Abstract
Langmuir turbulence is widely recognized for enhancing upper-ocean mixing and altering current dynamics; however, its influence on surface wave characteristics remains insufficiently understood. Due to the difficulty in resolving Langmuir turbulence in ocean models, its effect is usually parameterized. In this study, we implement a Langmuir turbulence parameterization into a coupled wave–circulation model and use it to investigate the effects of Langmuir turbulence on the evolution of surface waves under upwelling-favorable wind conditions over an idealized continental shelf. The results indicate that Langmuir turbulence significantly modifies the spatial distribution and gradients of wave height, primarily through the modulation of current-induced wave refraction. Specifically, Langmuir turbulence suppresses coastal currents and associated vorticity, thereby weakening the impact of current-induced wave refraction. This leads to diminished alongshore wavenumber gradients and weakens the focusing of wave energy, which, in turn, reduces alongshore wave height gradients. Furthermore, this attenuation of wave height gradients by Langmuir turbulence remains robust across different wave–wind misalignment angles. These findings provide evidence of Langmuir turbulence’s role in wave energy redistribution and underscore the importance of incorporating its dynamics into coupled wave–current modeling frameworks.
1. Introduction
Surface waves play a crucial role in upper-ocean mixing, turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) generation, and air-sea interactions, which are essential for understanding ocean circulation, heat exchange, and climate dynamics [1,2,3]. In addition, surface waves have a great impact on coastal environments, including beach erosion, pollutant transport, and coastal flooding [4]. Understanding the evolution and propagation of surface waves is essential for addressing challenges related to coastal protection, maritime safety, and climate modeling, with implications for both local and global communities [5,6].
Surface waves can be significantly influenced by currents via wave–current interactions, which alter their amplitude, period, and direction due to processes such as refraction, Doppler shifting, and energy transfer [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Recent studies have demonstrated that ocean currents can modulate the spatial distribution of significant wave height (Hs). For example, Ardhuin et al. [7] utilized satellite altimetry data combined with realistic numerical models to reveal that the modulation of the wave field by ocean currents is substantial across spatial scales ranging from tens to hundreds of kilometers. They notably found that Hs can vary by more than 50% over distances in the order of tens of kilometers. Similarly, Villas Bôas et al. [12] used idealized numerical simulations to show that Hs is highly sensitive to the underlying currents, with wave refraction playing a dominant role. Furthermore, Sun et al. [6] combined satellite observations and numerical modeling to determine that background currents dominate spatial gradients in Hs during tropical cyclone events.
Beyond wave height, currents significantly influence other aspects of wave dynamics. Quilfen et al. [10], using satellite altimetry and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) observations, demonstrated that strong currents can substantially modulate wave properties, including altering wave propagation direction, wavelength, and energy distribution. In the Agulhas Current region, they showed that current-induced refraction leads to wave focusing, directional spreading, and localized spectral shifts, underscoring the critical role of currents in reshaping swell characteristics at mesoscales. The result of Romero et al. [13] from airborne field observations showed that significant variability of the wave field is modulated by currents, particularly for the wave breaking statistics, including directional spreading variations of ±4° and changes in the whitecap coverage by ±50° or more. Additionally, Wang et al. [14] pointed out that ocean currents can significantly affect wave period, and that surface waves respond remarkably differently to summer and winter in the Kuroshio region.
Despite significant progress in understanding current effects on waves (CEW), there are still some aspects that are not well understood, such as Langmuir turbulence (LT). Typically, LT consists of counter-rotating vortices generated by wave–current interactions, with their axes of rotation aligned approximately parallel to the wind direction [15,16,17].
LT plays a vital role in enhancing vertical mixing within the upper ocean mixed layer. This enhanced mixing substantially influences the distribution of temperature, salinity, dissolved gases [18,19,20], and TKE [21,22]. This effect is particularly pronounced in shallow water [23,24,25]. In addition to enhancing vertical mixing, LT can accumulate floating material, such as oil slicks, seaweeds, and foam, forming narrow surface bands and reducing lateral dispersion [17,26]. These findings indicate that LT-induced processes fundamentally reshape the vertical and horizontal transport mechanisms within the upper ocean, highlighting their crucial role in modulating both subsurface stratification and convergence of surface materials.
