Assessing Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches Using Boussinesq Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FUNWAVE-TVD Model
2.2. Numerical Experiments
2.3. Rip Current Identification and Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Circulation Patterns of Rip Currents at Featureless Beaches
3.2. The Effects of Beach Morphology on Rip Current Characteristics
3.3. The Effects of Wave Incidences on Rip Current Characteristics
3.4. The Effects of Wave Height and Wave Period on Rip Current Characteristics
3.5. Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Predicting Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches
4.2. Sensitivity of Rip Occurrence to Directional Wave Spectra Parameters
4.3. Generation Mechanisms of Transient Rip Currents
4.4. Limitations, Uncertainties and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Brander, R.W.; McCarroll, R.J. Rip Current Types, Circulation and Hazard. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighton, B.; Sherker, S.; Brander, R.; Thompson, M.; Bradstreet, A. Rip Current Related Drowning Deaths and Rescues in Australia 2004–2011. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arozarena, I.; Houser, C.; Echeverria, A.; Brannstrom, C. The Rip Current Hazard in Costa Rica. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, E.; Beaumont, E.; Russell, P.; MacLeod, R. Public Understanding and Knowledge of Rip Currents and Beach Safety in the UK. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2015, 9, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Rip Current Hazards in South China Headland Beaches. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 121, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, B.C.; Gould, R.E.; Brander, R.W. Estimations of Rip Current Rescues and Drowning in the United States. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, R.W.; Bradstreet, A.; Sherker, S.; MacMahan, J. Responses of Swimmers Caught in Rip Currents: Perspectives on Mitigating the Global Rip Current Hazard. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2011, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, R.A.; MacMahan, J.H.; Reniers, A.J.; Nelko, V. Rip Currents. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 43, 551–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S.; Stewart, R.W. Radiation Stresses in Water Waves; a Physical Discussion, with Applications. Deep-Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1964, 11, 529–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.M.; Moulton, M.; Chickadel, C.C.; Nuss, E.S.; Palmsten, M.L.; Brodie, K.L. Two-Dimensional Inverse Energy Cascade in a Laboratory Surf Zone for Varying Wave Directional Spread. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 125140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reniers, A.J.; MacMahan, J.H.; Thornton, E.B.; Stanton, T.P. Modelling Infragravity Motions on a Rip-Channel Beach. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Barrett, G.; Labude, D. Alongshore Variation in the Rip Current Hazard at Pensacola Beach, Florida. Nat. Hazards 2011, 57, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Coco, G. Surf Zone Flushing on Embayed Beaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.; Austin, M.; Masselink, G.; Russell, P. Dynamics of Rip Currents Associated with Groynes—Field Measurements, Modelling and Implications for Beach Safety. Coast. Eng. 2016, 107, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Pattiaratchi, C. Boussinesq Modelling of Transient Rip Currents. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanda, S.H.; Feddersen, F. A Self-similar Scaling for Cross-shelf Exchange Driven by Transient Rip Currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.; Castelle, B.; Almar, R.; Senechal, N.; Floc’h, F.; Detandt, G. Controls on Flash Rip Current Hazard on Low-Tide Terraced Tropical Beaches in West Africa. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 81, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddersen, F. The Generation of Surfzone Eddies in a Strong Alongshore Current. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B. Vorticity Generation by Short-Crested Wave Breaking. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 24604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B. Field Evidence of Inverse Energy Cascades in the Surfzone. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2020, 50, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reniers, A.J.; Roelvink, J.A.; Thornton, E.B. Morphodynamic Modeling of an Embayed Beach under Wave Group Forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C01030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahan, J.H.; Reniers, A.J.; Thornton, E.B.; Stanton, T.P. Infragravity Rip Current Pulsations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109, C01033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.W.; Özkan-Haller, H.T. Low-Frequency Characteristics of Wave Group–Forced Vortices. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C08004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan-Haller, H.T.; Kirby, J.T. Nonlinear Evolution of Shear Instabilities of the Longshore Current: A Comparison of Observations and Computations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 25953–25984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.D.; Hogan, C.L. Rip Currents and Beach Hazards: Their Impact on Public Safety and Implications for Coastal Management. J. Coast. Res. 1994, 12, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Benedet, L.; Finkl, C.; Campbell, T.; Klein, A. Predicting the Effect of Beach Nourishment and Cross-Shore Sediment Variation on Beach Morphodynamic Assessment. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.D.; Short, A.D. Morphodynamic Variability of Surf Zones and Beaches: A Synthesis. Mar. Geol. 1984, 56, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.D. Beaches of the Victorian Coast Port Phillip Bay: A Guide to Their Nature, Characteristics, Surf and Safety; Sydney University Press: Camperdown, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, T.M.; Russell, P.; Masselink, G.; Austin, M.J.; Wills, S.; Wooler, A. Rip Current Hazards on Large-Tidal Beaches in the United Kingdom; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, L.D.; Short, A.D.; Green, M.O. Short-Term Changes in the Morphodynamic States of Beaches and Surf Zones: An Empirical Predictive Model. Mar. Geol. 1985, 62, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G.; Short, A.D. The Effect of Tide Range on Beach Morphodynamics and Morphology: A Conceptual Beach Model. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 785–800. [Google Scholar]
- Hamsan, M.A.S.; Ramli, M.Z. Monsoonal Influences on Rip Current Hazards at Recreational Beaches along Pahang Coastline, Malaysia. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Wang, B. Rip Current Hazard at Coastal Recreational Beaches in China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 210, 105734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, X.; Qiu, T.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G. Tidal and Wave Modulation of Rip Current Dynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 243, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Li, Z.; Zhu, D.; Zeng, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, Z.; Su, Q. Field Observation and Numerical Analysis of Rip Currents at Ten-Mile Beach, Hailing Island, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 276, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surisetty, V.A.K.; Venkateswarlu, C.; Ramesh, M.; Gireesh, B.; Naidu, C.V.; Nair, L.S.; Sharma, R. Practical Use of Smartphone Cameras in Rip Current Monitoring Studies. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 243, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucerino, L.; Carpi, L.; Schiaffino, C.F.; Pranzini, E.; Sessa, E.; Ferrari, M. Rip Current Hazard Assessment on a Sandy Beach in Liguria, NW Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebelhoer, L.; Koon, W.; Harley, M.D.; Lawes, J.C.; Brander, R.W. Characteristics and Beach Safety Knowledge of Beachgoers on Unpatrolled Surf Beaches in Australia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Z.; Hu, P.; Wang, B.; Su, Q.; Li, G. Preliminary Investigation and Analysis of Beachgoers’ Awareness of Rip Currents in South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahan, J.H.; Reniers, A.J.; Thornton, E.B. Vortical Surf Zone Velocity Fluctuations with 0 (10) Min Period. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouragues, A.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Jak McCarroll, R.; Rodriguez-Padilla, I.; Scott, T.; Sous, D. High-energy Surf Zone Currents and Headland Rips at a Geologically Constrained Mesotidal Beach. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2020JC016259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, Ç.; McWilliams, J.; Uchiyama, Y. Topographic and Coastline Influences on Surf Eddies. Ocean Model. 