Trends and Applications of Hydro-Morphological Modeling in Estuarine Systems: A Systematic Review of the Past 15 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Document Collection—Identification
- WoS: TS = (estuar*) AND TS = (morphodynamics OR morphological changes OR sediment transport OR hydrodynamics) AND TS = (numerical model* OR model).
- Scopus: TITLE-ABS-KEY(estuar*) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(morphodynamics OR morphological changes OR sediment transport OR hydrodynamics) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY(numerical model* OR model).
2.2. Processing Based on Defined Criteria—Screening
2.3. Analysis of Selected Documents—Inclusion
3. Results
- Estuary,
- Estuary country,
- Modeling software,
- Model type (MH: Hydrodynamic only, MT: Sediment transport (Morphological without bathymetry updates), MM: Morphological with bathymetry updates),
- Mesh topology (structured or unstructured),
- Dimension (1D, 2D, or 3D),
- Morphological acceleration factor or hydrodynamic timestep (dt hydro) and morphological timestep (dt mor), as applicable,
- Validation parameter (Skill Score (SS)) used in the articles to validate the simulations, where: is the number of values calculated for velocity validation and is the number of values calculated for water level validation.
3.1. Hydrodynamic Modeling Software (MH)
3.2. Configuration of Hydrodynamic Models
3.3. Precision of Hydrodynamic Models
3.4. Morphological Implementation of Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Author | Country Classification | Estuary | Software | Model Type | Topology | Dimension | Morfac | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [110] | Australia | Brisbane Estuary | Mike | MH | - | 2D | ||
| [60] | Australia | Currumbin Creek | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [111] | Australia | Currumbin Creek | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 4 | |
| [112] | Australia | Fitzroy Estuary | FVCOM | MM | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [113] | Australia | Port Curtis Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [62] | Australia | Shoalhaven Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [61] | Australia | Shoalhaven Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [114] | Bangladesh | Meghna estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 12 | |
| [115] | Bangladesh | Pussur River | HEC-RAS | MH | - | 1D | ||
| [116] | Brazil | Amazonian Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured/Unstructured | 1D/2D | ||
| [117] | Brazil | Caravelas Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [118] | Brazil | Paranagua Estuary Complex | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [63] | Brazil | Santos estuarine system | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [64] | Brazil | Santos estuarine system | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D/3D | ||
| [119] | Canada | St. Lawrence River Estuary | H2D2 | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [120] | Canada | St. Lawrence River Estuary | Non-commercial | MH | Unstructured | 1D/2D | ||
| [121] | China | Yangtze estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [47] | China | Yangtze estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [122] | China | Yangtze estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [123] | China | Yangtze estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [124] | China | Huangmaohai Estuary | COAWST | MT | Structured | 1D/3D | ||
| [125] | China | Huangmaohai Estuary | ECOM | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [126] | China | Jiaojiang Estuary | Mike | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [127] | China | Jiaojiang River Estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | (20) | |
| [13] | China | Lingdingyang Estuary | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | dt mor = 10 s/dt hydro = 30 s | (3) |
| [128] | China | Lingdingyang Estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | (23) | |
| [129] | China | Luanhe River Estuary | Non-commercial | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [130] | China | Modaomen Estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [131] | China | Modaomen estuary | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | dt mor = 10 s/dt hydro = 10 s | (1) |
| [132] | China | Oujiang Estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | SSwl (1) | |
| [133] | China | Oujiang Estuary | ADCIRC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [134] | China | Oujiang Estuary | EFDC | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [135] | China | Pearl River Delta | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | (1) | |
| [136] | China | Pearl River Delta | ROMS | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [137] | China | Pearl River Delta | [138] | MH | - | 1D | ||
| [139] | China | Pearl river Delta | Developed by the State Key Laboratory | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [140] | China | Pearl River Delta | ECOM/Riv1D | MT | Structured | 1D/3D | ||
| [141] | China | Pearl River Delta | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [142] | China | Pearl River Delta | SCHISM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [143] | China | Pearl River Delta | COAWST | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [144] | China | Pearl River Delta | ECOM | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [145] | China | Pearl River Delta | EFDC | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [146] | China | Pearl River Delta | EFDC | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [147] | China | Pearl River Delta | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 1 | |
| [148] | China | Pearl River Delta | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [149] | China | Pearl River Delta | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [150] | China | Qiantang Estuary | Non-commercial | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [151] | China | Qiantang Estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [152] | China | Qiantang Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [153] | China | Qiantang Estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [154] | China | Qiantang Estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [155] | China | Sheyang estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [156] | China | Xinyanggang River | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 1 | |
| [157] | China | Yalu River Estuary | FVCOM | MM | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [158] | China | Yalu River Estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [159] | China | Yangtze estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [160] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Non-commercial | MM | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [48] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | (20) | |
| [161] | China | Yangtze Estuary | SWEM3D | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [49] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | (6) | |
| [17] | China | Yangtze Estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [162] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Non-commercial | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [163] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [164] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [165] | China | Yangtze Estuary | - | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [166] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | - | 1D | ||
| [167] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Developed by the State Key Laboratory | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [168] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [169] | China | Yangtze Estuary | COAWST | MT | - | 3D | ||
| [170] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Unstructured | 3D | (12) | |
| [171] | China | Yangtze Estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [46] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [172] | China | Yangtze Estuary | Mike | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [45] | China | Yangtze Estuary | CCHE | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [173] | China | Yellow River | ECOM | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [174] | China | Yellow River | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [175] | China | Yellow River | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | (1) | |
| [176] | China | Yellow River | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [177] | China | Yellow River | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [178] | China | Yellow River/Yangtze River/Mekong River | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [179] | China | Zhujiang River Estuary | ROMS | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [180] | China | Zhujiang River Estuary | ROMS | MT | - | 3D | ||
| [181] | Colombia | Magdalena River | OpenFlow Flood | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [182] | France | Authie Estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [183] | France | Charente Estuary | MARS3D | MH | - | 2D | ||
| [184] | France | Gironde Estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [185] | France | Gironde Estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [186] | France | Gironde estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | (9) | |
| [187] | France | Rance estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [188] | France | Seine Estuary | MARS3D | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [189] | Germany | Elbe Estuary | TRIMNP | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [190] | Germany and Germany/Netherlands | Elbe estuary/Jade-Weser estuary/Ems Estuary | UnTRIM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [191] | Germany/Netherlands | Ems Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | - | 1D | ||
| [192] | Germany/Netherlands | Ems Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [193] | Germany | Weser estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [194] | Germany/Netherlands | Ems Estuary | SELFE | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [195] | India | Narmada Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [196] | India | Rushikulya River | Mike | MM | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [197] | India | Serayu River | Mike | MM | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [198] | India | Ulhas Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [199] | Indonesia | Jelitik River | Mike | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [40] | Indonesia | Kapuas River | Louvain-la-Neuve Ice-ocean Model | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [200] | Indonesia | Rokan River Estuary | Mike | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [201] | Italy | Misa Estuary | HEC-RAS | MH | - | 1D | ||
| [202] | Italy | Misa Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [203] | Malaysia | Pahang River | Mike | MT | - | 2D | ||
| [204] | Malaysia | Sibu Laut River | DYNHYD5 | MH | - | 1D | ||
| [205] | Morocco | Bouregreg Estuary | HYSED | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 1 | |
| [12] | Morocco | Oum-Errabia River | Mike | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [206] | Mozambique | Beira Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [207] | Myanmar | Sittaung Estuary | iRIC | MM | Structured | 2D | dt mor = 0.2 s/dt hydro = 1 s | |
| [208] | Netherlands | Rotterdam Waterway | Delft3D | MM | Unstructured | 2D | MORFAC = 26 | |
| [209] | Netherlands | Scheldt Estuary | Delft3D/Telemac | MH | Structured/Unstructured | 2D/3D | ||
| [210] | Netherlands | Scheldt Estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 20 | |
| [211] | Netherlands | Scheldt Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [212] | Netherlands | Scheldt Estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [213] | Netherlands | Western Scheldt estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [214] | New Zealand | Kaipara River | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D/3D | ||
| [215] | New Zealand | Tairua Estuary | Mike | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [216] | Peru | Virrilá Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [217] | Poland | Kacza river estuary | HEC-RAS | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [218] | Portugal | Douro Estuary | Xbeach | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 10 | |
| [219] | Portugal | Douro Estuary/Minho Estuary | Delft3D/Telemac | MH | - | -- | ||
| [220] | Portugal | Douro Estuary | Delft3D/Telemac | MH | Structured/Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [221] | Portugal | Douro Estuary | MOHID | MH | - | 2D | ||
| [222] | Portugal | Lima Estuary | SIMSYS | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [223] | Portugal | Douro Estuary/Minho Estuary | Delft3D/Telemac | MH | Structured/Unstructured | -- | ||
| [224] | Portugal | Mondego Estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | ||
| [225] | Portugal | Tagus Estuary | SCHISM | MM | - | 2D | MORFAC = 1 | |
| [226] | Portugal | Tagus Estuary | SIMSYS | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [227] | Portugal | Tagus Estuary | MOHID | MT | - | 2D | ||
| [228] | Rusia | Onega Estuary | Delft3D/Hec-Ras | MH | Structured/Structured | 1D/2D/3D | ||
| [229] | South Africa | Breede Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [230] | South Korea | Nakdong Estuary | COAWST | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [231] | South Korea | Nakdong Estuary | COAWST | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [232] | South Korea | Nakdong Estuary | CCHE | MM | Structured | 2D | ||
| [233] | Spain | Guadalquivir Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [234] | Spain | Oka estuary | SMC | MT | - | 2D | ||
| [235] | Spain | Ría de Ribadeo | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 12 | |
| [236] | Spain | Ría de Viveiro | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [237] | Spain | Ría de Ferrol | ROMS | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [238] | Spain | Suances Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [239] | Spain | Suances Estuary | H2D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [41] | Spain/Portugal | Guadiana Estuary | MOHID | MH | - | 2D | ||
| [240] | Spain/Portugal | Minho Estuary | TELEMAC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [241] | Spain/Portugal | Minho Estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 52/1/1/1 | |
| [242] | Taiwan | Beinan Estuary | Mike | MM | Unstructured | 2D | dt mor = 3600 s/dt hydro = 3600 s | |
| [243] | Taiwan | Danshui Estuary | SELFE | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [244] | Taiwan | Danshui Estuary | Mike | MH | - | 1D | ||
| [245] | Taiwan | Danshui Estuary | CCHE | MM | Structured | 2D | dt mor = 100 s/dt hydro = 10 s | |
| [246] | Taiwan | Lanyan Estuary | Non-commercial | MM | Structured | 2D | ||
| [247] | Taiwan | Tamsui Estuary | CCHE | MM | Structured | 2D | dt mor = 100 s/dt hydro = 10 s | |
| [248] | Taiwan | Tamsui Estuary | CCHE | MM | Non-orthogonal | 2D | dt mor = 100 s/dt hydro = 40 s | |
| [249] | Taiwan | Zengwen Estuary | NearCoM-TVD | MM | Structured | 3D | MORFAC = 12 | |
| [250] | United Kingdom | Taf Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | (1) | |
| [251] | United Kingdom | Avon Estuary | Non-commercial | MT | - | 1D | ||
| [252] | United Kingdom | Blyth Estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [253] | United Kingdom | Conwy Estuary | CAESAR-Lisflood | MH | - | 2D | ||
| [254] | United Kingdom | Deben Estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 12 | |
| [255] | United Kingdom | Deben Estuary | Delft3D | MM | Structured | 2D | MORFAC = 12 | |
| [256] | United Kingdom | Dyfi Estuary | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | dt mor = 10 s/dt hydro = 10 s | |
| [257] | United Kingdom | Ribble Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [258] | United Kingdom | Ribble Estuary | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 2D | ||
| [259] | United Kingdom | Mersey River/Ribble Estuary/Dee River | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D | dt mor = 600 s/dt hydro = 12 s | |
| [50] | United Kingdom | Severn Estuary | Galerkin model DG-SWEM | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [51] | United Kingdom | Severn Estuary | [260] | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [14] | United Kingdom | Severn Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [52] | United Kingdom | Severn Estuary | [260] | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [39] | Uruguay/Argentina | Río de la Plata | WQMAP | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [261] | United States | Breton Sound Estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [262] | United States | Cape Fear River Estuary | ROMS/WRF-Hydro | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [263] | United States | Chesapeake Bay | COAWST | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [264] | United States | Chesapeake Bay | ROMS | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [16] | United States | Columbia Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [54] | United States | Columbia Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D/3D | ||
| [265] | United States | Columbia Estuary | AdH | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [21] | United States | Delaware Estuary | Delft3D/Hec-Ras | MH | Structured/Unstructured | 1D/2D | ||
| [266] | United States | Delaware Estuary | Delft3D/Hec-Ras | MH | Unstructured | 1D/2D | ||
