Physiological–Biochemical Signatures and Genetic Diversity of Portunus pelagicus Cohorts in Guangdong Coastal Aquaculture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Nutritional Quality Assessment
2.4. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Assay
2.5. Genetic Diversity
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
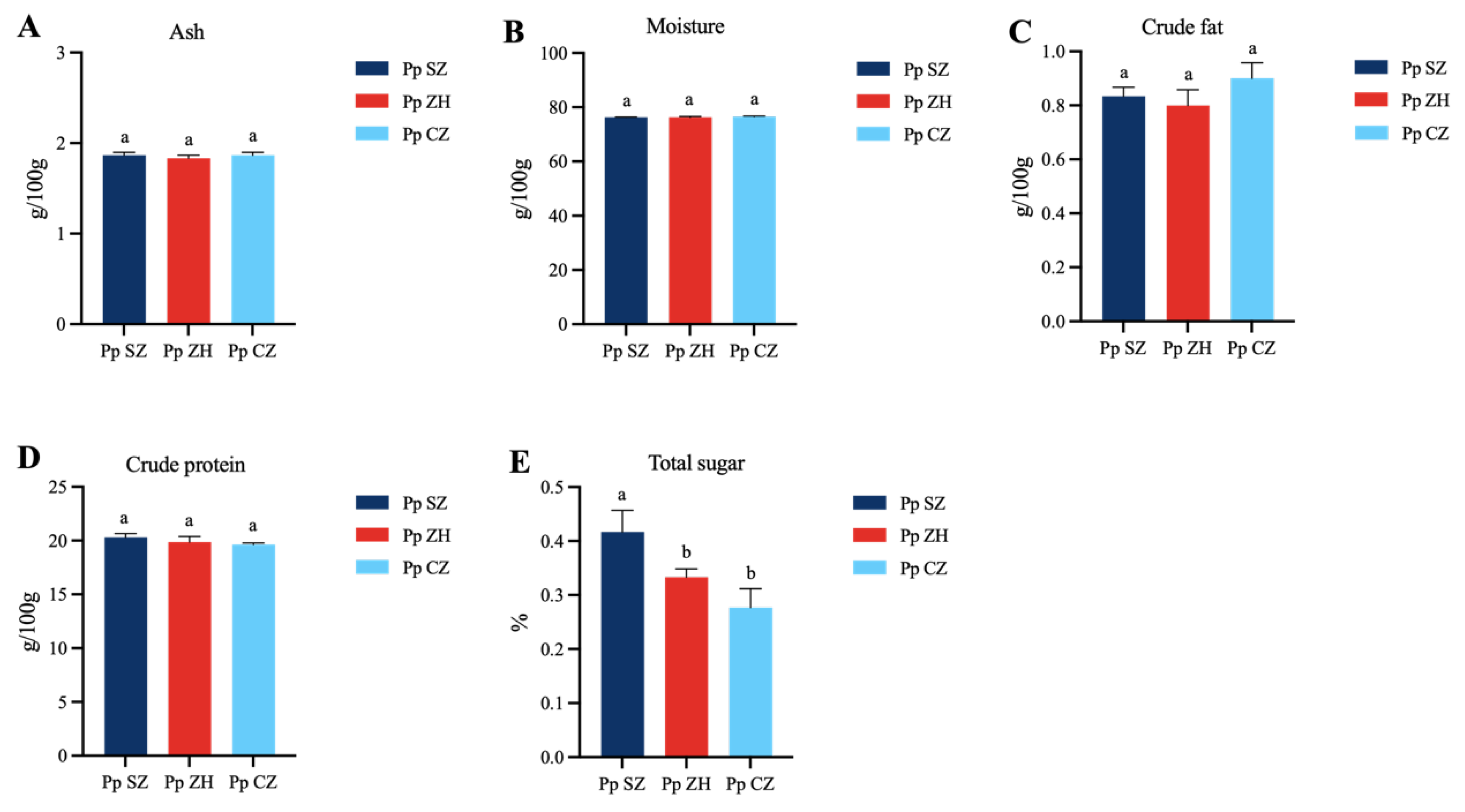
3.1. General Nutritional Composition Analysis
3.2. Amino Acid Profile and Quantification
3.3. Characterization of Fatty Acid Constituent Profiles and Quantitative Distribution Patterns
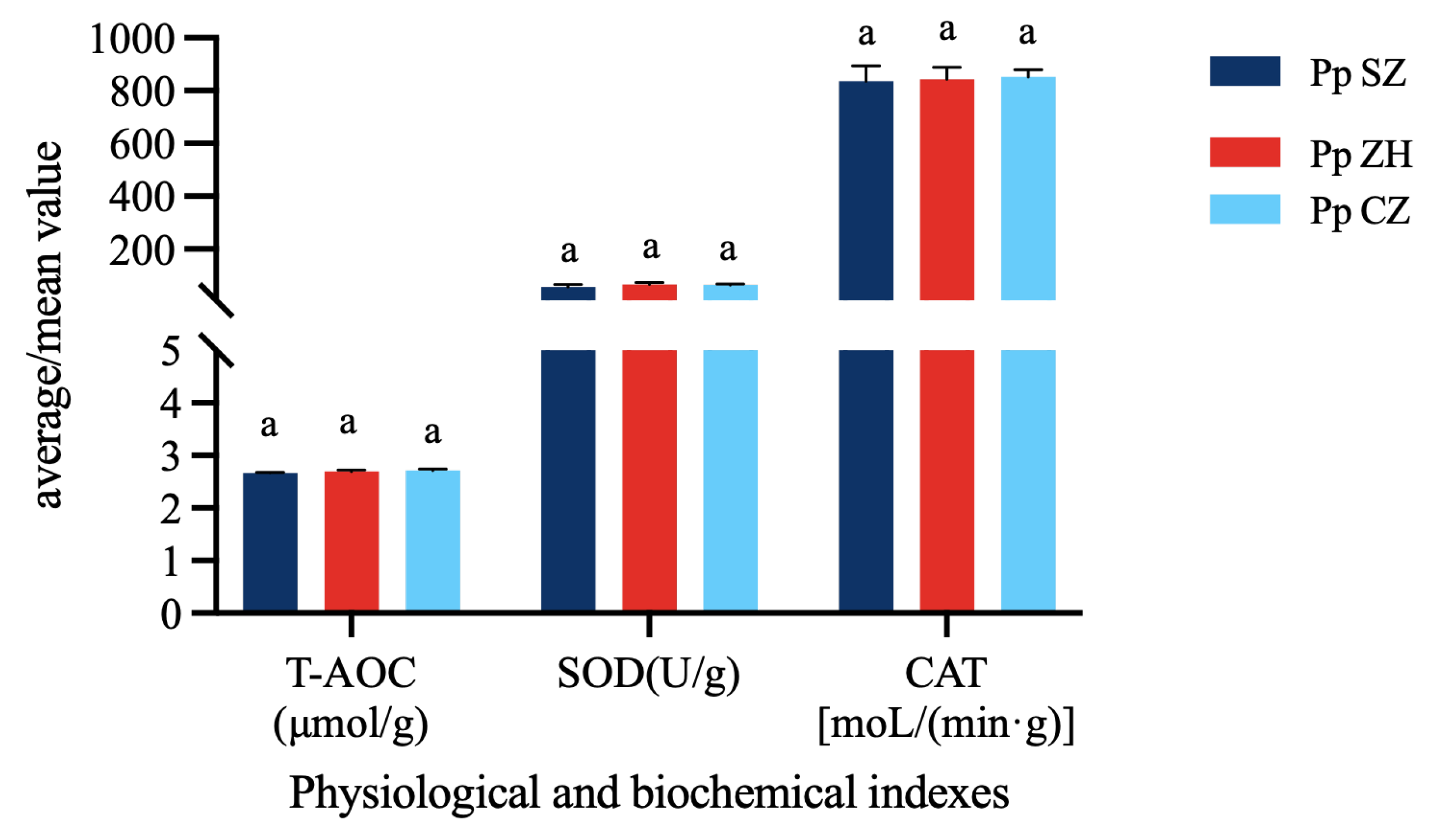
3.4. Physiological Indicator Analysis
3.5. Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Populations
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutritional Composition Differences in Portunus pelagicus
4.2. Analysis of Amino Acid Composition Differences in Portunus pelagicus
4.3. Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition Differences in Portunus pelagicus
4.4. Analysis of Physiological Indicator Differences in Portunus pelagicus
4.5. Analysis of Genetic Diversity Differences in Portunus pelagicus
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Long, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, T.; Cheng, Y. Nutritional quality of different grades of adult male chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primack, R.B. Tropical Community Dynamics and Conservation Biology. BioScience 1992, 42, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinbunga, S.; Yuvanatemiya, V.; Wongphayak, S.; Khetpu, K.; Menasveta, P.; Khamnamtong, B. Genetic population differentiation of the blue swimming crab Portunus pelagicus (Portunidae) in Thai waters revealed by RAPD analysis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2010, 9, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, B.T.; Rahman, M.A.; Tran, S.Q.; Glenner, H. Genome-wide SNP analyses reveal population structure of Portunus pelagicus along Vietnam coastline. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; Determination of Moisture in Food. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 6438-92; Determination of Crude Ash in Feedstuffs. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1992.
