Abstract
Underwater acoustic target recognition (UATR) technology plays a significant role in marine exploration, resource development, and national defense security. To address the limitations of existing methods in computational efficiency and recognition performance, this paper proposes an improved WS-ViT model based on Vision Transformers (ViTs). By introducing the Wavelet Transform Convolution (WTConv) module and the Simplified Linear Attention (SLAttention) module, WS-ViT can effectively extract spatiotemporal complex features, enhance classification accuracy, and significantly reduce computational costs. The model is validated using the ShipsEar dataset, and the results demonstrate that WS-ViT significantly outperforms ResNet18, VGG16, and the classical ViT model in classification accuracy, with improvements of 7.3%, 4.9%, and 2.1%, respectively. Additionally, its training efficiency is improved by 28.4% compared to ViT. This study demonstrates that WS-ViT not only enhances UATR performance but also maintains computational efficiency, providing an innovative solution for efficient and accurate underwater acoustic signal processing.
1. Introduction
Underwater acoustic target recognition (UATR) technology plays a vital role in fields such as marine exploration, resource development, and national defense security. With the increasing scale of marine activities, accurate identification and classification of underwater targets have become crucial for ensuring the safety and efficient utilization of underwater environments. Exploring advanced UATR methods contributes to the development of related fields, including seabed mapping, marine biodiversity monitoring, and ship target recognition [1]. Moreover, this technology is widely applied in scientific research areas such as marine behavioral analysis and underwater archeological investigations. As a result, UATR technology has become indispensable in modern underwater engineering and national defense, driving advancements in the safety and efficiency of marine activities. In the early stages, the identification of underwater acoustic targets relied solely on human effort, specifically using the human ear. To classify underwater acoustic signals more efficiently, researchers began leveraging the time–frequency characteristics of these signals, such as waveform structure [2], Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) [3], Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) [4], and Wavelet Transform (WT) [5]. Each method offers distinct advantages depending on the signal characteristics: Fourier transform proves particularly effective for analyzing stable acoustic signals, such as the continuous hum of an engine, while Wavelet Transform demonstrates superior performance in processing dynamic and non-stationary signals, particularly in the analysis of propeller noise. In recent years, with the advancement of computer technology, methods based on deep learning (DL) for UATR have rapidly developed [6,7] and have been widely applied in fields such as natural language processing, speech recognition, and medical diagnosis [8,9]. For instance, Song et al. [7] utilized a CNN model to process one-dimensional time-series signals for underwater target recognition, while Xue et al. designed and employed a ResNet model with an attention mechanism to improve recognition accuracy [10]. Additionally, Kamal et al. [11] extracted features using a combination of CNN and Bi-LSTM models.
Since its introduction, the Transformer architecture [12] has garnered widespread attention. Feng et al. [13] were the first to apply a Transformer-based model for underwater acoustic target recognition, achieving promising results. Li et al. [14] proposed a spectrogram Transformer model (STM) for underwater acoustic target recognition, which effectively overcomes the limitations of traditional CNNs in capturing rich spectral features. Yao et al. [15] proposed Mobile_ViT, a hybrid model that fuses local features from MobileNet with global context from a Transformer for underwater acoustic target recognition, achieving high accuracy with reduced complexity. Tang et al. [16] proposed an underwater acoustic target recognition method based on a pre-trained Transformer, which effectively overcomes the limitations of traditional CNNs in capturing global features. Dong et al. [17] proposed a Transformer network based on a cross-attention mechanism (CAF-ViT) that achieves efficient underwater acoustic target recognition by fusing time-frequency features such as LOFAR, Mel spectrograms, and wavelet packets. Despite its powerful performance, the high computational cost remains a significant challenge. To address this, Finder et al. proposed a method that leverages Wavelet Transform (WT) to expand the network’s receptive field without excessive parameterization [18]. On the other hand, Guo et al. introduced a Simplified Linear Attention (SLA) module aimed at enhancing the efficiency of Transformer models while maintaining or even improving their performance [19]. Inspired by these advancements, we propose a novel approach applied to the Vision Transformer (ViT) model. Our goal is to develop a model that is both efficient and powerful, balancing computational efficiency and performance. The main contributions of this paper include the following:
(1) We propose a novel WS-ViT model by integrating Wavelet Transform Convolution (WTConv) and Simplified Linear Attention (SLAttention) into the Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture. The WTConv module effectively complements the signal features obtained from the Short-Time Fourier Transform by employing multi-scale decomposition to further extract local time-frequency details, while the SLAttention module reduces computational complexity.
(2) Extensive experiments on the ShipsEar dataset demonstrate the superiority of WS-ViT. It outperforms ResNet18, VGG16, and the classical ViT in classification accuracy, showcasing higher computational efficiency and strong generalization capabilities.
2. Theory and Models
2.1. Attention in Transformer Models
Image classification, as a core task in computer vision, has evolved significantly over the years. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have achieved remarkable success in image classification tasks, with the introduction of classic architectures such as AlexNet and VGG laying the foundation for deep learning in the field of image processing. However, as network depth and computational power increased, the limitations of CNNs became apparent, particularly in handling long-range dependencies and capturing global contextual information. Against this backdrop, Transformer-based vision models have gradually emerged as a promising alternative.
The core component of the Transformer model is the self-attention mechanism, which determines the representation (embedding) of each position in the input sequence by calculating the similarity between all positions. The self-attention mechanism computes attention weights for each position relative to others using three sets of vectors: Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V). For each position in the input, we first map it to three distinct vectors through linear transformations: the Query vector, the Key vector, and the Value vector. The specific calculation formulas are as follows:
where represents the vector representation of the i-th token in the input sequence, where i ranges from 1 to N, and N denotes the length of the input sequence., , are weight matrices learned during training. Next, the similarity between the Query vector and the Key vectors of all other positions is calculated, typically using the dot product to measure their similarity. The formula is as follows:
where j ranges from 1 to N. To prevent excessively large values, the dot product is typically scaled, resulting in the Scaled Dot-Product Attention. The formula is as follows:
where represents the dimensionality of the Key vectors, and the scaling factor helps prevent the dot product from becoming too large, which could lead to gradient vanishing or exploding problems. Then, the similarities of all Keys are normalized using the Softmax function, resulting in the attention weight for each Key being as follows:
The Softmax function is commonly used in multi-class classification problems to convert a vector of raw scores (logits) into a probability distribution. Specifically, for a given vector , the Softmax function is defined as:
where represents the i-th element of the input vector. Finally, the attention weights are used to perform a weighted sum of the Value vectors, resulting in the output being:
The values of output reflect the importance of features at different positions in the input sequence.
To enable the model to learn diverse representations from multiple subspaces, the Transformer introduces the Multi-Head Attention mechanism. The core idea of Multi-Head Attention is to project the Query, Key, and Value vectors into multiple distinct subspaces, compute attention separately in each subspace, concatenate the results, and then apply a linear transformation to produce the final output.
2.2. Vision Transformer
The Vision Transformer (ViT), proposed by Google Research in 2020 [20], is a Transformer-based model for image classification. The innovation of ViT lies in its departure from traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Instead, it treats an image as a sequence of patches and processes them as sequential data within the Transformer architecture. The core idea of the model is that spatial information in images can be captured through the self-attention mechanism, enabling efficient image classification. The structure of the model is illustrated in Figure 1.
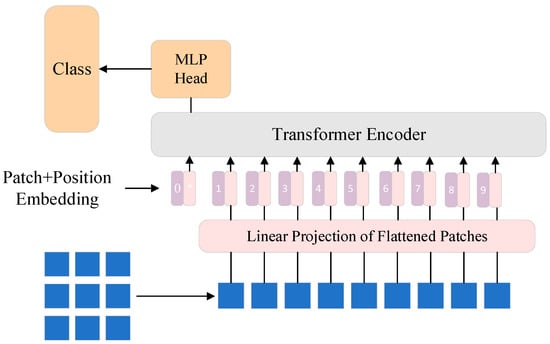
Figure 1.
The Main Structure of the ViT Model.
