Orbital-Scale Modulation of the Middle Miocene Third-Order Eustatic Sequences from the Northern South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Wireline-Logging Gamma Ray Series
3.2. Sequence Stratigraphic Subdivision
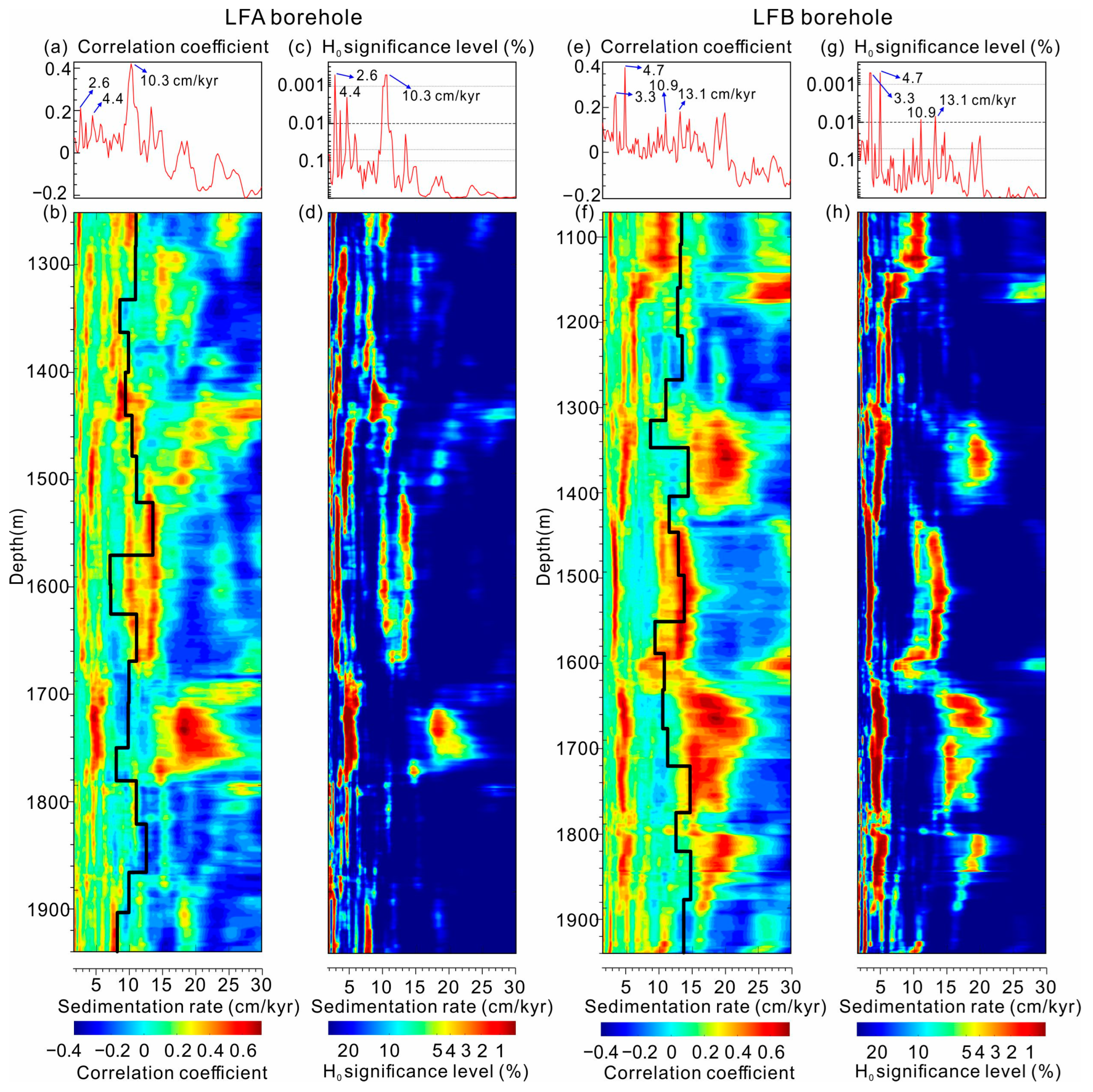
3.3. Time-Series Methods
4. Results
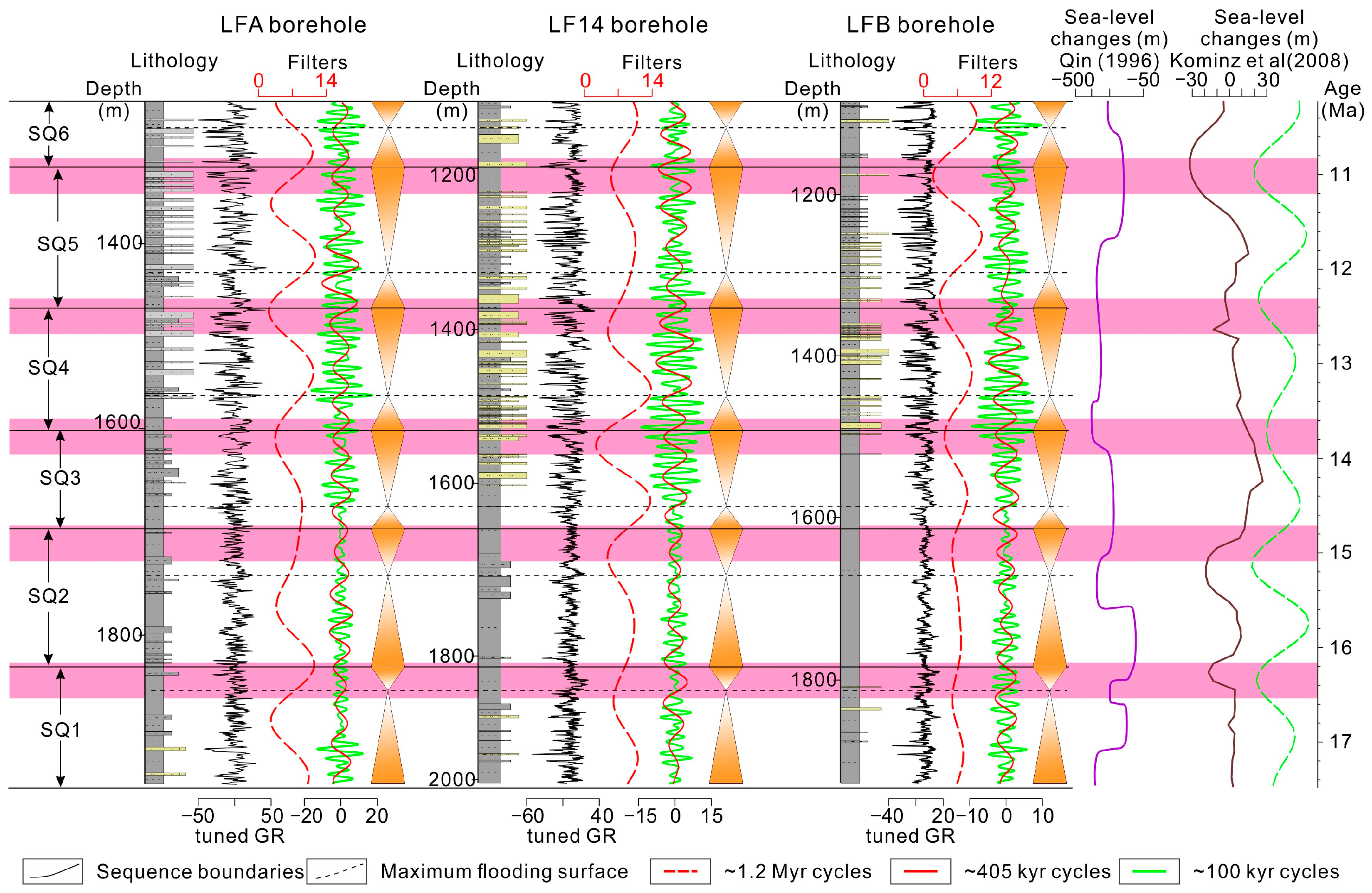
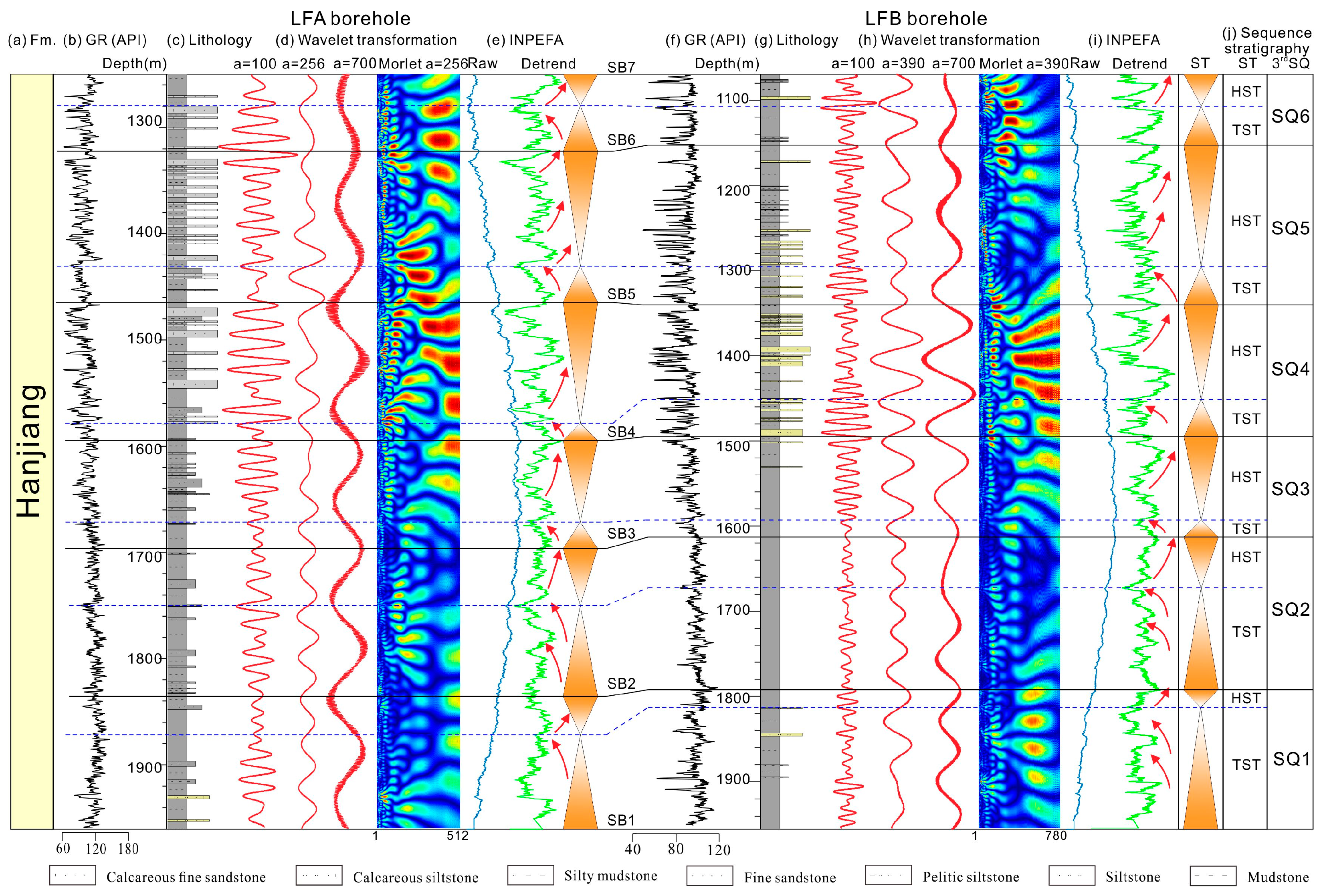
4.1. Sequence Stratigraphic Analyses Results
4.2. Cyclostratigraphy
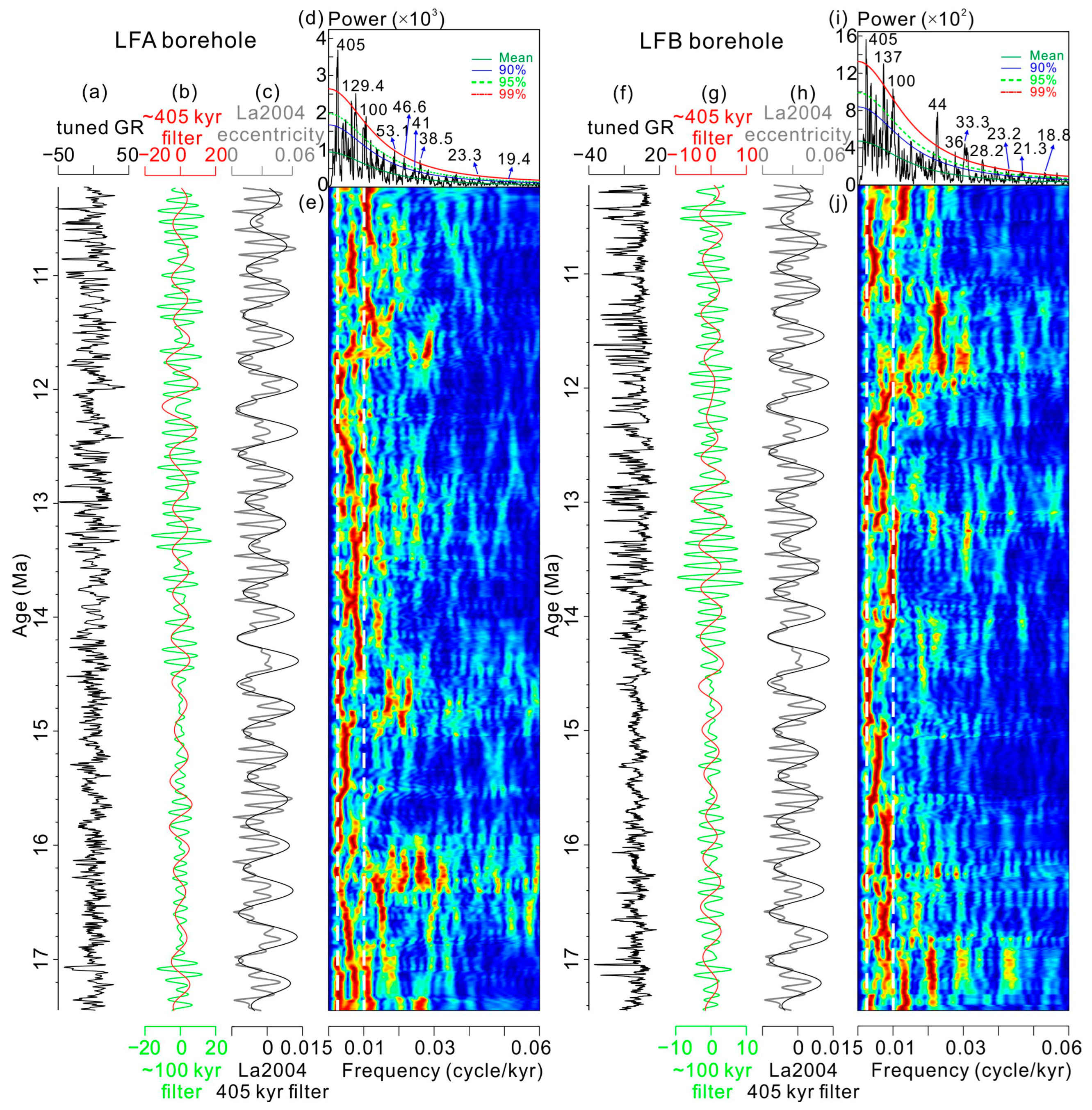
4.2.1. Power Spectral Analysis
4.2.2. Astronomical Calibrations
4.2.3. Long-Term Amplitude Modulation of Obliquity Cycles
5. Discussion
5.1. Verification of the Astrochronology in the Middle Miocene Pearl River Mouth Basin
5.2. Connection Between Sequence Stratigraphy and Cyclostratigraphy
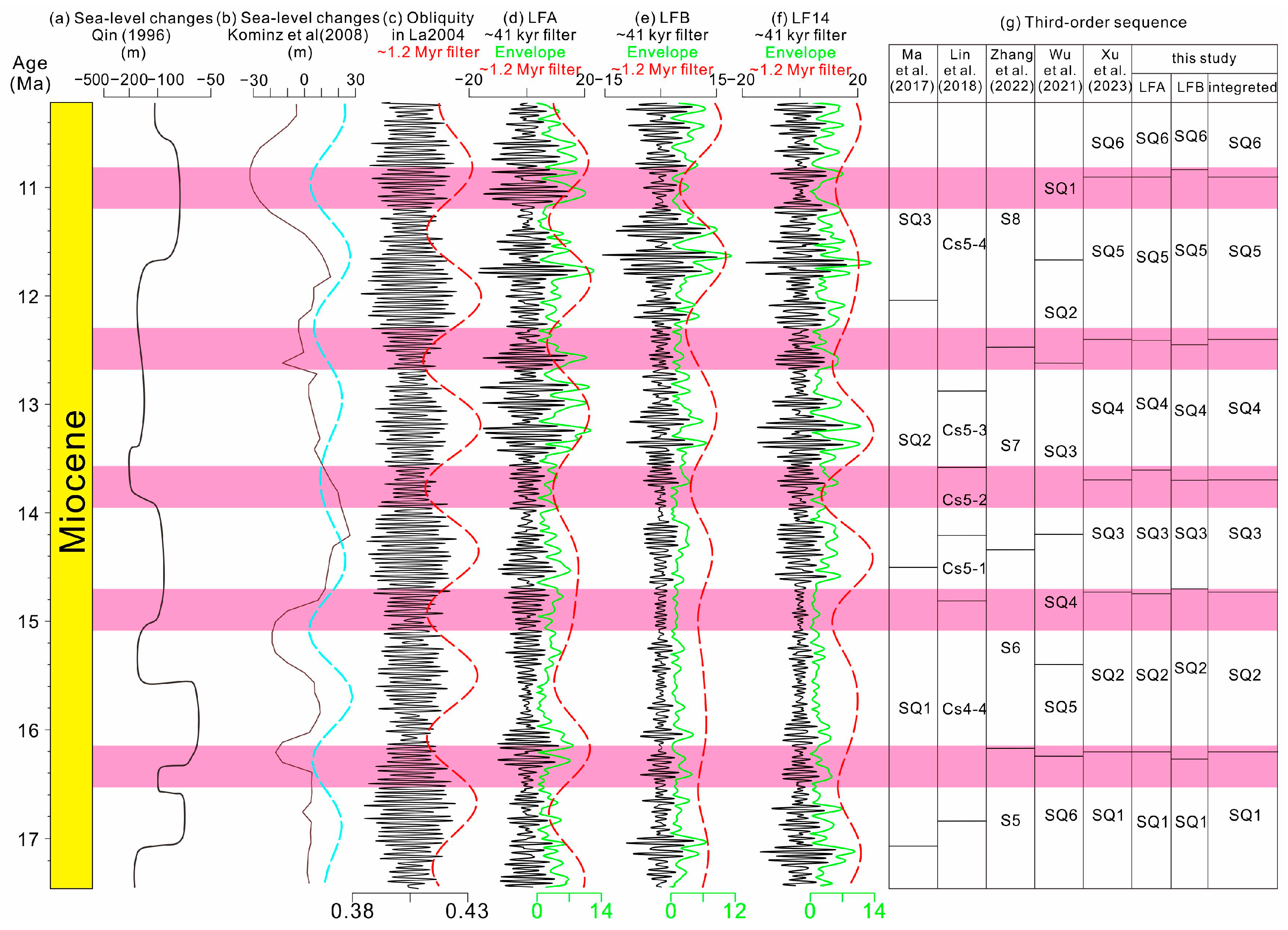
5.2.1. The 1.2-Myr Obliquity Cycles Modulation of Sea Level Changes and Third-Order Sequences
5.2.2. Third-Order Sequence Development in the PRMB Response to Obliquity Forcing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vail, P.R.; Mitchum, R.M., Jr.; Thompson, S., III. Seismic Stratigraphy and Global Changes of Sea Level: Part 3. Relative Changes of Sea Level from Coastal Onlap: Section 2. Application of Seismic Reflection Configuration to Stratigraphic Interpretation. In Seismic Stratigraphy—Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration; Payton, C.E., Ed.; AAPG Memoir: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; Volume 26, pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, B.U. Sequence Stratigraphy, Sea-level Change, and Significance for the Deep Sea. In Sedimentation, Tectonics and Eustasy: Sea-Level Changes at Active Margins; Macdonald, D.I.M., Ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Catuneanu, O. Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy. In Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–512. [Google Scholar]
