Surviving in a Warmer Marine World: A Study on the Impact of Thermal Effluent on Posidonia oceanica Meadows and Associated Fish Assemblages in the Maltese Islands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sampling Design
2.2. Environmental Parameters
2.3. Posidonia Oceanica Meadows
2.4. Fish Assemblages Sampling, Biodiversity Metrics and Functional Groups
2.5. Statistical Analysis
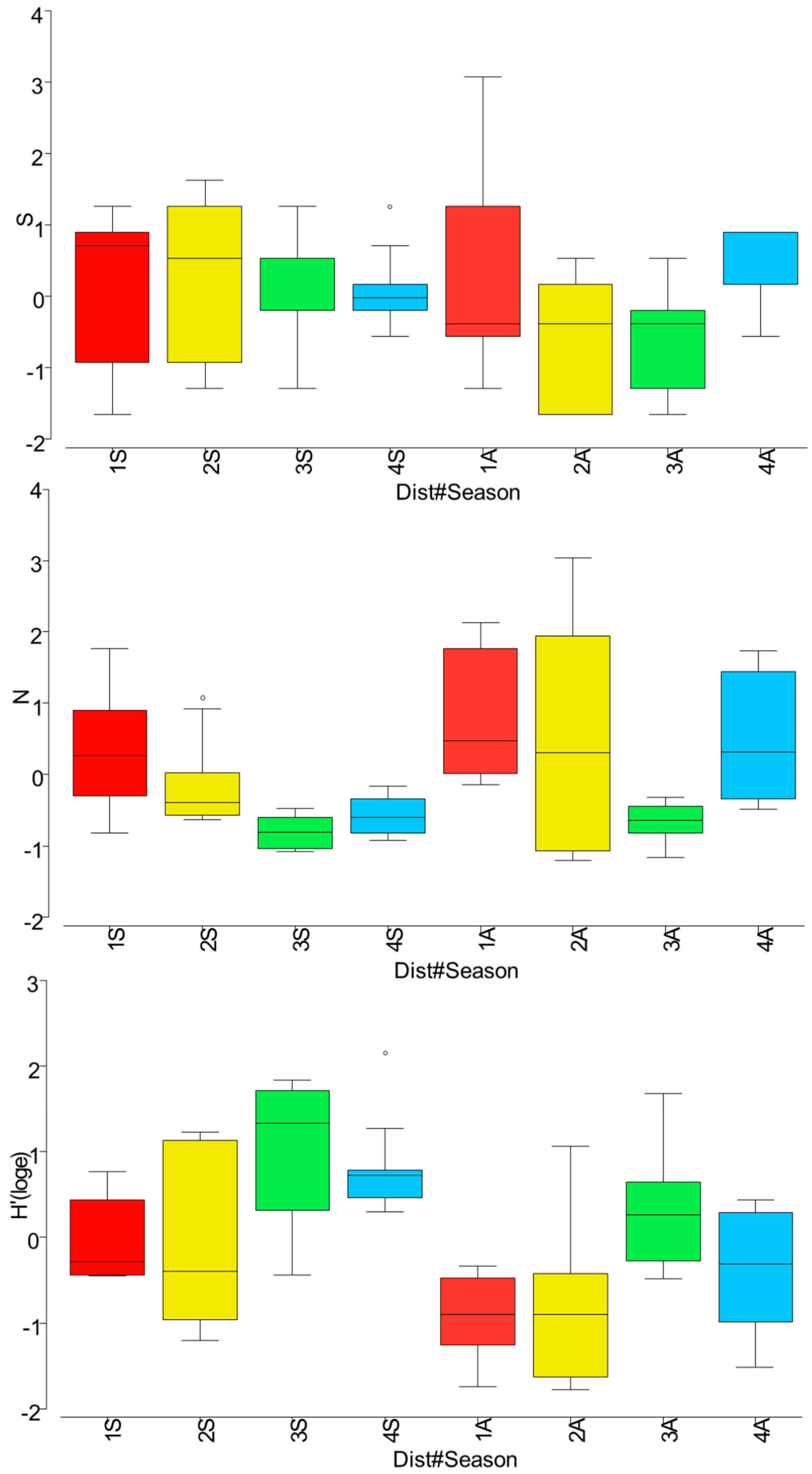
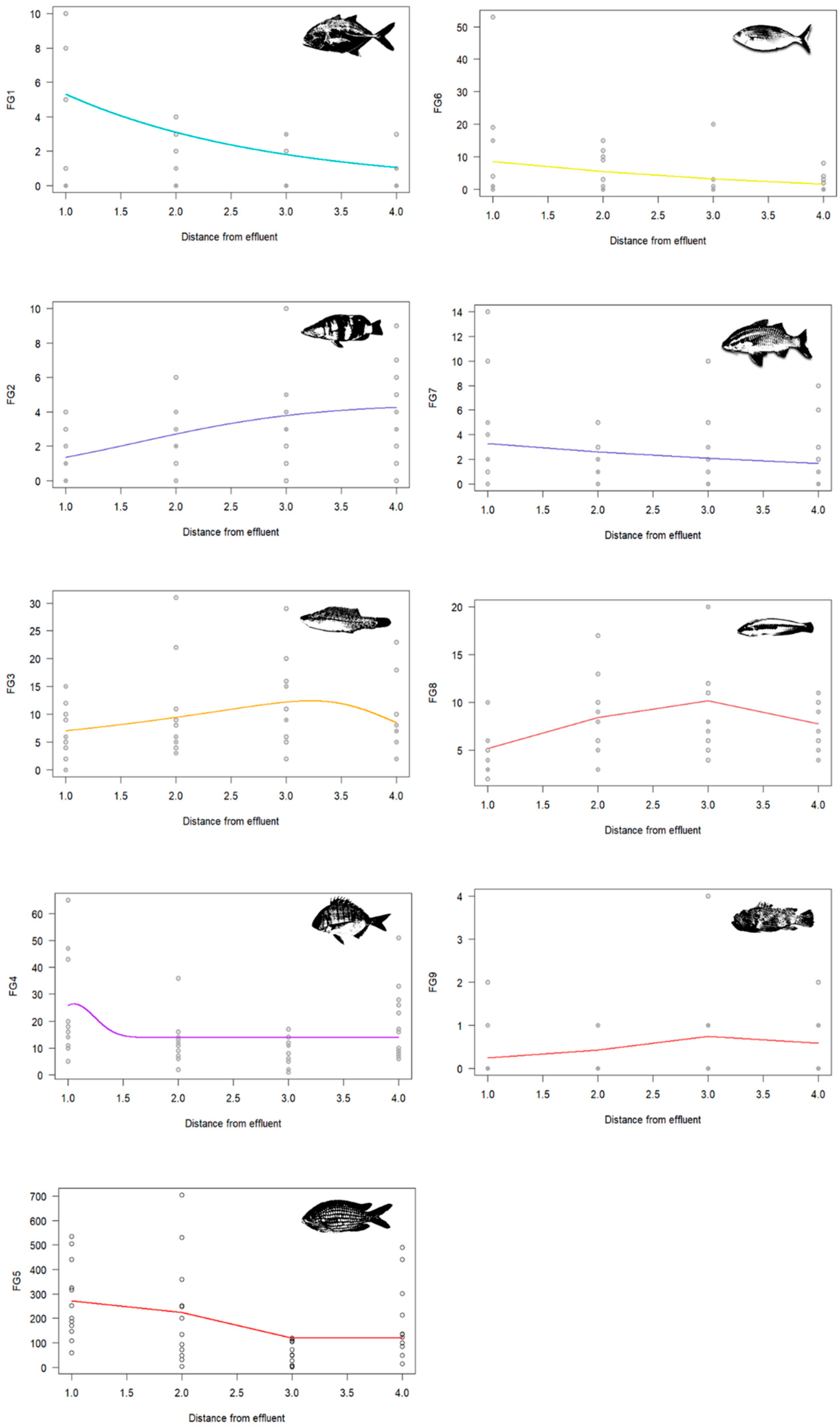
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Drivers and Impacts on Posidonia Oceanica Meadow Structure and Health
4.2. Fish Assemblage Responses to Thermal Pollution
4.3. Functional Group Dynamics and Ecosystem Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Diet | Position | Habitat | Climate Zone | Trophic Level |
| Apogon imberbis | macrofauna | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 3.55 |
| Caranx crysos | macrofauna/fish | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 4.13 |
| Chromis chromis | plankton | reef-associated | pelagic | subtropical | 3.38 |
| Dentex dentex | fish/cephalopods | demersal | all | subtropical | 4.53 |
| Symphodus mediterraneus | macrofauna | demersal | seagrass | subtropical | 3.15 |
| Centrolabrus melanocercus | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.17 |
| Symphodus ocellatus | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.34 |
| Symphodus roissali | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.47 |
| Symphodus rostratus | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.23 |
| Symphodus tinca | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.45 |
| Coris julis | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | temperate | 3.24 |
| Thalassoma pavo | macrofauna | reef-associated | seagrass | subtropical | 3.5 |
| Boops boops | plankton | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 3.11 |
| Diplodus sargus | macrofauna | demersal | all | subtropical | 3.38 |
| Diplodus vulgaris | macrofauna | demersal | all | subtropical | 3.34 |
| Diplodus annularis | macrofauna | demersal | seagrass | subtropical | 3.21 |
| Sarpa salpa | seagrass/algae | demersal | all | subtropical | 2 |
| Gobius sp. | macrofauna | demersal | sand/rock | temperate | 3.31 |
| Mugil spp | sediment macrofauna | demersal | sand/rock | subtropical | 2.48 |
| Mullus surmuletus | sediment macrofauna | demersal | sand/rock | subtropical | 3.45 |
| Murena helena | fish/cephalopods | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 4.18 |
| Oblada melanura | macrofauna | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 3.7 |
| Pagrus pagrus | macrofauna/fish | demersal | all | subtropical | 3.86 |
| Scorpaena porcus | macrofauna/fish | demersal | rock/cave | temperate | 3.78 |
| Serranus scriba | macrofauna/fish | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 3.82 |
| Sparisoma cretense | seagrass/algae | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 2.86 |
| Spicara maena | plankton | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 3.5 |
| Spondyliosoma cantharus | macrofauna | demersal | all | subtropical | 3.34 |
| Seriola dumerilii | fish/cephalopods | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 4.5 |
| Sparus aurata | macrofauna | demersal | all | subtropical | 3.7 |
| Syngnathus typhle | plankton | demersal | seagrass | temperate | 3.4 |
| Trachinus draco | macrofauna/fish | demersal | sand | temperate | 4.13 |
