1. Introduction
With the development of the economy, maritime transportation has become one of the most important modes of transportation in the global logistics network. As a key link in international trade, maritime transport not only undertakes the task of transporting commodities but also connects the world‘s major economies [
1,
2,
3]. As one of the key factors affecting ship transportation, weather directly affects the economy and safety of ships. Through the real-time acquisition and processing of weather information, ships can better cope with bad weather and optimize route planning, thereby improving the safety and efficiency of navigation [
4,
5,
6,
7]. Therefore, the accurate analysis of weather data is very important for ensuring navigation safety and improving the economic benefits of ships.
At present, many scholars have studied this field. For example, Du et al. [
8] introduced a refined three-dimensional dynamic programming approach to optimize ship routing. This method plans the ship’s course and speed according to weather conditions and limiting factors and generates an optimal solution for ship route planning. However, the optimization results of this method are greatly affected by the grid’s discrete step size. Zhao [
9] proposed a multi-objective optimal ship navigation planning model. The experimental results showed that the algorithm can achieve safe, efficient, and economical navigation goals. However, the model does not take visibility and other ship factors into account when calculating navigation risk. Nuñez et al. [
10] introduced a stochastic ship routing model that leverages a conditional risk value metric to guide an enhanced continuous belief tree search algorithm in identifying safe and fuel-efficient long-distance routes. Charalambopoulos et al. [
11] proposed an improved PRM algorithm, and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm was proved by the simulation of the Aegean Islands and the Mediterranean. However, the ship speed considered in this model is only affected by the waves, and the input characteristics are relatively simple. Wu et al. [
12] developed a Transformer-based time series model to reconstruct spatio-temporally discrete weather forecast data, aiming to enhance voyage optimization accuracy. The reconstructed forecasts were validated against observed weather data, confirming their reliability and precision. However, the model does not take into account the problems of ship stall and fuel consumption. Kaklis et al. [
13] presented a navigation planning approach aimed at delivering optimal route suggestions for vessels. Experimental comparisons with a leading routing method demonstrated that it could reduce voyage length, leading to cost savings for the maritime industry. However, the cost function designed by this method is relatively simple and lacks important factors such as weather and fuel consumption. Guzelbulut et al. [
14] used artificial neural networks to establish an energy model based on environmental conditions, ship routes, and ship speeds. Findings indicated that the method helped lower energy usage throughout a ship’s operational lifespan. However, the model lacks consideration of the dynamic environment, which may reduce the practicability of the model. Pennino et al. [
15] proposed an adaptive weather routing model based on Dijkstra’s shortest-path algorithm. The results of the study showed that high ship seaworthiness can be achieved without excessively increasing the length of the route and the duration of the voyage. However, this method requires further research on the incidence of selected seakeeping standards in route evaluation.
It can be seen that many studies have effectively improved the effectiveness of ship route planning. However, there are still some limitations in the existing research. For example, due to the insufficient coverage of the maritime network, the high cost of satellite communication, and the limited bandwidth, it is difficult for ships to obtain high-resolution weather forecast data during route planning. This limitation makes it impossible for ships to obtain accurate weather information in real time, which may lead to an increase in navigation distance. To solve this problem, in this paper, weather data recovery is carried out by combining super-resolution reconstruction technology and an attention mechanism to improve the accuracy and real-time performance of route planning, thereby reducing shipping costs and improving navigation efficiency.