- Vail, P.R.; Audemard, F.; Boeman, S.A.; Eisner, P.N.; Perez-Cruz, C. The Stratigraphic Signatures of Tectonics, Eustasy and Sedimentology—An Overview. In Cycles and Events in Stratigraphy; Einsele, G., Ricken, W., Seilacher, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 617–659. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C. Gaussian Processes in Machine Learning. In Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning: ML Summer Schools 2003; Bousquet, O., von Luxburg, U., Rätsch, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, A.; Hillgärtner, H.; Hug, W.; Pittet, B. Third-order Depositional Sequences Reflecting Milankovitch Cyclicity. Terra Nova 2000, 12, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulila, S.; Galbrun, B.; Miller, K.G.; Pekar, S.F.; Browning, J.V.; Laskar, J.; Wright, J.D. On the origin of Cenozoic and Mesozoic "third-order" eustatic sequences. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.J.; Demicco, R.V. Computer models of carbonate platform cycles driven by subsidence and eustasy. Geology 1989, 17, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osleger, D.A. Subtidal carbonate cycles: Implications for allocyclic vs. autocyclic controls. Geology 1991, 19, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, A.; Hilgen, F.J.; Heckel, P.H. Cyclostratigraphy; concepts, definitions, and applications. Newsl. Stratigr. 2006, 42, 75–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, F.; Zhu, F.; Cai, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Orbitally forced glacio-eustatic origin of third-order sequences and parasequences in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 99, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Ren, J.; Kemp, D.B.; Lei, C.; Zhu, H.