Seasonal Effects of Nakdong River Freshwater Inflow and Coastal Environmental Changes on Phytoplankton Community Structure, Including Harmful Species, in Eastern Jinhae Bay, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
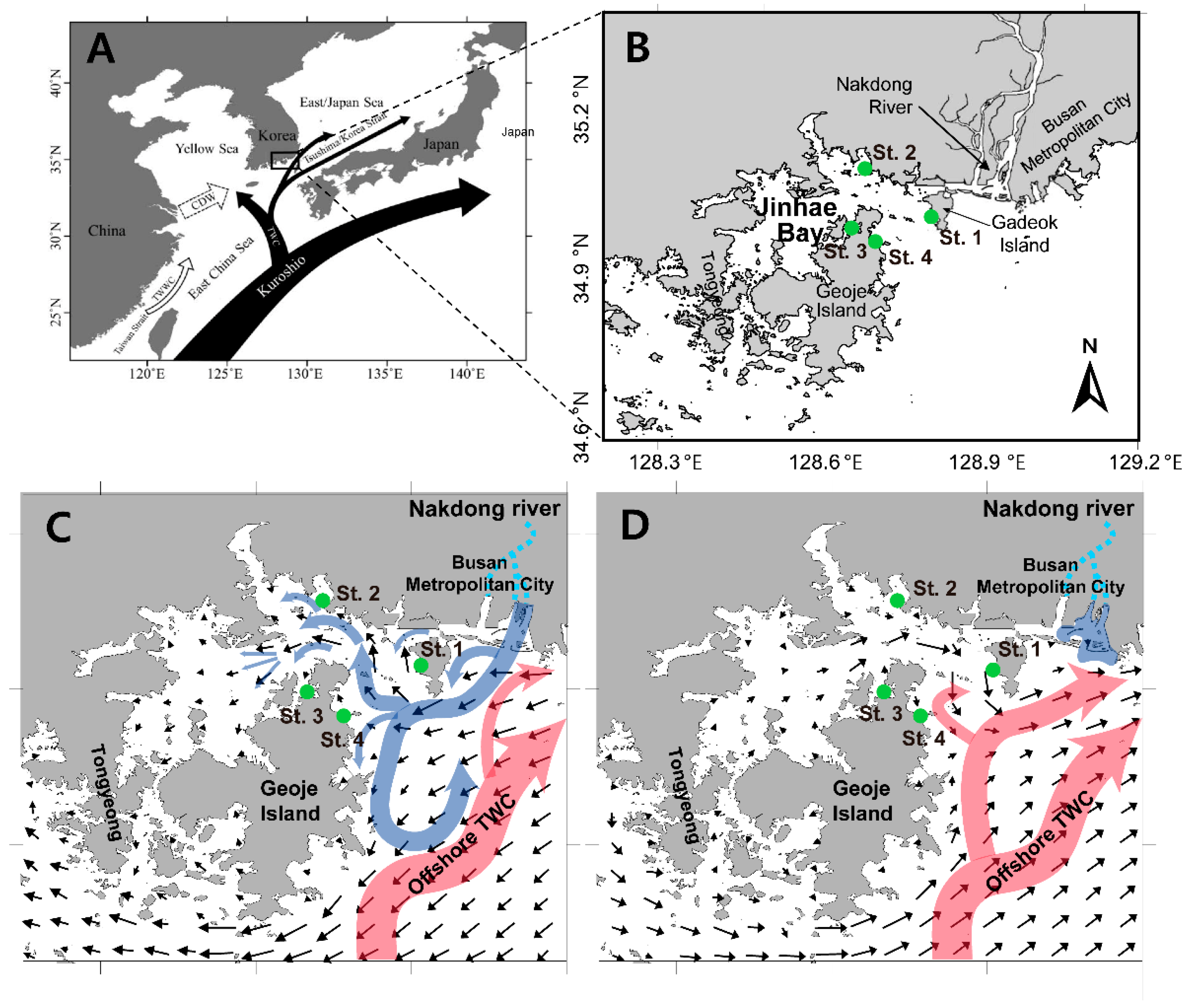
2.1. Field Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Sample Analyses
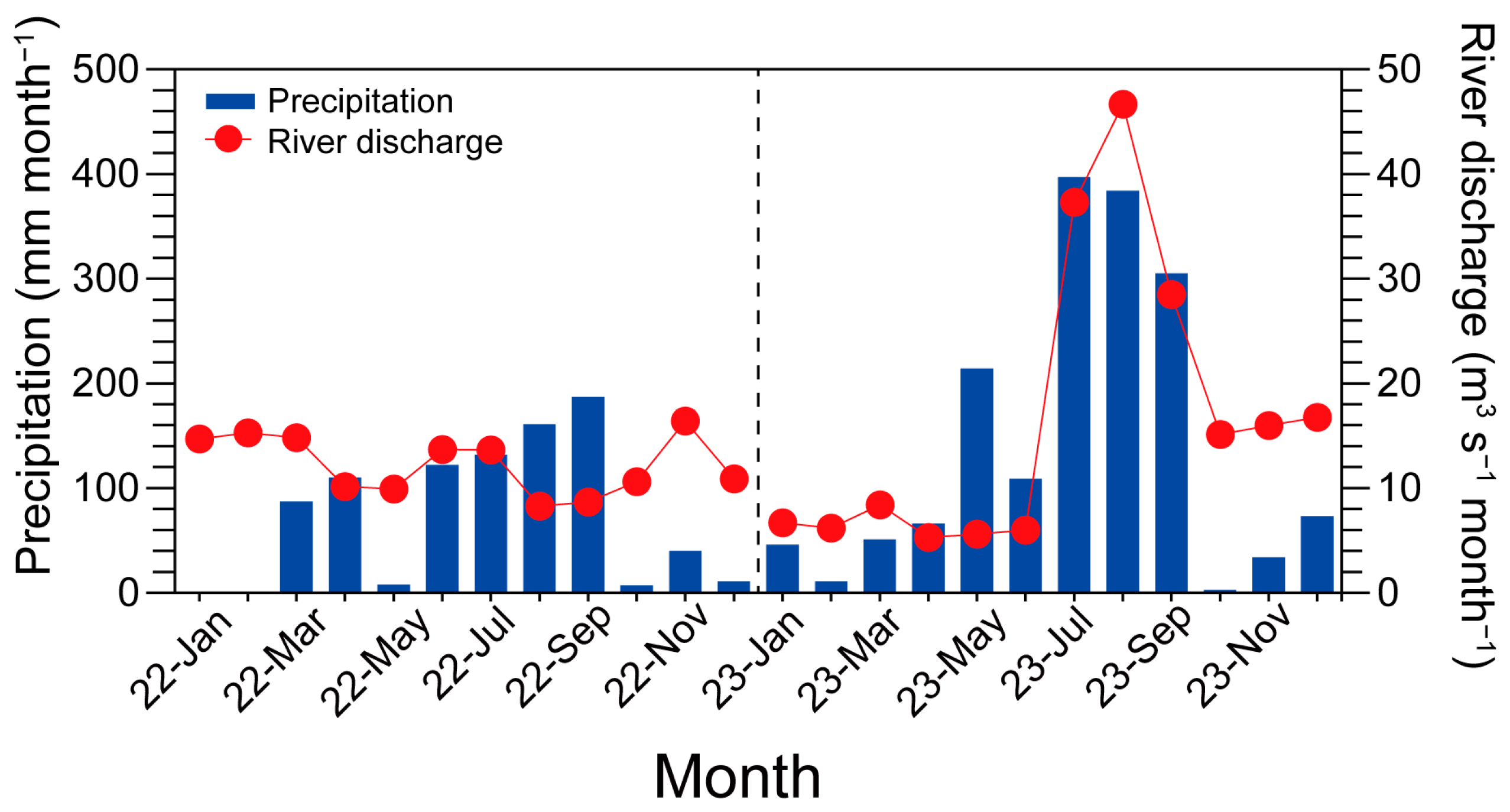
2.3. Hydrological Data Acquisition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
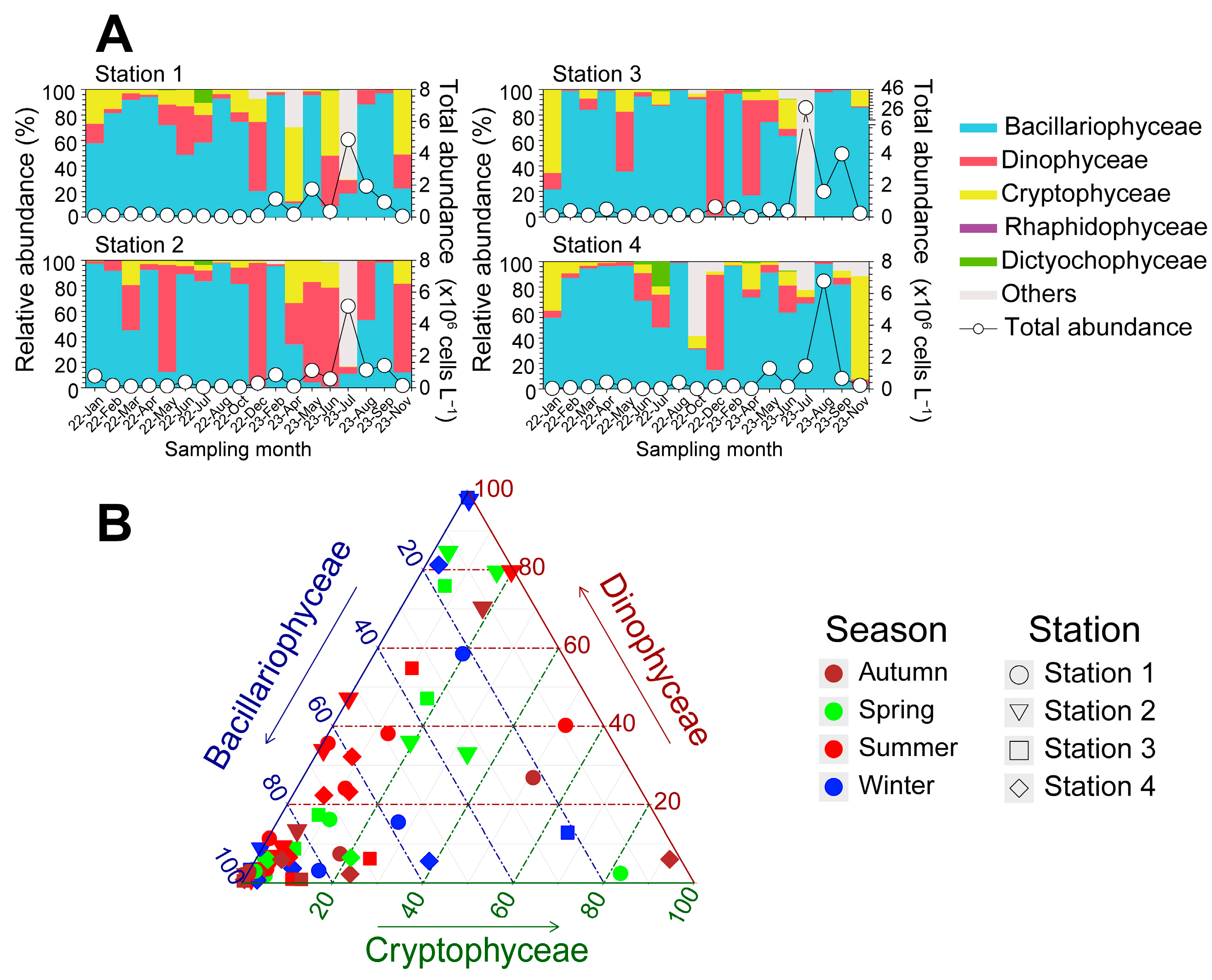
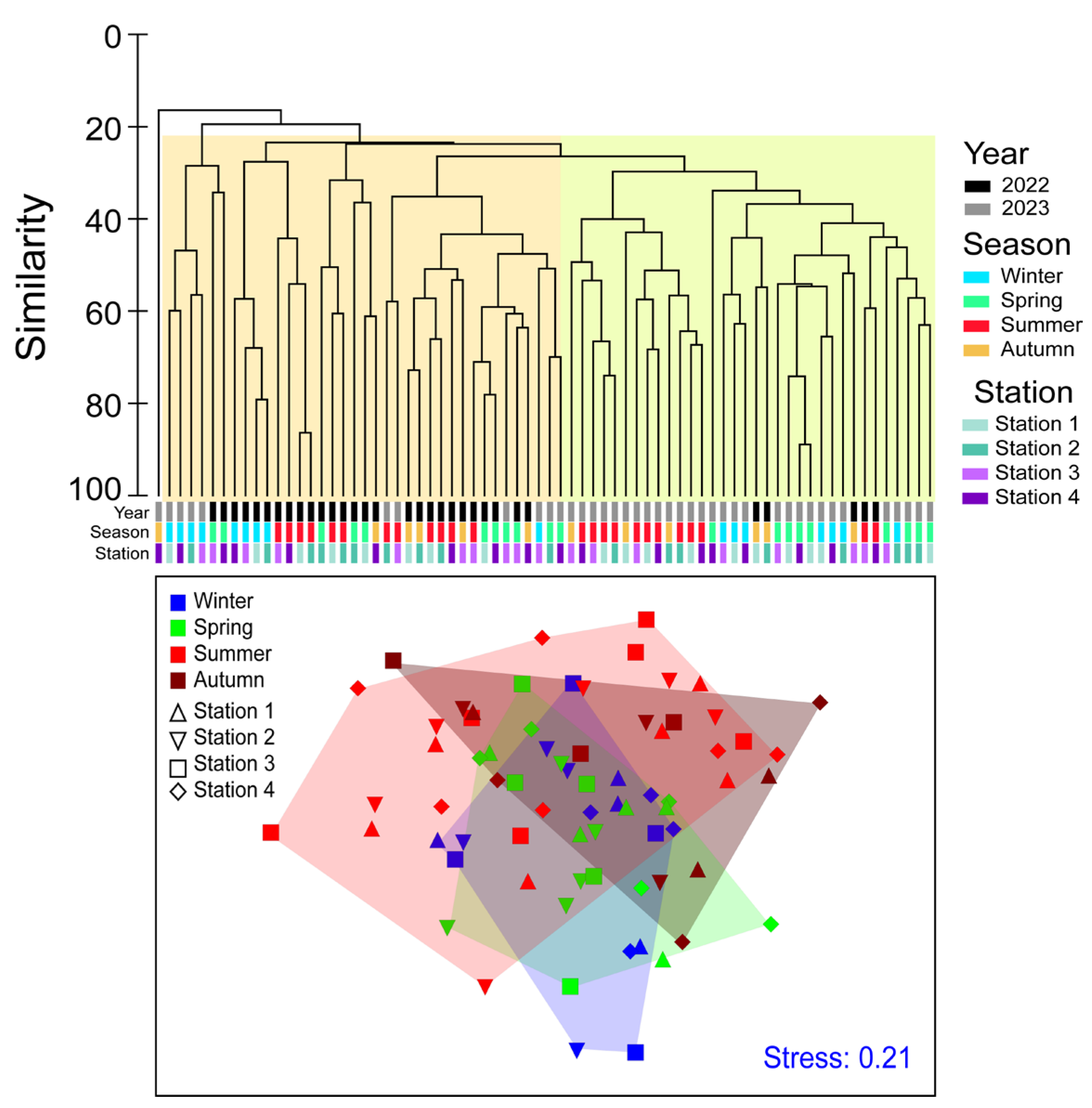
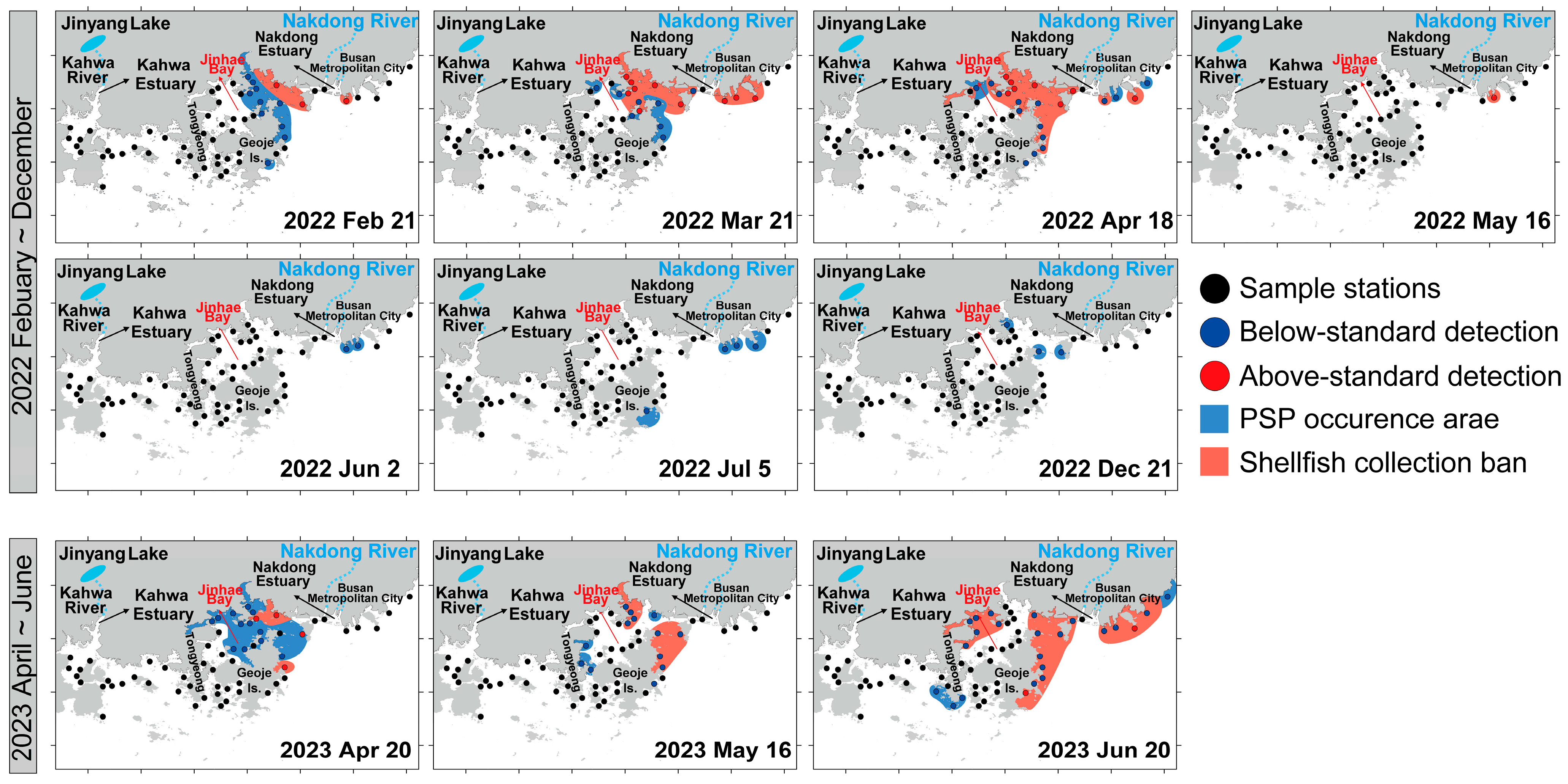
3. Results
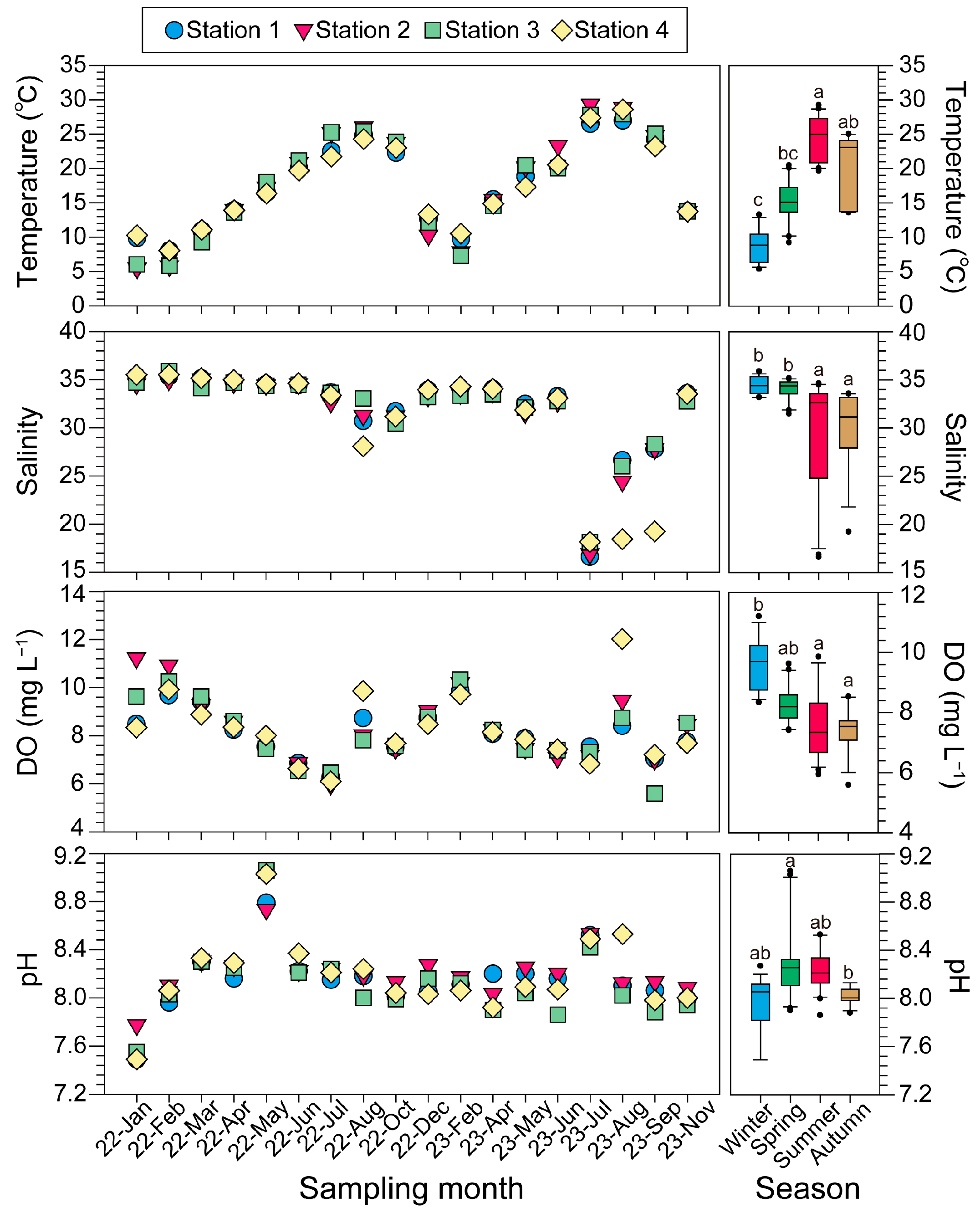
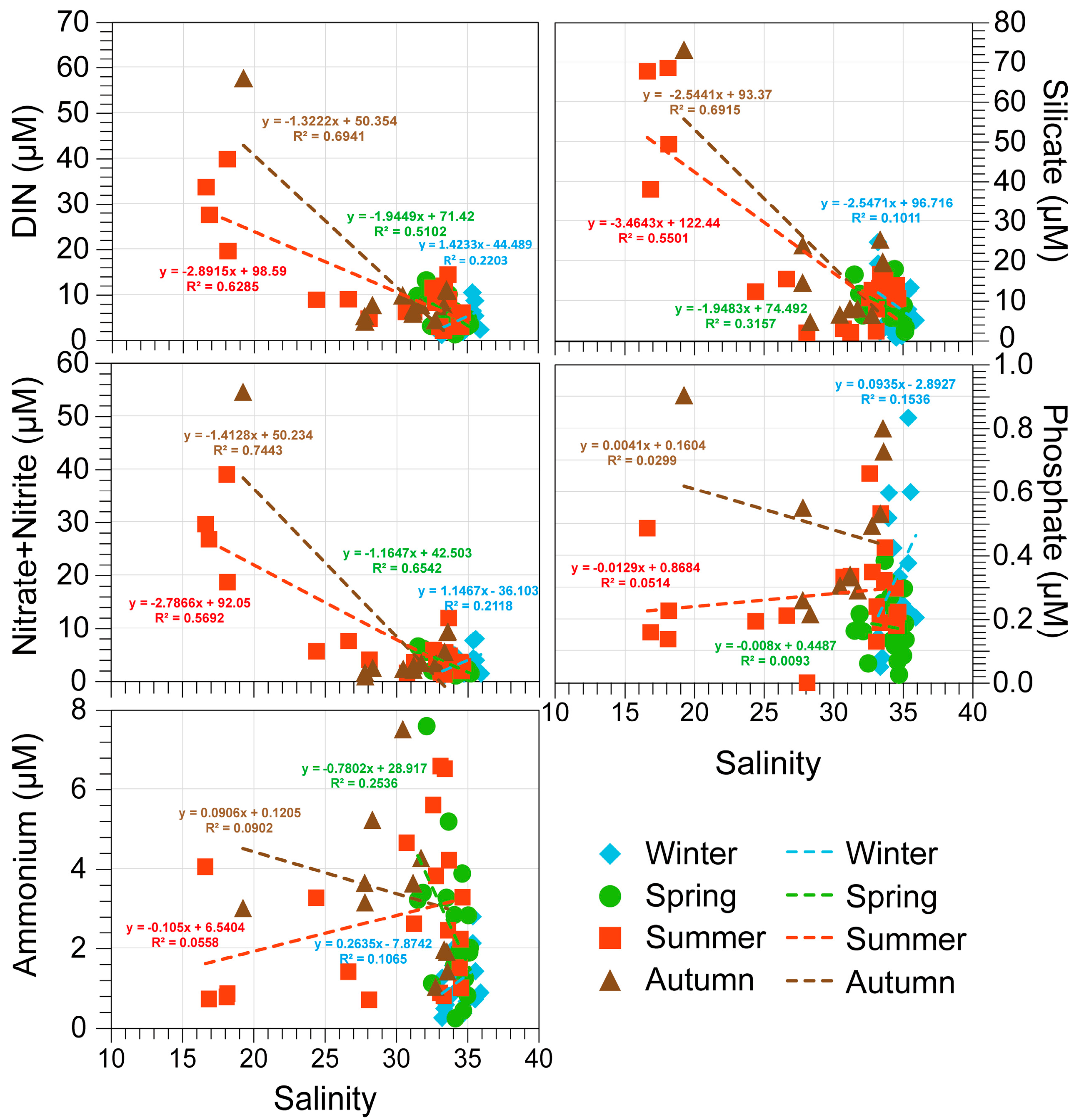
3.1. Environmental Factors
3.2. Seasonal Phytoplankton Abundances and Community in Each Coastal Region
4. Discussion
5. Summaries and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremp, A.; Godhe, A.; Egardt, J.; Dupont, S.; Suikkanen, S.; Casabianca, S.; Penna, A. Intraspecific variability in the response of bloom-forming marine microalgae to changed climate conditions. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Litchman, E. Understanding and predicting harmful algal blooms in a changing climate: A trait-based framework. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Son, M.; Yun, S.M.; Kim, Y.O. Seasonal distribution of phytoplankton assemblages and nutrient-enriched bioassays as indicators of nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in Gwangyang Bay, Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Ji, R.; Feng, Z.; Jang, J.; Lee, D.I.; Lee, W.C.; Kang, C.K. Estuarine dam water discharge enhances summertime primary productivity near the southwestern Korean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114971. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.O.; Son, M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S. Seasonal changes in abiotic environmental conditions in the Busan coastal region (South Korea) due to the Nakdong River in 2013 and effect of these changes on phytoplankton communities. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, K.B.; Jephson, T.; Hasper, T.B.; Carlsson, P. Species-specific dinoflagellate vertical distribution in temperature-stratified waters. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, N.S.; Paerl, H.W. Vertical migration patterns of phytoflagellates in relation to light and nutrient availability in a shallow microtidal estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 425, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zahir, M.; Su, Y.; Shahzad, M.I.; Ayub, G.; Rahman, S.U.; Ijaz, J. A review on monitoring, forecasting, and early warning of harmful algal bloom. Aquaculture 2024, 593, 741351. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.K.; Hong, S.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, M.; Baek, S.H. Influence of Region-Specific Marine Environments on Phytoplankton and Bacterial Communities in the Korean Coastal Waters in Winter 2021. Ocean Sci. J. 2024, 59, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Cotrim da Cunha, L.; Buitenhuis, E.T.; Le Quéré, C.; Giraud, X.; Ludwig, W. Potential impact of changes in river nutrient supply on global ocean biogeochemistry. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21, GB4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, C.G.; Diehl, S.; Schmidt, G.M. Influence of water-column depth and mixing on phytoplankton biomass, community composition, and nutrients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Shin, H.H.; Choi, H.-W.; Shimode, S.; Hwang, O.M.; Shin, K.; Kim, Y.-O. Ecological behavior of the dinoflagellate Ceratium furca in Jangmok harbor of Jinhae Bay, Korea. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Lim, Y.K. Variation in phytoplankton community due to an autumn typhoon and winter water turbulence in southern Korean coastal waters. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.N.; Lim, Y.K.; Hong, S.; Baek, S.H. Use of mesocosm and field studies to assess the effects of nutrient levels on phytoplankton population dynamics in Korean coastal waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1253708–1253725. [Google Scholar]
- Sournia, A. Phytoplankton Manual; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1978; ISBN 92-3-101572-9. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, T.; Lwataki, M.; Borja, V.; Takayama, H.; Fukuyo, Y. Marine Phytoplankton of the Western Pacific (Kouseisha Kouseikaku); Kouseisha Kouseikaku Co. Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, Y.D.; Kim, J.S.; Seong, K.A.; Kang, N.S.; Kim, T.H. Growth, feeding and ecological roles of the mixotrophic and heterotrophic dinoflagellates in marine planktonic food webs. Ocean Sci. J. 2010, 45, 65–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, P.; Shin, H.; Baek, S.; Jang, M.; Lee, T.; Shin, K. Nutrient distribution and effects on phytoplankton assemblages in the western Korea/Tsushima Strait. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 47, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Baek, S.H. Occurrence characteristics of harmful and non-harmful algal species related to coastal environments in the southern sea of Korea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 794–806. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Yin, W.; Huang, D.; Xuan, J.; He, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J. Synoptic Cross-Shore Movements of Outer Salinity Fronts in China’s Changjiang River Plume. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2024, 54, 2553–2578. [Google Scholar]