Super-resolution reconstruction is a technique for enhancing image resolution, commonly applied in computer vision and image processing. By combining multiple low-resolution images and using advanced algorithms, this technique can generate images with higher resolution than the original image, revealing more details and structures [
16,
17,
18]. Super-resolution reconstruction not only improves the clarity of the image but also plays an important role in medical imaging, remote sensing, video surveillance, and other fields [
19,
20,
21,
22]. Liu et al. [
23] introduced a unified framework leveraging deep learning-based super-resolution, which adapted cutting-edge natural image super-resolution techniques for MRI reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrated that this approach outperforms traditional methods in terms of reconstruction quality. Xi [
24] employed a deep autoencoder-based learning strategy to enhance the reconstruction algorithm, achieving an improved super-resolution performance through a refined network model. However, this method lacks the process of model convergence, which can easily lead to model underfitting. He et al. [
25] proposed a feature distillation-based reconstruction framework, which was shown to more effectively recover image features. Shao et al. [
26] developed an inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging method tailored for complex maneuvering ship targets. Simulation results indicate that the proposed algorithm addresses the trade-off between high-resolution imaging and motion error complexity under challenging sea conditions. However, the reconstruction effect of this method is low in multi-target and multi-static situations. Ying et al. [
27] designed a multi-granularity feature enhancement network (MFENet) to mitigate the decline in detection accuracy caused by sea fog interference in visible light images. However, due to changes in environmental factors, the image reconstructed by this method is unstable, which is likely to affect the robustness of the detection results. Additionally, Han et al. [
28] presented a dynamic multi-target tracking algorithm by integrating YOLOv7 with DeepSORT, with simulation outcomes showing a 9.4% improvement in the mAP50–95 compared to the baseline YOLOv7. However, the number of ships used in the model is small, and it is impossible to carry out multiple ship identification and tracking tests. Secondly, the attention mechanism has also been applied in many different fields. Liu et al. [
29] introduced a deep learning model incorporating a weighted pure attention mechanism, which demonstrated notable improvements in predictive accuracy through experimental validation. However, the model uses less evaluation methods, which cannot fully verify the validity of the model. Li [
30] developed a novel hybrid attention mechanism along with a high-resolution representation network utilizing efficient channel attention. Results indicated that this model delivers superior segmentation performance compared to similar approaches. However, this method lacks the input of noise data, which may affect the robustness of the model. Kardakis et al. [
31] applied an attention-based recurrent neural network (RNN) to emotion analysis, showing that attention fusion substantially enhances the predictive capabilities of deep neural networks. Li et al. [
32] proposed a segmentation and grasp detection network leveraging a dual-attention mechanism, achieving a high grasp success rate on a custom-built robotic arm platform. Yang et al. [
33] presented a nearshore water level forecasting model enhanced with attention mechanisms. Their findings suggested that the model can accurately predict water levels at coastal stations up to 48 h in advance, outperforming existing methods. However, this method lacks the consideration of the interaction between the water level changes in coastal stations and various influencing factors, and the combination of these factors helps to improve the prediction effect of the model. Messaoud et al. [
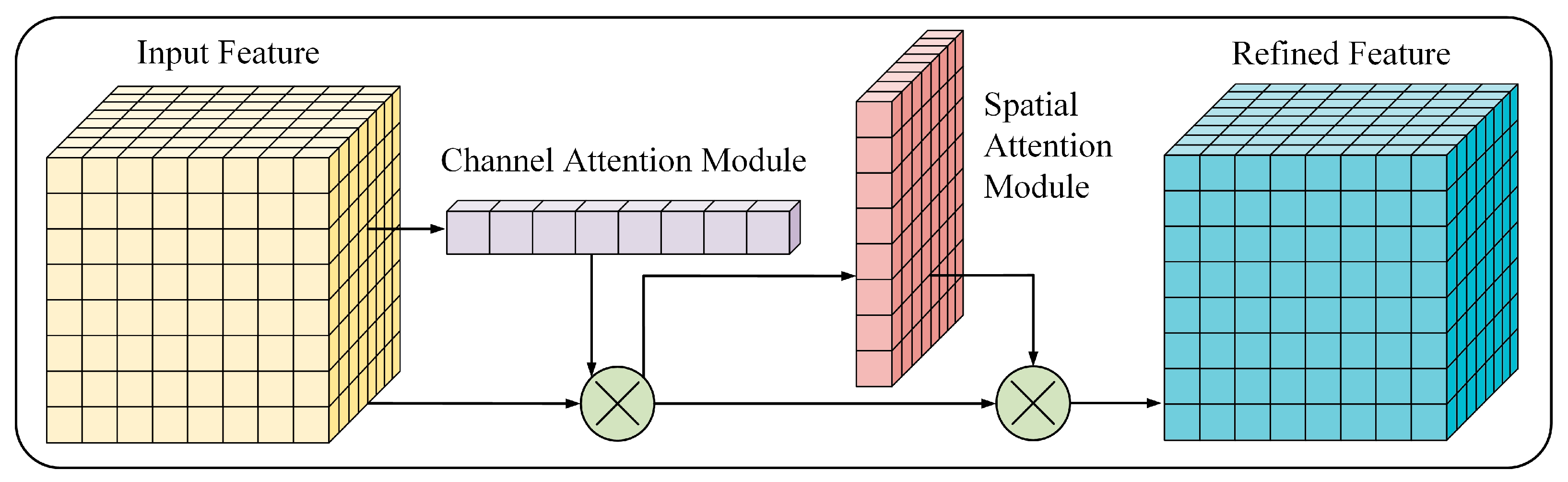
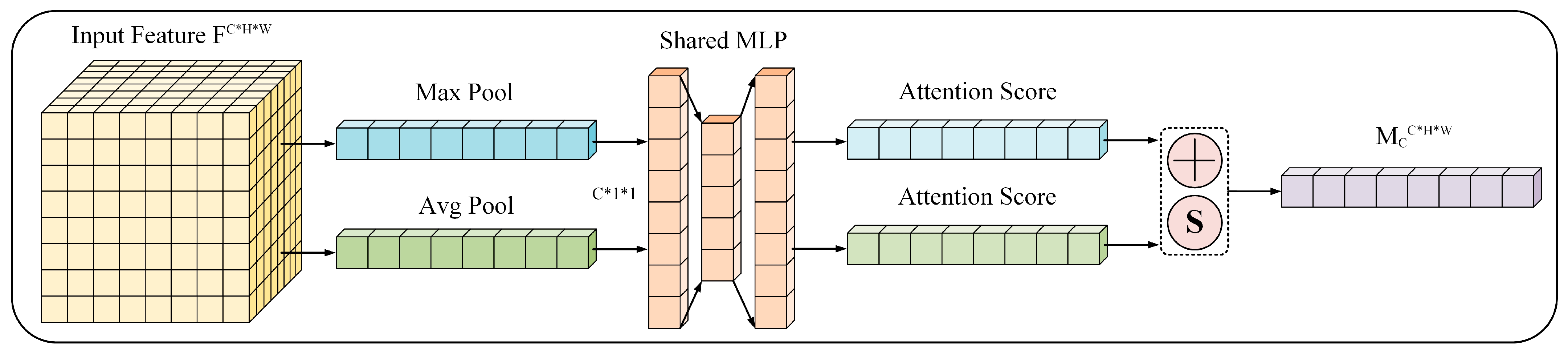
34] applied an attention mechanism and low-visibility enhancement network to enhance the detection of the marine environment. The results show that this method significantly enhances the target detection ability in low visibility scenes. However, this method lacks the key step of the ablation experiment, which may affect the stability and effectiveness of the model.
