Biofouling on Offshore Wind Energy Structures: Characterization, Impacts, Mitigation Strategies, and Future Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Factors Impacting the Biofouling Process
2.1. Environmental Conditions
2.1.1. Water Temperature, Season, and Salinity
2.1.2. Depth, Light Penetration, and Distance from Shore
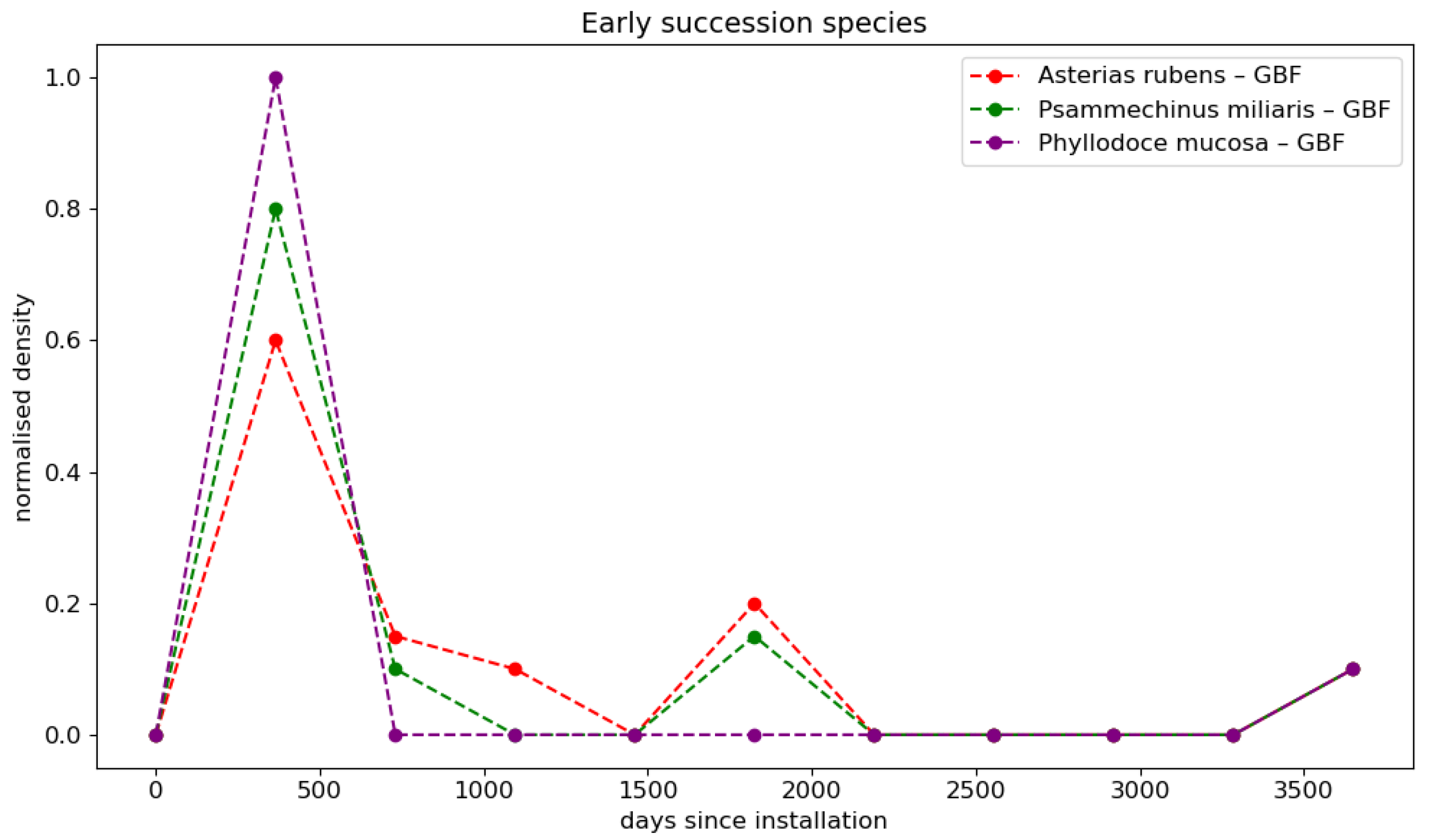
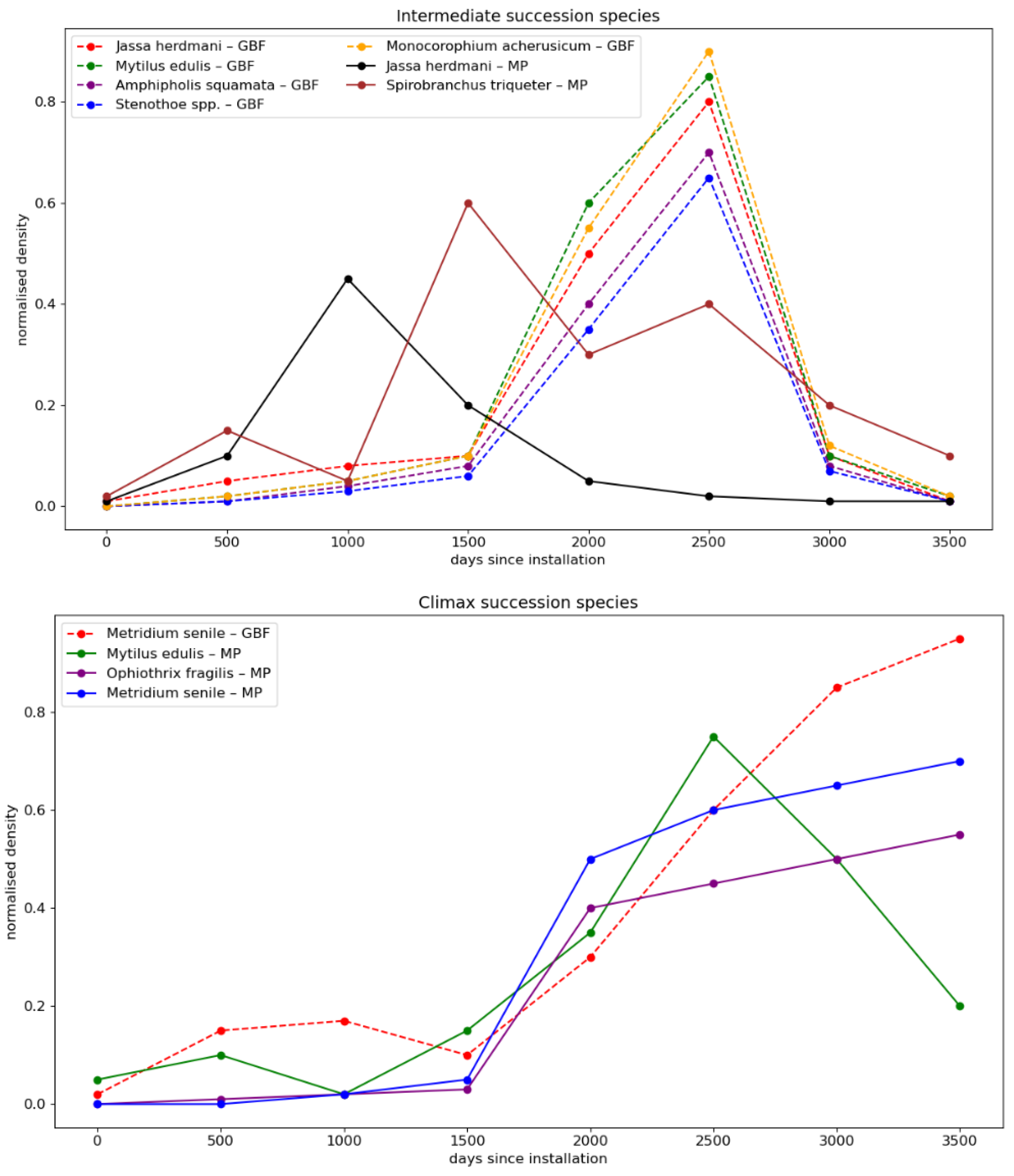
2.1.3. Immersion Time
2.2. Hydrodynamic Factors
2.3. Material Composition
2.3.1. Certain Materials Are More Prone to Colonization
2.3.2. Topography and Wettability of Substrata
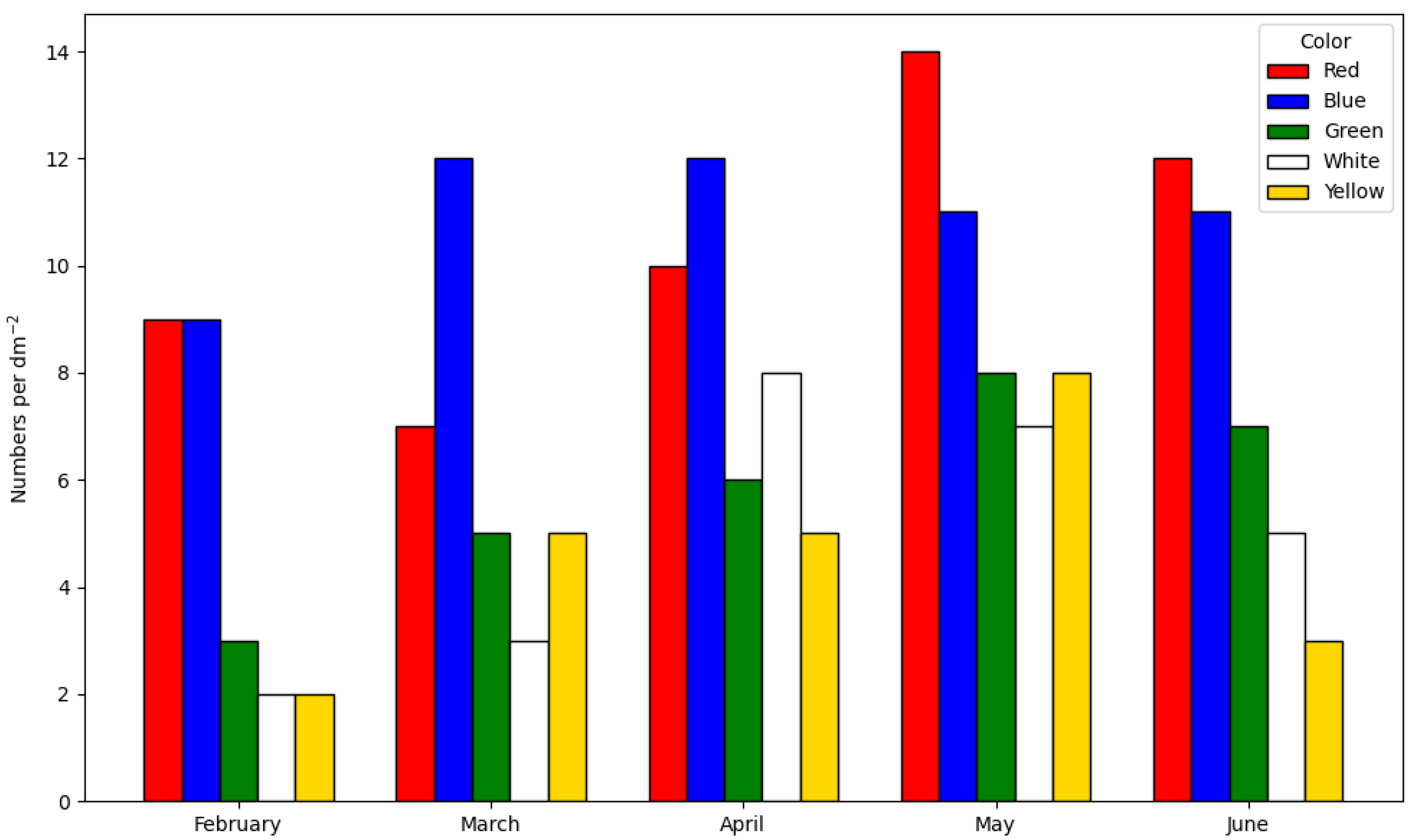
2.3.3. Color of the Surface
3. Impacts of Biofouling on Offshore Structures
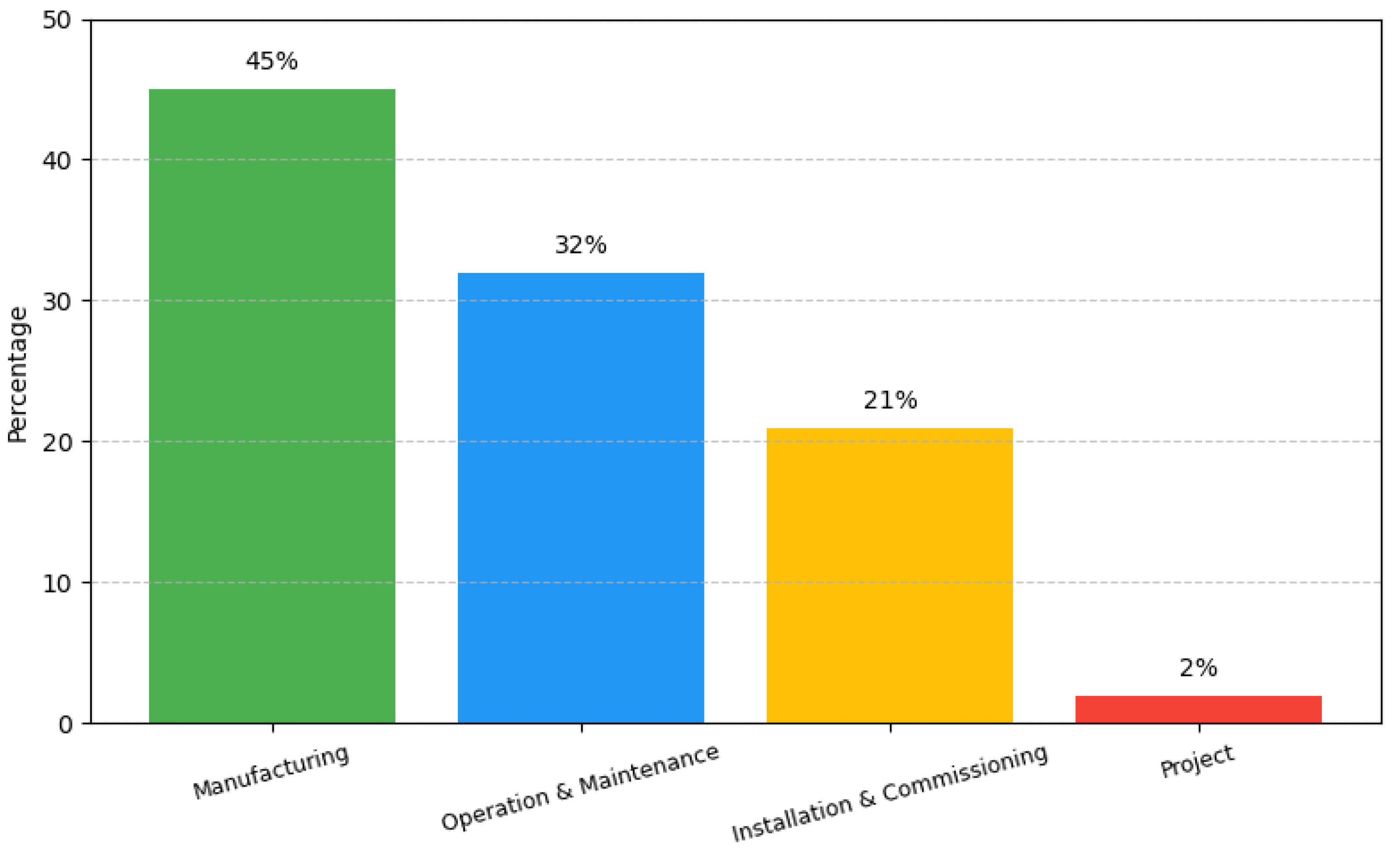
3.1. Economic Costs
3.2. Operational Challenges
3.3. Environmental Concerns
4. Current Antifouling Mitigation Technologies
4.1. Biocidal Coatings
4.2. High-Pressure Water Blasting
4.3. Underwater Robots (ROVs)
4.4. Ultrasound Waves
4.5. Biological Control
4.6. Wrapping and Encapsulation
5. Future Trends, Innovations and Active Lines of Research
5.1. Eco-Inspired Coatings
5.2. AI-Driven Monitoring of Biofouling Accumulation
5.3. Advanced Coating Materials
5.4. Physical Methods: Thermal and Electrical
5.5. Bubble Streams
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardi, U. Peak oil: The four stages of a new idea. Energy 2009, 34, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Haider, R.; Li, X. Design and coupled analysis of a novel floating offshore wind turbine combined with a fish cage for deep water. Renew. Energy 2025, 247, 123004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, L.; Knights, A.M.; Bridger, D.; Evans, A. Ocean Sprawl: Challenges and Opportunities for Biodiversity Management in a Changing World. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/310462801 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Hopkins, G.; Davidson, I.; Georgiades, E.; Floerl, O.; Morrisey, D.; Cahill, P. Managing Biofouling on Submerged Static Artificial Structures in the Marine Environment—Assessment of Current and Emerging Approaches. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 759194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, A.K.; Stanley, M.S.; Day, J.G.; Cook, E.J. Biofouling community composition across a range of environmental conditions and geographical locations suitable for floating marine renewable energy generation. Biofouling 2016, 32, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiades, E.; Kluza, D.; Bates, T.; Lubarsky, K.; Brunton, J.; Growcott, A.; Smith, T.; McDonald, S.; Gould, B.; Parker, N.; et al. Regulating Vessel Biofouling to Support New Zealand’s Marine Biosecurity System—A Blue Print for Evidence-Based Decision Making. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Environment, Fishers and Aquaculture Science [CEFAS]. Available online: https://www.cefas.co.uk/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Vinagre, P.A.; Simas, T.; Cruz, E.; Pinori, E.; Svenson, J. Marine Biofouling: A European Database for the Marine Renewable Energy Sector. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.; Coolen, J. Modelling thickness variations of macrofouling communities on offshore platforms in the Dutch North Sea. J. Sea Res. 2020, 156, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.C.; Branch, G.M. The Influence of Temperature on the Maintenance of Metabolic Energy Balance in Marine Invertebrates. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1980, 17, 329–396. [Google Scholar]
