Year-Round Acoustic Presence of Beaked Whales (Ziphiidae) Far Offshore off Australia’s Northwest Shelf
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
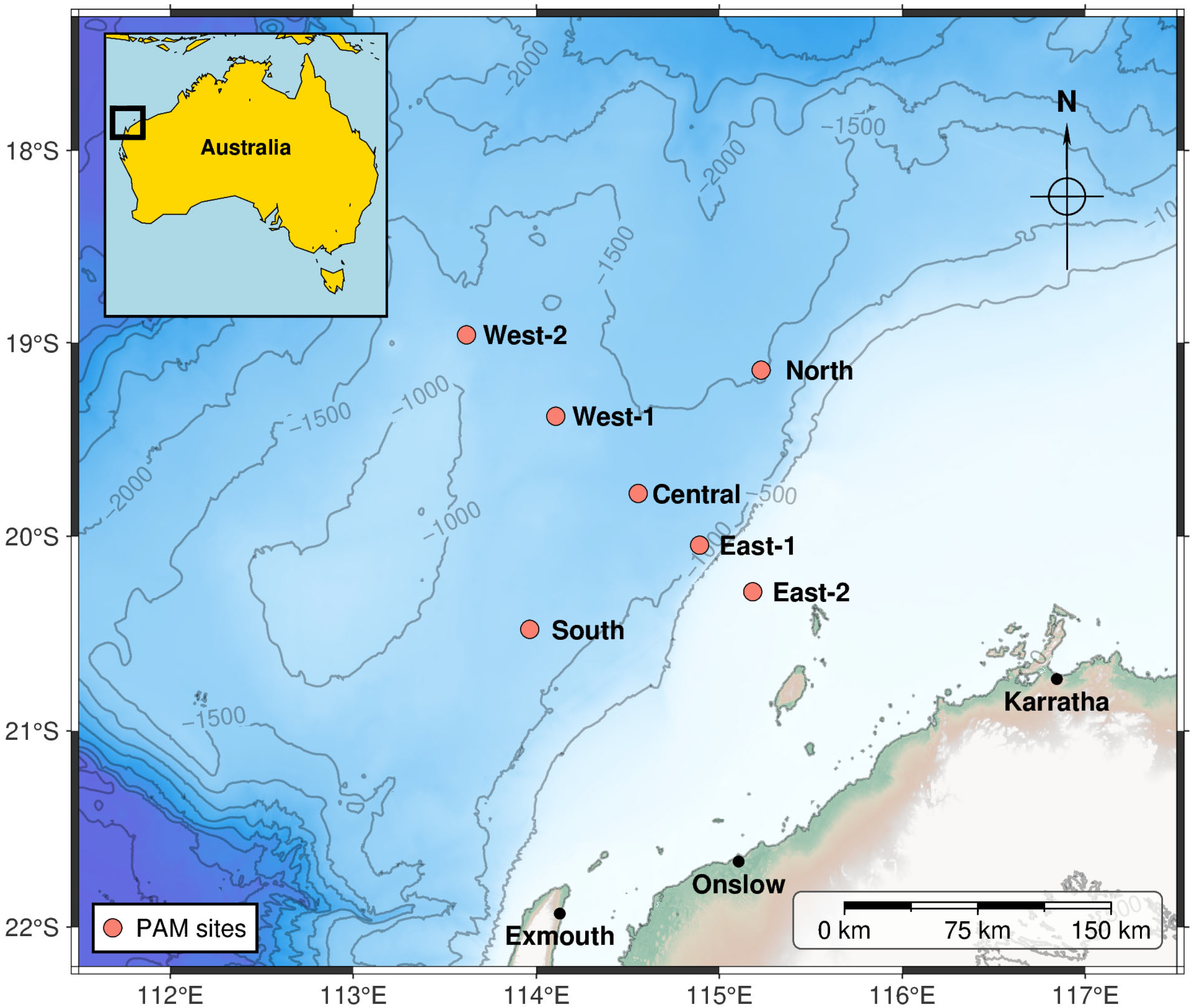
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Manual Compilation of Beaked Whale Click Templates
2.2.2. Automated Pulsive Signal Extraction
2.2.3. Correlation of Extracted Pulses with Templates of Beaked Whale Clicks
2.2.4. Manual Inspection of Extracted Pulses
2.2.5. Parameter Selection of the Automated Beaked Whale Detector
2.2.6. Execution of the Beaked Whale Click Detector
2.2.7. Spatio-Temporal Occurrence of Beaked Whales
3. Results
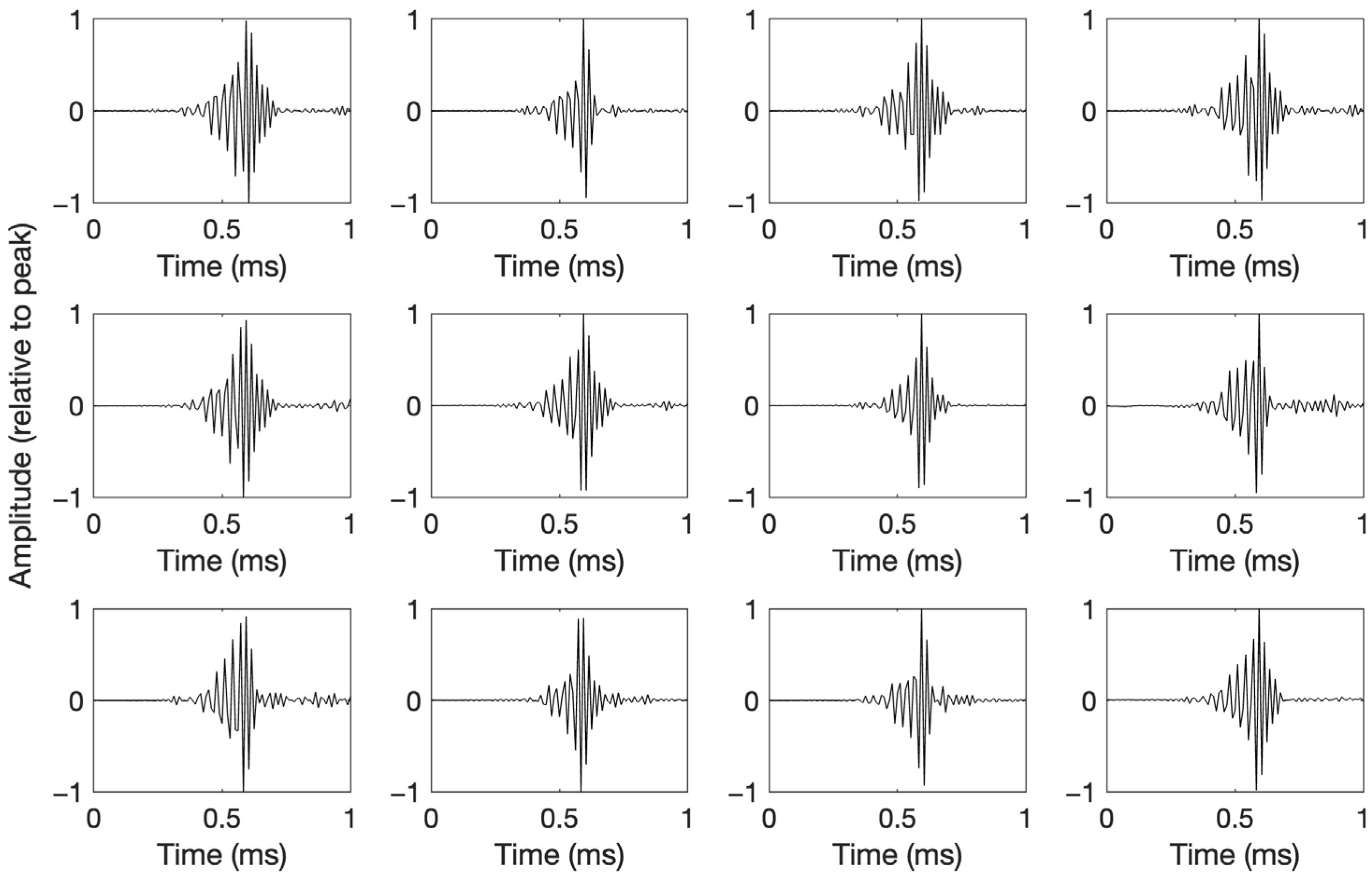
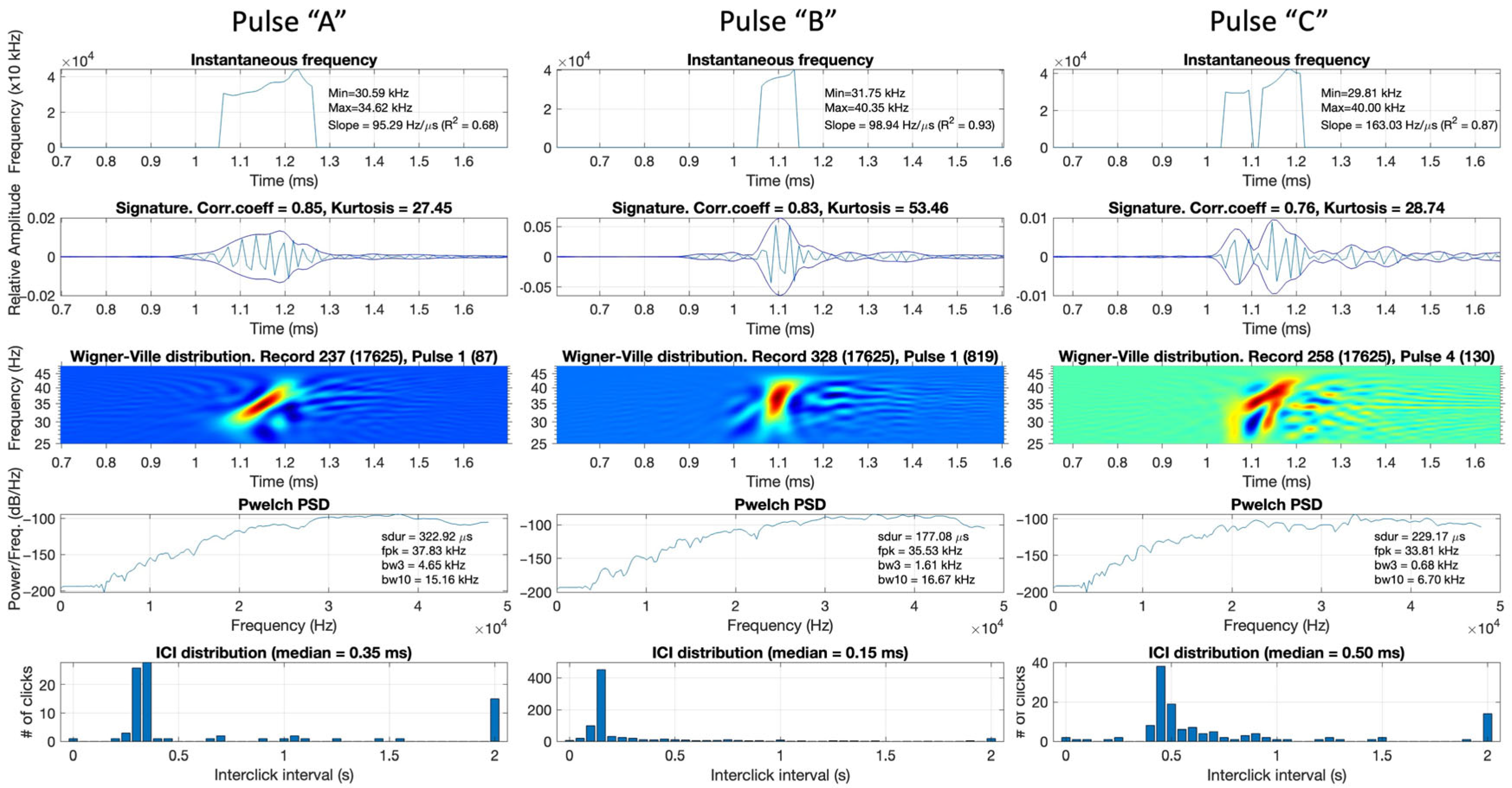
3.1. Beaked Whale Click Templates
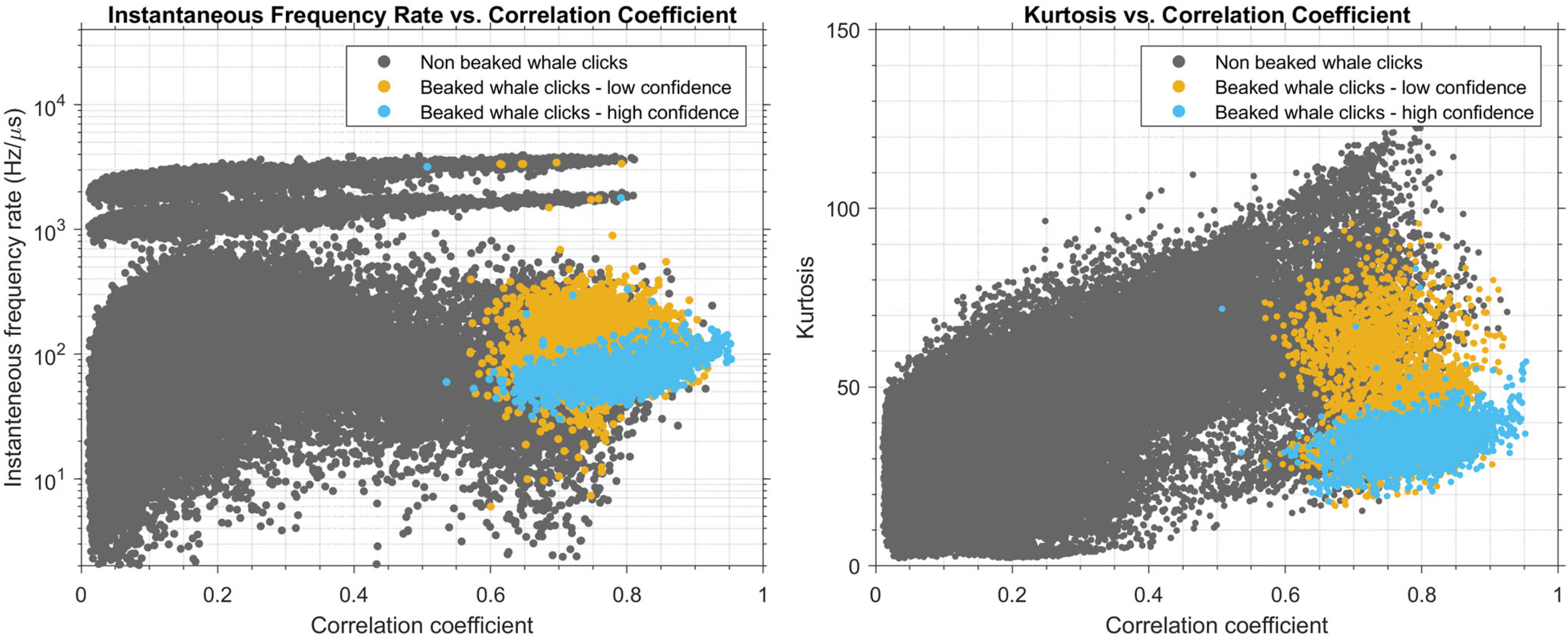
3.2. Beaked Whale Click Features
3.3. Detector Performance
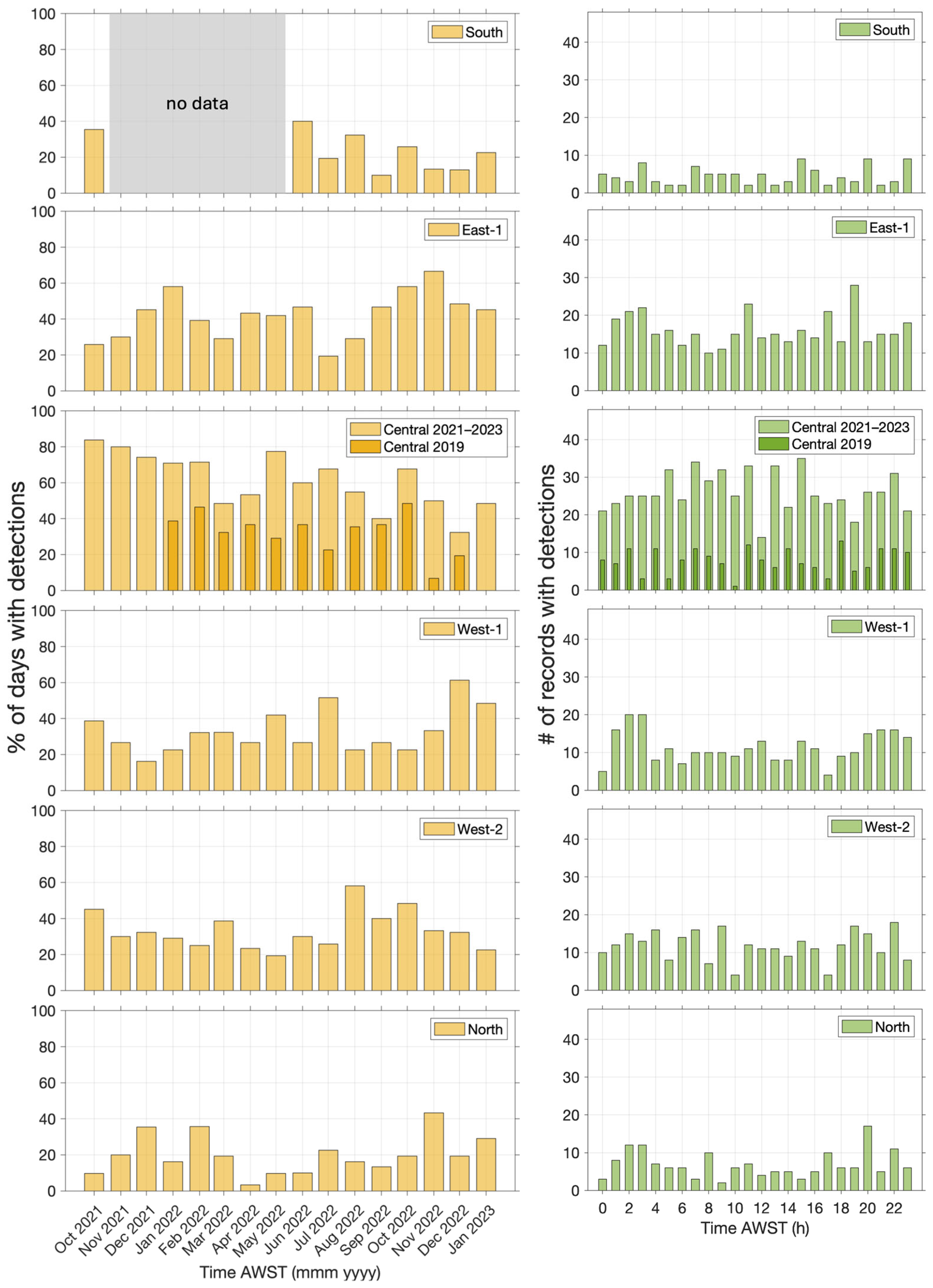
3.4. Spatio-Temporal Occurrence of Beaked Whale Clicks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groom, C.; Coughran, D.K.; Smith, H. Records of beaked whales (family Ziphiidae) in Western Australian waters. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2014, 7, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinck, H.; Mellinger, D.K.; Klinck, K.; Bogue, N.M.; Luby, J.C.; Jump, W.A.; Shilling, G.B.; Litchendorf, T.; Wood, A.S.; Schorr, G.S.; et al. Near-real-time acoustic monitoring of beaked whales and other cetaceans using a Seaglider™. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar-Treviño, J.; Johnson, M.; Arranz, P.; Warren, V.E.; Pérez-González, C.J.; Marques, T.; Madsen, P.T.; Soto, N.A.d. Deep-diving beaked whales dive together but forage apart. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20201905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Zimmer, W.M.X.; de Soto, N.A.; Tyack, P.L. Beaked whales echolocate on prey. Proc. R. Soc. B 2004, 271, S383–S386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Roch, M.A.; Brownell, R.L., Jr.; Simonis, A.E.; McDonald, M.A.; Solsona-Berga, A.; Oleson, E.M.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A. Spatio-temporal patterns of beaked whale echolocation signals in the North Pacific. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyack, P.L.; Johnson, M.P.; Zimmer, W.M.X.; de Soto, N.A.; Madsen, P.T. Acoustic behavior of beaked whales, with implications for acoustic monitoring. Ocean 2006, 1–4, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, J.L.K.; Wren, J.L.K.; Oleson, E.M.; Allen, A.N.; Siders, Z.A.; Norris, E.S. An acoustic survey of beaked whales and Kogia spp. in the Mariana Archipelago using drifting recorders. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 664292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellard, R.; Lightbody, K.; Fouda, L.; Blewitt, M.; Riggs, D.; Erbe, C. Killer whale (Orcinus orca) predation on beaked whales (Mesoplodon spp.) in the Bremer Sub-Basin, Western Australia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, W.M.X.; Harwood, J.; Tyack, P.L.; Johnson, M.P.; Madsen, P.T. Passive acoustic detection of deep-diving beaked whales. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Johnson, M.; de Soto, N.A.; Zimmer, W.M.X.; Tyack, P. Biosonar performance of foraging beaked whales (Mesoplodon densirostris). J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Zimmer, W.M.X.; de Soto, N.A.; Tyack, P.L. Foraging Blainville’s beaked whales (Mesoplodon densirostris) produce distinct click types matched to different phases of echolocation. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 5038–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, W.M.X.; Johnson, M.P.; Madsen, P.T.; Tyack, P.L. Echolocation clicks of free-ranging Cuvier’s beaked whales (Ziphius cavirostris). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 3919–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanistreet, J.E.; Nowacek, D.P.; Baumann-Pickering, S.; Bell, J.T.; Cholewiak, D.M.; Hildebrand, J.A.; Hodge, L.E.W.; Moors-Murphy, H.B.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Read, A.J. Using passive acoustic monitoring to document the distribution of beaked whale species in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 2098–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; McDonald, M.A.; Simonis, A.E.; Solsona Berga, A.; Merkens, K.P.B.; Oleson, E.M.; Roch, M.A.; Wiggins, S.M.; Rankin, S.; Yack, T.M.; et al. Species-specific beaked whale echolocation signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Kerr, I.; Payne, R. Echolocation clicks of two free-ranging, oceanic delphinids with different food preferences: False killer whales Pseudorca crassidens and Risso’s dolphins Grampus griseus. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Aguilar de Soto, N.; Arranz, P.; Johnson, M. Echolocation in Blainville’s beaked whales (Mesoplodon densirostris). J. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 199, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L.; Ford, J.K.B.; Horne, J.K.; Allman, K.A.N. Echolocation signals of free-ranging killer whales (Orcinus orca) and modelling of foraging for chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.W.L. The Sonar of Dolphins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, M.H.; Wahlberg, M.; Miller, L.A. Estimated transmission beam pattern of clicks recorded from free-ranging white-beaked dolphins (Lagenorhynchus albirostris). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotten, M.; Au, W.W.L.; Lammers, M.O.; Aubauer, R. Echolocation recordings and localization of wild spinner dolphins (Stenella longirostris) and pantropical spotted dolphins (S. attenuata) using a four-hydrophone array. In Echolocation in Bats and Dolphins; Thomas, J.A., Moss, C.F., Vater, M., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004; pp. 