Recent studies further highlight that LT plays an important role in modulating upper ocean circulation and thermohaline structure under various oceanic conditions, with its influence becoming particularly significant during periods of energetic wind and wave forcing, such as hurricanes. Both observational data and numerical modeling indicate that LT can markedly reduce surface current magnitudes, with reductions reaching up to 0.8 m/s, through the efficient downward transport of horizontal momentum. This process concurrently enhances subsurface currents and contributes to the deepening of the mixed layer [27,28]. Consequently, LT has the potential to influence surface waves indirectly by altering wave–current interactions, which, in turn, affect wave dynamics.
The spatial scale of LT typically ranges from tens to hundreds of meters [15,17]. However, due to computational limitations, LT is not explicitly resolved by existing ocean and climate models; instead, its mixing effects are usually parameterized [29]. For instance, Ali et al. [30] compared different LT parameterization schemes in a realistic ocean circulation model and found that LT has a greater impact on the mixed layer depth (MLD), sea surface temperature (SST), and ocean heat content than other wave effects, such as Coriolis–Stokes forcing, Stokes drift tracer advection and wave-dependent stress.
In this study, we incorporate the LT parameterization into a coupled wave–circulation modeling framework to systematically examine its effects on the evolution of surface waves over an idealized continental shelf. The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 provides a detailed description of the model configuration and the derivation of the CEW formulations. Section 3 presents the numerical results, followed by a discussion in Section 4. Finally, the main conclusions are summarized in Section 5.
2. Methods
2.1. Model Configuration
Numerical experiments were performed using a coupled wave circulation model, which is the Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) coupled with a spectrum-peak WKB wave-refraction model that includes CEW [31,32]. The wave model solves equations of wave action conservation and wave refraction, which are essential for accurately representing wave energy propagation and directional changes arising from currents and bathymetry. This coupled modeling framework has been widely applied in studies of wave–current interactions, including rip currents [31,33], wave-induced streaming [34,35], and coastal upwelling/downwelling processes [36,37].
The model domain is an idealized continental shelf with a slope of 0.005, chosen to simplify the analysis of wave–current interactions while retaining the key physical processes. The domain is 64 km long in the cross-shelf (shore-normal) direction and 32 km wide in the along-shelf (shore-parallel) direction (Figure 1), with 1 km horizontal grid spacing and 32 stretched vertical s-layers. Boundary conditions are configured as periodic along the northern and southern margins, while the eastern and western boundaries are enforced with zero Lagrangian transport to ensure mass conservation. Here, the Lagrangian transport is defined as the depth integral of Lagrangian velocity uL (i.e., uL = u + us with Eulerian velocity u plus Stokes drift us). The Coriolis parameter f is set to 7.29 × 10−5 s−1 for a midlatitude. The Eulerian velocity components u, v, and w correspond to cross-shelf (X), along-shelf (Y), and vertical (Z) directions, respectively. The eddy components (denoted by primes: u′, v′, and w′) are defined as deviations from the alongshore average; for example, u′ = u − <u>, where the angle brackets denote an alongshore average.
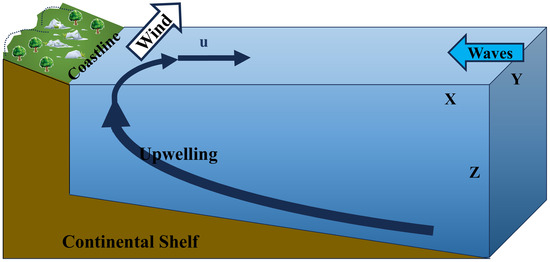
Figure 1.
Schematic of the numerical experiment setup. An along-shelf southerly wind drives coastal upwelling, and swells propagate shoreward from the eastern boundary.
In this study, we employ the K-profile parameterization (KPP) scheme [38] for vertical mixing. To account for the effects of LT, the KPP scheme has been extended, leading to the development of a KPPLT scheme. A key parameter in KPPLT is the turbulent Langmuir number (La), as defined by McWilliams et al. [16], where La = represents the ratio of friction velocity () to the surface Stokes drift (). For monochromatic waves, the Stokes drift is given as follows [39]:
where us is the Stokes drift vector. A is the wave amplitude, σ is the intrinsic frequency, k is the wavenumber vector, k is its magnitude, h is the resting water depth, and D is the wave-averaged total depth.
Following the McWilliams and Sullivan [19] formalism, the KPPLT scheme enhances turbulent velocity through a Langmuir enhancement factor (ε) that exhibits functional dependence on La. Recently, Wang et al. [40] proposed an enhancement factor as follows:
where the La−2/3 relationship aligns with the scaling of vertical turbulent kinetic energy associated with Langmuir turbulence [41]. Moreover, θ ranging from [−180°, 180°] quantifies the wave–wind misalignment angle. This angle captures the Langmuir turbulence suppression mechanism under misaligned wind–wave forcing [42,43]. A small Langmuir number La with aligned winds and waves (θ = 0°) yields a large enhancement factor and thereby strong vertical mixing. The spatial distribution of La under θ = 90°, as presented in Figure 2, illustrates its response under cross-aligned wind–wave conditions.