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Z. Astronomical Pacing of Third-Order Sea-Level Sequences During the Middle Miocene in the Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 154, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Garia-Hidalgo, J.F.; Mateos, R.; Segura, M. Orbital cycles in a late cretaceousshallow platform (Iberian Ranges, Spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 274, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagreich, M.; Lein, R.; Sames, B. Eustasy, its controlling factors, and the limnoeustatic hypothesis–concepts inspired by Eduard Suess. Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2014, 107, 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Catuneanu, O. Sequence Stratigraphy: Guidelines for a Standard Methodology. In Stratigraphy & Timescales, 1st ed.; Montenari, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Ogg, J.G.; Algeo, T.J.; Kemp, D.B.; Shen, W. Oscillations of Global Sea-Level Elevation During the Paleogene Correspond to 1.2-Myr Amplitude Modulation of Orbital Obliquity Cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 522, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokoph, A.; Agterberg, F.P. Wavelet Analysis of Well-Logging Data from Oil Source Rock, Egret Member, Offshore Eastern Canada. AAPG Bull. 2000, 84, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Nio, S.D.; Brouwer, J.H.; Smith, D.; de Jong, M.; Böhm, A.R. Spectral Trend Attribute Analysis: Applications in the Stratigraphic Analysis of Wireline Logs. First Break 2005, 23, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, V. Application of gamma deviation log (GDL) in sequence stratigraphy of carbonate strata, an example from offshore Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 2017, 156, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, J.; Ruffell, A.; Deconinck, J.