| [57] | United States | Hudson Estuary | ROMS | MT | - | -- | ||
| [56] | United States | Hudson Estuary | ROMS | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [55] | United States | Hudson Estuary | ROMS | MT | Structured | 3D | ||
| [267] | United States | Mobile Bay | ADCIRC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [268] | United States | Saint Johns Estuary | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D | ||
| [269] | United States | San Francisco Bay | Delft3D | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [270] | United States | San Francisco Bay | SUNTANS | MT | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [271] | United States | Skagit Estuary | FVCOM | MT | Unstructured | 3D | (6) | |
| [272] | United States | Snohomish Estuary | FVCOM | MH | Unstructured | 3D | ||
| [273] | United States | St. Johns and Nassau Estuary | ADCIRC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [38] | United States | Tillamook Bay | ADCIRC | MH | Unstructured | 2D | ||
| [274] | United States | Weeks Bay | EFDC | MH | Structured | 3D | ||
| [275] | Vietnam | Cua Dai Estuary | Delft3D/Mike | MT | Structured | 1D/3D | ||
| [276] | Vietnam | Mekong Delta | Delft3D | MH | Unstructured | 1D/2D | (6) | |
| [277] | Vietnam | Mekong Delta | Delft3D | MT | Structured/Unstructured | 2D/3D | ||
| [278] | Vietnam | Mekong Delta | Delft3D | MT | Structured | 3D | (2) | |
| [279] | Vietnam | Soai Rap Estuary | TELEMAC | MT | Structured/Unstructured | 2D | (4) | |
| [280] | Vietnam | Song Hau channel | Delft3D | MH | Structured | 2D/3D | ||
| [281] | Vietnam | Thu-Bon Estuary | TELEMAC | MM | Unstructured | 2D |
References
- Kennish, M.J. Environmental Threats and Environmental Future of Estuaries. Envir. Conserv. 2002, 29, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Estuaries. 2024. Available online: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/education/tutorial_estuaries/welcome.html (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Geyer, W.R. Influence of Wind on Dynamics and Flushing of Shallow Estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerer, W.J. Physical, Biological, and Management Responses to Variable Freshwater Flow into the San Francisco Estuary. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.T. Chapter 6 Tide-Dominated Estuaries and Tidal Rivers. In Developments in Sedimentology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 53, pp. 179–205. ISBN 978-0-444-88170-0. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.M.M.; Glover, H.E.; Josten, M.E.; Gomes, V.J.C.; Ogston, A.S.; Asp, N.E. Implications of a Large River Discharge on the Dynamics of a Tide-Dominated Amazonian Estuary. Water 2023, 15, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, A.W.; Braat, L.; Parsons, D.R. Control of River Discharge on Large-scale Estuary Morphology. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2023, 48, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, D.; Glamore, W.; Heimhuber, V.; Felder, S. Sea Level Rise Impacts on Estuarine Dynamics: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.M.; Montagna, P.A.; Hu, X.; Wetz, M.S. Timescales and Magnitude of Water Quality Change in Three Texas Estuaries Induced by Passage of Hurricane Harvey. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffier, F.F. The Stability of Tidal Inlets. Shore Beach 1940, 8, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Osei-Twumasi, A.; Falconer, R.A.; Bockelmann-Evans, B.N. Experimental Studies on Water and Solute Transport Processes in a Hydraulic Model of the Severn Estuary, UK. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1731–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouiche, I.; Sedrati, M.; Anthony, E.J. Modelling of Sediment Transport and Deposition in Generating River-Mouth Closure: Oum-Errabia River, Morocco. JMSE 2023, 11, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Jia, L. Combined Effects of Massive Reclamation and Dredging on the Variations in Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport in Lingdingyang Estuary, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 18, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyddon, C.; Brown, J.M.; Leonardi, N.; Plater, A.J. Uncertainty in Estuarine Extreme Water Level Predictions Due to Surge-Tide Interaction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passone, S.; Chung, P.W.H.; Nassehi, V. Case-Based Reasoning for Estuarine Model Design. In Advances in Case-Based Reasoning; Craw, S., Preece, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 2416, pp. 590–603. ISBN 978-3-540-44109-0. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, E.P.L.; Gelfenbaum, G.; Van Der Westhuysen, A.J. Validation of a Coupled Wave-flow Model in a High-energy Setting: The Mouth of the Columbia River. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2012JC008105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Townend, I.; Cai, H.; He, J.; Mei, X. The Influence of Seasonal Climate on the Morphology of the Mouth-Bar in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 153, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhong, L.; Boicourt, W.C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D. Hurricane-induced Storm Surges, Currents and Destratification in a Semi-enclosed Bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 2005GL024992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, N.M.; Laba, M.; Spector, S. Simulating the Effects of Sea Level Rise on the Resilience and Migration of Tidal Wetlands along the Hudson River. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlillah, L.N.; Widyastuti, M.; Sunarto; Marfai, M.A. Comparison of Tidal Model Using Mike21 and Delft3d-Flow in Part of Java Sea, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 451, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.F.; Yin, D.; Bakhtyar, R.; Moftakhari, H.; Xue, Z.; Mandli, K.; Ferreira, C. Inter-Model Comparison of Delft3D-FM and 2D HEC-RAS for Total Water Level Prediction in Coastal to Inland Transition Zones. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsapour-moghaddam, P.; Rennie, C.D.; Slaney, J. Hydrodynamic Simulation of an Irregularly Meandering Gravel-Bed River: Comparison of MIKE 21 FM and Delft3D Flow Models. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 40, 02004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupi, C. Numerical Modeling of Cohesive Sediment Transport and Bed Morphology in Estuaries. Ph.D. Thesis, Lausanne University, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunny, C.; Brennan, S.E.; McDonald, S.; McKenzie, J.E. Toward a Comprehensive Evidence Map of Overview of Systematic Review Methods: Paper 1—Purpose, Eligibility, Search and Data Extraction. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesser, G.R.; Roelvink, J.A.; Van Kester, J.A.T.M.; Stelling, G.S. Development and Validation of a Three-Dimensional Morphological Model. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 883–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelvink, J.A. Coastal Morphodynamic Evolution Techniques. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulinec, C.; Denis, C.; Pham, C.-T.; Rougé, D.; Hervouet, J.-M.; Razafindrakoto, E.; Barber, R.W.; Emerson, D.R.; Gu, X.-J. TELEMAC: An Efficient Hydrodynamics Suite for Massively Parallel Architectures. Comput. Fluids 2011, 51, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, A.; Slyman, A.; Wu, W. Capturing Citation Activity in Three Health Sciences Departments: A Comparison Study of Scopus and Web of Science. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2015, 34, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, J.F. Scopus Database: A Review. Biomed. Digit. Libr. 2006, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, M.; McGowan, J.; Cogo, E.; Horsley, T. Managing Database Overlap in Systematic Reviews Using Batch Citation Matcher: Case Studies Using Scopus. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2006, 94, 461. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, H.A.; Latimer, J.S.; Dettmann, E.H. Assessing the Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Stressors in the Potomac Estuary: Implications for Long-Term Monitoring. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2000, 63, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K.; Van Der Wal, D.; Neal, A. Long-Term Morphological Change and Its Causes in the Mersey Estuary, NW England. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, M.; Klein, M.; Zviely, D. Dynamic Morphology of Small South-eastern Mediterranean River Mouths: A Conceptual Model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathna, H. Modelling the Long-Term Morphological Evolution of the Clyde Estuary, Scotland, UK. J. Coast. Conserv. 2011, 15, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Jia, L. Long-Term Morphological Evolution and Its Mechanism of Lingdingyang Estuary: Interferences from Anthropogenic Forcings. Mar. Geol. 2022, 450, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liang, M.; Jia, L.; Dong, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Ou, J. Long-Term Morphological Modeling and Implication for Estuarine Regulation of the Modaomen Estuary, Pearl River Delta, China. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 123, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.K.; Hill, D.F.; Read, W. The Contributions to Storm Tides in Pacific Northwest Estuaries: Tillamook Bay, Oregon, and the December 2007 Storm. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 313, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prario, B.E.; Dragani, W.; Mediavilla, D.G.; D’Onofrio, E. Hydrodynamic Numerical Simulation at the Mouths of the Parana and Uruguay Rivers and the Upper Rio de La Plata Estuary: A Realistic Boundary Condition. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 5265–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampurno, J.; Vallaeys, V.; Ardianto, R.; Hanert, E. Modeling Interactions between Tides, Storm Surges, and River Discharges in the Kapuas River Delta. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 2741–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero Quesada, M.C.; García-Lafuente, J.; Garel, E.; Delgado Cabello, J.; Martins, F.; Moreno-Navas, J. Effects of Tidal and River Discharge Forcings on Tidal Propagation along the Guadiana Estuary. J. Sea Res. 2019, 146, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonina, D.; Jorde, K. Hydraulic Modelling Approaches for Ecohydraulic Studies: 3D, 2D, 1D and Non-Numerical Models. In Ecohydraulics; Maddock, I., Harby, A., Kemp, P., Wood, P., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 31–74. ISBN 978-0-470-97600-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, K.A.; Goodman, D.H.; Som, N.A.; Alvarez, J.; Martin, A.; Hardy, T.B. Improving Hydrodynamic Modelling: An Analytical Framework for Assessment of Two-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Models. River Res. Apps. 2017, 33, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Liu, B.; Hu, K.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z. Sedimentary Records of the Yangtze Estuary over the Past 70 Years and Their Implications for Provenance. Env. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.S.Y. Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Tidal Flows in the Yangtze River Estuary. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2011, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 19 May 2011; American Society of Civil Engineers: Palm Springs, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 2135–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, X. Remote Sensing Observations and Numerical Studies of a Super Typhoon-Induced Suspended Sediment Concentration Variation in the East China Sea. Ocean Model. 2016, 104, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xu, F.; He, Q.; Shen, J.; Guo, L.; Xie, W.; Zhu, L. The Role of a Remote Tropical Cyclone in Sediment Resuspension over the Subaqueous Delta Front in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Geomorphology 2021, 377, 107564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Tong, C.; Lee, D.; Zheng, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y. Propagation of Tidal Waves up in Y Angtze E Stuary during the Dry Season. JGR Ocean. 2015, 120, 6445–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, J.; Lin, B.; Huang, G. Seasonal Hydrodynamic Interactions between Tidal Waves and River Flows in the Yangtze Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 186, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Moreira, T.M.; Adcock, T.A.A. The Impact of a Tidal Barrage on Coastal Flooding Due to Storm Surge in the Severn Estuary. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2019, 5, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B. Hydrodynamic Impact of a Tidal Barrage in the Severn Estuary, UK. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B.; Tan, G. Estimation of Future Coastal Flood Risk in the Severn Estuary Due to a Barrage: Estimation of Future Coastal Flood Risk in the Estuary. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2011, 4, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P. Modelling Salinity and Circulation for the Columbia River Estuary. Prog. Oceanogr. 1990, 25, 113–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbach, S.D.; Nicholas, A.P.; Ashworth, P.J.; Best, J.L.; Keevil, C.E.; Parsons, D.R.; Prokocki, E.W.; Simpson, C.J. Hydrodynamic Modelling of Tidal-Fluvial Flows in a Large River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 212, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K. Changes in Estuarine Sediment Dynamics with a Storm Surge Barrier. Estuaries Coasts 2023, 46, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Warner, J.C. Bathymetric Controls on Sediment Transport in the Hudson River Estuary: Lateral Asymmetry and Frontal Trapping. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2012JC008124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Warner, J.C.; Geyer, W.R.; Wall, G.R. Sediment Transport Due to Extreme Events: The Hudson River Estuary after Tropical Storms Irene and Lee. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5451–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Bourget, J.; Molnar, N.; Strauss, D.; Deschamps, S.; Tomlinson, R. Dynamics of a Wave-Dominated Tidal Inlet and Influence on Adjacent Beaches, Currumbin Creek, Gold Coast, Australia. Coast. Eng. 2007, 54, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaeri, S.; Tomlinson, R.B.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Strauss, D.; Hughes, L.P. Hydrodynamics of a Small Trained Tidal Inlet (Currumbin Creek, Australia). Adv. Geosci. 2014, 39, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaeri, S.; Strauss, D.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Tomlinson, R. Hydrosedimentological Modelling of a Small, Trained Tidal Inlet System, Currumbin Creek, Southeast Queensland, Australia. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 342, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbier, K.; Carvalho, R.C.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Woodroffe, C.D. Investigating Compound Flooding in an Estuary Using Hydrodynamic Modelling: A Case Study from the Shoalhaven River, Australia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbier, K.; Carvalho, R.C.; Woodroffe, C.D. Modelling Hydrodynamic Impacts of Sea-Level Rise on Wave-Dominated Australian Estuaries with Differing Geomorphology. JMSE 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.; Seiler, L.; Siegle, E. The Influence of Dredging on Estuarine Hydrodynamics: Historical Evolution of the Santos Estuarine System, Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 279, 108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, L.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Schettini, C.A.F.; Siegle, E. Three-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Modeling of the Santos-São Vicente-Bertioga Estuarine System, Brazil. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddout, S. A Power-Law Multivariable Regression Equation for Salt Intrusion Length in the Bouregreg Estuary, Morocco. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2020, 38, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddout, S.; Priya, K.L.; Ljubenkov, I. The Calculation of Estuarine Flushing Times in Convergent Estuaries Using Fresh-Water Fraction Method. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2022, 20, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xian, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wu, C. Geographical Features and Development Models of Estuarine Cities. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyk, S.; Gaughan, A.E.; Adamo, S.B.; De Sherbinin, A.; Balk, D.; Freire, S.; Rose, A.; Stevens, F.R.; Blankespoor, B.; Frye, C.; et al. The Spatial Allocation of Population: A Review of Large-Scale Gridded Population Data Products and Their Fitness for Use. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1385–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, Y.; Hsu, T.-J.; Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B.; Quataert, E.; Van Dongeren, A. Modeling the Hydrodynamics and Morphodynamics of Sandbar Migration Events. Coast. Eng. 2021, 166, 103885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.J.; Esteves, L.S. Guidance on Setup, Calibration, and Validation of Hydrodynamic, Wave, and Sediment Models for Shelf Seas and Estuaries. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltares Delft3D-FLOW: Simulation of Multi-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Flows and Transport Phenomena, Including Sediments; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2016.
