Utilization of Marine-Dredged Sediment and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement for Preparing Non-Sintered Ceramsites: Properties and Microstructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
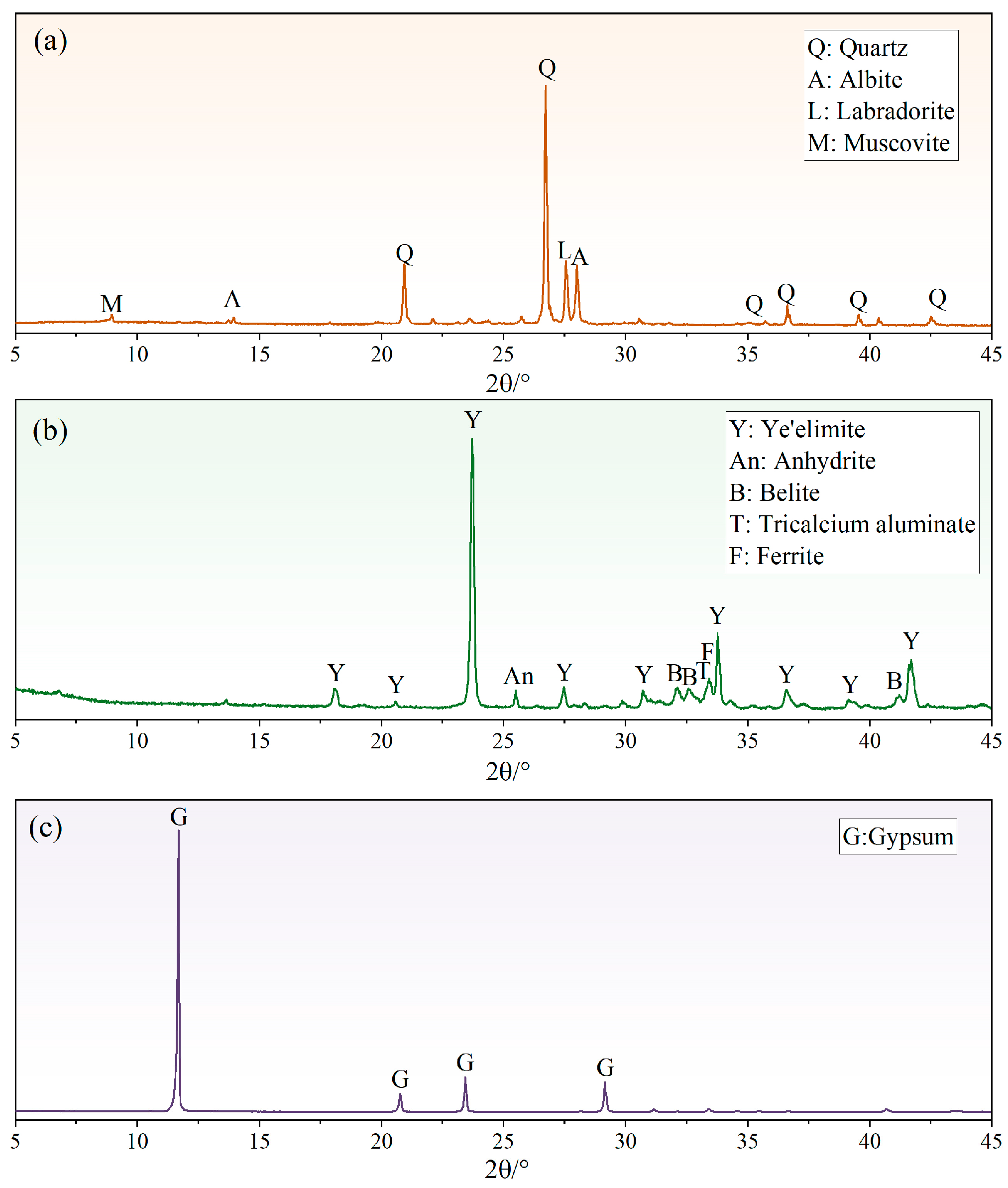
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Arrangements and Preparation of Ceramsite
2.3. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussions
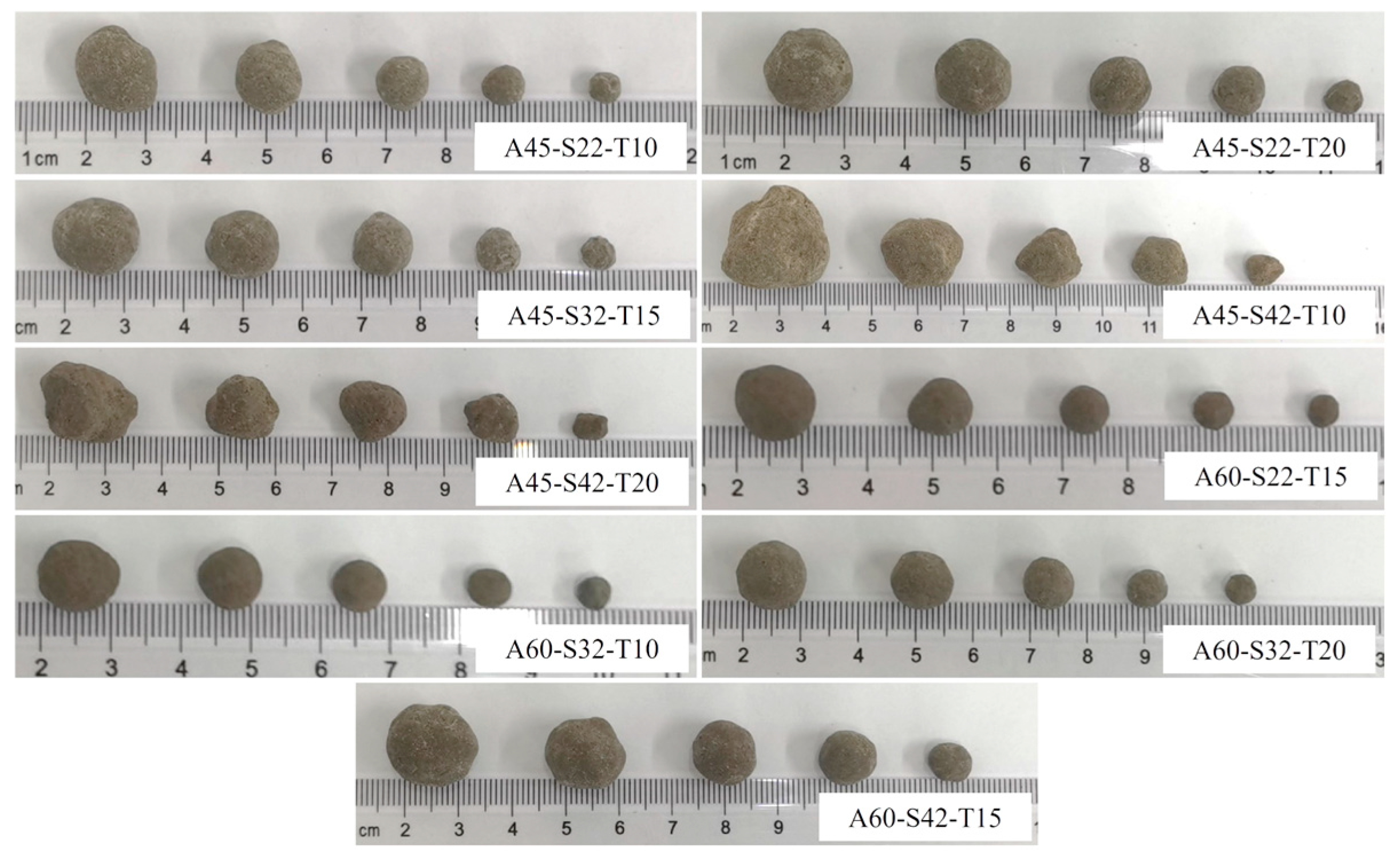
3.1. Appearance and Particle Size Distribution
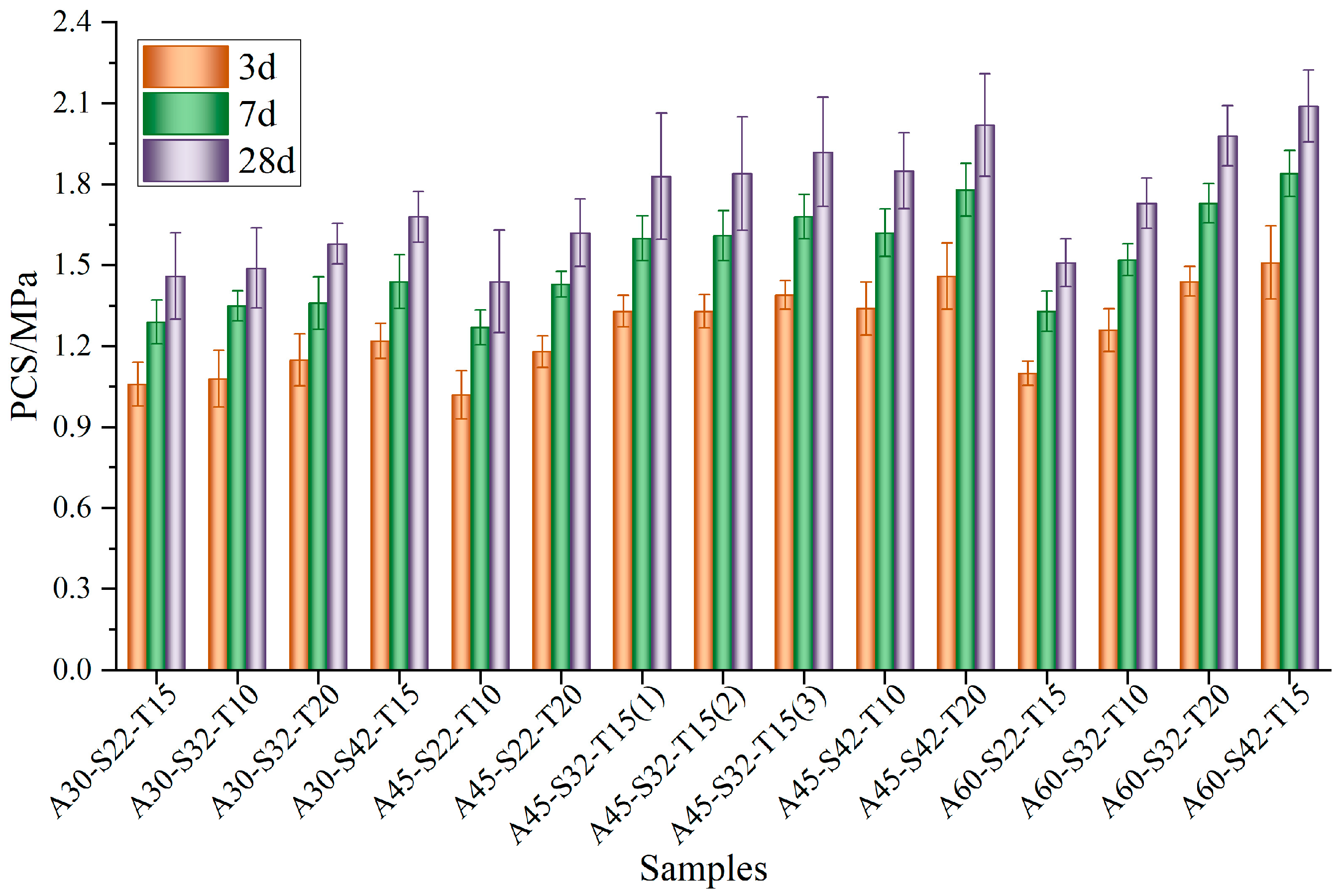
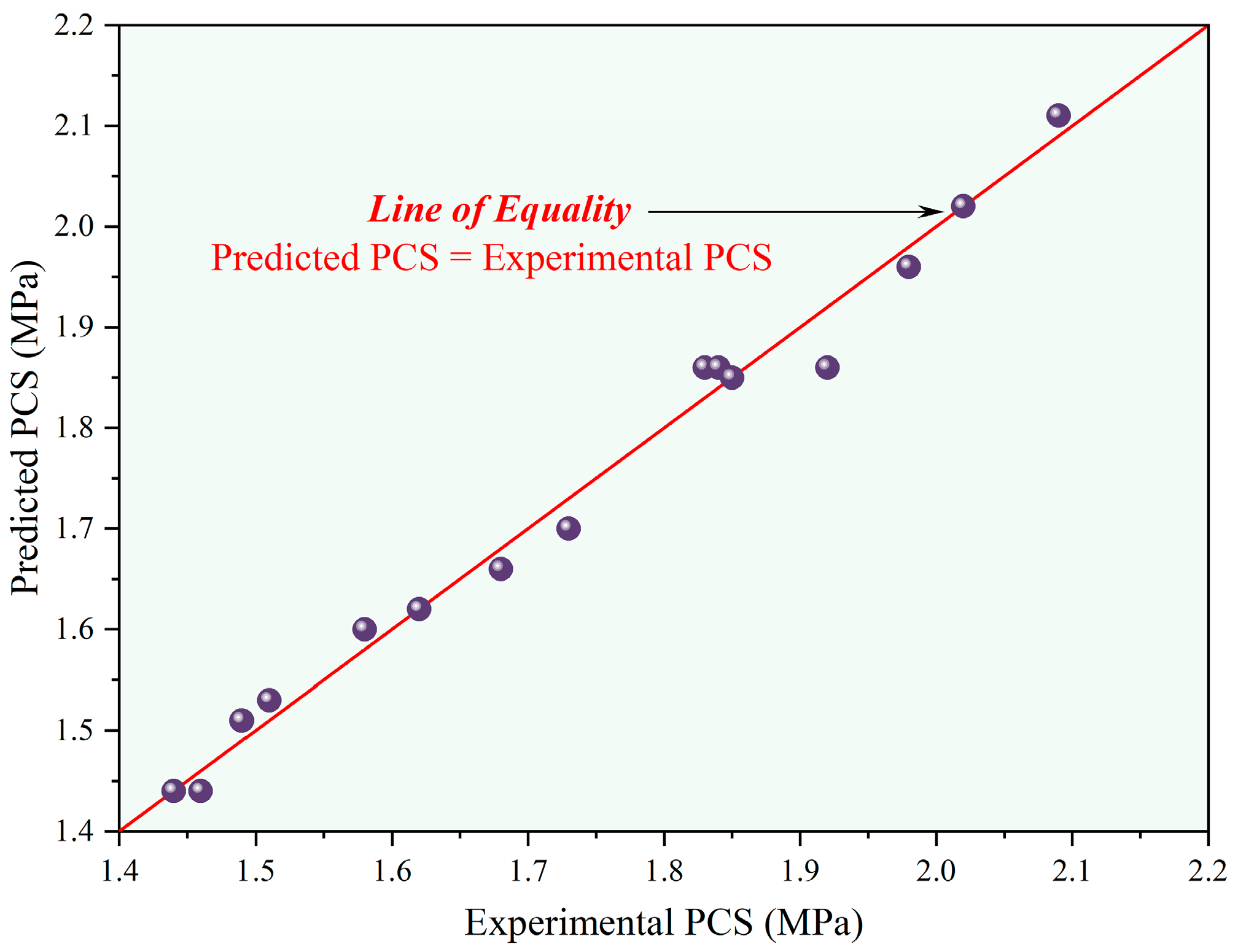
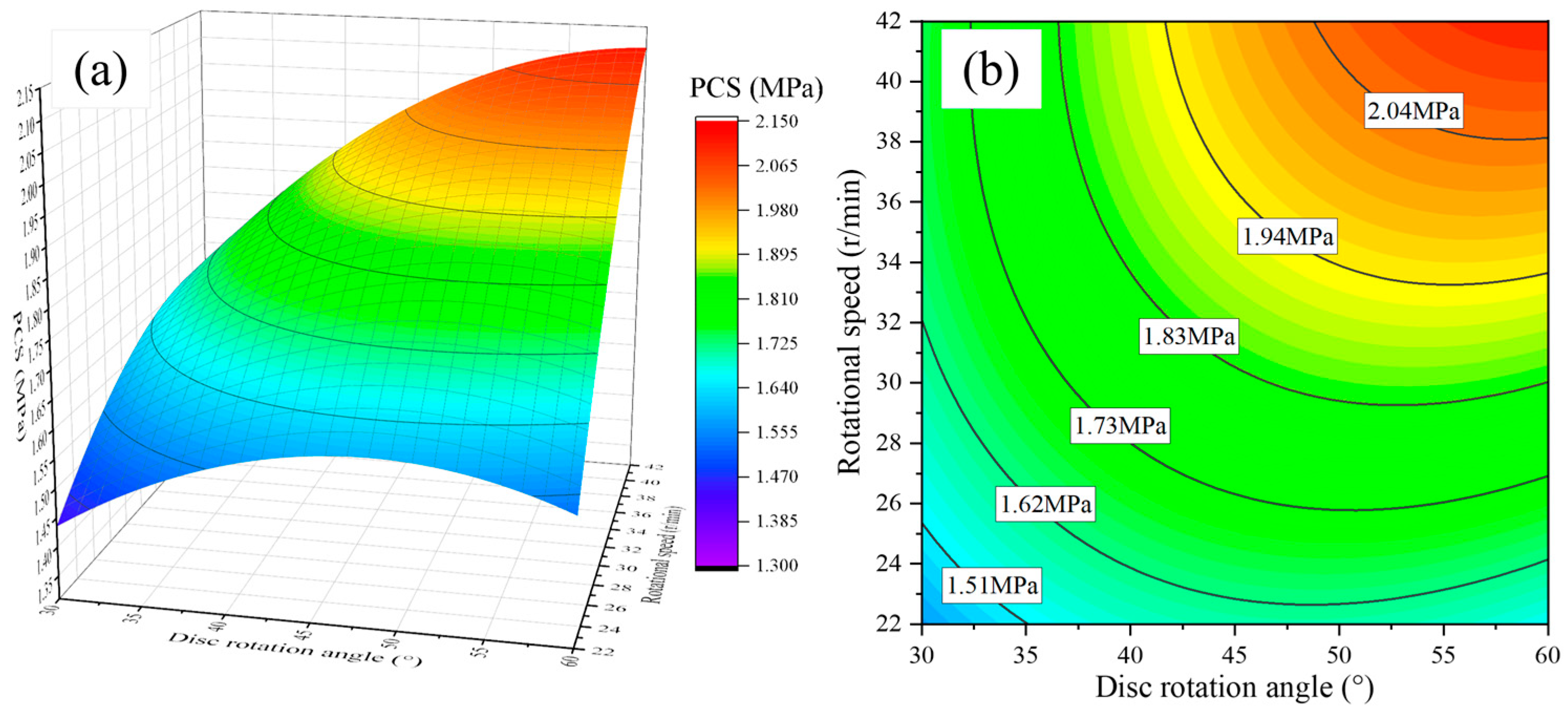
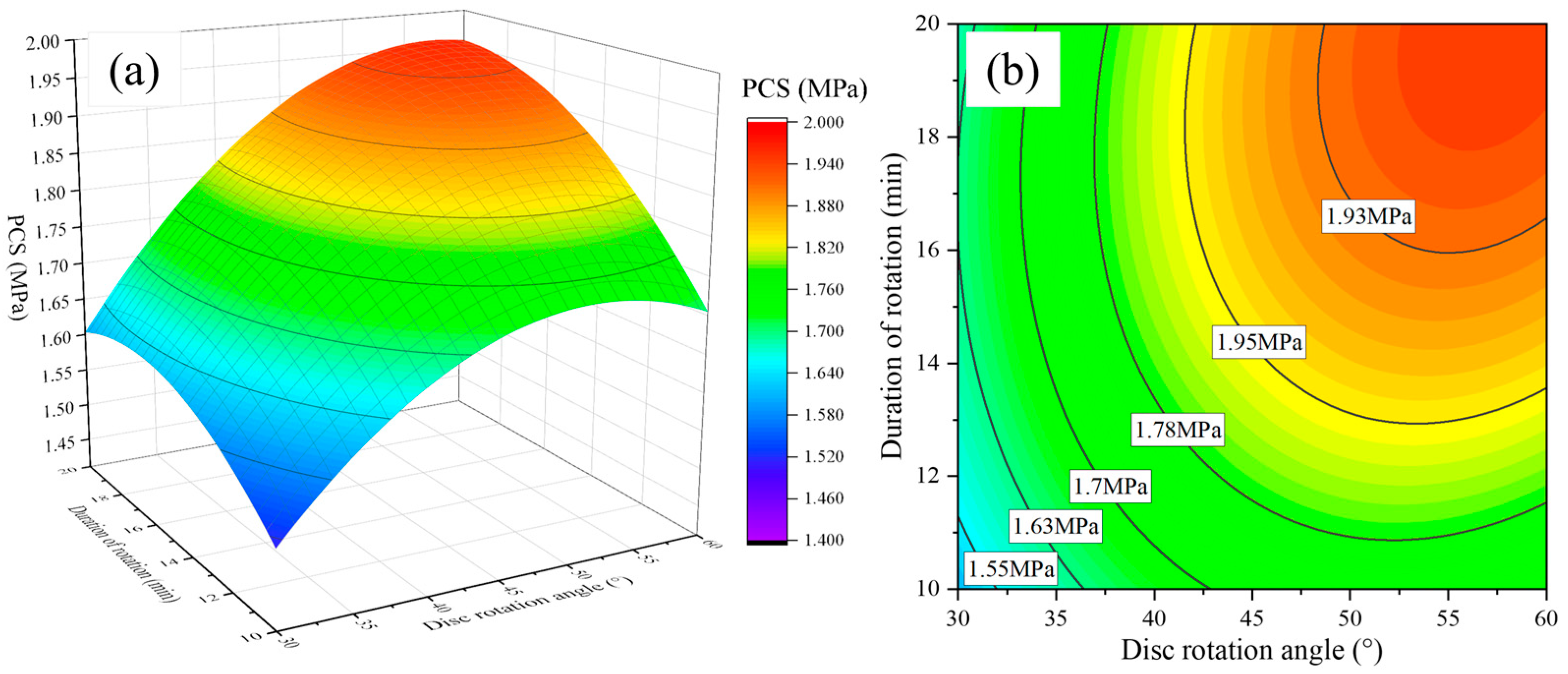
3.2. Mechanical Properties
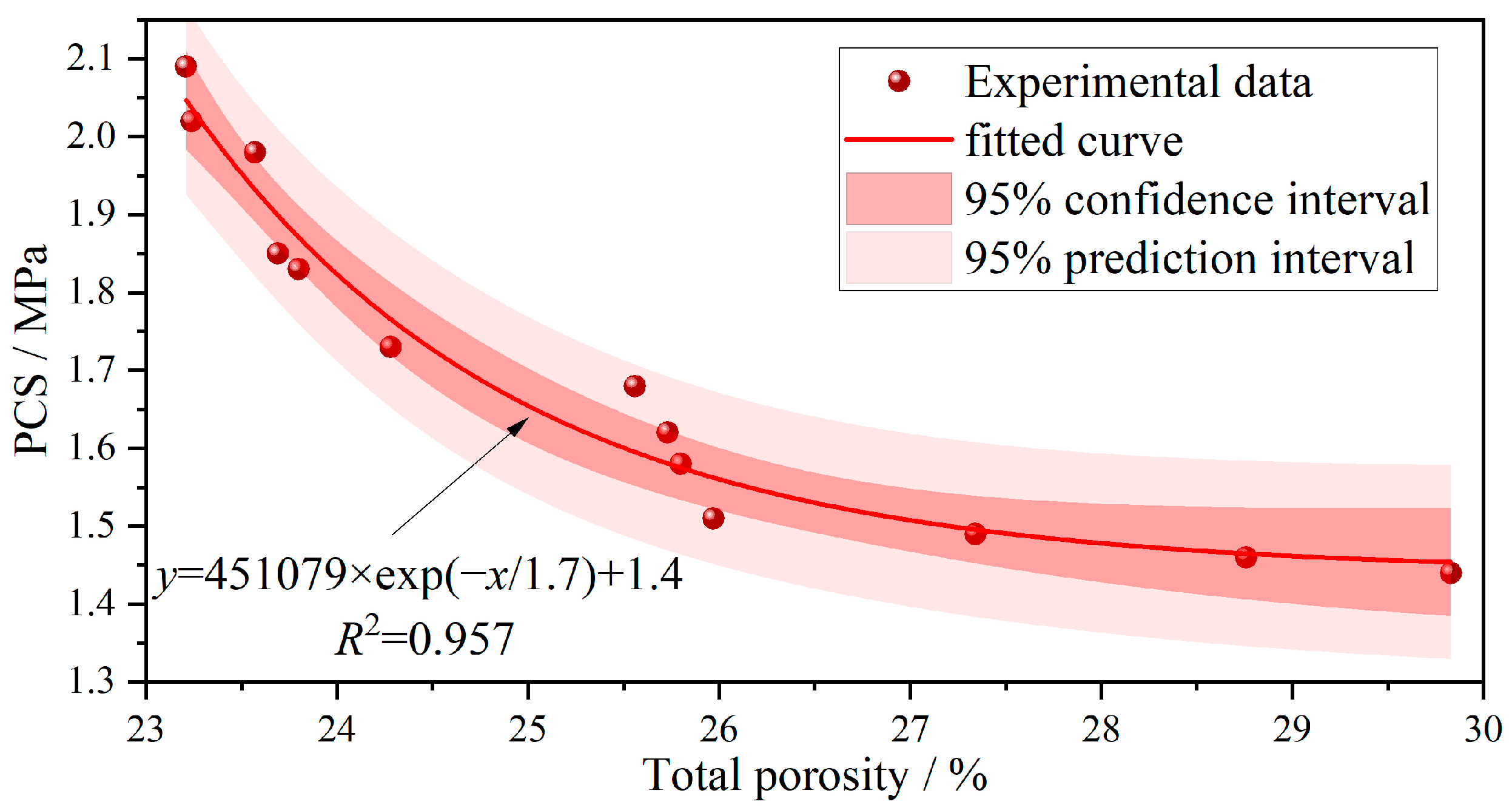
3.3. Porosity
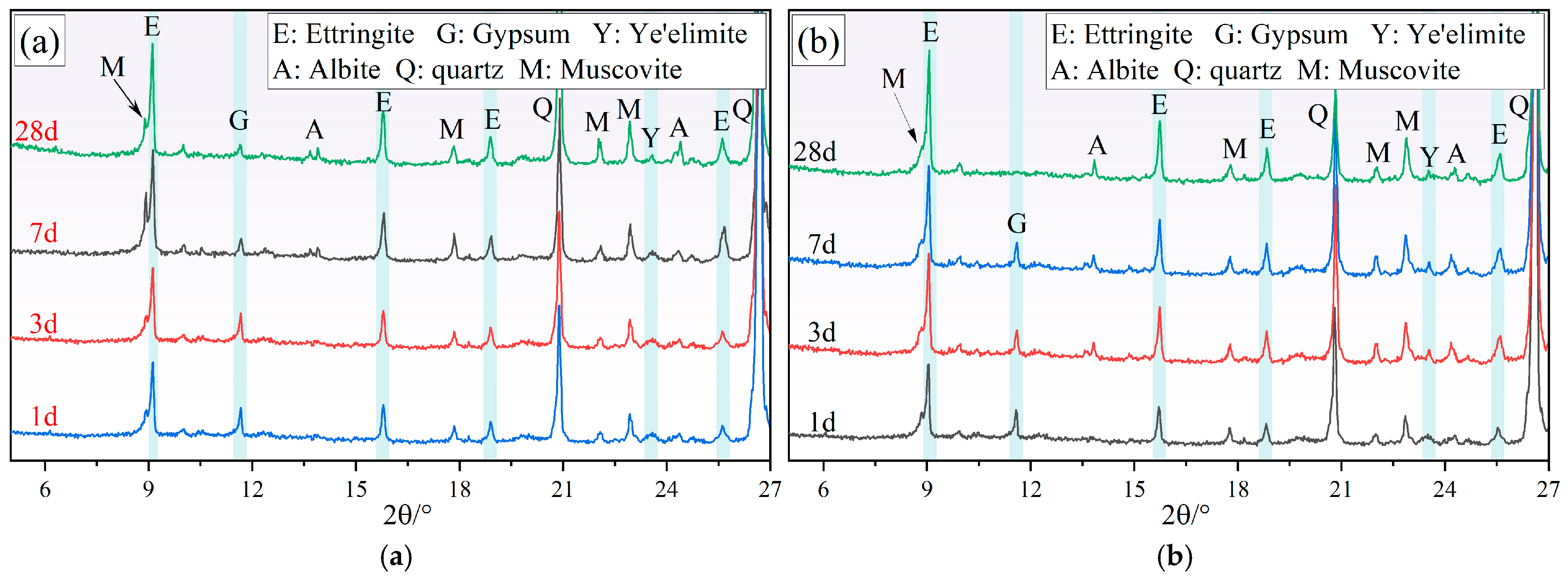
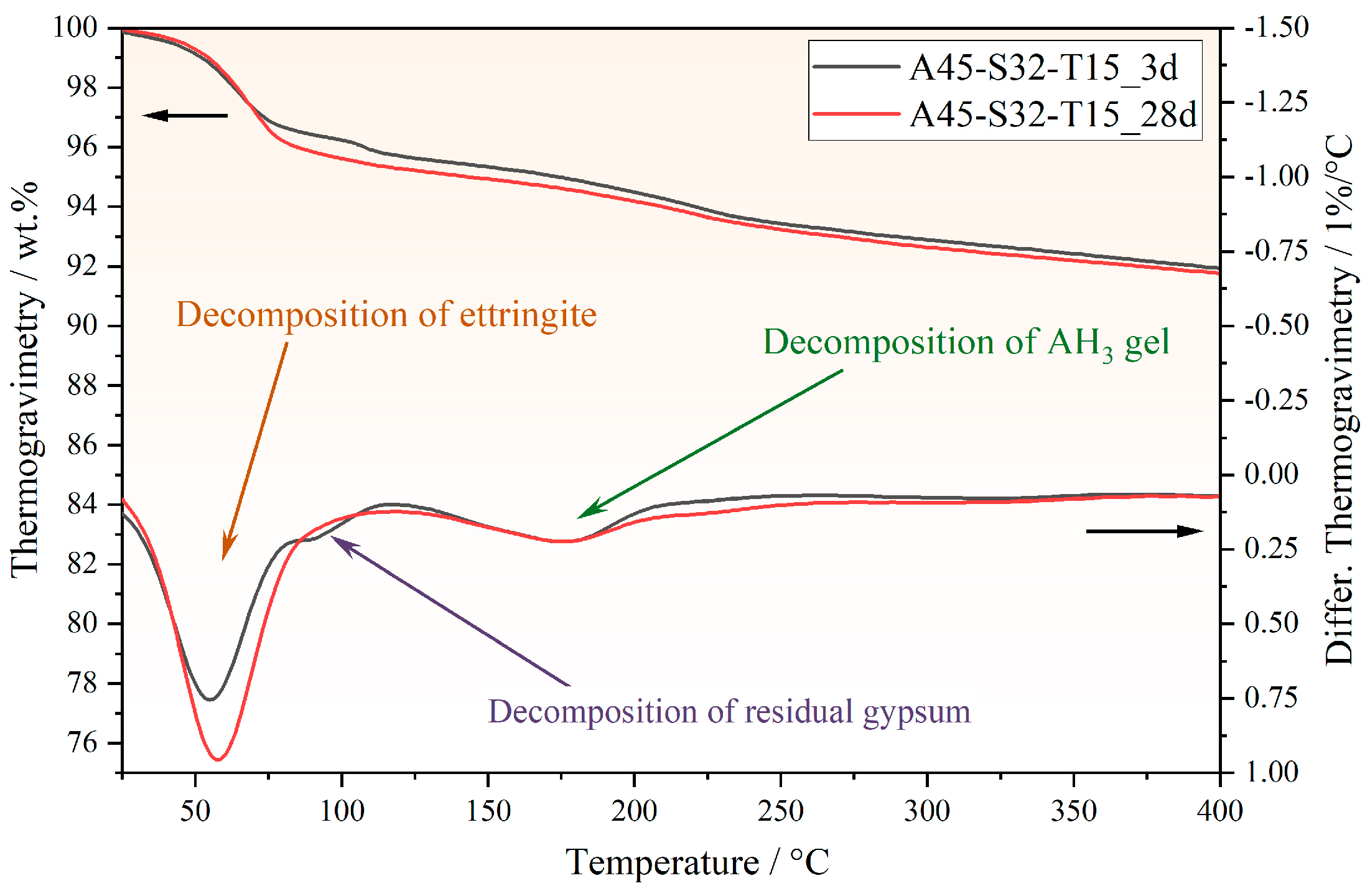
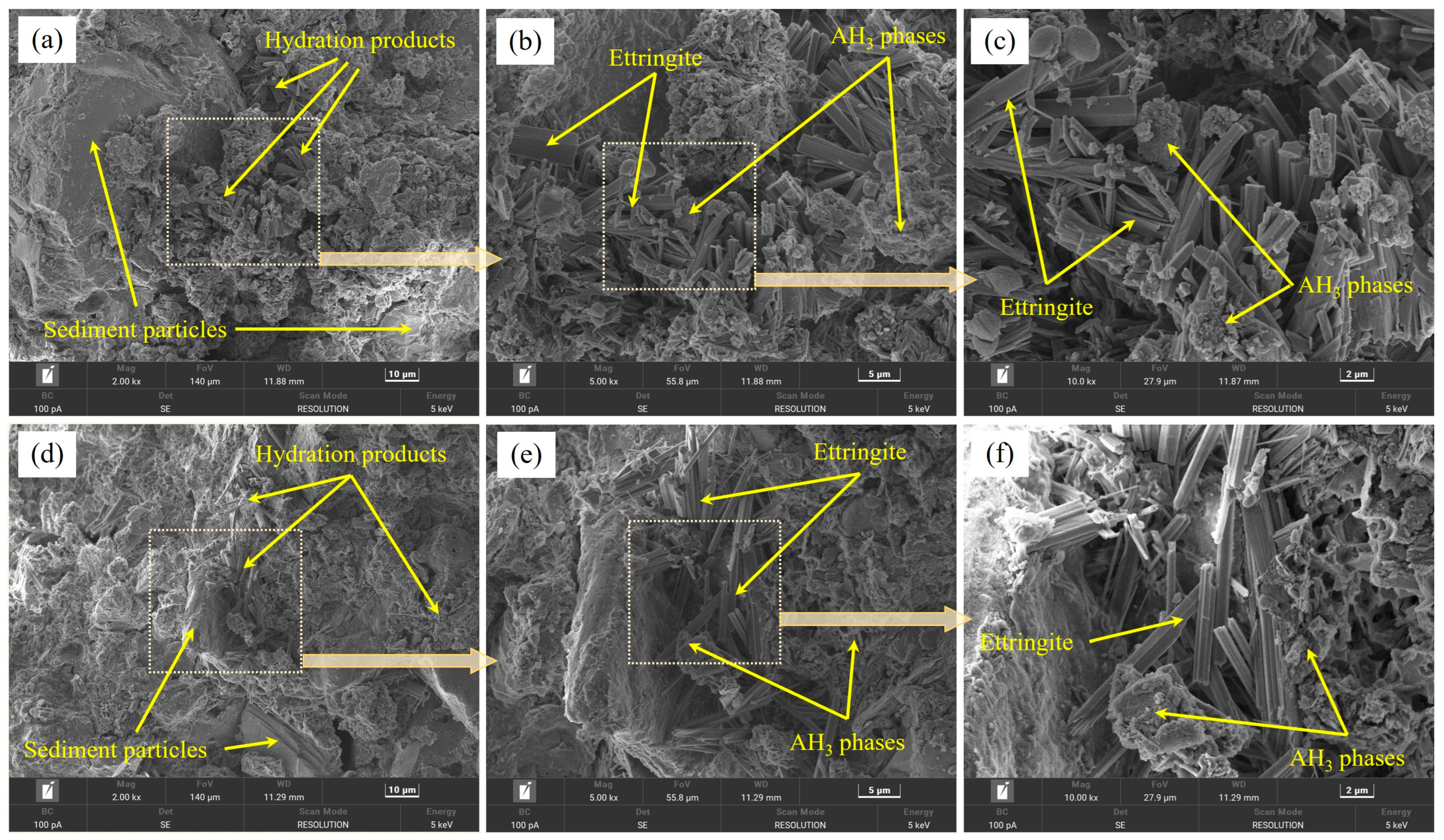
3.4. Phase Composition and Microstructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSA | Calcium sulfoaluminate. |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland Cement. |
| PCS | Plate Crush Strength. |
| RSM | Response surface methodology. |
Appendix A
| Factors | Factor Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| x1 | 30 | 45 | 60 |
| x2 | 22 | 32 | 42 |
| x3 | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Types of Correlation Coefficient | Value |
|---|---|
| Multiple Correlation Coefficient (R2) | 0.9862 |
| Adjusted Multiple Correlation Coefficient (RAdj2) | 0.9614 |
| Predicted Multiple Correlation Coefficient (RPred2) | 0.8825 |
References
- Žilinskas, G.; Janušaitė, R.; Jarmalavičius, D.; Pupienis, D. The Impact of Klaipėda Port Entrance Channel Dredging on the Dynamics of Coastal Zone, Lithuania. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.H.; Yao, J.J. A Strength Model for Concrete Made with Marine Dredged Sediment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, C. Reliability and Sensitivity Analyses of Monopile Supported Offshore Wind Turbines Based on Probability Density Evolution Method with Pre-Screening of Controlling Parameters. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310, 118746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola, D.; Hernandez, J.; Vesco, V.; Reddy, K.R. Dredged Material Decision Tool (DMDT) for Sustainable Beneficial Reuse Applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Li, W. An Evaluation of Treatment Effectiveness for Reclaimed Coral Sand Foundation in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaga, C.R.L.; Samaniego, J.O.; Tanciongco, A.M.; Quierrez, R.N.M. Pollution Assessment of Mercury and Other Potentially Toxic Elements in the Marine Sediments of Mambulao Bay, Jose Panganiban, Camarines Norte, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Environmental Impact and Optimization of Lake Dredged-Sludge Treatment and Disposal Technologies Based on Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, N.; Norén, A.; Modin, O.; Fedje, K.K.; Rauch, S.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Integrated Cost and Environmental Impact Assessment of Management Options for Dredged Sediment. Waste Manag. 2021, 138, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, T.; Hayek, M.; Junqua, G.; Salgues, M.; Souche, J.-C. Environmental, Economic and Experimental Assessment of the Valorization of Dredged Sediment through Sand Substitution in Concrete. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 858, 159980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Jia, H.; You, Z. Characterization, Pollution, and Beneficial Utilization Assessment of Dredged Sediments from Coastal Ports in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 211, 117389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Labianca, C.; Chen, L.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M.; Guo, B.; Sun, J.; Ding, S.; Wang, L. Sustainable Ex-Situ Remediation of Contaminated Sediment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraza, M.T.; Tambara, L.U.D.; Alexandre, J.; de Castro Xavier, G.; Carneiro, J.C.; da Silva, L.G.C.H.; Azevedo, A.R.G. de Characterization of Port Dredging Waste for Potential Used as Incorporation on Materials for Civil Construction: A Case Study in Brazil. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Shao, X. Optimized Utilization Studies of Dredging Sediment for Making Water Treatment Ceramsite Based on an Extreme Vertex Design. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Isabelle, C.; Frederic, H.; Catherine, P.; Marie-Anne, B. Demonstrating the Influence of Sediment Source in Dredged Sediment Recovery for Brick and Tile Production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 171, 105653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chompoorat, T.; Thepumong, T.; Taesinlapachai, S.; Likitlersuang, S. Repurposing of Stabilised Dredged Lakebed Sediment in Road Base Construction. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z. Evolution Mechanism of Pore Structure in Sintered Coal Gangue Ceramsites. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 31385–31395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Li, Z.; Shang, Q.; Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Wang, C. High Efficiency of Drinking Water Treatment Residual-Based Sintered Ceramsite in Biofilter for Domestic Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, J.; He, H.; Li, R.; Yu, J.; Shen, X.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, W. Study on the Impact of HTPP Fibers on the Mechanical Properties of Ceramsite Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhuang, S.; Wang, J. Evaluation and Prediction of Fatigue Life for Ceramsite Lightweight Concrete Considering the Effects of Ceramsite Aggregate Size and Content. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anting, N.; Din, M.F.M.; Iwao, K.; Ponraj, M.; Jungan, K.; Yong, L.Y.; Siang, A.J.L.M. Experimental Evaluation of Thermal Performance of Cool Pavement Material Using Waste Tiles in Tropical Climate. Energy Build. 2017, 142, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Ma, X.; Mei, R.; Li, C.; Sun, Z. The Formation of Porous Light Ceramsite Using Yellow River Sediment and Its Application in Concrete Masonry Production. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Fan, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, K.; Zhou, H. Preparation of Ultra-Lightweight Ceramsite from Waste Materials: Using Phosphate Tailings as Pore-Forming Agent. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 15218–15229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; An, S. Process and Property Optimization of Ceramsite Preparation by Bayan Obo Tailings and Blast Furnace Slag. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ma, D.; Huang, K.; Yang, X. Effect of Sludge Ceramsite Particle Grade on Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Alkali-Activated Slag Lightweight Concrete at Early Age. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Bao, S.; Jing, Z. Immobilization Mechanism of Mn2+ in Electrolytic Manganese Residue Using Sintered Ceramsites Prepared by Alkali-Mechanical-Roasting Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, T.; Chu, L.; Liu, Z. Preparation of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash-Based Ceramsite and Its Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Immobilization. Waste Manag. 