Figure 2.
Snapshot of the alongshore-averaged turbulent Langmuir number and enhancement factor on Day 3 for a wind–wave misalignment angle of θ = 90°.
Initially, the water temperature is horizontally uniform and decreases with depth. An alongshore wind stress of 0.05 N/m2 is applied to induce coastal upwelling. Surface waves are prescribed at the offshore (eastern) boundary and propagate shoreward, rather than being generated in the wave model. These incident waves represent swells originating in the open ocean and constantly propagate from the boundary toward the shore. The evolutions of these incident waves are governed by the wave model, which is detailed in Section 2.2 below. At the offshore boundary, the mean wave height is set to 3 m, and the period is 7 s. The incident angle (wave direction) is 180°, measured with respect to the shore normal, meaning the waves propagate perpendicular to the coastline.
In addition, we perform a comparison experiment in which LT is excluded. This comparison allows us to better understand how LT modulates surface waves.
2.2. Wave Equations with CEW
The wave model incorporated in our coupled wave circulation framework solves the equations of wave action conservation and wave refraction for a monochromatic wave field [32]:
where the symbol denotes the horizontal differential operator, is the wave action defined by , is the intrinsic frequency, E is the depth-integrated wave energy given by , is the reference density, is the gravitational acceleration, is the depth-averaged current in shallow water or an upper-ocean average over a depth ∝ k−1 in deep water, is the intrinsic wave group velocity, is the wavenumber vector, k is its magnitude, D is the water depth, and is the depth-integrated rate of wave energy dissipation (e.g., wave breaking and friction). The tilde convention identifies conjoined horizontal vectors in a dot product.
In what follows, we focus on the alongshore gradients () of wave action and wavenumber. Based on Equations (3) and (4), the governing equations incorporating CEW can be derived as follows:
In Equation (5), the left-hand side (LHS) term represents the tendency of wave action, which is related to wave height. On the right-hand side (RHS), the first and second terms are associated with the current divergence FDivcur and current advection FAdvcur, respectively; the third and fourth terms are linked with wave group velocity divergence FDivCg and its advection FAdvCg, respectively; the last is the term associated with wave dissipation.
In Equation (6), the LHS term represents the tendency of wavenumber; the first and second terms (F1 and F2) on the RHS represent advection by background currents and wave group velocity, respectively; the third and fourth terms (F3 and F4) represent wave refraction induced by current gradients and water depth variations.
3. Results
3.1. Impact of LT on Upwelling Frontal Instability
Under the persistent alongshore wind forcing, an offshore-directed surface current emerges as a result of Ekman transport (Figure 3a). This offshore flow induces the ascent of deep, cold waters onto the continental shelf, resulting in the formation of a pronounced upwelling front characterized by a strong horizontal temperature gradient (Figure 3b). Such frontal regions frequently become dynamically unstable due to this sharp gradient.

Figure 3.
Alongshore-averaged (a) cross-shelf Eulerian velocity u, (b) temperature T without LT. (c) Snapshots of the surface vertical vorticity ζ normalized using the Coriolis parameter f without LT at Day 6. (d) Time series of the vertical enstrophy ζ′2 with and without LT. (e,f) Alongshore-averaged vertical eddy viscosity Akv. Results shown in panels (a,b,e,f) are averaged over Day 3.
As the instability intensifies, submesoscale eddies are generated along the front. The elevated vertical vorticity observed near the frontal region confirms the presence of vigorous rotational flows and active instability (Figure 3c). Simultaneously, the vertical enstrophy (ζ′2), computed as ζ′2, increases substantially near the frontal interface (Figure 3d), further evidencing enhanced submesoscale activity.
When the effects of LT are incorporated, the vertical eddy viscosity (Akv) in the upper ocean significantly increases relative to the case without LT (Figure 3e,f), resulting in intensified vertical mixing. This enhanced mixing weakens the stratification and suppresses frontal instability. The suppression primarily arises from turbulent homogenization processes that vertically mix fluid parcels, depleting the baroclinic potential energy reservoir required for the development of instability. Consequently, both eddy activity and ζ′2 are markedly diminished with LT near the frontal interface (Figure 3d).
