Sand Distribution Controlled by Paleogeomorphology in Marine–Continental Rift Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
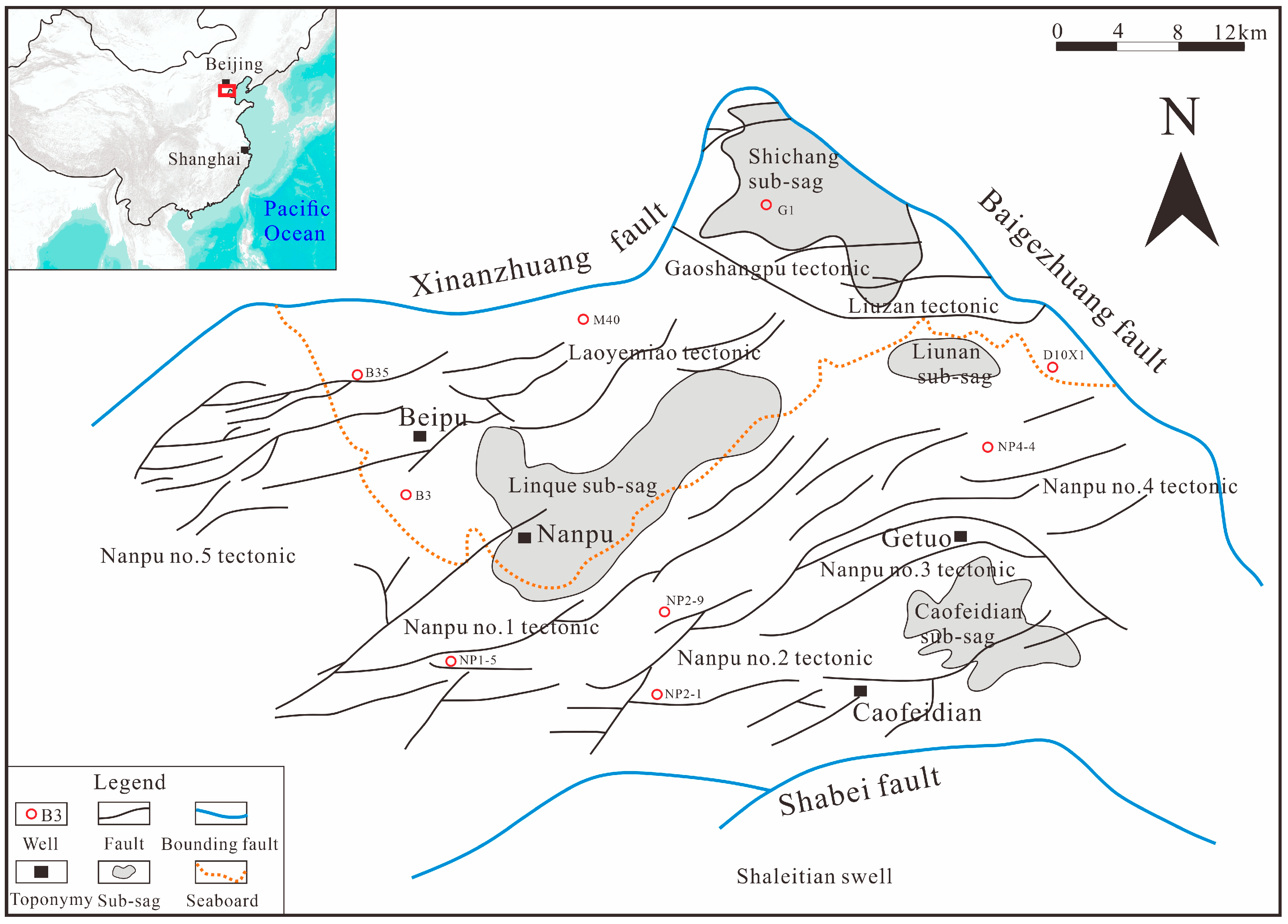
2. Regional Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geological Fieldwork and Indoor Testing
3.2. Stratigraphy and Sedimentary Phase Analysis
3.3. Paleomorphic Restoration
4. Results and Interpretations
4.1. Characterization of the Valley at Basin Margin
4.1.1. Faulted Trough
4.1.2. Fault Accommodation Zone
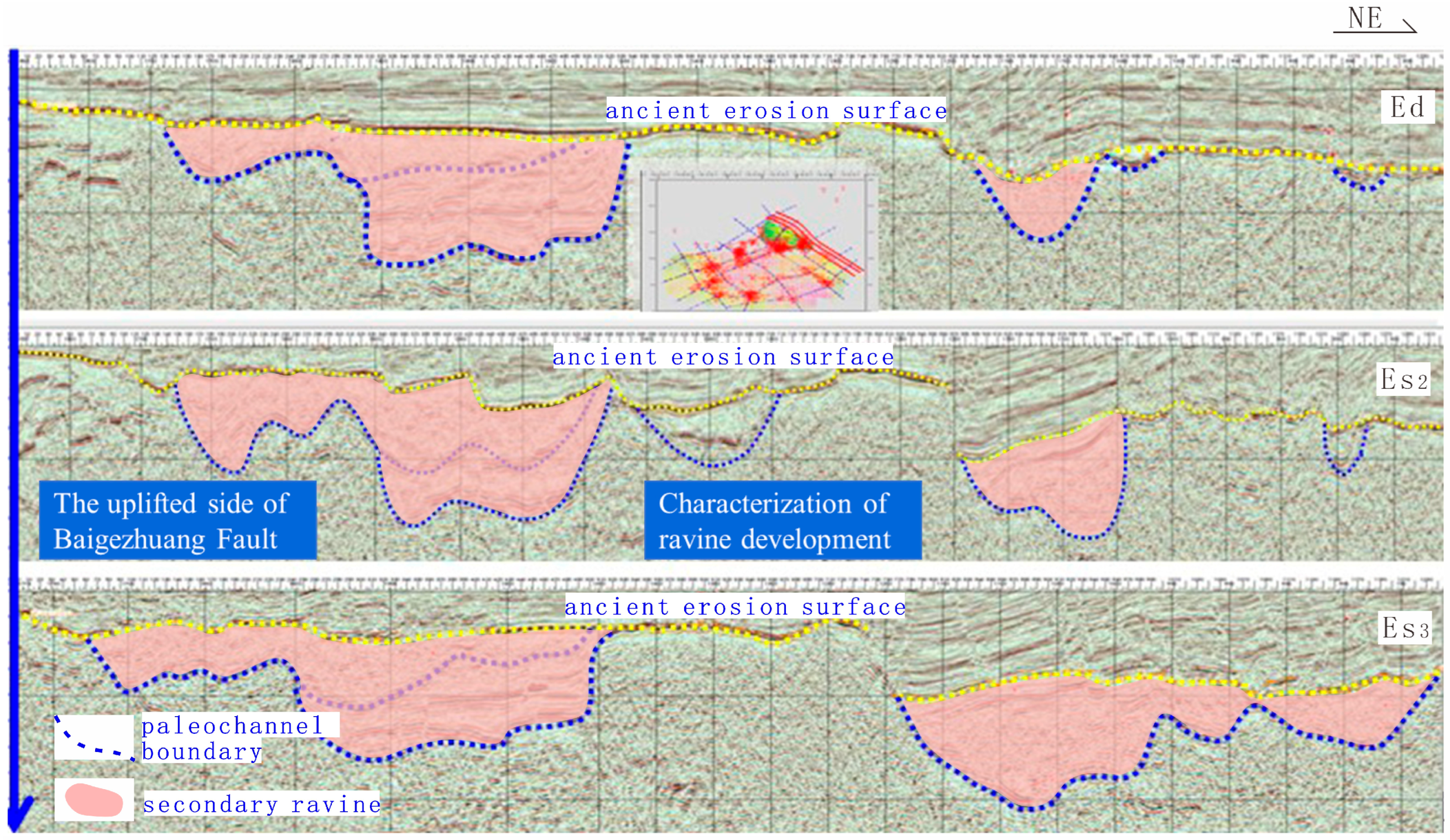
4.1.3. Incised Valley
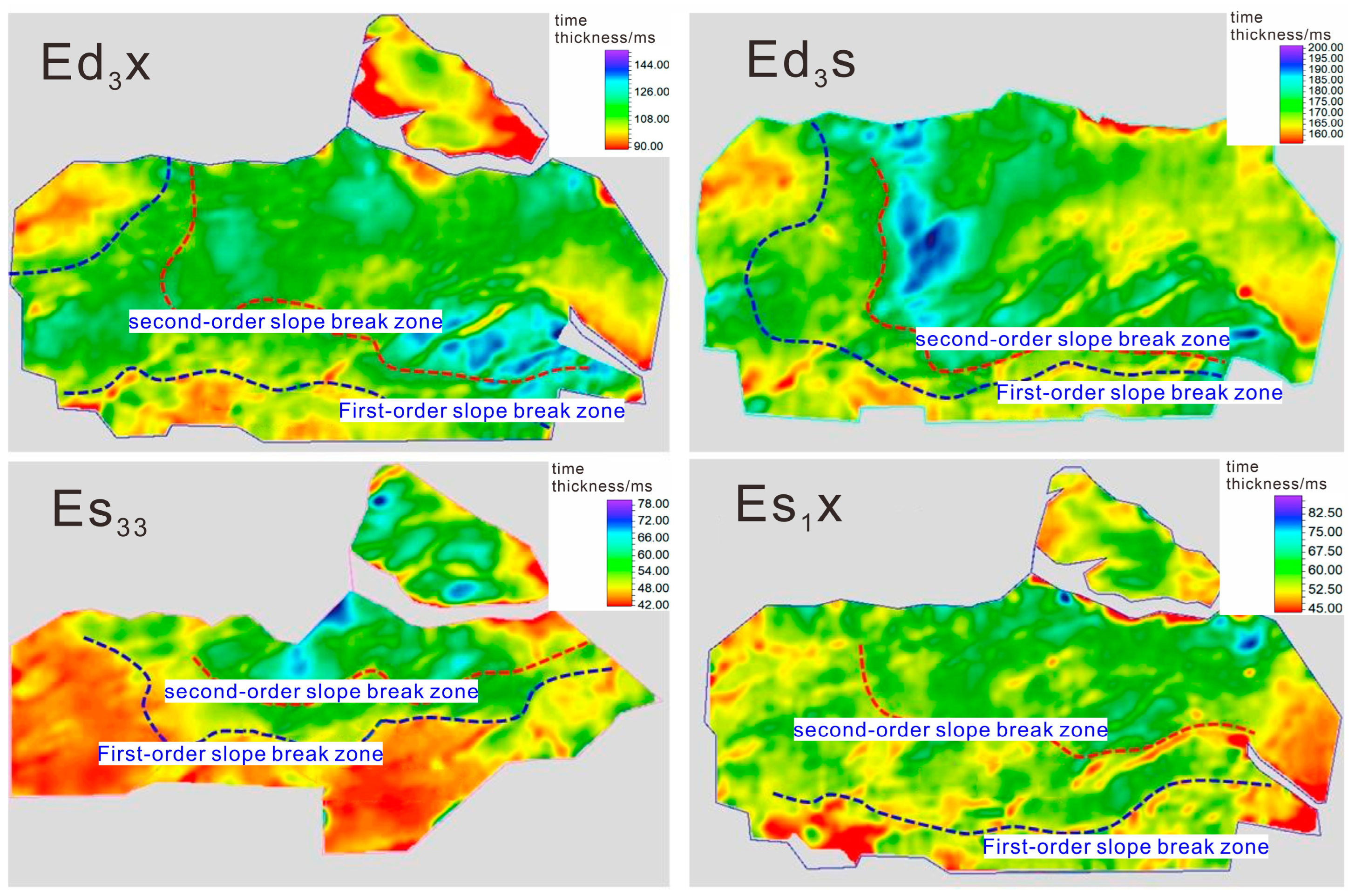