2022, 143, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; okeke, I.; He, C.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, J. Revealing the Intrinsic Sintering Mechanism of High-Strength Ceramsite from CFB Fly Ash: Focus on the Role of CaO. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 24281–24292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Y.; Ma, J. Preparation of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash/Granite Sawing Mud Ceramsite and the Morphological Transformation and Migration Properties of Chlorine. Waste Manag. 2023, 173, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gu, X.; Ni, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, R. Comparative Evaluation of Foam Concrete Blocks Derived from Non-Sintering and Sintered Ceramsites: Experimental Analysis, Simulation, and Carbon Emission Assessment. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R. Use of Cement Kiln Dust, Blast Furnace Slag and Marble Sludge in the Manufacture of Sustainable Artificial Aggregates by Means of Cold Bonding Pelletization. Materials 2013, 6, 3139–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajra, F.; Elrahman, M.A.; Stephan, D. The Production and Properties of Cold-Bonded Aggregate and Its Applications in Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, B.; Ren, J.; Fang, G. Stabilization/Solidification of Sand-Washing Slurry Used for Porous Cold-Bonded Ceramsite. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Xuan, D.; Li, J.; Cheng, H.W.; Poon, C.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Investigation of Cold Bonded Lightweight Aggregates Produced with Incineration Sewage Sludge Ash (ISSA) and Cementitious Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Guo, W.; Jia, Y.; Xue, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, D. Preparation of Non-Sintered Lightweight Aggregate Ceramsite Based on Red Mud-Carbide Slag-Fly Ash: Strength and Curing Method Optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, R.