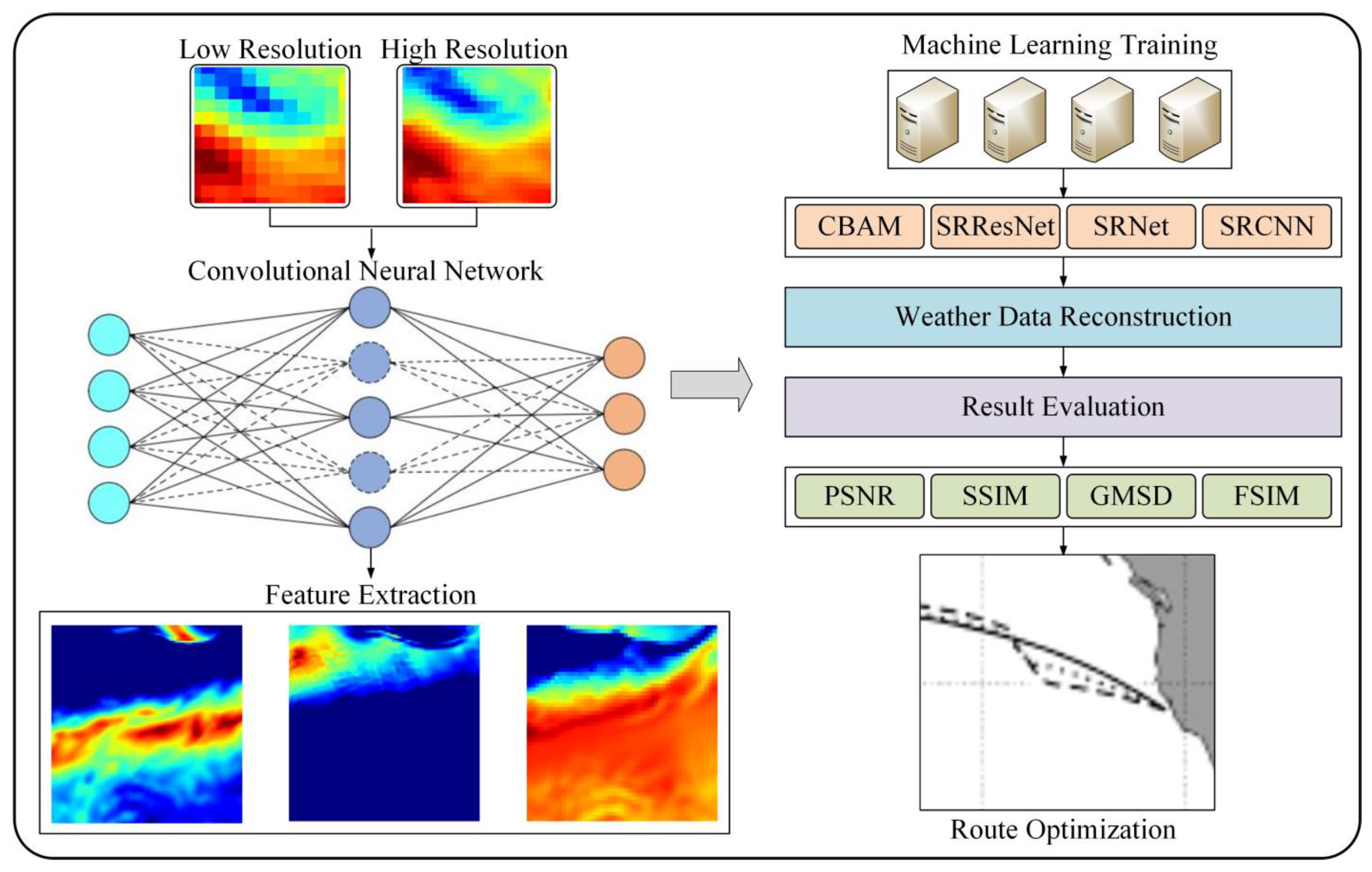
In summary, this paper proposed a deep learning model for marine weather data reconstruction by combining deep super-resolution reconstruction technology and attention mechanism, which can effectively improve the spatial detail expression ability of low-resolution observation data. Different from the traditional interpolation method or single-image reconstruction model, this method introduces the attention mechanism of weather structure perception, which not only strengthens the reconstruction accuracy of key areas but also provides higher quality environmental input for the ship route planning model, thus laying a data foundation for subsequent intelligent navigation decision-making. The modeling process is shown in
Figure 1.
As shown in
Figure 1, the low-resolution wave height and wind speed data are first used as input, and the corresponding low-resolution labels are used to guide the training of the machine learning model. Then, the super-resolution reconstruction algorithm is constructed by using the trained model to reconstruct the low-resolution data so as to generate high-resolution weather data. On this basis, the quality of the reconstruction results is verified by a variety of evaluation methods. Finally, combined with the evaluation results and the generated high-resolution weather data, the ship route is optimized. See below for details.
3. Weather Data Feature Extraction
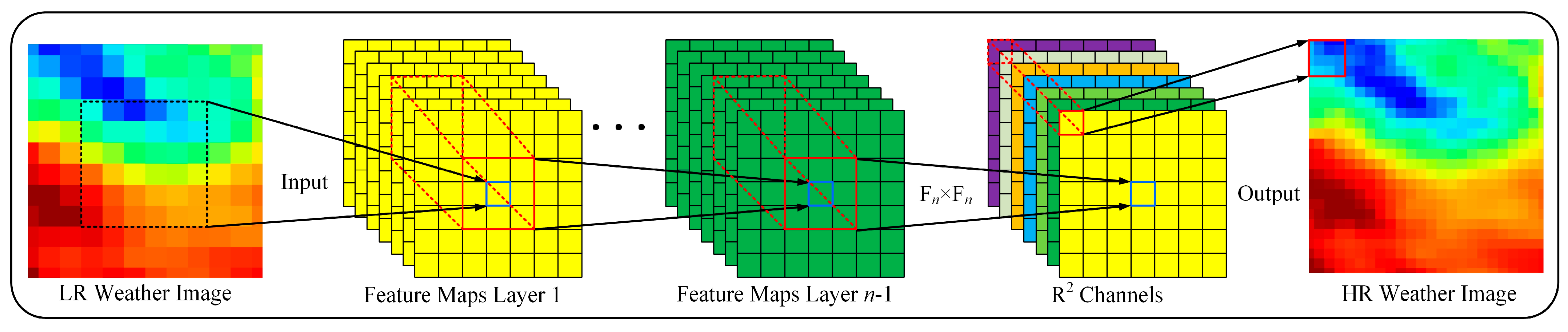
First, feature extraction is applied to the input data. Among many environmental factors, wind speed and wave height are the two most direct variables affecting ship navigation. Therefore, this study selects wind speed and wave height as the input data of the model. Secondly, a convolutional neural network [
40] is employed to extract three layers of features related to wind speed and wave height, which are then fed into a machine learning algorithm for model training. The feature extraction process is as follows:
(1) Input Layer
Let the input data be
, and its expression is
where
is the number of zonal grids,
is the number of meridional grids, and
is the number of grids in row
and column
.
(2) Convolution Layer
Each convolution kernel slides on the image, weights the local area, and adds bias terms to extract spatial local features:
where
is the
convolution kernel,
is the convolution kernel size,
is the bias term, and
is the convolution output value.
(3) Activation Function
The ReLU activation function can introduce nonlinearity to the network so that it can fit complex features:
where
is the feature value after activation, and
is the large value of 0 and
.