4.2. Characterization of the Slope Break Zone
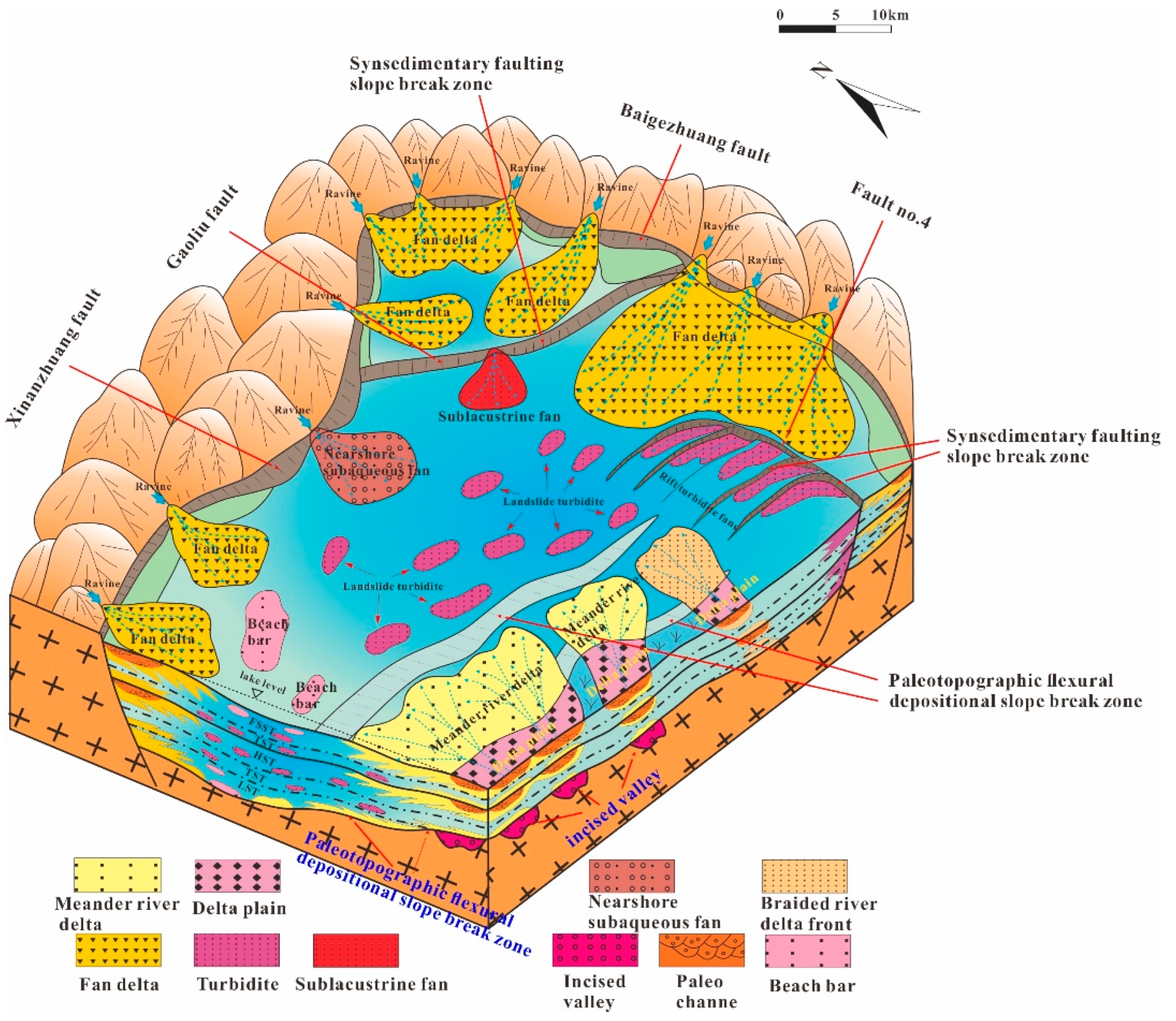
4.3. Sand Distribution Controlled by Valley–Slope Break Zone
4.3.1. Rifting Period I (Es3 Period)
4.3.2. Rifting Period II (Es2-Es1 Period)
4.3.3. Rifting Period III (Ed Period)
5. Discussion
5.1. Sand Architecture and Hydrocarbon Enrichment
5.2. Fan Deltas and Hydrocarbon Enrichment
5.3. Gravity Flow Deposits and Hydrocarbon Enrichment
- Slope failure triggered by syndepositional tectonic oversteepening;
- Hyperpycnal flows associated with seasonal flooding events [67].