- Wagawa, T.; Igeta, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Okuyama, S.; Abe, S.; Yabe, I. Freshwater spreading far offshore the Japanese coast. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14508. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, T.M.; Aleynik, D.; Davidson, K. Ensemble models improve near-term forecasts of harmful algal bloom and biotoxin risk. Harmful Algae 2025, 142, 102781. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, F.; Richlen, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Molecular characterization and morphology of Cochlodinium strangulatum, the type species of Cochlodinium, and Margalefidinium gen. nov. for C. polykrikoides and allied species (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, R.M.; Mustapa, N.I.; NOORDIN, M.A.; Rahim, M.A.; Hii, K.S.; Lim, P.T.; Leaw, C.; Muhd-Farouk, H.; Yaacob, K.K.K. Report of a fish kill due to a dinoflagellate bloom in Perak and Penang, Malaysia. Asian Fish. Sci. 2022, 35, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.O.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, J.H. Phytoplankton composition associated with physical and chemical variables during summer in the southern sea of Korea: Implication of the succession of the two toxic dinoflagellates Cochlodinium (aka Margalefidinium) polykrikoides and Alexandrium affine. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 516, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Cho, K.H.; Park, B.S. Potential cause of decrease in bloom events of the harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides in southern Korean coastal waters in 2016. Toxins 2020, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.E.; Watkins-Brandt, K.S.; McKibben, S.M.; Wood, A.M.; Hunter, M.; Forster, Z.; Du, X.; Peterson, W.T. Large-scale bloom of Akashiwo sanguinea in the Northern California current system in 2009. Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.W.; Kang, J.; Park, J.S.; Joo, H.M.; Suh, S.-S.; Kang, D.; Lee, T.-K.; Kim, H.