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, P.T.; Payne, R.; Kristiansen, N.U.; Wahlberg, M.; Kerr, I.; Møhl, B. Sperm whale sound production studied with ultrasound time/depth-recording tags. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.T.; Møhl, B.; Nielsen, B.K.; Wahlberg, M. Male sperm whale behavior during exposures to distant seismic survey pulses. Aquat. Mamm. 2002, 28, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Klinck, H.; Mellinger, D.K. The energy ratio mapping algorithm: A tool to improve the energy-based detection of odontocete echolocation clicks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, J.A.; Baumann-Pickering, S.; Frasier, K.E.; Trickey, J.S.; Merkens, K.P.; Wiggins, S.M.; Mcdonald, M.A.; Garrison, L.P.; Harris, D.; Marques, T.A.; et al. Passive acoustic monitoring of beaked whale densities in the Gulf of Mexico. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Song, Y.; Lin, W.; Liu, M.; Lin, M.; Li, S. Echolocation signals recorded in the presence of Deraniyagala’s beaked whales (Mesoplodon hotaula) in the western Pacific (South China Sea) indicate species-specificity and intraspecific variation. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2025, 41, e13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Trickey, J.S.; Solsona-Berga, A.; Rice, A.; Oleson, E.M.; Hildebrand, J.A.; Frasier, K.E. Geographic differences in Blainville’s beaked whale (Mesoplodon densirostris) echolocation clicks. Divers. Distrib. 2023, 29, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhana, S.; Gavrilov, A.N.; Erbe, C. Automatic detection of echolocation clicks based on a Gabor model of their waveform. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarski, K.; Delarue, J.; Martin, B.; O’Brien, J.; Meade, R.; Oliver, Ó.; Cadhla, O.; Berrow, S. Signals from the deep: Spatial and temporal acoustic occurrence of beaked whales off western Ireland. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solsona-Berga, A.; DeAngelis, A.I.; Cholewiak, D.M.; Trickey, J.S.; Mueller-Brennan, L.; Frasier, K.E.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Baumann-Pickering, S. Machine learning with taxonomic family delimitation aids in the classification of ephemeral beaked whale events in passive acoustic monitoring. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, S.; Sakai, T.; Archer, F.I.; Barlow, J.; Cholewiak, D.; DeAngelis, A.I.; McCullough, J.L.K.; Oleson, E.M.; Simonis, A.E.; Soldevilla, M.S.; et al. Open-source machine learning BANTER acoustic classification of beaked whale echolocation pulses. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Uieda, L.; Leong, W.J.; Fröhlich, Y.; Schlitzer, W.; Grund, M.; Jones, M.; Toney, L.; Yao, J.; Tong, J.-H.; et al. PyGMT: A Python interface for the Generic Mapping Tools, v0.15.0; Karlsruher Institut für Technologie: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, A.I.; Westell, A.; Baumann-Pickering, S.; Bell, J.; Cholewiak, D.; Corkeron, P.J.