- GB/T 6432-94; Determination of Crude Protein by Kjeldahl Method. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1994.
- GB 5009.6-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Crude Fat in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 9695.31-2008; Determination of Total Sugar in Food by Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometry. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 5009.124-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Amino Acids in Foods by Hydrochloric Acid Hydrolysis. National Health and Family Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 5009.168-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Fatty Acids in Foods by Gas Chromatography. National Health and Family Planning Commission: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhou, F.; Xiao, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, F.; Wu, J. The Muscular Proximate Composition and Activities of Digestive and Immune Enzymes in Different Sizes of Mozambican Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon. Fish. Sci. 2013, 32, 653–656. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y.; Xu, M.; Gu, J. AfterQC: Automatic filtering, trimming, error removing and quality control for fastq data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18 (Suppl. S3), 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, K.C.; Edwards, R.J.; Sherwin, W.B.; Rollins, L.A. Contrasting Patterns of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Structural Variation Across Multiple Invasions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Samollow, P.B.; Cao, W.; Metz, R.; Zhang, C.; Leandro, C.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Wang, X. Genetic and genomic architecture in eight strains of the laboratory opossum Monodelphis domestica. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2022, 12, jkab389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.Q.; Zhao, L.Y.; Wu, X.R.; Ying, Z.Z.; Lin, Y.R.; Cai, Z.; Ye, J.Z.; Li, Q.H.; Tong, W.Q.; Weng, X.D.; et al. Effects of different feeding strategies on growth, digestion, and antioxidant capacity of Chinese hook snout carp Opsariichthysbidens. Chin. J. Fish. 2004, 9, 339. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/23.1363.S.20240423.1051.002 (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Lu, C.T.; Yang, W.J.; Feng, Y.J.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, T.X.; Li, L.P.; Cao, Y.L.; Xu, C.P. Effect of heating temperature on volatile components of sweet potato caramel flavor. Flavour Fragr. Cosmet. 2024, 2, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.X.; Liu, F.; Zhu, G.M.; Ren, X.L.; Liu, X.X.; Ling, W.H.; Su, S.P. Analysis of genetic diversity of P. clarkii culture population in Chuzhou based on mitochondrial COI gene. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 111–113+125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.D.; Zhang, L.Y.; Huo, Y.L.; Li, H.P.; He, X.Q.; Zhuang, Y.P. Morphological differences and genetic diversity of Paratapes undulatus from the coastal areas of southern Fujian and Beihai Sea, Guangxi. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, J.; Li, J.T. Development of SSR markers from genomic data for Litopenaeus vannamei and analysis of genetic diversity in different cultured populations. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Wang, Y.Z.; Sun, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.X. Comparison of the contents of conventional nutrients and free amino acids in the edible tissues of female Eriocheir sinensis cultured in the Yangtze River Delta. Chin. J. Fish. Qual. Stand. 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Kong, L.J.; Du, Y.F.; Yang, X.; Gao, Q.J.; Guo, J.Y.; Liu, D.; Zang, L.; Zhou, S.H.; et al. Evaluation on germplasm resources of Suifenhe crab. Heilongjiang Fish. 2024, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Cheng, Y.X.; Jia, Z.Y.; Long, X.W.; Zhu, W.