Ensemble Modelling Predicts Habitat Shifts for Portunus trituberculatus Under Climate Change in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Distribution Data of Portunus Trituberculatus
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Construction, Optimization, and Evaluation of Integrated Models
2.4. Current and Future Projections of Potential Suitable Habitat Area
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
3.2. Analysis of the Importance of Environmental Variables
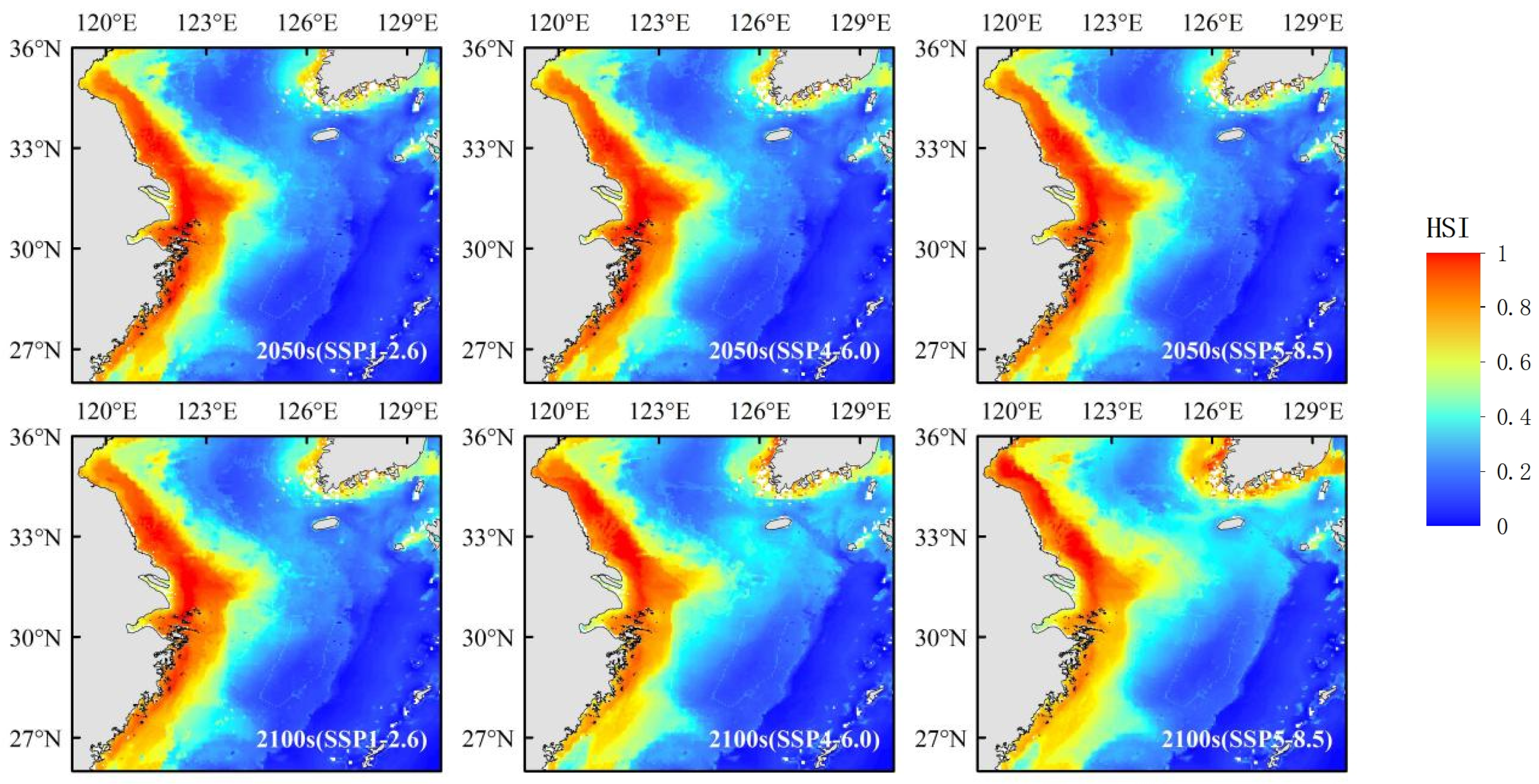
3.3. Current and Future Distribution of Portunus trituberculatus
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution and Habitat Projections of Portunus trituberculatus Under Future Climate Scenarios
Mechanistic Links Between Key Variables and Crab Biology
4.2. Impact on Protection and Management of Portunus trituberculatus
4.3. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, N.; Fan, X.; Penuelas, J.; Fu, Z.; Deng, Y.; et al. Global biogeography of microbes driving ocean ecological status under climate change. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Lü, B.; Li, R.; Zhu, A.; Wu, C. A preliminary analysis of fishery resource exhaustion in the context of biodiversity decline. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Bao, M.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Gao, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Qin, G.; et al. Advances of marine biogeography in China: Species distribution model and its applications. Biodivers. Sci. 2024, 32, 23453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarling, G.A.; Ward, P.; Thorpe, S.E. Spatial distributions of Southern Ocean mesozooplankton communities have been resilient to long-term surface warming. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, C.; Boughey, K.; Hawkins, C.; Reveley, S.; Spake, R.; Williams, C.; Altringham, J. A sequential multi-level framework to improve habitat suitability modelling. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varo-Cruz, N.; Bermejo, J.A.; Calabuig, P.; Cejudo, D.; Godley, B.J.; Lopez-Jurado, L.F.; Pikesley, S.K.; Witt, M.J.; Hawkes, L.A. New findings about the spatial and temporal use of the Eastern Atlantic Ocean by large juvenile loggerhead turtles. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, Q.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Ye, H. Are river protected areas sufficient for fish conservation? Implications from large-scale hydroacoustic surveys in the middle reach of the Yangtze River. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, D.G.; Du, H.; Wei, Q.W.; Kang, M. Spatial distribution and habitat choice of adult Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis Gray, 1835) downstream of Gezhouba Dam, Yangtze River, China. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Sommer, U.; Sihra, J.K.; Thorne, M.A.; Morley, S.A.; King, M.; Viant, M.R.; Peck, L.S. Biodiversity in marine invertebrate responses to acute warming revealed by a comparative multi-omics approach. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Wu, Q. Assessment of ecosystem energy flow and carrying capacity of swimming crab enhancement in the Yellow River estuary and adjacent waters. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Hurtado, L.A. Genetic differentiation of Portunus trituberculatus, the world’s largest crab fishery, among its three main fishing areas. Fish. Res. 2013, 148, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, T.W.; Tu, Z.; Xin, J.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, P.L. Review and consideration on Portunus trituberculatus stock enhancement in Shandong Province. Fish. Inf. Strateg. 2018, 33, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.P.; Zhang, G.G.; Wang, T.T.; Li, M.; Ren, Z.H.; Jiang, W.L.; Lv, Z.B.; Liu, D. Community structure and seasonal variation of demersal nekton in the eastern waters of Laizhou Bay. Mar. Fish. 2024, 46, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, L.; Gao, T. Preliminary study on spatial distribution pattern of fish in Zhoushan and its adjacent waters based on environmental DNA metabarcoding. J. Fish. China 2024, 48, 089311-1–089311-14. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Yan, X.J.; Song, W.H.; Zhou, Y.D.; Zhang, H.L.; Jiang, R.J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T. Speculation of migration routes of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea based on otolith microchemistry. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 45, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y. Climate-induced small pelagic fish blooms in an overexploited marine ecosystem of the South China Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.D. Stock assessment and management decision analysis of Portunus trituberculatus inhabiting Northern East China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2023, 53, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Doughty, C.L.; Gu, H.; Ambrose, R.F.; Stein, E.D.; Sloane, E.B.; Martinez, M.; Cavanaugh, K.C. Climate drivers and human impacts shape 35-year trends of coastal wetland health and composition in an urban region. Ecosphere 2024, 15, e4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, G.; Shao, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, F.; Geng, Z.; Li, X.; Tan, Q. Spatial-temporal distribution of resources and the relationship between environmental factors of Portulus trituberculus in the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 210, 107275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, X.; Gorfine, H.; Dai, F.; Wu, Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.; Jin, X. Ensemble projections of fish distribution in response to climate changes in the Yellow and Bohai Seas, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, M.; Ouled-Cheikh, J.; Julia, L.; Fuster-Alonso, A.; March, D.; Ramírez, F.; Cardona, L.; Coll, M. Fish and tips: Historical and projected changes in commercial fish species’ habitat suitability in the Southern Hemisphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snead, A.A.; Earley, R.L. Predicting the in-between: Present and future habitat suitability of an intertidal euryhaline fish. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 68, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, P.; Jácome, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Nam, K.; Yoo, C. Population response modeling and habitat suitability of Cobitis choii fish species in South Korea for climate change adaptation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.Q.; Xu, K.D.; Wang, H.X.; Zhou, Y.D. Spatial and temporal distribution of Portunus trituberculatus and its influencing factors in Ruian sea area, Zhejiang Province. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2024, 46, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, X. Impacts of shellfish aquaculture on the ecological carrying capacity of Portunus trituberculatus in Laizhou Bay. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Sui, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Potential effects of climate change on the habitat suitability of macrobenthos in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF Occurrence Download. Available online: https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.brtuev (accessed on 6 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shao, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, X. Habitat distribution and driving mechanisms of Portunus trituberculatus across different life history stages in the southern Bohai Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 210, 107347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GMED Environment Datasets Download. Available online: http://gmed.auckland.ac.nz (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Bio-ORACLE Environment Datasets Download. Available online: https://www.bio-oracle.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Schickele, A.; Leroy, B.; Beaugrand, G.; Goberville, E.; Hattab, T.; Francour, P.; Raybaud, V. Modelling European small pelagic fish distribution: Methodological insights. Ecol. Modell. 2020, 416, 108902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Lafourcade, B.; Engler, R.; Araújo, M.B. BIOMOD—A platform for ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Ecography 2009, 32, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, X.; Ovando, D.; Yang, T.; Dai, F.; Jin, X. Predicting current and future global distribution of black rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) under changing climate. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qin, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Duan, H.; Li, M. Forecast of potential suitable areas for forest resources in Inner Mongolia under the Shared Socioeconomic Pathway 245 scenario. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, H.; Ding, X.; Jo, D.; Li, K. Implications of RCP emissions on future concentration and direct radiative forcing of secondary organic aerosol over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 1187–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Han, X.; Han, Z. Effects of climate change on the potential habitat distribution of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus under the species distribution model. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yuan, W.; Ma, Y.J.; Zu, K.W.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of project to enhance the ecological carrying capacity of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) in Haizhou Bay. J. Hydroecol. 2022, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D.; Yu, L.; Pu, W.; Xu, X.; Xie, Y. Assessment of the carrying capacity of integrated pond aquaculture of Portunus trituberculatus at the ecosystem level. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 747891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Song, H.; Yao, G.; Lu, H. Composition and distribution of economic crab species in the East China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2006, 37, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, A.L.; Low, P.J.; Ellis, J.R.; Reynolds, J.D. Climate change and distribution shifts in marine fishes. Science 2005, 308, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, L.; Buisson, L.; Daufresne, M.; Grenouillet, G. Climate-induced changes in the distribution of freshwater fish: Observed and predicted trends. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Mu, X.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Ensemble predictions of high trophic-level fish distribution and species association in response to climate change in the coastal waters of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 214, 117800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, X.; Xiong, X. Distributions and seasonal changes of water temperature in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2013, 31, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Dong, S. Hypothermal effects on survival, energy homeostasis and expression of energy-related genes of swimming crabs Portunus trituberculatus during air exposure. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 60, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Dong, S. Responses of metabolism and haemolymph ions of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus to thermal stresses: A comparative study between air and water. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; An, Y.; Li, R.; Mu, C.; Wang, C. Strategy of metabolic phenotype modulation in Portunus trituberculatus exposed to low salinity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3496–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Signature of ocean warming in global fisheries catch. Nature 2013, 497, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Shan, X.; Jin, X.; Gorfine, H.; Yang, T.; Li, Z. Evaluating spatio-temporal dynamics of multiple fisheries-targeted populations simultaneously: A case study of the Bohai Sea ecosystem in China. Ecol. Modell. 2020, 422, 108987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.; Lavorel, S. Niche theory improves understanding of associations between ecosystem services. One Earth 2023, 6, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, F.; Cánovas, F. Predicting climate change impacts on marine fisheries, biodiversity and economy in the Canary/Iberia current upwelling system. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perryman, H.A.; Hansen, C.; Howell, D.; Olsen, E. A review of applications evaluating fisheries management scenarios through marine ecosystem models. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 800–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
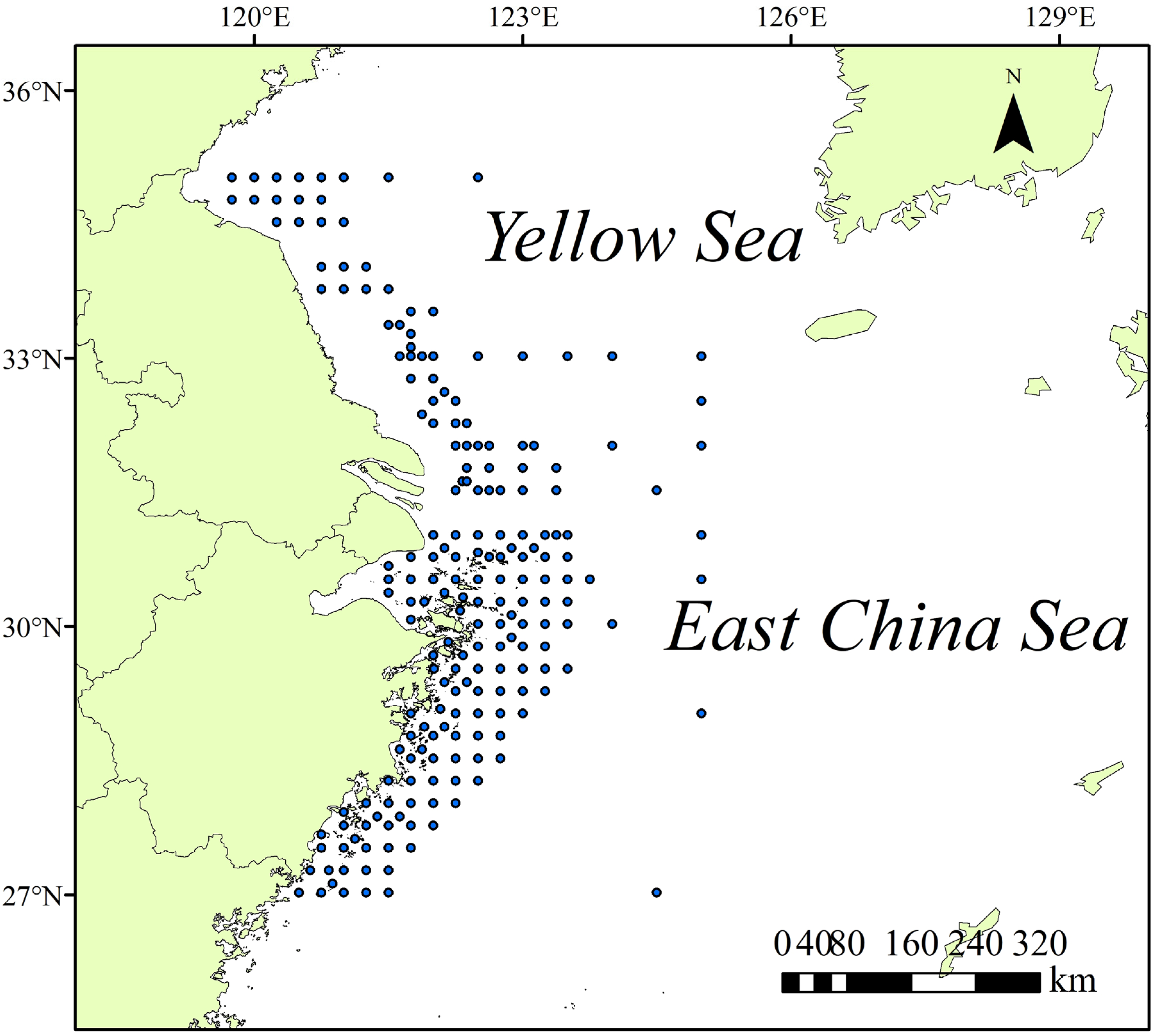
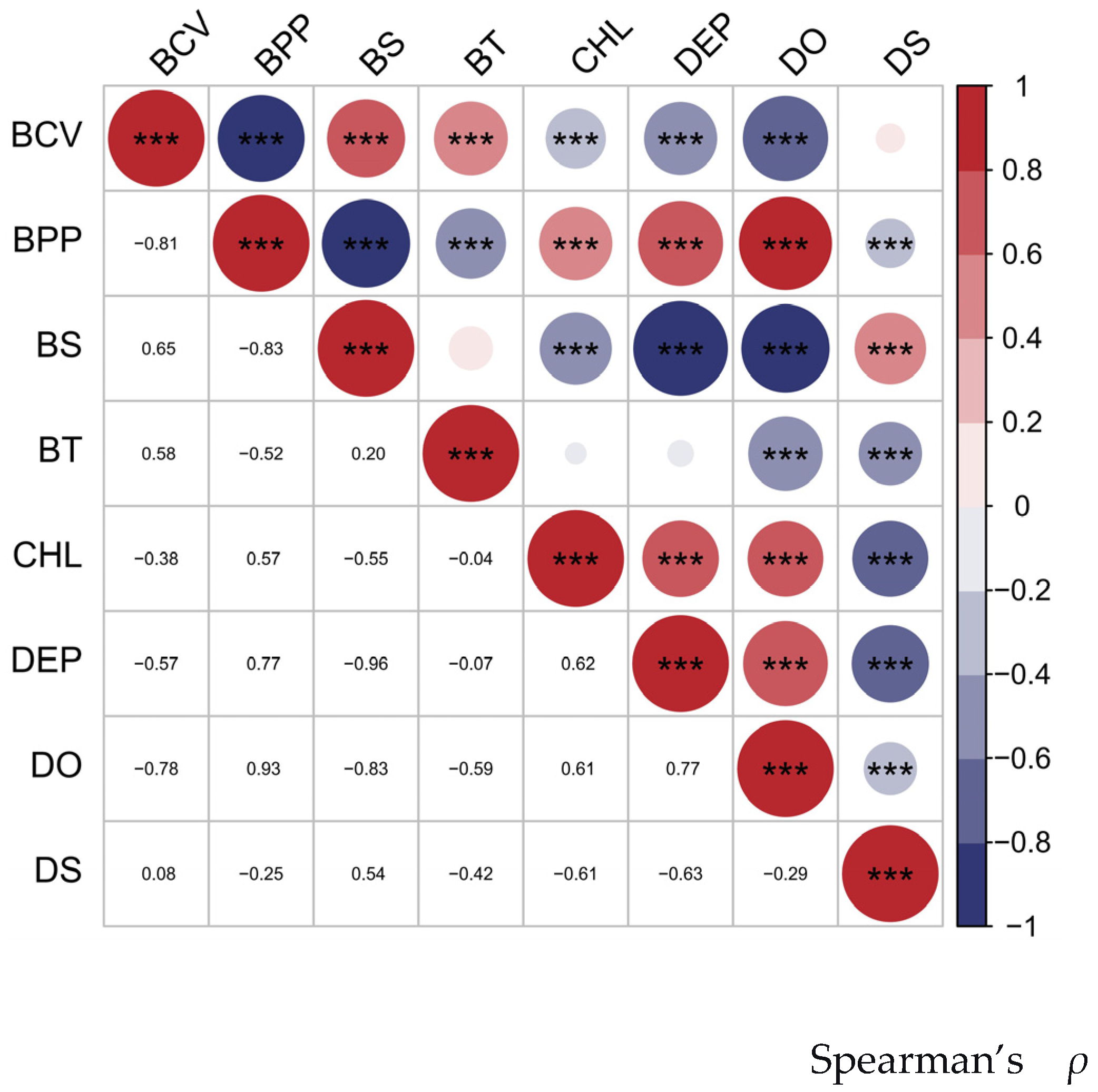
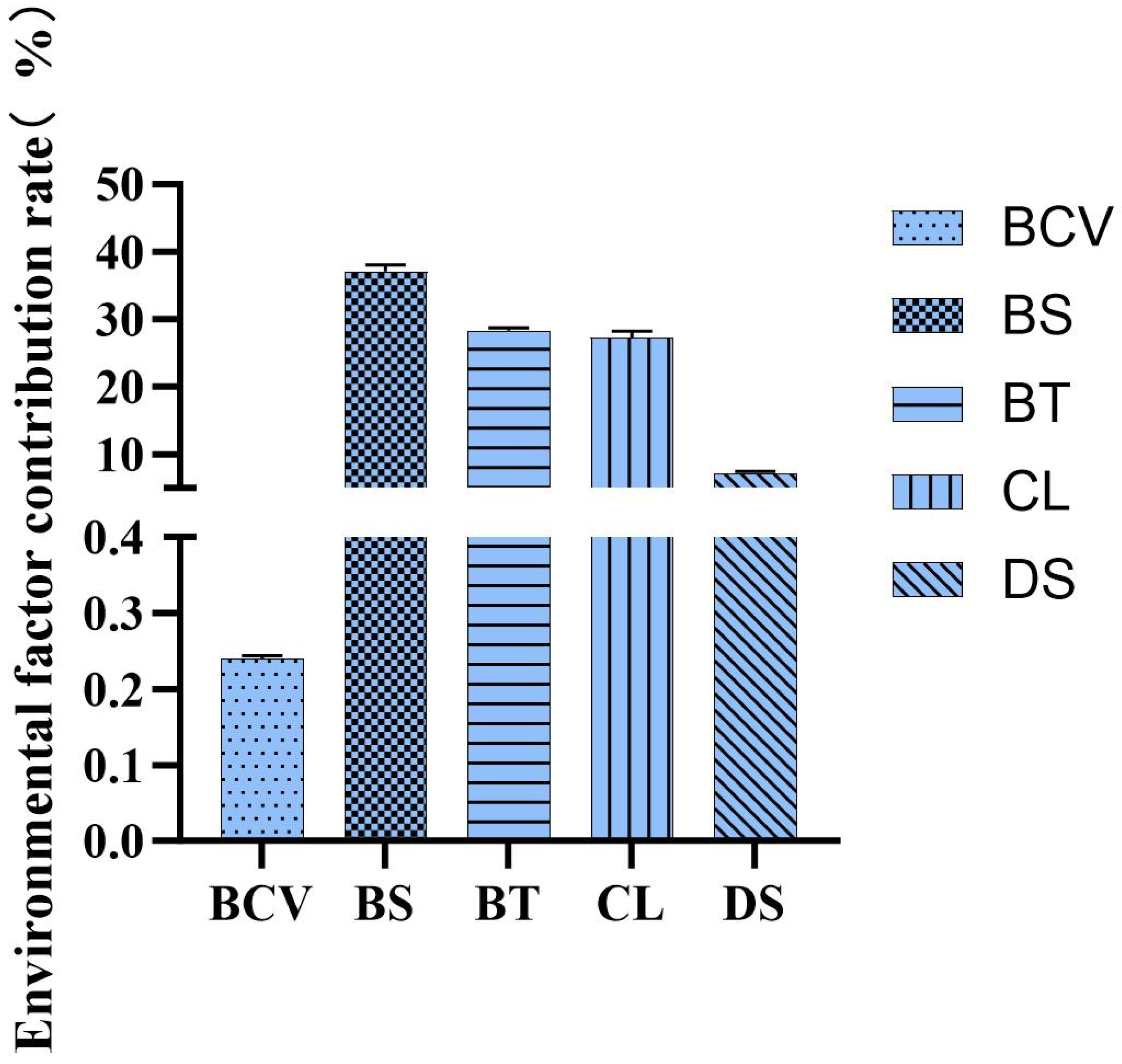
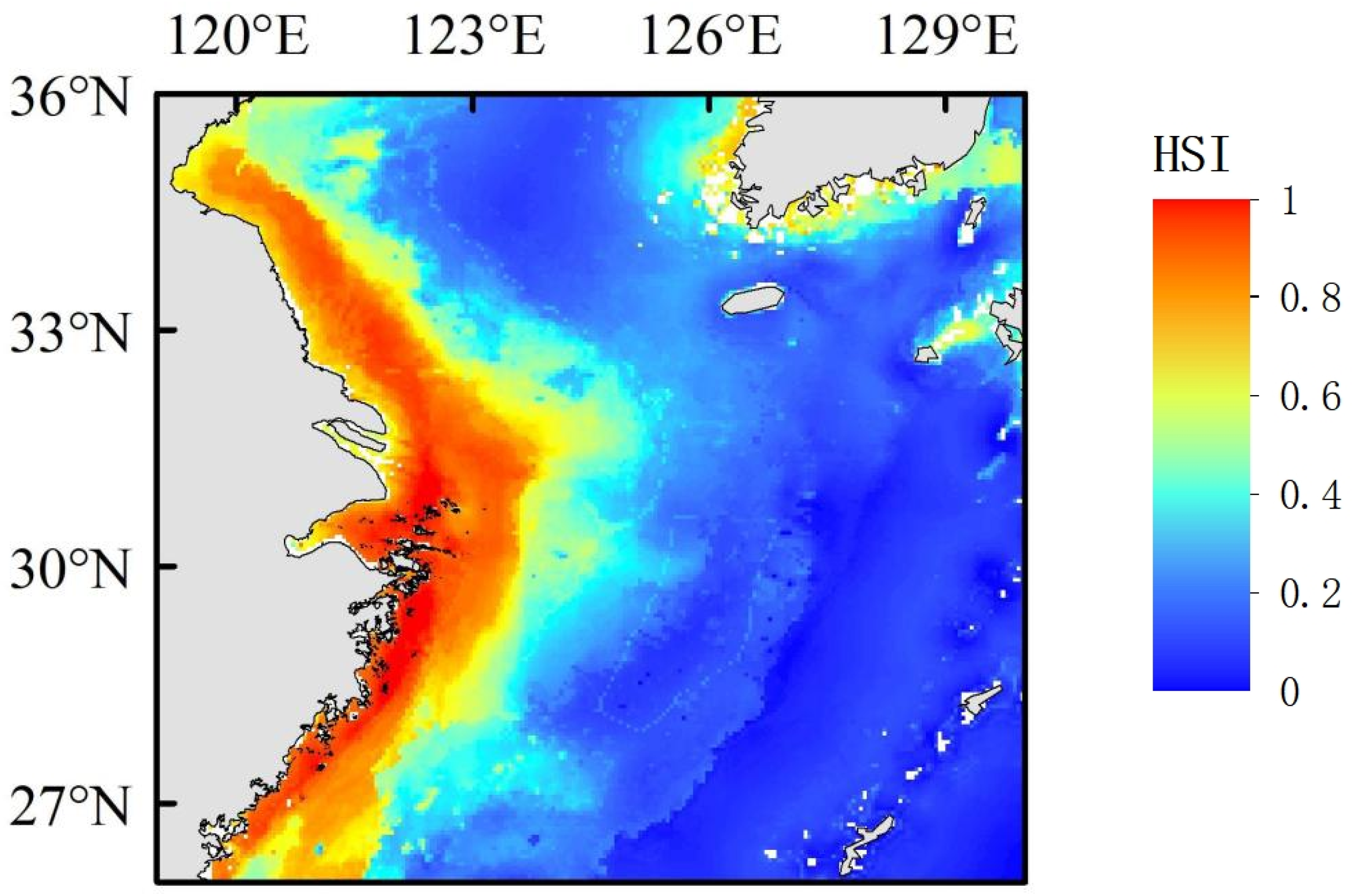
| Environmental Variables | Abbreviation | Unit | Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom temperature | BT | °C | 0.16–26.07 | Bio-ORACLE |
| Bottom salinity | BS | PSS | 1.44–34.85 | Bio-ORACLE |
| Bottom current velocity | BCV | m/s | 8.6 × 10−5–0.71 | Bio-ORACLE |
| Depth | DEP | m | 0.68–6503.48 | GMED |
| Distance from shore | DS | 100 km | 5.2 × 10−3–3.29 | GMED |
| Bottom primary productivity | BPP | g/m3/day | 1.2 × 10−2–34.52 | Bio-ORACLE |
| Dissolved oxygen | DO | μmol/m3 | 205.31–311.21 | Bio-ORACLE |
| Chlorophyll | CHL | mg/m3 | 0.17–8.32 | Bio-ORACLE |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network | 0.797 | 0.567 |
| CTA | Classification tree analysis | 0.863 | 0.705 |
| FDA | Flexible discriminant analysis | 0.836 | 0.595 |
| GBM | Generalized boosting model | 0.928 | 0.732 |
| GLM | Generalized linear model | 0.881 | 0.673 |
| MARS | Multivariate adaptive regression splines | 0.914 | 0.731 |
| MAXNET | Maximum entropy | 0.915 | 0.713 |
| RF | Random Forest | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| SRE | Surface range envelop | 0.727 | 0.453 |
| XGBOOST | Extreme gradient boosting | 0.967 | 0.900 |
| Period and Climate Scenarios | Inappropriate Area 0–0.4 (km2) | Low Suitability Zone 0.4–0.6 (km2) | Moderate Suitable Zone 0.6–0.8 (km2) | Highly Suitable Area 0.8–1.0 (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 106,872.2 | 99,083.6 | 90,305.6 | 97,081.6 |
| 2050s (SSP1-2.6) | 1,053,791.2 (−1.4%) | 114,791.6 (+15.9%) | 95,449.2 (+5.7%) | 91,168 (−6.1%) |