6. Conclusions
- The correspondence between the development of the Paleocene sand and paleogeomorphology in the Nanpu sag shows that the faulted trough can be categorized into three basic types: faulted trough, faulted regulating zone, and incised valley, according to the cause of the water carrying sediments into the lake. Marine–continental rift basins predominantly develop syn-sedimentary fracture tectonic and paleo-topographic flexural depositional slope break zones, with sand thickness markedly increasing beneath these zones.
- In marine–continental rift basins, tectonic activity, material source supply, and climatic fluctuations during distinct rifting periods drive variability in the valley–slope break zone’s control over sand development. In areas with favorable valley–slope break zone configurations, the foot and adjacent regions of these zones often serve as prime sites for diverse sand development, extending basinward under hydrodynamic influences.
- The study on sand distribution controlled by valley–slope break zones in the Nanpu sag demonstrates that braided river deltas and fan deltas near slope breaks (like Gaoshangpu and Liuzan oilfields) develop large-scale, high-continuity reservoirs, while gravity flow deposits in deep lacustrine environments, though spatially limited, form effective lithologic traps due to stratigraphic isolation. Temporal variations in tectonic activity and sediment supply—coarse-grained fan deltas dominating during the early rifting phase (Es3) and transitioning to finer-grained, smaller-scale deposits in later stages (Ed)—further define sand heterogeneity. This research elucidates the geomorphic–tectonic coupling mechanisms governing sand architecture, advances valley–slope break zone theory, and provides a practical framework for predicting lithologic traps, particularly in slope break–valley coupling regions and deep-water gravity flow systems. These findings offer both theoretical and operational insights for hydrocarbon exploration in analogous continental rift basins.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Fm | Formation |
References
- Lin, C.S.; Pan, Y.L.; Xiao, J.X. Structural slope-break zone: Key concept for stratigraphic sequence analysis and petroleum forecasting in fault subsidence basins. Earth Sci. 2000, 25, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.T.; Pan, Y.L.; Lu, Y.C. Key technology of prospecting and exploration of subtle traps in lacustrine fault basins: Sequence stratigraphic researches on the basis of high resolution seismic survey. Earth Sci. 2002, 27, 592–599. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.L.; Qiu, Y.G. Application of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy to exploration of Lower Tertiary subtle reservoirs in Jiyang Subbasin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2003, 24, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of slope breaks and their control on atectonic traps in downwarped lake basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2004, 25, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.L.; Pang, X.Q. Formation of Hidden Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Sag Basins; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.M.; Hou, G.W.; Feng, W.J. Fault distribution patterns and their control on sand bodies in Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2020, 41, 824–837. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.B.; Wang, G.W.; Wang, Q.M.; Yu, X.T.; Wang, X.Y. The source to sink systems and their exploration significance for the 1st and 2nd members of the Palaeogene Shahejie Formation in the middle part of the Bonan low uplift. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2019, 39, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhou, X.H.; Ding, F.; Yuan, J.; Shen, S.; Lv, P. “Multi–factor control of sandboies distribution” in the Pinghu Formation, Pingbei region of Baochu slop, the Xihu Sag. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2019, 39, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, C.H.; Xiang, K. Structural-paleogeomorphologic features of Chepaizi Area and mechanism of their control on sandbodies. Oil Gas Geol. 2008, 29, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.B.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Man, Y. Sand distribution mechanism of Liushagang Formation in eastern Wushi Area. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2017, 24, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.L.; Xu, C.G. New geological understandings and major hydrocarbon discoveries in the complex fault zone of Bohai Sea. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 37, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.Q.; Li, H.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, L.; Sun, X.J. Application of the Source-Sink Time-Space Coupling Sandbody-Controlling Principle in the Study of Sedimentary System: A Case Study of the Ed_3 Formation in Qinhuangdao A Area, Bohai. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 38, 580–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, S.C.; Feng, J.W.; Lan, Z.Q.; Zhang, B.M. Characteristics of fault activities and the controlling on sand bodies during Es_1 period in Nanpu No.3 unit. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2016, 40, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Fan, T.E.; Hu, G.Y.; Niu, T.; Wang, G.D. Characteristics of Fault Accommodation Structure Slope Break Zone and the Sand Control Pattern in a Oilfield. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. 2015, 37, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C. Controlling sand principle of source-sink coupling in time and space in continental rift basins: Basic idea, conceptual systems and controlling sand models. China Offshore Oil Gas 2013, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.G.; Gao, Y.D.; Liu, J.; Peng, G.R.; Liu, P.; Xiong, W.L.; Song, P.L. Discovery and inspiration of large- and medium-sized glutenite-rich oil and gas fields in the eastern South China Sea: An example from Paleogene Enping Formation in Huizhou 26 subsag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Q.; Yang, X.B.; Fan, C.W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Li, M. Sandy Debris Flow Sedimentary Characteristics and Patterns in the Meishan Formation of Northern Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1549, 022009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Zhou, X.H.; Li, J.P.; Niu, C.M. Unconfined Flow Deposits in Front Sandbodies of Shallow Water Deltaic Distributary Systems. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2014, 32, 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.L. Control of valley and tectonic slope-break zone on sand bodies in rift-subsidence basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2006, 27, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, B.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhou, T.Q. Distribution and controlling factors of glutinite bodies in the actic region of a rift basin: An example from Chezhen sag Bohai bay basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2007, 34, 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.W.; Guo, J.Y.; Wang, R.J. Tectono-sequence stratigraphic analysis in continental faulted basins. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.S.; Liu, H.; Lin, H.M.; Qiu, X.W.; Wang, X.D.; Ju, Y.T.; Jue, X.M. Controlling effect of slope-break zone and paleovalley on sedimentation in rifted lake basins: A case study of the Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Haifeng 33 Subsag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.B.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Types of Structural Slope-break Zone and Its Controls on Sand Bodies and Hydrocarbon of Huhehu Depression in Hailar Basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2013, 31, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.; Jin, L.; Zhang, B. Characterization of Architecture Bounding Surfaces in Fluvial Tight Sandstone Reservoirs and Their Influence on Remaining Gas: A Case Study from the Suzhong Block, Sulige Gas Field. Energies 2024, 17, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.J.; Wang, G.M.; Wang, Q.B.; Zhang, X.F. The reservoir characteristics and their controlling factors of the sublacustrine fan in the Paleogene Dongying Formation, Bohai Sea, China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2024, 13, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Xu, Y.X.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.L. Sandy accumulation law and reservoir development characteristics in Nanpu Structure 1 and Structure 2. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 53, 329–334+20. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Q.Q.; Fu, J.H.; Luo, S.S.; Li, S.X.; Zhou, X.P. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flow channel-lobe complex in a depression lake basin: A case study of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in southwestern Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Qi, Y.K.; Wang, H.Z.; Jin, Y.Y.; Huang, S.B.; Chang, W.X. Trap development patterns and exploration potential of Badaowan Formation in Baolangsumu structural belt-Sishilicheng slope belt in Yanqi Basin. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2023, 42, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Tan, J.; Wang, L.; Chang, W.Q.; Xu, J.Q. Characteristics and controlling factors of lacustrine source rocks in the Lower Cretaceous, Suhongtu Depression, Yin-E Basin, Northern China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 104, 943. [Google Scholar]
- Proverbs, I.P.; Bann, K.L.; Taylor, B. Depositional, stratigraphic and structural controls on the geometry of Montney Formation reservoirs: Lower Triassic, northeast British Columbia, northwest Alberta. Bull. Can. Energy Geosci. 2024, 71, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Characterization and Modernization of the Depositional System in Modern Ebinur Lake Basin, Northwest China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yu, X.H.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.M.; Hu, S.H.; Zhang, M.L. Control of slope-pattern on the deposition of fan-delta systems: A case study of the Upper Karamay Formation, Junggar Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 18, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; Yang, W.; Xie, W.R.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zeng, F.Y.; Mo, W.L.; Shen, J.H.; Jin, H. Formation conditions, accumulation models and exploration direction of large-scale gas fields in Sinian-Cambrian, Sichuan Basin, China. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Tan, L.