Sedimentary Processes of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layers in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Implications for Hydrate Accumulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
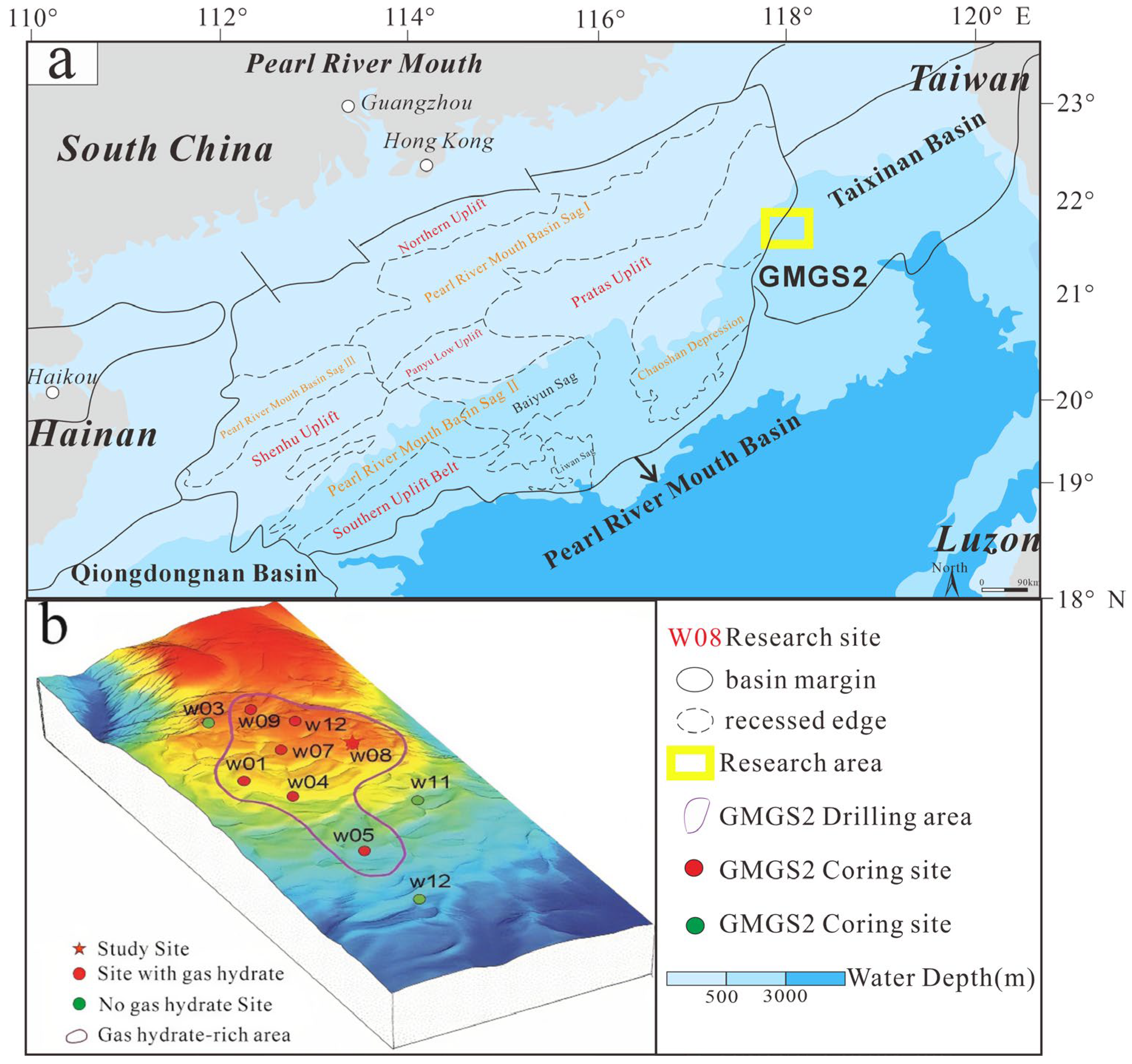
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Site and Samples
3.2. Grain-Size
3.3. Geochemistry
3.4. Microfossils
4. Results
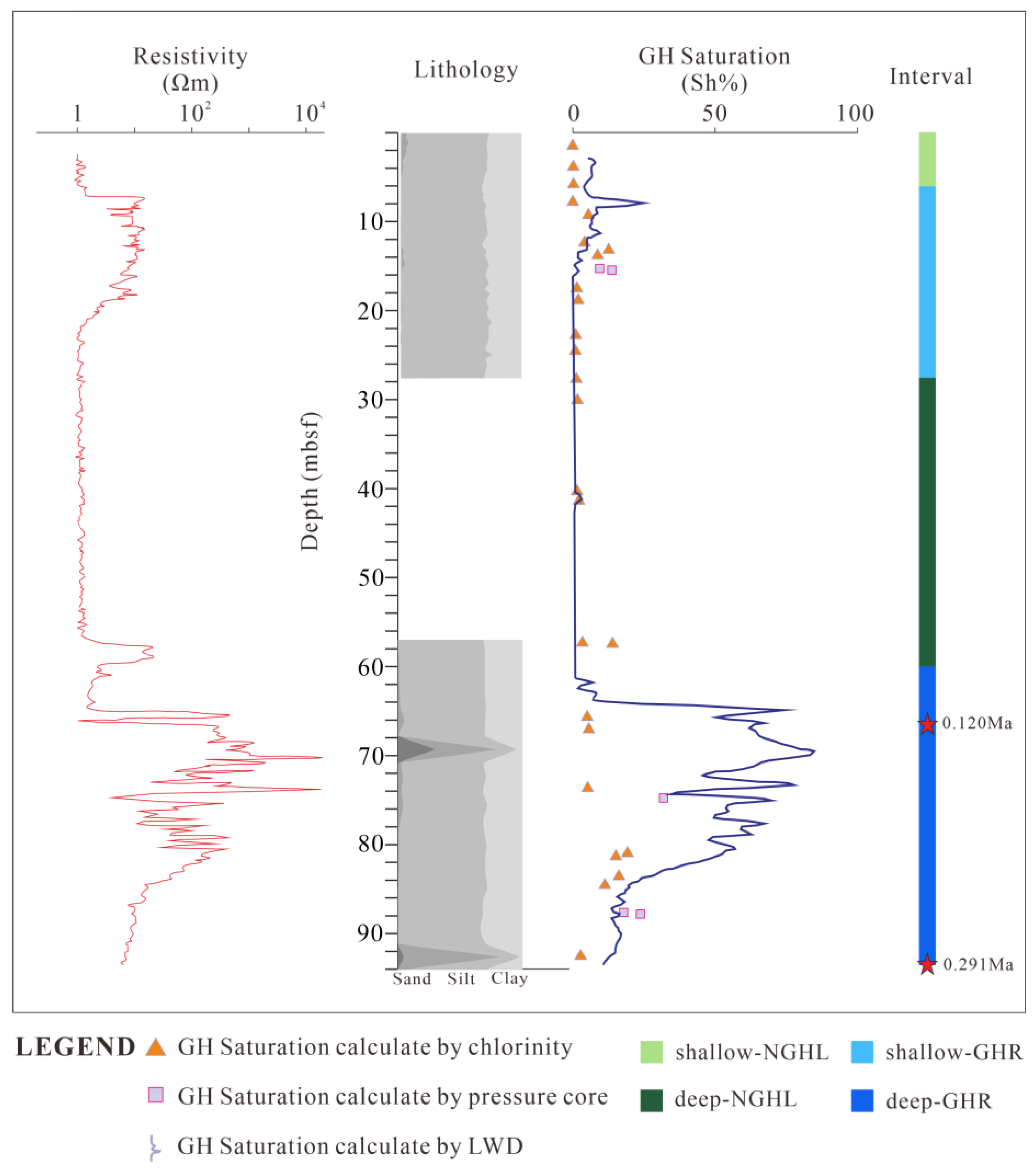
4.1. Hydrate Saturation
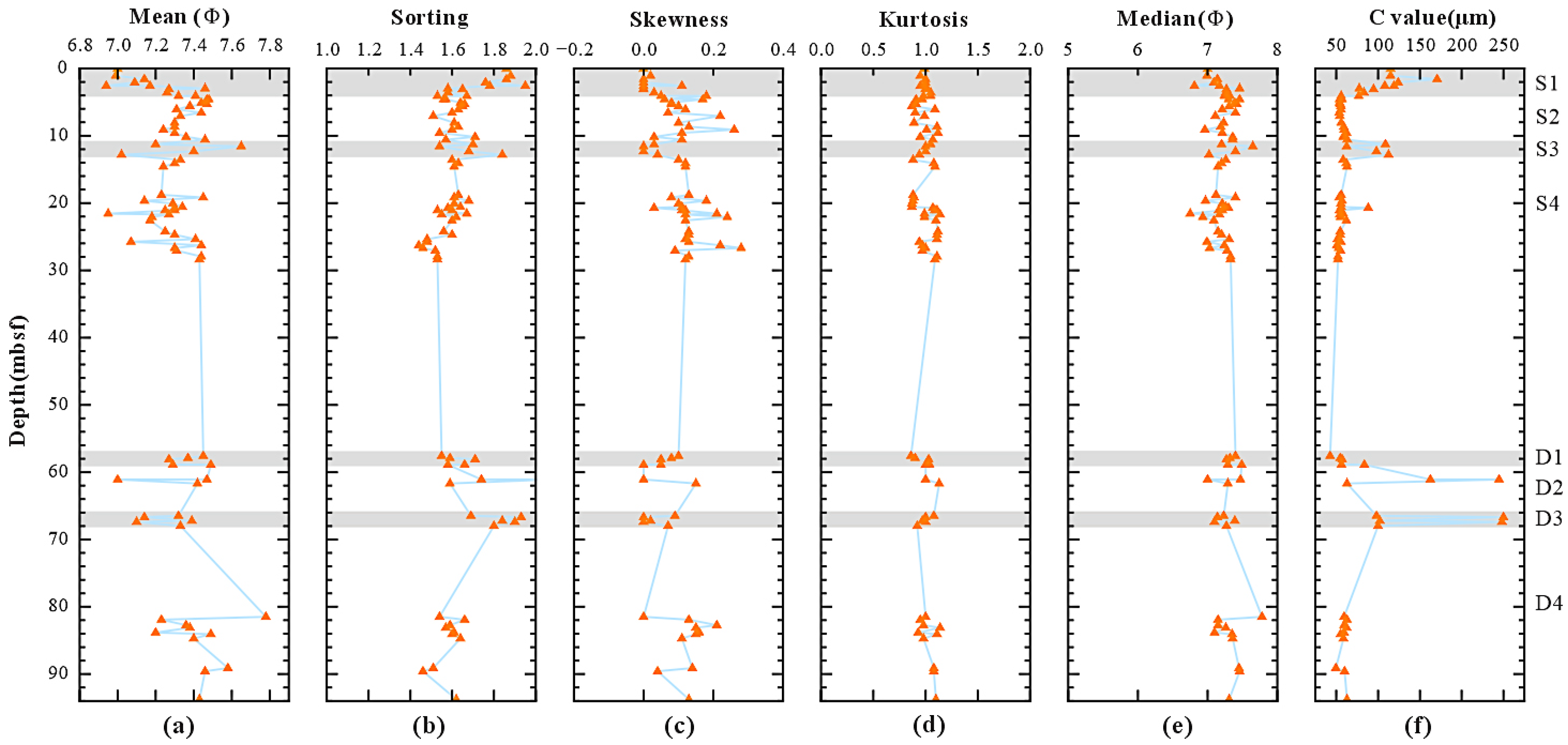
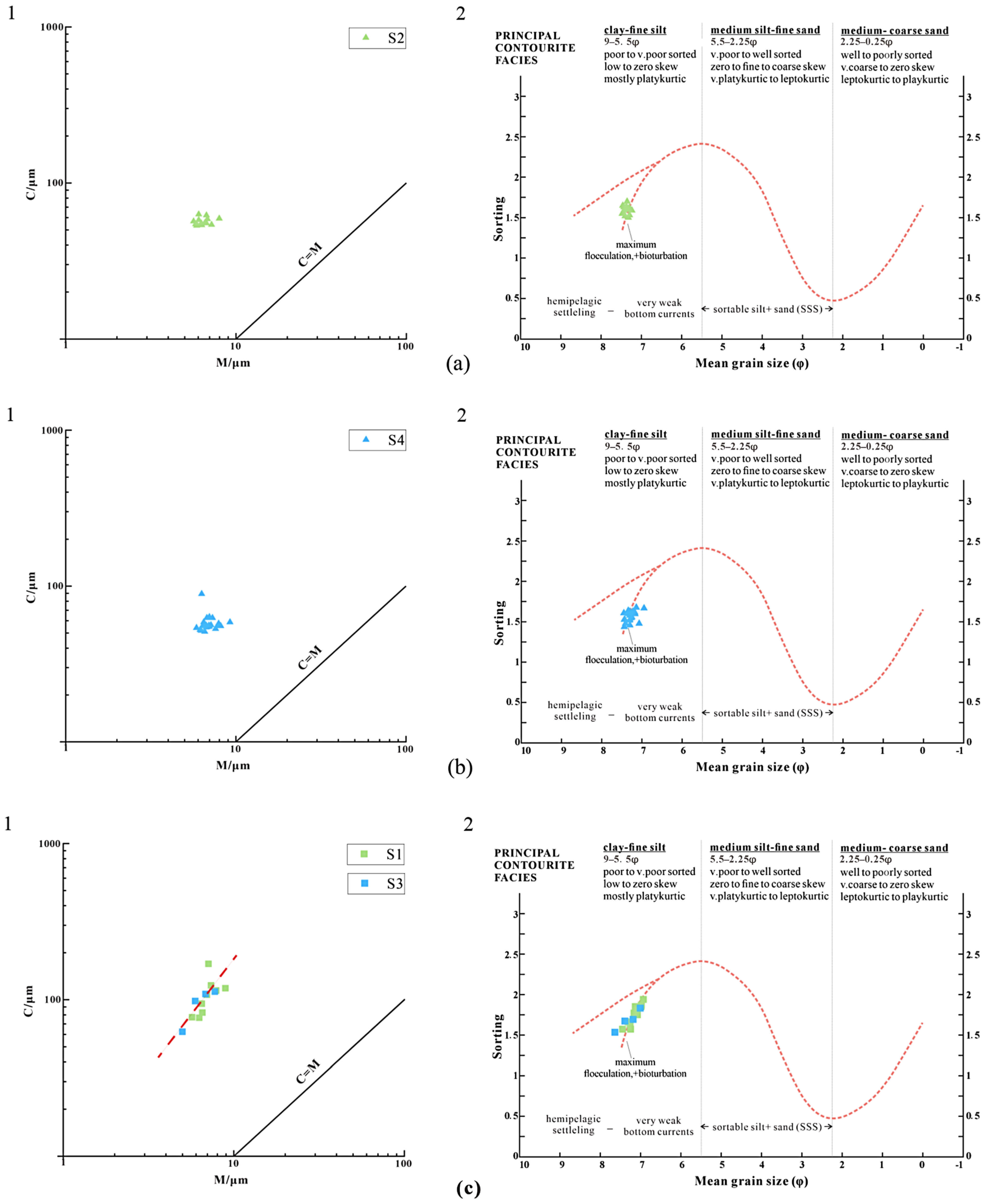
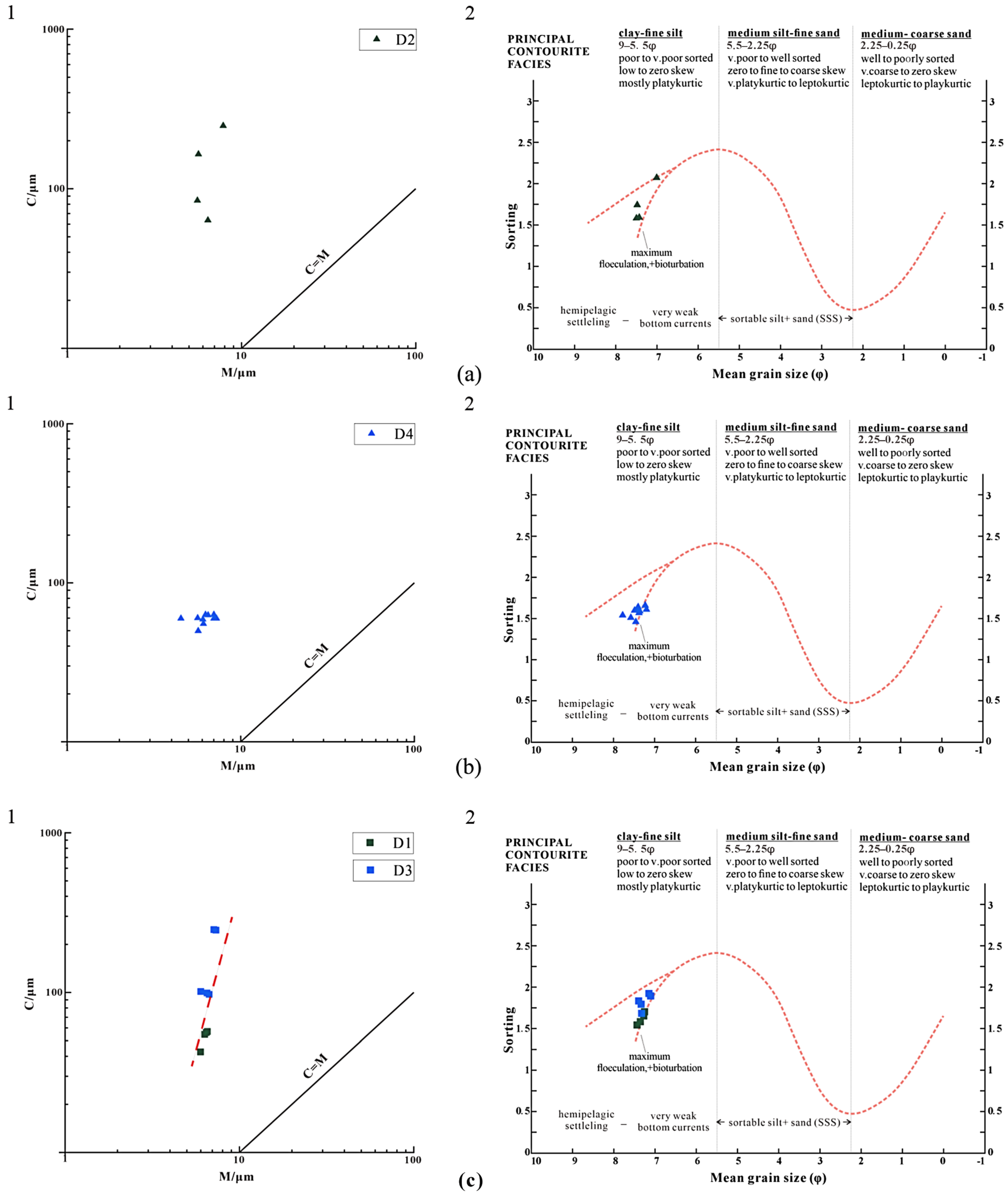
4.2. Particle Size
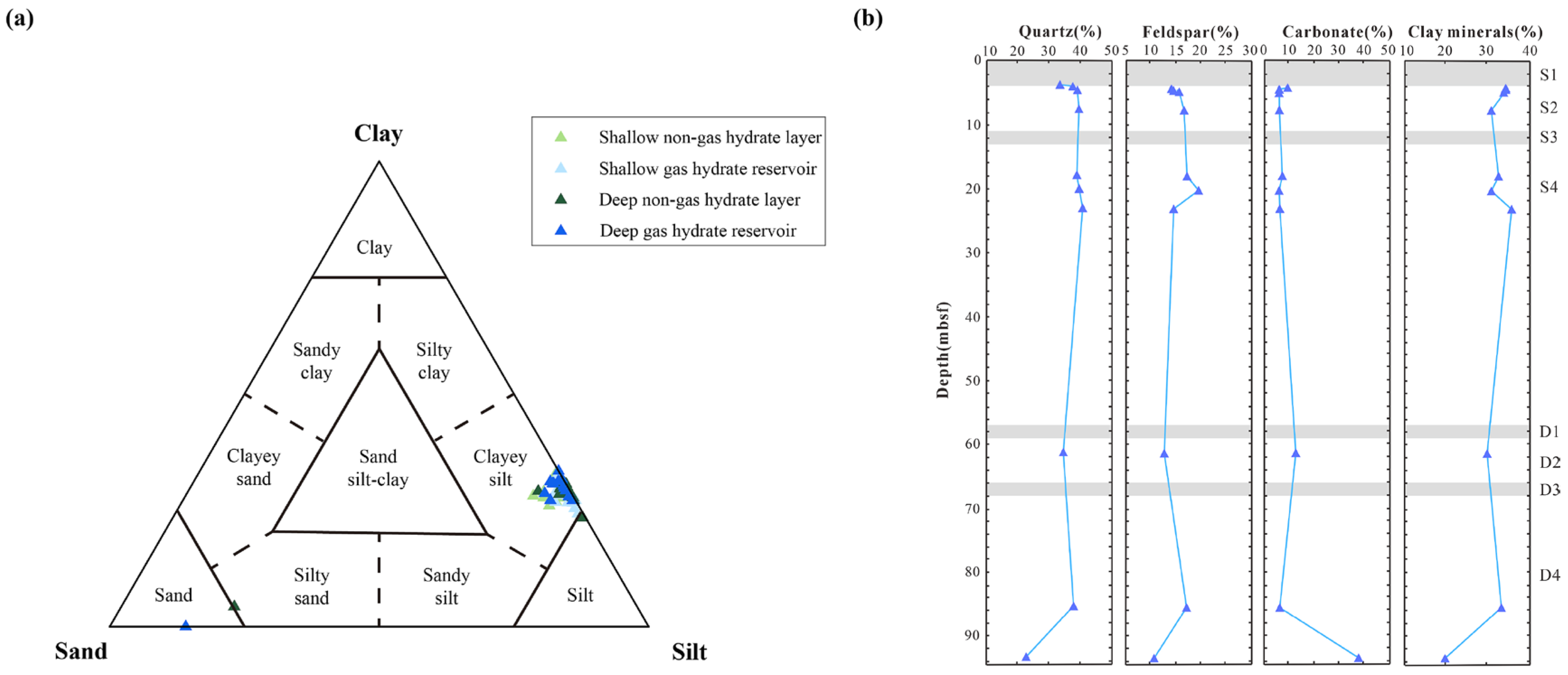
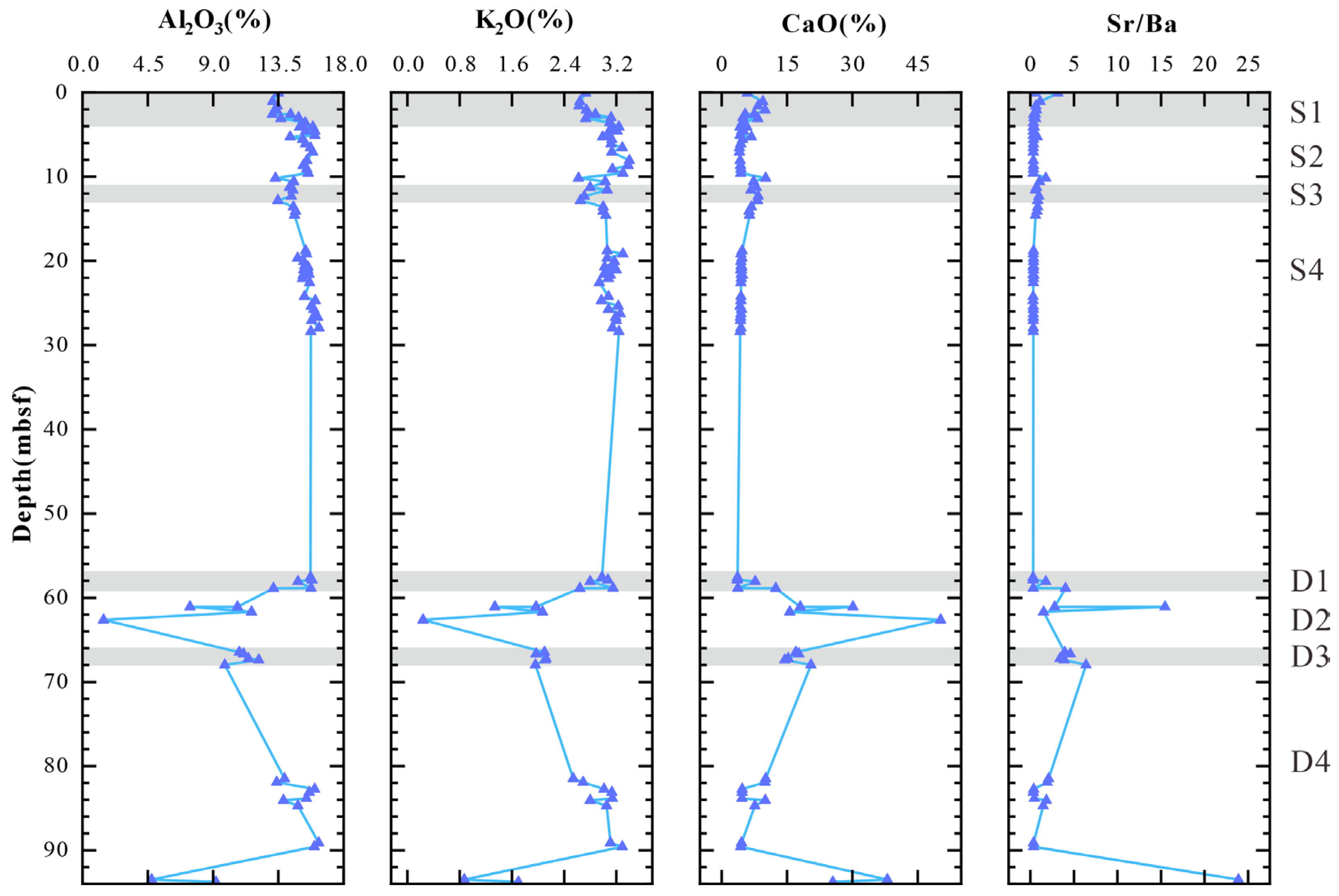
4.3. Geochemical Data
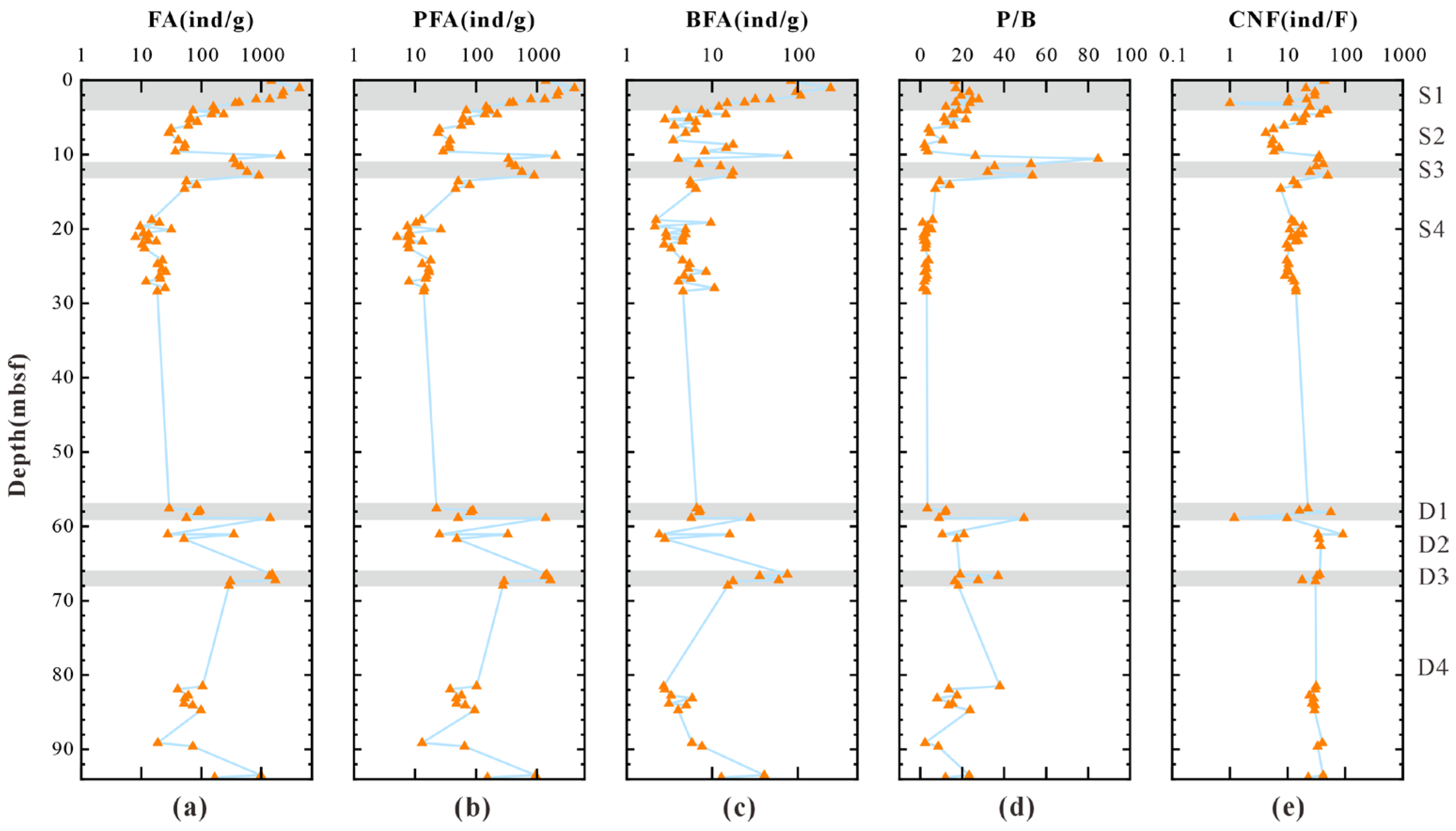
4.4. Microfossil Content
5. Discussion
5.1. Variation Pattern of Hydrate Saturation
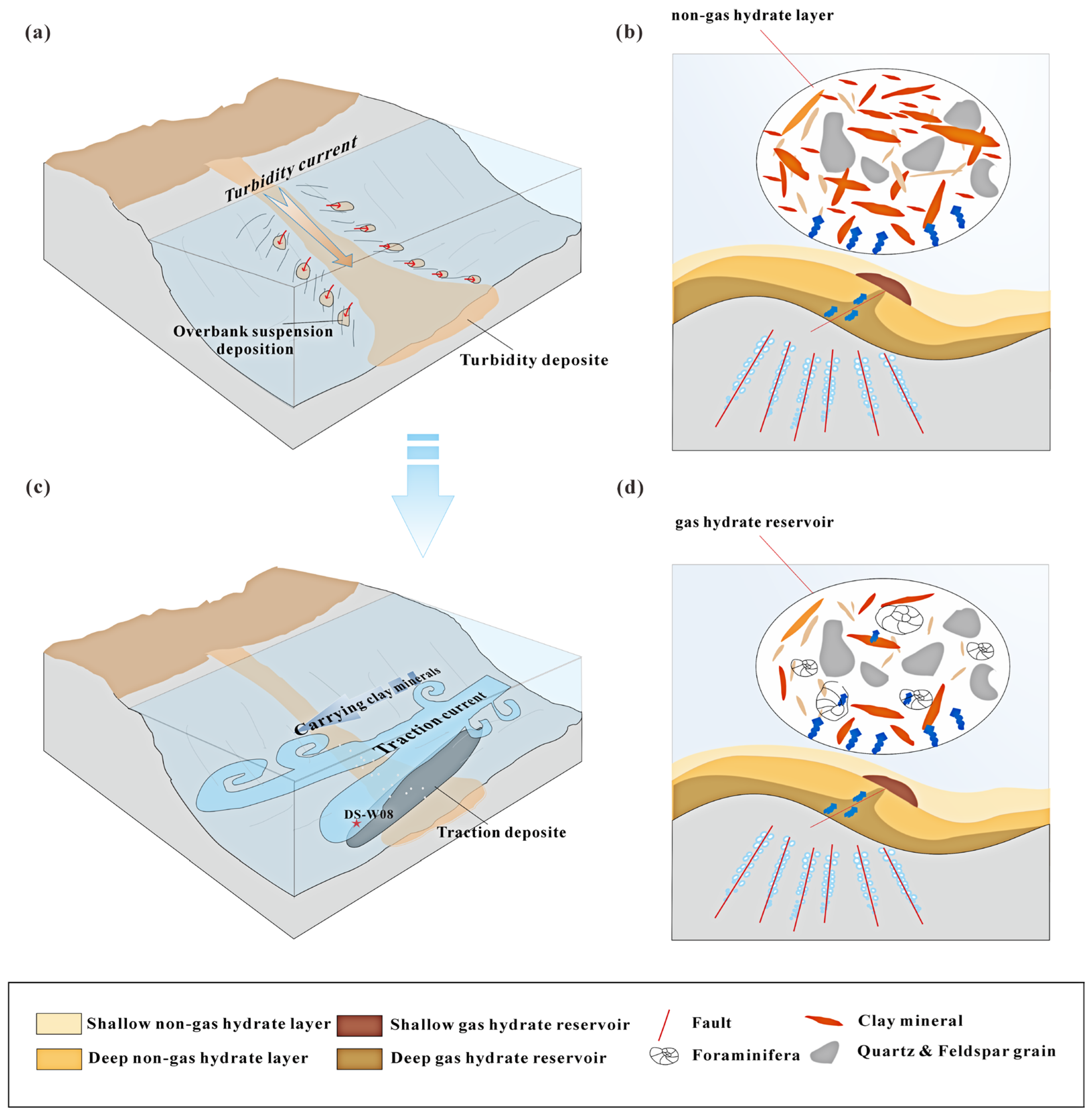
5.2. Sedimentary Process Identification
5.3. Sea-Level Change
5.4. Coupling Relationship Between Sedimentation Processes and Gas Hydrate Enrichment
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The sedimentary process of gas hydrate reservoirs and adjacent layers in the Dongsha Sea is complex. At Site DS-W08, overbank suspended sediments from turbidity currents are superimposed with deep-water traction current deposits. Traction currents dominate during the high sea level periods, while turbidity currents prevail during low sea level periods.
- (2)
- In the Dongsha area, both shallow and deep gas hydrate reservoirs are present. A strong coupling exists between the gas hydrate reservoirs and sedimentary processes. The tops of both shallow and deep gas hydrate reservoirs are associated with sedimentary layers influenced by traction currents.
- (3)
- Sedimentary layers formed by traction currents, rich in foraminifera fossils, promote the formation of high-saturation hydrate reservoirs. Fine-grained turbidites, resulting from turbidity flows, lack effective storage space, are not conducive to hydrate formation.
- (4)
- In foraminifera-rich sedimentary layers affected by traction flow transformation, gas hydrate accumulation leads to a sudden reduction in porosity and permeability. This results in the formation of a cap that inhibits the upward migration of gases and fluids, promoting hydrate growth into the overbank suspended sedimentary layers deposited by gravity-driven flows.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sloan, E.D. Fundamental Principles and Applications of Natural Gas Hydrates. Nature 2003, 426, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvenvolden, K.A. Methane Hydrate—A Major Reservoir of Carbon in the Shallow Geosphere? Chem. Geol. 1988, 71, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.D., Jr.; Koh, C.A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 0-429-12914-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel, C. Permafrost-Associated Gas Hydrate: Is It Really Approximately 1% of the Global System? J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.K.; Buelow, W.J.; Ussler, W., III; Borowski, W.S. Increased Continental-Margin Slumping Frequency during Sea-Level Lowstands above Gas Hydrate–Bearing Sediments. Geology 1996, 24, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.K.; Ussler, W., III; Dillon, W.P. Potential Role of Gas Hydrate Decomposition in Generating Submarine Slope Failures. Nat. Gas Hydrate Ocean. Permafr. Environ. 