Significant Wave Height Prediction Using LSTM Augmented by Singular Spectrum Analysis and Residual Correction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Data Source
2.1.2. Dataset Construction and Processing
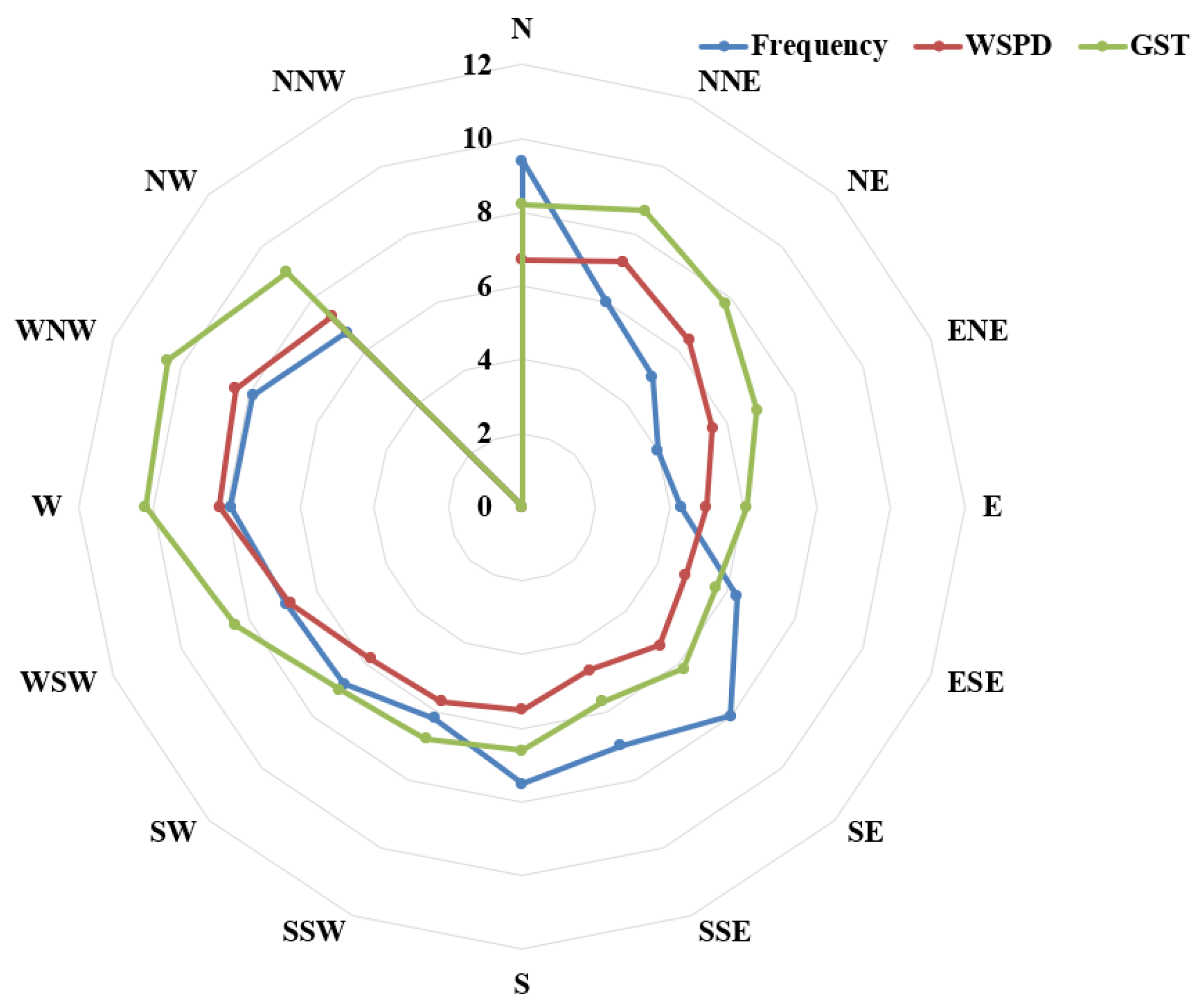
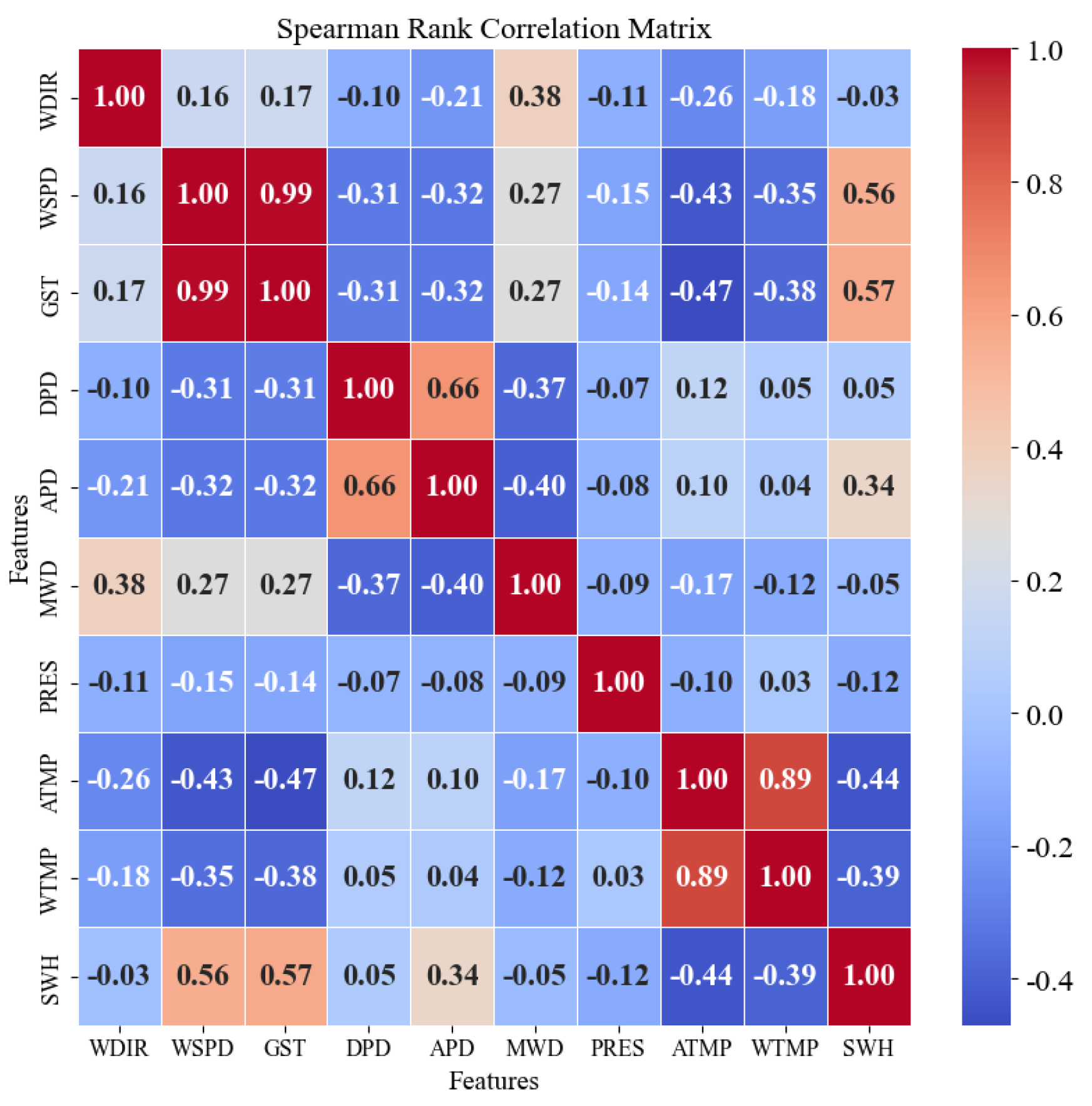
2.1.3. Feature Factor Selection
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. SSA Principle
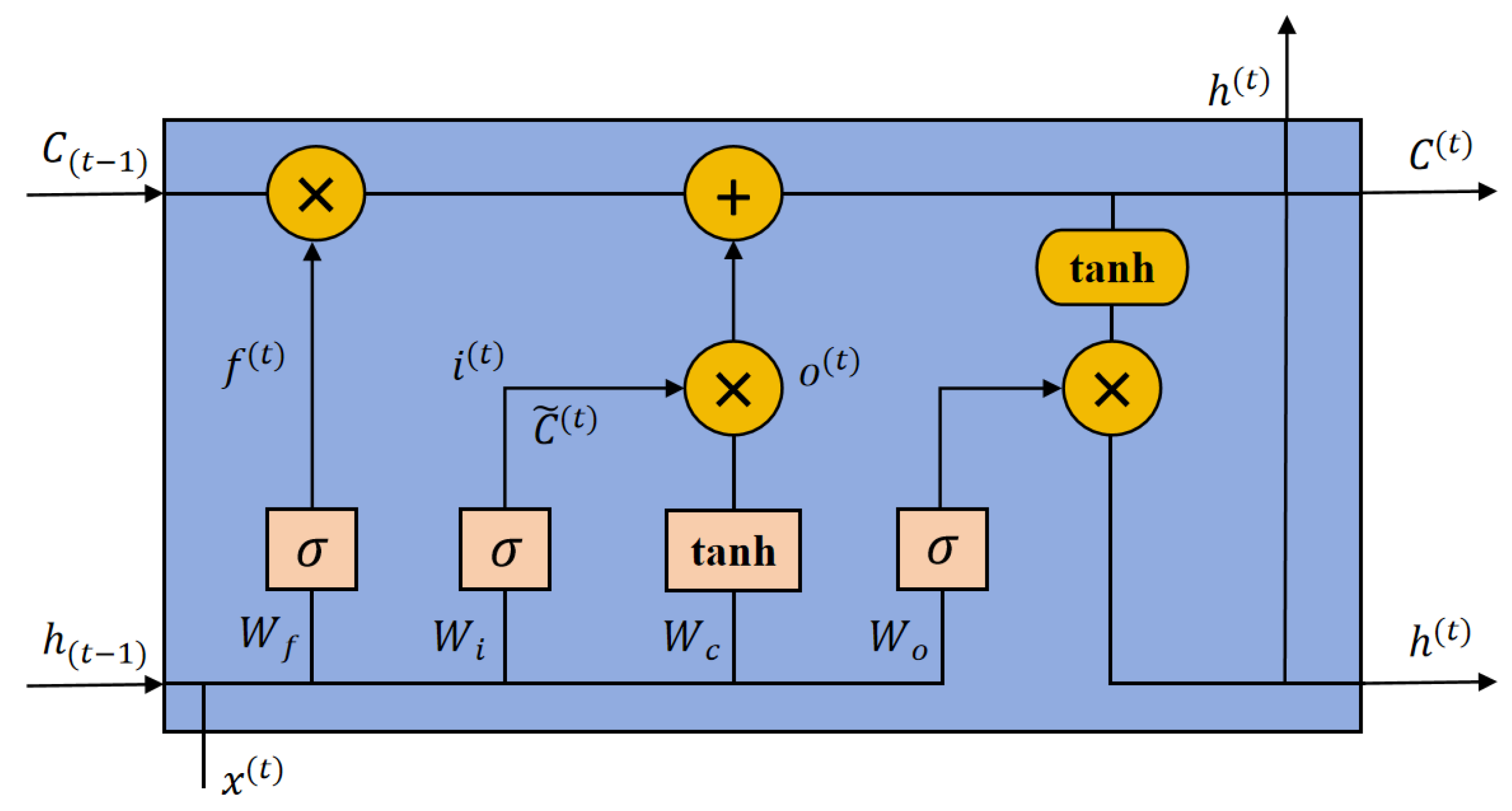
2.2.2. LSTM Principle
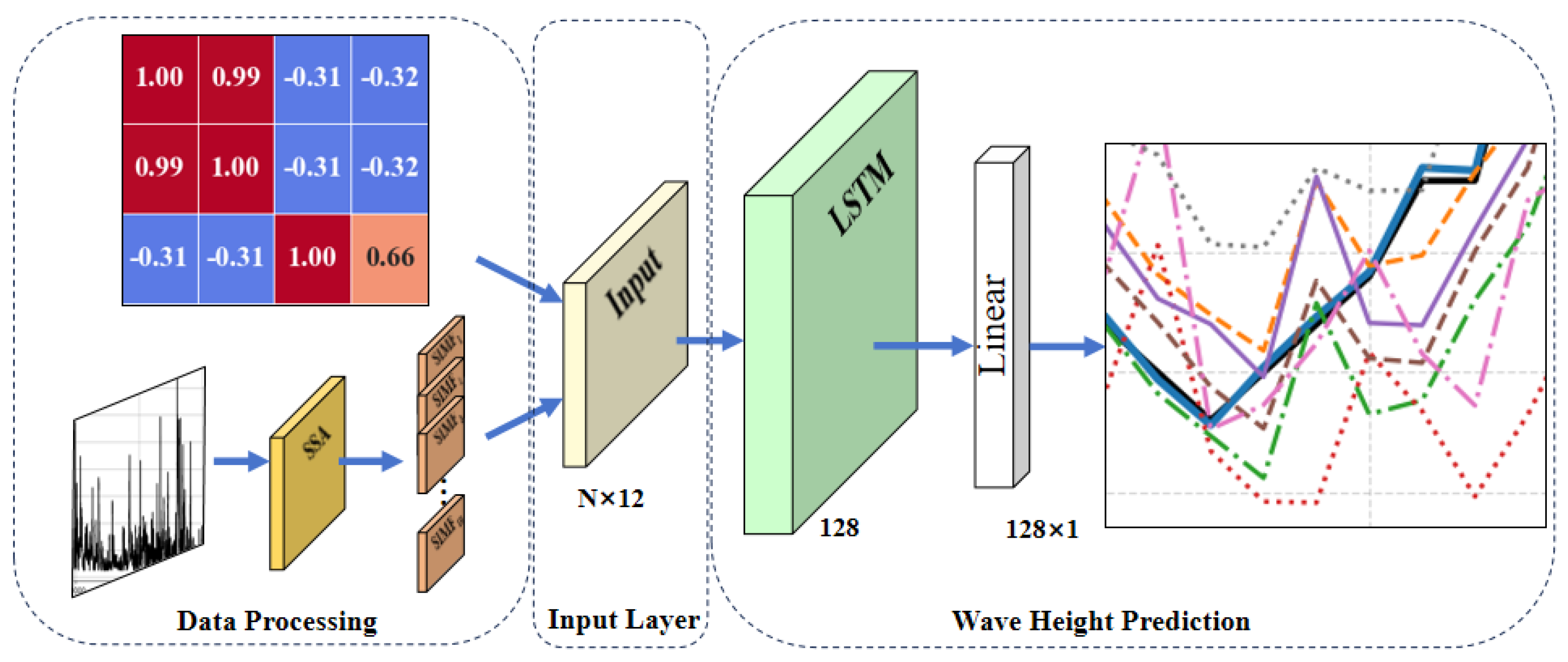
2.2.3. Design and Implementation of SWH Prediction Model
2.2.4. Definitions and Background Information of Comparative Models
2.2.5. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment and Parameter Settings
3.2. Comparative Analysis of SWH Prediction Effects
3.2.1. SSA Decomposition
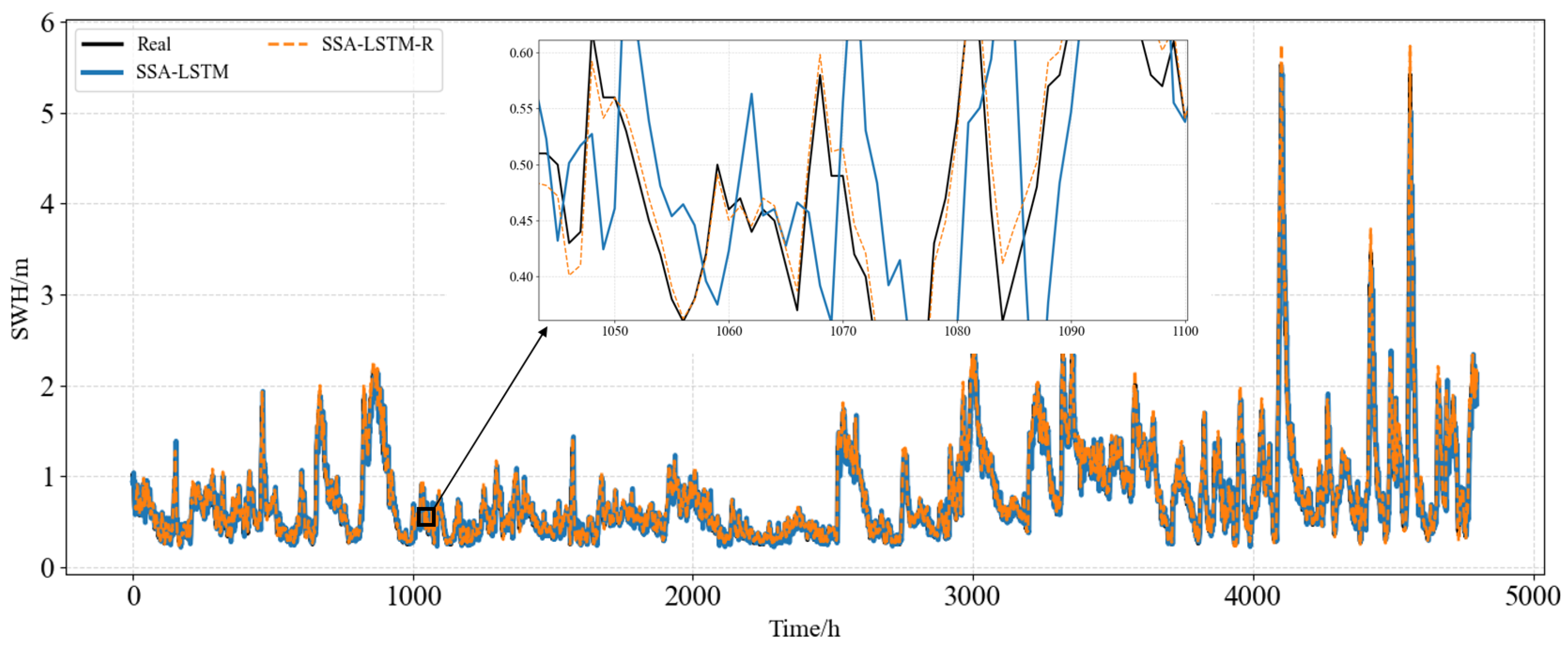
3.2.2. Comparison of Model Prediction Effects
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SWH | Significant Wave Height |
| SSA | Singular Spectrum Analysis |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Squared Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| VMD | Variational Mode Decomposition |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System |