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Solsona-Berga, A.; Trickey, J.S.; Van Parijs, S.M. Habitat utilization by beaked whales in the western North Atlantic Ocean using passive acoustics. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2025, 754, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, R.D.; Thomas, F.; Parsons, M.J.G.; Erbe, C.; Cato, D.; Duncan, A.J.; Gavrilov, A.N.; Parnum, I.M.; Salgado-Kent, C. Developing an underwater sound recorder. Acoust. Aust. 2017, 45, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, A.N.; Parsons, M.J.G. A Matlab tool for the characterisation of recorded underwater sound (CHORUS). Acoust. Aust. 2014, 42, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Godsill, S.J.; Rayner, P.J. Statistical reconstruction and analysis of autoregressive signals in impulsive noise using the Gibbs sampler. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1998, 6, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaman, R. AusBathyTopo (Australia) 250m 2023—A High-resolution Depth Model (20230004C); Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Au, W.W.L.; Floyd, R.W.; Haun, J.E. Propagation of Atlantic bottlenose dolphin echolocation signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 64, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A.; Roch, M.A.; Schnitzler, H.U. Discriminating features of echolocation clicks of melon-headed whales (Peponocephala electra), bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus), and Gray’s spinner dolphins (Stenella longirostris longirostris). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlberg, M.; Jensen, F.; Soto, N.; Beedholm, K.; Bejder, L.; Oliveira, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Simon, M.; Villadsgaard, A.; Madsen, P. Source parameters of echolocation clicks from wild bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus and Tursiops truncatus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.; Branstetter, B.; Moore, P.; Finneran, J. The biosonar field around an Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.; Branstetter, B.; Moore, P.; Finneran, J. Dolphin biosonar signals measured at extreme off-axis angles: Insights to sound propagation in the head. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Yack, T.M.; Barlow, J.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A. Baird’s beaked whale echolocation signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 4321–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pickering, S.; Roch, M.A.; Wiggins, S.M.; Schnitzler, H.-U.; Hildebrand, J.A. Acoustic behavior of melon-headed whales varies on a diel cycle. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2015, 69, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.W.; Moretti, D.; Jarvis, S.; Tyack, P.; Johnson, M. Effective beam pattern of the Blainville’s beaked whale (Mesoplodon densirostris) and implications for passive acoustic monitoring. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, P.; de Soto, N.A.; Madsen, P.T.; Brito, A.; Bordes, F.; Johnson, M.P. Following a foraging fish-finder: Diel habitat use of Blainville’s beaked whales revealed by echolocation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado Kent, C.; Bouchet, P.; Wellard, R.; Parnum, I.; Fouda, L.; Erbe, C. Seasonal productivity drives aggregations of killer whales and other cetaceans over submarine canyons of the Bremer Sub-Basin, south-western Australia. Aust. Mammal. 2020, 43, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeli, A.; Campana, I.; Marini, L.; MacLeod, C.D. Long-term presence and habitat use of Cuvier’s beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris) in the Central Tyrrhenian Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Trueman, C.N.; France, C.A.M.; Sparks, J.P.; Brownlow, A.C.; Dähne, M.; Davison, N.J.; Guðmundsson, G.; Khidas, K.; Kitchener, A.C.; et al. Stable isotope analysis of specimens of opportunity reveals ocean-scale site fidelity in an elusive whale species. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2021, 2, 653766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, G.T.; Hamazaki, T.; Sheehan, D.; Wood, G.; Baker, S. Characterization of beaked whale (Ziphiidae) and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) summer habitat in shelf-edge and deeper waters off the northeast U.S. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2001, 17, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, E.L.; Nowacek, D.P.; Laurent, L.S.; Halpin, P.N.; Moretti, D.J. The relationship among oceanography, prey fields, and beaked whale foraging habitat in the Tongue of the Ocean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.; Barlow, J.; Reilly, S.; Gerrodette, T. Predicting Cuvier’s (Ziphius cavirostris) and Mesoplodon beaked whale population density from habitat characteristics in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2006, 7, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar Soto, N.; Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.T.; Tyack, P.L.; Bocconcelli, A.; Borsani, J.F. Does intense ship noise disrupt foraging in deep-diving Cuvier’s beaked whales (Ziphius cavirostris)? Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2006, 22, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirotta, E.; Milor, R.; Quick, N.; Moretti, D.; Di Marzio, N.; Tyack, P.; Boyd, I.; Hastie, G. Vessel noise affects beaked whale behavior: Results of a dedicated acoustic response study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, J.R.; Bell, E.; Potts, J.; Babey, L.; Marley, S.A. Likely year-round presence of beaked whales in the Bay of Biscay. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.W.; Webster, D.L.; Schorr, G.S.; McSweeney, D.J.; Barlow, J. Diel variation in beaked whale diving behavior. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2008, 24, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, V.E.; Marques, T.A.; Harris, D.; Thomas, L.; Tyack, P.L.; Soto, N.A.d.; Hickmott, L.S.; Johnson, M.P. Spatio-temporal variation in click production rates of beaked whales: Implications for passive acoustic density estimation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 1962–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runte, K.L.; Kowarski, K.A.; Delarue, J.J.-Y.; Maxner, E.E.; Hedgeland, D.; Martin, S.B. We go signaling into the night: Describing an echolocation signal of an unknown beaked whale (Cetacea; Ziphiidae) off West Africa. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2025, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, J.L.K.; Henderson, E.E.; Trickey, J.S.; Barlow, J.; Baumann-Pickering, S.; Manzano-Roth, R.; Alongi, G.; Martin, S.; Fregosi, S.; Mellinger, D.K.; et al. Geographic distribution of the Cross Seamount beaked whale based on acoustic detections. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2024, 40, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Meyers, G.; Pearce, A.; Wijffels, S. Annual and interannual variations of the Leeuwin Current at 32 °S. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, D.M.; Baird, R.W.; Kratofil, M.A. Beaked whales and El Niño: Evidence for ENSO effects on Blainville’s beaked and goose-beaked whale space use in Hawaiian waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2024, 751, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar de Soto, N.; Madsen, P.; Tyack, P.; Arranz, P.; Marrero, J.; Fais, A.; Revelli, E.; Johnson, M. No shallow talk: Cryptic strategy in the vocal communication of Blainville’s beaked whales. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2012, 28, E75–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, S.K.; De Soto, N.A.; Baird, R.W.; Carroll, E.L.; Claridge, D.; Feyrer, L.; Miller, P.J.O.; Onoufriou, A.; Schorr, G.; Siegal, E.; et al. Future Directions in Research on Beaked Whales. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 00514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Scientific Name | Conservation Status (IUCN) |
|---|---|---|
| Andrew’s beaked whale | Mesoplodon bowdoini | DD (Data Deficient) |
| Arnoux’s beaked whale | Berardius arnuxii | LC (Least Concern) |
| Blainville’s beaked whale | Mesoplodon densirostris | LC (Least Concern) |
| Cuvier’s beaked whale | Ziphius cavirostris | LC (Least Concern) |
| Ginkgo-toothed beaked whale | Mesoplodon ginkgodens | DD (Data Deficient) |
| Gray’s beaked whale | Mesoplodon grayi | LC (Least Concern) |
| Hector’s beaked whale | Mesoplodon hectori | DD (Data Deficient) |
| Longman’s beaked whale | Indopacetus pacificus | LC (Least Concern) |