| Mycteroperca rubra | fish/cephalopods | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 4.18 |
| Lithognathus mormyrus | sediment macrofauna | demersal | sand/rock | subtropical | 3.42 |
| Sciaena umbra | macrofauna/fish | reef-associated | rock/cave | subtropical | 3.75 |
| Trachinotus ovatus | macrofauna/fish | open water | pelagic | subtropical | 3.73 |
References
- Venegas, R.M.; Acevedo, J.; Treml, E.A. Three decades of ocean warming impacts on marine ecosystems: A review and perspective. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2023, 212, 105318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, D.; Haghani, M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Moftakhari, H.; Sadat-Noori, M.; Mach, K.J.; Glamore, W. The evolving landscape of sea-level rise science from 1990 to 2021. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, L. Deep learning for ocean temperature forecasting: A survey. Intell. Mar. Technol. Syst. 2024, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivato, M.; Carniello, L.; Viero, D.P.; Soranzo, C.; Defina, A.; Silvestri, S. Remote sensing for optimal estimation of water temperature dynamics in shallow tidal environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embury, O.; Merchant, C.J.; Good, S.A.; Rayner, N.A.; Høyer, J.L.; Atkinson, C.; Donlon, C. Satellite-based time-series of sea-surface temperature since 1980 for climate applications. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Feng, M. A deep learning model for forecasting global monthly mean sea surface temperature anomalies. Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 932932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Khodayar, S. A warming Mediterranean: 38 years of increasing sea surface temperature. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Global sea warming and “tropicalization“ of the Mediterranean Sea: Biogeographic and ecological aspects. Biogeographia 2003, 24, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Harmelin, J.G. Marine heatwaves drive recurrent mass mortalities in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansch, C.; Hiebenthal, C. A new mesocosm system to study the effects of environmental variability on marine species and communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2019, 17, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, E.; Di Giacomo, S.; Gambi, C.; Bianchelli, S.; Da Ros, Z.; Tangherlini, M.; Danovaro, R. Effects of Local Acidification on Benthic Communities at Shallow Hydrothermal Vents of the Aeolian Islands (Southern Tyrrhenian, Mediterranean Sea). Biology 2022, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.; Schroeter, S.; Huang, D. Final Report on the Findings and Recommendations of the Experimental Phase of the SONGS Artificial Reef Mitigation Project; California Coastal Commission: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, R.N.; Spencer, J.F. The benthos of a coastal power station thermal discharge canal. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1984, 64, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, V.; Sastry, J.S.; Swamy, G.N. Implication of thermal discharges into the sea—A review. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 1991, 11, 525–527. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Zou, X.; Huang, F. Effects of the thermal discharge from an offshore power plant on plankton and macrobenthic communities in subtropical China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, S.; Clara, S.; Terlizzi, A. The impact assessment of thermal pollution on subtidal sessile assemblages: A case study from Mediterranean rocky reefs. Ecol. Quest. 2020, 31, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Lin, J.; Zheng, B. Effects of thermal discharge from coastal nuclear power plants and thermal power plants on the thermocline characteristics in sea areas with different tidal dynamics. Water 2019, 11, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, A.; Wright, L.S.; Borg, J.A. Impacts of thermal effluent on Posidonia oceanica and associated macrofauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2023, 707, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Statistics Office Malta. Electricity Supply 2023. Available online: https://nso.gov.mt/electricity-supply-2023 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Cardoso-Mohedano, J.G.; Bernardello, R.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Alonso-Rodriguez, R.; Cruzado, A. Thermal impact from a thermoelectric power plant on a tropical coastal lagoon. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Romero, J.; Ruiz, J.; Gacia, E.; Buceta, J.L.; Invers, O.; Manzanera, M. Salinity Tolerance of the Mediterranean Seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Recommendations to Minimize the Impact of Brine Discharges from Desalination Plants. Desalination 2008, 221, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.M.; Marín-Guirao, L.; García-Muñoz, R.; Ramos-Segura, A.; Bernardeau-Esteller, J.; Pérez, M.; Procaccini, G. Experimental evidence of warming-induced flowering in the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 134, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M. Ecosystem health assessment using the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Personnic, S.; Boudouresque, C.F.; Astruch, P.; Ballesteros, E.; Blouet, S.; Bellan-Santini, D.; Ruitton, S. An ecosystem-based approach to assess the status of a Mediterranean ecosystem, the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, A.; Pace, M.; Gobert, S.; Borg, J.A. Seascape ecology in Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows: Linking structure and ecological processes for management. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Martinez, M.; Badalamenti, F.; D’Anna, G.; Mirto, S.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Montalto, V. The ontogeny-specific thermal sensitivity of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1183728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, P.; Paoli, C.; Rovere, A.; Montefalcone, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. The value of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: A natural capital assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zrelli, R.; Hcine, A.; Yacoubi, L.; Roa-Ureta, R.H.; Gallai, N.; Castet, S.; Rabaoui, L.J. Economic losses related to the reduction of Posidonia ecosystem services in the Gulf of Gabes (Southern Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.E.; Kwak, T.J. Tropical insular fish assemblages are resilient to flood disturbance. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, D.M.; Emslie, M.J.; Richards, Z.T. Post-disturbance stability of fish assemblages measured at coarse taxonomic resolution masks change at finer scales. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubak, I.; Kruschel, C.; Schultz, S.T. Predators structure fish communities in Posidonia oceanica meadows: Meta-analysis of available data across the Mediterranean basin. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 566, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleishman, E.; Noss, R.F.; Noon, B.R. Utility and limitations of species richness metrics for conservation planning. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.J.; Baetens, J.M.; De Baets, B. Ecological Diversity: Measuring the Unmeasurable. Mathematics 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam-Gordillo, O.; Baring, R.; Dittmann, S. Ecosystem functioning and functional approaches on marine macrobenthic fauna: A research synthesis towards a global consensus. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardicci, C.; Rossi, F.; Maltagliati, F. Detection of thermal pollution: Variability of benthic communities at two different spatial scales in an area influenced by a coastal power station. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buia, M.C.; Gambi, M.C.; Dappiano, M. Seagrass systems. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2004, 10, 133–183. [Google Scholar]
- Samoilys, M.A.; Carlos, G. Determining methods of underwater visual census for estimating the abundance of coral reef fishes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2000, 57, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, A.; Mangano, M.C.; Deidun, A.; Berlino, M.; Sarà, G. Effects of habitat fragmentation of a Mediterranean marine reef on the associated fish community: Insights from biological traits analysis. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C.; Sweatman, W.L.; Punnett, A.J. Non-linear models of species’ responses to environmental and spatial gradients. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance; University of Auckland: Auckland, New Zealand, 2005; Volume 26, pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER: Getting Started with v6; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet, G.; Pernet, C.R.; Wilcox, R.R. An introduction to the bootstrap: A versatile method to make inferences by using data-driven simulations. Meta Psychol. 2023, 7, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, R. Climate Change: Global Sea Level. Available online: https://www.climate.gov (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Ventura, P.; Gautier-Debernardi, J.; Di Franco, E.; Francour, P.; Di Franco, A.; Pey, A. Habitat-specific response of fish assemblages in a small fully protected urban MPA. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2024, 81, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalloniati, K.; Christou, E.D.; Kournopoulou, A.; Gittings, J.A.; Theodorou, I.; Zervoudaki, S.; Raitsos, D.E. Long-term warming and human-induced plankton shifts at a coastal Eastern Mediterranean site. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolloni, L.; Pagliarani, A.; Cocozza di Montanara, A.; Rendina, F.; Donnarumma, L.; Ciorciaro, D.; Russo, G.F. Benthic fish communities associated with Posidonia oceanica beds may reveal the fishing impact and effectiveness of marine protected areas: Two case studies in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Water 2023, 15, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.E.; Schenone, S.; Delille, J.; Díaz-Castañeda, V.; Alliouane, S.; Gattuso, J.P.; Gazeau, F. Effects of ocean acidification on Posidonia oceanica epiphytic community and shoot productivity. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1594–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, J.A.; Rowden, A.A.; Attrill, M.J.; Schembri, P.J.; Jones, M.B. Spatial variation in the composition of motile macroinvertebrate assemblages associated with two bed types of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 406, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cornwall, C.E.; Nelson, W.A.; Aguirre, J.D.; Blain, C.O.; Coyle, L.; D’Archino, R.; Thomsen, M.S. Predicting the impacts of climate change on New Zealand’s seaweed-based ecosystems. N. Z. J. Bot. 2023, 63, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipcich, P.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Pansini, A.; Pinna, F.; Procaccini, G.; Pusceddu, A.; Ceccherelli, G. Effects of current and future summer marine heat waves on Posidonia oceanica: Plant origin matters? Front. Clim. 2022, 4, 844831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Almela, E.; Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M. Consequences of Mediterranean warming events in seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) flowering records. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sley, A.; Taieb, A.H.; Jarboui, O.; Ghorbel, M.; Bouain, A. Feeding Behaviour of Greater Amberjack Seriola dumerili (Risso, 1810) from Central Mediterranean (Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2016, 96, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sley, A.; Taieb, A.H.; Jarboui, O.; Ghorbel, M.; Bouain, A. Food and Feeding Habits of Caranx crysos from the Gulf of Gabès (Tunisia). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beca-Carretero, P.; Winters, G.; Teichberg, M.; Procaccini, G.; Schneekloth, F.; Zambrano, R.H.; Reuter, H. Climate change and the presence of invasive species will threaten the persistence of the Mediterranean seagrass community. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Andrés, C.; Ramírez-Romero, E.; Guijarro, B.; Farre, M.; Macias, D.; Massutí, E. Warming promotes expansion of a key demersal fishing resource of the western Mediterranean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1494177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidun, A.; Azzopardi, F.; Marrone, A.; Massa-Gallucci, A.; Cutajar, K.; Hayden, B. Assessing the contribution of Posidonia oceanica to Mediterranean secondary production through stable isotope analysis. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, P. Differences among fish assemblages associated with nearshore Posidonia oceanica seagrass beds, rocky–algal reefs and unvegetated sand habitats in the Adriatic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 50, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlaque, M.; Giraud, G.; Boudouresque, C.F. Effects of a thermal power plant on the Mediterranean marine phytobenthos: The area of high frequency temperature changes. Bot. Mar. 1981, 24, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchard, O.; Veríssimo, H.; Queirós, A.M.; Herman, P.M.J. The use of multiple biological traits in marine community ecology and its potential in ecological indicator development. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirintanis, K.; Azzurro, E.; Crocetta, F.; Dimiza, M.; Froglia, C.; Gerovasileiou, V.; Katsanevakis, S. Bioinvasion impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health in the Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2022, 17, 308–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, M.; Kröncke, I.; Meyer, J.; Mathis, M.; Pohlmann, T.; Reiss, H. Benthic ecosystem functioning under climate change: Modelling the bioturbation potential for benthic key species in the southern North Sea. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragkousis, M.; Zenetos, A.; Souissi, J.B.; Hoffman, R.; Ghanem, R.; Taşkın, E.; Karachle, P.K. Unpublished Mediterranean and Black Sea records of marine alien, cryptogenic, and neonative species. BioInvasions Rec. 2023, 12, 339–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino, F.; González, J.A.; Haroun, R.; Tuya, F. Abundance and Biomass of the Parrotfish Sparisoma cretense in Seagrass Meadows: Temporal and Spatial Differences between Seagrass Interiors and Seagrass Adjacent to Reefs. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buñuel, X.; Alcoverro, T.; Romero, J.; Arthur, R.; Ruiz, J.M.; Pérez, M.; Pages, J.F. Warming intensifies the interaction between the temperate seagrass Posidonia oceanica and its dominant fish herbivore Sarpa salpa. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 165, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Garcon, J.; Bennett, S.; Marbà, N.; Vergés, A.; Arthur, R.; Alcoverro, T. Tropicalization shifts herbivore pressure from seagrass to rocky reef communities. Proc. R. Soc. B 2023, 290, 20221744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, M.; El-Haweet, A.E.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Tirasin, E.M.; Fortibuoni, T.; Ronchi, F.; Vasconcellos, M. Risks and adaptation options for the Mediterranean fisheries in the face of multiple climate change drivers and impacts. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Quattrocchi, F.; Azzurro, E.; Palmeri, A.; Chemello, R.; Di Franco, A.; García-Charton, J.A. Warming-related shifts in the distribution of two competing coastal wrasses. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| BTs | Categories | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diet | macrofauna | macrofauna/fish | fish/cephalopods | plankton | seagrass/algae | sediment macrofauna |
| Position | open water | reef-associated | demersal | |||
| Habitat | pelagic | rock/cave | seagrass | sand/rock | all | |
| Climate zone | subtropical | temperate | ||||
| trophic Level | 2–4.53 |
| Diversity Metrics PERMANOVA Distance × Season × Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | df | MS | P (perm) |
| Distance | 3 | 8.1732 | 0.001 *** |
| Season | 1 | 14.085 | 0.001 *** |
| Year | 1 | 2.7891 | 0.185 |
| Distance × Season | 3 | 1.4887 | 0.541 |
| Distance × Year | 3 | 3.4462 | 0.05 * |
| Season × Year | 1 | 4.4167 | 0.062 |
| Distance × Season × Year | 3 | 8.693 | 0.001 *** |
| Fish Assemblage PERMANOVA Distance × Season × Year | ||||||||
| Source | df | MS | P (perm) | |||||
| Distance | 3 | 3312.3 | 0.0001 *** | |||||
| Season | 1 | 3997.5 | 0.0001 *** | |||||
| Year | 1 | 2826.6 | 0.0001 *** | |||||
| Distance × Season | 3 | 1466 | 0.0017 ** | |||||
| Distance × Year | 3 | 1470.2 | 0.0011 ** | |||||
| Season × Year | 1 | 1250.4 | 0.0754 | |||||
| Distance × Season × Year | 3 | 1333.1 | 0.0042 * | |||||
| Pairwise t-tests for pairs of levels of factor Distance | ||||||||
| Within level ‘S’ of factor ‘Season’ | