Modelling of the Present Oceanographic Situation of the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth
Abstract
1. Introduction
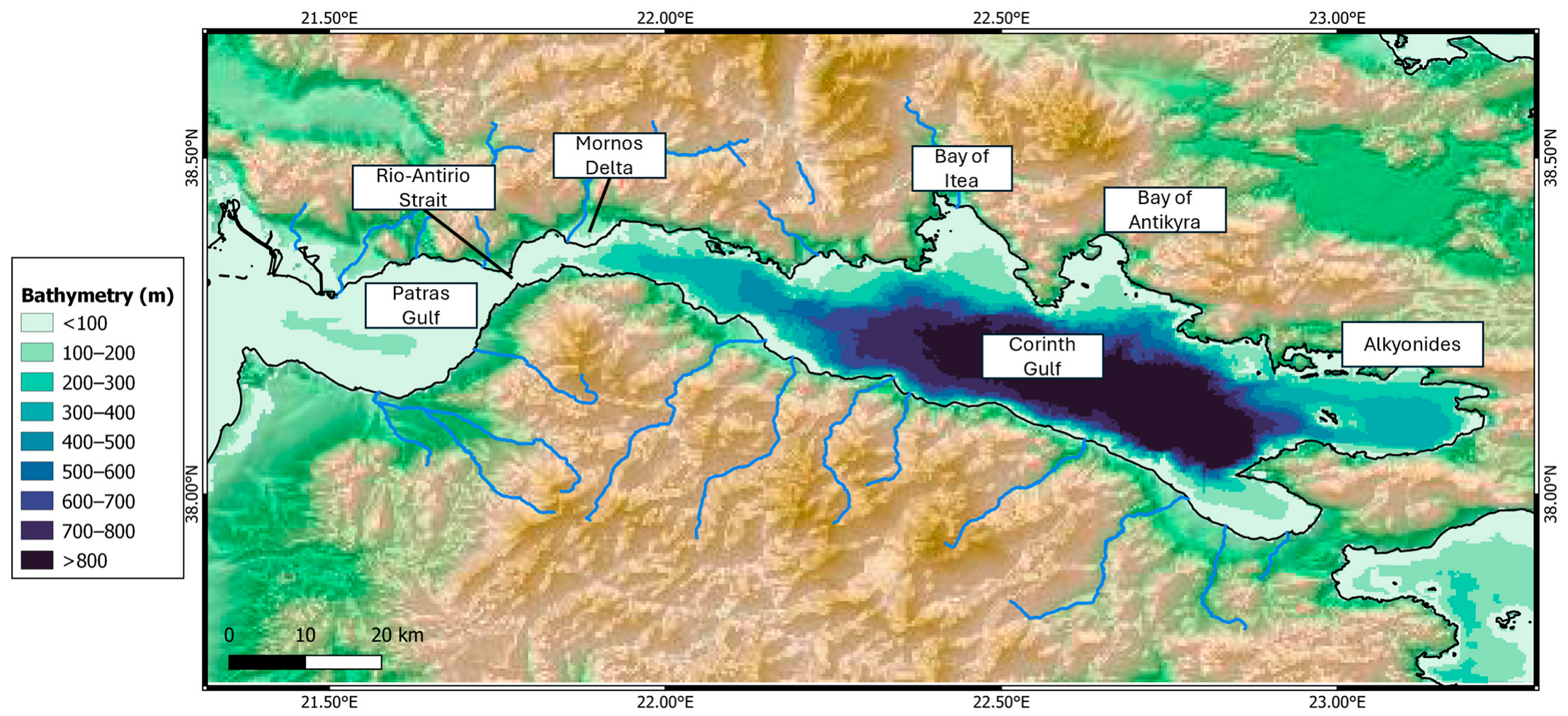
2. Settings of the Corinthian Gulf
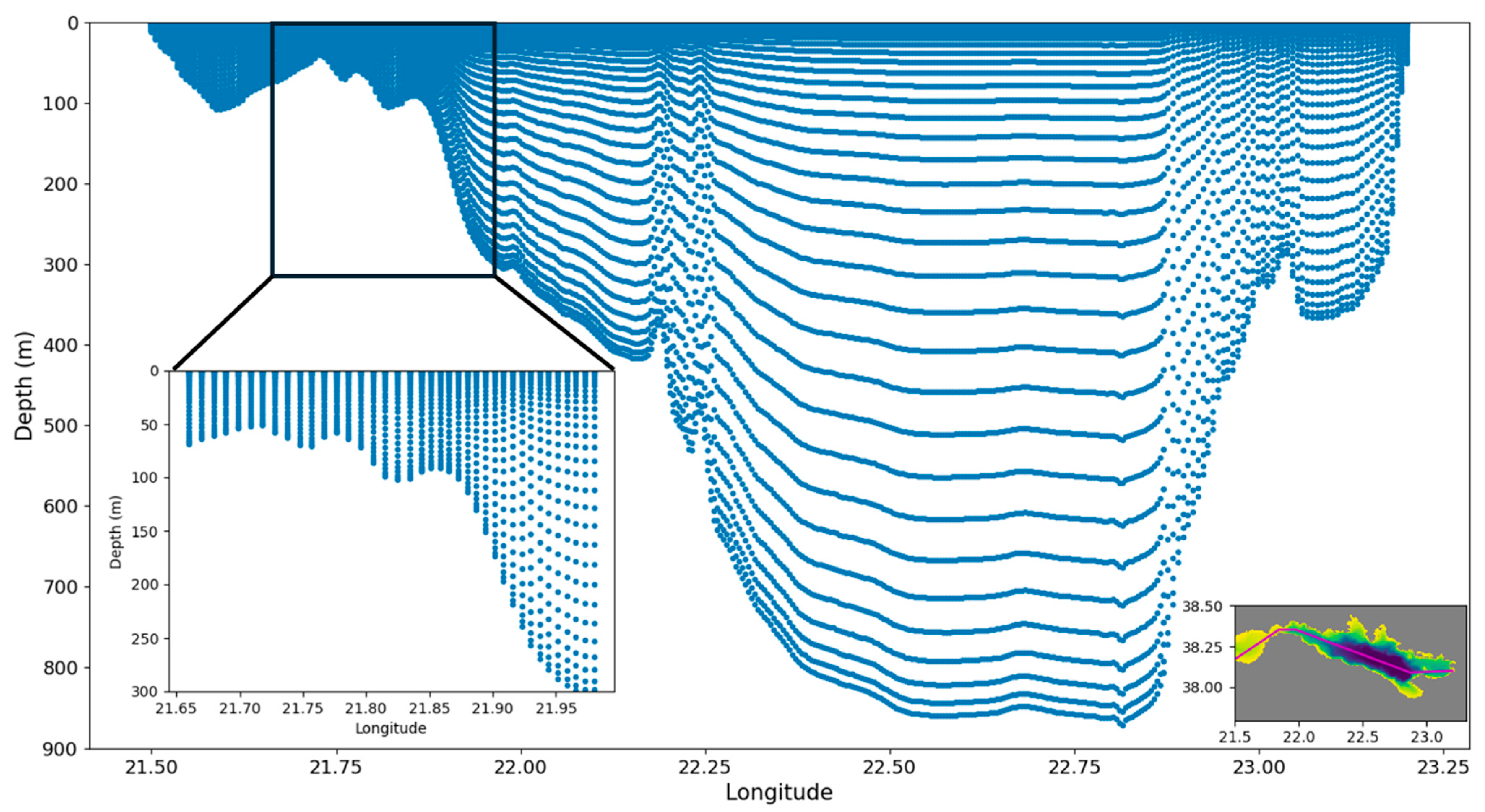
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Regional Ocean Modeling System
3.2. Data for the Validation of the Model
4. Results
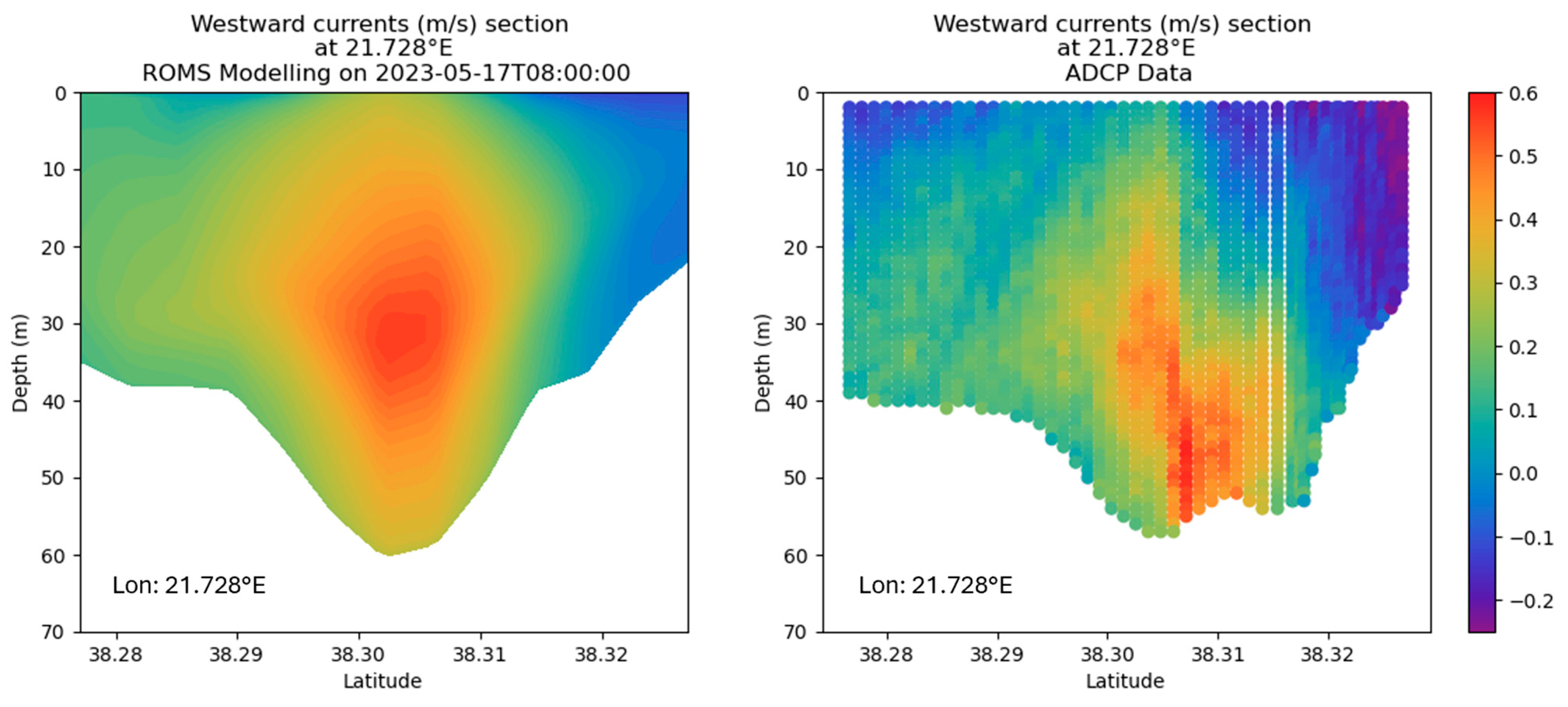
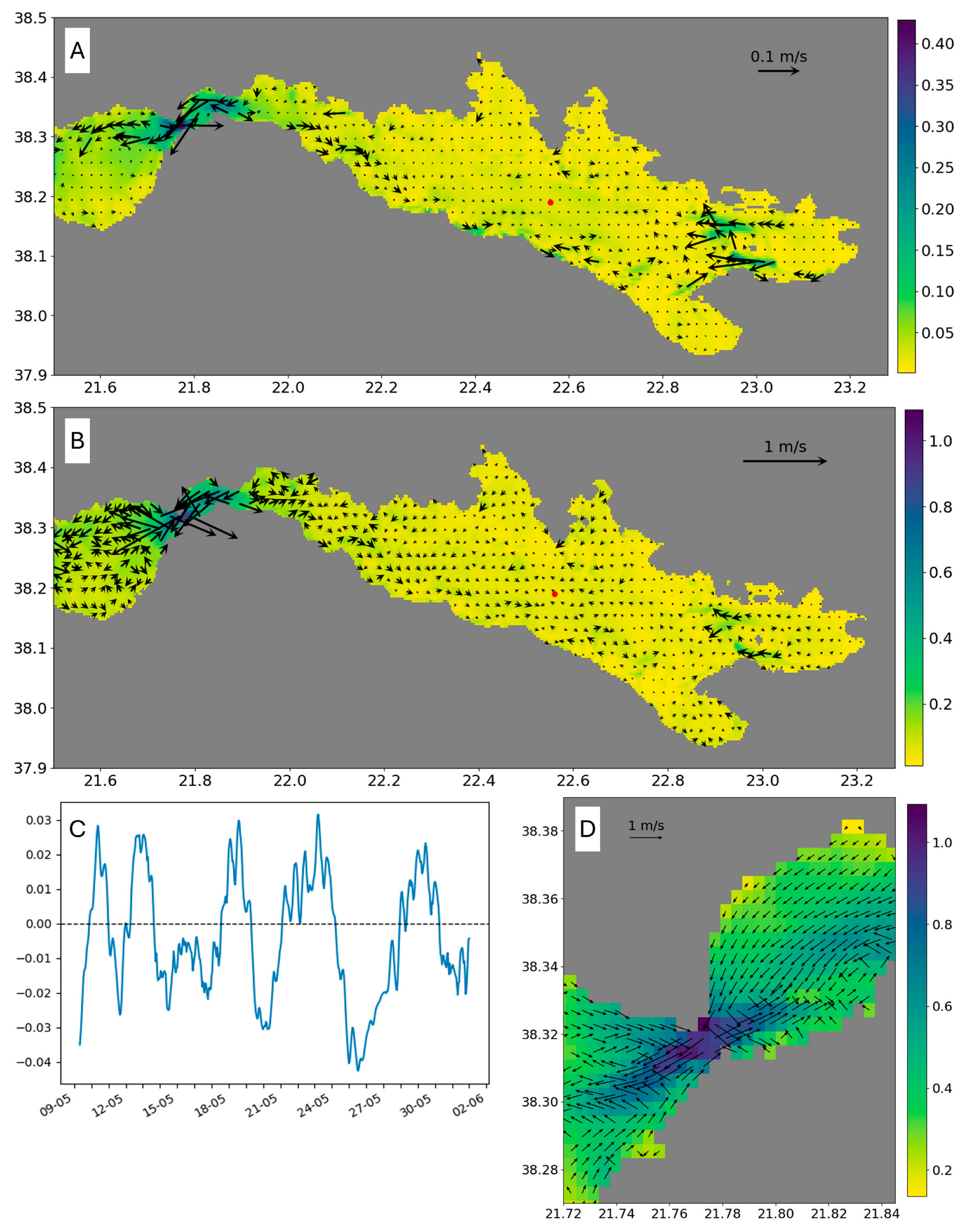
4.1. Model Validation
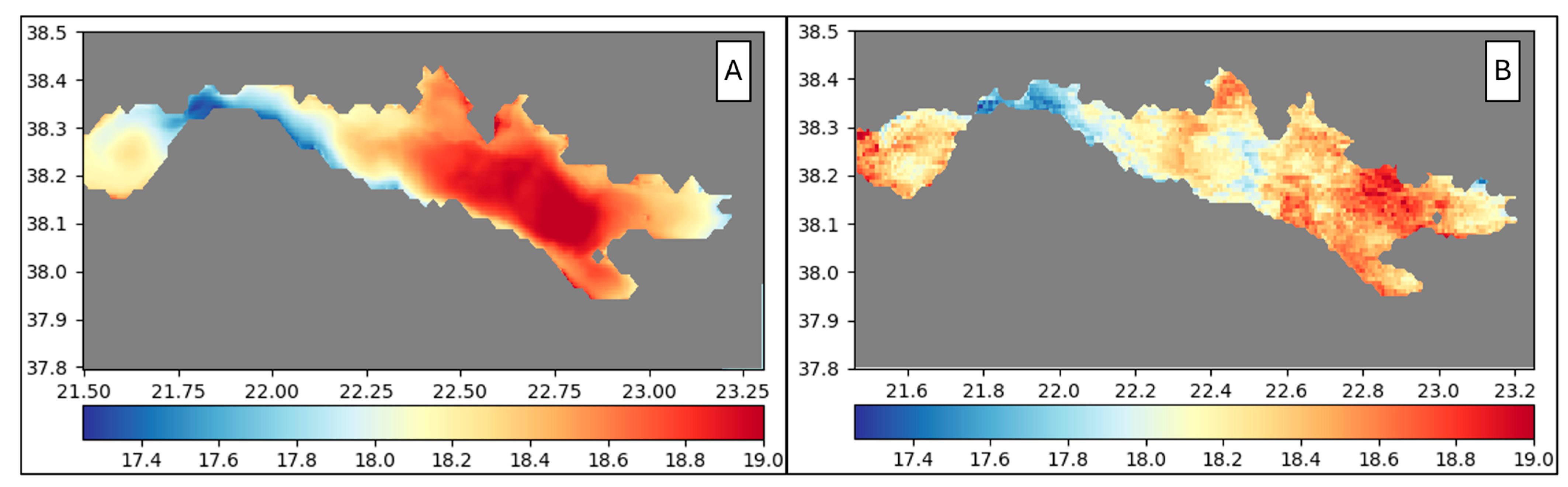
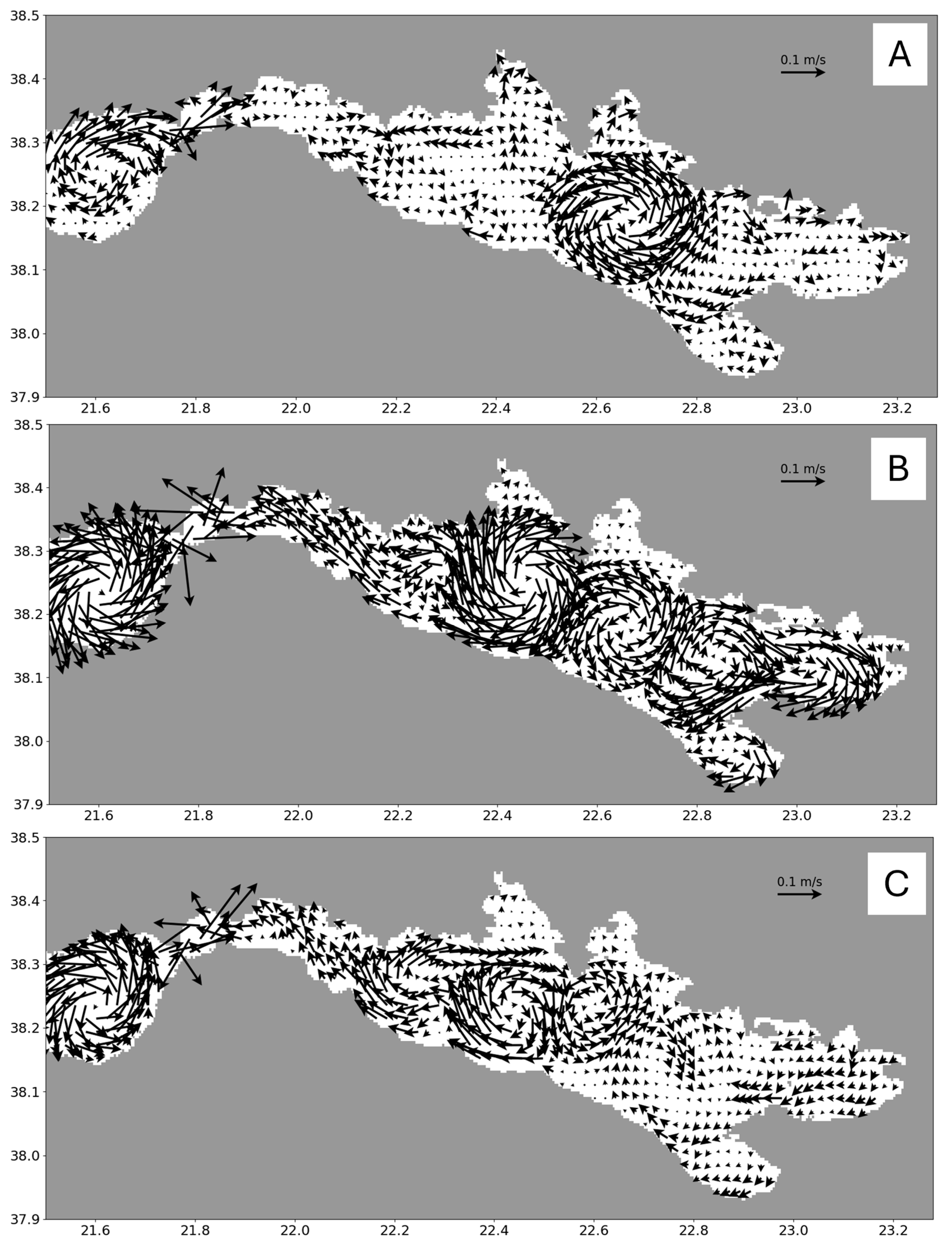
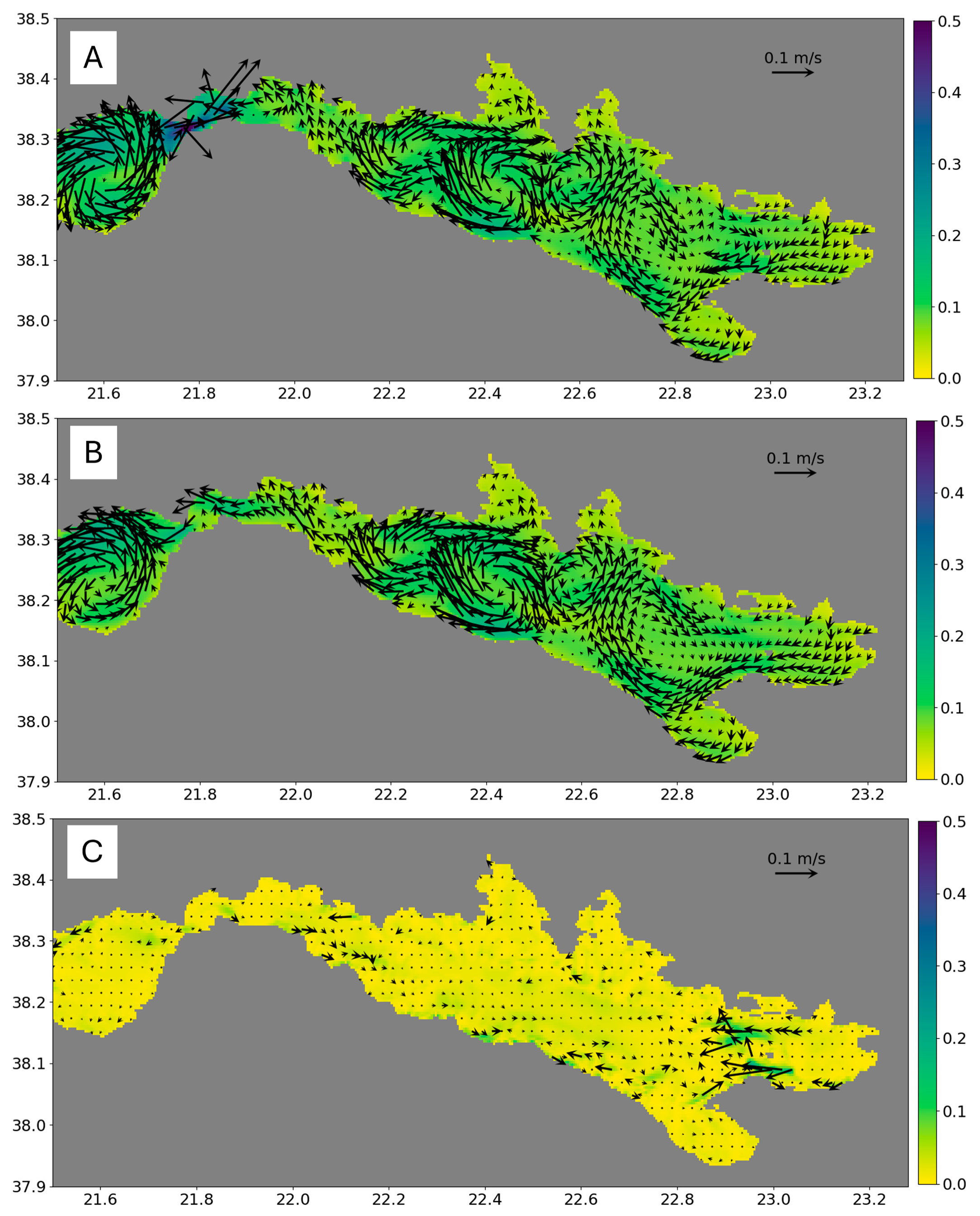
4.2. General Circulation Patterns
4.2.1. Patraic Gulf
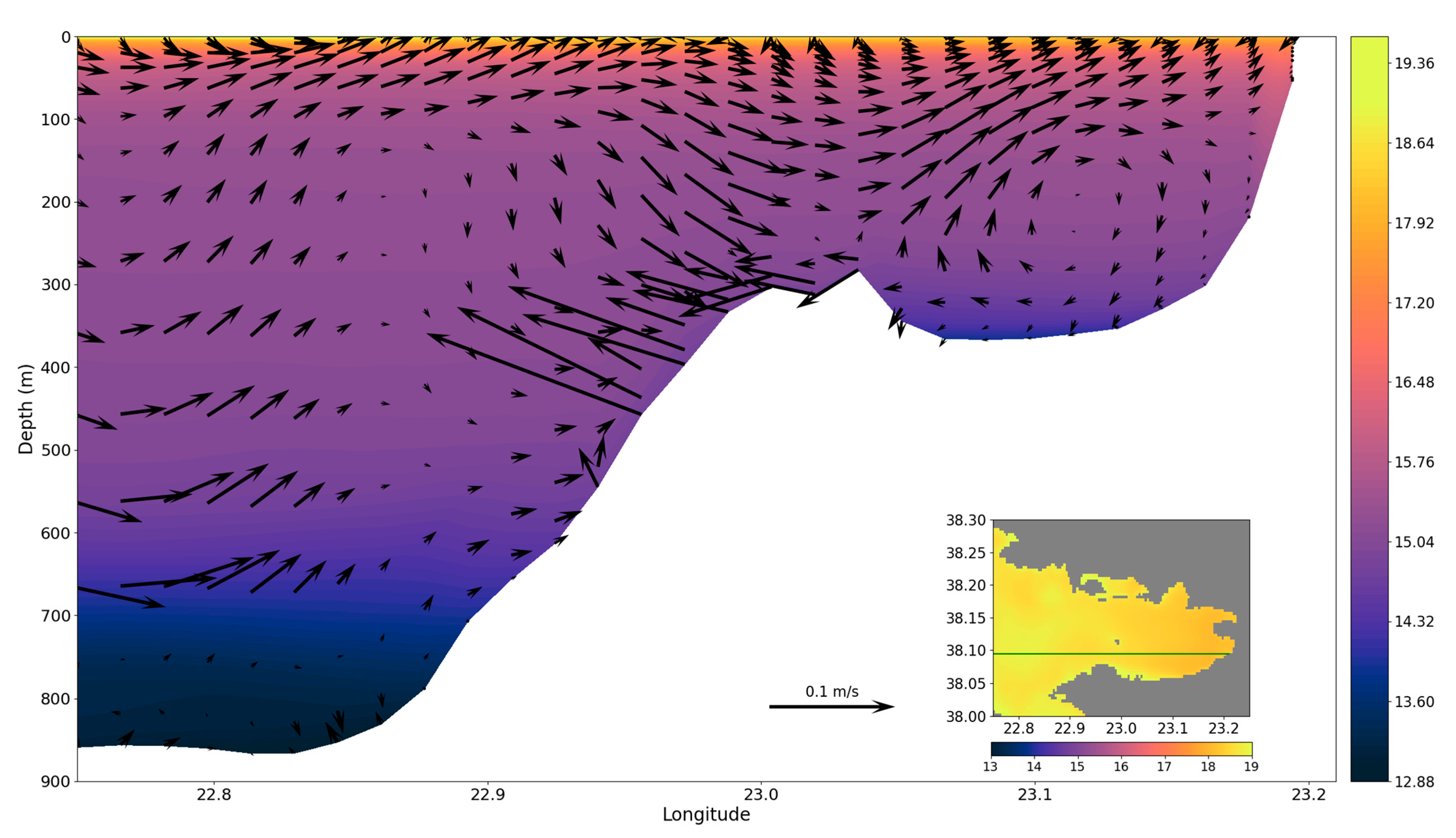
4.2.2. Corinthian Gulf
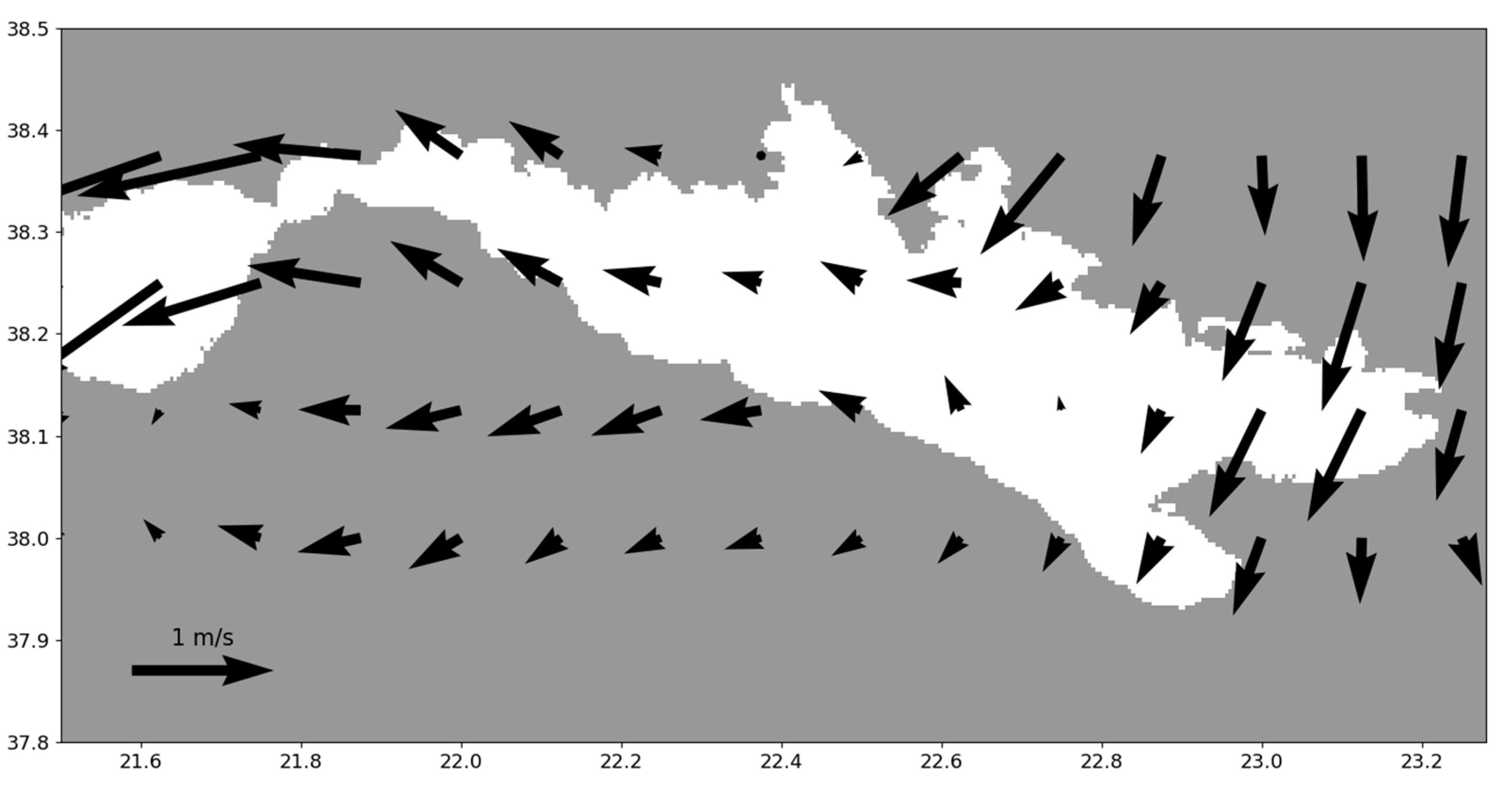
4.3. Wind Impact over the Patras and Corinthian Gulf
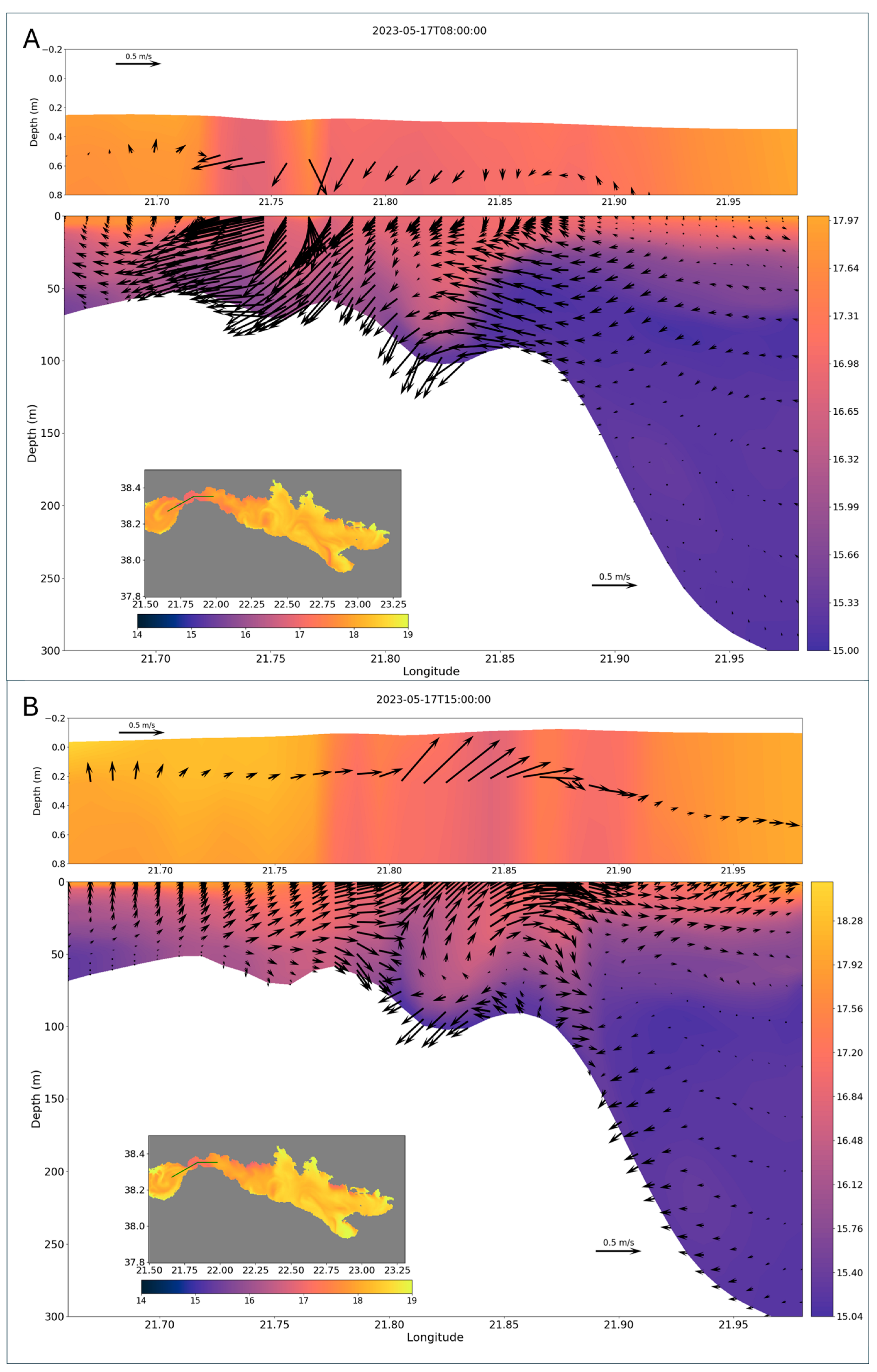
4.4. Dynamics at the Bottom
4.5. Influence of the Tide
5. Discussion
5.1. Genreal Circulation Patterns
5.2. Main Forcings for the Hydrodynamic Circulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caterina, B.; Hubert-Ferrari, A. Using 14 Years of Satellite Data to Describe the Hydrodynamic Circulation of the Patras and Corinth Gulfs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascaratos, A.; Salusti, E.; Papageorgaki, G. Wind-Induced Upwellings and Currents in the Gulfs of Patras, Nafpaktos and Korinthos, Western Greece. Oceanol. Acta 1989, 12, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Fourniotis, N.T. Effect of Internal Waves on the Hydrodynamics of a Mediterranean Sea Strait. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ori, G.G. Geologic History of the Extensional Basin of the Gulf of Corinth (?Miocene-Pleistocene), Greece. Geology 1989, 17, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohais, S.; Eschard, R.; Ford, M.; Guillocheau, F.; Moretti, I. Stratigraphic Architecture of the Plio-Pleistocene Infill of the Corinth Rift: Implications for Its Structural Evolution. Tectonophysics 2007, 440, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, L.C.; Shillington, D.J.; Carter, G.D.O.; Everest, J.D.; Gawthorpe, R.L.; Miller, C.; Phillips, M.P.; Collier, R.E.L.; Cvetkoska, A.; De Gelder, G.; et al. High-Resolution Record Reveals Climate-Driven Environmental and Sedimentary Changes in an Active Rift. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, C.W.; McNeill, L.C.; Bull, J.M.; Bell, R.E.; Gawthorpe, R.L.; Henstock, T.J.; Christodoulou, D.; Ford, M.; Taylor, B.; Sakellariou, D.; et al. Rapid Spatiotemporal Variations in Rift Structure during Development of the Corinth Rift, Central Greece. Tectonics 2016, 35, 1225–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, A.; Hubert-Ferrari, A.; Beck, C.; Bodeux, S.; Tripsanas, E.; Sakellariou, D.; De Batist, M. Active Faulting at the Western Tip of the Gulf of Corinth, Greece, from High-Resolution Seismic Data. Mar. Geol. 2015, 360, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, A.; Beck, C.; Hubert-Ferrari, A.; Tripsanas, E.; Crouzet, C.; Sakellariou, D.; Papatheodorou, G.; De Batist, M. Influence of Bottom Currents on the Sedimentary Processes at the Western Tip of the Gulf of Corinth, Greece. Mar. Geol. 2016, 378, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, S.E.; Collins, M.B.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Cramp, A.; Gull, W.; Tsimplis, M.; Papatheodorou, G. Oceanography and Sedimentation in the Semi-Enclosed, Deep-Water Gulf of Corinth (Greece). Mar. Geol. 1996, 134, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourniotis, N.T.; Horsch, G.M. Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Wind-Induced Barotropic Circulation in the Gulf of Patras. Ocean Eng. 2010, 37, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourniotis, N.T.; Horsch, G.M. Baroclinic Circulation in the Gulf of Patras (Greece). Ocean Eng. 2015, 104, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspioti, A.G.; Fourniotis, N.T. Numerical Study of Barotropic Circulation in the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth System. Oceans 2025, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubi, R.; Hubert-Ferrari, A.; Fakiris, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Dimas, X.; Geraga, M.; Papatheodorou, G.; Caterina, B. Hydrodynamics and Sedimentary Processes in the Modern Rion Strait (Greece): Interplay between Tidal Currents and Internal Tides. Mar. Geol. 