3.2. Effects of LT on Wave Height
Ocean currents exert a significant influence on surface wave characteristics [7,13,14]. Ocean currents can modify surface wave propagation, causing wave refraction and inducing gradients in wave properties [7]. These wave–current interactions are further complicated by upper-ocean turbulence, which plays a pivotal role in modulating current structures and dynamics. In particular, LT can indirectly modulate wave dynamics by regulating the development of frontal instability and shaping the evolution of ocean currents.
As illustrated in Figure 4, the inclusion of LT leads to marked changes in the spatial distribution and alongshore gradients of wave height (H). Following the onset of frontal instability (after Day 5.5), both the alongshore variation and gradient of H are significantly reduced in the LT scenario compared to the case without LT (Figure 4a). To systematically examine the impact of LT on the alongshore wave gradients, we employ Equations (5) and (6) to formulate a quantitative framework linking current structural modifications to wave property responses.

Figure 4.
(a) Time series of alongshore gradient of wave height. Snapshots of wave height (b) without and (c) with LT at Day 10. Snapshots of the magnitude of surface current () (d) without and (e) with LT at Day 10.
In terms of the wavenumber evolution described by Equation (6), the group velocity advection term F2 exhibits the largest magnitude prior to the onset of upwelling frontal instability and remains nearly identical between the cases with and without LT (Figure 5a). During this early stage, the current-induced wave refraction term F3 is slightly smaller in the LT case. The other two terms, F1 and F4, are comparatively minor in magnitude and contribute little to the overall evolution. As a result, F3 predominantly governs the evolution of alongshore wavenumber gradients under both LT and non-LT conditions, with LT exerting limited influence on wavenumber evolution during the pre-instability phase.
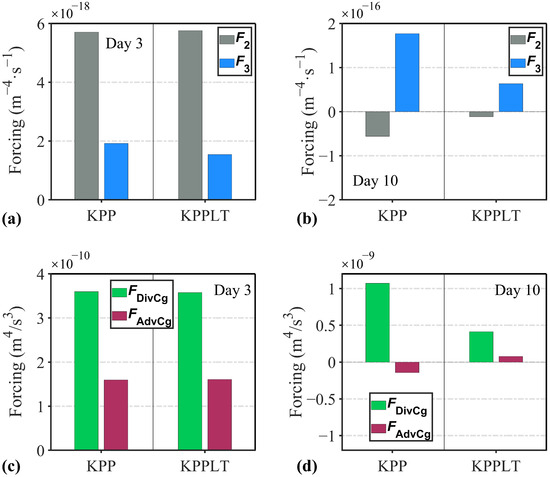
Figure 5.
The RHS terms of Equation (6) for the change of wavenumber gradient, averaged over (a) Day 3 and (b) Day 10, corresponding to periods before and after frontal instability. The RHS terms of Equation (5) for the change of wave action gradient, averaged over (c) Day 3 and (d) Day 10.
Following the onset of frontal instability (after Day 5.5), however, the current-induced wave refraction term F3 emerges as the dominant term, and its magnitude is significantly reduced in the presence of LT compared to that without LT (Figure 5b). This reduction is primarily due to the LT-induced suppression of submesoscale frontal eddies, which would generate the localized convergence and divergence zones in the surface current field. By damping these energetic structures, LT facilitates the development of a more alongshore uniform background current field (Figure 4d,e), thereby mitigating current-induced wave refraction. In the absence of strong shear and vorticity, the incident waves experience much less spatial variability in their propagation environment. This results in a more coherent wave direction and less alongshore-variable wavenumber. Consequently, the alongshore wavenumber gradients are significantly reduced in the presence of LT.
This weakening of wavenumber gradients directly affects the phase structure and energy distribution of the wave field. Smaller alongshore variations in wavenumber lead to more coherent wave groups, reducing the localized distortions. As wave energy propagates shoreward, it is less subject to convergence and divergence effects that would otherwise arise from refractive focusing and defocusing by eddies. Instead, wave energy remains more evenly distributed alongshore. This smoother energy landscape results in a more uniform distribution of wave heights across the alongshore direction, as reflected by the significantly diminished wave height gradients observed in the LT case after Day 5.5 (Figure 4a–c).