-F.; Baudin, F. Conjunctive Use of Spectral Gamma-Ray Logs and Clay Mineralogy in Defining Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous Palaeoclimate Change (Dorset, U.K.). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 229, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, G.; Hinnov, L.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Wan, X.; Wang, C. Astrochronology of the Early Turonian–Early Campanian terrestrial succession in the Songliao Basin, northeastern China and its implication for long-period behavior of the Solar System. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 385, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulila, S.; Dupont-Nivet, G.; Galbrun, B.; Bauer, H.; Châteauneuf, J.J. Age and Driving Mechanisms of the Eocene–Oligocene Transition from Astronomical Tuning of a Lacustrine Record (Rennes Basin, France). Clim. Past 2021, 17, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ogg, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hinnov, L.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Z. Astronomical Tuning of the End-Permian Extinction and the Early Triassic Epoch of South China and Germany. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 441, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Long, Z.; Shi, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhang, X. Source Rock Characteristics and Resource Potential in Pearl River Mouth Basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 40, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Q. Sedimentary Microfacies and Lithologic Trap Types of the Hanjiang Formation in the Enping Depression. Mar. Geol. Front. 2022, 38, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ge, J.; Qu, H.; Ma, C. Sequence stratigraphy driven by tectonic subsidence and astronomical forcing: A case study from the Miocene Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 169, 107074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lin, C.; Tao, Z.; Jiang, J. Sedimentary Architecture and Evolution of Slope Channel System and Sequence Stratigraphic Framework: A Case from Northeast of Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2017, 41, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Jiang, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Qin, C.; Li, H.; Ran, H.; Wei, A.; Tian, H.; et al. Sequence Architecture and Depositional Evolution of the Northern Continental Slope of the South China Sea: Responses to Tectonic Processes and Changes in Sea Level. Basin Res. 2018, 30, 568–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, H.; Zheng, X.; Cai, G.; Li, Z. Miocene Tidal Control System and Its Exploration Significance of Lithologic Trap in Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 3673–3689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, B.; Bei, R.; Shu, L.; Jiang, J.; Xing, Z.; Sun, H. Shoreline Migration Paths and Depositional Architecture of Early–Mid Miocene Deltaic Clinoforms in Response to Sea-Level Changes in the North-Eastern Shelf Margin, South China Sea. Sedimentology 2022, 69, 1456–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ding, X.; Pei, R.; Wan, X. Miocene Paleoenvironmental Evolution Based on Benthic Foraminiferal Assemblages in the Lufeng Sag, Northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Luo, P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, C.; Chao, P. Structural, Sedimentary and Magmatic Records During Continental Breakup at Southwest Sub-Basin of South China Sea. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 2287–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, X.; Tan, M.; Zhuo, H.; Liu, C.; Jones, B.G. Sequence Stratigraphy and Depositional Evolution of the North-Eastern Shelf (33.9–10.5 Ma) of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 