2000, 12, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslin, M.; Owen, M.; Betts, R.; Day, S.; Dunkley Jones, T.; Ridgwell, A. Gas Hydrates: Past and Future Geohazard? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 2369–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gupta, S.; Rutqvist, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, K.; Fan, C.; Yan, W. Can Glacial Sea-Level Drop-Induced Gas Hydrate Dissociation Cause Submarine Landslides? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL106772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvenvolden, K.A. Methane Hydrate in the Global Organic Carbon Cycle. Terra Nova 2002, 14, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppel, C.D.; Kessler, J.D. The Interaction of Climate Change and Methane Hydrates. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 126–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, Z.F.; Kroeger, K.F.; Hosford Scheirer, A.; Seol, Y.; Burgreen-Chan, B.; Graham, S.A. Tectonic Uplift Destabilizes Subsea Gas Hydrate: A Model Example from Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffine, L.; Tang, A.M.; O’neill, N.; Toffin, L.; Paris, J.-D.; Yang, J.; Georgiev, V.; Fietzek, P.; Giustiniani, M.; Tinivella, U. Environmental Challenges Related to Methane Hydrate Decomposition from Climate Change Scenario and Anthropic Activities: State of the Art, Potential Consequences and Monitoring Solutions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 246, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, T.S. Energy Resource Potential of Natural Gas Hydrates. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1971–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R. Is Gas Hydrate Energy within Reach? Science 2009, 325, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makogon, Y.F.; Holditch, S.A.; Makogon, T.Y. Natural Gas-Hydrates—A Potential Energy Source for the 21st Century. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 56, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R.; Collett, T.S. Current Perspectives on Gas Hydrate Resources. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.R.; Yang, S.H.B.; Babu, P.; Linga, P.; Li, X.-S. Review of Natural Gas Hydrates as an Energy Resource: Prospects and Challenges. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1633–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Ni, Y.; Huang, S.; Peng, W.; Han, W.; Gong, D.; Wei, W. Genetic Types of Gas Hydrates in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handwerger, A.L.; Rempel, A.W.; Skarbek, R.M. Submarine Landslides Triggered by Destabilization of High-saturation Hydrate Anomalies. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 2429–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Santamarina, J.C.; Waite, W.F.; Kneafsey, T.J. Hydrate Morphology: Physical Properties of Sands with Patchy Hydrate Saturation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, 2012JB009667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Su, X.; Sha, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. Geological Features, Controlling Factors and Potential Prospects of the Gas Hydrate Occurrence in the East Part of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Sun, J.; Gu, Y.; Qin, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ning, F. Revised Inflow Performance Relationship for Productivity Prediction from Marine Sandy Hydrate Reservoirs in Nankai Trough. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 238, 212845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Collett, T.S.; Lewis, K.A. Anisotropic Models to Account for Large Borehole Washouts to Estimate Gas Hydrate Saturations in the Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrate Joint Industry Project Leg II Alaminos Canyon 21 B Well. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2012, 34, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Collett, T.S. Gas Hydrate Saturations Estimated from Fractured Reservoir at Site NGHP-01-10, Krishna-Godavari Basin, India. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2009, 114, 2008JB006237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Cheng, C.; Xiong, P.; Kuang, Z.; Liang, J.; Lai, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Jiang, T. Sand-Rich Gas Hydrate and Shallow Gas Systems in the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Luo, K.; Fang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liang, J.; Liang, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Grain-Size Characteristics of Fine-Grained Sediments and Association with Gas Hydrate Saturation in Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 129, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fang, Y.; Lu, H.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, S. Distribution and Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrates in the Shenhu Sea Area, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J.Q.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Fu, S.Y.; Sha, Z.B. Preliminary Results of China’s Third Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition: A Critical Step from Discovery to Development in the South China Sea. Cent. Nat. Gas Oil 2015, 412, 386–7614. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, B.-J.; Collett, T.S.; Riedel, M.; Kim, G.Y.; Chun, J.-H.; Bahk, J.-J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Yoo, D.-G. Scientific Results of the Second Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition in the Ulleung Basin (UBGH2). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentino, C.; Conti, S.; Fioroni, C.; Fontana, D. Evidences for Paleo-Gas Hydrate Occurrence: What We Can Infer for the Miocene of the Northern Apennines (Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Su, P.