| BN | Bayesian Network |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| BPNN | Backpropagation Neural Network |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| BiGRU | Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit |
| TCN | Temporal Convolutional Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| CNN-LSTM | Convolutional Neural Network–Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNN-GRU | Convolutional Neural Network–Gated Recurrent Unit |
References
- Young, I.R.; Zieger, S.; Babanin, A.V. Global trends in wind speed and wave height. Science 2011, 332, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temarel, P.; Bai, W.; Bruns, A.; Derbanne, Q.; Dessi, D.; Dhavalikar, S.; Fonseca, N.; Fukasawa, T.; Gu, X.; Nestegård, A.; et al. Prediction of wave-induced loads on ships: Progress and challenges. Ocean Eng. 2016, 119, 274–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Collazo, C.; Greaves, D.; Iglesias, G. A review of combined wave and offshore wind energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, P.A.J.; Bryden, I.G.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Social and ecological impacts of marine energy development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Andreu, J.; Ceballos, S.; de Alegría, I.M.; Kortabarria, I. Review of wave energy technologies and the necessary power-equipment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.K.; Hubble, E.N. Six-parameter wave spectra. In Coastal Engineering 1976; Coastal Engineering Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1976; pp. 301–328. [Google Scholar]
- Group, T.W. The WAM model—A third generation ocean wave prediction model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1775–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, H.L. User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCH III TM Version 3.14; Technical Note; MMAB Contribution No. 276; U. S. Department of Commerce; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration; National Weather Service; National Centers for Environmental Prediction: Camp Springs, MD, USA, 2009.