141, 105697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Ahmed, N.; Usman, M.; Umar, M.; Rahim, H.u.; Imran, Q.S. Facies Analysis and Sedimentary Architecture of Hybrid Event Beds in Submarine Lobes: Insights from the Crocker Fan, NW Borneo, Malaysia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Usman, M.; Wahid, A.; Umar, M.; Ahmed, N.; Haq, I.U.; El-Ghali, M.A.K.; Imran, Q.S.; Rahman, A.H.A.; et al. Facies analysis and distribution of Late Palaeogene deep-water massive sandstones in submarine-fan lobes, NW Borneo. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 4489–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G. Application of Micropaleontology to the Sequence Stratigraphic Studies of Late Cenozoic in the Zhujiang River Mouth Basin. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1996, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Pas, D.; Krijgsman, W.; Wei, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Astronomical Forcing of the Paleogene Coal-Bearing Hydrocarbon Source Rocks of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 406, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.P.; Hinnov, L.A. Rock Magnetic Cyclostratigraphy. In Rock Magnetic Cyclostratigraphy, 1st ed.; Wiley–Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Kump, L.R.; Hinnov, L.A.; Mann, M.E. Tracking Variable Sedimentation Rates and Astronomical Forcing in Phanerozoic Paleoclimate Proxy Series with Evolutionary Correlation Coefficients and Hypothesis Testing. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 501, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.R.; Sageman, B.B. Quantification of Deep-Time Orbital Forcing by Average Spectral Misfit. Am. J. Sci. 2007, 307, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, M.; Ogg, J.G.; Zhang, C.; Feng, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. East Asian lake hydrology modulated by global sea-level variations in the Eocene warmhouse. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 602, 117925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.J. Spectrum Estimation and Harmonic Analysis. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, J.; Robutel, P.; Joutel, F.; Gastineau, M.; Correia, A.C.M.; Levrard, B. A Long-Term Numerical Solution for the Insolation Quantities of the Earth. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 428, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnov, L.A.; Hilgen, F.J. Cyclostratigraphy and Astrochronology. In The Geologic Time Scale; Gradstein, F.M., Ogg, J.G., Schmitz, M.D., Ogg, G.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Hinnov, L.; Kump, L. Acycle: Time-Series Analysis Software for Paleoclimate Research and Education. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 127, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominz, M.; Browning, J.; Miller, K.; Sugarman, P.; Mizintseva, S.; Scotese, C. Late Cretaceous to Miocene Sea-Level Estimates from the New Jersey and Delaware Coastal Plain Coreholes: An Error Analysis. Basin Res. 2008, 20, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Fang, N.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, T. Cyclostratigraphy Research on the Hanjiang-Wanshan Formations in the Zhu I Depression. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Raymo, M.; Nisancioglu, K. The 41 kyr World: Milankovitch’s Other Unsolved Mystery. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2003, 18, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, J.; Abdul Aziz, H.; Álvarez Sierra, M. Long-Period Astronomical Forcing of Mammal Turnover. Nature 2006, 443, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.R.; Sageman, B.B.; Arthur, M.A. Obliquity Forcing of Organic Matter Accumulation During Oceanic Anoxic Event 2. Paleoceanography 2012, 27, PA3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wu, H.; Hinnov, L.A.