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Liang, J. Controlling Effect of Particle Size on Gas Hydrate Enrichment in Fine-Grained Sediments. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2024EA003594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hutchinson, D.R.; Wu, S.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y. Elevated Gas Hydrate Saturation within Silt and Silty Clay Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B05102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Qin, X.; Sun, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, C.; Zhu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhou, Y. The Impact of Mineral Compositions on Hydrate Morphology Evolution and Phase Transition Hysteresis in Natural Clayey Silts. Energy 2023, 274, 127303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Balomajumder, C.; Arora, A.; Dixit, G.; Gomari, S.R. Physio-Chemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments of the Kerala-Konkan, Krishna-Godavari, and Mahanadi Basins. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, C.; Liang, J.; Yang, J. Mineralogy and Pore Characteristics of Marine Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 141, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Gupta, K.M.; Linga, P.; Jiang, J. Molecular Insights into the Nucleation and Growth of CH4 and CO2 Mixed Hydrates from Microsecond Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 25225–25236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Gu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z. Experimental Study on Permeability of Methane Hydrate Clayey Interbedded Sediments Considering Effective Stress and Hydrate Dissociation. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 11113–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quainoo, A.K.; Negash, B.M.; Bavoh, C.B.; Idris, A.; Shahpin, H.B.A.; Yaw, A.D. Inhibition Impact of Amino Acids on Swelling Clays: An Experimental and COSMO-RS Simulation Evaluation. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 13985–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Relations between Biogenic Component (Foraminifera) and Highly Saturated Gas Hydrates Distribution from Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2013, 38, 0907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.D.; Pittman, E.D. Authigenic Clays in Sandstones; Recognition and Influence on Reservoir Properties and Paleoenvironmental Analysis. J. Sediment. Res. 1977, 47, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Esteban, M. Paleoclimatic Controls on Sedimentation, Diagenesis, and Reservoir Quality: Lessons from Miocene Carbonates. AAPG Bull. 1994, 78, 519–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, Z.F.; McHargue, T.; Kremer, C.H.; Bloch, R.B.; Gooley, J.T.; Jaikla, C.; Harrington, J.; Graham, S.A. Peak Cenozoic Warmth Enabled Deep-Sea Sand Deposition. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, Z.F.; McHargue, T.R.; Graham, S.A. Global Eocene-Oligocene Unconformity in Clastic Sedimentary Basins. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 258, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R.; Rose, K.; Collett, T.S.; Lee, M.; Winters, W.; Lewis, K.A.; Agena, W. Geologic Controls on Gas Hydrate Occurrence in the Mount Elbert Prospect, Alaska North Slope. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Flemings, P.B.; Malinverno, A.; Collett, T.S.; Darnell, K. Mechanisms of Methane Hydrate Formation in Geological Systems. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 1146–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafov, L.N.; Burton, Z.F.; Haines, S.S.; Scheirer, A.H.; Masurek, N.; Boswell, R.; Frye, M.; Seol, Y.; Graham, S.A. Terrebonne Basin, Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrate Resource Evaluation and 3-D Modeling of Basin-Scale Sedimentation, Salt Tectonics, and Hydrate System Evolution since the Early Miocene. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2025, 176, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.A.; Wei, J.; Kuang, Z.; He, Y. Geological Occurrence and Accumulation Mechanism of Natural Gas Hydrates in the Eastern Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea: Insights from Site GMGS5-W9-2018. Mar. Geol. 2019, 418, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengqiang, Y.; Shiguo, W.; Thomas, L.; Genshun, Y.; Fuliang, L.; Feng, C.; Hairong, W.; Li, L. Fine-Grained Pleistocene Deepwater Turbidite Channel System on the Slope of Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.R. Sediment Gravity Flows; II, Depositional Models with Special Reference to the Deposits of High-Density Turbidity Currents. J. Sediment. Res. 1982, 52, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G. 50 Years of the Turbidite Paradigm (1950s–1990s): Deep-Water Processes and Facies Models—A Critical Perspective. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 285–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, D.J.; Normark, W.R. Processes That Initiate Turbidity Currents and Their Influence on Turbidites: A Marine Geology Perspective. J. Sediment. Res. 2009, 79, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiburg, E.; Kneller, B. Turbidity Currents and Their Deposits. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.; Hayes, D.E. The Tectonic Evolution of the South China Basin. In Geophysical Monograph Series; Hayes, D.E., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; Volume 23, pp. 89–104. ISBN 978-0-87590-023-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Liu, S. Differences in the Tectonic Evolution of Basins in the Central-Southern South China Sea and Their Hydrocarbon Accumulation Conditions. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.; Hayes, D.E. Origin and History of the South China Sea Basin. In Geophysical Monograph Series; Hayes, D.E., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 27, pp. 23–56. ISBN 978-0-87590-053-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Z. Formation and Evolution of the South China Sea since the Late Mesozoic: A Review. China Geol. 2023, 6, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; McConnell, D.R.; Humphrey, G. A Seepage Gas Hydrate System in Northern South China Sea: Seismic and Well Log Interpretations. Mar. Geol. 2015, 366, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, C.-T.; Hsu, S.-K.; Liu, C.-S. Heat Flows off Southwest Taiwan: Measurements over Mud Diapirs and Estimated from Bottom Simulating Reflectors. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1998, 9, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Deng, H.; Liu, H. The Geological Structure and Prospect of Gas Hydrate over the Dongsha Slope, South China Sea. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2006, 17, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bai, C.; Zhang, G.; Lu, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhu, D.; Tian, Y. Deep-Water Sediment Waves as a Special Gas Hydrate Reservoirs in the Northeastern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 101, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jing, J.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, M.; Deng, M. High-Resolution Resistivity Imaging of a Transversely Uneven Gas Hydrate Reservoir: A Case in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Du, R.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Xia, Q.; Shi, B.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Comparison of the Graphic and Moment Methods for Analyzing Grain-Size Distributions: A Case Study for the Chinese Inner Continental Shelf Seas. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Controls on Deep and Shallow Gas Hydrate Reservoirs in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Evidence from Sediment Properties. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Qu, C.; Song, H.; Zhuang, X. A Method for Calculating Gas Hydrate Saturation by Dual Parameters of Logging. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 986647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Yi, B.; Kang, N.K.; Yoo, D.-G.; Lee, J.Y. Comparison of Logging-While-Drilling and Wireline Logging Data from Gas Hydrate-Bearing Deep-Sea Sediments, the Ulleung Basin, East Sea. Explor. Geophys. 2022, 53, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchyn, A.V.; Bradbury, H.J.; Walker, K.; Sun, X. Controls on the Precipitation of Carbonate Minerals Within Marine Sediments. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 618311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, W.; Magalhães, V.H.; Chen, Z.; Pinheiro, L.M.; Gussone, N. Factors Influencing Methane-Derived Authigenic Carbonate Formation at Cold Seep from Southwestern Dongsha Area in the Northern South China Sea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Feng, D.; Cheng, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Min, A.G.; Edwards, R.L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D. Authigenic Carbonates from Seeps on the Northern Continental Slope of the South China Sea: New Insights into Fluid Sources and Geochronology. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 43, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, J.; Oshima, M.; Kida, M.; Kato, A.; Konno, Y.; Jin, Y.; Jang, J.; Waite, W.F.; Kumar, P.; Tenma, N. Permeability Variation and Anisotropy of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Pressure-Core Sediments Recovered from the Krishna–Godavari Basin, Offshore India. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 108, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passega, R. Grain Size Representation by CM Patterns as a Geologic Tool. J. Sediment. Res. 1964, 34, 830–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, F.; Sun, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q. Tectonic and Oceanographic Controls on the Slope-Confined Dendritic Canyon System in the Dongsha Slope, South China Sea. Geomorphology 2022, 410, 108285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kneller, B.; Sun, Q. Sediment Waves Control Origins of Submarine Canyons. Geology 2023, 51, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, D.; Smillie, Z. Distinguishing between Deep-Water Sediment Facies: Turbidites, Contourites and Hemipelagites. Geosciences 2020, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Chen, F.; Cheng, S.; Lu, H.; Wu, C.; Cao, J.; Duan, X. Light Carbon Isotope Events of Foraminifera Attributed to Methane Release from Gas Hydrates on the Continental Slope, Northeastern South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Feng, D.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Cao, J.; Lu, H.; Chen, D. Evidence of Intense Methane Seepages from Molybdenum Enrichments in Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments of the Northern South China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2016, 443, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackenridge, R.E.; Stow, D.A.V.; Hernández-Molina, F.J.; Jones, C.; Mena, A.; Alejo, I.; Ducassou, E.; Llave, E.; Ercilla, G.; Nombela, M.A.; et al. Textural Characteristics and Facies of Sand-rich Contourite Depositional Systems. Sedimentology 2018, 65, 2223–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passega, R. Significance of CM Diagrams of Sediments Deposited by Suspensions. Sedimentology 1977, 24, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Chang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xin, S.; Xiao, D.; Guanghu, L.; Cong, W.; Xia, J. Calcareous Nannofossils and Foraminifera Biostratigraphy on the Northeastern Slope of the South China Sea and Variation in Sedimentation Rates. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2016, 41, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, E.; Jin, X.; Tian, J. Glacial Methane Hydrate Dissociation in the South China Sea Margin During the Oligocene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL114439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.; Li, C.; Liu, N. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of the Gas Hydrate Stability Zone and Accumulation Patterns of Double BSRs Formation in the Shenhu Area. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 880933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yin, Z.; Lu, H.; Xu, C.; Kuang, Z.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y.; Linga, P. Effects of South China Sea Clayey-Silty Sediments on the Kinetics and Morphology of CH4 Hydrate: Implication on Energy Recovery. Appl. Energy 2024, 367, 123399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhu, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Linga, P.; Yin, Z. Comprehensive Characterizations of Core Sediments Recovered from Shenhu W17 Well in South China Sea and Its Impact on Methane Hydrate Kinetics. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 131, 205482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Yan, W. Gas Hydrate Dissociation Events During LGM and Their Potential Trigger of Submarine Landslides: Foraminifera and Geochemical Records From Two Cores in the Northern South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 876913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Foraminifera Associated with Cold Seeps in Marine Sediments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1157879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, G.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, J. Influence of Foraminifera on Formation and Occurrence Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrates in Fine-Grained Sediments from Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Jo, J. Morphodynamics and Stratigraphic Architecture of Compound Dunes on the Open-Coast Macrotidal Flat in the Northern Gyeonggi Bay, West Coast of Korea. Mar. Geol. 2015, 366, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Bai, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, H. Sedimentary Processes of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layers in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Implications for Hydrate Accumulation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081550
Wang Y, Bai C, Wang Z, Chen W, Xu X, Xu H, Wang H. Sedimentary Processes of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layers in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Implications for Hydrate Accumulation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081550
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuhan, Chenyang Bai, Zhe Wang, Wenlin Chen, Xiaolei Xu, Hongyuan Xu, and Hongbin Wang. 2025. "Sedimentary Processes of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layers in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Implications for Hydrate Accumulation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081550
APA StyleWang, Y., Bai, C., Wang, Z., Chen, W., Xu, X., Xu, H., & Wang, H. (2025). Sedimentary Processes of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layers in the Dongsha Area, South China Sea: Implications for Hydrate Accumulation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081550