- Precht, H.; Christophersen, J.; Hensel, H.; Larcher, W. Temperature and Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.E. A review on the knowledge of suspension-feeding in lamellibranchiate bivalves, with special reference to artificial aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1978, 13, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.J. Temperature acclimation in Actinia equina L. (Anthozoa). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1977, 28, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.V.; Venkatesan, R.; Beyline, M.; Mol, V.P.L.; Divya, L.; García, M.R. Influence of environmental factors on macrofoulant assemblages on moored buoys in the eastern Arabian Sea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0223560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, I.; Wiencke, C.; Bischof, K.; Buchholz, C.M.; Buck, B.H.; Eggert, A.; Feuerpfeil, P.; Hanelt, D.; Jacobsen, S.; Karez, R.; et al. The genus Laminaria sensu lato: Recent insights and developments. Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraer, S.; Carey, D.; Coolen, J.; Hutchison, Z.; Kerckhof, F.; Rumes, B.; Vanaverbeke, J. Offshore Wind Farm Artificial Reefs Affect Ecosystem Structure and Functioning: A Synthesis. Oceanography 2020, 33, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Stap, T.; Coolen, J.W.P.; Lindeboom, H.J.; Davies, A. Marine Fouling Assemblages on Offshore Gas Platforms in the Southern North Sea: Effects of Depth and Distance from Shore on Biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraer, S.; Brabant, R.; Rumes, B.; Vigin, L. Environmental Impacts of Offshore Wind Farms in the Belgian Part of the North Sea: Marking a Decade of Monitoring, Research and Innovation; Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, OD Natural Environment, Marine Ecology and Management: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; 134p. [Google Scholar]
- Railkin, A.I. Marine Biofouling: Colonization Processes and Defenses, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehl, M.R.A. Mini review: Hydrodynamics of larval settlement into fouling communities. Biofouling 2007, 23, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittschof, D.; Orihuela, B.; Stafslien, S.; Daniels, J.; Christianson, D.; Chisholm, B.; Holm, E. Barnacle reattachment: A tool for studying barnacle adhesion. Biofouling 2008, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Verran, J. The Effect of Substratum Properties on the Survival of Attached Microorganisms on Inert Surfaces. In Marine and Industrial Biofouling; Springer Series on Biofilms; Flemming, H.C., Murthy, P.S., Venkatesan, R., Cooksey, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, M.D.; Seed, R. A review of marine macrofouling communities with special reference to animal fouling. Biofouling 1991, 3, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Duan, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, F.; Sand, W.; Hou, B. Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Biocorrosion/Biofouling: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardino, A.J.; de Nys, R. Mini review: Biomimetic models and bioinspired surfaces for fouling control. Biofouling 2010, 27, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.; Rittschof, D.; Holm, E.; Schmidt, A. Factors influencing initial larval settlement: Temporal, spatial and surface molecular components. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 150, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.S.; Aldred, N. Surface Colonisation by marine organisms and its impact on antifouling research. In Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologies; Hellio, C., Yebra, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Metals and Surface Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 46–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlem, C.; Moran, P.; Grant, T. Larval settlement of marine sessile invertebrates on surfaces of different colour and position. Ocean Sci. Eng. 1984, 9, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, G.; Herpe, S.; Ralston, E.; Tribou, M. Short-term testing of antifouling surfaces: The importance of colour. Biofouling 2006, 22, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Abed, R.M.; Voolstra, C.R. The effect of surface colour on the formation of marine micro and macrofouling communities. Biofouling 2013, 29, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.; Wesley, S.G. Influence of substratum colour on the recruitment of macrofouling communities. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2010, 90, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, C. Latest research progress of marine microbiological corrosion and bio-fouling, and new approaches of marine anti-corrosion and anti-fouling. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel University London. Biofouling Management System for Offshore Wind Turbine Foundations (RobFMS). 2023. Available online: https://www.brunel.ac.uk/research/projects/biofouling-management-system-for-offshore-wind-turbine-foundations (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Atlantic Maritime Strategy. Economic Impact of Biofouling on Maritime Industries in the Atlantic Area. 2017. Available online: https://atlantic-maritime-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/funding/projects/economic-impact-biofouling-maritime-industries-atlantic-area (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Maduka, M.; Schoefs, F.; Thiagarajan, K.; Bates, A. Hydrodynamic effects of biofouling-induced surface roughness—Review and research gaps for shallow water offshore wind energy structures. Ocean Eng. 2023, 272, 113798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, C. Corrosion and Biofouling of Offshore Wind Monopile Foundations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Schoefs, F.; Tran, T.