| 2050s (SSP4-6.0) | 1,055,639.2 (−1.2%) | 111,804 (+12.8%) | 93,878.4 (+4.0%) | 93,878.4 (−3.3%) |
| 2050s (SSP5-8.5) | 1,049,879.6 (−1.7%) | 114,945.6 (+16.0%) | 102,410 (+13.4%) | 87,964.8 (−9.4%) |
| 2100s (SSP1-2.6) | 1,027,488 (−3.8%) | 119,966 (+21.1%) | 105,613.2 (+16.9%) | 102,132.8 (+5.2%) |
| 2100s (SSP4-6.0) | 1,027,765.2 (−3.8%) | 125,879.6 (+27.0%) | 114,360.4 (+26.6%) | 87,194.8 (−10.2%) |
| 2100s (SSP5-8.5) | 986,585.6 (−7.7%) | 136,936.8 (+38.2%) | 169,985.2 (+88.2%) | 61,692.4 (−36.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Sun, F.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Ge, H.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Ensemble Modelling Predicts Habitat Shifts for Portunus trituberculatus Under Climate Change in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea of China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2026, 14, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010069
Sun F, Zhang H, Xu G, Ge H, Wu L, Li Z, Yu S, Zhou J, Wang S, Zhou Y. Ensemble Modelling Predicts Habitat Shifts for Portunus trituberculatus Under Climate Change in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea of China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2026; 14(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Fengqi, Hongliang Zhang, Guoqiang Xu, Hui Ge, Lei Wu, Zhenhua Li, Shuwen Yu, Jiayi Zhou, Shihao Wang, and Yongdong Zhou. 2026. "Ensemble Modelling Predicts Habitat Shifts for Portunus trituberculatus Under Climate Change in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea of China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 14, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010069
APA StyleSun, F., Zhang, H., Xu, G., Ge, H., Wu, L., Li, Z., Yu, S., Zhou, J., Wang, S., & Zhou, Y. (2026). Ensemble Modelling Predicts Habitat Shifts for Portunus trituberculatus Under Climate Change in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea of China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 14(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse14010069






