Calibration of High-Frequency Reflectivity of Sediments with Different Grain Sizes Using HF-SSBP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Total Reflection Method for a Static Water Surface
2.2. Theoretical Framework: Grain Size and Frequency Attenuation
- Rayleigh scattering (d << λ)
- 2.
- Mie scattering (d ≈ λ)
2.3. Method of Obtaining the Reflection Coefficient
2.4. Data Processing Methods
- Quadrature demodulation of time domain signals
- 2.
- Filter processing
- 3.
- The matched filter of the LFM single is the conjugate negative form of the single emission:
- 4.
- The matched filter to obtain complex signals is as follows:
3. Experimental Tests
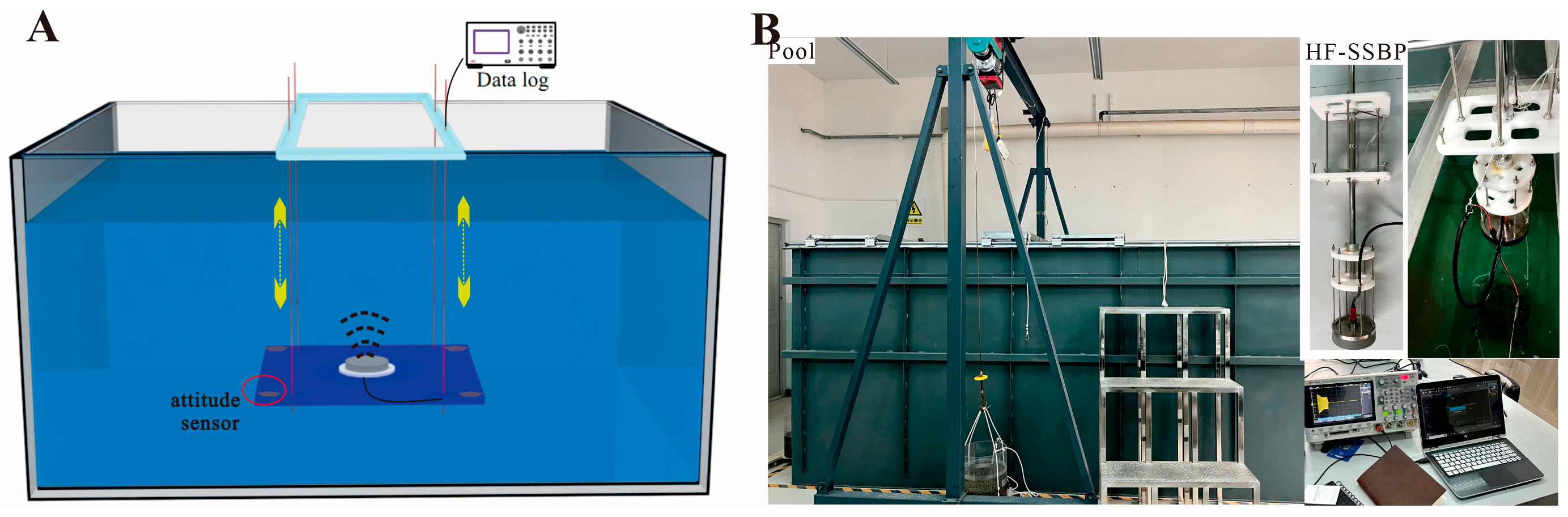
3.1. Experimental Equipment
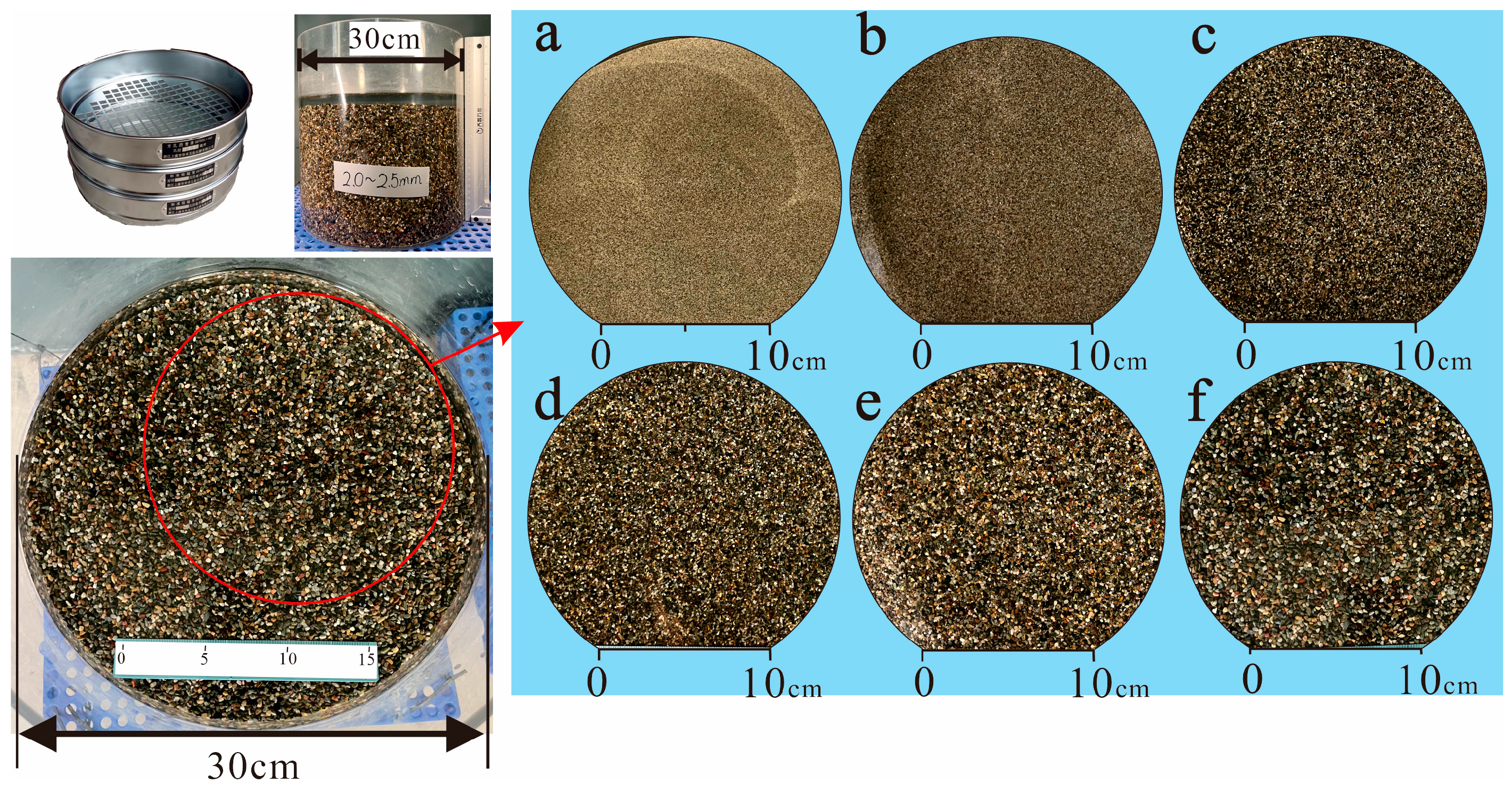
3.2. Sediment Preparation
3.3. Tank Experiments
3.3.1. Acrylic Standard Plate Tank Experiment
3.3.2. Sediment Tank Experiment
4. Results and Discussion
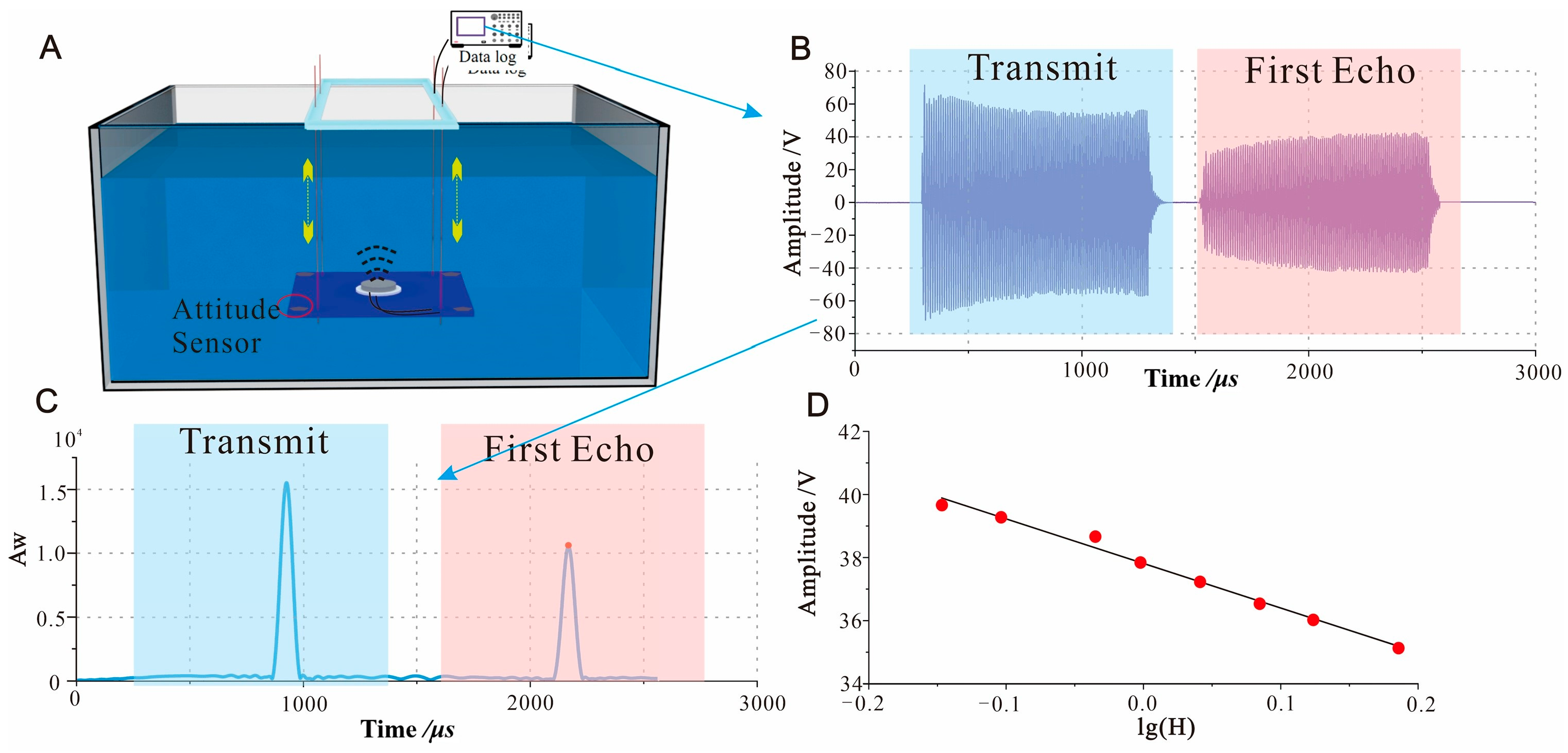
4.1. Static Water Surface Total Reflection Test Results
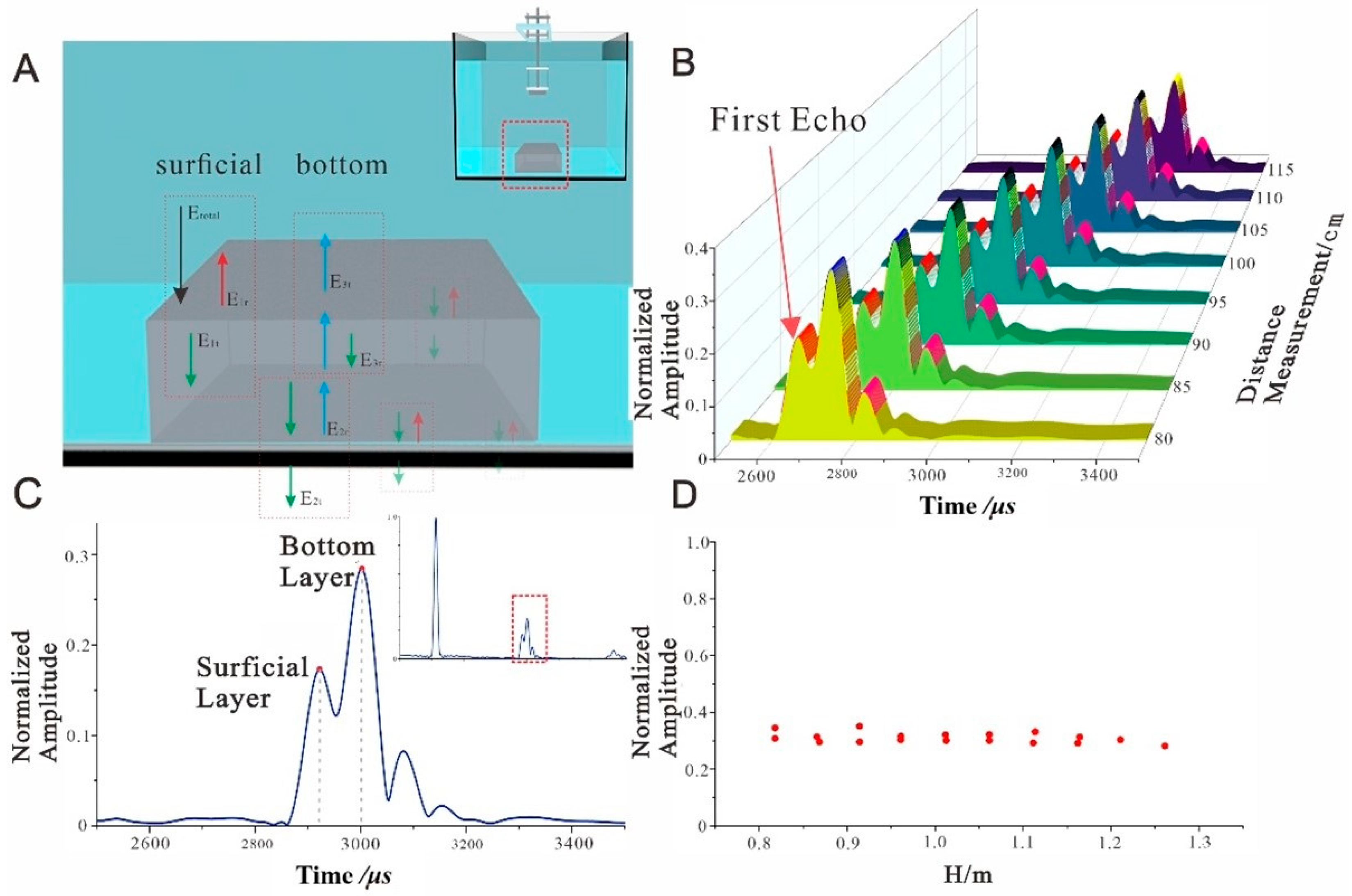
4.2. Acrylic Sample Plate Sound Reflection Test Results
4.3. Sediment Reflection Coefficient Measurements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.H.; Kan, G.M.; Li, G.B.; Yu, S.Q. Measurement Techniques and Applications of Acoustic Properties of Submarine Sediments; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oelze, M.L.; Sabatier, J.M.; Raspet, R. Roughness measurements of soil surfaces by acoustic backscatter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanic, S.; Briggs, K.B.; Fleischer, P.; Sawyer, W.B.; Ray, R.I. High-frequency acoustic backscattering from a coarse shell ocean bottom. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallaudet, T.C.; de Moustier, C.P. High-frequency volume boundary acoustic backscatter fluctuations in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, F.A.; Chotiros, N.P. A model for acoustic backscatter from muddy sediments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Han, T.C.; Kan, G.M.; Li, G.B. Correlations between the in situ acoustic properties and geotechnical parameters of sediments in the Yellow Sea, China. J. Aslan Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Siwabessy, J.; Cheng, H.; Nichol, S. Using multibeam backscatter data to investigate sediment-acoustic relationships. J. Geophys. Res-Ocean. 2018, 123, 4649–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Li, G.B.; Kan, G.M.; Liu, B.H.; Meng, X.M. Experiment study of the in-situ acoustic measurement in seafloor sediments from deep sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 4463–4472. Available online: http://www.geophy.cn/article/doi/10.6038/cjg2020N0427 (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Rizvi, Z.H.; Mustafa, S.H.; Sattari, A.S.; Ahmad, S.; Furtner, P.; Wuttke, F. Dynamic lattice element modelling of cemented geomaterials. In Advances in Computer Methods and Geomechanics: IACMAG Symposium; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Trzcinska, K.; Tegowski, J.; Pocwiardowski, P.; Janowski, L.; Zdroik, J.; Kruss, A.; Rucinska, M.; Lubniewski, Z.; Schneider von Deimling, J. Measurement of seafloor acoustic backscatter angular dependence at 150 kHz using a multibeam echosounder. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.L.; Jackson, D.R.; Tang, D.; Briggs, K.B.; Thorsos, E.I. Acoustic backscattering from a sand and a sand/mud environment: Experiments and data/model comparisons. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 34, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicki, F.L.; Roger, F.D. The effects of fine-scale surface roughness and grain size on 300 kHz multibeam backscatter intensity in sandy marine sedimentary environments. Mar. Geol. 2006, 228, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Q.; Liu, B.H.; Yu, K.B.; Yang, Z.G.; Kan, G.M.; Zhang, X.B. Comparison of acoustic backscattering from a sand and a mud bottom in the South Yellow Sea of China. Ocean Eng. 2020, 202, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.P.; Ye, G.C.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, T.B. Effect of temperature on the acoustic reflection characteristics of seafloor surface sediments. J. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 21, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.P.; Xie, J.; Meng, X.M.; Han, S.; Feng, J.C.; Kan, G.M. Analysis of the variation of in situ seafloor sediments acoustic characteristics with porosity based EDFM. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1270673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.M.; Anderson, C.D. Measurements of Backscatterin of Sound from the Ocean Bottom. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1964, 36, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.R.; Baird, A.M.; Crisp, J.J.; Thomson, P.A.G. High-frequency bottom backscatter measurements in shallow water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 80, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Q.; Liu, B.H.; Yu, K.B.; Yang, Z.G.; Kan, G.M. Backscattering Characteristics over a Wide Band of a Sand Bottom in the South Yellow Sea of China. In Proceedings of the 2021 OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 14–17 July 2021; pp. 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, T.C.; Ward, L.G. Observations of backscatter from sand and gravel seafloors between 170 and 250 kHz. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, P.C.; Osler, J.C.; MacDougald, D.J. Acoustic backscatter measurements from littoral seabeds at shallow grazing angles at 4 and 8 kHz. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 3504–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Anu, A.P. Characterization of seafloor roughness from high-frequency acoustic backscattering measurements in shallow water off the west coast of India. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Wu, L.; Zou, D.P.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.J.; Yan, P.; Fan, C.Y. Predicting the acoustic characteristics of seafloor sediments containing cold spring carbonate rocks. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1243780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.M.; Liu, B.H.; Yang, Z.G.; Yu, S.Q.; Qi, L.H.; Yu, K.B.; Pei, Y.L. Acoustic backscattering measurement from sandy seafloor at 6–24 kHz in the South Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanic, S.; Briggs, K.B.; Fleischer, P.; Ray, R.I.; Sawyer, W.B. Shallow-water high-frequency bottom scattering off Panama City, Florida. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1988, 83, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Kan, G.M.; Pei, Y.L.; Yang, Z.G.; Yu, S.Q.; Yu, K.B. A review on the progress of bottom acoustic scattering research. Haiyang Xuebao 2017, 39, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, L.B.; Zhao, J.H.; Lu, J.H.; Qiu, Z.G. High-accuracy acoustic sediment classification using sub-bottom profile data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 265, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelboe, G.; Hefner, T.; Ivakin, A. Observed correlations between the sediment grain size and the high-frequency backscattering strength. JASA Express Lett. 2023, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, G.M.; Liu, B.H.; Zhao, Y.X.; Li, G.B.; Pei, Y.L. Self-contained in situ sediment acoustic measurement system based on hydraulic driving