Further insight is gained by examining the wave action conservation Equation (5), where the forcings associated with group velocity (comprising the divergence term FDivCg and the advection term FAdvCg) overwhelmingly dominate over the current-related forcings (i.e., FDivcur and FAdvcur), exceeding them by approximately O(102) in magnitude. Prior to the development of frontal instability, both FDivCg and FAdvCg exhibit minimal differences between the two cases (Figure 5c), consistent with the similar wave height gradients observed during this early period (Figure 4a). Nevertheless, after the instability develops, the net forcing of FDivCg and FAdvCg becomes significantly smaller in the LT case (Figure 5d), leading to reduced alongshore gradients in wave height. Notably, the divergence term FDivCg shows the most pronounced reduction under LT, underscoring its key role in shaping the observed differences. This FDivCg is a nonlinear term involving the wavenumber field, wave energy distribution, and group velocity divergence. The reduction in FDivCg is mainly caused by the alongshore smoothing of ocean current and wavenumber by LT effects, which further weakens the focusing of wave energy. Accordingly, the capacity of FDivCg to sustain or amplify alongshore variations in wave action (height) is substantially diminished, further reinforcing the smoothing influence of LT on the coastal wave field.
3.3. Sensitivity to Wave Direction
In the previous analysis, the wave incident angle (wave direction) at the offshore boundary was set to 180°, i.e., a westward propagation (perpendicular to the coastline orientation). Under this configuration, the wave direction is also perpendicular to the wind direction, resulting in a wave–wind angle of 90°. Given that the intensity of LT is influenced by the alignment between wind and wave, where greater misalignment tends to suppress LT generation [42,43], we conducted two additional experiments with wave directions of 120° and 240°. The 120° and 240° represent the northwestward (downwind) and southwestward (upwind) wave propagation, respectively. For wave directions of 120° and 240°, the wind–wave angles are 30° and 150°, respectively.
Consistent with the 180° scenario, the inclusion of the LT results in a pronounced suppression of frontal instability in both the 120° and 240° cases, as evidenced by a systematic reduction in the vertical enstrophy ζ′2 (Figure 6a,b). This suppression reflects the impact of LT on upper-ocean current dynamics, which, in turn, modulates wave–current interactions, particularly the current-induced wave refraction that governs the spatial distribution of wave energy.
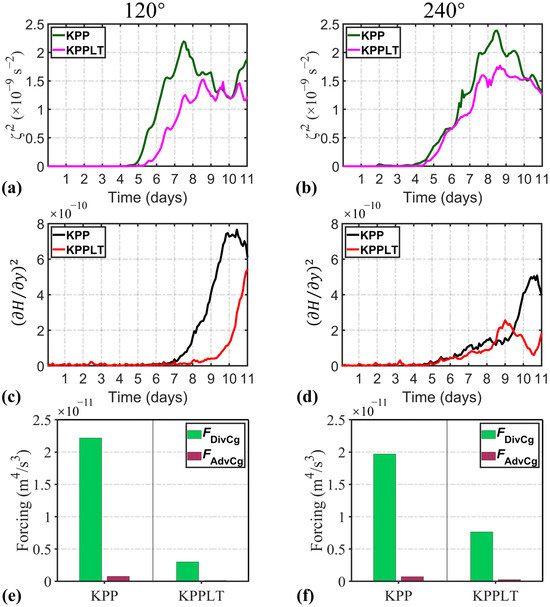
Figure 6.
Time series of (a,b) the vertical enstrophy ζ′2, and (c,d) alongshore gradient of wave height. (e,f) The RHS terms of Equation (5) for the change of wave action gradient, averaged over (e) Day 10 and (f) Day 11. Left and right columns show results with wave directions of 120° and 240°, respectively.
In both the 120° and 240° cases, the alongshore wave height gradient and associated forcing term FDivCg are markedly reduced when LT is present (Figure 6c–f), aligning with the pattern observed under the 180° wave direction. These consistent patterns across different wave directions highlight the robust role of LT in weakening frontal processes and reducing the alongshore gradients of wave height.
These findings align with previous studies, which have demonstrated that LT generally intensifies when wind and wave directions are more closely aligned [42,43,44]. Both the theoretical analyses and numerical simulations have shown that such alignment enhances the Craik–Leibovich vortex force, resulting in more vigorous vertical mixing.
However, although our KPPLT parameterization explicitly accounts for wind–wave directional alignment, our results show that the reduction in frontal instability and flow smoothing does not vary linearly with the wind–wave angle. While these effects are present across all tested angles, their magnitude does not simply increase with greater alignment.
This nonlinearity arises from the inherent complexity of LT, where the response of the vortex force and the LT intensity depend nonlinearly on the wind–wave angle [42,43]. Additionally, the sensitivity of frontal instability to mixing is itself nonlinear, shaped by the spatial structure of turbulence and its interaction with frontal gradients.