- Deltares D-Flow Flexible Mesh: Computational Cores and User Interface; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2024.
- Villaret, C.; Hervouet, J.-M.; Kopmann, R.; Merkel, U.; Davies, A.G. Morphodynamic Modeling Using the Telemac Finite-Element System. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 53, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Telemac TELEMAC-3D—3D Hydrodynamics. Available online: https://www.opentelemac.org/index.php/presentation?id=18 (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Hervouet, J.M. TELEMAC, a Hydroinformatic System. La Houille Blanche 1999, 85, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.; Cowles, G.; Qi, J.; Lai, Z.; Gao, G.; Stuebe, D.; Xu, Q.; Xue, P.; Ge, J. An Unstructured-Grid, Finite-Volume Community Ocean Model: FVCOM User Manual; Sea Grant College Program, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Beardsley, R.C. An Unstructured Grid, Finite-Volume, Three-Dimensional, Primitive Equations Ocean Model: Application to Coastal Ocean and Estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Beardsley, R.C.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Cowles, G. A Finite Volume Numerical Approach for Coastal Ocean Circulation Studies: Comparisons with Finite Difference Models. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 2006JC003485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Chen, C.; Cowles, G.W.; Beardsley, R.C. A Nonhydrostatic Version of FVCOM: 1. Validation Experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 2009JC005525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHI MIKE 3 Flow Model FM: Hydrodynamic and Transport Module; DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2024.
- DHI MIKE 21 Flow Model FM: Hydrodynamic and Transport Module; DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2024.
- DHI MIKE 21 & MIKE 3 Flow Model FM: Sand Transport Module; DHI: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2024.
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. A Coupled 1D–2D Hydrodynamic Model for Flood Simulation in Flood Detention Basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1303–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; García-Navarro, P.; Burguete, J.; Brufau, P. A Conservative Strategy to Couple 1D and 2D Models for Shallow Water Flow Simulation. Comput. Fluids 2013, 81, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi Kuhanestani, P.; Bomers, A.; Booij, M.J.; Warmink, J.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Increasing the Water Level Accuracy in Hydraulic River Simulation by Adapting Mesh Level Elevation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 180, 106135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajithkumar, N.; Verma, P.A.; Osei, F.B.; Shankar, H. Comparison of Surface Water Flow Simulation over Structured and Unstructured Grids. Spat. Inf. Res. 2022, 30, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomers, A.; Schielen, R.M.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. The Influence of Grid Shape and Grid Size on Hydraulic River Modelling Performance. Env. Fluid. Mech. 2019, 19, 1273–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bars, Y.L.; Vallaeys, V.; Deleersnijder, É.; Hanert, E.; Carrere, L.; Channelière, C. Unstructured-Mesh Modeling of the Congo River-to-Sea Continuum. Ocean Dyn. 2016, 66, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, C.; Xu, F. Two-Dimensional Numerical Modeling of Flow Pattern and Bed Topography in Channel Bend. Env. Model. Assess. 2022, 27, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kuang, C.; Fan, D.; Xing, W.; Qin, R.; Zou, Q. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Suspended Sediment during Typhoon Ampil under Wave–Current Interactions in the Yangtze River Estuary. Water 2024, 16, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, T.; Villaret, C.; Kelly, D.M.; Baugh, J. Improvements in 3D Sediment Transport Modelling with Application to Water Quality Issues. In Proceedings of the 21st TELEMAC-MASCARET User Conference, Grenoble, France, 15–17 October 2014; Volume 2014, pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, C. Structured and Unstructured Grid Properties. In Numerical Computation of Internal and External Flows; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 249–277. ISBN 978-0-7506-6594-0. [Google Scholar]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Technical Note: Inherent Benchmark or Not? Comparing Nash–Sutcliffe and Kling–Gupta Efficiency Scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Swinkels, C.; Luijendijk, A.; Roelvink, D.; Bosboom, J.; Stive, M.; Walstra, D. Morphodynamic Upscaling with the MORFAC Approach: Dependencies and Sensitivities. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, P.; Shi, M.; Qi, J.; Ge, J. A FVCOM-Based Unstructured Grid Wave, Current, Sediment Transport Model, I. Model Description and Validation. J. Ocean Univ. China 2011, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.C.; Sherwood, C.R.; Signell, R.P.; Harris, C.K.; Arango, H.G. Development of a Three-Dimensional, Regional, Coupled Wave, Current, and Sediment-Transport Model. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1284–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaret, C. SISYPHE 6.0 User Manual; EDF: Palaiseau, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Pähtz, T.; Jiao, P.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Z. The Role of Hydrodynamics for the Spatial Distribution of High-Temperature Hydrothermal Vent-Endemic Fauna in the Deep Ocean Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Navas, J.; Telfer, T.C.; Ross, L.G. Application of 3D Hydrodynamic and Particle Tracking Models for Better Environmental Management of Finfish Culture. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, I.; Lubello, C.; Cappietti, L. On the Use of Hydrodynamic Modelling and Random Forest Classifiers for the Prediction of Hypoxia in Coastal Lagoons. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, L.; Bao, M.; Zhang, W.; Yao, W. Distinctive Hydrodynamic Properties and Ecological Responses of Multi-Thread Rivers under Different Degrees of Multiplicity in the Upper Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, R.D.S.; Rosman, P.C.C.; Vinzon, S.B. A Morphodynamic Model for Cohesive Sediments Transport. RBRH 2017, 22, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teisson, C. Cohesive Suspended Sediment Transport: Feasibility and Limitations of Numerical Modeling. J. Hydraul. Res. 1991, 29, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J.; Ma, X. The Response of Sediment Transport and Morphological Evolution to Storms with Different Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 173987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Ren, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. Response of Sediment Transport Capacity to Soil Properties and Hydraulic Parameters in the Typical Agricultural Regions of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golder, S.; McIntosh, H.M.; Loke, Y. Identifying Systematic Reviews of the Adverse Effects of Health Care Interventions. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2006, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Levasseur, A.; Gousset, H.; Le Bris, D. Estimation of the Tidal Energy Potential in the Scheldt Estuary Using a Three-Dimensional Unstructured Hydrodynamic Model. In Proceedings of the 23rd EGU General Assembly, Online, 19–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.-H.; Woo, S.-B.; Kim, S. Optimization of Influencing Factors in Tidal Current Data Assimilation Modeling in Macro Tidal Estuary, Gyeonggi Bay, South Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 114, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lim, S. Flood Inundation Modelling for Mid-Lower Brisbane Estuary: Flood Inundation Modelling. River Res. Applic. 