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Mahjoobi, J. Comparison between M5′ model tree and neural networks for prediction of significant wave height in Lake Superior. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoobi, J.; Mosabbeb, E.A. Prediction of significant wave height using regressive support vector machines. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohamadi, I.; Bazargan-Lari, M.R.; Kerachian, R.; Nikoo, M.R.; Fallahnia, M. Evaluating the efficacy of SVMs, BNs, ANNs and ANFIS in wave height prediction. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ma, G.; Su, S.-F.; Huang, C.; Boswell, M.K.; Xue, P. A multi-layer perceptron approach for accelerated wave forecasting in Lake Michigan. Ocean Eng. 2020, 211, 107526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Wang, Y.W. Improving coastal ocean wave height forecasting during typhoons by using local meteorological and neighboring wave data in support vector regression models. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, R.; Niculescu-Mizil, A. An empirical comparison of supervised learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghifar, T.; Motlagh, M.N.; Azad, M.T.; Mahdizadeh, M.M. Coastal wave height prediction using Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) in the south Caspian Sea. Mar. Geod. 2017, 40, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J. A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xiao, N.; Dong, S. A novel model to predict significant wave height based on long short-term memory network. Ocean Eng. 2020, 205, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörges, C.; Berkenbrink, C.; Stumpe, B. Prediction and reconstruction of ocean wave heights based on bathymetric data using LSTM neural networks. Ocean Eng. 2021, 232, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minuzzi, F.C.; Farina, L. A deep learning approach to predict significant wave height using long short-term memory. Ocean Model. 2023, 181, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Bi, F.; Bai, Z. A forecasting model for wave heights based on a long short-term memory neural network. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.-F.; Chen, Z.; Khoo, B.C.; Zhang, A.-M. Long-time prediction of sea wave trains by LSTM machine learning method. Ocean Eng. 2022, 262, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Ying, F.