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y. Preparation of Non-Sintered Lightweight Aggregates from Dredged Sediments and Modification of Their Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Peng, X.; Yang, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, W.; Tang, X.; Wu, Y. The Performances of the Baking-Free Bricks of Non-Sintered Wrap-Shell Lightweight Aggregates from Dredged Sediments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cho, S.; Pyo, S.; Bae, Y.; Oh, J.E. New Cold-Bonded Artificial Aggregate Using a Ba(OH)2-Activated Cementless Binder for Cement-Free Concrete Production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Chau, C.K.; Leung, L.M.; Duan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Sham, M.L.; Poon, C.S. Developing Low-Carbon High-Strength Core-Shell Aggregates Using Solid Waste by Cold-Bonding Techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; An, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Song, Z. Safety and Environmental Protection Application of High Performance Solid Waste Unburned Ceramsite and Its Lightweight High Strength Concrete. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 40, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Che, Q.; Gao, D.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Long-Term Performance of Sulphoaluminate Cement Blended with Different Contents of Limestone. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 36, 04023496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, G.; Moon, S.-W.; Moon, J.; Ku, T. Early Strength Development in Cement-Treated Sand Using Low-Carbon Rapid-Hardening Cements. Soils Found. 2018, 58, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Khan, Q.; Ku, T. Strength Development and Prediction of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Treated Sand with Optimized Gypsum for Replacing OPC in Ground Improvement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Moon, S.-W.; Satyanaga, A.; Kim, J. Assessing Durability and Stability of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement-Stabilized Soils Under Cyclic Wet–Dry Conditions. Buildings 2025, 15, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Shen, C.; Long, K. Durability of Solidified Sludge with Composite Rapid Soil Stabilizer under Wetting–Drying Cycles. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Gan, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, A.; Qi, Y. Study on the Early Strength Characteristics and Source Mechanism of Solidified Dredged Marine Sediment Based on Moisture Transformation. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023, 74, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zentar, R.; Wang, D.; Ouendi, F. New Applications of Ordinary Portland and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Composite Binder for Recycling Dredged Marine Sediments as Road Materials. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 04022068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentar, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. Comparative Study of Stabilization/Solidification of Dredged Sediments with Ordinary Portland Cement and Calcium Sulfo-Aluminate Cement in the Framework of Valorization in Road Construction Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooni, J.; Robert, D.; Giustozzi, F.; Setunge, S.; Xie, Y.M.; Xia, J. Performance Evaluation of Calcium Sulfoaluminate as an Alternative Stabilizer for Treatment of Weaker Subgrades. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 27, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocheme, J.I.; Kim, J.; Moon, S.-W. Enhancing Geomechanical Characteristics of Calcium Sulfoaluminate (CSA) Cement-Treated Soil under Low Confining Pressures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgaro, L.; Contessi, S.; Bonetto, A.; Badetti, E.; Ferrari, G.; Artioli, G.; Marcomini, A. Calcium Aluminate Cement as an Alternative to Ordinary Portland Cement for the Remediation of Heavy Metals Contaminated Soil: Mechanisms and Performance. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Xue, C.; Jia, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y. Investigation of Various Curing Methods on the Properties of Red Mud-Calcium Carbide Slag-Based Artificial Lightweight Aggregate Ceramsite Fabricated through Alkali-Activated Cold-Bonded Pelletization Technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Si, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Bao, K.; Zhao, Q. Preparation of Low-Carbon and Environmentally Friendly Non-Sintered Ceramsite (NSC) Employing Steel Slag, GGBS and Fly Ash: Experiment and Performance Regulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Li, Z.; Pang, Q.; Ni, L.; Cui, H. Preparation Strategy and Performance Development Mechanism of River Sediment Based Non-Sintered Lightweight Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 473, 141061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yi, N.; Cui, C. Strength Performance and Microstructure of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement-Stabilized