2017, 33, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaeri, S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Strauss, D. Wave Parameter Classification Based on Morphological Changes around a Small Wave-Dominated Tidal-Inlet Using a Schematized Delft3D Model. In Proceedings of the MODSIM2015, 21st International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Broadbeach, Australia, 29 November 2015; Weber, T., McPhee, M.J., Anderssen, R.S., Eds.; Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand: Melbourne, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Carlin, G.; Steven, A.D.L.; Livsey, D.N.; Song, D.; Crosswell, J.R. A Measurement-to-Modelling Approach to Understand Catchment-to-Reef Processes: Sediment Transport in a Highly Turbid Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1215161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.; Zigic, S.; Burling, M.; Lin, H.-H. Hydrodynamic and Sediment Modelling within a Macro Tidal Estuary: Port Curtis Estuary, Australia. JMSE 2015, 3, 720–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Estimate of Uncertain Cohesive Suspended Sediment Deposition Rate from Uncertain Floc Size in Meghna Estuary, Bangladesh. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 281, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Ali, M.S. Drivers of Tidal Flow Variability in the Pussur Fluvial Estuary: A Numerical Study by HEC-RAS. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, T.A.C.; Rollnic, M. Runoff Quantification on Amazonian Estuary Based on Hydrodynamic Model. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegle, E.; Couceiro, M.A.A.; Sousa, S.H.D.M.E.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Schettini, C.A.F. Shoreline Retraction and the Opening of a New Inlet: Implications on Estuarine Processes. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 2004–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerle, R.; Narayanan, R.; Etri, T.; Abd Wahab, A.K. A Case Study of Sediment Transport in the Paranagua Estuary Complex in Brazil. Ocean Eng. 2015, 106, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, P.; Secretan, Y.; Morin, J. Hydrodynamic Modeling of the St. Lawrence Fluvial Estuary. I: Model Setup, Calibration, and Validation. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. Ocean Eng. 2017, 143, 04017010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, P.; Secretan, Y.; Morin, J. Reconstruction of Tidal Discharges in the St. Lawrence Fluvial Estuary: The Method of Cubature Revisited. JGR Ocean. 2018, 123, 5500–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, D.; Feng, T.; Tu, J.; Guo, X. Impacts of Land Reclamation Projects on Hydrodynamics and Morphodynamics in the Highly Altered North Branch of the Changjiang Estuary. Anthr. Coasts 2022, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Shi, F.; Liu, S.; Qi, D. Hydrodynamic Modeling of Changjiang Estuary: Model Skill Assessment and Large-Scale Structure Impacts. Appl. Ocean Res. 2011, 33, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, F.; Jia, J.; Feng, Z.; Tang, J.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.P. The Role of Tropical Cyclone on Changjiang River Subaqueous Delta Geomorphology: A Numerical Investigation of Tropical Cyclone Danas (2019). JGR Ocean. 2023, 128, e2022JC019190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gong, W.; Scully, M.E.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, W. Axial Wind Effects on Stratification and Longitudinal Sediment Transport in a Convergent Estuary During Wet Season. JGR Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wu, X. Dynamic Structures and Their Sedimentation Effects of the Yamen Inlet, Huangmaohai Estuary. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, H.; Dai, W.; Tao, J.; Xu, F.; Cybele, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H. 3-D Simulation of the Suspended Sediment Transport in the Jiao Jiang Estuary: Based on Validating by Remote Sensing Retrieval. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Guan, W. Fluid Mud Dynamics and Its Correlation to Hydrodynamics in Jiaojiang River Estuary, China. Ocean Sci. J. 2023, 58, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Jia, L.; He, Z.; Yu, M.; Shi, Y. Application of Parameters and Paradigms of the Erosion and Deposition for Cohesive Sediment Transport Modelling in the Lingdingyang Estuary, China. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 94, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, Z.; Su, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Hydrodynamic Interactions between Tide and Runoff in the Luanhe Estuary in Bohai Sea, China: From Aquaculture Reclamation to Restoration. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 239, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wen, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, J.T.; He, J. Wave–Current Interaction in a River and Wave Dominant Estuary: A Seasonal Contrast. Appl. Ocean Res. 2015, 52, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, F.; Jia, L.; Wei, W. Flood-Driven Jet Flow and Sedimentary Regime in a River-Dominated Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1186371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, T. Suspended Sediment Transport and Turbidity Maximum in a Macro-Tidal Estuary with Mountain Streams: A Case Study of the Oujiang Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2023, 255, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, M. Numerical Modeling of Hydrodynamic and Sediment Siltation Due to Typhoon in Estuary Channel Regulation. Pol. Marit. Res. 2015, 22, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; You, X. Numerical Simulation of Suspended Sediment Concentration by 3D Coupled Wave-Current Model in the Oujiang River Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 137, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jia, L.; Jia, Y.; He, J. Effects of Flood Events on Sediment Transport and Deposition in the Waterways of Lingding Bay, Pearl River Delta, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 185, 105062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H. Plume-to-Plume Interactions in the Pearl River Delta in Winter. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 175, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Impacts of Tidal Species on Water Level Variations in Pearl River Delta Channel Networks. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Numerical Simulation and Analysis of Saltwater Intrusion Lengths in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 29, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, W. Tidal Influence on the Discharge Distribution over the Pearl River Delta, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, S.; Geng, B. Modeling the Mass Flux Budgets of Water and Suspended Sediments for the River Network and Estuary in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 88, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; He, Z.; Jia, L. Study on the Mechanism of the Diversion of Flow and Sediment in the Complex Estuarine River Network. River Res. Apps. 2024, 40, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guan, W.; Deleersnijder, E.; He, Z. Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport Modelling in the Pearl River Estuary and Adjacent Chinese Coastal Zone during Typhoon Mangkhut. Cont. Shelf Res. 2022, 233, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W. Transport of Riverine Sediment from Different Outlets in the Pearl River Estuary during the Wet Season. Mar. Geol. 2019, 415, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Guan, W.; Cai, S.; Wei, X.; Huang, D. A Model Study of the Effects of River Discharges and Interannual Variation of Winds on the Plume Front in Winter in Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 73, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Huang, W.; Gong, W. Estimation of Riverine Sediment Fate and Transport Timescales in a Wide Estuary with Multiple Sources. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 214, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhan, H.; Cai, S.; Zhan, W.; Ni, P. Detecting the Transport Barriers in the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China with the Aid of Lagrangian Coherent Structures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 205, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Xu, S.; Huang, W. Modeling Sediment Concentration and Transport Induced by Storm Surge in Hengmen Eastern Access Channel. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 617–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.; Zhang, D.; Hu, D.; Yu, Z.; Yue, S. Tide–Surge Interactions in Lingdingyang Bay, Pearl River Estuary, China: A Case Study from Typhoon Mangkhut, 2018. Estuaries Coasts 2023, 47, 330–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wai, O.W.H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P. Flow Prediction Using ENVISAT RA-2 Sea Surface Height Validated Model: A Case Study for the Effect of Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2014, 17, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z. Modelling Study of Hydrodynamics in a Macro Tidal Estuary. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.—Marit. Eng. 2019, 172, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, C. Three-Dimensional Modelling of Sediment Transport under Tidal Bores in the Qiantang Estuary, China. J. Hydraul. Res. 2018, 56, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Huang, W. Numerical Modeling of Suspended Sediment Transport Affected by Tidal Bore in Qiantang Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, C.; Pan, D. Numerical Study of the Effect of Typhoon Yagi on the Qiantang River Tidal Bore. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, C.; Chen, F. Study on the Tidal Bore Energy along the Qiantang River Estuary, China. Water Resour. 2024, 51, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J. Simulation of Sedimentary Dynamics in a Small-Scale Estuary: The Role of Human Activities. Env. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J. Modeling Morphological Change in Anthropogenically Controlled Estuaries. Anthropocene 2017, 17, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, Z.; You, Z. Morphological Changes in a Macro-Tidal Estuary during Extreme Flooding Events. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1112494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Jalon-Rójas, I.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, Y. Impacts of Land Reclamation on Sediment Transport and Sedimentary Environment in a Macro-Tidal Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Xie, T.; Townend, I.; Zhao, T.; Cai, H. The Influence of River Discharge on Energy Transport in Estuaries and Its Implication for the Equilibrium Bed Profile. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid. Mech. 2024, 18, 2327440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, M.; Yao, S.; Jin, Z. Study on the Spillover of Sediment during Typical Tidal Processes in the Yangtze Estuary Using a High-Resolution Numerical Model. JMSE 2019, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Gu, F.; Qi, D.; Huang, W. Numerical Study of Flow and Sediment Variation Affected by Sea-Level Rise in the North Passage of the Yangtze Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 68, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, M.; Yao, S.; Jin, Z. A Case Study: Response Mechanics of Irregular Rotational Tidal Flows to Outlet Regulation in Yangtze Estuary. Water 2019, 11, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Wang, Z.; Vriend, H.; Stive, M. A Process-Based Approach to Sediment Transport in the Yangtze Estuary. Coast. Eng. 2010, 1–12. Available online: http://journals.tdl.org/icce/index.php/icce/article/view/1387/pdf_352 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Fagherazzi, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Hydro-Morphodynamics Triggered by Extreme Riverine Floods in a Mega Fluvial-Tidal Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 152076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.-J. Effects of Recent Morphological Change on the Redistribution of Flow Discharge in the Yangtze River Delta. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 208, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Dong, P. An Application of Two-Phase 1DV Model in Studying Sedimentary Processes on an Erosional Mudflat at Yangtze River Delta, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Hoitink, A.J.F.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, F.; Zheng, J. Tidal Impacts on the Subtidal Flow Division at the Main Bifurcation in the Yangtze River Delta. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Huang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Su, L.; Hong, Y.; Lu, T.; Wang, X. Numerical Analysis of Sediment Deposition in Yangtze River Estuary: Insight from Conceptual Estuary Models. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 104, 102372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xing, F.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, F.; He, H.; Zhang, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.P. Sediment Exchange between Southern Yellow Sea and Yangtze River Estuary in Response to Storm Events. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 293, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, B.; Tang, Q. Integrated Modeling Analysis of Estuarine Responses to Extreme Hydrological Events and Sea-Level Rise. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 261, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Deng, G.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J. Effects of Sea Level Rise on Storm Surge and Waves within the Yangtze River Estuary. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 13, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhu, D.; He, L.; Huang, H. Numerical Assessment of the Impacts of Potential Future Sea-Level Rise on Hydrodynamics of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S. Dynamic Response of Water Flow and Sediment Transport off the Yellow River Mouth to Tides and Waves in Winter. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1181347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Yi, Y. Numerical Study of the Water-Sediment Regulation Scheme (WSRS) Impact on Suspended Sediment Transport in the Yellow River Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1135118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, S.; Pan, S.; Dou, S. Storm-Induced Hydrodynamic Changes and Seabed Erosion in the Littoral Area of Yellow River Delta: A Model-Guided Mechanism Study. Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 205, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Pan, S.; Chen, S. Impact of River Discharge on Hydrodynamics and Sedimentary Processes at Yellow River Delta. Mar. Geol. 2020, 425, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, B.; Okon, S.U.; Li, L. Numerical Investigation of the Sediment Hyperpycnal Flow in the Yellow River Estuary. JMSE 2022, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, J.; Jia, Y. Comparison of the Causes of Erosion–Deposition between Yellow River, Yangtze River, and Mekong River Subaqueous Delta l: Model Building. Water 2022, 14, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Cai, S. Modeling of Suspended Sediment by Coupled Wave-Current Model in the Zhujiang (Pearl) River Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Niu, J.; Liu, G.; Wei, X.; Cai, S. Variations of Suspended Sediment Transport Caused by Changes in Shoreline and Bathymetry in the Zhujiang (Pearl) River Estuary in the Wet Season. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Marchena, C.A.; Flores, R.P.; Aiken, C.M. Impacts of Training Wall Construction on Littoral Sedimentation under Seasonal Flow Variability and Sea-Level Rise: A Case Study of the Magdalena River (Colombia). Coast. Eng. 2023, 183, 104306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.T.K.; Huybrechts, N.; Sergent, P. Sand Net Device to Control the Meanders of a Coastal River: The Case of the Authie Estuary (France). JMSE 2021, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toublanc, F.; Brenon, I.; Coulombier, T.; Le Moine, O. Fortnightly Tidal Asymmetry Inversions and Perspectives on Sediment Dynamics in a Macrotidal Estuary (Charente, France). Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 94, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, L.; Valle-Levinson, A.; Sottolichio, A.; Huybrechts, N. Lateral Variability of Subtidal Flow at the Mid-reaches of a Macrotidal Estuary. JGR Ocean. 2017, 122, 7651–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orseau, S.; Huybrechts, N.; Tassi, P.; Pham Van Bang, D.; Klein, F. Two-Dimensional Modeling of Fine Sediment Transport with Mixed Sediment and Consolidation: Application to the Gironde Estuary, France. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborie, V.; Ricci, S.; De Lozzo, M.; Goutal, N.; Audouin, Y.; Sergent, P. Quantifying Forcing Uncertainties in the Hydrodynamics of the Gironde Estuary. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 24, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rtimi, R.; Sottolichio, A.; Tassi, P. Hydrodynamics of a Hyper-Tidal Estuary Influenced by the World’s Second Largest Tidal Power Station (Rance Estuary, France). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Grasso, F.; Le Hir, P.; Verney, R.; Thouvenin, B. Suspended Sediment Dynamics in the Macrotidal Seine Estuary (France): 2. Numerical Modeling of Sediment Fluxes and Budgets Under Typical Hydrological and Meteorological Conditions. JGR Ocean. 2018, 123, 578–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothmann, J.; Schuster, D.; Kappenberg, J.; Ohle, N. Efficiency of Artificial Sandbanks in the Mouth of the Elbe Estuary for Damping the Incoming Tidal Energy; RWTH Aachen University: Aachen, Germany, 2011; Volume 6, p. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, E. Storm Surges in the Elbe, Jade-Weser and Ems Estuaries. Die Küste 2014, 81, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Dong, P. Two-Phase Flow Modelling of Sediment Suspension in the Ems/Dollard Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 191, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberrecht, D.; Wurpts, A. Impact of Controlled Tidal Barrier Operation on Tidal Dynamics in the Ems Estuary. Die Küste 2014, 81, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Herrling, G.; Becker, M.; Lefebvre, A.; Zorndt, A.; Krämer, K.; Winter, C. The Effect of Asymmetric Dune Roughness on Tidal Asymmetry in the Weser Estuary. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 2211–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pein, J.U.; Stanev, E.V.; Zhang, Y.J. The Tidal Asymmetries and Residual Flows in Ems Estuary. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1719–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Jena, G.; Jain, I.; Rao, A.; Husain, M.L. Numerical Modelling of Tidal Circulation and Sediment Transport in the Gulf of Khambhat and Narmada Estuary, West Coast of India. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 18, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, U.K.; Mishra, P.; Mohanty, P.K.; Panda, U.S.; Ramanamurthy, M.V. Modeling of Tidal Circulation and Sediment Transport near Tropical Estuary, East Coast of India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudi, N.R.; Suntoyo; Pratikto, W.A. Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport Simulation at The Port of The Electric Steam Power Plant Adipala and Serayu Estuary, Central Java Province, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 698, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Velamala, S.N.; Prasad, K.V.S.R. Numerical Simulation of Tidal Constituents in Thane Creek and the Ulhas Estuary, West Coast of India. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, M.; Hendriyono, W.; Rahman, R.A.; Susatijo, G.; Kongko, W.; Istiyanto, D.C.; Widagdo, A.B.; Nugroho, S.; Khoirunnisa, H.; Wiguna, E.; et al. Sediment Transport Modeling at Jelitik Estuary, Sungailiat—Bangka Regency for the Design of Sediment Control Structures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1625, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisha, U.J.; Wijaya, Y.J.; Hisaki, Y. Tidal Bore Generation and Transport Mechanism in the Rokan River Estuary, Indonesia: Hydro-Oceanographic Perspectives. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postacchini, M.; Darvini, G.; Perugini, E.; Martinelli, J.; Ilari, M.; Brocchini, M. Upriver Propagation of Tidal Waves and Mouth Bar Influence at a Microtidal Estuary: Observations and Modeling; IAHR: Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Baldoni, A.; Perugini, E.; Penna, P.; Parlagreco, L.; Brocchini, M. A Comprehensive Study of the River Plume in a Microtidal Setting. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 275, 107995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Salleh, S.H.; Ahmad, A.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Lim, C.H.; Abdul Maulud, K.N. Effect of Projected Sea Level Rise on the Hydrodynamic and Suspended Sediment Concentration Profile of Tropical Estuary. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 24, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, C.-L.; Ling, T.-Y.; Nyanti, L. Hydrodynamic Modeling of a Tropical Tidal River Using the Dynamic Estuary Model (DYNHYD5): A Case Study in Sibu Laut River, Sarawak, Malaysia. Model. Simul. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Assaoui, N.; Sadok, A.; Bendaraa, A.; Charafi, M.M. Two-Dimensional Numerical Modeling of Morphodynamic Evolution in Bouregreg Estuary (Morocco). Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzualo, T.N.M.; Gallo, M.N.; Vinzon, S.B. Short-Term Tidal Asymmetry Inversion in a Macrotidal Estuary (Beira, Mozambique). Geomorphology 2018, 308, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.S.; Egashira, S.; Harada, D. Tidal Currents and Sand Bar Evolution in Sittaung River Estuary, Myanmar. In Proceedings of the IAHR-APD Congress, Sapporo, Japan, 14–17 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Siemes, R.W.A.; Duong, T.M.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Morphological Response of a Highly Engineered Estuary to Altering Channel Depth and Restoring Wetlands. JMSE 2023, 11, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plancke, Y.; Stark, J.; Meire, D.; Schrijver, M. Complex Flow Patterns in the Scheldt Estuary: Field Measurements and Validation of a Hydrodynamic Model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 146, 05020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, W.M.; Hiatt, M.R.; Van Der Werf, J.J.; Kleinhans, M.G. Effects of Shoal Margin Collapses on the Morphodynamics of a Sandy Estuary. JGR Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, T.; Vanlede, J.; De Kok, J. Development of a Mud Transport Model for the Scheldt Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S165–S181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stark, J.; Smolders, S.; Meire, P.; Temmerman, S. Impact of Intertidal Area Characteristics on Estuarine Tidal Hydrodynamics: A Modelling Study for the Scheldt Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Toorman, E.A. Mixed-Sediment Transport Modelling in Scheldt Estuary with a Physics-Based Bottom Friction Law. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 555–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejeans, B.S.; Mullarney, J.C.; MacDonald, I.T.; Reeve, G.M. Assessment of the Performance of a Turbulence Closure Model: Along the Tidally-Influenced Kaipara River to the Estuary, NZ. In Australasian Coasts & Ports 2017: Working with Nature: Working with Nature; Engineers Australia, PIANC Australia and Institute of Professional Engineers: Barton, Australia, 2017; pp. 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.C.; De Lange, W.P.; Bryan, K.R. Estuary Rejuvenation in Response to Sea Level Rise: An Example from Tairua Estuary, New Zealand. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2020, 40, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoch, P.; Christian, F.; Emanuel, G.; Leo, G.; Carlos, A.; Jorge, D. Analysis of Hydrodynamic Patterns and Suspended Sediment Transport in the Virrilá Estuary-Peru; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Szydłowski, M. Hydraulic Analysis of Causes of Washout of Gdynia-Orłowo Sea-Shore during the Flood in the Kacza River Estuary. Pol. Marit. Res. 2019, 26, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeiro-Gonçalves, F.; Bio, A.; Iglesias, I.; Avilez-Valente, P. Sea Level Rise Effects on the Sedimentary Dynamics of the Douro Estuary Sandspit (Portugal). Water 2023, 15, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, I.; Bio, A.; Melo, W.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Pinho, J.; Cruz, M.; Gomes, A.; Vieira, J.; Bastos, L.; Veloso-Gomes, F. Hydrodynamic Model Ensembles for Climate Change Projections in Estuarine Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, I.; Venâncio, S.; Pinho, J.L.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Vieira, J.M.P. Two Models Solutions for the Douro Estuary: Flood Risk Assessment and Breakwater Effects. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Vaz, N.; Dias, J.M. Potential Impacts of the Mean Sea Level Rise on the Hydrodynamics of the Douro River Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 165, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, L.; Dias, J. The Effect of Tidal Regime and River Flow on the Hydrodynamics and Salinity Structure of the Lima Estuary: Use of a Numerical Model to Assist on Estuary Classification. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 1604–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, I.; Pinho, J.L.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Melo, W.; Bio, A.; Gomes, A.; Vieira, J.; Bastos, L.; Veloso-Gomes, F. Improving Estuarine Hydrodynamic Forecasts Through Numerical Model Ensembles. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 812255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fernández, S.; Ferreira, C.C.; Silva, P.A.; Baptista, P.; Romão, S.; Fontán-Bouzas, Á.; Abreu, T.; Bertin, X. Assessment of Dredging Scenarios for a Tidal Inlet in a High-Energy Coast. JMSE 2019, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, A.B.; Freire, P.; Mengual, B.; Bertin, X.; Pinto, C.; Martins, K.; Guérin, T.; Azevedo, A. Sediment Dynamics and Morphological Evolution in the Tagus Estuary Inlet. Mar. Geol. 2021, 440, 106590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.; Valentim, J. Numerical Modeling of Tagus Estuary Tidal Dynamics. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, G.; Pinto, L.; Ascione, I.; Mateus, M.; Fernandes, R.; Leitão, P.; Neves, R. Modelling of Cohesive Sediment Dynamics in Tidal Estuarine Systems: Case Study of Tagus Estuary, Portugal. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, E.; Leummens, M.; Lebedeva, S. Hydrodynamic Modelling of the Onega River Tidal Estuary. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 163, 01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, S.; Santamaria-Aguilar, S.; Van Niekerk, L.; Lück-Vogel, M.; Vafeidis, A.T. Investigating the Interaction of Waves and River Discharge during Compound Flooding at Breede Estuary, South Africa. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Lee, G.; Harris, C.K.; Song, Y.; Figueroa, S.M.; Schieder, N.W.; Lagamayo, K.D. Sediment Transport Mechanisms in Altered Depositional Environments of the Anthropocene Nakdong Estuary: A Numerical Modeling Study. Mar. Geol. 2020, 430, 106364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Lee, G.; Harris, C.K.; Figueroa, S.M.; Jung, N.W. Relative Contribution of the Presence of an Estuarine Dam and Land Reclamation to Sediment Dynamics of the Nakdong Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, U.; Jang, E.-K.; Kim, G. Numerical Modeling of Sedimentation Control Scenarios in the Approach Channel of the Nakdong River Estuary Barrage, South Korea. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Winterwerp, J.C.; He, Q. Interaction between Suspended Sediment and Tidal Amplification in the Guadalquivir Estuary. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge-Ganuzas, M.; Evans, G.; Cearreta, A. Sand-Spit Accumulations at the Mouths of the Eastern Cantabrian Estuaries: The Example of the Oka Estuary (Urdaibai Biosphere Reserve). Quat. Int. 2015, 364, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prumm, M.; Iglesias, G. Impacts of Port Development on Estuarine Morphodynamics: Ribadeo (Spain). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 130, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, G.; Carballo, R. Can the Seasonality of a Small River Affect a Large Tide-Dominated Estuary? The Case of Ría de Viveiro, Spain. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 277, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestres, M.; Cerralbo, P.; Grifoll, M.; Sierra, J.P.; Espino, M. Modelling Assessment of the Tidal Stream Resource in the Ria of Ferrol (NW Spain) Using a Year-Long Simulation. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, J.F.; García-Alba, J.; García, A.; Álvarez, C. Analysis of Stratification Patterns in River-Influenced Mesotidal and Macrotidal Estuaries Using 3D Hydrodynamic Modelling and K-Means Clustering. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, J.F.; García, A.; García, J.; Álvarez, C.; Revilla, J.A. Surface Analysis of Free Surface and Velocity to Changes in River Flow and Tidal Amplitude on a Shallow Mesotidal Estuary: An Application in Suances Estuary (Nothern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, I.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Bio, A.; Bastos, L. Modelling the Main Hydrodynamic Patterns in Shallow Water Estuaries: The Minho Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, W.; Pinho, J.; Iglesias, I.; Bio, A.; Avilez-Valente, P.; Vieira, J.; Bastos, L.; Veloso-Gomes, F. Hydro- and Morphodynamic Impacts of Sea Level Rise: The Minho Estuary Case Study. JMSE 2020, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.P. Modelling the Effects of Typhoons on Morphological Changes in the Estuary of Beinan, Taiwan. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 135, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-B.; Liu, W.-C.; Kimura, N.; Hsu, M.-H. Particle Release Transport in Danshuei River Estuarine System and Adjacent Coastal Ocean: A Modeling Assessment. Env. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 407–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Shahkolahi, A.; Liu, W.-C. Modeling of Hydrodynamics and Cohesive Sediment Processes in an Estuarine System: Study Case in Danshui River. Env. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hsieh, T.-C.; Yeh, K.-C. Modeling Morphological Changes Due to Multiple Typhoons in the Danshui River Estuary. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2015, Austin, TX, USA, 15 May 2015; American Society of Civil Engineers: Austin, TX, USA, 2015; pp. 1522–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Fang, H.-M. Sung-Shan Hsiao Morphological Characteristics of Tidal Inlets Subject to a Short Term Typhoon Event: A Case Study in Lanyan River Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2018, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-C.; Ding, Y.; Yeh, K.-C.; Jhong, R.-K. Investigation of Morphological Changes in the Tamsui River Estuary Using an Integrated Coastal and Estuarine Processes Model. Water 2020, 12, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-C.; Ding, Y.; Yeh, K.-C.; Jhong, R.-K. Numerical Investigation of Sediment Flushing and Morphological Changes in Tamsui River Estuary through Monsoons and Typhoons. Water 2022, 14, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, C.-H.; Chen, J.-L.; Su, S.-F.; Huang, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-H.; Kuo, C.-H. The Effect of Wave-Induced Current and Coastal Structure on Sediment Transport at the Zengwen River Mouth. JMSE 2021, 9, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.G.; Van Veelen, T.J.; Fairchild, T.P.; Griffin, J.N.; Karunarathna, H. Computational Modelling of the Impacts of Saltmarsh Management Interventions on Hydrodynamics of a Small Macro-Tidal Estuary. JMSE 2020, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Stephens, J.A.; Harris, C. Towards Predicting the Influence of Freshwater Abstractions on the Hydrodynamics and Sediment Transport of a Small, Strongly Tidal Estuary: The Devonshire Avon. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 79, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.R. Critical Perspectives on the Evaluation and Optimization of Complex Numerical Models of Estuary Hydrodynamics and Sediment Dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyddon, C.; Chien, N.