Therefore, while the reduction in frontal instability and wave impact occurs across all wind–wave angles, its magnitude does not decrease linearly with decreasing alignment, reflecting the complex interplay of waves, currents, and turbulence interactions within the parameterized system.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have established that ocean currents can significantly modulate surface waves through mechanisms such as refraction, Doppler shifting, and energy focusing or defocusing. In particular, Kudryavtsev et al. [8] and Romero et al. [13] emphasized that small-scale current gradients can induce strong spatial heterogeneity in wave height by driving refraction-induced wave energy convergence. Villas Bôas et al. [12] showed that strong vorticity fields during winter can result in significant spatial Hs gradients, with changes of up to 20%, whereas weaker vorticity fields in summer produce more uniform wave height distributions. Similarly, Sun et al. [6] further demonstrated that mesoscale cyclonic and anticyclonic eddies contribute to wave energy convergence and divergence through ray refraction, resulting in pronounced spatial variability in wave fields.
Our results complement and extend these findings by showing that LT plays a crucial modulatory role in this context. Specifically, we demonstrate that LT suppresses the submesoscale eddies and vorticity gradients by enhancing vertical mixing, thereby homogenizing the upper-ocean current structure. This suppression weakens the current-induced refraction mechanisms that are responsible for the spatial variability of wave properties. As a consequence, we observe a significant decrease in alongshore wavenumber gradients and forcing related to group velocity divergence, leading to smoother and more uniform wave height distributions along the coast. These results are also consistent with Ardhuin et al. [7], who concluded that (sub)mesoscale eddies, fronts, and filaments represent primary sources of significant wave height variability.
This proposed mechanism is also broadly supported by previous studies investigating the influence of LT on the upper-ocean frontal dynamics. For instance, Sullivan and McWilliams [45] showed that LT can influence the evolution of submesoscale filaments by modifying secondary circulations and weakening frontal sharpening under specific wave and current conditions. Their results underscore the sensitivity of frontal structure and intensity to LT-induced mixing and vortex-force dynamics. Although the dynamical regime they considered differs from that of the present study, their findings suggest that LT can modulate current gradients that are critical for wave refraction and energy convergence.
Moreover, recent studies highlight that wave–turbulence interactions can also occur at local scales. For instance, Scully and Zippel [46] showed that wave groups can modulate turbulence via pressure work and vertical energy flux convergence within the wave-affected surface layer, indicating a localized coupling between surface waves and Langmuir cells. Likewise, Smeltzer et al. [47] demonstrated that turbulence eddies with length scales comparable to surface wavelengths can scatter wave energy and broaden directional spectra. These processes are particularly relevant under strong wind and wave conditions and represent a promising direction for future high-resolution coupled modeling aimed at capturing the fine-scale structure of wave–turbulence interactions.
While our findings offer novel insights into the modulation of wave fields using LT, several limitations of the present study should be acknowledged. First, the simulations were conducted over an idealized continental shelf with uniform slope and simplified forcing conditions, which may limit the generalizability of the results to more complex real-world coastlines. Second, the LT parameterization employed in this study, though grounded in existing theory (e.g., the KPPLT scheme based on Wang et al. [40]), may still underrepresent the full range of LT variability observed in nature. Furthermore, the model relies on the prescribed incident waves and wind stress, rather than dynamically evolving sea states, which may affect the feedback mechanisms between LT generation and wave evolution.
Future work should aim to incorporate more realistic bathymetry and wind–wave variability, extend the simulations to three-dimensional and more realistic coastal domains, and explore observational validation using in situ or remote sensing data. Also, simulations resolving both wave phase and Langmuir turbulence could provide more detailed insights into the nonlinear feedback between turbulence and wave evolution. Ultimately, integrating LT dynamics into operational coastal forecasting systems could improve the wave energy predictions, especially in regions where wave–current interactions are critical.
5. Conclusions
This study investigates the role of Langmuir turbulence (LT) in modulating surface wave dynamics over an idealized continental shelf under upwelling-favorable wind conditions. By incorporating LT parameterization into a coupled wave–circulation model, the results reveal that LT substantially alters the evolution of wave fields, particularly through its impact on current-induced wave refraction.