Soft Soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; Su, J.; Yuan, J. Preparation of Artificial Aggregates from Marine Dredged Material: CO2 Uptake and Performance Regulation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kockal, N.U.; Ozturan, T. Effects of Lightweight Fly Ash Aggregate Properties on the Behavior of Lightweight Concretes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.R.R.; Francisco, M.B.; Martins, R.M.; Gonçalves, P.C.; dos Santos, V.C.; Gomes, G.F.; Melo, M.d.L.N.M. RSM-Based Modeling and Optimization of Cementitious Composites with Polyurethane Powder Waste and Foundry Exhaust Sand. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04022480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Dong, Q.; Yan, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Development of Flexible Grouting Material for Cement-Stabilized Macadam Base Using Response Surface and Genetic Algorithm Optimization Methodologies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Su, L.; Gao, Z.; Yin, C.; Ye, Z. Optimization of Ultra-High Performance Concrete Based on Response Surface Methodology and NSGA-II. Materials 2024, 17, 4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Ji, J. AH3 Phase in the Hydration Product System of AFt-AFm-AH3 in Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements: A Microstructural Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Y. Nanostructural Characterization of Al(OH)3 Formed during the Hydration of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 4262–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Z.; Chang, J. Microstructure Control of AH3 Gel Formed in Various Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements as a Function of pH. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11534–11547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagidullina, N.; Abdialim, S.; Kim, J.; Satyanaga, A.; Moon, S.-W. Influence of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement-Treated Silty Sand. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

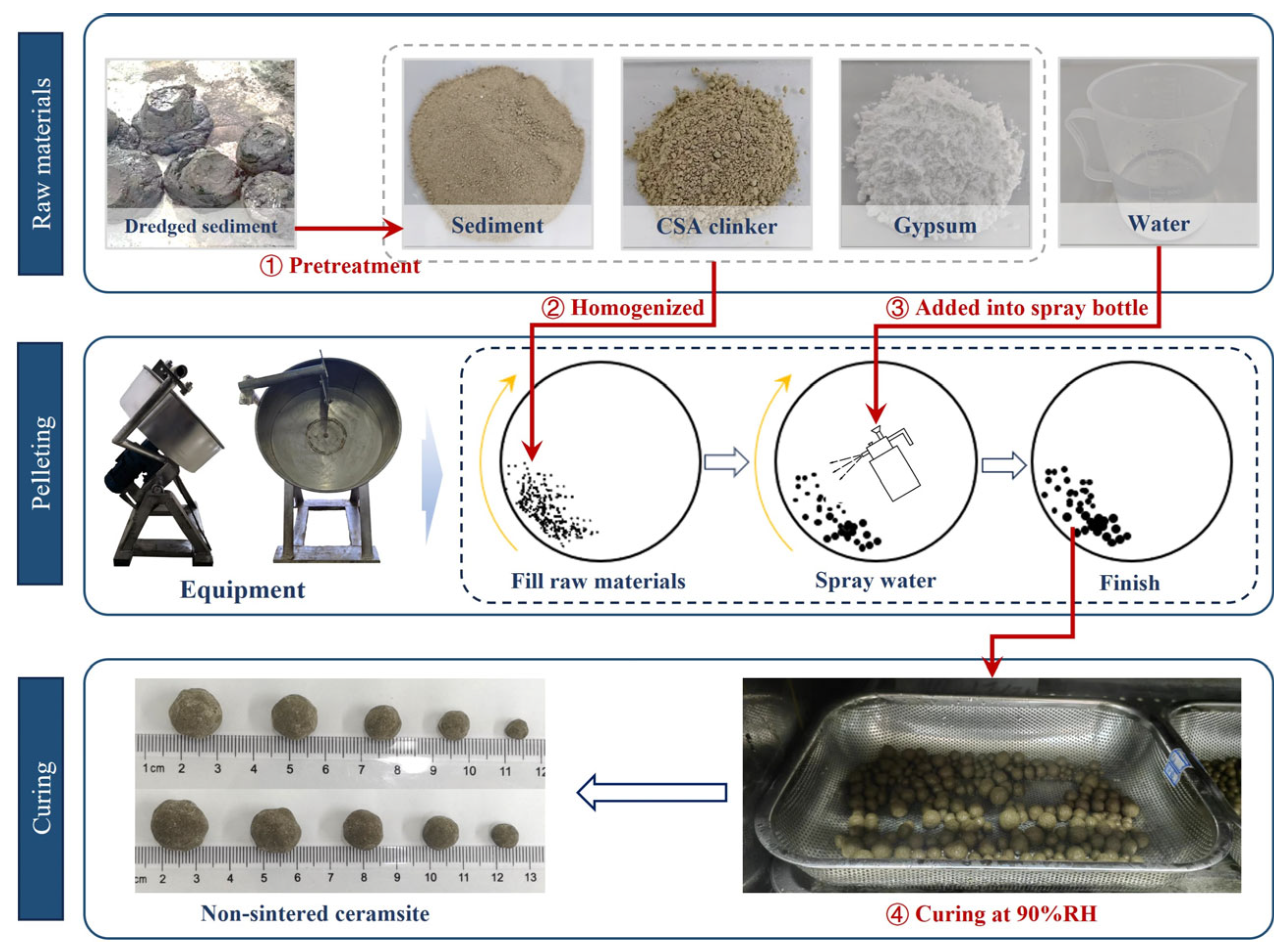



| Specific Gravity | Liquid Limit | Plastic Limit | Plasticity Index | Dry Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.72 | 39.6 | 21.1 | 18.5 | 1.52 g/cm3 |
| Nomenclature | Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| x1/° | x2/(r/min) | x3/min | |