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Wu, M.; Zhang, D.M. Comparison of nutritional quality of adult Chinese mitten-handed crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with different hepatic color. Chin. J. Fish. 2021, 34, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Long, X.W.; Zu, L.; Wu, X.; Cheng, Y.X. Gonadal development and nutritional composition of adult Eriocheir sinensis from Xishuangbanna. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2019, 28, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Y.; Xie, J.Y.; Wu, C.W. Analysis and evaluation of the nutritional composition in Chlorostoma rusticum. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 8, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Gao, K.R.; Liang, F.; Wu, H.R.; Li, X.C.; Jiang, S.T.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.F. Comparison and evaluation of nutritional qualities of gonads from female mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) in different growth-forms. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.B.; Wang, C.L.; MU, C.K.; Song, W.W.; Li, R.H. An analysis of the digestive enzymes activities and nutritive composition in the hepatopancreas of soft shell Portunus tritubercnlatus. Ecol. Sci. 2014, 31, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Bi, X.C.; Zhang, S.S.; Li, L.H.; Chen, Y. Comparison of amino acid and fatty acid nutritional components in Urechis unicinctus under different geographical environments and farming modes. China Fish. 2024, 8, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Uauy, R.D.; Birch, D.G.; Birch, E.E.; Tyson, J.; Hoffman, D. Effect of Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Retinal Function of Very-Low-Birth-Weight Neonates. Pediatr. Res. 1990, 28, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capel, F.; Acquaviva, C.; Pitois, E.; Laillet, B.; Rigaudiere, J.P.; Jouve, C.; Pouyet, C.; Gladine, C.; Comte, B.; Saban, C.V. DHA at nutritional doses restores insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle by preventing lipotoxicity and inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Long, X.W.; Zhu, W.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Wu, M.; Zhang, D.M. Comparison on nutritional quality of adult female Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with different colored hepatopancreases. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2075–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhou, F. A comprehensive study on nutritional quality, physiological enzyme activity and genetic diversity in six populations of Penaeus monodon. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 10141–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Cao, S.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Ma, Z.; et al. A Comprehensive Assessment of the Nutritional Value, Antioxidant Potential, and Genetic Diversity of Fenneropenaeus merguiensis from Three Different Regions in China. Biology 2024, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, S.; Jiang, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Zhou, F. Comparative Study of Nutritional Composition, Physiological Indicators, and Genetic Diversity in Litopenaeus vannamei from Different Aquaculture Populations. Biology 2024, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meessen, E.C.E.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Soeters, M.R. Human Postprandial Nutrient Metabolism and Low-Grade Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Huang, K.; Qin, X.; Wu, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Q.; Huang, X.Y. Effects of dietary carbohydrate levels on immunity and serum biochemical indices under low temperature stress in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish. Sci. 2014, 33, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, X.X. Effects of dietary energy sources and levels on growth, antioxidant capacity, and protein utilization of Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Fish. Sci. China 2023, 30, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Liu, W. The effect of different breeding densities on the liver immunity and antioxidant capacity of Aristichthys nobilis. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2024, 63 (Suppl. S1), 175–176+206. Available online: http://222.186.61.87:8083/kcms/detail/42.1255.S.20241129.1357.004.html (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Peng, S.M.; Shi, Z.H.; Gao, Q.X.; Yin, F.; Sun, P.; Wang, J.G. Effects of increasing dietary vitamin C on serum lysozyme activity and antioxidant ability of tissues in Pampus argenteus. South China Fish. Sci. 2013, 9, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, R.; Su, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Bao, J. Effects of Acute Cold Stress After Long-Term Cold Stimulation on Antioxidant Status, Heat Shock Proteins, Inflammation and Immune Cytokines in Broiler Heart. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.Z.; Cao, D.C.; Lu, C.Y.; Sun, X.W.; Liang, L.Q. Comparison of genetic diversity in two families of German mirror carp using microsatellite markers. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2008, 35, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.S.; Goudet, J.; Weir, B.S. Rank-invariant estimation of inbreeding coefficients. Heredity 2022, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wu, P.; Pan, H.; Liu, G.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zha, L.; Deng, Y.B.; Bai, X.Q. Genetic Structure Analysis of Neijiang Pig Population Based on SNP Chip. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 60, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebret, K.; Kritzberg, E.S.; Figueroa, R.; Rengefors, K. Genetic diversity within and genetic differentiation between blooms of a microalgal species. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Name | Average Nail Width (mm) | Average Nail Length (mm) | Weight (g) | Water Temperature (°C) | Month (Year) | Longitude and Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpSZ | 61.03 ± 1.64 | 32.42 ± 0.88 | 117.59 ± 8.98 | 25 | 1 | 22°55′ N, 114°54′ E |
| PpZH | 64.03 ± 1.64 | 30.23 ±1.34 | 123.30 ± 8.98 | 27 | 1 | 22°14′ N, 113°37′ E |
| PpCZ | 6.05 ± 0.08 | 34.25 ± 0.77 | 158.42 ± 5.65 | 26 | 1 | 22°54′ N, 117°00′ E |
| Amino Acids | PpSZ | PpZH | PpCZ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threonine Thr * | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 0.50 ± 0.00 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 a |
| Aspartic acid Asp @ | 1.09 ± 0.02 a | 1.13 ± 0.01 a | 1.12 ± 0.03 a |
| Serine Ser | 0.38 ± 0.01 a | 0.42 ± 0.00 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a |
| Leucine Leu * | 0.88 ± 0.02 a | 0.90 ± 0.00 a | 0.84 ± 0.02 a |
| Glycine Gly @ | 1.10 ± 0.02 a | 1.15 ± 0.01 a | 1.22 ± 0.03 a |
| Methionine Met * | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a |
| Arginine Arg & | 1.31 ± 0.02 a | 1.46 ± 0.01 a | 1.21 ± 0.03 b |
| Alanine Ala @ | 0.66 ± 0.02 a | 0.68 ± 0.01 a | 0.69 ± 0.02 a |
| Isoleucine IIe * | 0.48 ± 0.02 a | 0.44 ± 0.01 a | 0.32 ± 0.02 b |
| Cystine Cys | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 a |
| Glutamic acid Glu @ | 1.60 ± 0.03 a | 1.67 ± 0.02 a | 1.81 ± 0.03 a |
| Tyr tyrosine | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | 0.34 ± 0.00 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| Proline Pro | 0.44 ± 0.01 a | 0.43 ± 0.00 a | 0.50 ± 0.02 a |
| Lys * | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 0.88 ± 0.02 b |
| Histidine His & | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.21 ± 0.00 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 a |
| Val * | 0.53 ± 0.02 a | 0.49 ± 0.00 a | 0.38 ± 0.02 b |