| Southern Bottlenose Whale | Hyperoodon planifrons | LC (Least Concern) |
| Shepherd’s beaked whale | Tasmacetus shepherdi | DD (Data Deficient) |
| Strap-toothed beaked whale | Mesoplodon layardii | LC (Least Concern) |
| True’s beaked whale | Mesoplodon mirus | LC (Least Concern) |
| Baird’s beaked whale | Berardius bairdii | LC (Least Concern) |
| Site | Deployed | Recording End | Latitude | Longitude | Bottom Depth [m] | Recorder Depth [m] | Sample Length [s] | Repetition Interval [s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 31.12.2018 | 15.02.2019 | 19°47.469′ S | 114°34.476′ E | 1361 | 1300 | 180 | 900 |
| Central | 15.05.2019 | 11.08.2019 | 19°49.859′ S | 114°38.097′ E | 1361 | 1300 | 180 | 900 |
| Central | 11.08.2019 | 29.12.2019 | 19°46.663′ S | 114°37.285′ E | 1361 | 1300 | 180 | 900 |
| South | 29.09.2021 | 30.10.2021 | 20°28.727′ S | 113°58.023′ E | 1128 | 1039 | 300 | 1200 |
| 31.05.2022 | 01.02.2023 | 20°28.748′ S | 113°57.860′ E | 1133 | 1039 | 300 | 1200 | |
| East-2 | 30.09.2021 | 12.05.2022 | 20°17.154′ S | 115°10.763′ E | 73 | 73 | 300 | 1200 |
| 02.06.2022 | 13.01.2023 | 20°17.125′ S | 115°10.974′ E | 73 | 73 | 300 | 1200 | |
| East-1 | 30.09.2021 | 02.06.2022 | 20°2.781′ S | 114°53.699′ E | 1091 | 1003 | 300 | 1200 |
| 02.06.2022 | 03.02.2023 | 20°2.766′ S | 114°53.541′ E | 1097 | 1003 | 300 | 1200 | |
| Central | 01.10.2021 | 01.06.2022 | 19°46.844′ S | 114°33.766′ E | 1361 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 |
| 01.06.2022 | 02.02.2023 | 19°46.754′ S | 114°33.457′ E | 1357 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 | |
| West-1 | 01.10.2021 | 03.06.2022 | 19°22.996′ S | 114°6.722′ E | 1178 | 1085 | 300 | 1200 |
| 03.06.2022 | 04.02.2023 | 19°22.819′ S | 114°6.408′ E | 1179 | 1085 | 300 | 1200 | |
| West-2 | 01.10.2021 | 03.06.2022 | 18°57.512′ S | 113°37.136′ E | 1255 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 |
| 02.06.2022 | 04.02.2023 | 18°57.530′ S | 113°37.148′ E | 1261 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 | |
| North | 02.10.2021 | 03.06.2022 | 19°8.573′ S | 115°13.980′ E | 1520 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 |
| 03.06.2022 | 26.01.2023 | 19°8.491′ S | 115°13.726′ E | 1517 | 1100 | 300 | 1200 |
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Duration of observation (signal) window for estimating an AR model | 1 s |
| Maximum duration of a click to be considered a detected click | 0.7 ms |
| Minimum duration of a click to be considered a background signal but not a pulsive signal (click) | 2 ms |
| Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) threshold for detecting pulsive signals after AR filtering | 10 dB |
| Maximum order of AR model. The algorithm adjusts the AR model order according to the time gap between clicks. This parameter limits the maximum possible order, which reduces the computational time. | 30 |