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Li, H.N.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, H.T. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of beach-bar sandstones in the southern slope of the Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Sci. 2014, 11, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, T.; Wang, F.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.G.; Feng, C. Control of slope break zone on sandy debris flow deposition: A case study of Jurassic Sangonghe Formation in west sag of Well Pen-1 and its periphery in Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2020, 27, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wu, S.H.; Hu, G.Y.; Yue, D.L.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Yu, J.T.; Xiong, Q.C.; Wang, L.Q. Sedimentarye-tectonic interaction on the growth sequence architecture within the intraslope basins of deep-water Niger Delta Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2023, 12, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.A.; Wu, H.B.; Li, J.H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y. Type classification of the slope area in the continental faulted lake basin and the hydrocarbon enrichment characteristics: Taking Wuerxun-Beier Sag in Hailar Basin as an example. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2019, 38, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Yang, S.C.; Zhao, Y.F. Cretaceous paleogeomorphology and its control on the sedimentation in Chepaizi area of Junggar Basin. Pet. Geol. Oilfield Dev. Daqing 2019, 38, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.Y.; Jiang, T.; Pan, T.; Ou, Y.P. Control of Slope Breaks of Karagansky Formation on Sand Bodies in Baojingen Graben, Kazakhstan. Offshore Oil 2019, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J. Analysis of sand-controlling mechanism in valley-slope break system under low source supply mode: A case study of the Hutubi Formation of Cretaceous in the eastern wing of the Chepaizi Uplift. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2019, 43, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Raham, A.H.B.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Ismail, M.S.B.; Ahmed, N.; Usman, M.; Gul, Z.; Imran, Q.S. Facies Heterogeneity and Lobe Facies Multiscale Analysis of Deep-Marine Sand-Shale Complexity in the West Crocker Formation of Sabah Basin, NW Borneo. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z.L. Periodic rifting activity and its controlling on sedimentary filling of Paleogene period in Nanpu sag. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2009, 27, 976–982. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Lin, Z.L. Relations between synsedimentary tectonic activity and sedimentary framework of dongying formation in Nanpu sag. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2011, 33, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.F.; Xian, B.Z.; Li, Z.P. Different levels of rift activity and its impact on deposition in offshore area, Nanpu sag. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2013, 31, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.F.; Qu, X.J.; Yi, J. Characteristics of volcanic reservoirs and distribution rules of effective reservoirs in the Changling fault depression, Songliao Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2015, 2, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.J.; Liang, L.X.; Xiong, J.; Wu, J.J.; Li, B. Fracture characteristics of reservoirs with different lithologies in marine-continental transitional facies and its influence on fracturing. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2024, 31, 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.Z.; Wang, G.; Cao, W.; Su, Y.H.; Lu, L.L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.Y. Cenozoic Oil-gas Distribution and Tectonic Evolution of the Basins in the Northwest Pacific Continent-ocean Connection Zone. Geotecton. Metallogenia 2019, 43, 839–857. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.Q.; Ma, X.Y.; Hua, S.H.; Ma, X.; Wang, B.H.; Zhang, B.M.; Tian, W.; Jiang, S.; Hu, R.N. Influence of Sedimentary Environments on Organic Matter Enrichment in Marine-Continental Transitional Shale: A Case Study of the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in the Central Hunan Depression, China. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Norbert, K.; Jin, Y.; Li, C.Z.; Gong, L.X.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, X.D. Assessment of Shale Gas Potential of Marine-Continental Transitional Longtan Formation from Southwestern Guizhou Province, China. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Qin, L.Z.; Liu, Y.H. Differentiation and Coupling Model of Source-to-Sink Systems with Transitional Facies in Pingbei Slope of Xihu Sag. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 880–897. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Jing, A.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhao, M.H. Paleogene tectonic styles and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation in the shallow sea of the Jiyang Depression. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2018, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Mao, X.; Li, H.; Li, K.; Bao, Z. The Distribution Characteristics and Favorable Exploration Zones of Karst Reservoirs in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. In Proceedings of the 45th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford, CA, USA, 7–9 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, K.Y.; Yan, J.H.; Wang, Q.; Pu, X.G.; Yang, H.Y. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of shallow water delta systems of the Lower Permian Shanxi Formation in the Bohai Bay Basin region. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Yu, C.F.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, R.; Zhi, F.Q. Reservoir characteristics and geological implications of marine sandstone on the periphery of Awati Sag, Tarim Basin, China: Case study of Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Kepingtage Formation. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2025, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Feng, C.; Qu, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, M. Depositional pattern and source-to-sink process of submarine fans in Lingshui and Sanya formations, Baodao Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2024, 9, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.F.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, M.S.; Bu, S.F. Reservoir prediction of glutenite fan based on time-frequency analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 24–29 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Loon, V.; Xu, J.; Tian, L.X.; Du, X.F.; Zhang, X.T.; Chen, D.L. Relationships between tectonic activity and sedimentary source-to-sink system parameters in a lacustrine rift basin: A quantitative case study of the Huanghekou Depression (Bohai Bay Basin, E China). Basin Res. 2020, 32, 587–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, G. Study on Buried Channel Systems in the Western South Yellow Sea. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2013, 31, 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.Y.; Qiu, X.M.; Liu, Y.R. Prediction of Concealed Oil and Gas Reservoir Sand Bodies in Complex Continental Depression Basins: A Case Study of the Gaoyou Depression in North Jiangsu; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Z.; Yang, Z.J.; Ji, Y.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, S.W.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Z.L. Paleogene clastic reservoir which mainly controlled by the syndepositional faults in Shanghe Oilfield. Offshore Oil 2010, 30, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- You, D.H.; Qian, Y.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Cai, X.Y.; Li, H.L. Carbonate Dissolution of Lianglitage Formation in Southern Slope Break of Tazhong Area. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2010, 31, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, S.; Lin, C.M.; Yang, Z.S. Characteristics of the Slope Break Belt and Its Control on the Depositional Sequence: The Quantou Formation of the Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin. Geol. J. China Univ. 2018, 24, 425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, B.; Song, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kong, Y.H.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, T. A seismic quantitative identification method of slope break belt. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Yang, C.Q.; Zou, M.S.; Qi, Z.; Fang, X.Y. Control of tectonic slope-break zones in the first member of Liushagang Formation of Weixinan Sag on sequence and sedimentary systems. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 49–57+58–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. Research on the Role of the Basin-marginal Sequence Architectural Model in Controlling the Development of Sand-bodies and Traps—A Case Study of the Jurassic System in Hashan Area. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, T.S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.L.; Gao, L.B.; Zhang, J.X. The Sedimentary Record of Marine–Continental Transitional Shales in the Upper Triassic of Xujiahe Formation, Southeast Sichuan Basin, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Umar, M.; Usman, M.; Ahmed, N.; Raham, A.H.B.A.; Zaidi, F.K. Aseismic and seismic impact on development of soft-sediment deformation structures in deep-marine sand-shaly Crocker fan in Sabah, NW Borneo. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Usman, M.; Wahid, A.; Umar, M.; Ahmed, N.; Haq, I.U.; EI-Ghali, M.A.K.; Imran, Q.S.; Rahman, A.H.A. Facies analysis and distribution of Late Palaeogene deep-water massive sandstones in submarine-fan lobes, NW Borneo. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 4489–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, B.; Su, P.; Wang, S. Sand Distribution Controlled by Paleogeomorphology in Marine–Continental Rift Basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061077
Geng B, Su P, Wang S. Sand Distribution Controlled by Paleogeomorphology in Marine–Continental Rift Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061077
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Bochuan, Peidong Su, and Shilin Wang. 2025. "Sand Distribution Controlled by Paleogeomorphology in Marine–Continental Rift Basin" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061077
APA StyleGeng, B., Su, P., & Wang, S. (2025). Sand Distribution Controlled by Paleogeomorphology in Marine–Continental Rift Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061077