| Phenylalanine Phe * | 0.44 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.00 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a |
| NEAA | 8.13 ± 0.47 a | 8.17 ± 0.21 a | 7.97 ± 0.28 b |
| EAA | 5.86 ± 0.31 a | 5.70 ± 0.13 b | 5.55 ± 0.16 c |
| TAA | 15.27 ± 0.84 a | 15.13 ± 0.38 a | 14.73 ± 0.47 a |
| DAA | 5.97 ± 0.34 a | 6.04 ± 0.15 a | 5.95 ± 0.17 a |
| SEAA | 1.28 ± 0.07 a | 1.27 ± 0.04 a | 1.22 ± 0.03 a |
| EAA/TAA | 0.38 ± 0.00 a | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 0.37 ± 0.00 a |
| EAA/NEAA | 0.72 ± 0.00 a | 0.70 ± 0.00 a | 0.70 ± 0.00 a |
| Fatty Acids | PpSZ | PpZH | PpCZ |
|---|---|---|---|
| C15:0 (Pentadecanoic acid) | 3.60 ± 0.02 a | 3.40 ± 0.00 a | 3.50 ± 0.10 b |
| C16:0 (Palmitic acid) | 64.00 ± 4.30 a | 63.60 ± 2.90 a | 54.10 ± 3.90 b |
| C16:1 (Palmitoleic acid) | 18.10 ± 1.20 a | 18.80 ± 1.00 a | 18.40 ± 1.30 a |
| C17:0 (Heptadecanoic acid) | 8.60 ± 0.20 b | 11.20 ± 0.60 a | 7.20 ± 0.50 b |
| C18:0 (Stearic acid) | 72.50 ± 5.20 a | 71.40 ± 3.10 a | 55.20 ± 3.90 b |
| C18:1n9c (Oleic acid) | 77.90 ± 5.50 a | 55.70 ± 2.40 b | 53.20 ± 3.80 b |
| C18:2n6c (Linoleic acid) | 8.10 ± 0.90 b | 10.70 ± 0.40 a | 5.40 ± 0.20 c |
| C20:2 (Eicosadienoic acid) | 4.80 ±0.40a | 3.50 ± 0.10 b | 3.60 ± 0.20 b |
| C20:4n6 (Arachidonic acid) | 35.90 ± 2.00 a | 37.10 ± 1.40 a | 28.50 ± 2.00 b |
| C22:1n9 (Erucic acid) | 11.90 ± 1.00 a | 8.80 ± 0.40 c | 9.40 ± 1.00 b |
| C20:5n3 (EPA) | 72.00 ± 4.30 b | 90.10 ± 3.80 a | 57.90 ± 3.90 ab |
| C22:6n3 (DHA) | 72.20 ± 4.30 a | 67.70 ± 3.00 b | 53.00 ± 3.60 c |
| Total Unsaturated Fatty Acids | 205.00 ± 15.50 a | 220.20 ± 11.10 a | 155.00 ± 12.30 b |
| Total Fatty Acid Content | 440.00 ± 30.00 a | 450.00 ± 30.00 a | 350.00 ± 20.00 b |
| Total Saturated Fatty Acids (ΣSFA) | 148.70 ± 0.00 a | 149.60 ± 0.00 a | 116.50 ± 0.00 b |
| Monounsaturated Fatty Acids (ΣMUFA) | 96.00 ± 0.00 a | 74.50 ± 0.00 b | 71.60 ± 0.00 b |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (ΣPUFA) | 309.10 ± 0.00 a | 325.90 ± 0.00 a | 204.40 ± 0.00 b |
| DHA ± EPA | 144.20 ± 0.00 a | 157.80 ± 0.00 a | 110.90 ± 0.00 b |
| n − 3 Series PUFA (Σn − 3PUFA) | 144.20 ± 0.00 a | 157.80 ± 0.00 a | 110.90 ± 0.00 b |
| n − 6 Series PUFA (Σn − 6PUFA) | 116.90 ± 0.00 a | 144.10 ± 0.00 a | 82.50 ± 0.00 b |
| Population | SNP Number | SNP Density (SNP/Kb) | Nucleotide Diversity (π) | Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) | Observed Heterozygosity (Ho) | Inbreeding Coefficient (FHOM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpSZ | 6615993 | 6.583 | 1.268 × 10−3 | 0.162 ± 0.127 | 0.197 ± 0.218 | −3.337 × 10−2 ± 4.527 × 10−2 |
| PpZH | 6190898 | 6.16 | 1.285 × 10−3 | 0.171 ± 0.126 | 0.213 ± 0.224 | −5.270 × 10−2 ± 2.856 × 10−2 |
| PpCZ | 6215622 | 6.08 | 1.52 × 10−3 | 0.166 ± 0.134 | 0.205 ± 0.191 | −5.110 × 10−2 ± 8.120 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cao, S.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Z.; et al. Physiological–Biochemical Signatures and Genetic Diversity of Portunus pelagicus Cohorts in Guangdong Coastal Aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040747
Li Y, Cao S, Jiang Z, Jiang S, Yang Q, Yang L, Huang J, Shi J, Ding Y, Ma Z, et al. Physiological–Biochemical Signatures and Genetic Diversity of Portunus pelagicus Cohorts in Guangdong Coastal Aquaculture. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yundong, Siyao Cao, Ziyi Jiang, Song Jiang, Qibin Yang, Lishi Yang, Jianhua Huang, Jianzhi Shi, Yangyang Ding, Zhenhua Ma, and et al. 2025. "Physiological–Biochemical Signatures and Genetic Diversity of Portunus pelagicus Cohorts in Guangdong Coastal Aquaculture" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040747
APA StyleLi, Y., Cao, S., Jiang, Z., Jiang, S., Yang, Q., Yang, L., Huang, J., Shi, J., Ding, Y., Ma, Z., & Zhou, F. (2025). Physiological–Biochemical Signatures and Genetic Diversity of Portunus pelagicus Cohorts in Guangdong Coastal Aquaculture. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040747