The first step in ViT is to divide the input image into a set of fixed-size, non-overlapping patches. Suppose the input image has dimensions H × W × C, where H is the height, W is the width, and C is the number of channels. The image is divided into patches of size P × P, with each patch containing P × P × C pixels. Each patch is flattened and mapped to a vector through a linear transformation (typically a fully connected layer), where the dimensionality of the vector usually matches the input dimension of the Transformer model. In this way, the input image is transformed into a sequence of embeddings, with each patch corresponding to a token in the Transformer. Typically, the input image size for the ViT model is 224 × 224 × 3, and each patch size is 16 × 16. This results in 14 × 14 = 196 patches, with each patch having dimensions 16 × 16 × 3. Each patch is flattened into a vector, and after linear embedding, a sequence of size 196 × D is obtained, where D is the dimensionality of the embedding space. Since the Transformer architecture inherently lacks positional information, ViT introduces positional encoding to incorporate the spatial relationships between patches. Positional encoding allows the model to recognize the relative or absolute positions of patches within the image. ViT adopts a method similar to the original Transformer, using sine and cosine functions to generate positional encodings. These encodings are added element-wise to the patch embeddings, providing positional information for each patch. This enables ViT to capture spatial structures in the image through the self-attention mechanism, even without convolutional operations. The Transformer encoder is the core component of ViT. It processes the sequence of patch embeddings through multiple self-attention layers and feed-forward neural networks. For classification, a special classification token ([CLS] token) is typically introduced, serving as the global representation of the image. After processing by the Transformer encoder, the model extracts global features from the final representation of the [CLS] token. These global features are then passed to a classification head (usually a fully connected layer) for the final category prediction.
2.3. WS-ViT Model
The model proposed in this paper improves on the traditional ViT by integrating the WTConv and SLAttention modules into the ViT architecture for ship radiation noise recognition. This enhancement allows the model to better extract effective features when processing input data with high spatiotemporal complexity, thereby improving the accuracy of image classification. The main structure of the model is shown in Figure 2. First, the audio signal is converted into a time–frequency spectrogram using the Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT), which is then fed into the network. The basic calculation formula is as follows:
where x(k) represents the signal sequence, and g(k − m) is the window function. The ranges of m and n are determined by the signal length L and the window length N. Specifically, 0 ≤ m ≤ L − N and 0 ≤ n ≤ N − 1.
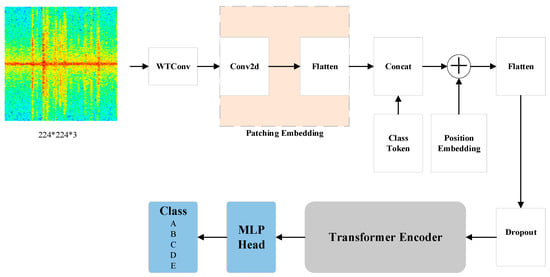
Figure 2.
Main Architecture of the WS-ViT Model.
Before the image enters the Patch Embedding stage, it is processed through a Wavelet Transform Convolution (WTConv) layer to obtain enhanced features. The principle involves convolving the input image with decomposition filters to generate multi-scale feature components , , and . These components represent the low-frequency parts in both horizontal and vertical directions, the low-frequency part in the horizontal direction and the high-frequency part in the vertical direction, the high-frequency part in the horizontal direction and the low-frequency part in the vertical direction, and the high-frequency parts in both horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. After wavelet decomposition, each feature component is further convolved to produce enhanced features , which can be expressed as:
where is convolution kernel.
After decomposition and convolution, the inverse Wavelet Transform (IWT) is used to reconstruct the multi-scale features back to the original feature dimensions. The reconstruction can be expressed as:
where is the wavelet reconstruction filter and is the reconstructed signal. Finally, residual connections are used to retain the original input information on top of the wavelet convolution operation. The formula for the residual connection is:
where is original input image.
In the Transformer encoder part, the traditional attention mechanism (Attention) can be expressed as:
where , , are the weight matrices, is the similarity function and N is the length of the input sequence. For traditional attention, the similarity function can be expressed as:
where represents the dimensionality of the Key vectors. The represents using the softmax function to characterize the similarity between the Query and the Key.
The attention mechanism based on softmax leads to high computational complexity. In the SLA module, the similarity function modified with the ReLU function, along with the use of Depthwise Separable Convolution (DWC) technology, can improve computational efficiency. Its formula is expressed as:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
The ship noise dataset used in this paper is the ShipsEar dataset [21]. This dataset was recorded between 2012 and 2013 from various regions along the Spanish coast. The original classification of the dataset divides 90 different ship noises and background noises into five categories, A, B, C, D, and E, with detailed classifications, shown in Table 1. The raw audio lengths vary, so normalization was applied to the dataset. The audio was sampled at a rate of 48,000 Hz, and silent segments were removed. The processed audio signals were then framed and labeled with a length of 1 s, resulting in labeled samples from categories A to E, with 1888, 1574, 4286, 2465, and 1147 samples per category, totaling 11,360 samples. Subsequently, for each category, 1000 samples were randomly selected and split into training and validation sets, and Test Set I, with a 6:2:2 ratio. An additional 1000 samples were randomly selected from the remaining data as Test Set II.

Table 1.
Detailed Classification of the ShipsEar Dataset.
3.2. Training Parameters
Combined with the model method proposed in this paper, the training parameters used in the experiments are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Training parameters.
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy is one of the most commonly used metrics in classification models. It represents the ratio of correctly predicted samples to the total number of samples. The calculation formula is:
where True Positive (TP) represents the number of samples that are actually positive and correctly predicted as positive by the model. True Negative (TN) denotes the number of samples that are actually negative and correctly predicted as negative by the model. False Positive (FP) refers to the number of samples that are actually negative but incorrectly predicted as positive by the model. False Negative (FN) indicates the number of samples that are actually positive, but incorrectly predicted as negative by the model. Accuracy provides an intuitive measure of the overall prediction correctness of the model and is widely applicable to various classification problems. It is particularly effective in scenarios where the class distribution is relatively balanced, as it can better reflect the model’s performance.
The confusion matrix is a visualization tool widely used in supervised learning for evaluating the performance of classification models. It is constructed based on the actual labels and predicted labels, effectively summarizing the model’s classification results and presenting them in a visual format.
3.4. Analysis of Experimental Results
By using Test Set I, the confusion matrix of the experimental results in this paper is shown in Figure 3. Subfigures (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) in Figure 3 represent the recognition performance of categories A, B, C, D, and E, respectively.
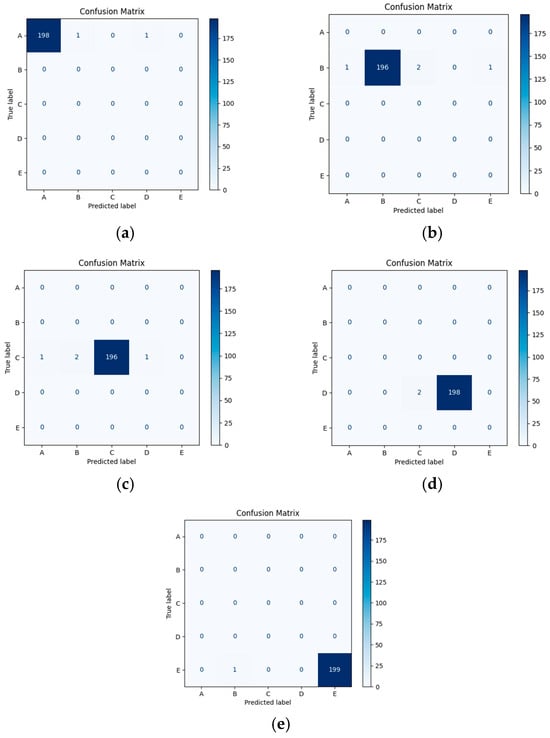
Figure 3.
Confusion matrix for Recognition Results of Each Category.
From the confusion matrix, it can be observed that the WS-ViT model performs excellently in terms of recognition accuracy for each category. Specifically, the recognition accuracies for categories A, D, and E all reached 99%, while the recognition accuracies for categories B and C were 98%, respectively. The overall average recognition accuracy was 98.6%. The reason for these results might be that the ship noise features of categories B and C are relatively similar to those of the other categories, which made it somewhat difficult for the model to distinguish between them. Despite the slightly lower recognition accuracy for categories B and C compared to the other categories, the accuracy remains high, indicating that the model demonstrates good robustness when handling these categories.