2020, 147, 101565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouragues, A.; Martins, K.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B. Headland Rip Very Low Frequency Fluctuations and Surfzone Eddies During High-Energy Wave Events. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 2935–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, A.D.D.; Leibovich, S. A Rational Model for Langmuir Circulations. J. Fluid Mech. 1976, 73, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C.; Restrepo, J.M.; Lane, E.M. An Asymptotic Theory for the Interaction of Waves and Currents in Coastal Waters. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 511, 135–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Voulgaris, G.; Warner, J.C. Implementation and Modification of a Three-Dimensional Radiation Stress Formulation for Surf Zone and Rip-Current Applications. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 1097–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; McWilliams, J.C.; Akan, C. Three-dimensional Transient Rip Currents: Bathymetric Excitation of Low-frequency Intrinsic Variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 5826–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, M.; Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B.; Warner, J.C.; Kumar, N. Rip Currents and Alongshore Flows in Single Channels Dredged in the Surf Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 3799–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Dong, B.; Ma, G.; Feng, W. Topographic and Hydrodynamic Influence on Rip Currents and Alongshore Currents on Headland Beaches in China. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.M.; Iskander, M.M.; El-Gindy, A.A.; Nafeih, A.M.; Moghazy, H.E.-D.M. Hydrodynamic Simulation of Rip Currents Along Al-Nakheel Beach, Alexandria, Egypt: Case Study. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2023, 22, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhofer, J.; Dudkowska, A. Rip Currents in the Southern Baltic Sea Multi-Bar Nearshore Zone. Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 212, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, Á.; Wu, C.H.; Bechle, A.J.; Anderson, E.J.; Kristovich, D.A. Unexpected Rip Currents Induced by a Meteotsunami. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.; Bertin, X.; Mengual, B.; Pezerat, M.; Lavaud, L.; Guérin, T.; Zhang, Y.J. Wave-Induced Mean Currents and Setup over Barred and Steep Sandy Beaches. Ocean Model. 2022, 179, 102110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, C.H. Drowning Incidents and Conditions Due to Hidden Flash Rips in Lake Michigan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, J.T. Recent Advances in Nearshore Wave, Circulation, and Sediment Transport Modeling. J. Mar. Res. 2017, 75, 263–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, M.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Russell, P. Water-Level Controls on Macro-Tidal Rip Currents. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 75, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Castelle, B.; Brander, R.W.; Scott, T. Modelling Rip Current Flow and Bather Escape Strategies across a Transverse Bar and Rip Channel Morphology. Geomorphology 2015, 246, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; McCarroll, R.J.; Brander, R.W.; Scott, T.; Dubarbier, B. Modelling the Alongshore Variability of Optimum Rip Current Escape Strategies on a Multiple Rip-Channelled Beach. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 663–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.; Poate, T.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Instance, S. New Insights into Combined Surfzone, Embayment, and Estuarine Bathing Hazards. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 24, 4049–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Brander, R.; McCarroll, R.J.; Tellier, E.; De Korte, E.; Tackuy, L.; Robinet, A.; Simonnet, B.; Salmi, L.-R. Wave and Tide Controls on Rip Current Activity and Drowning Incidents in Southwest France. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouragues, A.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B.; Martins, K. Headland Rip Modelling at a Natural Beach under High-Energy Wave Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, A.; Kumar, N.; Haller, M.C. Simulations of the Surf Zone Eddy Field and Cross-Shore Exchange on a Nonidealized Bathymetry. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC016619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Nie, Y. Numerical Simulations of Rip Currents off Arc-Shaped Coastlines. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Xing, C. A Wave-Resolving Modeling Study of Rip Current Variability, Rip Hazard, and Swimmer Escape Strategies on an Embayed Beach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 23, 3487–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J. Numerical Study of Rip Currents Interlaced with Multichannel Sandbars. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Xu, C.; Ren, Z.; Yan, S.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z. Study on the Formation Characteristics and Disaster Mitigation Mechanisms of Rip Currents on Arc-Shaped Beach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, B.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; You, Z.; Yan, S.; Lu, L. Modeling Rip Current Systems around Multiple Submerged Breakwaters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Zou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; You, Z. Flow Characteristics of the Rip Current System Adjacent to a Coastal Vertical Structure for Irregular Waves. Ocean Eng. 2024, 312, 119128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Zou, Z.; Chang, C.; Fang, K.; Wang, Y. Flow Characteristics of the Rip Current System near a Shore-Normal Structure with Regular Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Xu, M.; Garnier, R.; Derakhti, M. Short-crested Waves in the Surf Zone. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4143–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesiello, P.; Auclair, F.; Debreu, L.; McWilliams, J.; Almar, R.; Benshila, R.; Dumas, F. Tridimensional Nonhydrostatic Transient Rip Currents in a Wave-Resolving Model. Ocean Model. 2021, 163, 101816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Jung, T.-H.; Shi, F. Vertical Structure of Rip-Currents in the Nearshore Circulation. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Nam, J.; Son, S.; Kim, I.H.; Jung, T.-H. Field Observation and Numerical Modelling of Rip Currents within a Pocket Beach. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 79, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Kirby, J.T.; Harris, J.C.; Geiman, J.D.; Grilli, S.T. A High-Order Adaptive Time-Stepping TVD Solver for Boussinesq Modeling of Breaking Waves and Coastal Inundation. Ocean Model. 2012, 43, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.T.; Wei, G.; Chen, Q.; Kennedy, A.B.; Dalrymple, R.A. FUNWAVE 1.0: Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Wave Model-Documentation and User’s Manual; Center for Applied Coastal Research, University of Delaware: Newark, DE, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; Kirby, J.T.; Grilli, S.T.; Subramanya, R. A Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq Model for Surface Waves. Part 1. Highly Nonlinear Unsteady Waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 294, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Fully Nonlinear Boussinesq-Type Equations for Waves and Currents over Porous Beds. J. Eng. Mech. 2006, 132, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, R.; Chen, Q.; Bak, A.S.; Shi, F.; Brandt, S.R. Effects of Wave Coherence on Longshore Variability of Nearshore Wave Processes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouws, E.; Günther, H.; Rosenthal, W.; Vincent, C.L. Similarity of the Wind Wave Spectrum in Finite Depth Water: 1. Spectral Form. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1985, 90, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.R.; Evans, C. Parabolic Bay Shapes and Applications. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1989, 87, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanda, S.H.; Perez, S.; Feddersen, F. Evaluation of a Source-Function Wavemaker for Generating Random Directionally Spread Waves in the Sea-Swell Band. Coast. Eng. 2016, 114, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J.; Lam, M.-A.Y.-H.; Malej, M. Practical Guidance for Numerical Modeling in FUNWAVE-TVD; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Hanover, NH, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tonelli, M.; Petti, M. Hybrid Finite Volume–Finite Difference Scheme for 2DH Improved Boussinesq Equations. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.B.; Chen, Q.; Kirby, J.T.; Dalrymple, R.A. Boussinesq Modeling of Wave Transformation, Breaking, and Runup. I: 1D. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2000, 126, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Brander, R.W.; Turner, I.L.; Power, H.E.; Mortlock, T.R. Lagrangian Observations of Circulation on an Embayed Beach with Headland Rip Currents. Mar. Geol. 2014, 355, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B.; Clark, D.B.; Moulton, M. Extremely Low Frequency (0.1 to 1.0 mHz) Surf Zone Currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, S.; Dooley, C.; Gorrell, L.; Raubenheimer, B. Observations of Two-Dimensional Turbulence in the Surfzone. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 085142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floc’h, F.; Mabiala, G.R.; Almar, R.; Castelle, B.; Hall, N.; Du Penhoat, Y.; Scott, T.; Delacourt, C. Flash Rip Statistics from Video Images. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 81, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hally-Rosendahl, K.; Feddersen, F.; Clark, D.B.; Guza, R.T. Surfzone to Inner-shelf Exchange Estimated from Dye Tracer Balances. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 6289–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, C.H. Lifeguarding Operational Camera Kiosk System (LOCKS) for Flash Rip Warning: Development and Application. Coast. Eng. 2019, 152, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.H.; Stewart, D.; De Silva, A.; Palinkas, A.; Dusek, G.; Davis, J.; Pang, A. RipScout: Realtime ML-Assisted Rip Current Detection and Automated Data Collection Using UAVs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 7742–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushine, J.B. A Study of Rip Current Drownings and Related Weather Factors. Natl. Weather Dig. 1991, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, J.; MacMahan, J.; Thieke, R.J.; Hanes, D.M.; Dean, R.G. Formulation of a Rip Current Predictive Index Using Rescue Data. In Proceedings of the 2002 National Conference on Beach Preservation Technology, Biloxi, MS, USA, 23–25 January 2002; Florida Shore & Beach Preservation Association: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lascody, R.L. East Central Florida Rip Current Program. Natl. Weather Dig. 1998, 22, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, M. Evaluation of the Modified ECFL LURCS Rip Current Forecasting Scale and Conditions of Selected Rip Current Events in Florida. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, G.; Purcell, H.; Guenther, D.; Meadows, L.; Kinnunen, R.; Clark, G. Rip Currents in the Great Lakes: An Unfortunate Truth. In Rip Currents: Beach Safety, Physical Oceanography, and Wave Modeling; CRC Press International: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 199–214. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Kirby, J.T.; Yoon, S.B. Boussinesq Modeling of Longshore Currents in the SandyDuck Experiment under Directional Random Wave Conditions. Coast. Eng. 2015, 101, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Brander, R.W.; Turner, I.L.; Leeuwen, B.V. Shoreface Storm Morphodynamics and Mega-Rip Evolution at an Embayed Beach: Bondi Beach, NSW, Australia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 116, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.F.; Raubenheimer, B.; Elgar, S. The Roles of Bathymetry and Waves in Rip-Channel Dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2024, 129, e2023JF007389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddersen, F.; Clark, D.B.; Guza, R.T. Modeling Surf Zone Tracer Plumes: 1. Waves, Mean Currents, and Low-frequency Eddies. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, 2011JC007210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
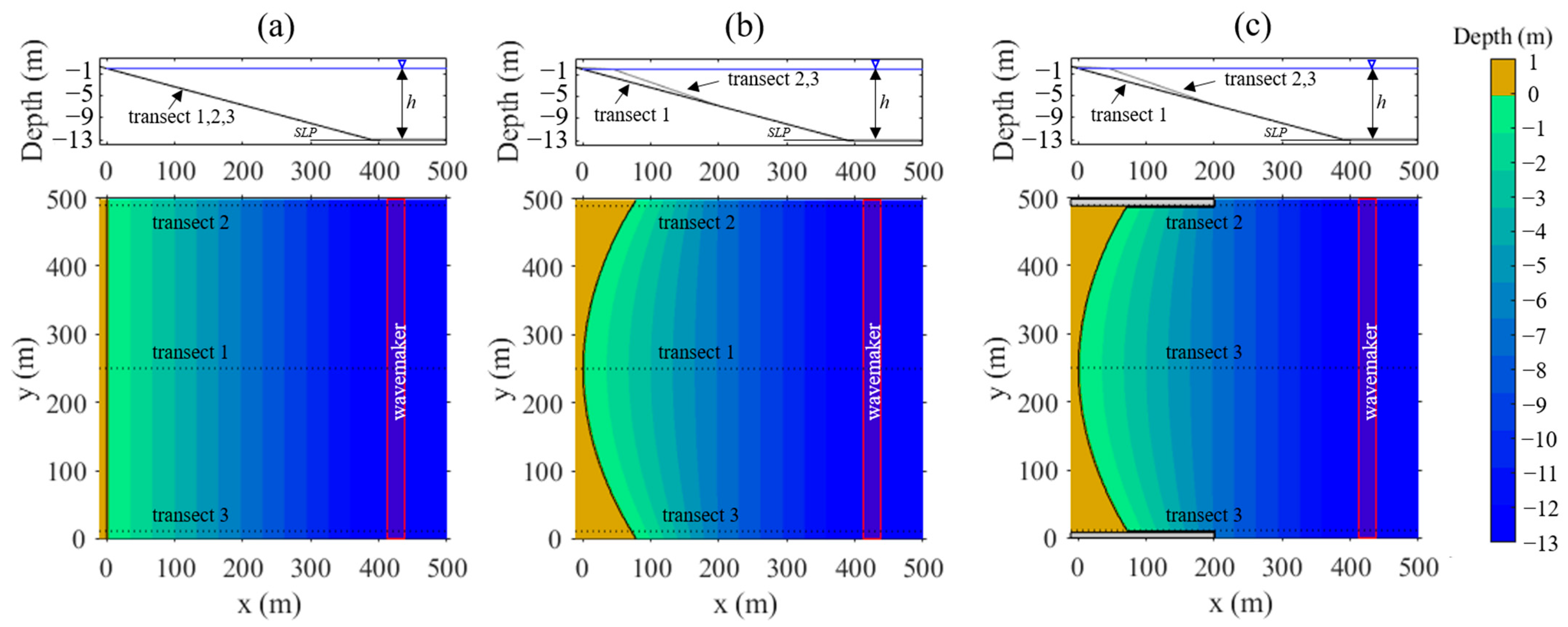
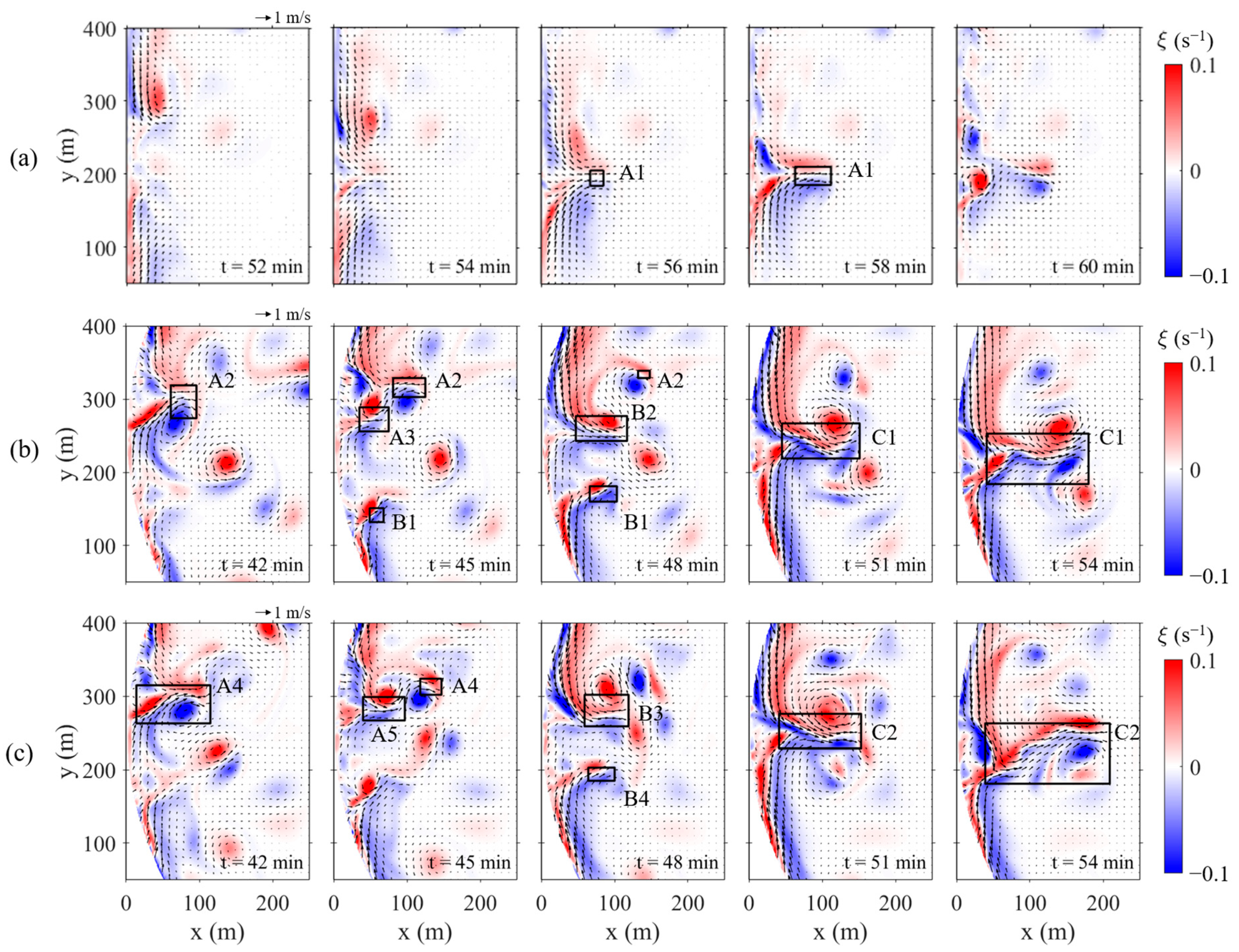
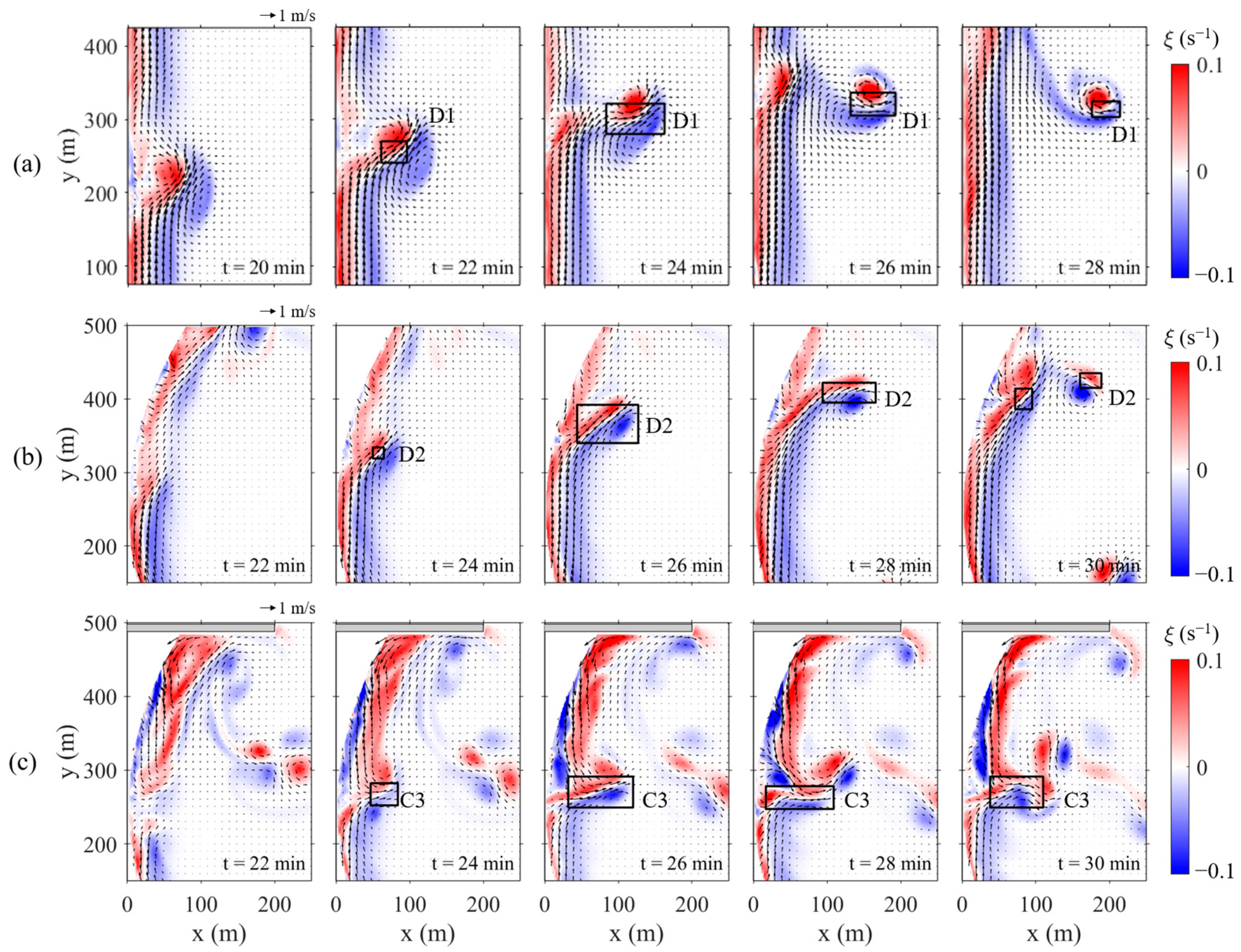

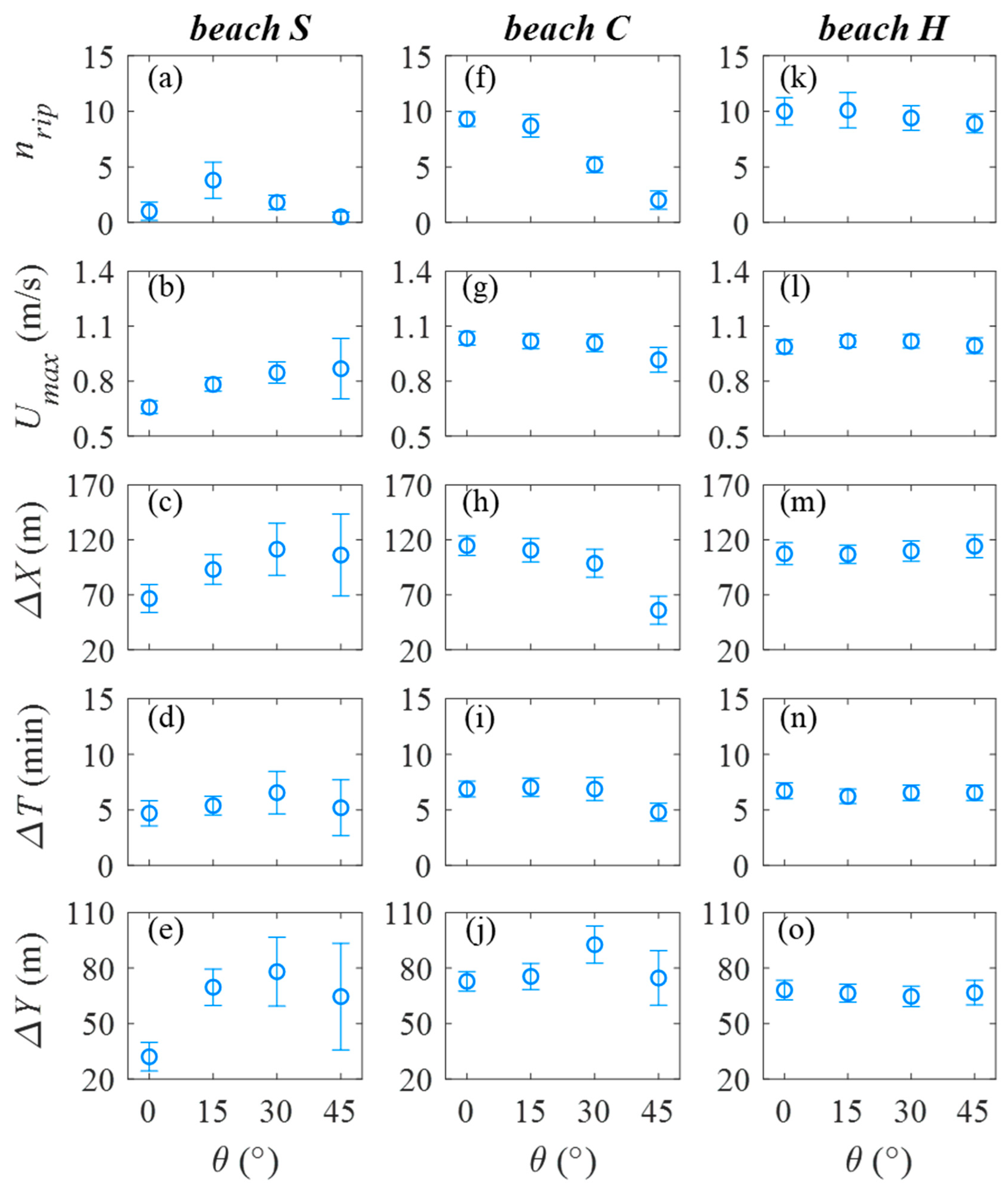
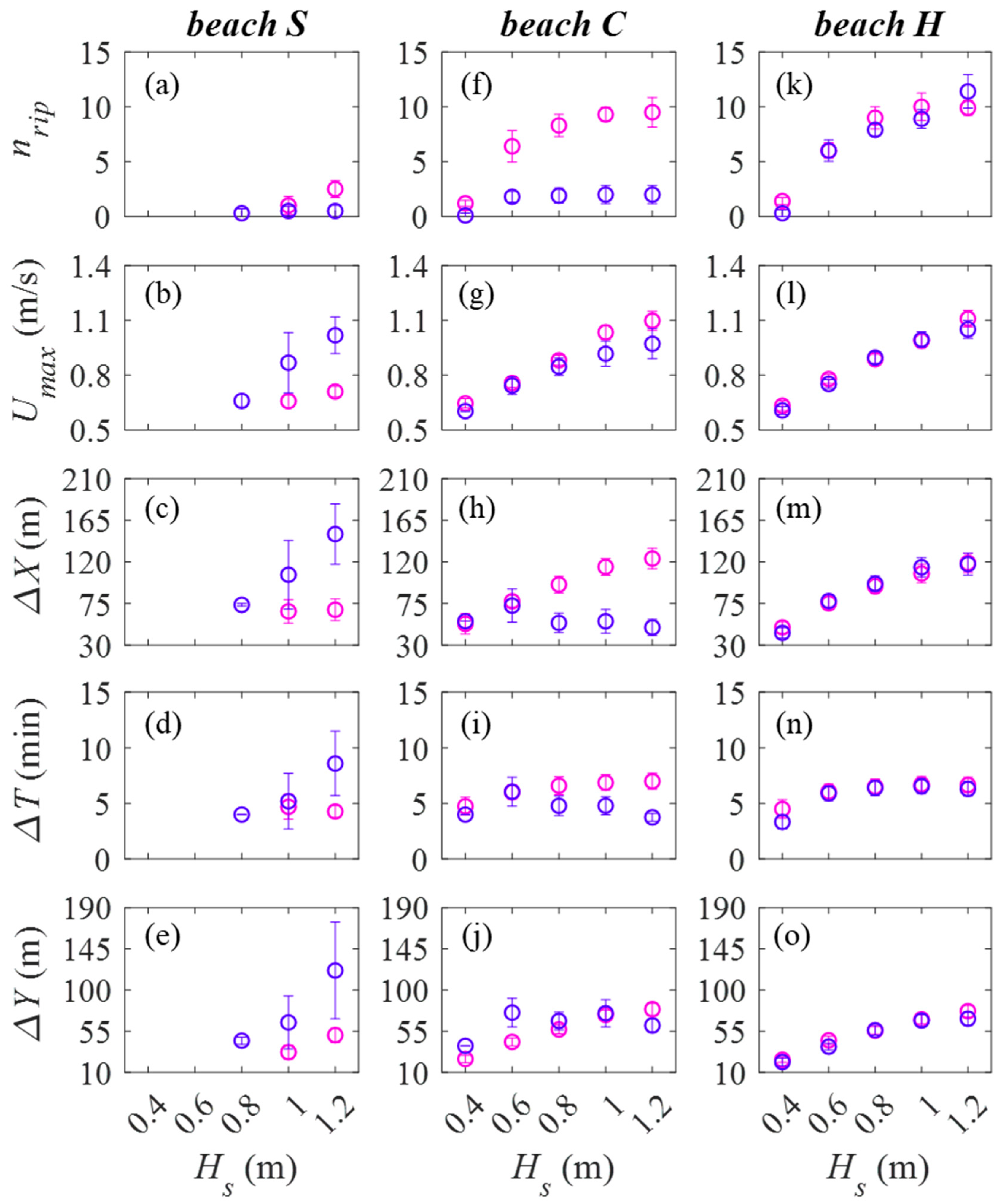
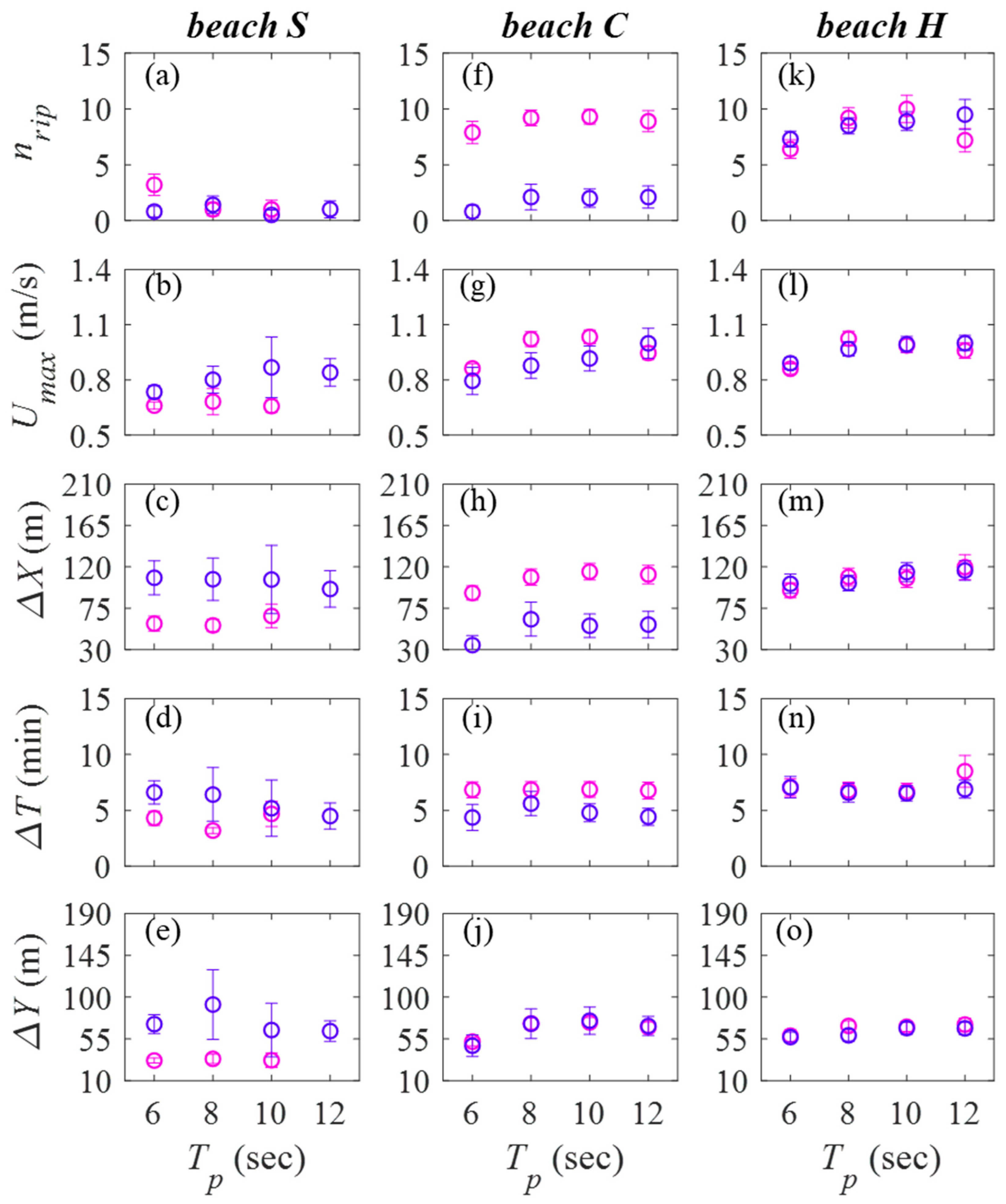
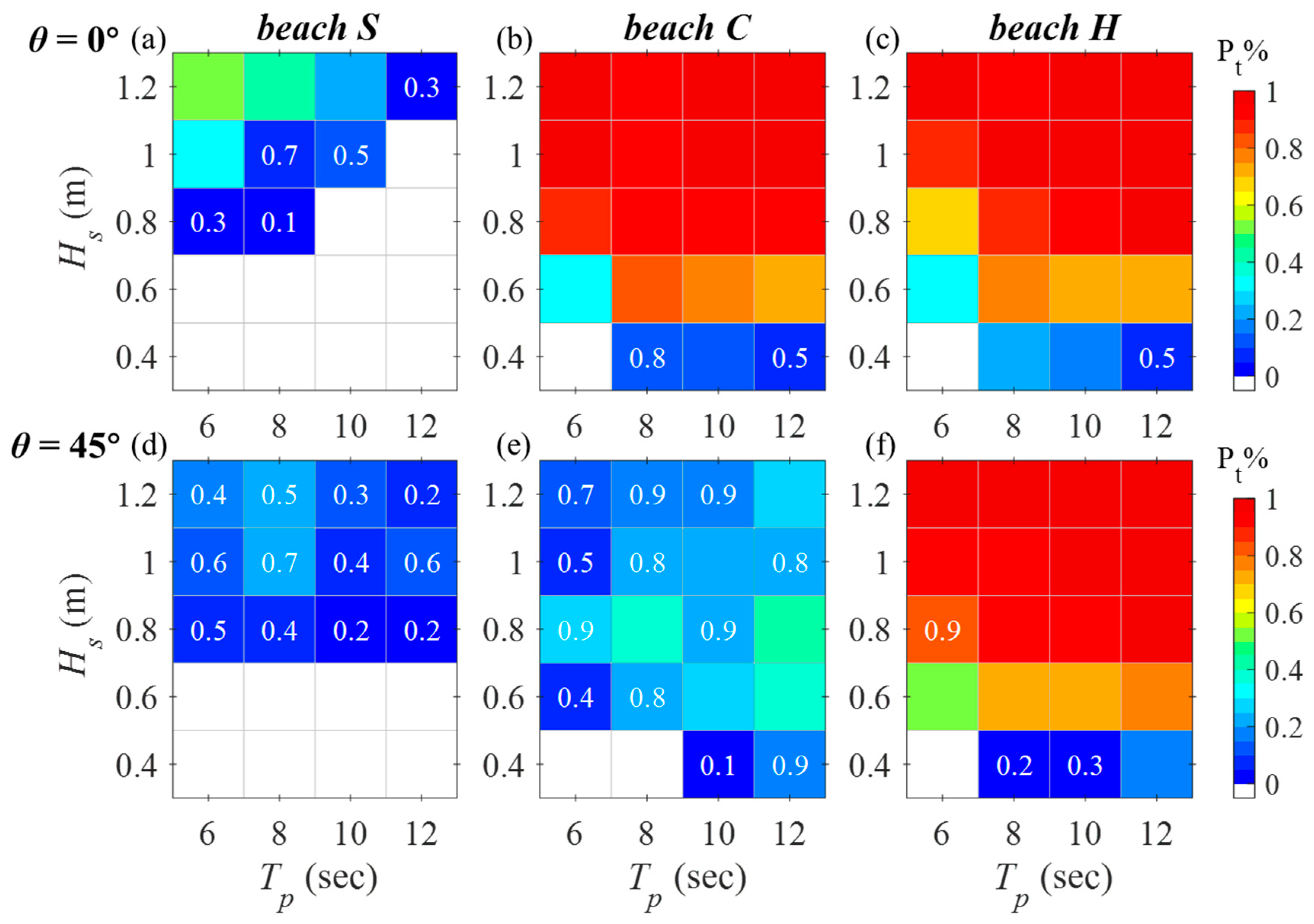

| Exp | θ (°) | Hs (m) | Tp (s) | SLP | h (m) | λ (m) | a/h | kh | Ur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 45 | 1.0 | 10 | 0.015 0.02 0.03 0.05 | 6 8 13 20 | 74 84 103 121 | 0.059 0.044 0.027 0.018 | 0.77 0.89 1.16 1.48 | 0.099 0.055 0.020 0.008 |
| 2 | 0 15 30 45 | 1.0 | 10 | 0.03 | 13 | 103 | 0.027 | 1.16 | 0.02 |
| 3 | 0 45 | 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 | 10 | 0.03 | 13 | 103 | 0.011 0.016 0.022 0.027 0.033 | 1.16 | 0.008 0.012 0.016 0.020 0.024 |
| 4 | 0 45 | 1.0 | 6 8 10 12 | 0.03 | 13 | 52 78 103 127 | 0.027 | 2.13 1.47 1.16 0.96 | 0.006 0.012 0.020 0.030 |
| 5 | 0 45 | 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 | 6 8 10 12 | 0.03 | 13 | 52–127 | 0.011–0.033 | 0.96–2.13 | 0.002–0.036 |
| θ | σθ | γTMA | Beach S | Beach C | Beach H | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prip | Pt | Prip | Pt | Prip | Pt | |||
| 0° | 2° | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.98 | 1 | 0.99 |
| 0° | 10° | 5 | 0.5 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.97 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 0° | 10° | 20 | 1 | 0.31 | 1 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.95 |
| 45° | 2° | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 45° | 10° | 5 | 0.4 | 0.07 | 1 | 0.24 | 1 | 0.96 |
| 45° | 10° | 20 | 0.9 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.49 | 1 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Li, X.; Yang, F. Assessing Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches Using Boussinesq Modeling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061139
Liu Y, Dong C, Li X, Yang F. Assessing Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches Using Boussinesq Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuli, Changming Dong, Xiang Li, and Fan Yang. 2025. "Assessing Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches Using Boussinesq Modeling" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061139
APA StyleLiu, Y., Dong, C., Li, X., & Yang, F. (2025). Assessing Rip Current Occurrences at Featureless Beaches Using Boussinesq Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061139





