Stability Analysis of Marine Scaffold Under Coupled Environmental Loads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Fundamental Assumption
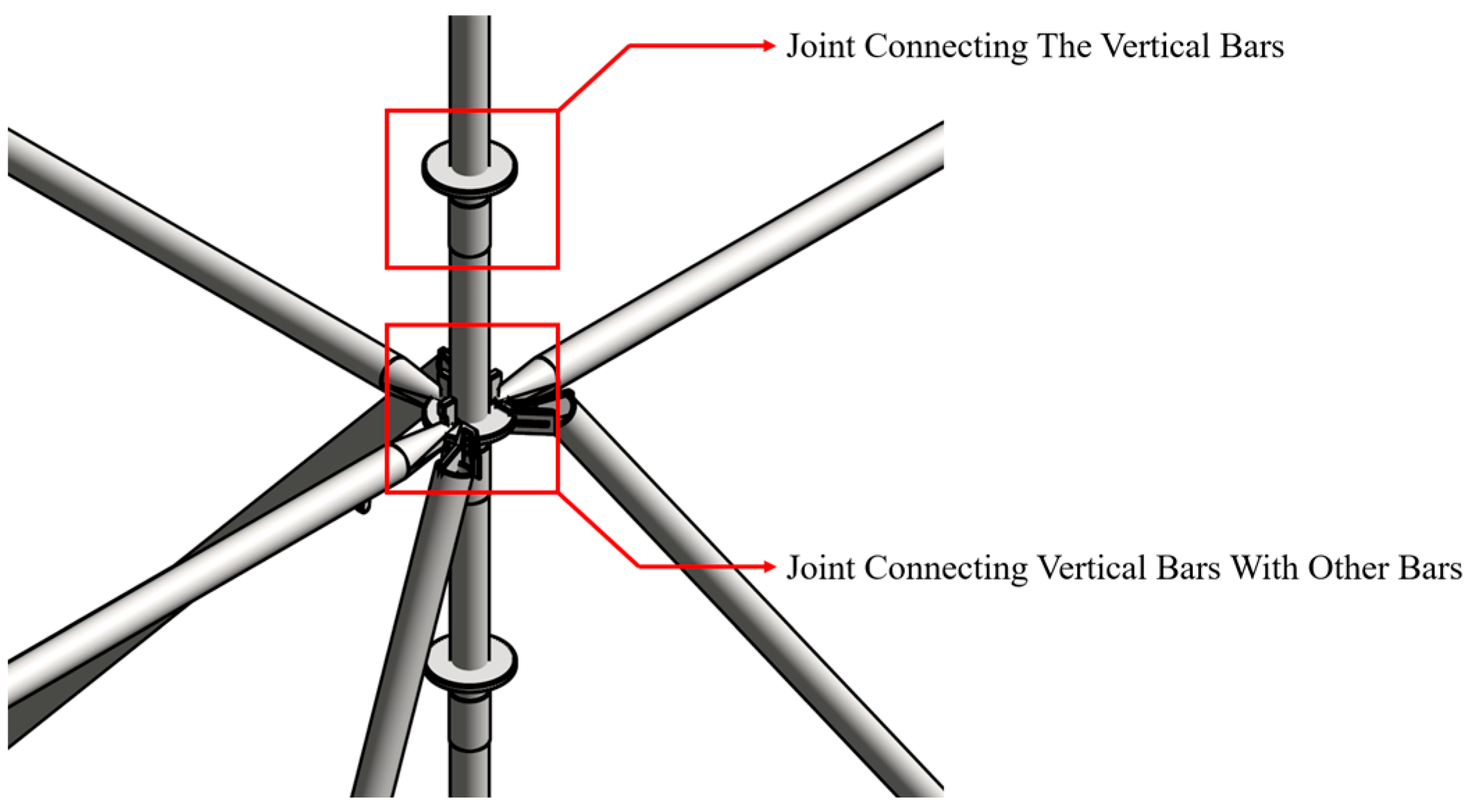
2.2. Model Construction
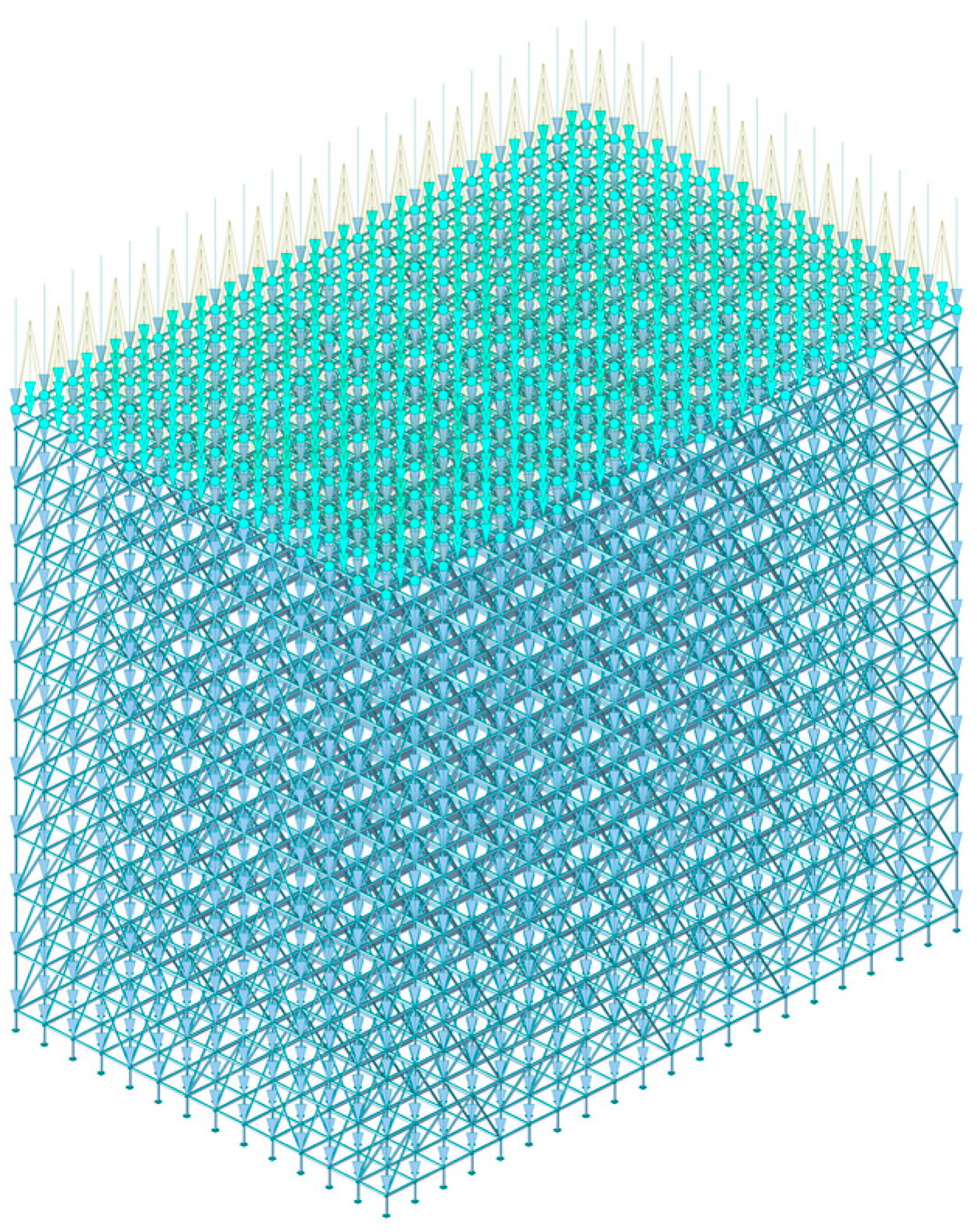
2.3. Boundary Condition
2.4. Loading Conditions
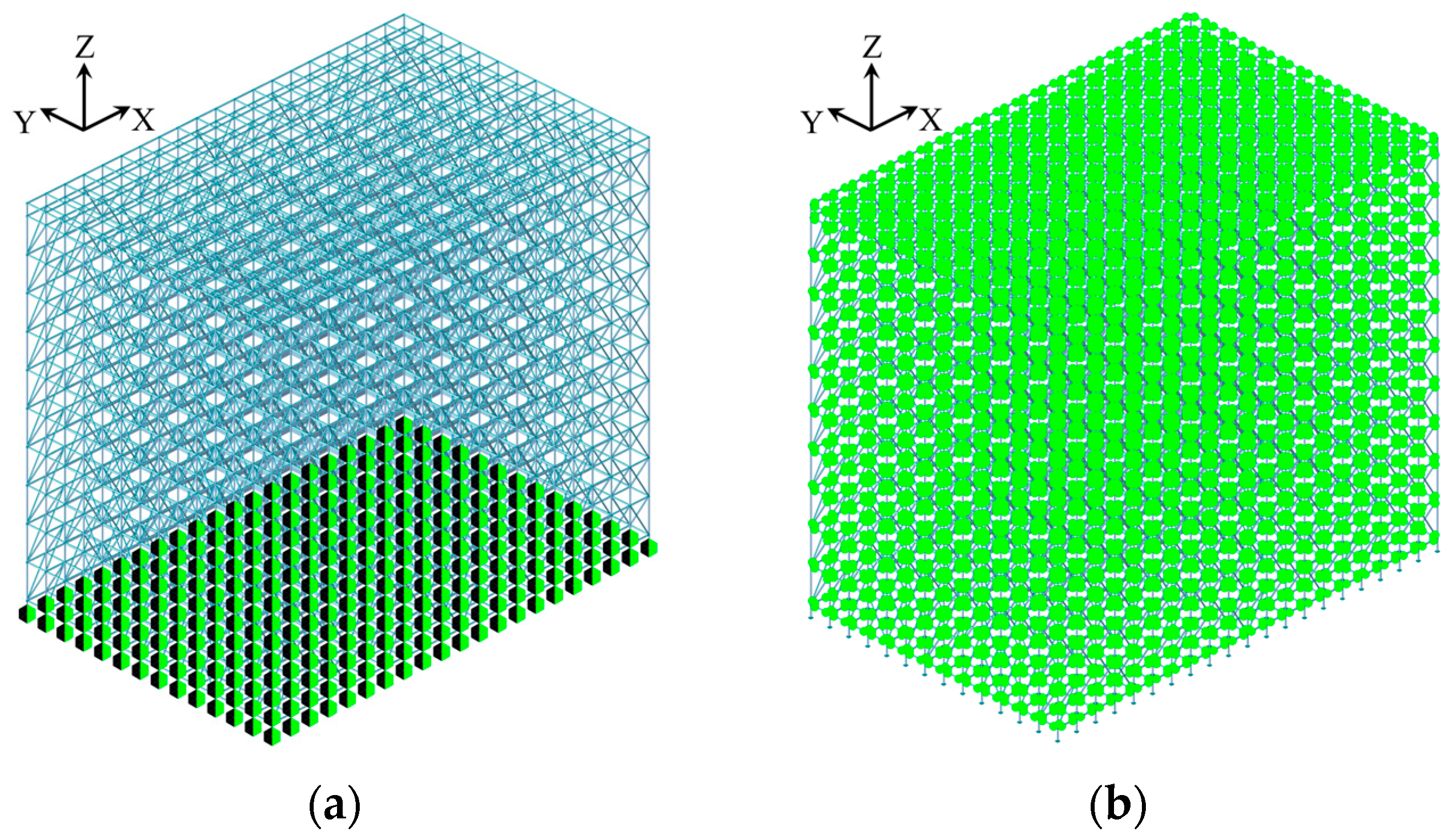