(4) Pooling Layer
The pooling layer can down-sample each channel, retain the most significant features in the region, reduce size, and enhance invariance:
where
is the size of the pooling window,
is the location of the pooling result, and
is the pooling step size.
(5) Multilayer Stack
More abstract and meaningful features can be extracted layer by layer by multiple convolution + activation + pooling layers:
where
is the output of layer
,
is the convolution operation,
is the activation function, and
is the pooling operation.
(6) Global Pooling
Global pooling is the global average of each channel and retains the global spatial statistical information, which is suitable for lightweight modeling :
where
is the value of channel
at position
in feature map
.
(7) Output Features
The final output feature vector:
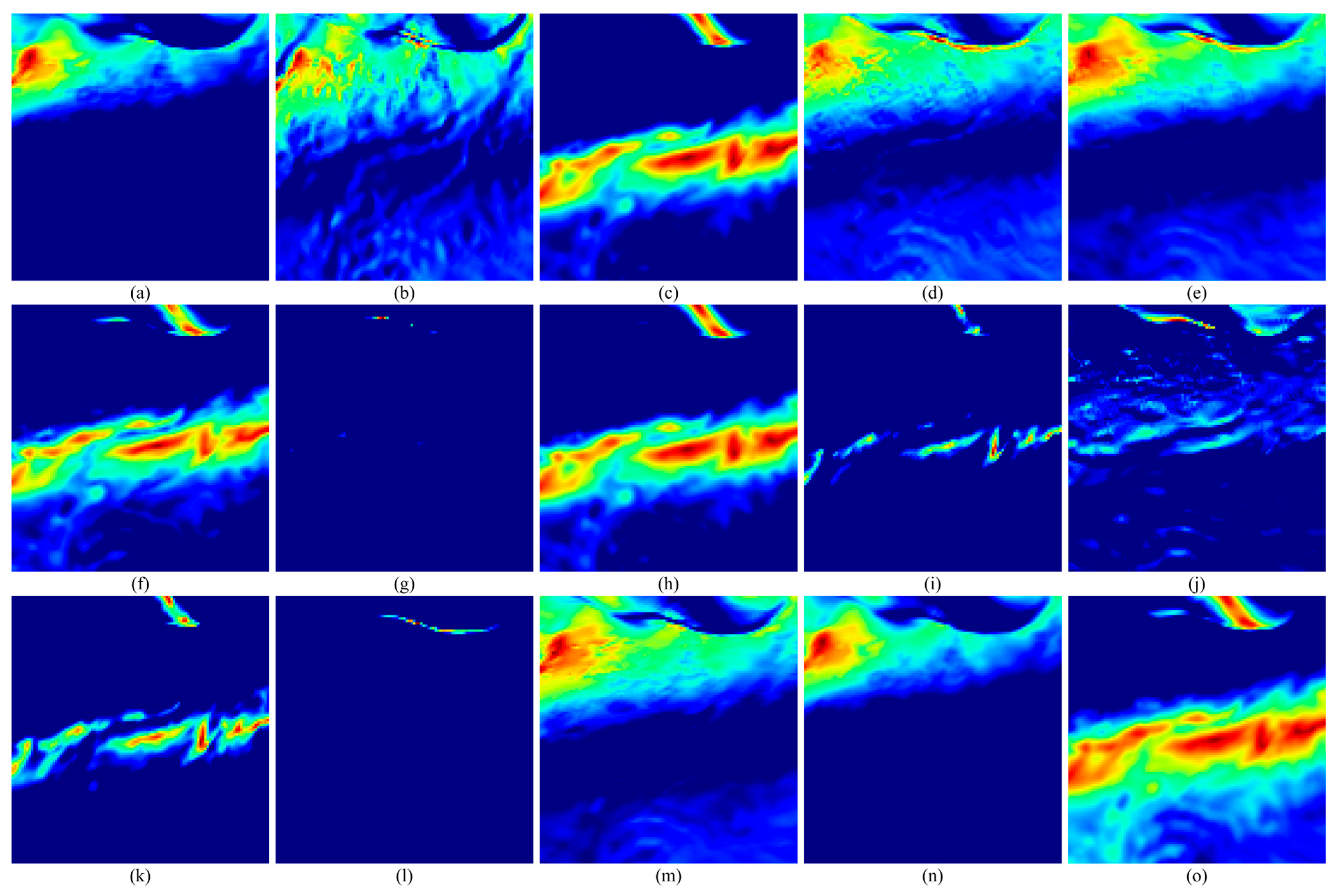
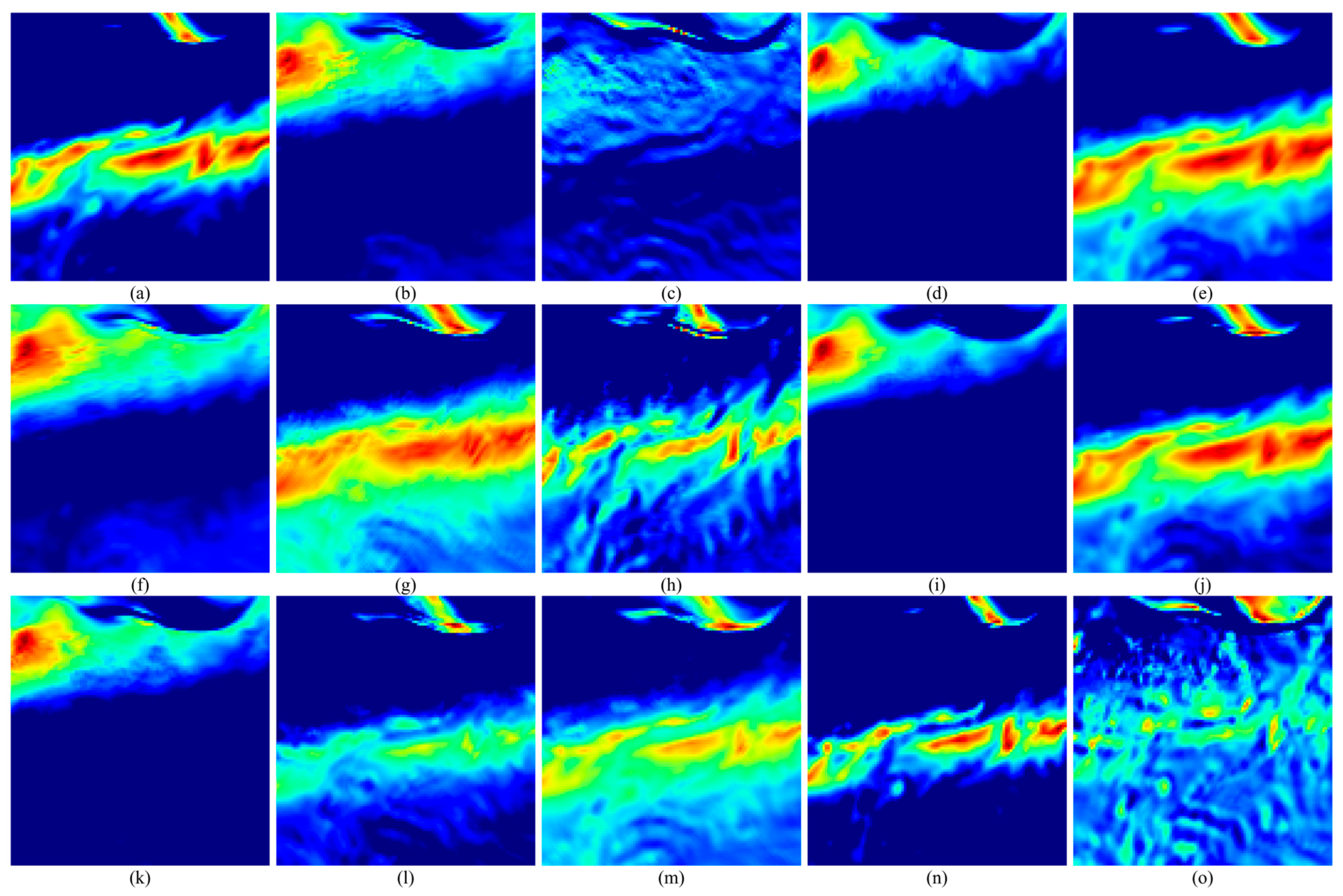
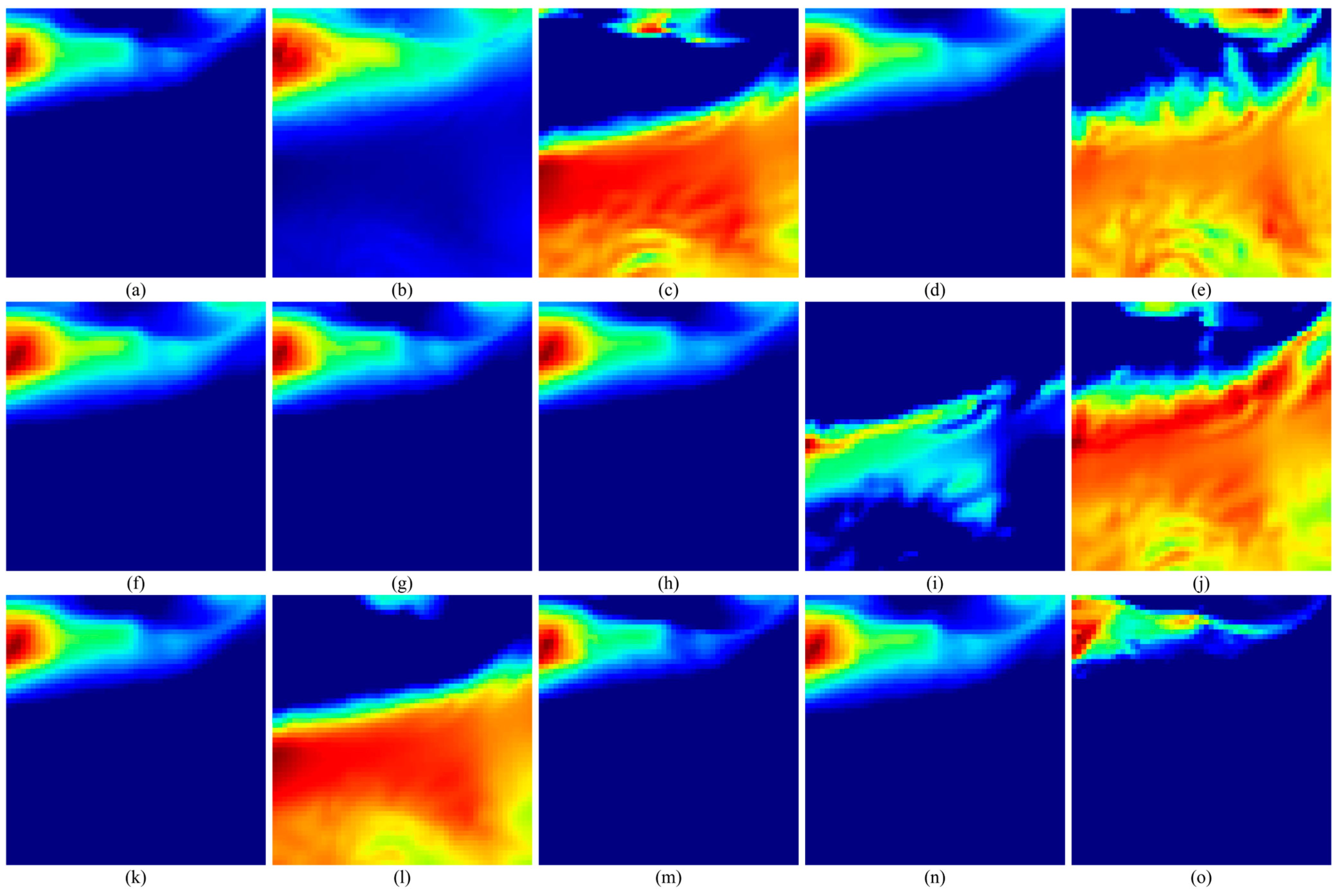
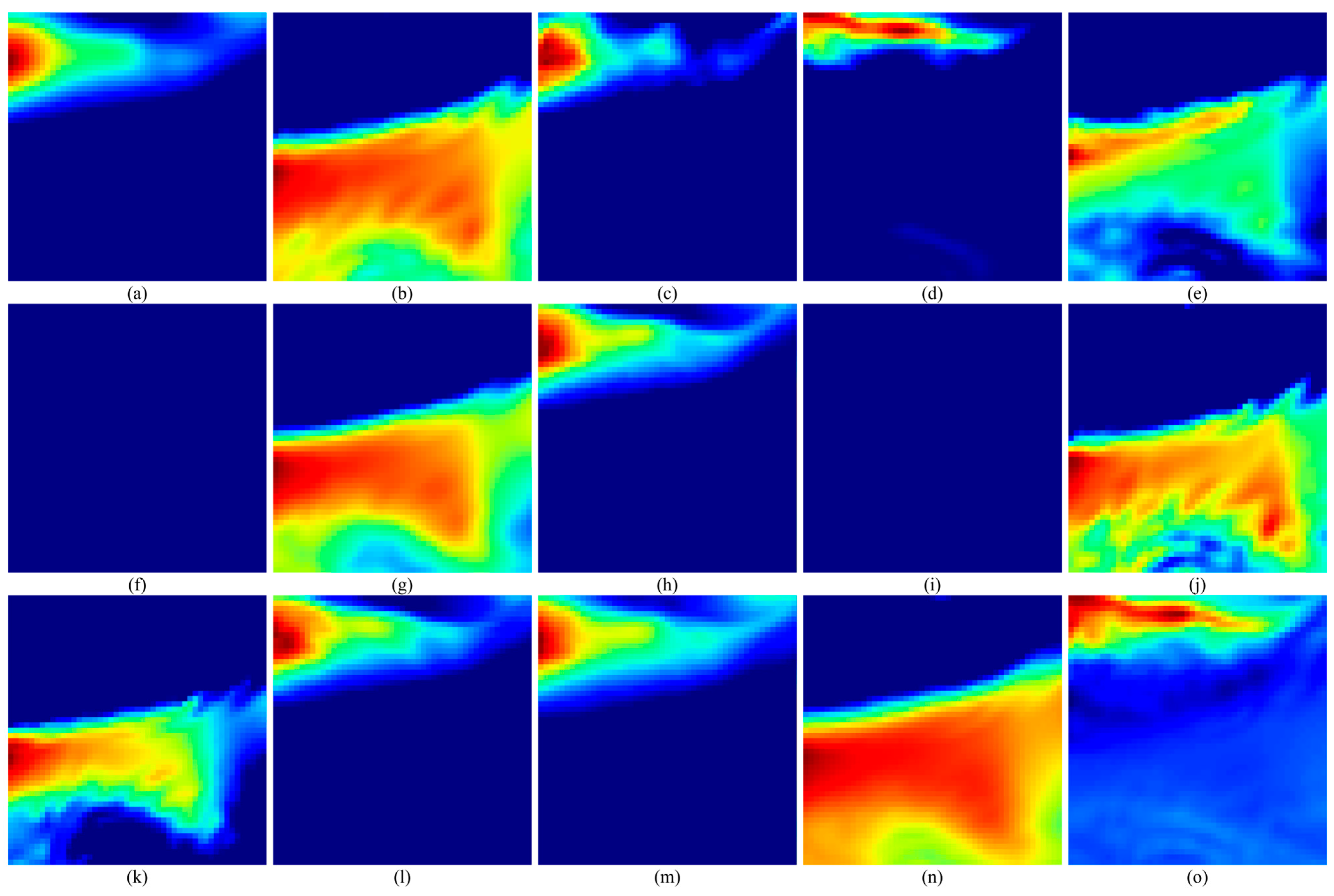
According to the above method, the feature extraction of the extracted model parameters is carried out. Taking the feature extraction process of 1 May 2021 00:00:00 UTC as an example, the three-layer feature extraction of the data is carried out, the extraction parameter settings are shown in