To further validate the superiority of the WS-ViT model, this paper compares it with the ResNet18, VGG16, and classic ViT models. The comparative experiments for all models were conducted on Test Set II, which consists of 1000 randomly selected samples covering five categories. The comparison results are shown in Table 3. The WS-ViT model achieved a classification accuracy of 99.5%. on Test Set II, significantly outperforming the other models. Specifically, the WS-ViT model improved upon the ResNet18 model by 7.3%, the VGG16 model by 4.9%, the ResNet152model by2.7% and the classic ViT model by 2.1%. This result indicates that after incorporating the WTConv and SLAttention modules, the WS-ViT model not only maintains the superior performance of the ViT model in classification tasks, but also further enhances classification accuracy.

Table 3.
Classification results of different networks.
To evaluate the computational efficiency of the WS-ViT model, this paper compares the training time of the WS-ViT model with the classic ViT model. The classic ViT model has a training time of 194 s per epoch, while the WS-ViT model has a training time of only 139 s per epoch, reducing the training time by 28.4%. The experiments further compared the floating-point operations (FLOPs) of the two models: the classic ViT model requires 11.29 G FLOPs, while the WS-ViT model reduces this to 9.03 G FLOPs, representing a 20% decrease. The experimental results are shown in Table 4. This optimization is due to the introduction of the WTConv and SLAttention modules in the WS-ViT model, which effectively reduce computational redundancy and decrease the reliance on global attention computations, thus significantly improving computational efficiency. Specifically, the WTConv module performs multi-scale feature extraction on the input image through a Wavelet Transform Convolution layer, and the SLAttention module further reduces computation by simplifying the linear attention mechanism, thereby enhancing the model’s training efficiency. As a result, the WS-ViT model not only maintains high classification accuracy but also significantly improves training efficiency, providing strong support for large-scale data processing in practical applications.

Table 4.
Comparison of training time and FLOPs.
To further validate the generalization ability of the WS-ViT model, experiments were conducted using Test Set II. The confusion matrix for Test Set II is shown in Figure 4. From the confusion matrix, it can be seen that the WS-ViT model performs excellently on Test Set II as well. Specifically, the recognition accuracies for categories A, C, and E all reached 100%, while the recognition accuracies for categories B and D were 98.93% and 98.51%, respectively. This result indicates that the WS-ViT model not only performs outstandingly on the training and validation sets but also demonstrates strong generalization ability on unseen test data.
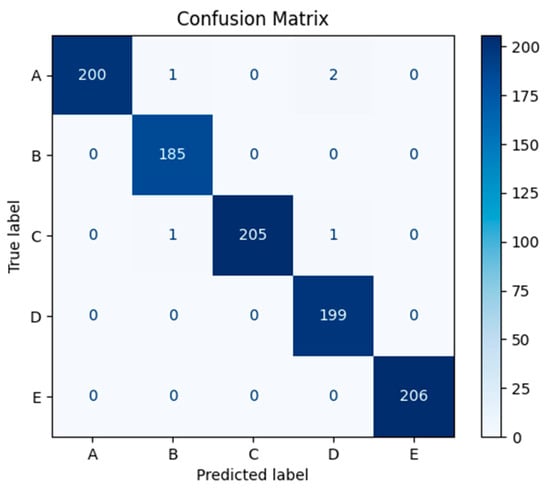
Figure 4.
Classification Results of Test Set II Under the Proposed Method.
Based on the above experimental results, the WS-ViT model performs excellently in the underwater acoustic target recognition task. It not only significantly outperforms other comparative models in classification accuracy, but also achieves a notable improvement in training efficiency. Specifically, the WS-ViT model effectively extracts the spatiotemporal complex features of underwater acoustic signals by introducing the WTConv and SLAttention modules, thereby enhancing the model’s classification performance. At the same time, the WTConv module performs multi-scale feature extraction on the input image using Wavelet Transform Convolution layers, reducing the model’s reliance on global attention computations, which in turn lowers computational complexity. The SLAttention module simplifies the linear attention mechanism, further reducing computation burden and improving the model’s training efficiency. Furthermore, the performance of the WS-ViT model on Test Set II further validates its strong generalization ability. The model still maintains a high classification accuracy on unseen test data, demonstrating its broad potential for practical applications. In particular, in areas such as marine exploration, resource development, and national defense security, the WS-ViT model provides an innovative solution for efficient and precise underwater acoustic signal processing.