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S. Abiotic and Biotic Responses to Milankovitch-Forced Megamonsoon and Glacial Cycles Recorded in South China at the End of the Late Paleozoic Ice Age. Glob. Planet. Change 2018, 163, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Jin, S.; Hou, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, A. Astronomical Cycles Calibrated the Sea-Level Sequence Durations of Late Miocene to Pliocene in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 143, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, H.A.; Baldini, J.; Challands, T.J.; Gröcke, D.R.; Owen, A.W. Response of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone to Southern Hemisphere Cooling During Upper Ordovician Glaciation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 284, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Wu, N.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Xu, K. Orbital-Scale Modulation of the Middle Miocene Third-Order Eustatic Sequences from the Northern South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050921
Xu H, Wu N, Xu X, Yu B, Xu K. Orbital-Scale Modulation of the Middle Miocene Third-Order Eustatic Sequences from the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050921
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Haichun, Nan Wu, Xinyan Xu, Bo Yu, and Ke Xu. 2025. "Orbital-Scale Modulation of the Middle Miocene Third-Order Eustatic Sequences from the Northern South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050921
APA StyleXu, H., Wu, N., Xu, X., Yu, B., & Xu, K. (2025). Orbital-Scale Modulation of the Middle Miocene Third-Order Eustatic Sequences from the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050921