penetration. High Technol. Lett. 2011, 17, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, P.D.; Hurther, D. An overview on the use of backscattered sound for measuring suspended particle size and concentration profiles in noncohesive inorganic sediment transport studies. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 73, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerdon, A.; Van Der, A.; To, M. Measurement of Near-Bed sediment load, particle size, settling velocity and turbulence from a multi-frequency acoustic backscatter instrument. In Coastal Sediments 2023: The Proceedings of the Coastal Sediments; World Scientific: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1597–1606. [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht, D.D.; de Moustier, C.P. Time-dependent seafloor acoustic backscatter (10–100 kHz). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 2709–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wang, C. Effects of grain size distributions on scattering attenuation of elastic waves in polycrystalline materials. Acta Mech. 2024, 235, 3231–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.G.; Cao, X.H.; Shen, B.J.; Zhang, Y.H. Near bottom acoustic detection of canyon Mousse layers in the South China Sea. Acta Acust. 2021, 46, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.H.; Qu, Z.G.; Shen, B.J.; Zhang, H.Y. Illuminating centimeter-level resolution stratum via developed high-frequency sub-bottom profiler mounted on Deep-Sea Warrior deep-submergence vehicle. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2021, 39, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zou, D.; Qu, Z.; Zhen, H.; Cheng, H.; Wei, Z. Calibration and application of high-frequency submersible sub-bottom profiler for deep-sea surficial sediment measurement. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2022, 41, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

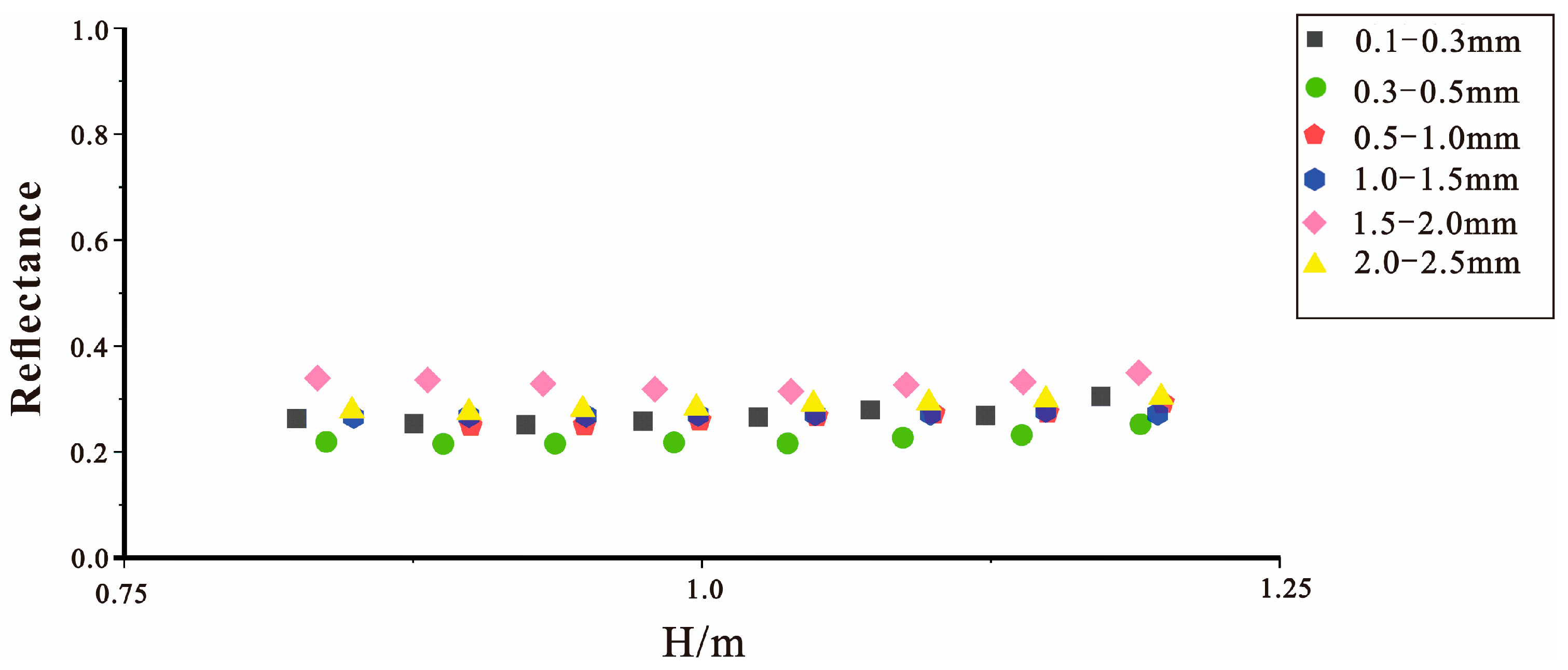
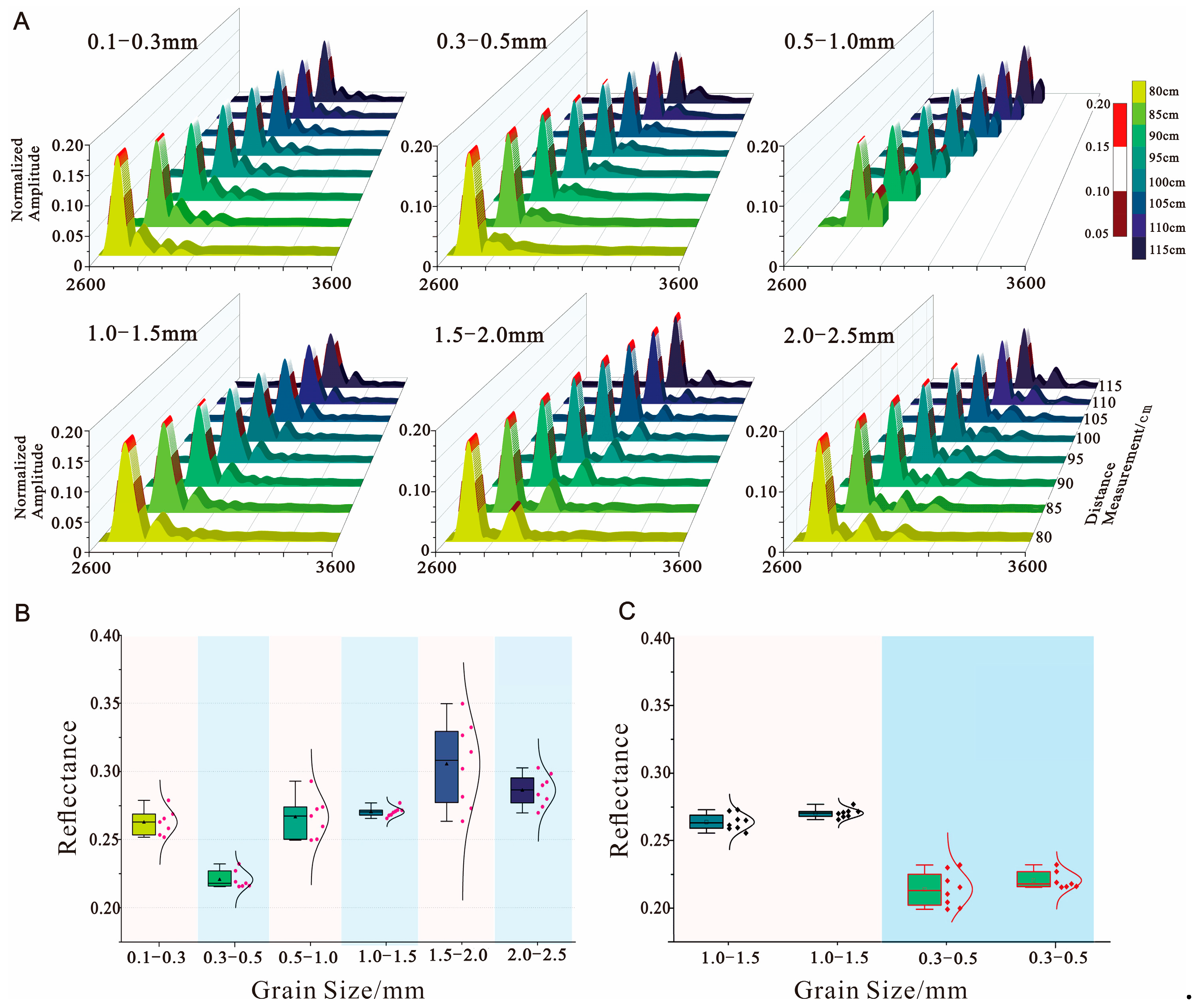
| Study | Frequency Range | Sediment Types | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| McKinney & Anderson (1964) [16] | 12.5–290 kHz | Sand, Gravel, Rocks | Sand exhibits 5–8 dB lower scattering intensity than gravel and rocks. |
| Jackson et al. (1986) [17] | 20–85 kHz | Silt, Sand, Gravel | Unique backscatter signatures per sediment type; weak frequency dependence. |
| Weber & Ward (2015) [19] | 170–250 kHz | Sand, Gravel, Bedrock | Backscatter correlates strongly with grain size and sediment density. |
| Yu et al. (2020) [13] | 6–24 kHz | Mud, Sand | Mud reflection intensity exceeds sand by 15–23 dB under identical conditions. |
| Kan et al. (2019) [23] | 6–24 kHz | Sand | Scattering trends vary nonlinearly with frequency in sandy substrates. |
| Distance Measurement | Time Difference Between Water–Sediment Surface and Sediment–Acrylic Acoustic Reflection (μs) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 cm | 85 cm | 90 cm | 95 cm | 100 cm | 105 cm | 110 cm | 115 cm | ||