3. Validation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Key Parameters Sensitivity Analyses
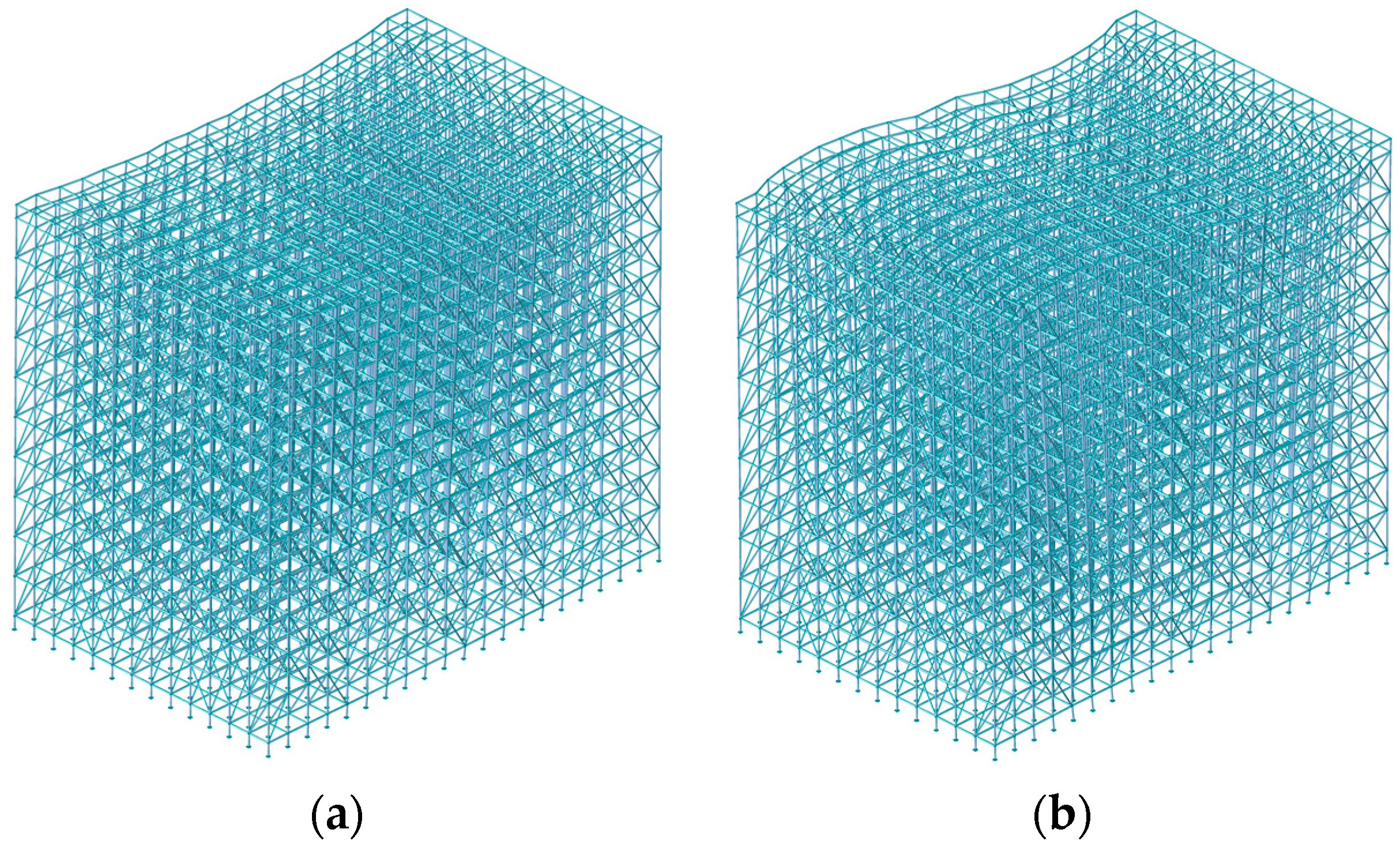
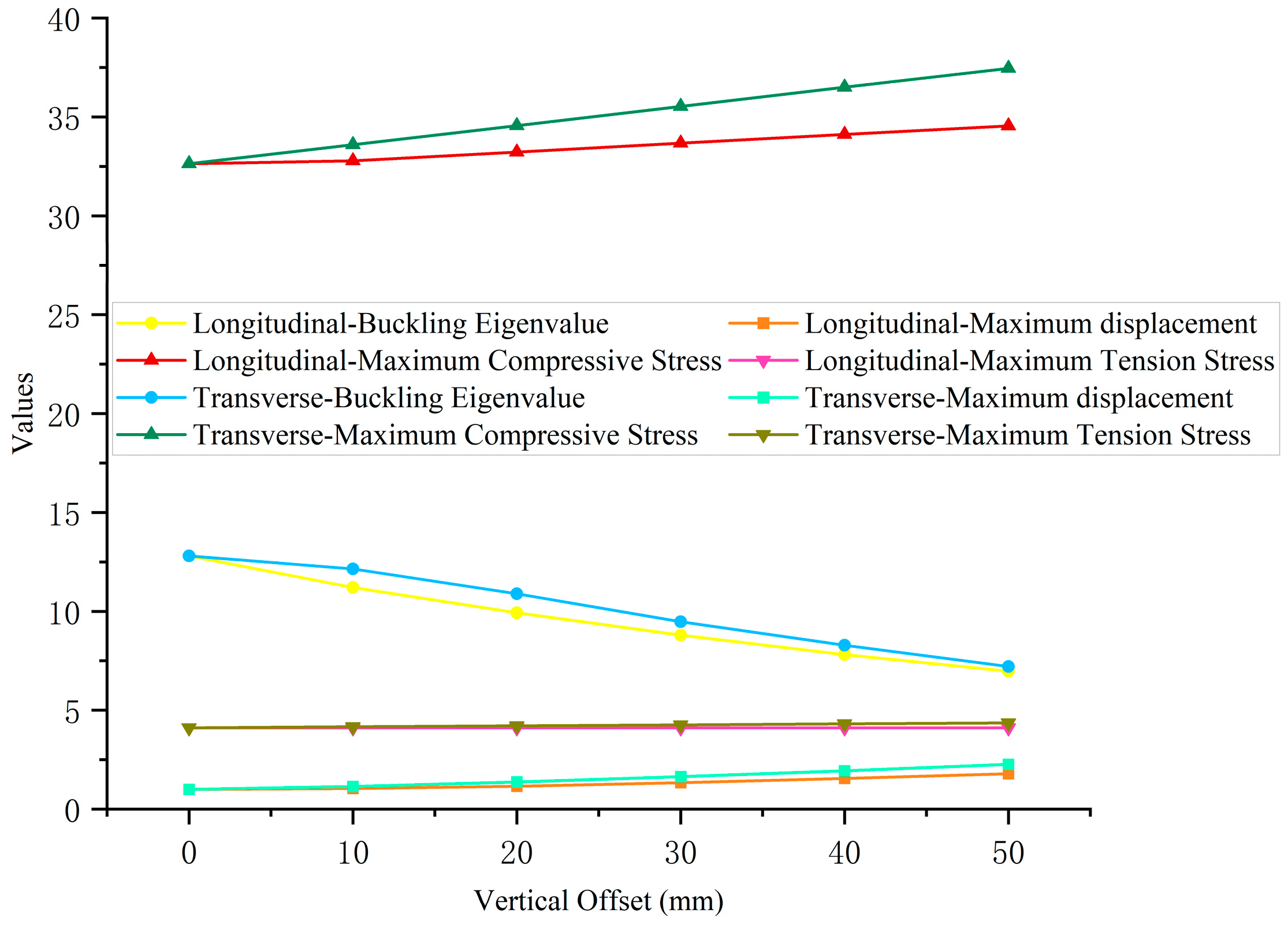
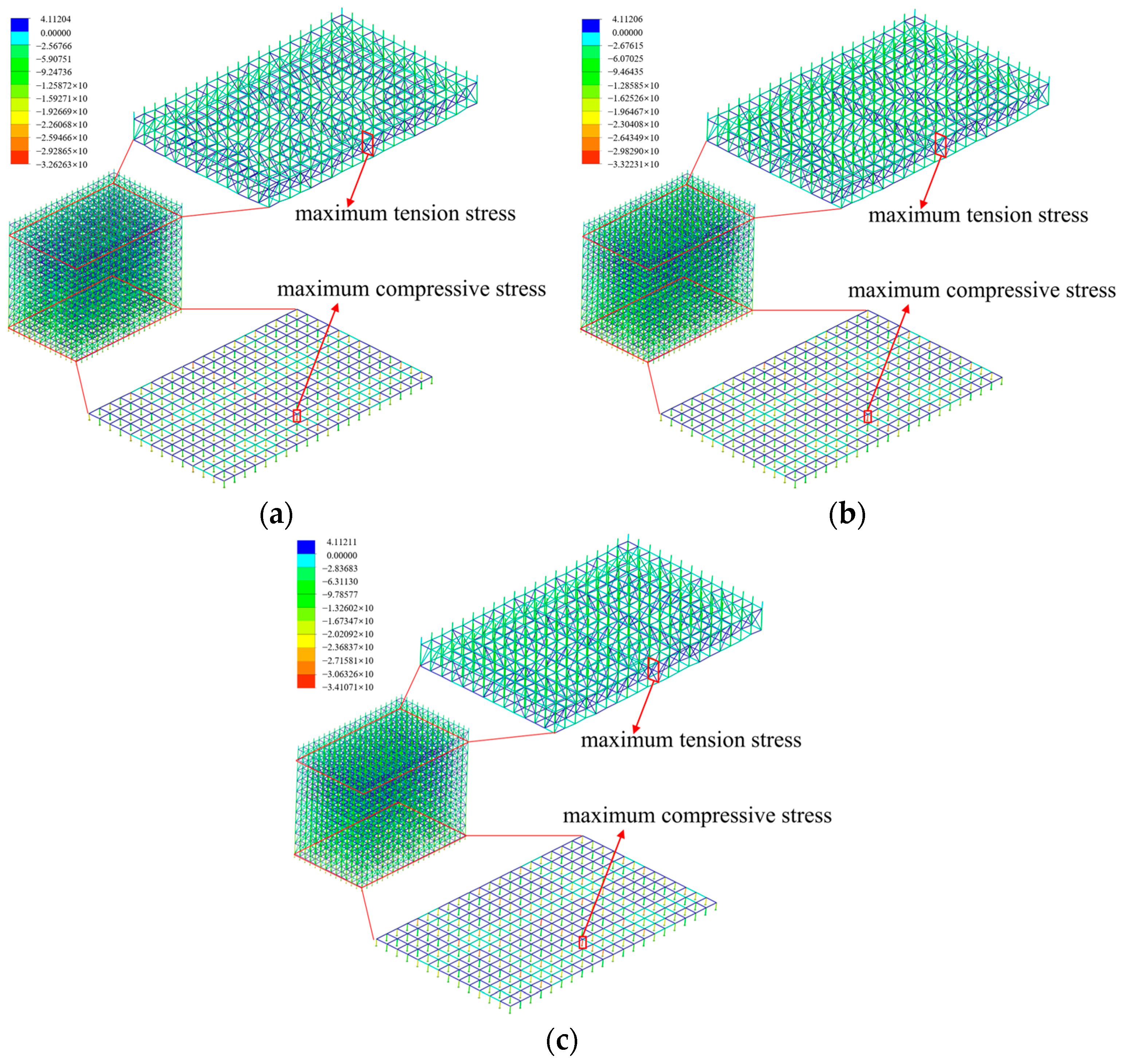
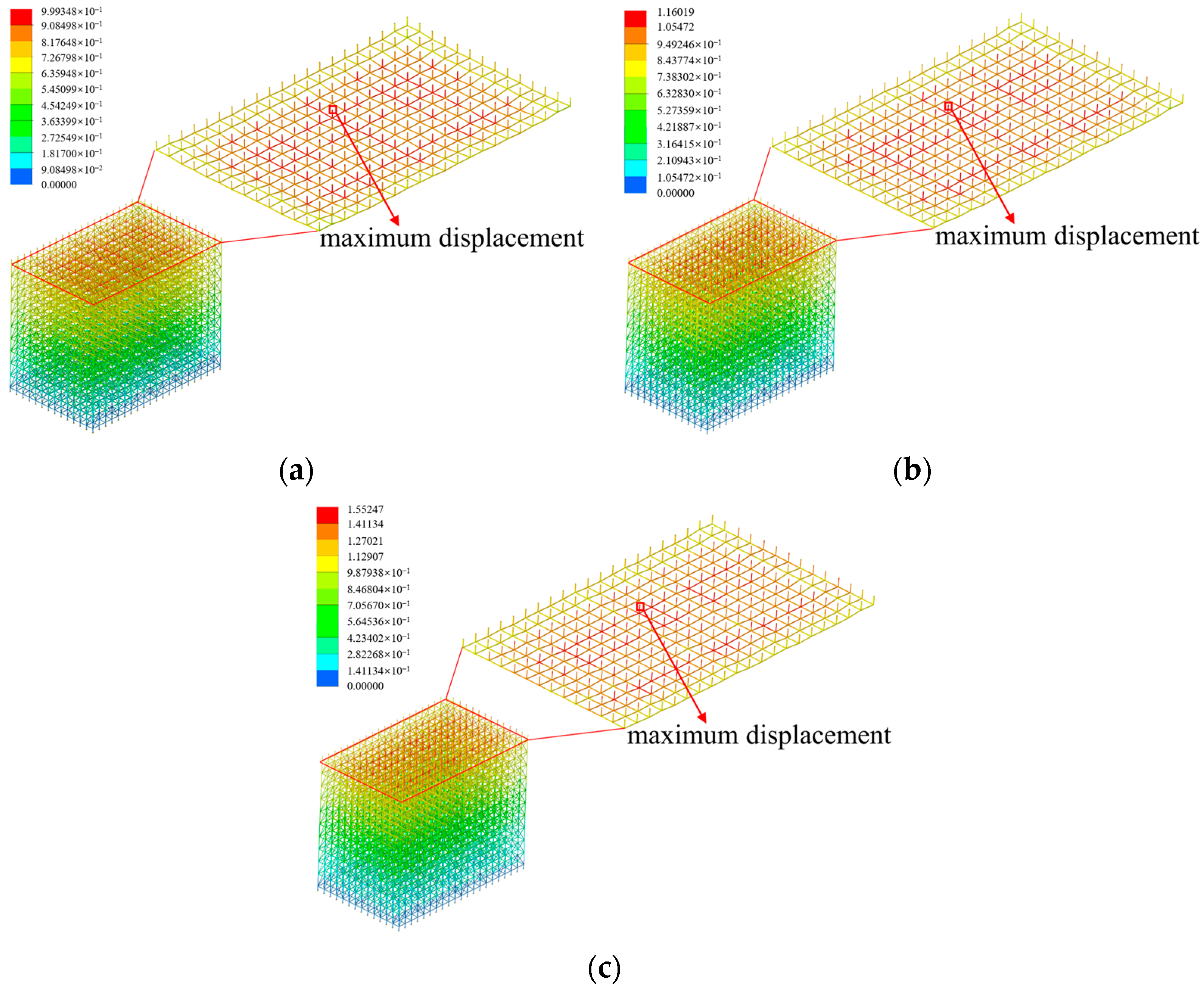
4.1.1. Bars Offset Magnitude
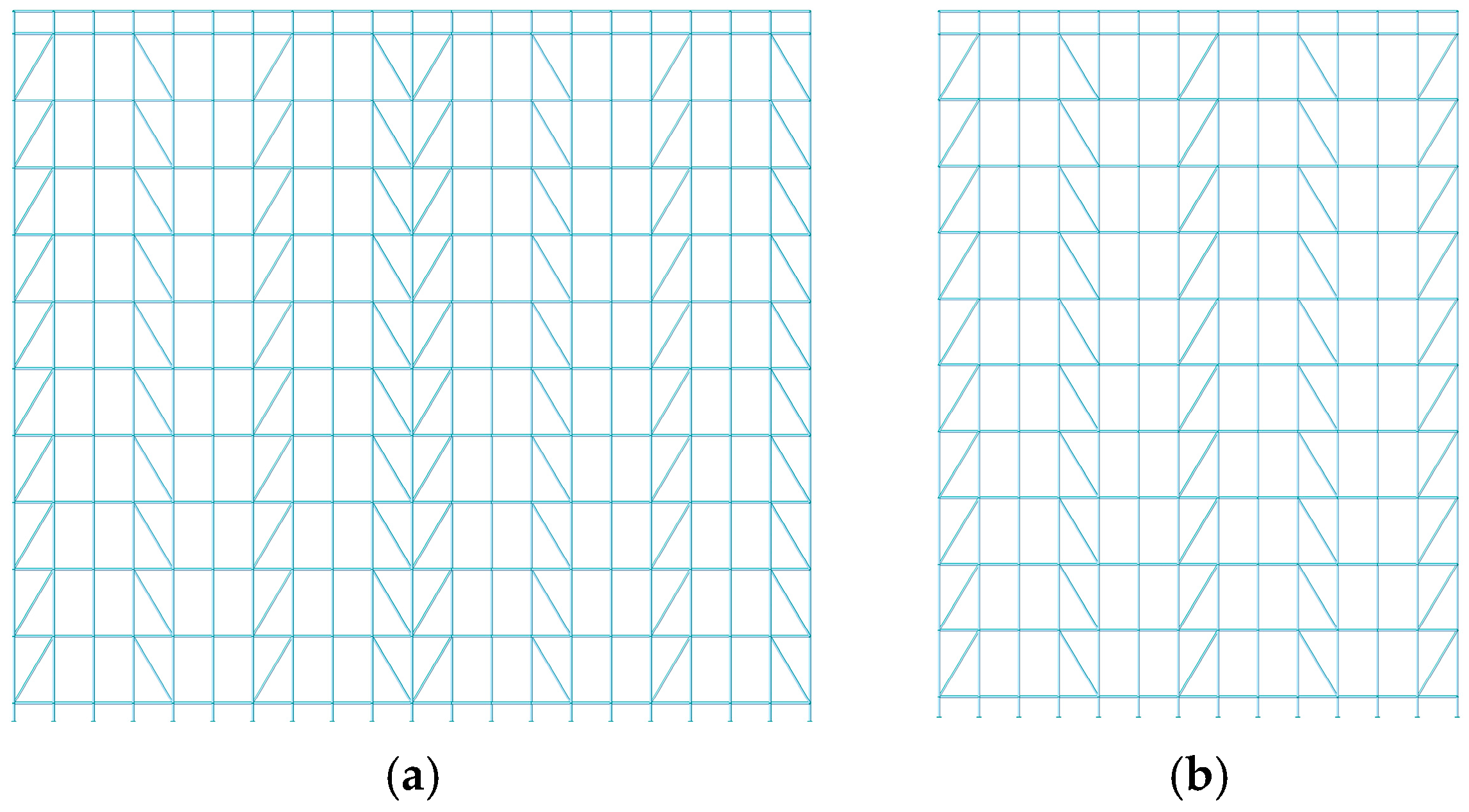
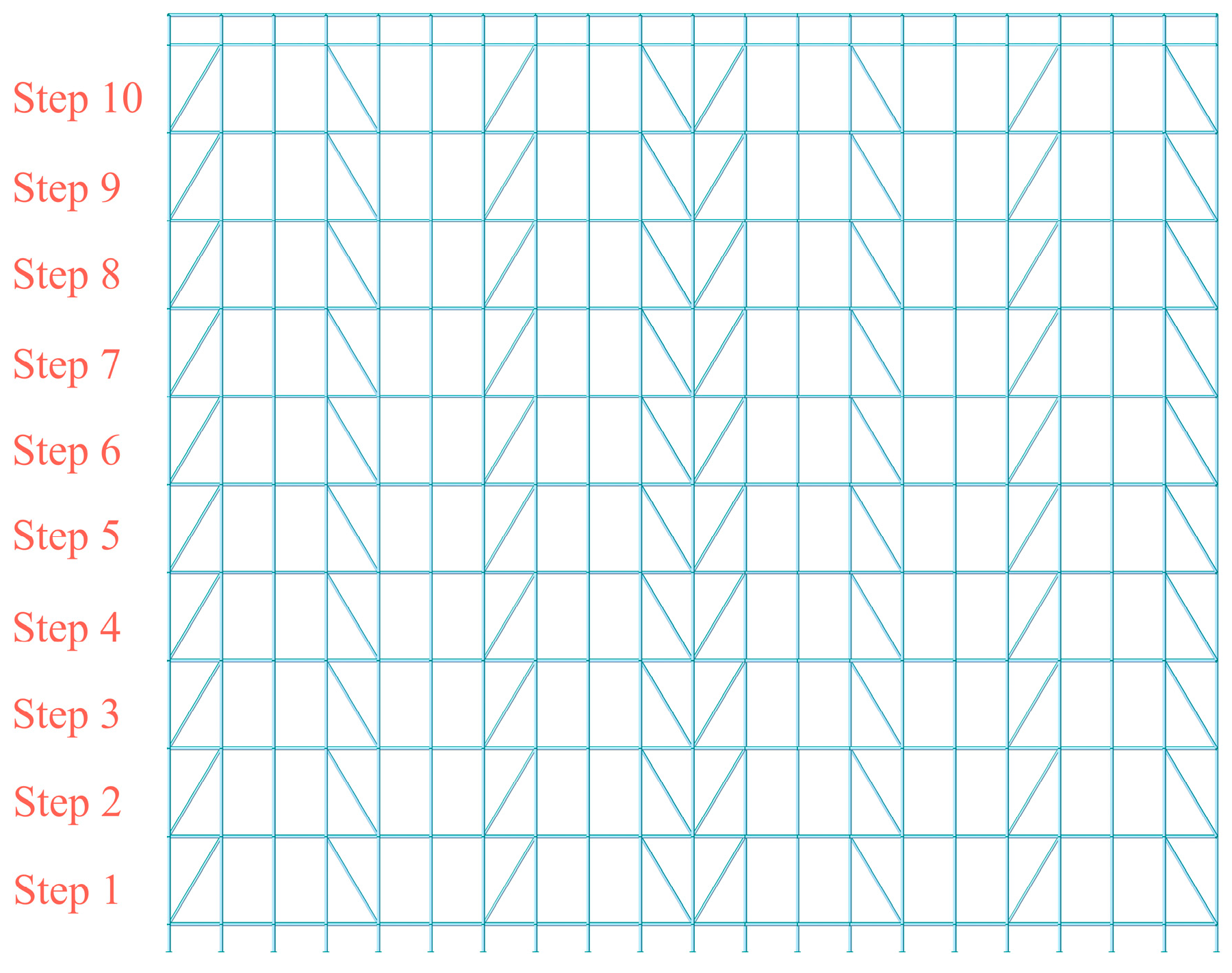
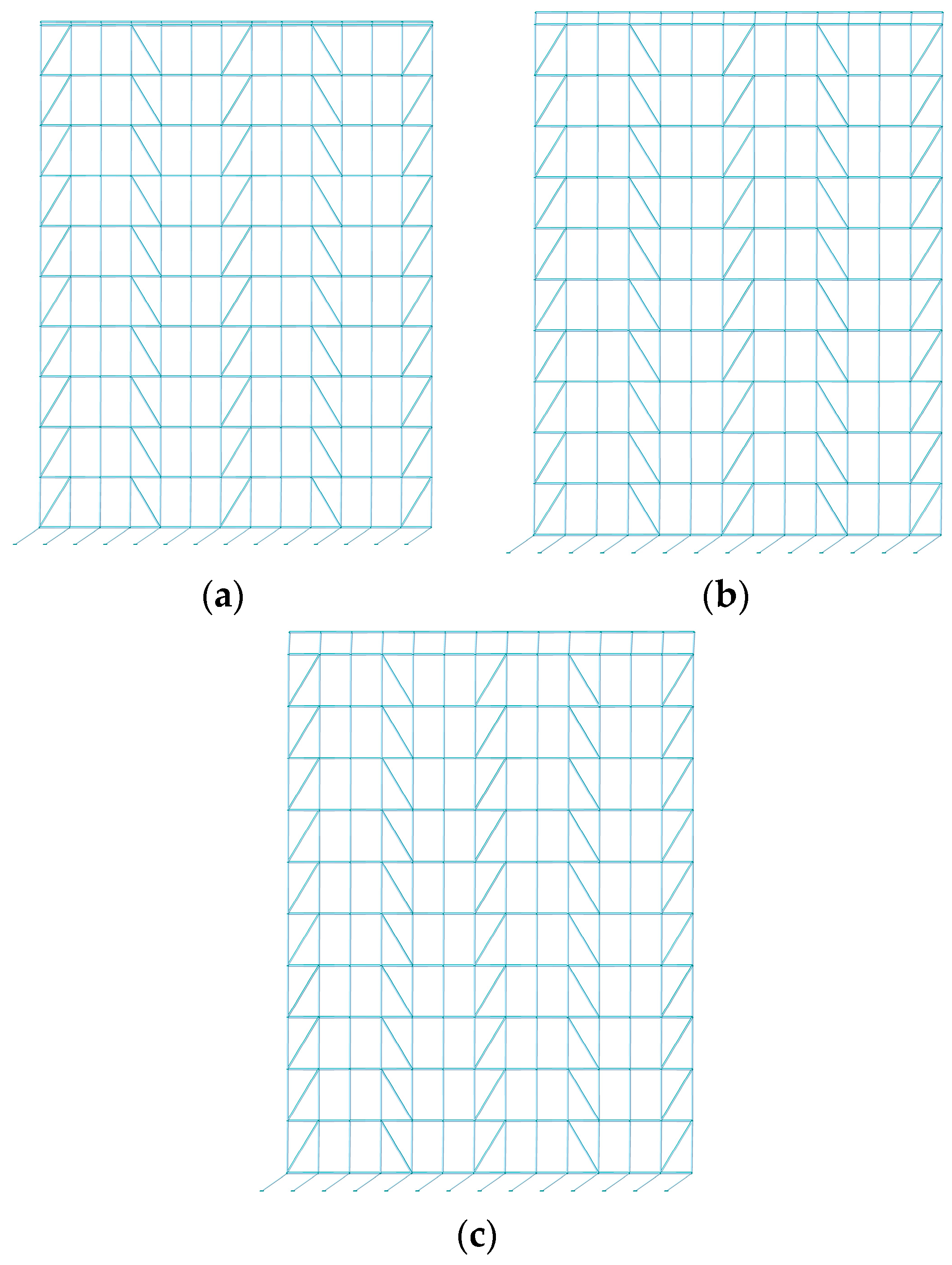
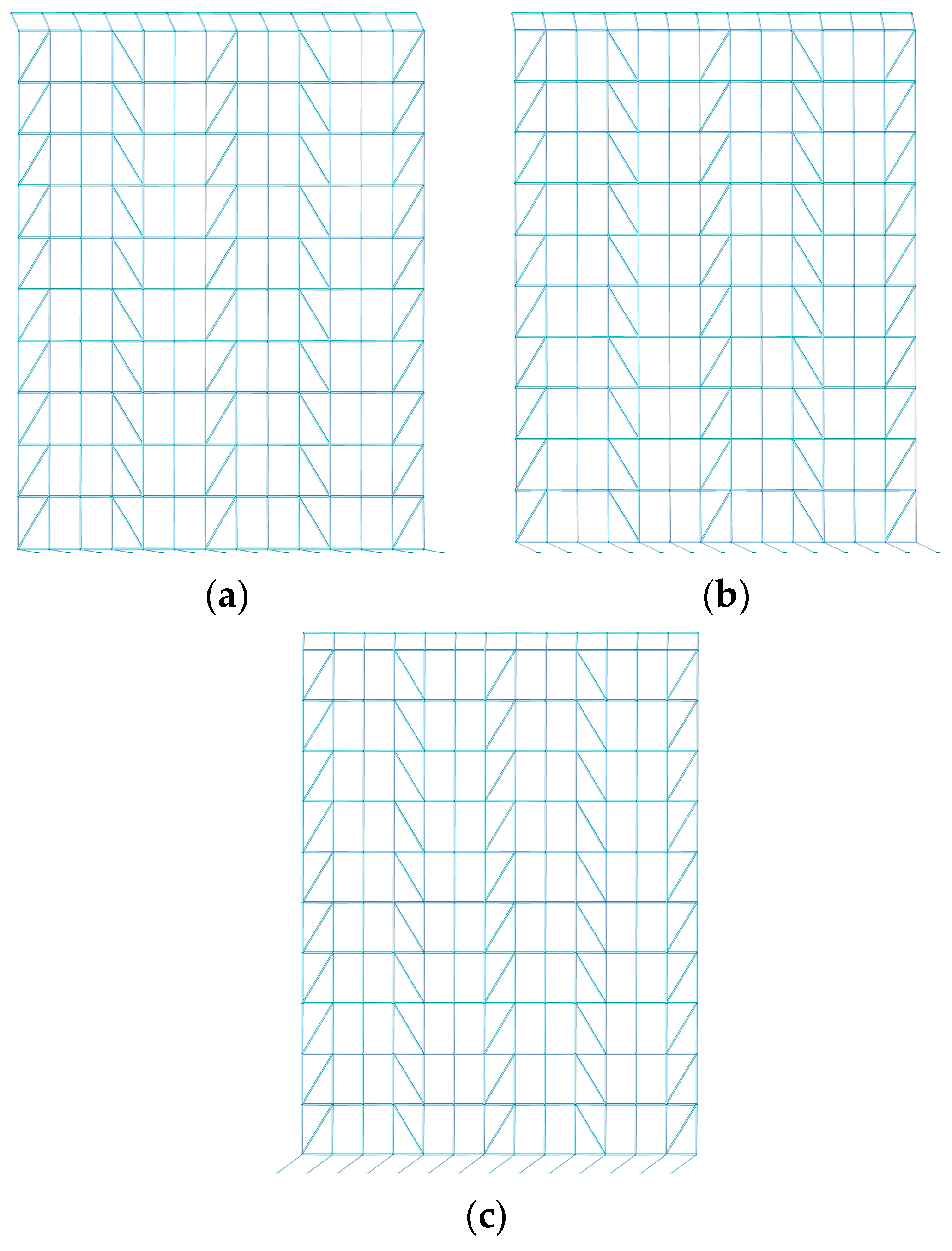
4.1.2. Layout of Diagonal Braces
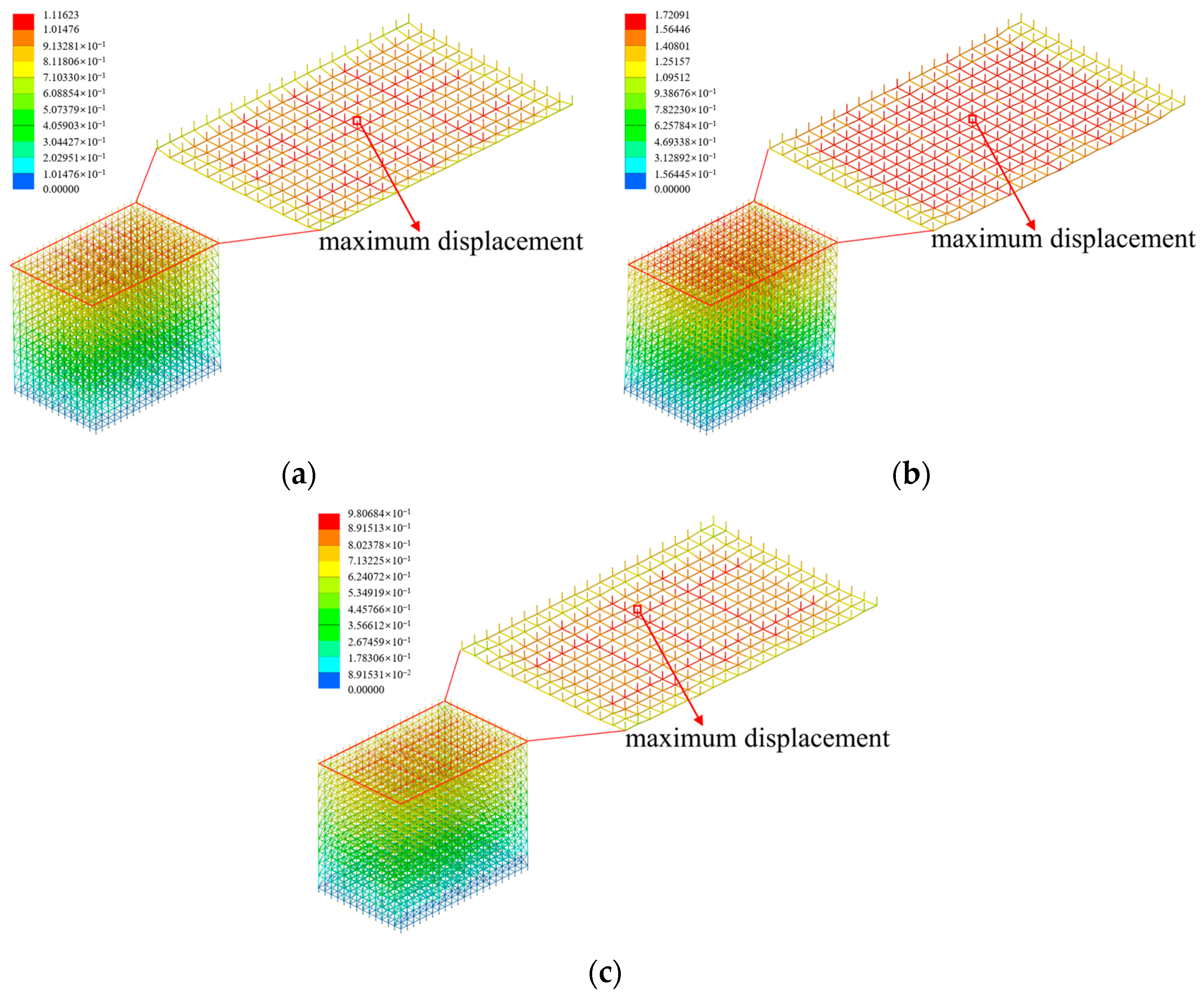
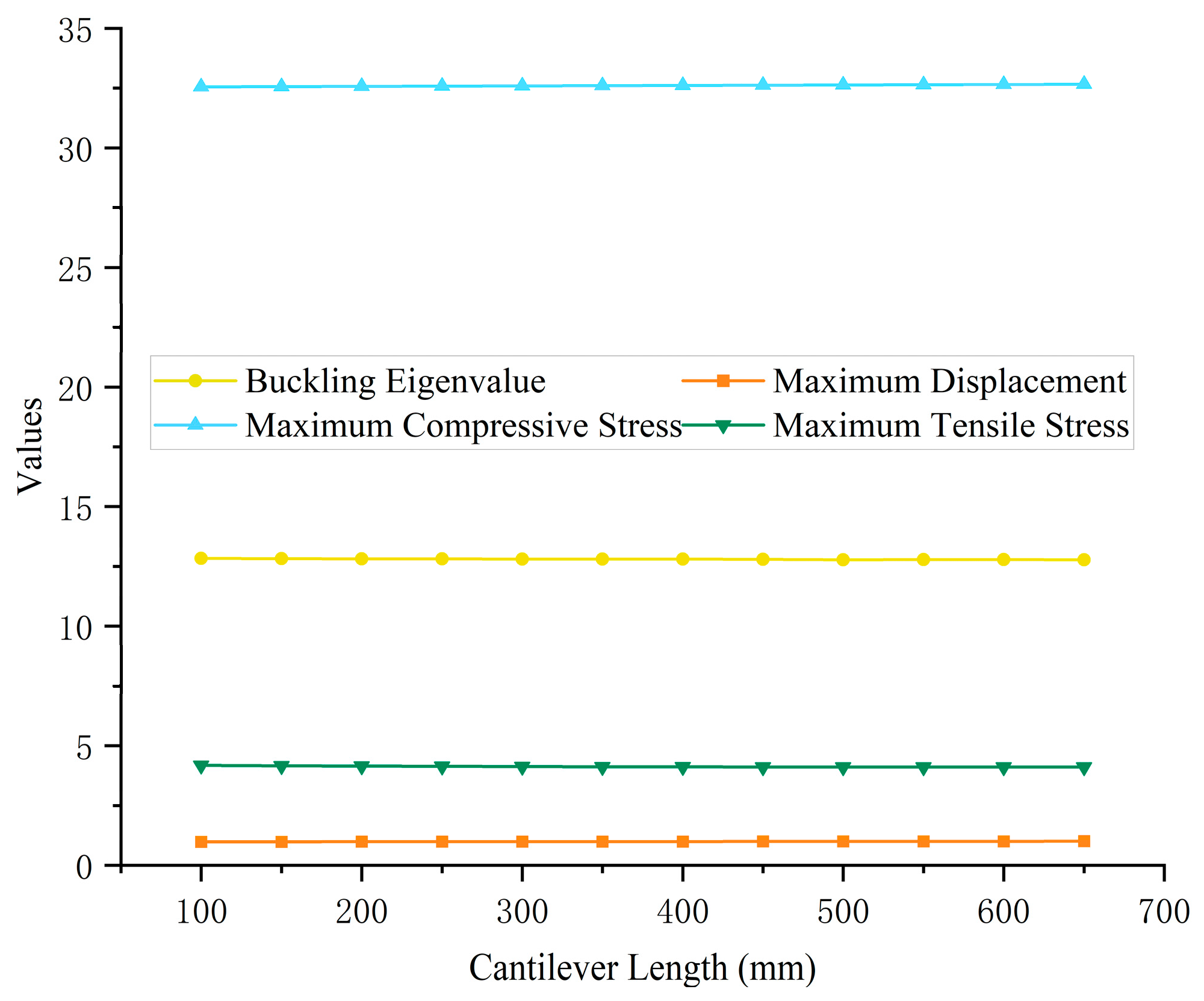
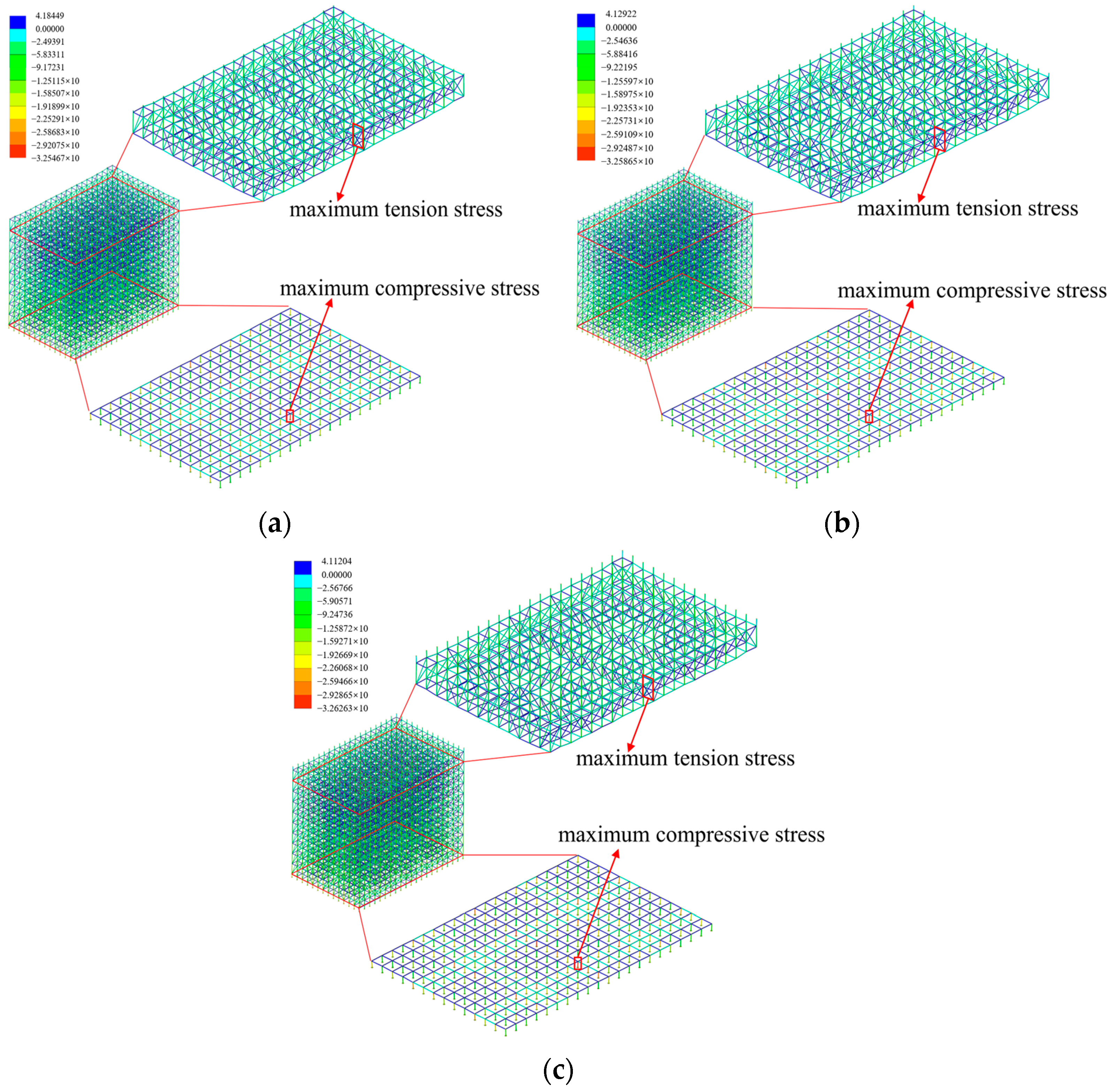
4.1.3. Adjustable Bracket Cantilever Length
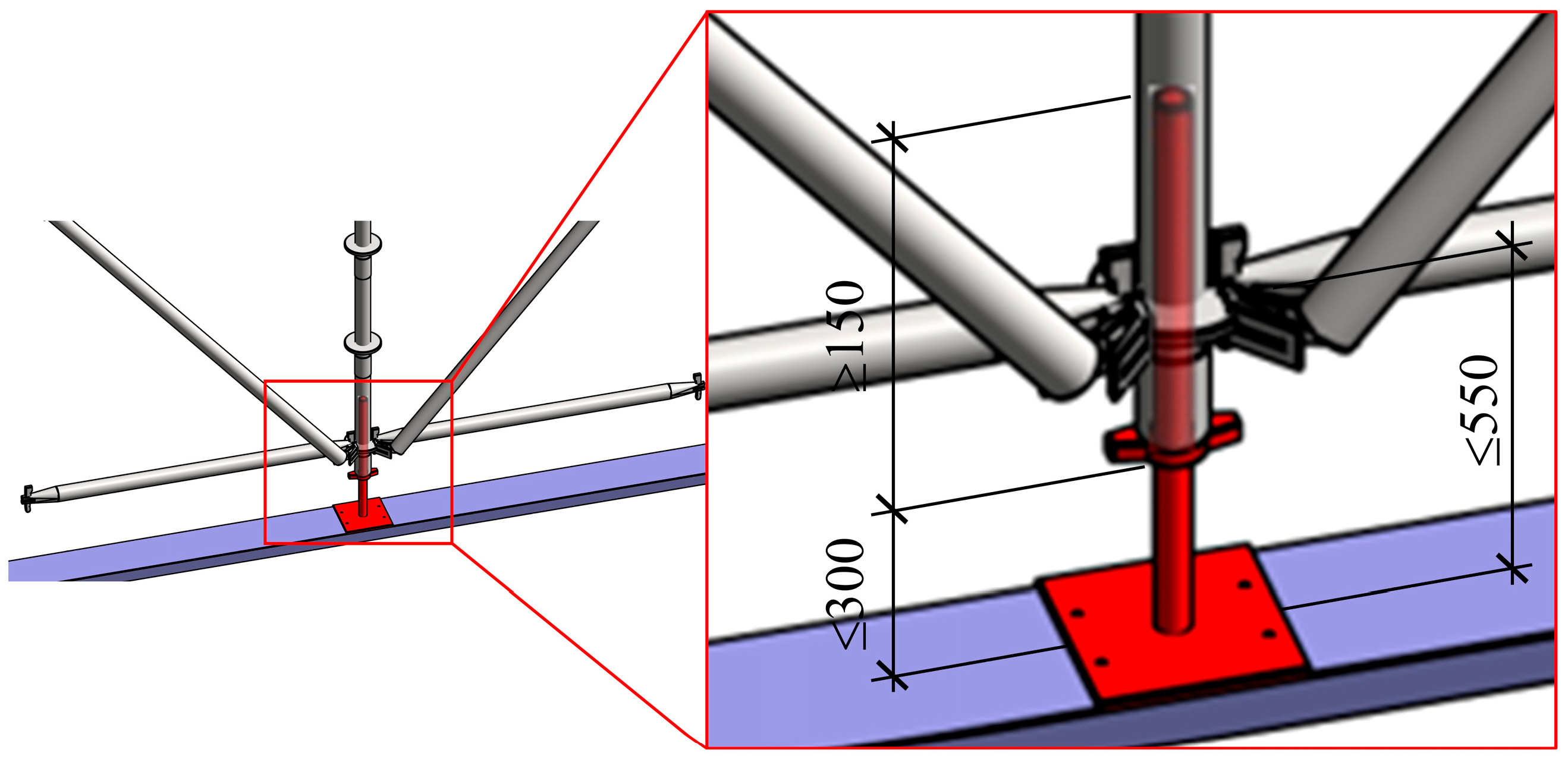
4.1.4. Adjustable Base Height
4.2. Establishment of Early Warning Mechanism for Frame Instability
4.2.1. Weight Analysis of Key Parameters
4.2.2. Determination of Compliance Testing Indicators
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- With the adjustable base height increasing, the overall stability of the scaffold system shows a nonlinear change trend, which increases first and then decreases. The scaffold system exhibits optimal overall stability when the adjustable base height is 350 mm. In contrast, the overall stability of the scaffold system remains relatively constant within the range of 100–650 mm adjustable bracket cantilever length.
- (2)
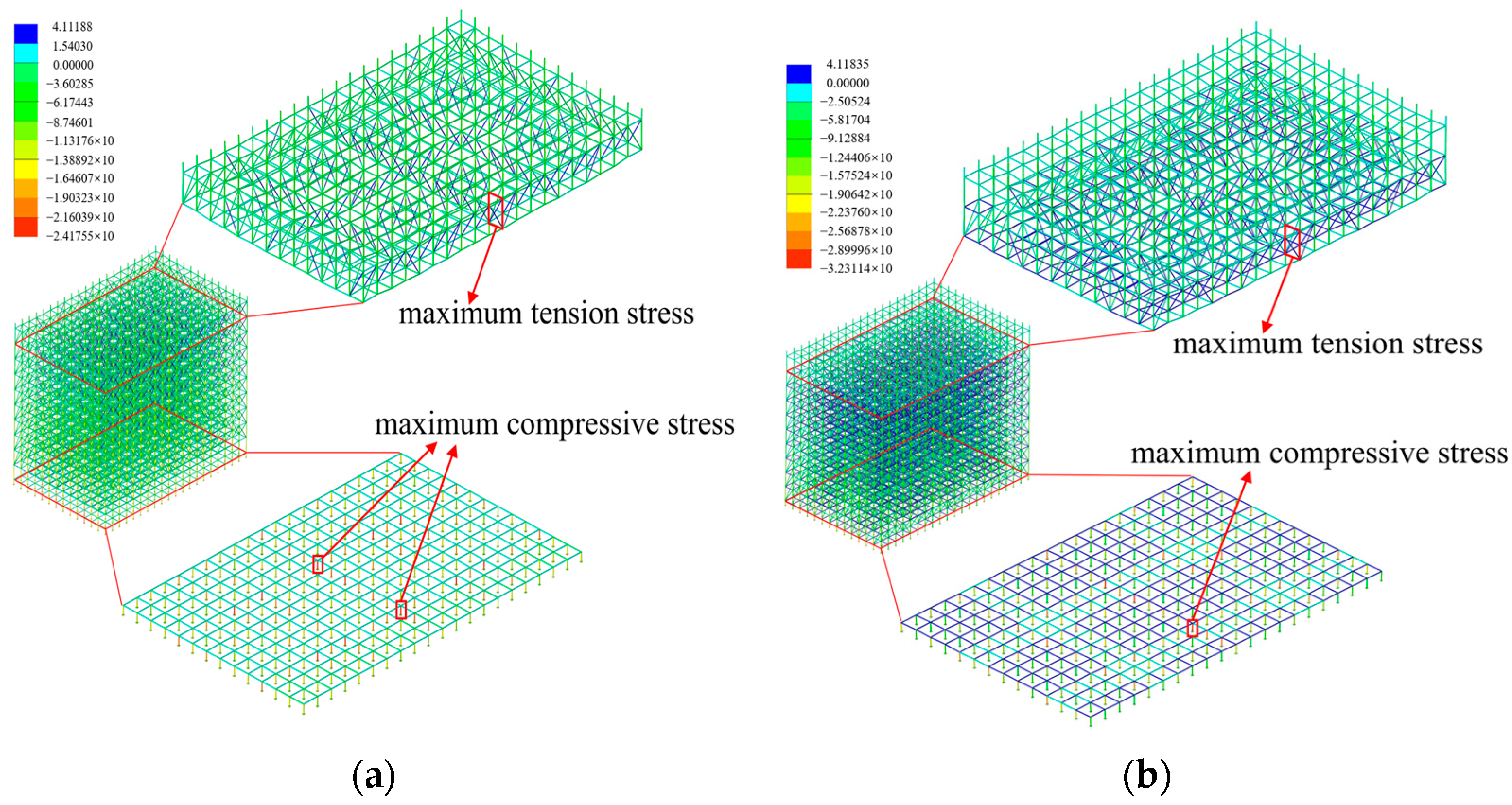
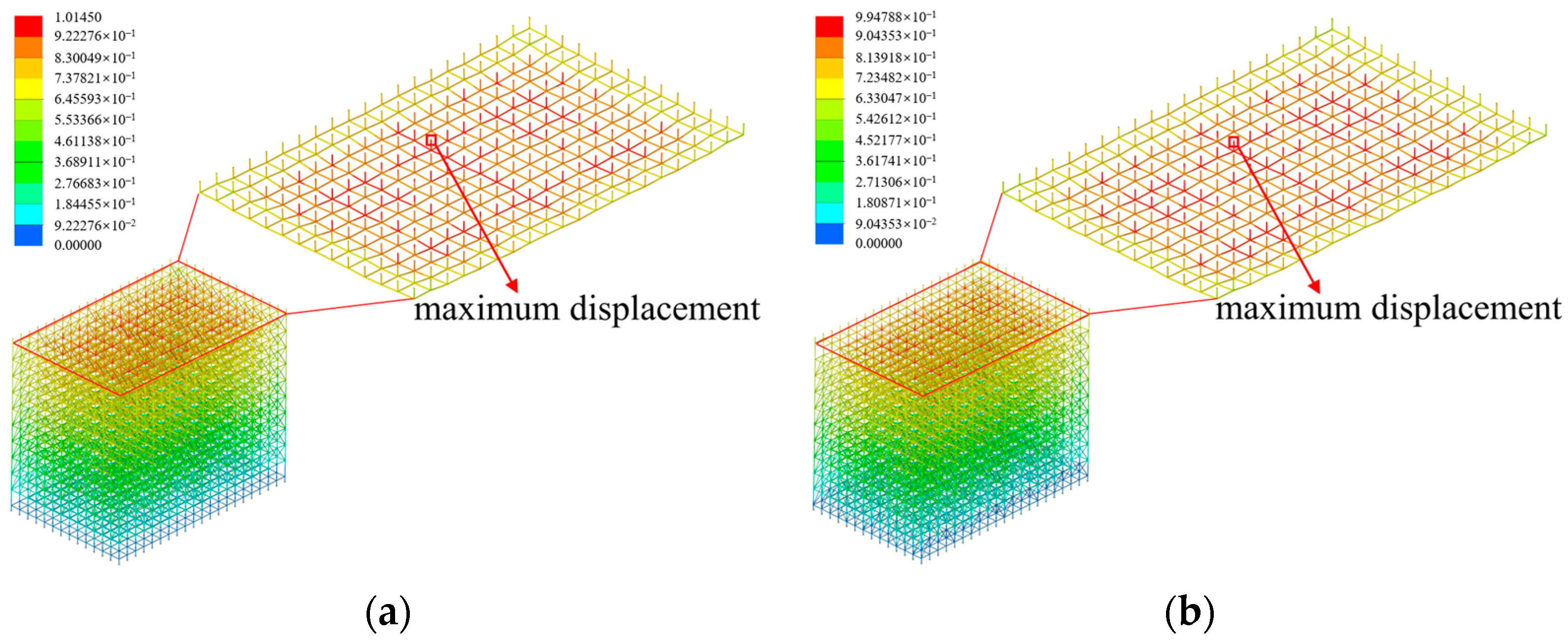
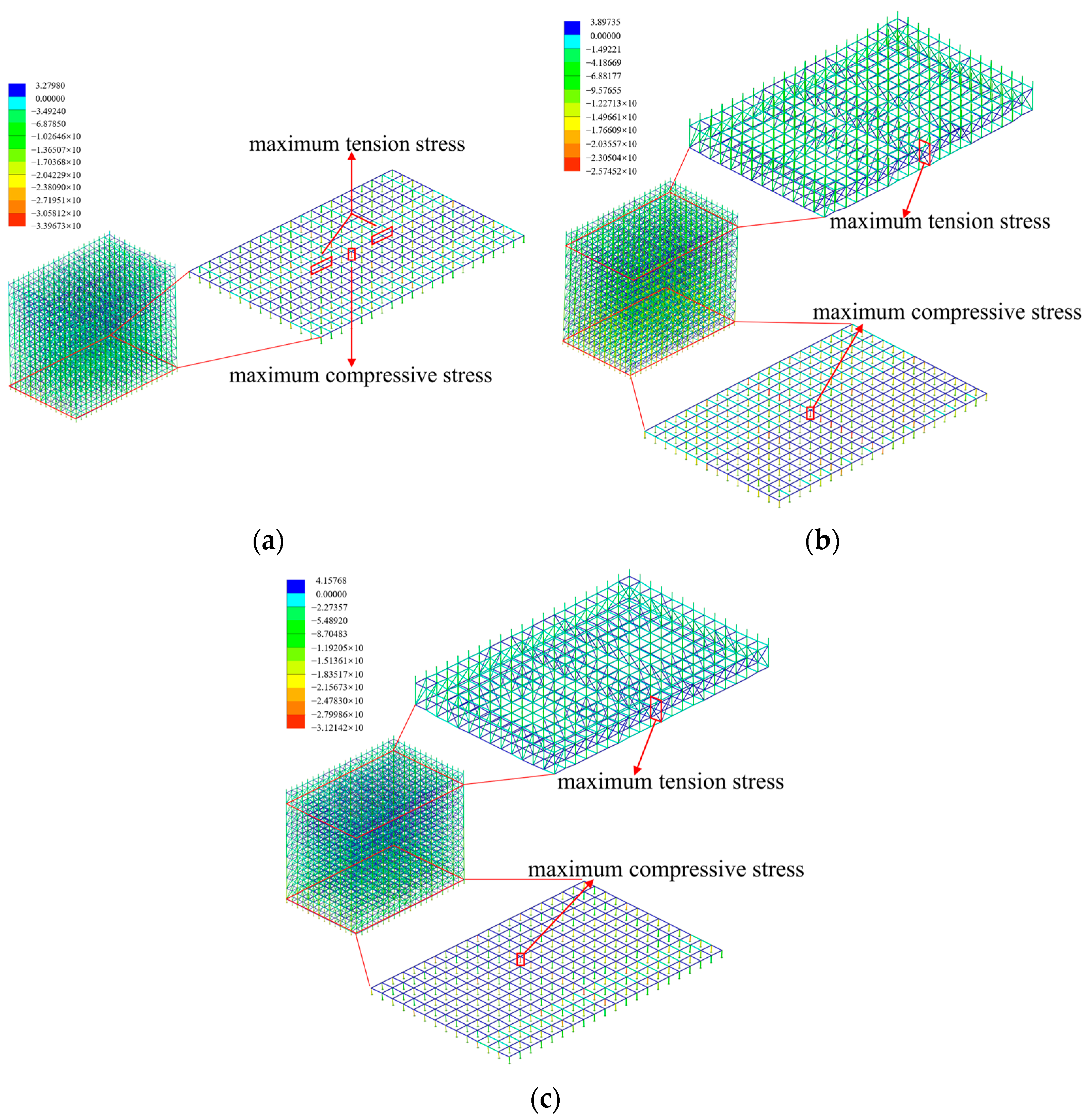
- The overall stability of the scaffold system demonstrates pronounced sensitivity to the absence of diagonal braces. The absence of the diagonal braces located at the bottom, top, and ends of the scaffold system induces a significant attenuation of the overall stability, and the maximum buckling eigenvalue decreases by 81.45%. The overall stability of the scaffold system decreases significantly with the increase in the verticality offset, while the horizontality offset within the range of ±5 mm exhibits negligible influence on the overall stability of the scaffold system.
- (3)
- The results of orthogonal test and range analysis indicate that the influence weight of the five key parameters on the scaffold stability from high to low is the lack of bracing, verticality offset of the vertical bar, adjustable base height, horizontality offset of the horizontal bar, and adjustable bracket cantilever length.
- (4)
- The working conditions of the key parameters that trigger a red warning for the scaffold system are as follows: absence of the first-step diagonal brace at either the bottom or top of the scaffold; an adjustable base height less than 150 mm or an exposed screw length exceeding 300 mm; an adjustable bracket cantilever length exceeding 650 mm or an exposed screw length exceeding 400 mm; a verticality offset exceeding 50 mm; or a horizontal offset exceeding 5 mm or a verticality exceeding H/500.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H. 3D Reconstruction of Large-Scale Scaffolds with Synthetic Data Generation and an Upsampling Adversarial Network. Autom. Constr. 2023, 156, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadoon, Z.A.; Barakat, S.; Abed, F.; Ateyat, A.A. Stability of Structural Steel Tubular Props: An Experimental, Analytical, and Theoretical Investigation. Steel Compos. Struct. 2023, 49, 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Peng, G.; Niu, D.; Fan, Y. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Steel Tube-Coupler Connections in Corroded Scaffolds. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 176, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Liu, Z.; Miao, J.Y. The Investigation of Stability Analysis of Tube and Coupler Scaffold. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 594–597, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, K.-Y.; Tserng, H.-P. A Study of Automated Intelligent Monitoring of Scaffolding Safety for Construction Projects. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2024, 47, 626–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qiu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S. Influence of Random Geometrical Imperfection on Loading Capacity of Scaffold Based on Stochastic Numerical Model. Adv. Eng. Software 2024, 197, 103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimellaro, G.P.; Domaneschi, M. Stability Analysis of Different Types of Steel Scaffolds. Eng. Struct. 2017, 152, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowobilski, T.; Hoła, B. Methodology Based on Causes of Accidents for Forcasting the Effects of Falls from Scaffoldings Using the Construction Industry in Poland as an Example. Saf. Sci. 2023, 157, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Yurdusev, M.A.; Yildizel, S.A.; Calis, G. Investigation of Scaffolding Accident in a Construction Site: A Case Study Analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 120, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Ge, F.; Yang, F. Human Reliability Assessment on Building Construction Work at Height: The Case of Scaffolding Work. Saf. Sci. 2023, 159, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.K.; Chung, K.F.; Chan, S.L. Structural Instability of Multi-Storey Door-Type Modular Steel Scaffolds. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Won, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-C.; Kim, S. Investigation of the Global Structural Behavior of the Prefabricated Shoring System Considering Structural Details. Buildings 2023, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, C.; Khelil, A.; Al Mahmoud, F.; Blin-Lacroix, J.-L.; Pamies, A. Experimental Investigations of Buckling Behaviour of Steel Scaffolds. Structures 2021, 33, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Rasmussen, K.J.R.; Ellingwood, B.R. Reliability Assessment of Steel Scaffold Shoring Structures for Concrete Formwork. Eng. Struct. 2012, 36, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Gao, W.; Li, C.X.; Huo, X.X. Influence of the Structural Performance of Steel Tubular Scaffold Based on Measured Imperfection. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 256–259, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-L.; Wu, C.-W.; Chan, S.-L.; Huang, C.-H. Experimental and Numerical Studies of Practical System Scaffolds. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2013, 91, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. Experimental Study on Bearing Capacity of Reinforced Steel Tubular Scaffold under Uniform Loads. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4324528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, H.; Lei, M.; Fang, Z.; Guo, L. Safety and Stability Analysis of Variable Cross-Section Disc-Buckle Type Steel Pipe High Support System. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 2022, 200, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.-L.; Wang, S.-H.; Wang, C.-S. Stability Study on Scaffolds with Inclined Surfaces and Extended Jack Bases in Construction; The Hong Kong Institute of Steel Construction: Hong Kong, China, 2021; pp. 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; He, Y. Experimental Studies and Finite Element Analysis of Socket-Type Keyway Steel Pipe Scaffolding. Buildings 2024, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chandrangsu, T.; Rasmussen, K.J.R. Probabilistic Study of the Strength of Steel Scaffold Systems. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liang, B.; Li, S.; Qiu, R.; Gu, X.; Zhang, N. Buckling Capacity of Socket Template Scaffold with Random Bending Stiffness and Capacity. Structures 2025, 71, 108152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.L.Y.; Chan, S.-L.; Liu, Y.-P.; Liu, S.-W. Progressive Collapse of System Scaffolds with Accidental Removal of Bracing Members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 218, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Peng, Z.; Hou, J.; Zheng, X.; Ding, Y.; Wu, H. Study on the Ultimate Load-Bearing Capacity of Disc Buckle Tall Formwork Support Considering Uncertain Factors. Buildings 2024, 14, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czepiżak, D.; Ramezantitkanloo, A.; Pieńko, M. Problems of monitoring critical elements of scaffolding. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2024, 70, 233–254. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Wind Load Analysis on Temporary Scaffolding Structures in High-Altitude Venues Based on Numerical Simulation: A Case Study From the 2022 Beijing Olympics. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2024, 2024, 3746675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieńko, M.; Błazik-Borowa, E. Experimental Studies of Ringlock Scaffolding Joint. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 173, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, S.; Liu, W.; Gao, R. Experimental Study on Stable Bearing Capacity of Wheel-Buckle Formwork Support Frames. Structures 2023, 48, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jia, L.; Wen, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, Z. Experimental and Theoretical Studies on the Stability of Steel Tube–Coupler Scaffolds with Different Connection Joints. Eng. Struct. 2016, 106, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcik, J.; Arora, V.; Dolejs, J. Design of New Scaffold Anchor Based on the Updated Finite Element Model. Eng. Struct. 2016, 118, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, Y.; Jia, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wen, S. Structural Behavior of Steel Tube and Coupler Scaffolds with Stability Strengthening Details. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2018, 18, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chu, S.; Qin, S.; Ding, H.; Luo, N.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, G. Optimisation of Prestressed Stayed Steel Columns Based on Strengthen Elitist Genetic Algorithm. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2025, 227, 109324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Koo, N.; Kim, H. Automating Scaffold Safety Inspections Using Semantic Analysis of 3D Point Clouds. Autom. Constr. 2024, 166, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhakarmi, S.; Park, J.; Cho, C. Enhanced Machine Learning Classification Accuracy for Scaffolding Safety Using Increased Features. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2019, 145, 04018133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Parametric Index | Data |