-B. Reliability Updating of Offshore Structures Subjected to Marine Growth. Energies 2022, 15, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorostidi, N.; Nava, V.; Aristondo, A.; Pardo, D. Predictive Maintenance of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Mooring Lines using Deep Neural Networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2257, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.; Ruiz-Minguela, P.; Perez-Moran, G.; Arias, R.R.; Mendia, J.L.; Villate-Martinez, J.L. Installation, operation and maintenance of offshore renewables. In Renewable Energy from the Oceans: From Wave, Tidal and Gradient Systems to Offshore Wind and Solar; Institution of Engineering and Technology: Stevenage, UK, 2019; pp. 397–424. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, E.; Gkantou, M.; Malekjafarian, A.; Bali, S.; Baniotopoulos, C.; van Beeck, J.; Borg, R.P.; Bruschi, N.; Cardiff, P.; Chatzi, E.; et al. Offshore renewable energies: Exploring floating modular energy islands—Materials, construction technologies, and life cycle assessment. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhr, A.; Bjerkseter, C.; Ågotnes, A.; Nygaard, T.A. Levelised cost of energy for offshore floating wind turbines in a life cycle perspective. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mogollón, J.M.; Tukker, A.; Steubing, B. Environmental impacts of global offshore wind energy development until 2040. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11567–11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, G.; Garcia-Teruel, A.; Jeffrey, H.; Thies, P.R.; Johanning, L. Incorporating stochastic operation and maintenance models into the techno-economic analysis of floating offshore wind farms. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.K.; Pawar, S.S.; Rath, S.K.; Kandasubramanian, B. Anti-barnacle biofouling coatings for the protection of marine vessels: Synthesis and progress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 26078–26112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Ringsberg, J.W.; Johnson, E.; Hu, Z. Biofouling on mooring lines and power cables used in wave energy converter systems—Analysis of fatigue life and energy performance. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2017, 65, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.; Pakrashi, V.; Murphy, J. The dynamic effects of marine growth on a tension moored floating wind turbine. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Renewable Energies Offshore, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Spraul, C.; Pham, H.-D.; Arnal, V.; Reynaud, M. Effect of Marine Growth on Floating Wind Turbines Mooring Lines Responses. In Proceedings of the 23th Congrès Français de Mécanique, Lille, France, 28 August–1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maksassi, Z.; Garnier, B.; El Moctar, A.O.; Schoefs, F.; Schaeffer, E. Thermal Characterization and Thermal Effect Assessment of Biofouling around a Dynamic Submarine Electrical Cable. Energies 2022, 15, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeboom, H.; Degraer, S.; Dannheim, J.; Gill, A.B.; Wilhelmsson, D. Offshore wind park monitoring programmes, lessons learned and recommendations for the future. Hydrobiologia 2015, 756, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhamer, O. Artificial Reef Effect in relation to Offshore Renewable Energy Conversion: State of the Art. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 386713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolen, J.W.P.; van der Weide, B.; Cuperus, J.; Blomberg, M.; Van Moorsel, G.W.N.M.; Faasse, M.A.; Bos, O.G.; Degraer, S.; Lindeboom, H.J.; Norkko, J. Benthic biodiversity on old platforms, young wind farms, and rocky reefs. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 77, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mesel, I.; Kerckhof, F.; Norro, A.; Rumes, B.; Degraer, S. Succession and seasonal dynamics of the epifauna community on offshore wind farm foundations and their role as stepping stones for non-indigenous species. Hydrobiologia 2015, 756, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.P.; Miller, R.G.; Aleynik, D.; Burrows, M.T. Offshore marine renewable energy devices as stepping stones across biogeographical boundaries. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumes, B.; Coates, D.; De Mesel, I.; Derweduwen, J.; Kerckhof, F.; Reubens, J.; Vandendriessche, S. Does it really matter? Changes in species richness and biomass at different spatial scales. In Environmental Impacts of Offshore Wind Farms in the Belgian Part of the North Sea: Learning from the Past to Optimise Future Monitoring Programmes; Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology—Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yan, K.; Bazher, S.A.; Oh, J.; Seo, D.; Cho, S.-G.; Kim, H. Evaluation of Influencing Factors in Cleaning Performance for Bio-Fouling Removal Based on High-Pressure Water Jets. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Fang, Z.; Kang, D. Experimental study on cavitation water jet cleaning of marine fouling. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2756, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenko, V.V.; Bykanova, A.Y.; Tolstonogov, A.Y. Underwater Robotics Complex for Inspection and Laser Cleaning of Ships from Biofouling. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 272, 022103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloecher, N.; Floerl, O. Towards cost-effective biofouling management in salmon aquaculture: A strategic outlook. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Design of a new composite underwater hull cleaning robot. J. Sea Res. 2024, 198, 102488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsidopoulos, A.; Wavell, D.; Gray, A. Quantifying the Impact of Robotics in Offshore Wind; Industry Insights Series; ORE Catapult: Aberdeen, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Han, F.; Qiu, X.; Peng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Research on the identification and distribution of biofouling using underwater cleaning robot based on deep learning. Ocean Eng. 2023, 273, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, M.; Yücel, M.; de Carellan, I.G.; Kappatos, V.; Selcuk, C.; Gan, T. Acoustic methods for biofouling control: A review. Ocean Eng. 2015, 103, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, S.; Stanley, J.; Jeffs, A. Induction of settlement in mussel (Perna canaliculus) larvae by vessel noise. Biofouling 2011, 28, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRG Marine. Sonihull—Transforming Offshore Wind. Available online: https://sonihull.com/sonihull-transforming-offshore-wind/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Salimi, M.; Livadas, M.; Teyeb, A.; El Masri, E.; Gan, T.