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Multi-step-ahead significant wave height prediction using a hybrid model based on an innovative two-layer decomposition framework and LSTM. Renew. Energy 2023, 203, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Ma, X. An integrated long-short term memory algorithm for predicting polar westerlies wave height. Ocean Eng. 2020, 215, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VS, F.E. Forecasting significant wave height using RNN-LSTM models. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 1141–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilling, G.; Flandrin, P.; Goncalves, P. On empirical mode decomposition and its algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing NSIP-03, Grado, Italy, 8–11 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, R.; Roy, C.; Motamedi, S.; Shamshirband, S.; Petković, D. Selection of climatic parameters affecting wave height prediction using an enhanced Takagi-Sugeno-based fuzzy methodology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Dong, S. A novel multivariable hybrid model to improve short and long-term significant wave height prediction. Appl. Energy 2023, 351, 121813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabique, L.; Annapurnaiah, K.; Nair, T.B.; Srinivas, K. Contribution of Southern Indian Ocean swells on the wave heights in the Northern Indian Ocean—A modeling study. Ocean Eng. 2012, 43, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Hou, Y.; Hung, Y.S.; Zou, Y.X. A comparative analysis of Spearman’s rho and Kendall’s tau in normal and contaminated normal models. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Winter, J.C.F.; Gosling, S.D.; Potter, J. Comparing the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients across distributions and sample sizes: A tutorial using simulations and empirical data. Psychol. Methods 2016, 21, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, P.H. Critical values for Spearman’s rank order correlation. J. Educ. Stat. 1989, 14, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Mu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, F. Feature genes selection using supervised locally linear embedding and correlation coefficient for microarray classification. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018, 5490513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.D.; Ginger, J.D. The gust wind speed duration in AS/NZS 1170.2. Aust. J. Struct. Eng. 2012, 13, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhunen, K. Über lineare Methoden in der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. 1947, 37, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H. Singular spectrum analysis: Methodology and comparison. J. Data Sci. 2007, 05, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yule, G.U. On the theory of correlation. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1897, 60, 812–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchkarev, A. Performance metrics (error measures) in machine learning regression, forecasting and prognostics: Properties and typology. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitha, R.; Al Mamun, A. Regional ocean wave height prediction using sequential learning neural networks. Ocean Eng. 2017, 129, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X. Wave height prediction based on CNN-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence (MLBDBI), Taiyuan, China, 23–25 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar]
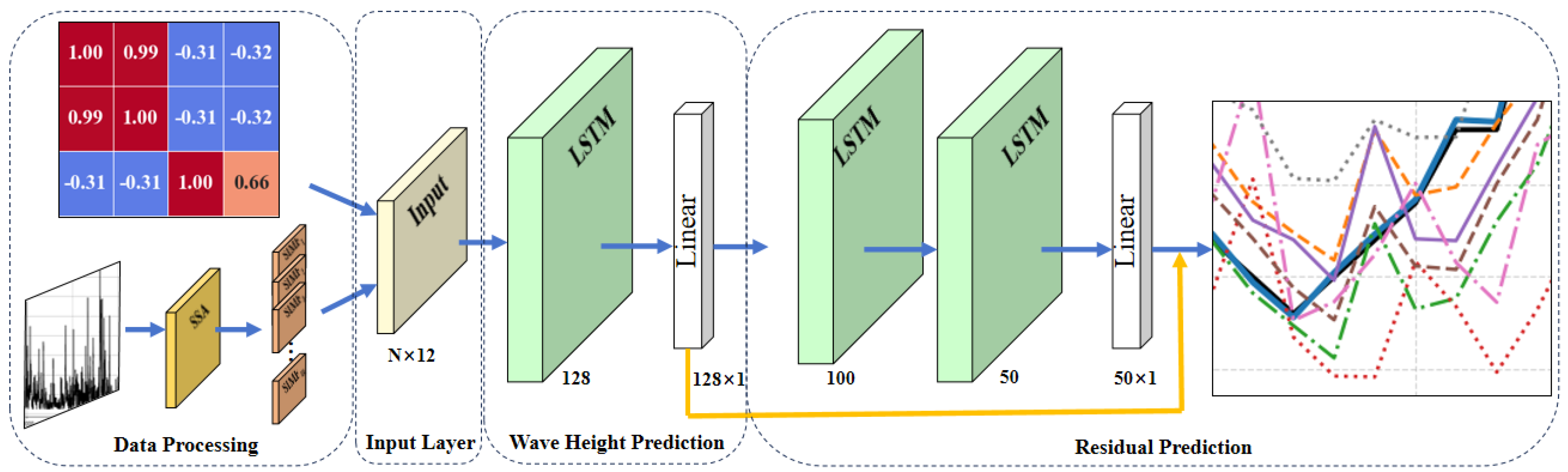
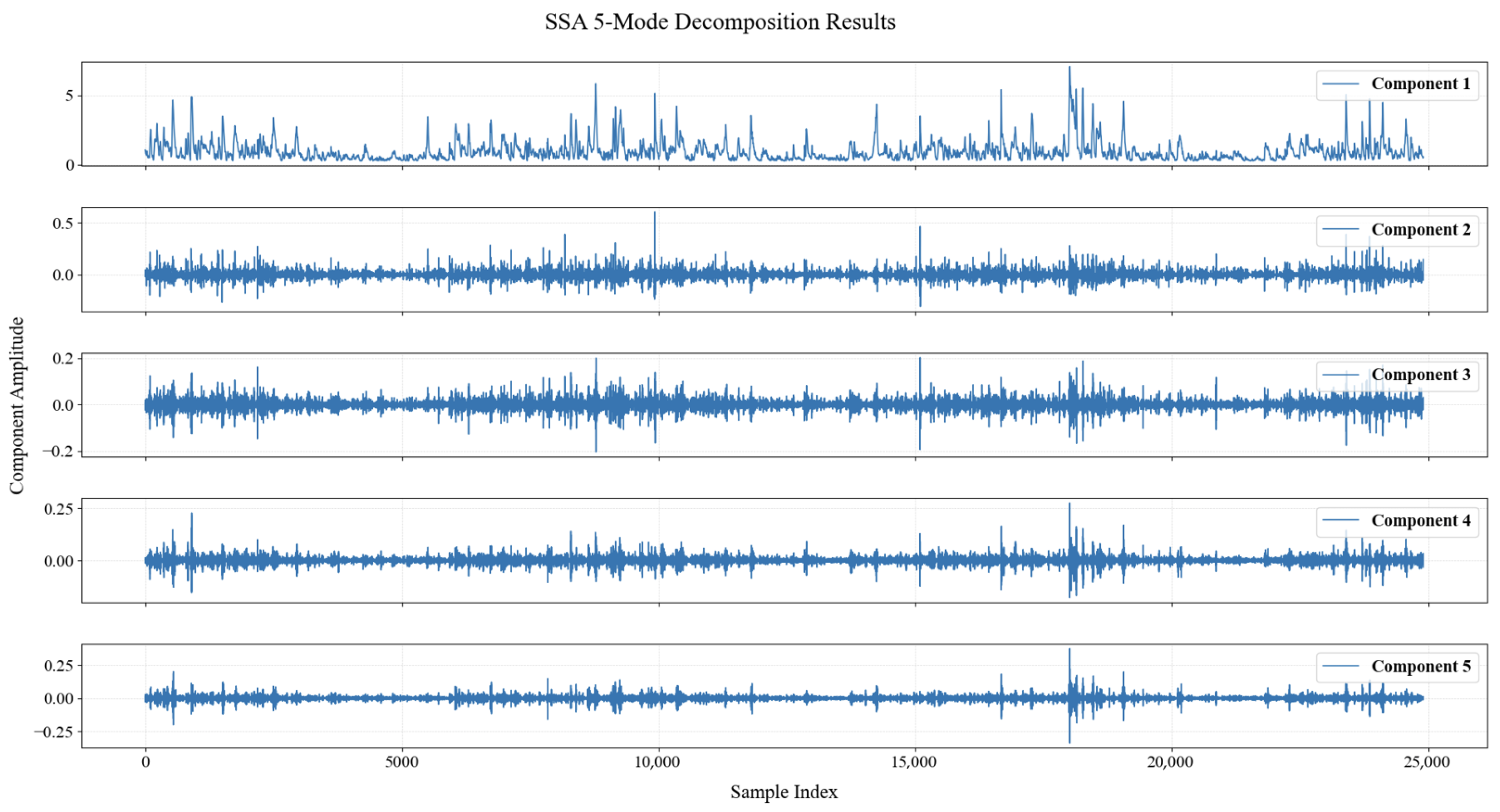
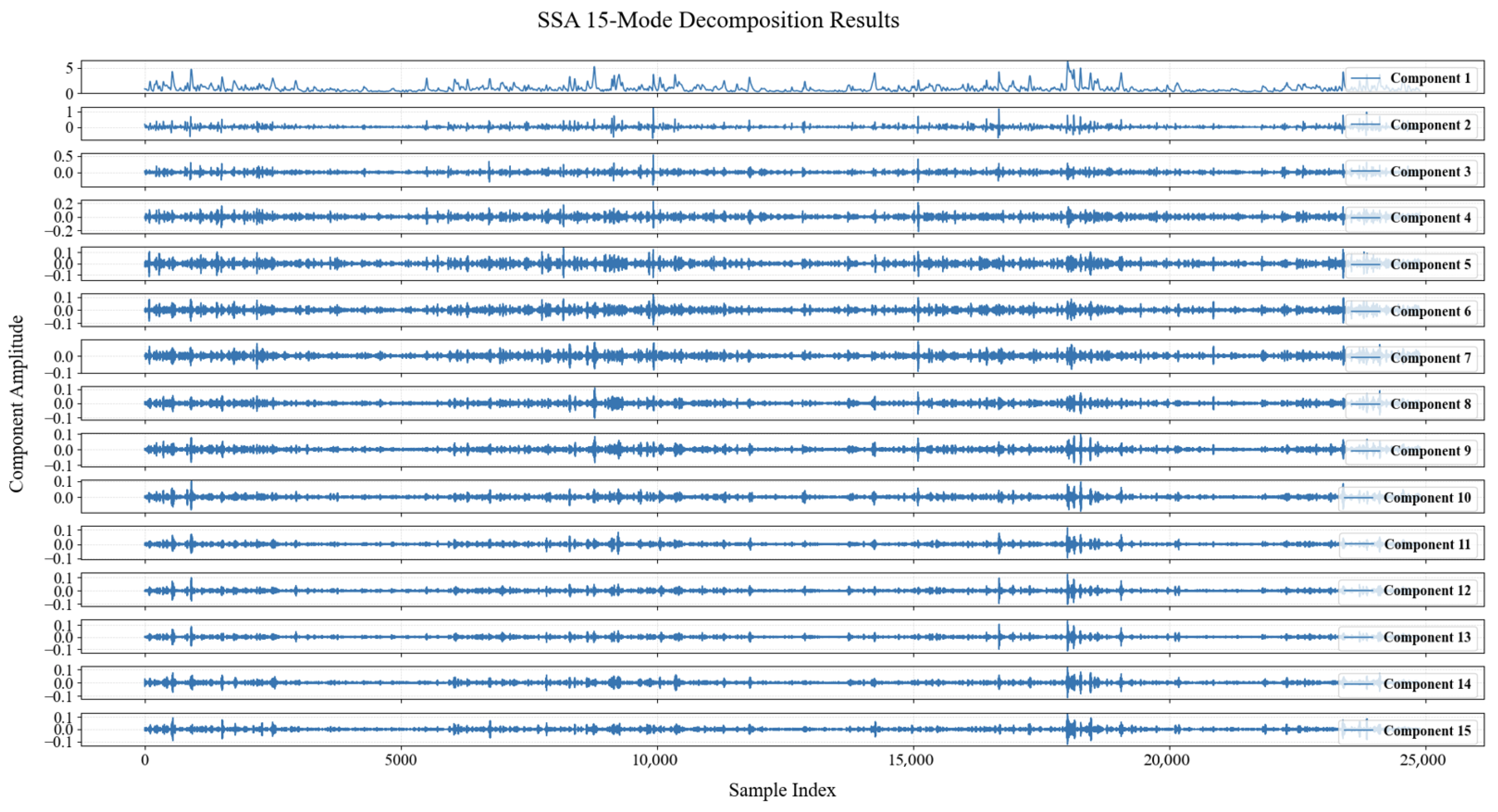
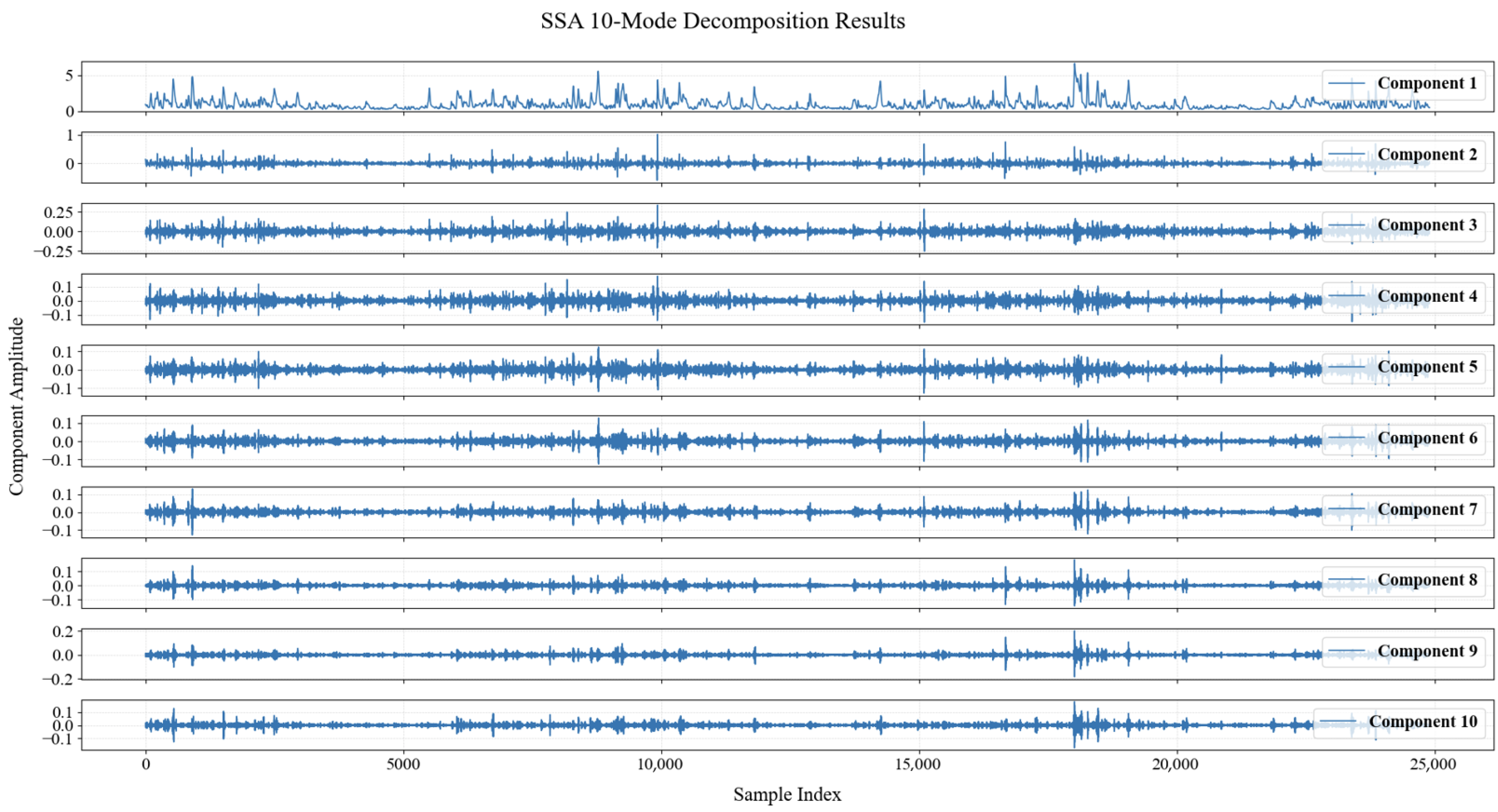
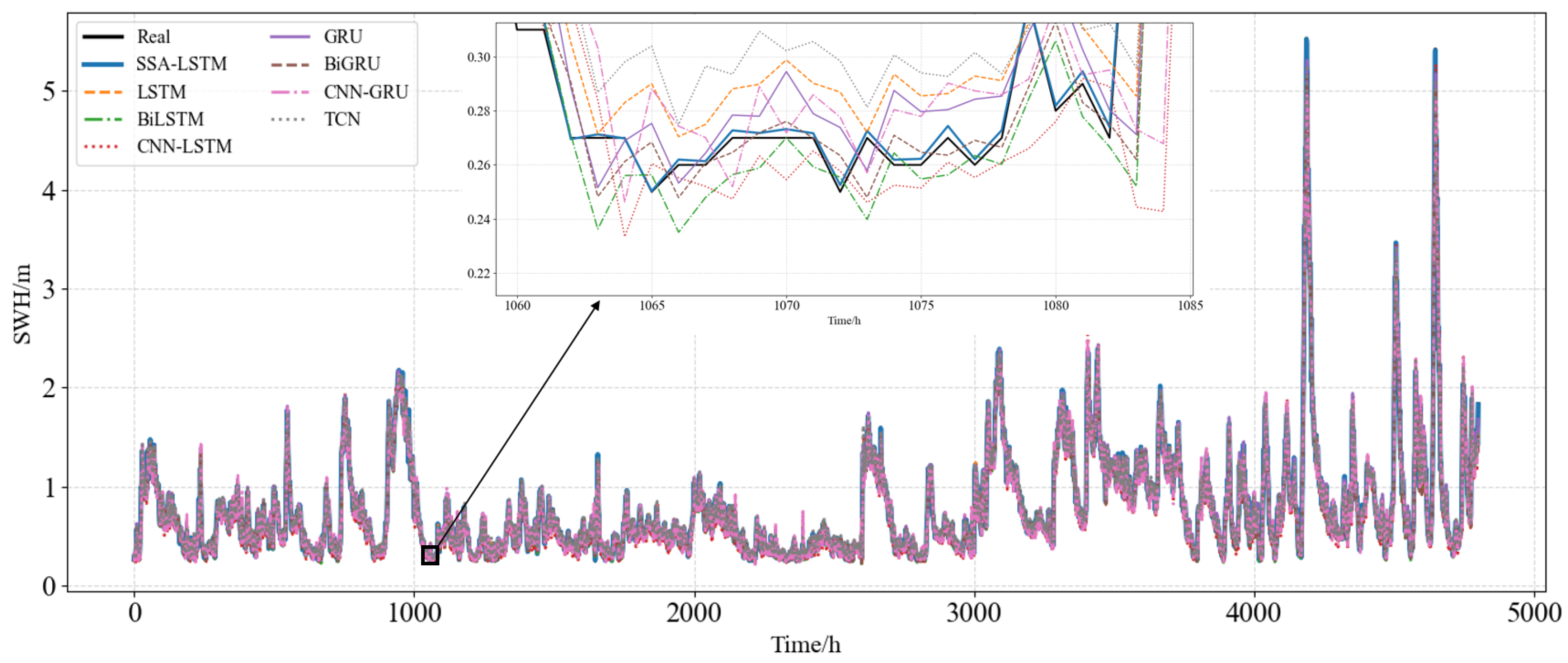
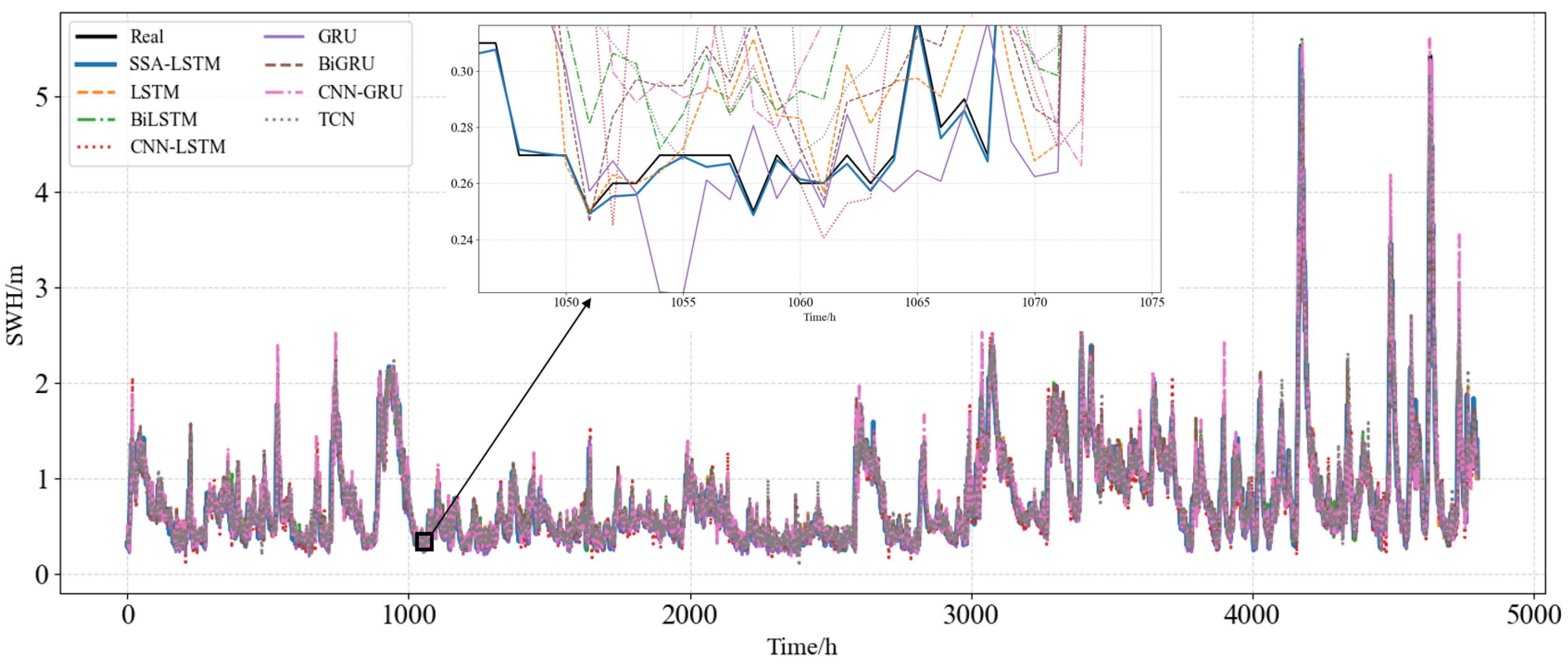
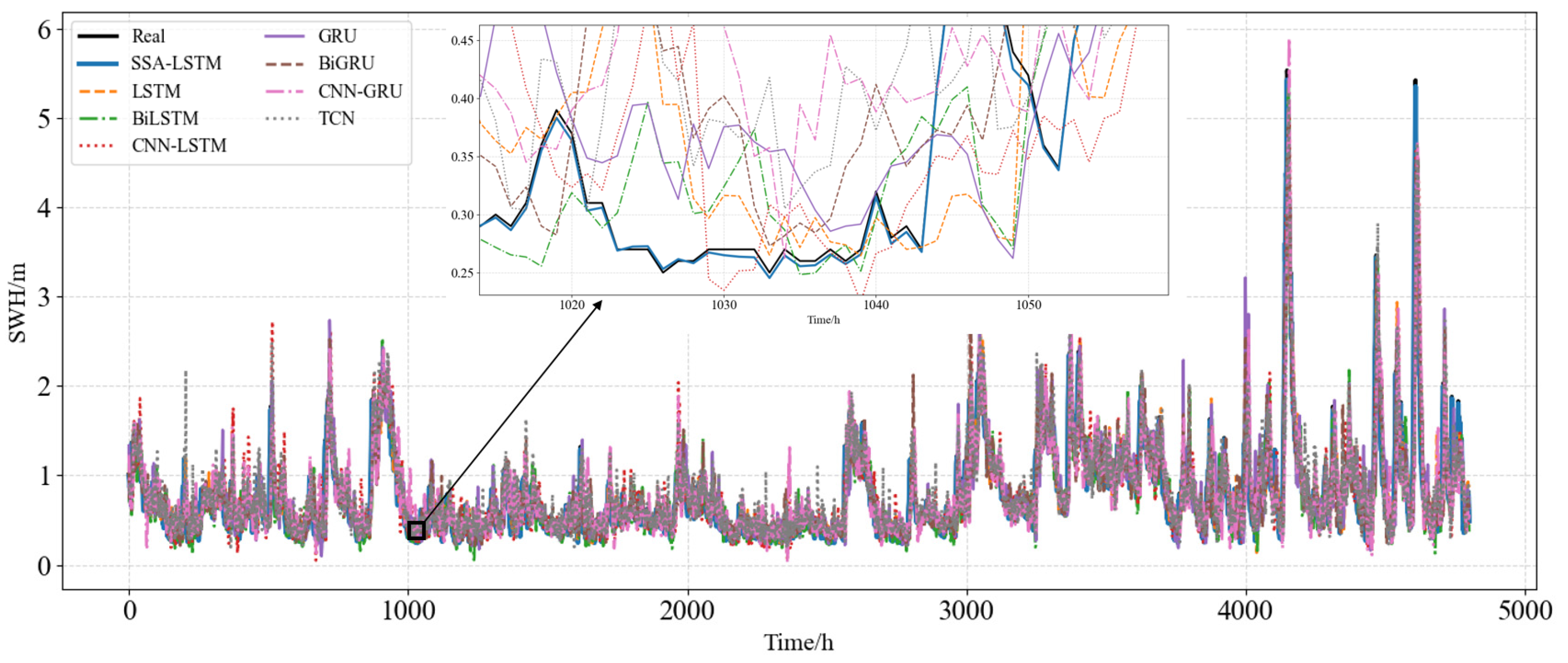
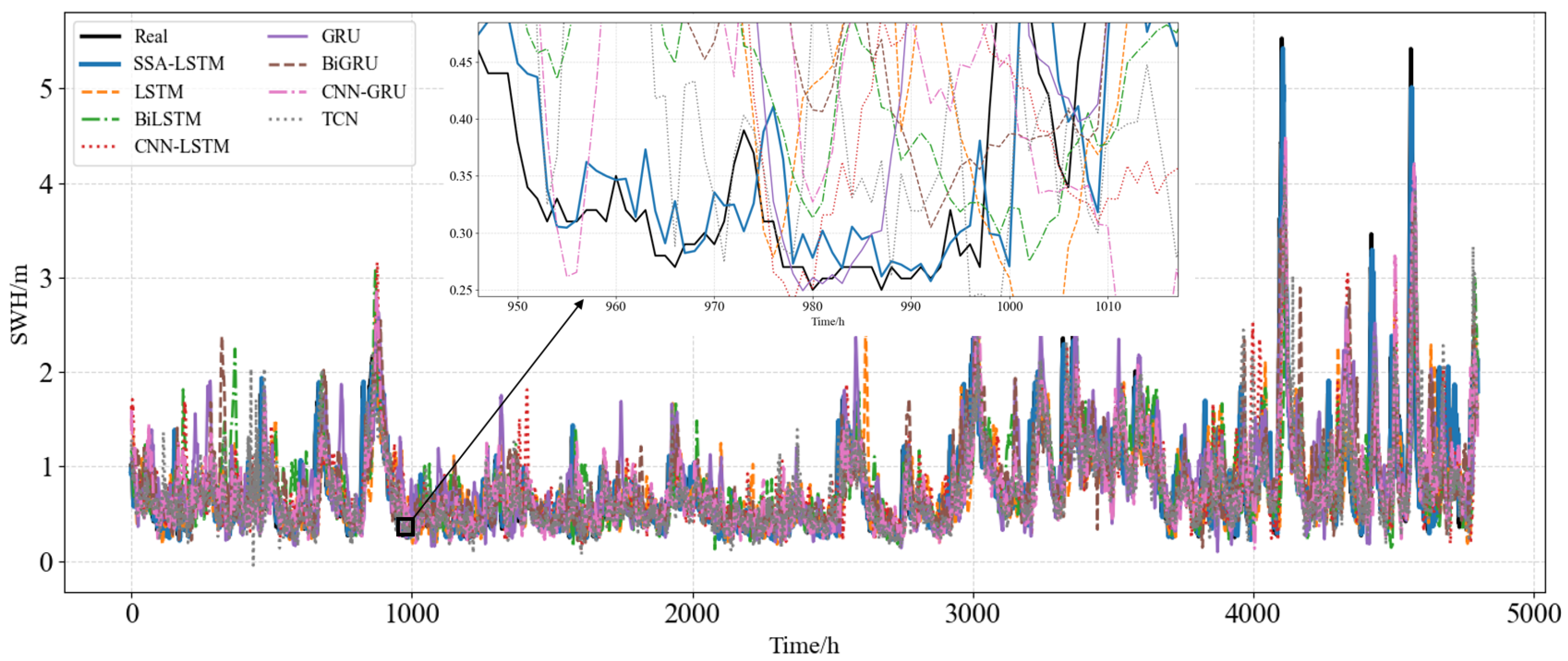
| Indicator | Unit | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WDIR | ° | 189.60 | 360.00 | 1.00 | 98.99 |
| WSPD | m/s | 6.32 | 22.80 | 0 | 3.36 |
| GST | m/s | 7.68 | 28.70 | 0.10 | 4.15 |
| SWH | m | 0.94 | 8.16 | 0.25 | 0.74 |
| DPD | s | 7.40 | 19.05 | 2.25 | 3.03 |
| APD | s | 4.83 | 11.73 | 2.66 | 1.32 |
| MWD | ° | 126.01 | 360.00 | 1.00 | 85.83 |
| PRES | hPa | 1015.61 | 1043.90 | 972.50 | 8.65 |
| ATMP | °C | 10.26 | 29.30 | −19.50 | 7.97 |
| WTMP | °C | 11.73 | 25.50 | 2.40 | 5.68 |
| Epochs | Batch Size | Learning Rate | Optimizer | Loss | Units | Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 36 | 0.001 | Adam | MSE | 128 | 3 |
| Model | Prediction Duration /h | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE /% | R2 /% | Parameter Count | T—Time /s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA-LSTM | 1 | 0.00001 | 0.00309 | 0.00211 | 0.34991 | 99.99733 | 72,321 | 171.17 |
| LSTM | 0.00561 | 0.07607 | 0.05022 | 7.04013 | 97.88904 | 67,201 | 160.27 | |