|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus (N/mm2) | 2.0600 × 105 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 |
| Linear Expansion Coefficient (1/[F]) | 6.6667 × 10−6 |
| Volume Weight (N/mm3) | 7.85 × 10−5 |
| Tension Strength (MPa) | 470 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 235 |
| Elongation Rate (%) | 26 |
| Damping Ratio | 0.02 |
| Material | Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | P | Fe | |
| Q235B | 0.13 | 0.49 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Parametric Index | Standard Value (KN/m2) |
|---|---|
| Frame Weight G1 | Value According to the Actual Weight |
| Template Weight G2 | 0.5 |
| Ordinary Beam or Slab Reinforced Concrete Self-weight G3 | 25.1 |
| Construction Personnel and Equipment Load Q1 | 2.5 |
| Wind Load Q3 | 0.276 |
| Mode | Natural Frequency (Hz) | Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical Calculation | Actual Measurement | ||
| 1 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 3.26% |
| 2 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 3.03% |
| 3 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 5.00% |
| 4 | 1.10 | 1.13 | 2.72% |
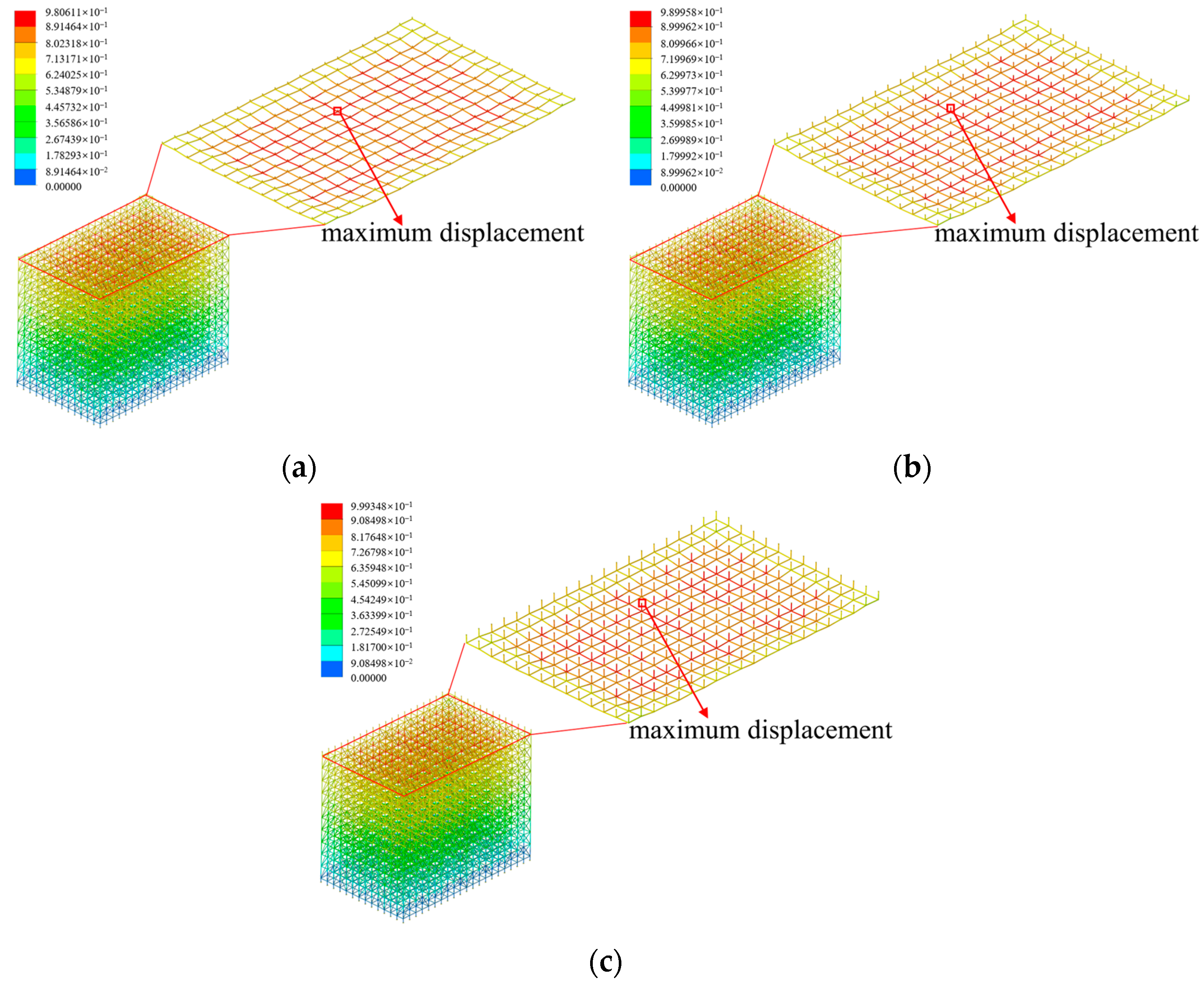
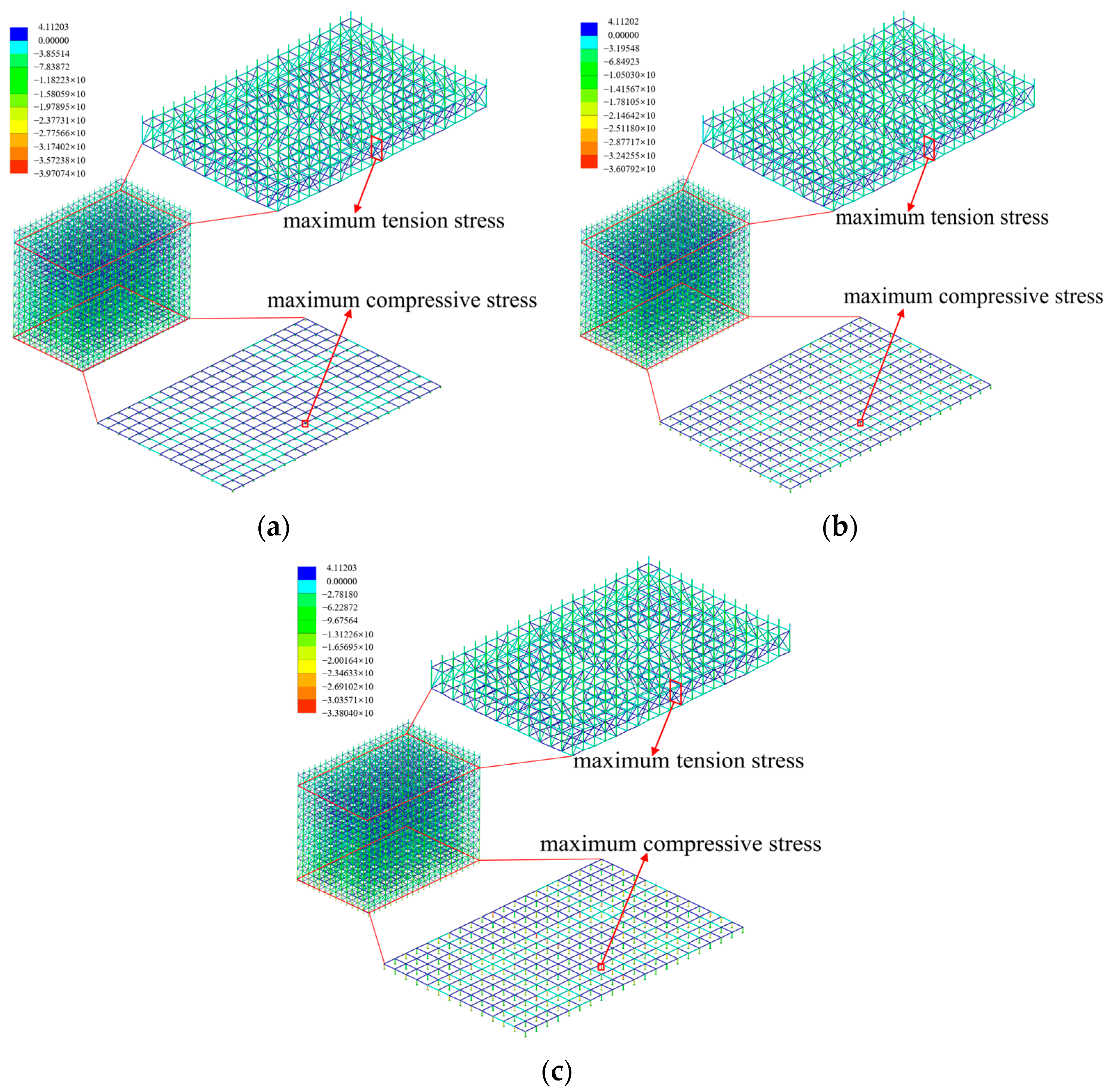
| Horizontality Offset | Buckling Eigenvalue | Maximum Displacement/mm | Maximum Compressive Stress/MPa | Maximum Tensile Stress/MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| Longitudinal | 1 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 |
| 2 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 3 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 4 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 5 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| Transverse | 1 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 |
| 2 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 3 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 4 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| 5 | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 | |
| Horizontal Absence Position/Column | Longitudinal Absence Position/Column | Buckling Eigenvalue | Maximum Displacement/mm | Maximum Compressive Stress/MPa | Maximum Tensile Stress/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| complete | complete | 12.80 | 1.00 | 32.63 | 4.11 |
| C | 4, 5 | 12.98 | 0.97 | 26.66 | 4.07 |
| 3, 6 | 12.92 | 0.98 | 31.02 | 4.15 | |
| 2, 7 | 10.78 | 0.98 | 31.21 | 4.16 | |
| 1, 8 | 12.91 | 0.98 | 31.11 | 4.14 | |
| B, D | 4, 5 | 12.86 | 1.70 | 21.88 | 3.78 |
| 3, 6 | 12.82 | 1.72 | 25.59 | 3.89 | |
| 2, 7 | 10.54 | 1.72 | 25.75 | 3.90 | |
| 1, 8 | 12.80 | 1.72 | 25.67 | 3.89 | |
| A, E | 4, 5 | 12.97 | 1.10 | 29.16 | 3.11 |
| 3, 6 | 12.93 | 1.12 | 33.76 | 3.11 | |
| 2, 7 | 10.78 | 1.12 | 33.97 | 3.28 | |
| 1, 8 | 12.91 | 1.12 | 33.85 | 2.82 |
| Level | Key Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Height/mm | Cantilever Length/mm | Absence Position of Diagonal Braces | Verticality Offset/mm | Horizontality Offset/mm | |
| 1 | 550 | 650 | Step 1 | 50 | 5 |
| 2 | 500 | 600 | Step 2 | 40 | 4 |
| 3 | 450 | 550 | Step 3 | 30 | 3 |
| 4 | 400 | 500 | Step 4 | 20 | 2 |
| Level Assembly | Base Height/mm | Cantilever Length/mm | Absence Position of Diagonal Braces | Verticality Offset/mm | Horizontality Offset/mm | Buckling Eigenvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 550 | 650 | Step 1 | 50 | 5 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 550 | 600 | Step 2 | 40 | 4 | 4.75 |
| 3 | 550 | 550 | Step 3 | 30 | 3 | 5.42 |
| 4 | 550 | 500 | Step 4 | 20 | 2 | 7.51 |
| 5 | 500 | 650 | Step 2 | 30 | 2 | 5.82 |
| 6 | 500 | 600 | Step 1 | 20 | 3 | 2.03 |
| 7 | 500 | 550 | Step 4 | 50 | 4 | 4.41 |
| 8 | 500 | 500 | Step 3 | 40 | 5 | 4.68 |
| 9 | 450 | 650 | Step 3 | 20 | 4 | 7.05 |
| 10 | 450 | 600 | Step 4 | 30 | 5 | 6.42 |
| 11 | 450 | 550 | Step 1 | 40 | 2 | 1.62 |
| 12 | 450 | 500 | Step 2 | 50 | 3 | 4.36 |
| 13 | 400 | 650 | Step 4 | 40 | 3 | 5.52 |
| 14 | 400 | 600 | Step 3 | 50 | 2 | 4.32 |
| 15 | 400 | 550 | Step 2 | 20 | 5 | 7.22 |
| 16 | 400 | 500 | Step 1 | 30 | 4 | 1.93 |
| Evaluation Indexes | Base Height | Cantilever Length | Absence of Diagonal Braces | Verticality Offset | Horizontality Offset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 18.97 | 19.68 | 6.87 | 14.38 | 19.61 |
| T2 | 16.94 | 17.52 | 22.15 | 16.57 | 18.14 |
| T3 | 19.45 | 18.67 | 21.47 | 19.59 | 17.33 |
| T4 | 18.99 | 18.48 | 23.86 | 23.81 | 19.27 |
| t1 | 4.74 | 4.92 | 1.72 | 3.60 | 4.90 |
| t2 | 4.24 | 4.38 | 5.54 | 4.14 | 4.54 |
| t3 | 4.86 | 4.67 | 5.37 | 4.90 | 4.33 |
| t4 | 4.75 | 4.62 | 5.97 | 5.95 | 4.82 |
| Ri | 0.62 | 0.54 | 4.25 | 2.35 | 0.57 |
| Design Axial Force of Vertical Bar N (KN) | Scaffold Height H (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H ≤ 8 | 8 < H ≤ 16 | 16 < H ≤ 24 | 24 < H | |
| N ≤ 25 | Every 3 spans | Every 3 spans | Every 2 spans | Every 1 span |
| 25 < N ≤ 40 | Every 2 spans | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every 1 span |
| 40 < N | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every span |
| Design Axial Force of Vertical Bar N (KN) | Scaffold Height H (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H ≤ 8 | 8 < H ≤ 16 | 16 < H ≤ 24 | 24 < H | |
| N ≤ 40 | Every 3 spans | Every 3 spans | Every 2 spans | Every 1 span |
| 40 < N ≤ 65 | Every 2 spans | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every 1 span |
| 65 < N | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every 1 span | Every span |
| Warning Level | Adjustable Base Height H1 | Exposed Screw Length L1 |
|---|---|---|
| Red warning | 0 mm < H1 ≤ 150 mm | 300 mm < L1 |
| Blue warning | 150 mm < H1 ≤ 350 mm | |
| Green warning | 350 mm < H1 ≤ 450 mm | 0 mm < L1 ≤ 300 mm |
| Yellow warning | 450 mm < H1 ≤ 550 mm | |
| Red secondary warning | 550 mm < H1 |
| Warning Level | Adjustable Bracket Cantilever Length H2 | Exposed Screw Length L2 |
|---|---|---|
| Green warning | 0 mm < H2 ≤ 300 mm | 0 mm < L2 ≤ 400 mm |
| Blue warning | 300 mm < H2 ≤ 500 mm | |
| Yellow warning | 500 mm < H2 ≤ 650 mm | |
| Red warning | 650 mm < H2 | 400 mm < L2 |
| Warning Level | Verticality Offset δ1 | Horizontality Offset δ2 |
|---|---|---|
| Green warning | 0 mm < δ1 ≤ 10 mm | 0 mm < δ2 ≤ 5 mm |
| Blue warning | 10 mm < δ1 ≤ 30 mm | |
| Yellow warning | 30 mm < δ1 ≤ 50 mm | |
| Red warning | 50 mm < δ1 | 5 mm < δ2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Yao, G.; Yang, Y.; Qin, H. Stability Analysis of Marine Scaffold Under Coupled Environmental Loads. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061141
Wang P, Yao G, Yang Y, Qin H. Stability Analysis of Marine Scaffold Under Coupled Environmental Loads. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061141
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pengkai, Gang Yao, Yang Yang, and Haiyang Qin. 2025. "Stability Analysis of Marine Scaffold Under Coupled Environmental Loads" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061141
APA StyleWang, P., Yao, G., Yang, Y., & Qin, H. (2025). Stability Analysis of Marine Scaffold Under Coupled Environmental Loads. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061141