-H. Biofouling Removal Using a Novel Electronic System for Driving an Array of High Power Marinised Transducers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalah, J.; Newcombe, E.M.; Zaiko, A. Biocontrol of fouling pests: Effect of diversity, identity and density of control agents. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 115, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalah, J.; Newcombe, E.M.; Hopkins, G.A.; Forrest, B.M. Potential biocontrol agents for biofouling on artificial structures. Biofouling 2014, 30, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalah, J.; Brook, R.; Cahill, P.; Fletcher, L.M.; Hopkins, G.A. It’s a wrap: Encapsulation as a management tool for marine biofouling. Biofouling 2016, 32, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenashen, M.; El-Safty, S.A.; Higazy, S.; Selim, M.; Isago, H.; Elmarakbi, A. Recent progress in marine foul-release polymeric nanocomposite coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 87, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Stafslien, S.J.; Vanderwal, L.; Bahr, J.; Safaripour, M.; Finlay, J.A.; Clare, A.S.; Webster, D.C. Critical Amphiphilic Concentration: Effect of the Extent of Amphiphilicity on Marine Fouling-Release Performance. Langmuir 2021, 37, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, S.L.; Burke, C.M.; Bissett, A.P. Biofouling of fish-cage netting: The efficacy of a silicone coating and the effect of netting colour. Aquaculture 2000, 184, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Paetzold, S.C.; Quijón, P.; Davidson, J. The use of food grade oil in the prevention of vase tunicate fouling on mussel aquaculture gear. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2011, 2, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myan, F.W.Y.; Walker, J.; Paramor, O. The interaction of marine fouling organisms with topography of varied scale and geometry: A review. Biointerphases 2013, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.; O’callaghan, I. Recent Developments in Biomimetic Antifouling Materials: A Review. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munther, M.; Palma, T.; Angeron, I.A.; Salari, S.; Ghassemi, H.; Vasefi, M.; Beheshti, A.; Davami, K. Microfabricated Biomimetic placoid Scale-Inspired surfaces for antifouling applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 453, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, J.; Jung, J.; Hyun, J.; Kwon, J.; Kim, I.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.-T. Light-Designed Shark Skin-Mimetic Surfaces. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 5500–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
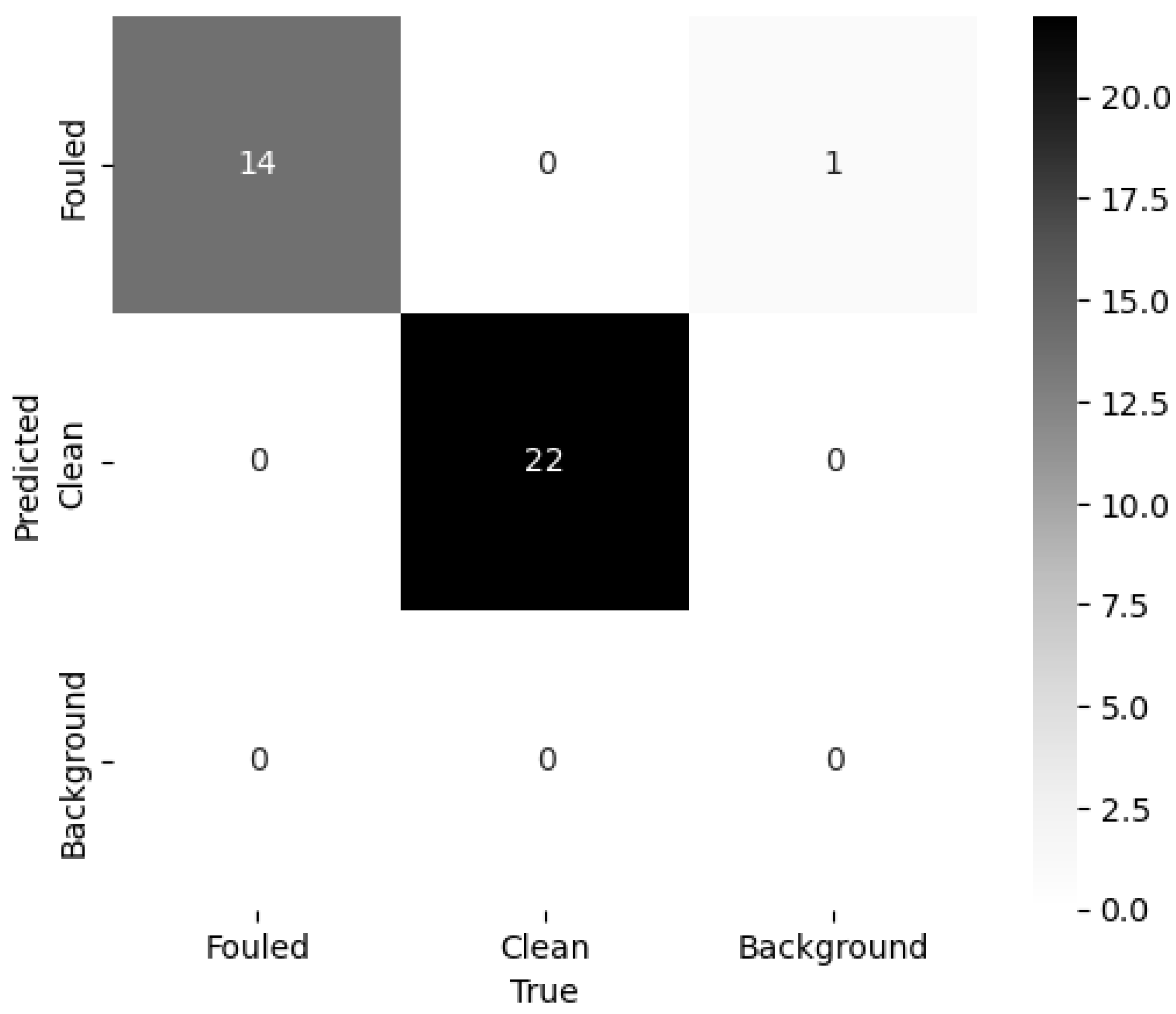
