coast. Eng. 2012, 68, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Symbol | Verification 1 | Verification 2 | Verification 3 | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Depth | d | 0.488 | 0.3 | 10 | m |
| Wave Height | H | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.1 | m |
| Wave Period | T | 1.5 | 1.4 | 12 | s |
| Waveform Coefficient | 0 | 0.44 | 0 | - | |
| Asymmetry Coefficient | r | 0 | 0.48 | 0 | - |
| Seabed density | 2.65 × | 2.65 × | 2.65 × | kg/ | |
| permeability coefficient | k | 5 × ∼1 × | 1.4 × | 1.0 × | m/s |
| Pore Fluid Density | 1.0 × | 1.0 × | 1.0 × | kg/ | |
| Young’s Modulus | 1.3 × | 1.4 × | 2.67 × | Pa | |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.3333 | - | |
| Degree of Saturation | 0.985, 0.988 | 0.98 | 0.975 | - | |
| Porosity | n | 0.3 | 0.39 | 0.3 | - |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Depth | d | 10 | m |
| Wave Height | H | 4 | m |
| Wave Period | T | 10 | s |
| Wavelength | L | 92.32 | m |
| Benchmark amplitude of wave pressure | 15,810 | Pa | |
| Waveform Coefficient | 0, , | - | |
| Asymmetry Coefficient | r | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 | - |
| Soil Density | 2.0 × | kg/ | |
| Pore Fluid Density | 1.0 × | kg/ | |
| Young’s Modulus | 1.0 × | Pa | |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 | - | |
| Bulk Modulus of Pore Fluid | 2.0 × | Pa | |
| Degree of Saturation | 0.99 | - | |
| Porosity | n | 0.476 | - |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Depth | d | 5∼9 | m |
| Wave Height | H | ∼ | m |
| Wave Period | T | 4 | s |
| Wave Form Coefficient | /4 | - | |
| Asymmetry Coefficient | r | 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 | - |
| Soil Density | kg/ | ||
| Pore Fluid Density | kg/ | ||
| Young’s Modulus | Pa | ||
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 | - | |
| Soil Permeability Coefficient | k | ∼ | m/s |
| Bulk Modulus of Pore Fluid | Pa | ||
| Degree of Saturation | 0.97 | - | |
| Porosity | n | 0.4 | - |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum Peak Period | 1.6 | s | |
| Characteristic Wave Height | 0.145 | m | |
| Soil Density | kg/ | ||
| Pore Fluid Density | kg/ | ||
| Young’s Modulus | Pa | ||
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 | - | |
| Compression Modulus of Pore Fluid | m | ||
| Soil Permeability Coefficient | k | m/s | |
| Bulk Modulus of Pore Fluid | Pa | ||
| Degree of Saturation | 0.99 | - | |
| Porosity | n | 0.4 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zeng, M.; Sui, T.; Yang, M.; Peng, L. Parametrization of Seabed Liquefaction for Nonlinear Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2026, 14, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010094
Zeng M, Sui T, Yang M, Peng L. Parametrization of Seabed Liquefaction for Nonlinear Waves. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2026; 14(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010094
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Mantang, Titi Sui, Musheng Yang, and Li Peng. 2026. "Parametrization of Seabed Liquefaction for Nonlinear Waves" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 14, no. 1: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010094
APA StyleZeng, M., Sui, T., Yang, M., & Peng, L. (2026). Parametrization of Seabed Liquefaction for Nonlinear Waves. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 14(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010094