| Site | Number of Detections | Number of Audio Samples with Detections | Number of Days with Detections | Days of Monitoring | Percentage of Days with Beaked Whale Detections | Percentage of Audio Files with Beaked Whale Detections |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South | 4825 | 108 | 65 | 276 | 23.55% | 0.54% |
| East-2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 488 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| East-1 | 15940 | 386 | 212 | 488 | 43.44% | 1.10% |
| Central | 22960 | 626 | 310 | 488 | 63.52% | 1.78% |
| West-1 | 12957 | 274 | 168 | 488 | 34.43% | 0.78% |
| West-2 | 10086 | 283 | 168 | 488 | 34.43% | 0.81% |
| North | 6000 | 165 | 98 | 488 | 20.08% | 0.47% |
| Central (2019) | 2185 | 188 | 119 | 365 | 32.60% | 0.54% |
| Parameter(s) | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|
| (−0.4876 × Distance to Central [km]) + (−667.16 × Mean Gridded Sea Level [m]) + 1799.8 | 0.91 |
| Distance to Central [km] | −0.82 |
| Standard Deviation of Gridded Sea Level [m] | 0.56 |
| Mean Gridded Sea Level [m] | 0.48 |
| Net primary productivity [mg m−3 d−1] | 0.32 |
| Slope of the seafloor [degrees] | 0.23 |
| Depth [m] | −0.12 |
| Mean SST [°C] | −0.03 |
| Standard Deviation of SST [°C] | −0.03 |
| Parameter(s) | Correlation Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| Central | East-1 | |
| Mean Gridded Sea Level + Standard Deviation of Gridded Sea Level | 0.65 | 0.59 |
| Net primary productivity + Standard Deviation of Gridded Sea Level | 0.51 | 0.78 |
| Net primary productivity + Mean Gridded Sea Level | 0.62 | 0.5 |
| Mean Gridded Sea Level [m] | 0.61 | −0.01 |
| Standard Deviation of Gridded Sea Level [m] | 0.45 | −0.59 |
| Net primary productivity [mg m−3 d−1] | −0.34 | −0.48 |
| Mean SST [°C] | 0.12 | −0.07 |
| Standard Deviation of SST [°C] | 0.11 | −0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidenko, E.; Parnum, I.; Gavrilov, A.; McCauley, R.; Erbe, C. Year-Round Acoustic Presence of Beaked Whales (Ziphiidae) Far Offshore off Australia’s Northwest Shelf. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050927
Sidenko E, Parnum I, Gavrilov A, McCauley R, Erbe C. Year-Round Acoustic Presence of Beaked Whales (Ziphiidae) Far Offshore off Australia’s Northwest Shelf. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050927
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidenko, Evgenii, Iain Parnum, Alexander Gavrilov, Robert McCauley, and Christine Erbe. 2025. "Year-Round Acoustic Presence of Beaked Whales (Ziphiidae) Far Offshore off Australia’s Northwest Shelf" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050927
APA StyleSidenko, E., Parnum, I., Gavrilov, A., McCauley, R., & Erbe, C. (2025). Year-Round Acoustic Presence of Beaked Whales (Ziphiidae) Far Offshore off Australia’s Northwest Shelf. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050927