-J. Dynamic bacterial community response to Akashiwo sanguinea (Dinophyceae) bloom in indoor marine microcosms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6983. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Peterson, W.; McCulloch, A.; Liu, G. An unusual bloom of the dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea off the central Oregon, USA, coast in autumn 2009. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yang, W.; Leaw, C.P.; Pospelova, V.; Bilien, G.; Liow, G.R.; Lim, P.T.; Gu, H. Cryptic diversity within the harmful dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in coastal Chinese waters is related to differentiated ecological niches. Harmful Algae 2017, 66, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islabão, C.A.; Odebrecht, C. Influence of salinity on the growth of Akashiwo sanguinea and Prorocentrum micans (Dinophyta) under acclimated conditions and abrupt changes. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 965–973. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Kang, Y.; Kim, D.; Hyun, B.; Baek, S.H. High and fine resolution of bloom dynamics using HPLC analysis in a semi-enclosed harbour. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 309, 108950. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, O.-M.; Shin, K.-S.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, W.-J.; Kim, S.-A.; Jang, M.-C. Annual variations in community structure of mesozooplankton by short-term sampling in Jangmok Harbor of Jinhae Bay. Ocean Polar Res. 2011, 33, 235–253. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Jang, P.-G.; Cha, H.-G.; Hyun, B.; Lee, E.H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Shin, K.; Seo, M.H.; Soh, H.Y.; Youn, S.H. Dynamics of Noctiluca scintillans blooms: A 20-year study in Jangmok Bay, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.