| BiLSTM | 0.00697 | 0.0842 | 0.05455 | 7.36843 | 97.60021 | 134,401 | 243.63 | |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.01612 | 0.12594 | 0.08667 | 11.79888 | 94.37273 | 99,265 | 159.34 | |
| GRU | 0.00638 | 0.07896 | 0.05172 | 7.13618 | 97.78301 | 50,817 | 205.73 | |
| BiGRU | 0.00637 | 0.08243 | 0.05331 | 7.10264 | 97.57611 | 16,301 | 298.83 | |
| CNN-GRU | 0.01466 | 0.12037 | 0.08103 | 10.95153 | 94.92639 | 74,945 | 399.11 | |
| TCN | 0.00672 | 0.08324 | 0.05726 | 8.55907 | 97.51558 | 136,577 | 1062.66 | |
| SSA-LSTM | 3 | 0.00007 | 0.00638 | 0.00472 | 0.77113 | 99.98361 | 72,579 | 419.36 |
| LSTM | 0.02257 | 0.14912 | 0.09893 | 13.92864 | 91.92131 | 67,459 | 388.31 | |
| BiLSTM | 0.02637 | 0.16249 | 0.10502 | 15.02073 | 90.71068 | 134,915 | 701.28 | |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.03901 | 0.19822 | 0.13309 | 18.51217 | 85.77199 | 99,523 | 333.25 | |
| GRU | 0.02422 | 0.15305 | 0.10106 | 13.74597 | 91.76214 | 51,075 | 528.44 | |
| BiGRU | 0.02422 | 0.15735 | 0.10276 | 14.82183 | 91.07953 | 16,503 | 834.77 | |
| CNN-GRU | 0.04337 | 0.20778 | 0.13497 | 18.91261 | 84.90501 | 75,203 | 566.32 | |
| TCN | 0.02499 | 0.15886 | 0.10588 | 15.31471 | 90.97502 | 136,707 | 1672.13 | |
| SSA-LSTM | 6 | 0.00029 | 0.01373 | 0.00997 | 1.22876 | 99.93202 | 72,966 | 918.71 |
| LSTM | 0.06702 | 0.25889 | 0.16029 | 22.14553 | 75.76151 | 67,846 | 793.07 | |
| BiLSTM | 0.07781 | 0.27802 | 0.17627 | 23.91034 | 72.61257 | 135,686 | 1522.28 | |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.09638 | 0.30982 | 0.20441 | 29.21059 | 65.44921 | 99,910 | 679.61 | |
| GRU | 0.08407 | 0.28961 | 0.19223 | 26.91282 | 70.29759 | 51,462 | 1182.32 | |
| BiGRU | 0.07951 | 0.28148 | 0.18059 | 25.48862 | 71.51824 | 16,806 | 1471.71 | |
| CNN-GRU | 0.11804 | 0.34483 | 0.22162 | 31.91234 | 57.94445 | 75,590 | 1367.73 | |
| TCN | 0.08934 | 0.29829 | 0.19547 | 28.48735 | 68.05859 | 136,902 | 1783.93 | |
| SSA-LSTM | 12 | 0.03089 | 0.17434 | 0.11047 | 15.01539 | 89.49211 | 73,740 | 1762.43 |
| LSTM | 0.19399 | 0.44031 | 0.28235 | 38.88538 | 31.78927 | 68,620 | 1517.26 | |
| BiLSTM | 0.23507 | 0.48571 | 0.30402 | 43.26738 | 18.05041 | 137,228 | 3061.17 | |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.20062 | 0.44817 | 0.29819 | 43.55292 | 29.42923 | 100,684 | 1253.46 | |
| GRU | 0.21351 | 0.46173 | 0.31849 | 46.48286 | 24.81872 | 52,236 | 2206.91 | |
| BiGRU | 0.18188 | 0.4276 | 0.28571 | 41.32891 | 36.84573 | 17,412 | 3192.65 | |
| CNN-GRU | 0.18127 | 0.42583 | 0.27601 | 38.50116 | 36.08692 | 76,364 | 1681.33 | |
| TCN | 0.16293 | 0.40338 | 0.25327 | 34.01271 | 43.43838 | 137,292 | 1854.22 |
| Model | Prediction Duration /h | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE /% | R2 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA-LSTM | 12 | 0.03089 | 0.17434 | 0.11047 | 15.01539 | 89.49211 |
| SSA-LSTM-R | 0.00286 | 0.05553 | 0.04061 | 5.62437 | 98.91838 |
| Model | Prediction Duration /h | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE /% | R2 /% | Parameter Count | T—Time /s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA-LSTM | 1 | 0.00001 | 0.00309 | 0.00211 | 0.34991 | 99.99733 | 72,321 | 171.17 |
| VMD-LSTM | 0.00172 | 0.04034 | 0.02651 | 3.65238 | 99.42166 | 672,010 | 1799.08 | |
| SSA-LSTM | 3 | 0.00007 | 0.00638 | 0.00472 | 0.77113 | 99.98361 | 72,579 | 419.36 |
| VMD-LSTM | 0.00259 | 0.04862 | 0.03312 | 4.65024 | 99.15418 | 674,590 | 4817.43 | |
| SSA-LSTM | 6 | 0.00029 | 0.01373 | 0.00997 | 1.22876 | 99.93202 | 72,966 | 918.71 |
| VMD-LSTM | 0.00457 | 0.06539 | 0.04886 | 7.25499 | 98.49747 | 678,460 | 8561.29 | |
| SSA-LSTM-R | 12 | 0.00286 | 0.05553 | 0.04061 | 5.62437 | 98.91838 | 145,191 | 1793.41 |
| VMD-LSTM | 0.00429 | 0.06798 | 0.04672 | 6.87207 | 98.36697 | 686,200 | 16,936.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zeng, L.; Shao, W.; Nie, S. Significant Wave Height Prediction Using LSTM Augmented by Singular Spectrum Analysis and Residual Correction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091635
Ning C, Li H, Wang Z, Li C, Zeng L, Shao W, Nie S. Significant Wave Height Prediction Using LSTM Augmented by Singular Spectrum Analysis and Residual Correction. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091635
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Chunlin, Huanyong Li, Zongsheng Wang, Chao Li, Lingkun Zeng, Wenmiao Shao, and Shiqiang Nie. 2025. "Significant Wave Height Prediction Using LSTM Augmented by Singular Spectrum Analysis and Residual Correction" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091635
APA StyleNing, C., Li, H., Wang, Z., Li, C., Zeng, L., Shao, W., & Nie, S. (2025). Significant Wave Height Prediction Using LSTM Augmented by Singular Spectrum Analysis and Residual Correction. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1635. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091635