- Signor, J.; Schoefs, F.; Quillien, N.; Damblans, G. Automatic classification of biofouling images from offshore renewable energy structures using deep learning. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 115928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Habbouche, H.; Amirat, Y.; Mamoune, A.; Titah-Benbouzid, H.; Benbouzid, M. B-FLOWS: Biofouling Focused Learning and Observation for Wide-Area Surveillance in Tidal Stream Turbines. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, M.; Zhou, P.; Ren, Y. Research Strategies to Develop Environmentally Friendly Marine Antifouling Coatings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhao, T.; Liu, M. Recent Progress of Biomimetic Antifouling Surfaces in Marine. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.-Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009–2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-L.; Wu, C.-H.; Qian, P.-Y. Marine natural products as antifouling molecules—A mini-review (2014–2020). Biofouling 2020, 36, 1210–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.-Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Mini-review: Molecular mechanisms of antifouling compounds. Biofouling 2013, 29, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodie, L.W.K.; Trepos, R.; Cervin, G.; Larsen, L.; Larsen, D.S.; Pavia, H.; Hellio, C.; Cahill, P.; Svenson, J. Probing the Structure–Activity Relationship of the Natural Antifouling Agent Polygodial against both Micro- and Macrofoulers by Semisynthetic Modification. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.-Y.; Wang, C.-F.; Wang, K.-L.; Qian, P.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Shao, C.-L. Preparation, Structure, and Potent Antifouling Activity of Sclerotioramine Derivatives. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.R.; Moreira, J.; Pereira, D.; Pereira, S.; Antunes, J.; Palmeira, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pinto, M.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Cidade, H. Potential of synthetic chalcone derivatives to prevent marine biofouling. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loxton, J.; Macleod, A.; Nall, C.; McCollin, T.; Machado, I.; Simas, T.; Vance, T.; Kenny, C.; Want, A.; Miller, R. Setting an agenda for biofouling research for the marine renewable energy industry. Int. J. Mar. Energy 2017, 19, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, C.; A Future-Proof Approach to Hard Fouling Prevention. Selektope, 28 June 2019. Available online: https://selektope.com/a-future-proof-approach-to-hard-fouling-prevention/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, G.; Liu, F.-Q. A marine coating: Self-healing, stable release of Cu2+, anti-biofouling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spera, N.C.; Salazar-Castro, C.; de Eulate, P.C.Á.; Kolenko, Y.V.; Sousa, J.P. Self–healing core–shell nanofibers for corrosion protective coatings for offshore structures. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 191, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Duan, J.; Sui, K.; Zhai, X.; Zhao, X. AgNP Composite Silicone-Based Polymer Self-Healing Antifouling Coatings. Materials 2024, 17, 4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, D.M.; O’BRien, C.; Stuart, M.D.; Fergus, D.J. Eradication success down under: Heat treatment of a sunken trawler to kill the invasive seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, R.F.; Hopkins, G.A. Thermal treatment as a method to control transfers of invasive biofouling species via vessel sea chests. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyadasa, C.; Ridgway, H.F.; Yeager, T.R.; Stewart, M.B.; Pelekani, C.; Gray, S.R.; Orbell, J.D. The application of electromagnetic fields to the control of the scaling and biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes––A review. Desalination 2017, 418, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardino, A.J.; Fletcher, L.E.; Lewis, J.A. Fouling control using air bubble curtains: Protection for stationary vessels. Proc. Inst. Mar. Eng. Sci. Technol. Part A J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2009, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, G.A.; Scott, N.; Cahill, P. Application of bubble streams to control biofouling on marine infrastructure—Pontoon-scale implementation. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, G.A.; Gilbertson, F.; Floerl, O.; Casanovas, P.; Pine, M.; Cahill, P. Continuous bubble streams for controlling marine biofouling on static artificial structures. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Species | Temperature (°C) | Ingested Ration (mg 24 h−1) | Absorption Efficiency (%) | Absorbed Ration (mg 24 h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modiolus modiolus (2.31 g dry tissue weight) | 4 | 33.5 | 77.5 | 26 |
| 12 | 70.4 | 82.5 | 58 | |
| 20 | 101.5 | 92.9 | 94.3 | |
| Arctica islandica (4.4 g dry tissue weight) | 4 | 80.4 | 67.3 | 54 |
| 12 | 161.3 | 67.2 | 108 | |
| 20 | 172.7 | 83.6 | 144 |
| Species | Season | Temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anemonia natalensis | Summer | 19 | 0.5 |
| 25 | 0.6 | ||
| 31 | 1.15 | ||
| 37 | 1.2 | ||
| Winter | 19 | 0.5 | |
| 25 | 0.6 | ||
| 31 | 1.2 | ||
| 37 | 1.35 | ||
| Actinia equina | Summer | 19 | 0.25 |
| 25 | 0.27 | ||
| 31 | 0.27 | ||
| 37 | 0.28 | ||
| Winter | 19 | 0.25 | |
| 25 | 0.27 | ||
| 31 | 0.39 | ||
| 37 | 0.42 |
| Pre-Construction | Post-Construction | |
|---|---|---|
| Epibenthos | 201 | 827 |
| Endobenthos | 4624 | 15,280 |
| Hard-substrate epifauna | 0 | 53,511 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poozesh, P.; Nieto, F.; Fernández, P.M.; Ríos, R.; Díaz-Casás, V. Biofouling on Offshore Wind Energy Structures: Characterization, Impacts, Mitigation Strategies, and Future Trends. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071363
Poozesh P, Nieto F, Fernández PM, Ríos R, Díaz-Casás V. Biofouling on Offshore Wind Energy Structures: Characterization, Impacts, Mitigation Strategies, and Future Trends. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(7):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071363
Chicago/Turabian StylePoozesh, Poorya, Felix Nieto, Pedro M. Fernández, Rosa Ríos, and Vicente Díaz-Casás. 2025. "Biofouling on Offshore Wind Energy Structures: Characterization, Impacts, Mitigation Strategies, and Future Trends" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 7: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071363
APA StylePoozesh, P., Nieto, F., Fernández, P. M., Ríos, R., & Díaz-Casás, V. (2025). Biofouling on Offshore Wind Energy Structures: Characterization, Impacts, Mitigation Strategies, and Future Trends. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(7), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13071363