| A30-S22-T15 | 30 | 22 | 15 |
| A30-S32-T10 | 30 | 32 | 10 |
| A30-S32-T20 | 30 | 32 | 20 |
| A30-S42-T15 | 30 | 42 | 15 |
| A45-S22-T10 | 45 | 22 | 10 |
| A45-S22-T20 | 45 | 22 | 20 |
| A45-S32-T15(1) a | 45 | 32 | 15 |
| A45-S32-T15(2) | 45 | 32 | 15 |
| A45-S32-T15(3) | 45 | 32 | 15 |
| A45-S42-T10 | 45 | 42 | 10 |
| A45-S42-T20 | 45 | 42 | 20 |
| A60-S22-T15 | 60 | 22 | 15 |
| A60-S32-T10 | 60 | 32 | 10 |
| A60-S32-T20 | 60 | 32 | 20 |
| A60-S42-T15 | 60 | 42 | 15 |
| Samples/Statistic | Closed Porosity/% | Open Porosity/% | Total Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| A30-S22-T15 | 15.64 | 13.11 | 28.76 |
| A30-S32-T10 | 18.59 | 8.75 | 27.34 |
| A30-S32-T20 | 15.30 | 10.50 | 25.80 |
| A30-S42-T15 | 17.95 | 7.62 | 25.56 |
| A45-S22-T10 | 15.39 | 14.44 | 29.83 |
| A45-S22-T20 | 18.26 | 7.47 | 25.73 |
| A45-S32-T15 | 15.49 | 8.30 | 23.80 |
| A45-S42-T10 | 13.16 | 10.53 | 23.69 |
| A45-S42-T20 | 15.24 | 8.01 | 23.24 |
| A60-S22-T15 | 15.28 | 10.69 | 25.97 |
| A60-S32-T10 | 15.07 | 9.21 | 24.28 |
| A60-S32-T20 | 15.35 | 8.23 | 23.57 |
| A60-S42-T15 | 13.38 | 9.82 | 23.21 |
| Mean value | 15.70 | 9.74 | 25.44 |
| Standard deviation | 1.59 | 2.03 | 2.05 |
| Range | 5.43 | 6.70 | 6.62 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Cui, C.; Liu, H. Utilization of Marine-Dredged Sediment and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement for Preparing Non-Sintered Ceramsites: Properties and Microstructure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050891
Zhao J, Wang Z, Xiao M, Cui C, Liu H. Utilization of Marine-Dredged Sediment and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement for Preparing Non-Sintered Ceramsites: Properties and Microstructure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050891
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiuye, Zijian Wang, Mengying Xiao, Chunyi Cui, and Hailong Liu. 2025. "Utilization of Marine-Dredged Sediment and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement for Preparing Non-Sintered Ceramsites: Properties and Microstructure" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050891
APA StyleZhao, J., Wang, Z., Xiao, M., Cui, C., & Liu, H. (2025). Utilization of Marine-Dredged Sediment and Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement for Preparing Non-Sintered Ceramsites: Properties and Microstructure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050891