Table 1, and the extracted features are shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12.
As shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12, the three-layer convolutional neural network is used to extract the features of wind speed and wave height and extract the key spatio-temporal structure features layer by layer, the subgraphs a–o are respectively represented as the feature maps corresponding to 15 output channels. The first layer extracts local change patterns, such as wind and wave mutations or edge features; the second layer identifies the coupling relationship between wind speed and wave height and extracts the mesoscale evolution structure. The third layer aggregates higher-level spatio-temporal patterns, captures the dynamic characteristics of the overall wind and wave system, and provides deep-level feature support for subsequent tasks.
4. Data Reconstruction and Route Optimization
The experiment was conducted on a Windows platform with an i5-13490F CPU and an NVIDIA® GeForce® RTX 4060 Ti GPU. The development environment was Spyder, with the framework implemented in Python 3.12.4. The deep learning setup included Python 3.11.7, Spyder IDE 5.4.3, PyTorch 1.12.1 + cu117, CUDA 12.2, and cuDNN 8.7.0.0. The area of the experiment was (130.25° W–118.25° W, 19.75° N–31.75° N). The experimental data were wind speed and wave height data at 1 January 2021 00:00 UTC–31 December 2022 23:00. There were 8760 images with a resolution of 24 × 24 in each group, 60% of which were used as a training set, 20% as a validation set, and 20% as a test set.
In the process of model training, the calculation of loss value is very important, including training loss and verification loss. To ensure model stability in practical applications, these losses must converge gradually to guarantee good generalization. In this experiment,
loss is used to measure the absolute error between the predicted and true values, as shown in Equation (16).
where
is the predicted value of the model,
is the true value of the model, and
is the total sample.
The learning rate is set to 0.001, the optimizer is Adam, and the number of iterations is set to 100 times. The loss value of the model is calculated according to Equation (4), and the loss function curve is constructed, as shown in
Figure 13 and
Figure 14.
According to
Figure 13 and
Figure 14, when the model training is iterated to the 100-th round, the training loss and val loss have basically converged, indicating that the constructed model has good stability and robustness in this task. Subsequently, the weather data are reconstructed based on the trained model, and some results are shown in
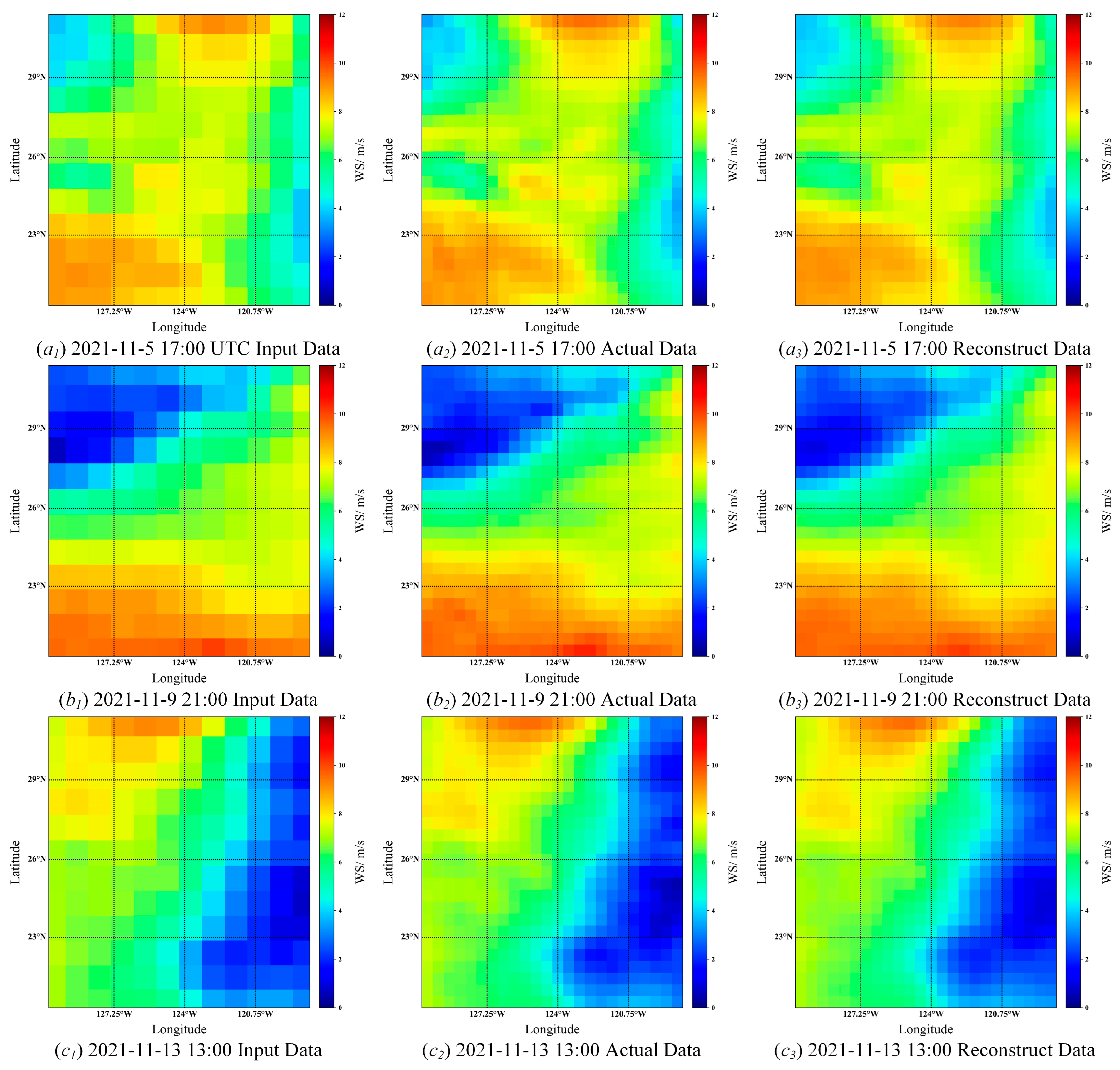
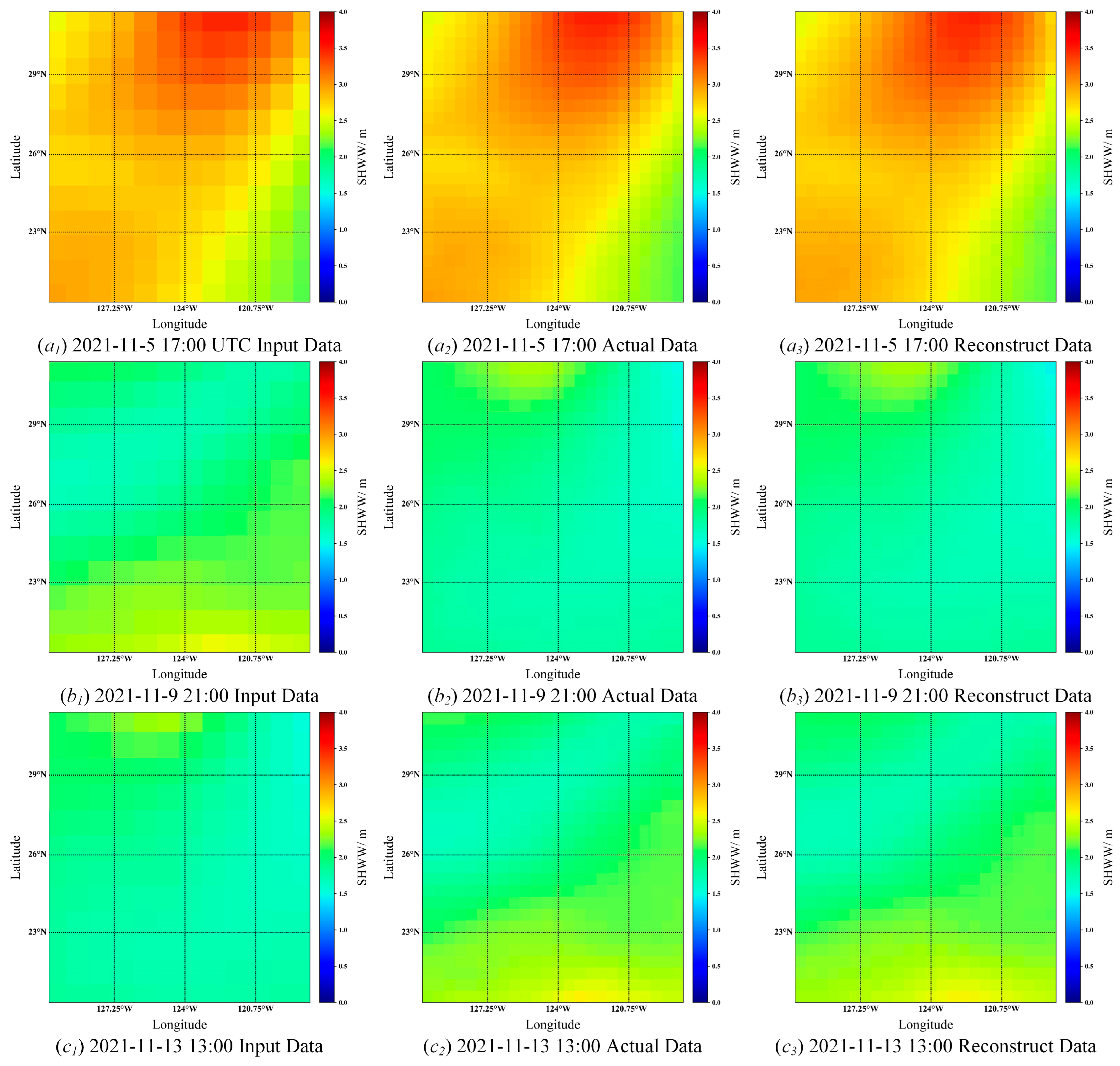
Figure 15 and
Figure 16.