| Grain size | 0.1–0.3 mm | 83 | 84 | 85 | 84 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| 0.3–0.5 mm | 69 | 69 | 69 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 69 | 70 | |
| 0.5–1.0 mm | 81 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | - | |
| 1.0–1.5 mm | 83 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 83 | 83 | 83 | |
| 1.5–2.0 mm | 73 | 74 | 75 | 75 | 76 | 76 | 77 | 77 | |
| 2.0–2.5 mm | 73 | 73 | 73 | 72 | 72 | 72 | 73 | 73 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, S.; Cao, X.; Qu, Z.; Zou, D.; Zhen, H.; Zeng, T. Calibration of High-Frequency Reflectivity of Sediments with Different Grain Sizes Using HF-SSBP. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040741
Xiong S, Cao X, Qu Z, Zou D, Zhen H, Zeng T. Calibration of High-Frequency Reflectivity of Sediments with Different Grain Sizes Using HF-SSBP. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040741
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Shuai, Xinghui Cao, Zhiguo Qu, Dapeng Zou, Huancheng Zhen, and Tong Zeng. 2025. "Calibration of High-Frequency Reflectivity of Sediments with Different Grain Sizes Using HF-SSBP" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040741
APA StyleXiong, S., Cao, X., Qu, Z., Zou, D., Zhen, H., & Zeng, T. (2025). Calibration of High-Frequency Reflectivity of Sediments with Different Grain Sizes Using HF-SSBP. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040741