The inclusion of LT enhances vertical mixing and suppresses frontal instability by weakening submesoscale eddies and reducing upper-ocean vorticity. This suppression leads to a more uniform current structure, which, in turn, significantly diminishes the alongshore gradients of wavenumber. As a result, the forcing related to group velocity divergence, which plays a critical role in the alongshore redistribution of wave energy, is notably reduced, resulting in smoother alongshore wave height distributions.
Furthermore, sensitivity experiments under different wave incident angles confirm the robustness of these findings. Regardless of wave–wind alignment, LT consistently reduces the intensity of frontal eddies and the associated alongshore wave height gradients. These results demonstrate that LT plays a critical role in regulating wave–current interactions and reshaping coastal wave energy distributions.
Overall, this work highlights the importance of accounting for Langmuir turbulence in coupled wave–ocean modeling frameworks, particularly for studies involving coastal dynamics, wave energy prediction, and air–sea interaction processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.W.; methodology, P.W.; formal analysis, J.W.; investigation, J.W. and P.W.; resources, P.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, P.W.; visualization, J.W.; supervision, P.W.; project administration, P.W.; funding acquisition, P.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant 2023YFC3008200 and 2024YFC3013200) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant 42206017).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their time and insightful feedback on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ardhuin, F.; Jenkins, A.D. On the interaction of surface waves and upper ocean turbulence. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Yuan, Y.; Deng, J.; Dai, D.; Song, Z. Wave–turbulence interaction-induced vertical mixing and its effects in ocean and climate models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Rutgersson, A.; Sahlée, E. Upper-ocean mixing due to surface gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 8210–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melet, A.; Teatini, P.; Le Cozannet, G.; Jamet, C.; Conversi, A.; Benveniste, J.; Almar, R. Earth observations for monitoring marine coastal hazards and their drivers. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 1489–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H.; Traylor, M.A. Refraction of ocean waves: A process linking underwater topography to beach erosion. J. Geol. 1947, 55, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Villas Bôas, A.B.; Subramanian, A.C.; Cornuelle, B.D.; Mazloff, M.R.; Miller, A.J.; Langodan, S.; Hoteit, I. Focusing and defocusing of tropical cyclone generated waves by ocean current refraction. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2021JC018112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhuin, F.; Gille, S.T.; Menemenlis, D.; Rocha, C.B.; Rascle, N.; Chapron, B.; Gula, J.; Molemaker, J. Small-scale open ocean currents have large effects on wind wave heights. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4500–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, V.; Yurovskaya, M.; Chapron, B.; Collard, F.; Donlon, C. Sun glitter imagery of surface waves. Part 2: Waves transformation on ocean currents. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 1384–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, G.; Ardhuin, F. Surface Currents and Significant Wave Height Gradients: Matching Numerical Models and High-Resolution Altimeter Wave Heights in the Agulhas Current Region. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC016564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilfen, Y.; Yurovskaya, M.; Chapron, B.; Ardhuin, F. Storm waves focusing and steepening in the Agulhas current: Satellite observations and modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.; Hypolite, D.; McWilliams, J.C. Submesoscale current effects on surface waves. Ocean Model. 2020, 153, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas Bôas, A.B.; Cornuelle, B.D.; Mazloff, M.R.; Gille, S.T.; Ardhuin, F. Wave–current interactions at meso- and submesoscales: Insights from idealized numerical simulations. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2020, 50, 3483–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.; Lenain, L.; Melville, W.K. Observations of surface wave–current interaction. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, C.; Yu, K. The influences of the Kuroshio on wave characteristics and wave energy distribution in the East China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 158, 103228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich, S. The form and dynamics of Langmuir circulations. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1983, 15, 391–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C.; Sullivan, P.P.; Moeng, C.H. Langmuir turbulence in the ocean. J. Fluid Mech. 1997, 334, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. Langmuir circulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulka, T.; Plueddemann, A.J.; Trowbridge, J.H.; Sullivan, P.P. Significance of Langmuir circulation in upper ocean mixing: Comparison of observations and simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C.; Sullivan, P.P. Vertical mixing by Langmuir circulations. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2000, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Özgökmen, T.M. Langmuir Circulation with Explicit Surface Waves from Moving-Mesh Modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Thomson, J.; Shcherbina, A.Y.; Harcourt, R.R.; Cronin, M.F.; Hemer, M.A.; Fox-Kemper, B. Quantifying upper ocean turbulence driven by surface waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harcourt, R.R.; D’Asaro, E.A. Large-eddy simulation of Langmuir turbulence in pure wind seas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2008, 38, 1542–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargett, A.; Wells, J.; Tejada-Martinez, A.E.; Grosch, C.E. Langmuir supercells: A mechanism for sediment resuspension and transport in shallow seas. Science 2004, 306, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargett, A.E.; Wells, J.R. Langmuir turbulence in shallow water. Part 1. Observations. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 576, 27–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargett, A.E.; Savidge, D.K.; Wells, J.R. Anatomy of a Langmuir supercell event. J. Mar. Res. 2014, 72, 127–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chamecki, M.; Meneveau, C. Inhibition of oil plume dilution in Langmuir ocean circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.J.; Liu, G.; Perrie, W.; Sheng, J. Impact of Langmuir turbulence, wave breaking, and Stokes drift on upper ocean dynamics under hurricane conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hara, T.; Ginis, I.; D’Asaro, E.; Reichl, B.G. Evidence of Langmuir mixing effects in the upper ocean layer during tropical cyclones using observations and a coupled wave-ocean model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2023, 128, e2023JC020062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Reichl, B.G.; Fox-Kemper, B.; Adcroft, A.J.; Belcher, S.E.; Danabasoglu, G.; Grant, A.L.M.; Griffies, S.M.; Hallberg, R.; Hara, T.; et al. Comparing ocean surface boundary vertical mixing schemes including Langmuir turbulence. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 3545–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Christensen, K.H.; Breivik, Ø.; Malila, M.; Raj, R.P.; Bertino, L.; Chassignet, E.P.; Bakhoday-Paskyabi, M. A comparison of Langmuir turbulence parameterizations and key wave effects in a numerical model of the North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans. Ocean Model. 2019, 137, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesiello, P.; Benshila, R.; Almar, R.; Uchiyama, Y.; McWilliams, J.C.; Shchepetkin, A. On Tridimensional Rip Current Modeling. Ocean Model. 2015, 96, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; McWilliams, J.C.; Shchepetkin, A.F. Wave–Current Interaction in an Oceanic Circulation Model with a Vortex-Force Formalism: Application to the Surf Zone. Ocean Model. 2010, 34, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; McWilliams, J.C.; Akan, C. Three-Dimensional Transient Rip Currents: Bathymetric Excitation of Low-Frequency Intrinsic Variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 5826–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; McWilliams, J.C.; Uchiyama, Y.; Chekroun, M.D.; Yi, D.L. Effects of Wave Streaming and Wave Variations on Nearshore Wave-Driven Circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2020, 50, 3025–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; McWilliams, J.C.; Uchiyama, Y. A Nearshore Oceanic Front Induced by Wave Streaming. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 51, 1967–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; McWilliams, J.C.; Wang, D.; Yi, D.L. Conservative Surface Wave Effects on a Wind-Driven Coastal Upwelling System. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2023, 53, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, P. How Do Conservative Surface Wave Effects Influence a Coastal Upwelling Front? J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2025, 130, e2024JC021404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, W.G.; McWilliams, J.C.; Doney, S.C. Oceanic Vertical Mixing: A Review and a Model with a Nonlocal Boundary Layer Parameterization. Rev. Geophys. 1994, 32, 363–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C.; Restrepo, J.M.; Lane, E.M. An Asymptotic Theory for the Interaction of Waves and Currents in Coastal Waters. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 511, 135–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; McWilliams, J.C.; Yuan, J.; Liang, J.-H. Langmuir Mixing Schemes Based on a Modified K-Profile Parameterization. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2025, 17, e2024MS004729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.L.; Belcher, S.E. Characteristics of Langmuir Turbulence in the Ocean Mixed Layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 1871–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, J.C.; Huckle, E.; Liang, J.; Sullivan, P.P. Langmuir Turbulence in Swell. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 870–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roekel, L.P.; Fox-Kemper, B.; Sullivan, P.P.; Hamlington, P.E.; Haney, S.R. The Form and Orientation of Langmuir Cells for Misaligned Winds and Waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C05001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Anderson, W.; Tejada-Martinez, A.; Kuehl, J. Orientation of coastal-zone Langmuir cells forced by wind, wave and mean current at variable obliquity. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 879, 716–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.P.; McWilliams, J.C. Langmuir turbulence and filament frontogenesis in the oceanic surface boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 879, 512–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Zippel, S.F. Vertical energy fluxes driven by the interaction between wave groups and Langmuir turbulence. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2024, 54, 1347–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeltzer, B.K.; Rømcke, O.; Hearst, R.J.; Ellingsen, S.Å. Experimental study of the mutual interactions between waves and tailored turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 962, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).