As shown in
Figure 15 and
Figure 16, the super-resolution model is used to reconstruct the weather data of wave height and wind speed, and the resolution is increased to two times. The left side is the input low-resolution weather data, the middle side is the actual high-resolution weather data, and the right side is the result of the model reconstruction. From the subjective effect, the reconstruction effect is good, indicating that the model has good reconstruction ability. To evaluate the performance of the model more objectively, this paper introduces the PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio), SSIM (Structural Similarity Index), GMSD (Gradient Magnitude Similarity Deviation), and the FSIM (Feature Similarity Index Method) to evaluate the reconstruction results of the model and compares it other the reconstruction algorithms. The evaluation results are shown in
Table 2, and the confidence interval is shown in
Table 3. Secondly, the
T test was used to calculate the significance level of multiple models. When the
p value was less than 0.05, it was considered that the two models had statistical differences. When the
p value was greater than 0.05, it indicated that there was no significant difference, and the significance test results are shown in
Table 4.
where
and
are represented as the high-resolution image output by the model and the actual high-resolution image, respectively, and
is represented as the maximum possible value of the image pixel.
where
and
are represented as the high-resolution image of the model output and the actual high-resolution image, respectively.
and
are the average pixel values of
and
;
and
are the variances of the pixel values of
and
;
is the covariance between the pixel values of
and
;
and
are constants for stable calculations.
where
and
are the gradient amplitudes of the reference image and the reconstructed image at pixel
i, respectively.
c is the stability constant (prevents the denominator from being zero);
is the average value of the GMS similarity graph;
n is the total number of pixels.
where
is the feature similarity of the
i-th pixel,
is the weight of the
i-th pixel, and
is the image domain.
As shown in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4, compared with other algorithms, the Super-Resolution Convolutional Block Attention Module (SRCBAM) shows the best reconstruction effect on all four evaluation indicators. Compared with SRResNet, the PSNR of wave height of the SRCBAM is increased by 0.6, the SSIM is increased by 0.0002, and the GMSD is increased by 0.0112. The PSNR of wind speed of the SRCBAM is increased by 0.4, the SSIM is increased by 0.0005, and the GMSD is increased by 0.0006. And, compared with other models, the t-values of the significance test are all less than 0.05, indicating that the results of the model are statistically significant and the differences are real, not accidental. Next, on this basis, route optimization is further carried out based on the reconstructed weather results, and the optimization results are shown in
Figure 17 and
Figure 18.
As shown in
Figure 17 and
Figure 18, in the low-resolution wave height and wind speed weather map, the red circle is expressed as the scope of ship safety field, the route shows that the ship is about to sail into the orange high-risk area. In this area, the wave height is about 3.5 m, and the wind speed is about 11 m/s. When the ship cannot withstand the sea conditions, the system often chooses to detour or drift, which significantly increases the navigation time and cost. However, after the super-resolution optimization of the weather map, the area corresponding to the same path becomes a yellow medium-risk area, the wave height is about 3 m, and the wind speed is about 10 m/s. This situation can ensure the normal operation of the ship ’s route and avoid unnecessary detour. It can be seen that by the super-resolution reconstruction of weather data, the accuracy of environmental information can be effectively improved, thereby reducing the time and cost of ship navigation.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a marine weather data reconstruction model based on deep super-resolution. The model uses convolutional neural networks to extract features from wind speed and wave height data. Secondly, the model takes SRResNet as the reconstruction framework and effectively captures the complex nonlinear feature relationship in weather data through the residual block structure to realize the fine reconstruction of low-resolution weather data. In addition, the attention mechanism is integrated into the model to dynamically adjust the weights of different weather features, which further enhances the attention to key features. The results show that the model has a good effect on the super-resolution reconstruction of weather data. However, there are still some limitations in this study. First of all, the ship’s route planning is a multi-factor comprehensive decision-making process, which is not only affected by wind speed and wave height but also includes multi-source environmental and operational factors such as water flow, sea ice, and safety regulations. Secondly, limited by experimental resources and computational conditions, the experimental area selected in this study is relatively small, which may affect the generalization ability of the model. Although this study has made some progress in the reconstruction of high-resolution weather fields, there are still some directions worthy of further improvement. First, the current model is only trained and validated in specific sea areas, and subsequent studies will be extended to areas with different climatic conditions and hydrological characteristics to evaluate the generalization ability of the model. Secondly, limited by the amount of data available, the amount of data currently used is small. In the future, we will consider introducing larger data sets and further analyze the robustness performance of the model under small-sample conditions. Finally, although this study preliminarily demonstrates the application potential of reconstructed data in route planning, it does not integrate a complete route optimization module. In the future, the coupling mechanism between high-resolution reconstructed data and a dynamic route optimization algorithm will be further explored to improve its practicability and decision support ability.