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Ridgill, M.; Moradian, S.; Olbert, A.; Coulthard, T.; Barkwith, A.; Robins, P. Thresholds for Estuarine Compound Flooding Using a Combined Hydrodynamic–Statistical Modelling Approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 24, 973–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Karunarathna, H.; Reeve, D.E. A Computational Investigation of Storm Impacts on Estuary Morphodynamics. JMSE 2019, 7, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Karunarathna, H.; Reeve, D.E. Numerical Modelling of Hydrodynamic and Morphodynamic Response of a Meso-Tidal Estuary Inlet to the Impacts of Global Climate Variabilities. Mar. Geol. 2019, 407, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, P.E.; Davies, A.G. Morphological Controls in Sandy Estuaries: The Influence of Tidal Flats and Bathymetry on Sediment Transport. Ocean Dyn. 2010, 60, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Leonardi, N.; Plater, A.J. Wave-Driven Sediment Resuspension and Salt Marsh Frontal Erosion Alter the Export of Sediments from Macro-Tidal Estuaries. Geomorphology 2019, 325, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Plater, A.; Leonardi, N. Modelling the Transport and Export of Sediments in Macrotidal Estuaries with Eroding Salt Marsh. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 1551–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, M.; Sun, Z.; O’Connor, B.A. Numerical Modelling of Hydrodynamics and Sand Transport in the Tide-Dominated Coastal-to-Estuarine Region. Mar. Geol. 2013, 342, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B.; Tan, G. Modelling Flood Routing on Initially Dry Beds with the Refined Treatment of Wetting and Drying. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2010, 8, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Justic, D.; Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W.; Cable, J.E. Hydrodynamic Response of the Breton Sound Estuary to Pulsed Mississippi River Inputs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Xue, Z.G.; Warner, J.C.; Moulton, M.; Yin, D.; Hegermiller, C.A.; Zambon, J.B.; He, R. A Numerical Investigation of Hurricane Florence-Induced Compound Flooding in the Cape Fear Estuary Using a Dynamically Coupled Hydrological-Ocean Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2022MS003131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, M.; Ni, W. Roles of Wind-Driven Currents and Surface Waves in Sediment Resuspension and Transport During a Tropical Storm. JGR Ocean. 2018, 123, 8638–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Generation of an Estuarine Sediment Plume by a Tropical Storm. JGR Ocean. 2013, 118, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savant, G.; McAlpin, T.O. Tidal Hydrodynamics in the Lower Columbia River Estuary through Depth Averaged Adaptive Hydraulics Modeling. J. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyar, R.; Maitaria, K.; Velissariou, P.; Trimble, B.; Mashriqui, H.; Moghimi, S.; Abdolali, A.; Van Der Westhuysen, A.J.; Ma, Z.; Clark, E.P.; et al. A New 1D/2D Coupled Modeling Approach for a Riverine-Estuarine System Under Storm Events: Application to Delaware River Basin. JGR Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Marr, C. Spatial Variability of Hydrodynamic Timescales in a Broad and Shallow Estuary: Mobile Bay, Alabama. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talke, S.A.; Familkhalili, R.; Jay, D.A. The Influence of Channel Deepening on Tides, River Discharge Effects, and Storm Surge. JGR Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, L.; Erikson, L.; Barnard, P. Storm Surge Propagation and Flooding in Small Tidal Rivers during Events of Mixed Coastal and Fluvial Influence. JMSE 2018, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.; Nelson, K.S.; Holleman, R.C.; Fringer, O.B.; Stacey, M.T.; Lacy, J.R.; Monismith, S.G.; Koseff, J.R. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Fine Sediment Transport by Waves and Currents in a Shallow Estuary. JGR Ocean. 2018, 123, 4177–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Traykovski, P.A.; Nidzieko, N.J. Effects of Estuarine and Fluvial Processes on Sediment Transport over Deltaic Tidal Flats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 60, S40–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Khangaonkar, T.; Calvi, M.; Nelson, K. Simulation of Cumulative Effects of Nearshore Restoration Projects on Estuarine Hydrodynamics. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacopoulos, P.; Hagen, S.C.; Cox, A.T.; Dally, W.R.; Bratos, S.M. Observation and Simulation of Winds and Hydrodynamics in St. Johns and Nassau Rivers. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Camacho, R.A.; Martin, J.L.; Diaz-Ramirez, J.; McAnally, W.; Rodriguez, H.; Suscy, P.; Zhang, S. Uncertainty Analysis of Estuarine Hydrodynamic Models: An Evaluation of Input Data Uncertainty in the Weeks Bay Estuary, Alabama. Appl. Ocean Res. 2014, 47, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, C.D. Effects of Hydrodynamical Regime on Morphological Evolution at Cua Dai Estuary and Coastlines of Quang Nam Province. Vietnam J. Earth Sci. 2020, 42, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, S.; Hoekstra, P.; Kernkamp, H.; Nguyen Trung, N.; Do Duc, D.; Tran Quang, T.; Februarianto, M.; Van Dam, A.; Van Der Vegt, M. Flow Division Dynamics in the Mekong Delta: Application of a 1D-2D Coupled Model. Water 2019, 11, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, V.Q.; Reyns, J.; Wackerman, C.; Eidam, E.F.; Roelvink, D. Modelling Suspended Sediment Dynamics on the Subaqueous Delta of the Mekong River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy Vinh, V.; Ouillon, S.; Van Thao, N.; Ngoc Tien, N. Numerical Simulations of Suspended Sediment Dynamics Due to Seasonal Forcing in the Mekong Coastal Area. Water 2016, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Anh, L.; Duc Tran, D.; Thong, N.; Thu Van, C.; Hoa Vinh, D.; Hai Au, N.; Park, E. Drastic Variations in Estuarine Morphodynamics in Southern Vietnam: Investigating Riverbed Sand Mining Impact through Hydrodynamic Modelling and Field Controls. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Meselhe, E.A.; Allison, M.A.; Weathers, H.D. Analysis and Numerical Modeling of the Flow and Sand Dynamics in the Lower Song Hau Channel, Mekong Delta. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 147, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, N.; Duc, H.T.; Hung, P.Q.; Yen, T.H. Numerical Study of Sediment Transport in Thu-Bon Estuary and Coastal Areas of Hoi-An City. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 964, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
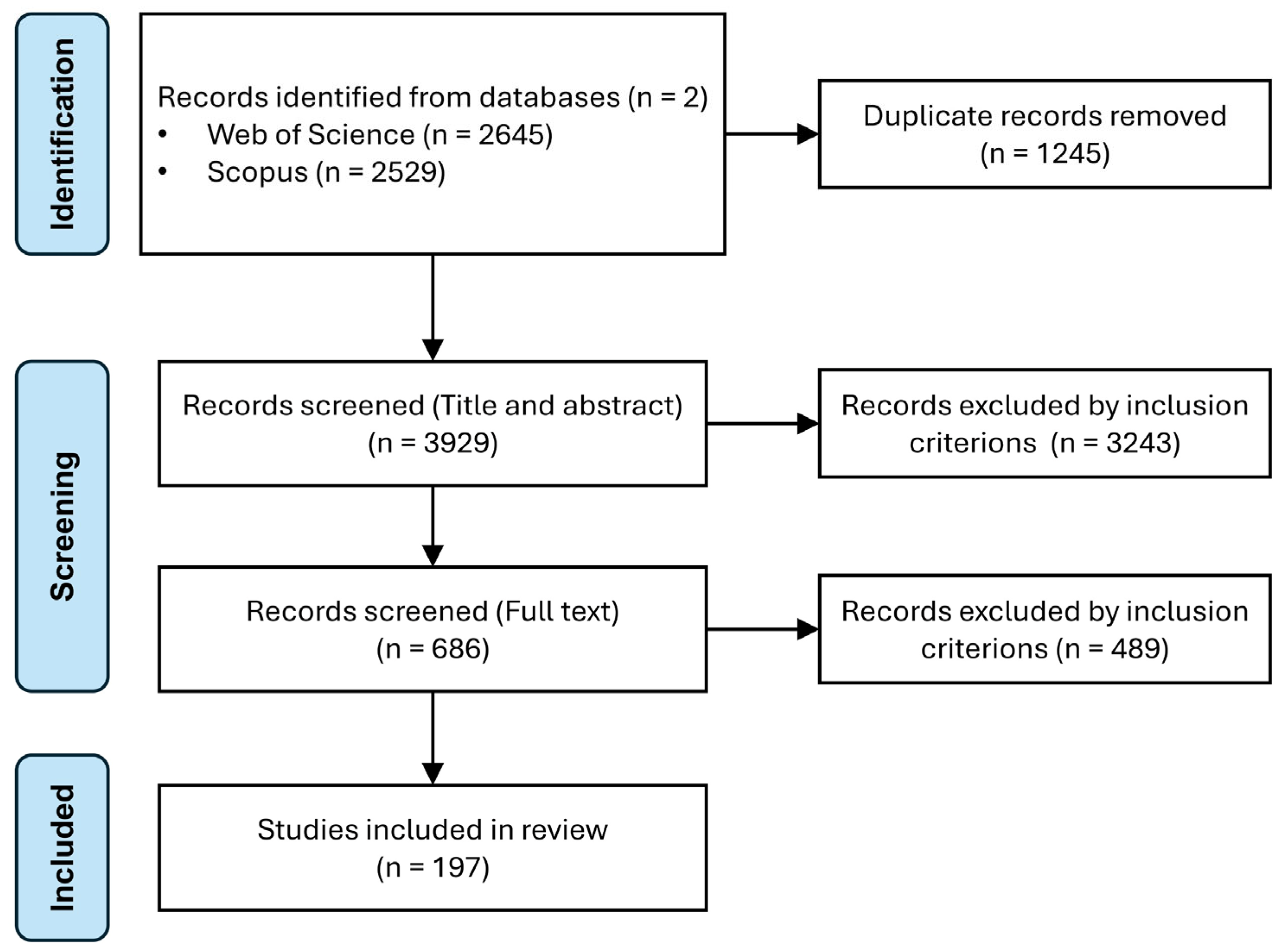
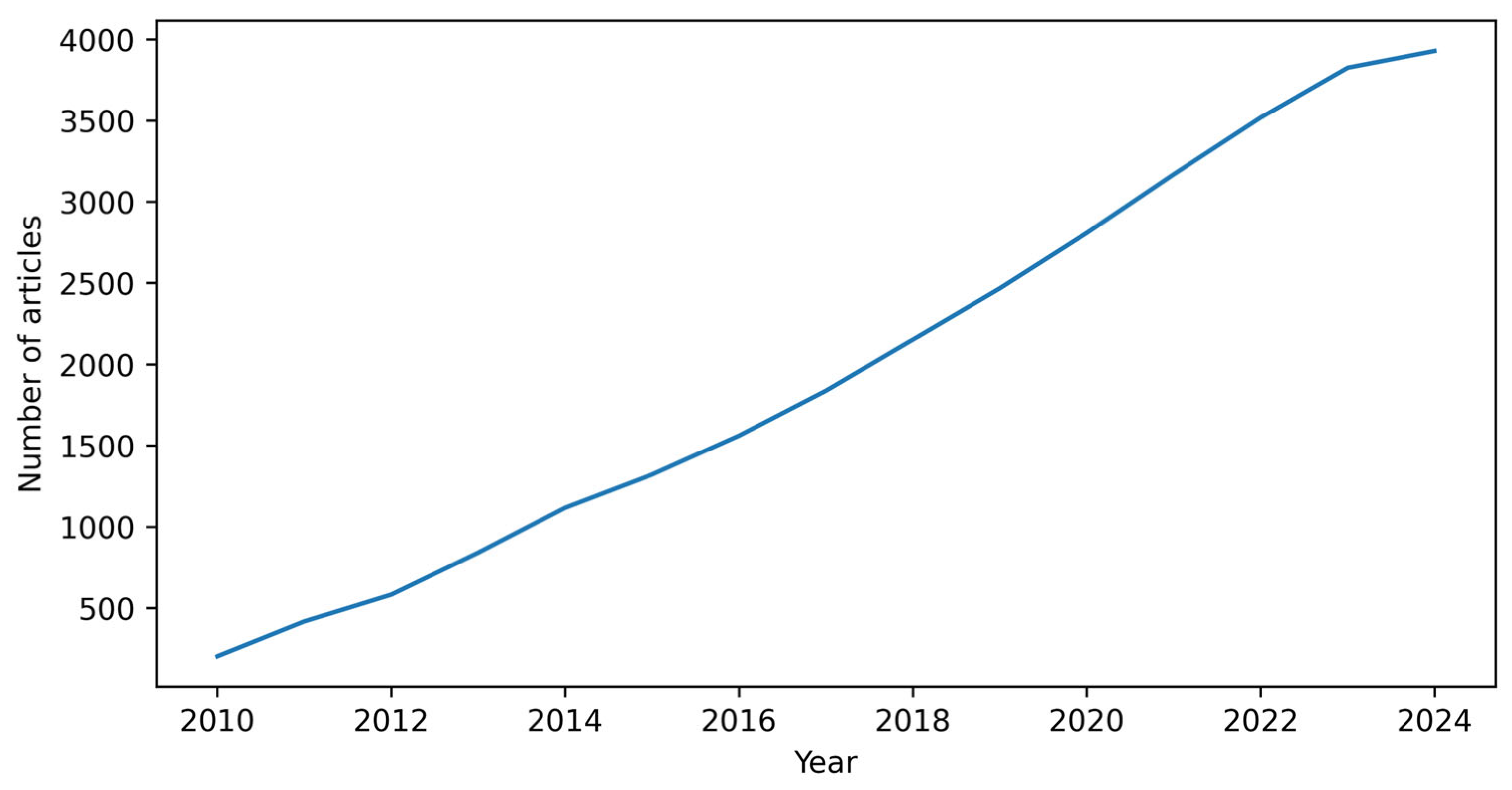
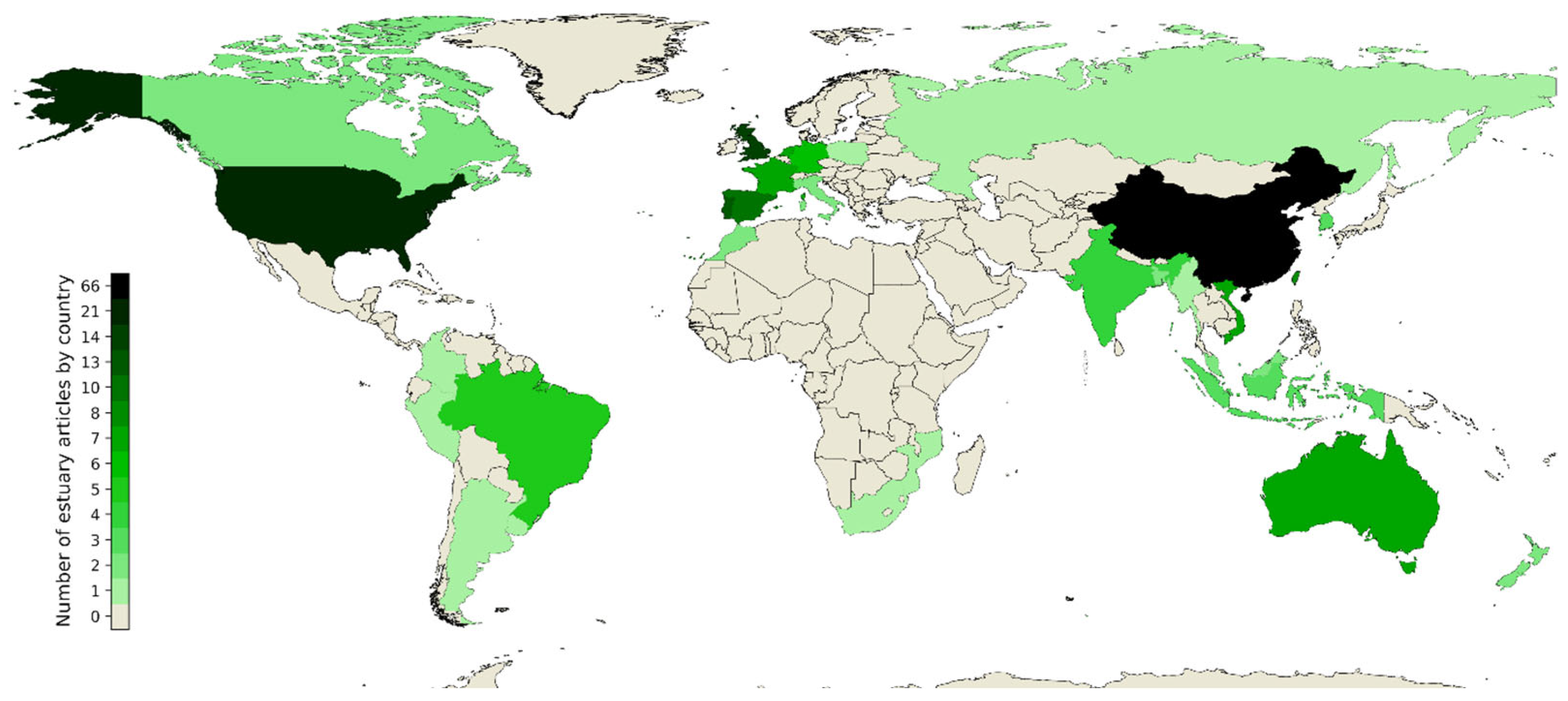
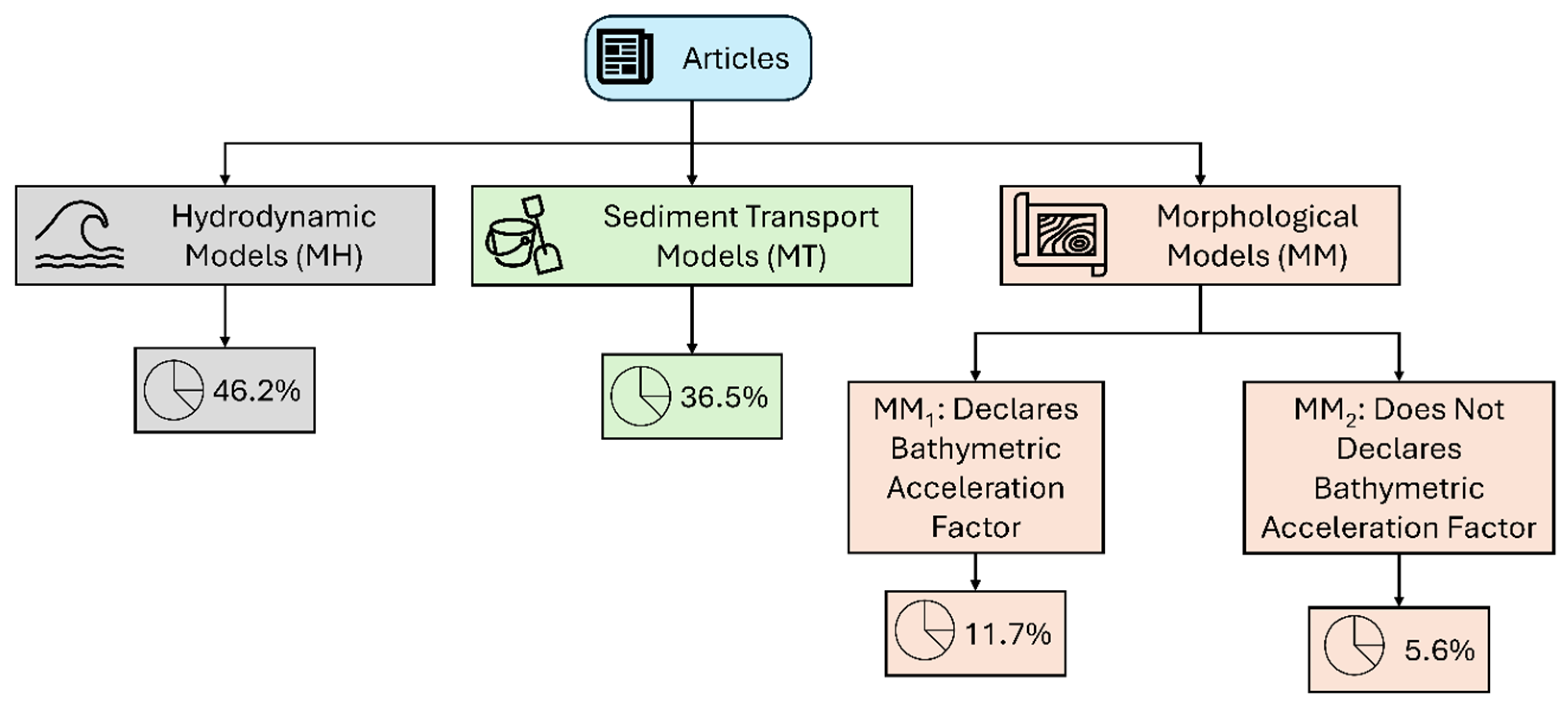
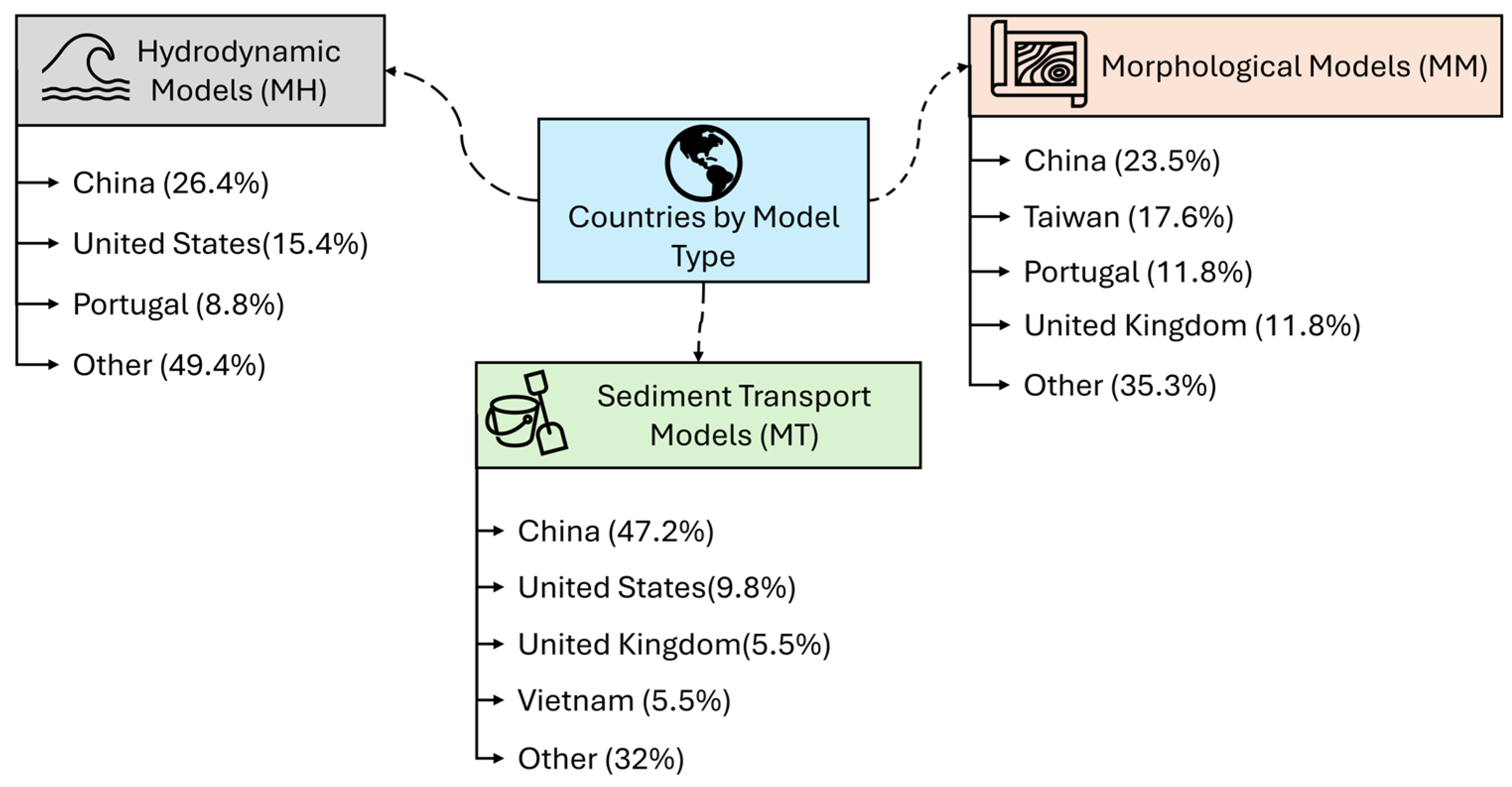
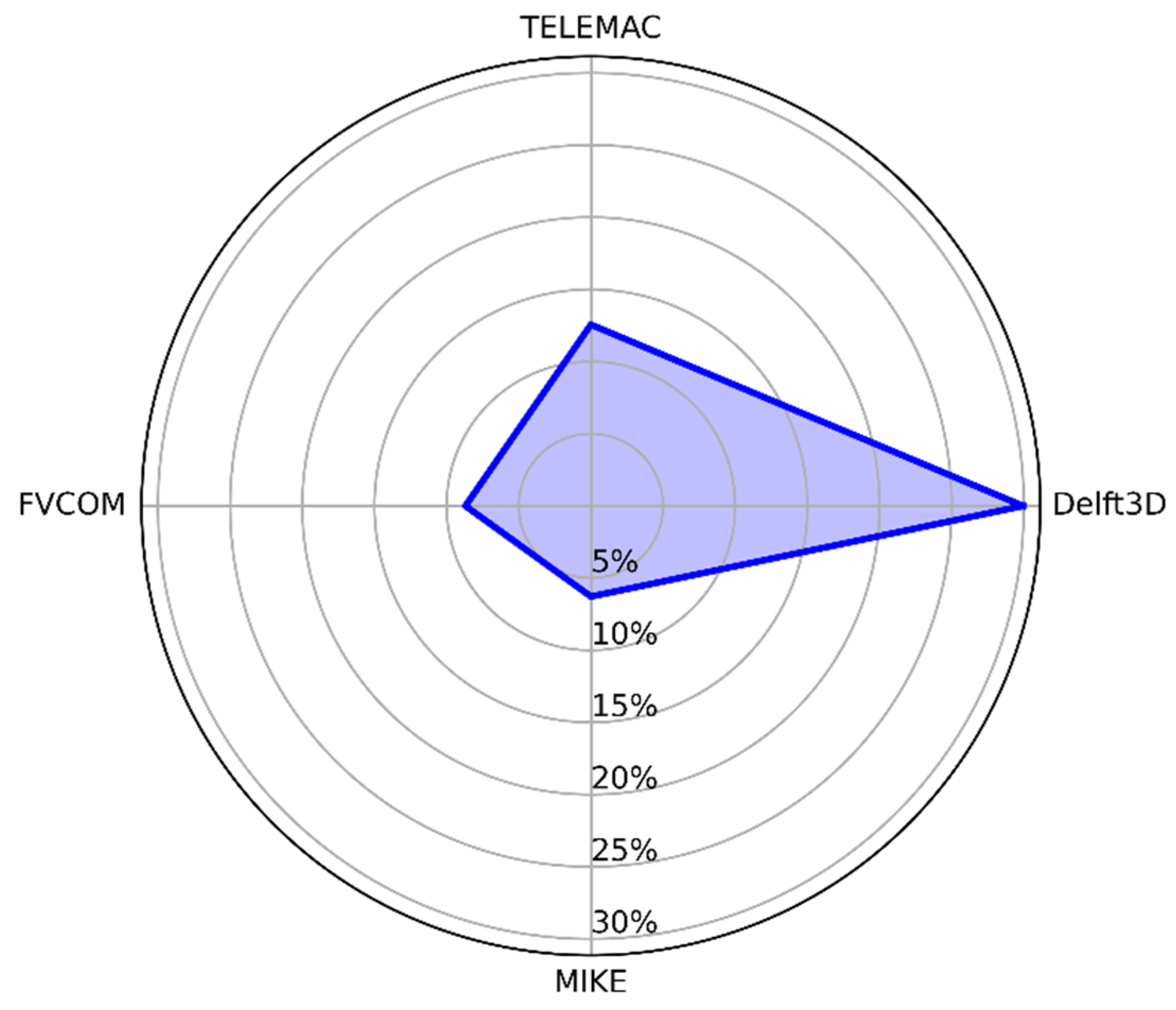

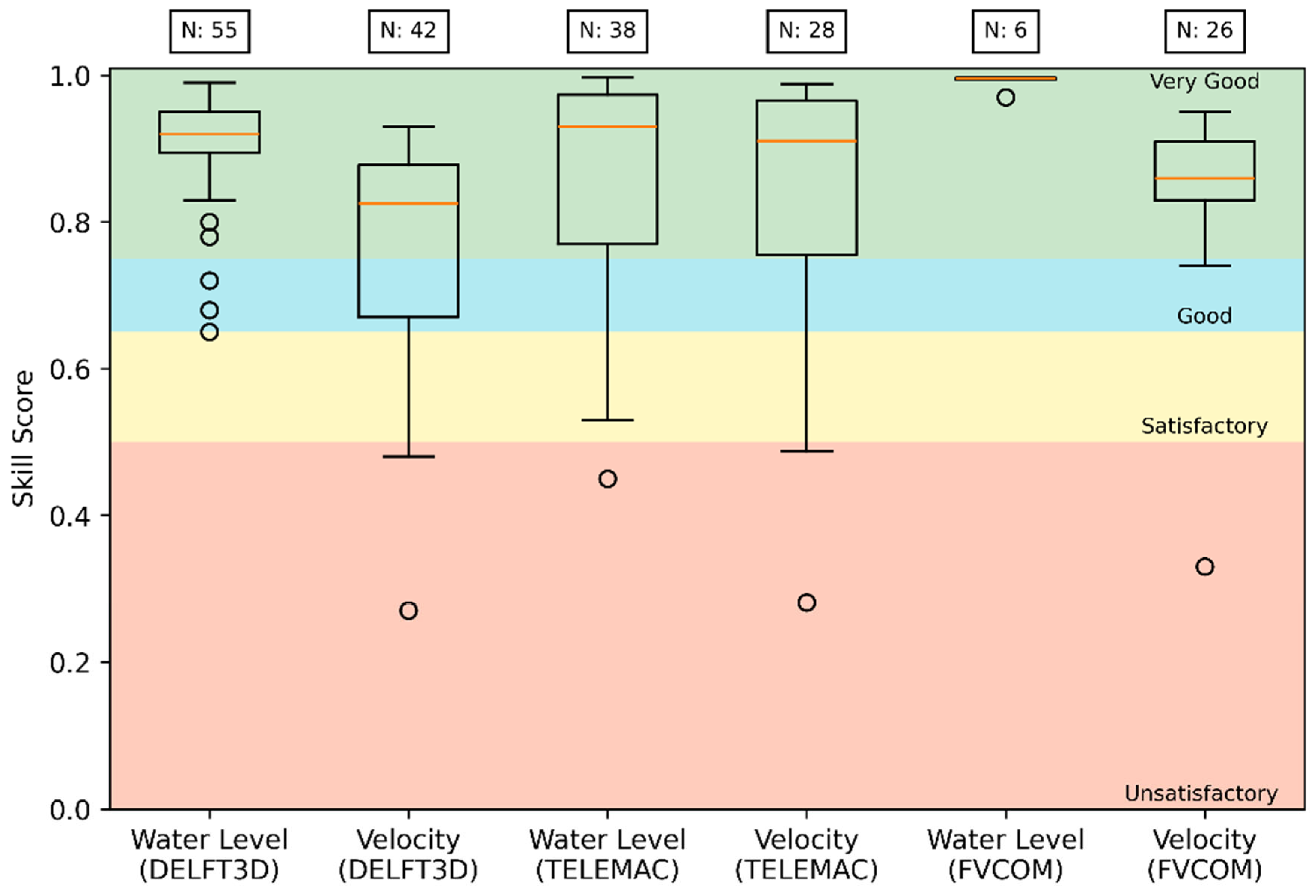

| Language | English and Spanish |
|---|---|
| Document Type ** | WoS: Articles, proceeding papers, and early access Scopus: Articles and conference papers. |
| Subject of Interest * | Maximum 1 year of modeling performed in estuaries. |
| Search Period ** | From 2010 to 2024. |
| Access Type * | All articles meeting the criteria were selected from Open Access journals or accessible through a subscription held by the Universidad Católica de la Santísima Concepción. |
| MH | MT | MM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | 3D | Total | 2D | 3D | Total | 2D | 3D | Total | |
| Structured | 34% | 16% | 50% | 19% | 40% | 60% | 53% | 3% | 56% |
| Unstructured | 38% | 12% | 50% | 21% | 19% | 40% | 38% | 6% | 44% |
| Total | 72% | 28% | 100% | 40% | 60% | 100% | 91% | 9% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora-Uribe, N.; Caamaño-Avendaño, D.; Villagrán-Valenzuela, M.; Roco-Videla, Á.; Alcayaga, H. Trends and Applications of Hydro-Morphological Modeling in Estuarine Systems: A Systematic Review of the Past 15 Years. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061056
Mora-Uribe N, Caamaño-Avendaño D, Villagrán-Valenzuela M, Roco-Videla Á, Alcayaga H. Trends and Applications of Hydro-Morphological Modeling in Estuarine Systems: A Systematic Review of the Past 15 Years. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora-Uribe, Nicolás, Diego Caamaño-Avendaño, Mauricio Villagrán-Valenzuela, Ángel Roco-Videla, and Hernán Alcayaga. 2025. "Trends and Applications of Hydro-Morphological Modeling in Estuarine Systems: A Systematic Review of the Past 15 Years" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061056
APA StyleMora-Uribe, N., Caamaño-Avendaño, D., Villagrán-Valenzuela, M., Roco-Videla, Á., & Alcayaga, H. (2025). Trends and Applications of Hydro-Morphological Modeling in Estuarine Systems: A Systematic Review of the Past 15 Years. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061056