2022, 446, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramana, T.; Karditsa, A.; Petrakis, S.; Milatou, N.; Megalofonou, P.; Dassenakis, M.; Poulos, S. Ecosystem-Based Blue Growth: The Case of the Semi-Enclosed Embayment of the Inner NE Ionian Sea and Adjacent Gulfs. Water 2023, 15, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferentinos, G.; Brooks, M.; Doutsos, T. Quaternary Tectonics in the Gulf of Patras, Western Greece. J. Struct. Geol. 1985, 7, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletsis, I.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K. A Model-Based Study of the Wind Regime over the Corinthian Gulf. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.M.; Arango, H.G.; Broquet, G.; Powell, B.S.; Weaver, A.T.; Zavala-Garay, J. The Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) 4-Dimensional Variational Data Assimilation Systems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, H.; Di Lorenzo, E.; El-Gindy, A. The Impact of Climate Change on Circulation Patterns in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea Upper Layer Using Med-ROMS Model. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 175, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujiasih, S.; Beckers, J.-M.; Barth, A. Implementation and Validating of the Regional Ocean Model System (ROMS) for the Sunda Strait Connecting the Java Sea to the Indian Ocean. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, A. ROMS.Jl. Available online: https://alexander-barth.github.io/ROMS.jl/dev/ (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. The Regional Oceanic Modeling System (ROMS): A Split-Explicit, Free-Surface, Topography-Following-Coordinate Oceanic Model. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 347–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, B.; Rubi, R.; Hubert-Ferrari, A. Stratigraphic Architecture, Sedimentology and Structure of the Middle Pleistocene Corinth Canal (Greece). Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2022, 523, 279–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WikiROMS. Vertical S-Coordinate. Available online: https://www.myroms.org/wiki/Vertical_S-coordinate (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. Correction and Commentary for “Ocean Forecasting in Terrain-Following Coordinates: Formulation and Skill Assessment of the Regional Ocean Modeling System” by Haidvogel et al., J. Comp. Phys. 227, pp. 3595–3624. J. Comput. Phys. 2009, 228, 8985–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Tronconi, C.; Pisano, A.; Santoleri, R. High and Ultra-High Resolution Processing of Satellite Sea Surface Temperature Data over Southern European Seas in the Framework of MyOcean Project. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Bennett, A.F.; Foreman, M.G.G. TOPEX/POSEIDON Tides Estimated Using a Global Inverse Model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1994, 99, 24821–24852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.D.; Erofeeva, S.Y. Efficient Inverse Modeling of Barotropic Ocean Tides. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oceanus-Lab. Oceanus-Lab. Available online: https://www.oceanus-lab.gr/ (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Tideschart. Rio Tide Times. Available online: https://www.tideschart.com/Greece/West-Greece/Nomos-Achaias/Rio/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. 2021. Available online: https://odv.awi.de (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- CMEMS. Mediterranean Sea—High Resolution and Ultra High Resolution L3S Sea Surface Temperature. Available online: https://data.marine.copernicus.eu/product/SST_MED_SST_L3S_NRT_OBSERVATIONS_010_012/description (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ). Sea Level Station Monitoring Facility. Available online: https://www.ioc-sealevelmonitoring.org (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Tsimplis, M.N. Tidal Oscillations in the Aegean and Ionian Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 39, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsch, G.M.; Fourniotis, N.T. Wintertime Tidal Hydrodynamics in the Gulf of Patras, Greece. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspioti, A.G.; Fourniotis, N.T. A Brief Review of Hydrodynamic Circulation in the Mediterranean Gulfs. Dynamics 2024, 4, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E.L. Upwelling and Upsloping in Three-Dimensional Marine Models. Appl. Math. Model. 1989, 13, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, P.L.; Hanes, D.M.; Rubin, D.M.; Kvitek, R.G. Giant Sand Waves at the Mouth of San Francisco Bay. Eos 2006, 87, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilloux, A.; Valet, J.-P.; Bassinot, F.; Joron, J.-L.; Dewilde, F.; Blanc-Valleron, M.-M.; Moreno, E. Influence of Seawater Exchanges across the Bab-El-Mandeb Strait on Sedimentation in the Southern Red Sea during the Last 60 Ka. Paleoceanography 2013, 28, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, G.H.; Richards, A.F. Sediments of the Malacca Strait, Southeast Asia. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1967, 37, 102–127. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarche, G.; Lurton, X.; Verdier, A.-L.; Augustin, J.-M. Quantitative Characterisation of Seafloor Substrate and Bedforms Using Advanced Processing of Multibeam Backscatter—Application to Cook Strait, New Zealand. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S93–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, S.G. Between Scylla and Charybdis (Part 1): The Sedimentary Dynamics of the Modern Messina Strait (Central Mediterranean) as Analogue to Interpret the Past. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 259–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhitano, S.G.; Chiarella, D. Tidal Straits: Basic Criteria for Recognizing Ancient Systems from the Rock Record; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780444641342. [Google Scholar]
- Baines, P.G.; Garnek, H. Hydraulic Models of Deep Stratified Flows over Topography. In The Physical Oceanography of Sea Straits; Pratt, L.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; p. 318. ISBN 978-94-010-6789-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, G. Modem Internal Waves and Internal Tides along Oceanic Pycnoclines: Challenges and Implications for Ancient Deep-Marine Baroclinic Sands. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2013, 97, 799–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caterina, B.; Hubert-Ferrari, A.; Barth, A.; Beckers, J.-M. Modelling of the Present Oceanographic Situation of the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091827
Caterina B, Hubert-Ferrari A, Barth A, Beckers J-M. Modelling of the Present Oceanographic Situation of the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091827
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaterina, Basile, Aurélia Hubert-Ferrari, Alexander Barth, and Jean-Marie Beckers. 2025. "Modelling of the Present Oceanographic Situation of the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091827
APA StyleCaterina, B., Hubert-Ferrari, A., Barth, A., & Beckers, J.-M. (2025). Modelling of the Present Oceanographic Situation of the Gulfs of Patras and Corinth. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091827