-C.; Shin, K.; Lee, T.; Noh, I. Feeding selectivity of calanoid copepods on phytoplankton in Jangmok Bay, south coast of Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2010, 45, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.-S.; Jeon, J.-K.; Kim, Y.-O. Occurrence of dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense, a causative organism of paralytic shellfish poisoning in Chinhae Bay, Korea. J. Plankton Res. 1992, 14, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, J.-S.; Song, K.-C.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Variation and profile of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in Jinhae bay, Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 16, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hyung, J.H.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J. Quantification of Alexandrium catenella (Group I) using sxtA4-based digital PCR for screening of paralytic shellfish toxins in Jinhae-Masan Bay, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116048. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, P.J.; Walstad, L.J. Phytoplankton patches at fronts: A model of formation and response to wind events. J. Mar. Res. 1997, 55, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Choi, J.M.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Jeon, J.-K.; Kim, Y.O. Change in paralytic shellfish toxins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis depending on dynamics of harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje coast (South Korea) during bloom season. Toxins 2020, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Stock, C.A.; Keafer, B.A.; Nelson, A.B.; Thompson, B.; McGillicuddy Jr, D.J.; Keller, M.; Matrai, P.A.; Martin, J. Alexandrium fundyense cyst dynamics in the Gulf of Maine. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 2522–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lim, Y.K.; Baek, S.H.; Hong, S. Nationwide seasonal monitoring of lipophilic marine algal toxins in shellfish and causative microalgae along the coasts of South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 207, 116855. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorendino, J.M.; Smith, J.L.; Campbell, L. Growth response of Dinophysis, Mesodinium, and Teleaulax cultures to temperature, irradiance, and salinity. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamiyama, T.; Suzuki, T. Production of dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-2 by a culture of Dinophysis acuminata (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Vishal, C.R.; Parvathi, A.; Anil, P.; Mohammed Iqbal, P.M.; Muraleedharan, K.R.; Abdul Azeez, S.; Furtado, C.M. In situ measurements of bioluminescence response of Gonyaulax spinifera to various mechanical stimuli. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Boivin-Rioux, A.; Starr, M.; Lavoie, D.; Chass, J.; Scarratt, M.; Perrie, W.; Long, Z.; Lavoie, D. Harmful algae and climate change on the Canadian East Coast: Exploring occurrence predictions of Dinophysis acuminata, D. norvegica, and Pseudo-nitzschia seriata. Harmful Algae 2022, 112, 102183. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, S.S.; Garrison, D.L.; Horner, R.A. Bloom dynamics and physiology of domoic-acid-producing Pseudo-nitzschia species. NATO ASI Ser. G Ecol. Sci. 1998, 41, 267–292. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.P.; Kumar, S.P.; Nair, G.A. Risk assessment of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid, on animals and humans. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Scholin, C.A.; Gulland, F.; Doucette, G.J.; Benson, S.; Busman, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Cordaro, J.; DeLong, R.; De Vogelaere, A.; Harvey, J. Mortality of sea lions along the central California coast linked to a toxic diatom bloom. Nature 2000, 403, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lifanchuk, A.V.; Mikaelyan, A.S.; Sergeeva, A.V.; Silkin, V.A. Seasonal dynamics and ecology of the Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima group in the Black Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 68, 103249. [Google Scholar]
- Thorel, M.; Claquin, P.; Schapira, M.; Le Gendre, R.; Riou, P.; Goux, D.; Le Roy, B.; Raimbault, V.; Deton-Cabanillas, A.-F.; Bazin, P. Nutrient ratios influence variability in Pseudo-nitzschia species diversity and particulate domoic acid production in the Bay of Seine (France). Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 192–205. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, M.; Hong, S.; Lim, Y.K. Seasonal Effects of Nakdong River Freshwater Inflow and Coastal Environmental Changes on Phytoplankton Community Structure, Including Harmful Species, in Eastern Jinhae Bay, Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040669
Baek SH, Lee CH, Kim M, Hong S, Lim YK. Seasonal Effects of Nakdong River Freshwater Inflow and Coastal Environmental Changes on Phytoplankton Community Structure, Including Harmful Species, in Eastern Jinhae Bay, Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040669
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Seung Ho, Chung Hyeon Lee, Mungi Kim, Seongjin Hong, and Young Kyun Lim. 2025. "Seasonal Effects of Nakdong River Freshwater Inflow and Coastal Environmental Changes on Phytoplankton Community Structure, Including Harmful Species, in Eastern Jinhae Bay, Korea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040669
APA StyleBaek, S. H., Lee, C. H., Kim, M., Hong, S., & Lim, Y. K. (2025). Seasonal Effects of Nakdong River Freshwater Inflow and Coastal Environmental Changes on Phytoplankton Community Structure, Including Harmful Species, in Eastern Jinhae Bay, Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040669