4. Conclusions
This paper proposes an improved WS-ViT model to meet the efficiency and accuracy requirements for underwater acoustic target recognition (UATR). By integrating the WTConv and SLAttention modules into the ViT architecture, the WS-ViT model achieves optimization in both computational efficiency and classification performance. Experimental results show that the WS-ViT model outperforms ResNet18, VGG16, and the classic ViT model in terms of classification accuracy, with improvements of 7.3%, 4.9%, and 2.1%, respectively, while its training efficiency has improved by 28.4% compared to the classic ViT model. The research in this paper provides an efficient and powerful solution for underwater acoustic target recognition, with broad application potential and practical value. However, despite the promising performance of the proposed method on the existing dataset, several limitations remain. First, the dataset used in this study (e.g., ShipsEar) is limited in terms of diversity and scale, potentially failing to fully represent the complex acoustic environments encountered in real-world scenarios. Second, the absence of recently published public datasets has hindered further validation and comprehensive performance evaluations of underwater acoustic target recognition algorithms. Future work should prioritize the development of more diverse and representative datasets to enable more accurate and reliable assessment of algorithm performance in practical applications. Additionally, we will enhance inference speed to meet real-time requirements through lightweight network architecture design, model compression via knowledge distillation, integrated with multi-threaded asynchronous processing and hardware acceleration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G., B.W., T.F. and B.L.; funding acquisition, B.W.; experiments, H.G., B.W., T.F. and B.L.; method, H.G., B.W., T.F. and B.L.; data analysis, H.G., B.W., T.F. and B.L.; writing, H.G., B.W., T.F. and B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, grant number KYCX24_4181.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuan, F.; Ke, X.; Cheng, E. Joint Representation and Recognition for Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Multimodal Deep Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Yang, S. A Wave Structure Based Method for Recognition of Marine Acoustic Target Signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 2015, 137, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Han, X.; Zhu, Z. Feature Extraction of Underwater Target Signal Using Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients Based on Acoustic Vector Sensor. J. Sensors 2016, 2016, 7864213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Da, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. Integrated Neural Networks Based on Feature Fusion for Underwater Target Recognition. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108261. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Dai, W.; Li, Z. A Method Based on Wavelet Packets-Fractal and SVM for Underwater Acoustic Signals Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Hangzhou, China, 19–23 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Qiu, M.; Shi, J.; Liu, L. Deep Learning Methods for Underwater Target Feature Extraction and Recognition. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 1214301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoping, S.; Jinsheng, C.; Yuan, G. A New Deep Learning Method for Underwater Target Recognition Based on One-Dimensional Time-Domain Signals. In Proceedings of the 2021 OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 14–17 July 2021; pp. 1048–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hershey, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Gemmeke, J.F.; Jansen, A.; Moore, R.C.; Plakal, M.; Platt, D.; Saurous, R.A.; Seybold, B.; et al. CNN Architectures for Large-Scale Audio Classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Zeng, X.; Jin, A. A Novel Deep-Learning Method with Channel Attention Mechanism for Underwater Target Recognition. Sensors 2022, 22, 5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, S.; Satheesh Chandran, C.; Supriya, M.H. Passive Sonar Automated Target Classifier for Shallow Waters Using End-to-End Learnable Deep Convolutional LSTMs. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 860–871. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Zhu, X. A Transformer-Based Deep Learning Network for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1505805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lan, Q.; Xiao, W. STM: Spectrogram Transformer Model for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, X. Mobile_ViT: Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on Local–Global Feature Fusion. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ma, E.; Qu, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, L. UAPT: An Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on Pre-Trained Transformer. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Fu, J.; Zou, N.; Zhao, C.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. CAF-ViT: A Cross-Attention Based Transformer Network for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition. Ocean Eng. 2025, 318, 120049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finder, S.E.; Amoyal, R.; Treister, E.; Freifeld, O. Wavelet Convolutions for Large Receptive Fields. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. SLAB: Efficient Transformers with Simplified Linear Attention and Progressive Re-parameterized Batch Normalization. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.11582. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Domínguez, D.; Torres-Guijarro, S.; Cardenal-López, A.; Pena-Gimenez, A. ShipsEar: An Underwater Vessel Noise Database. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).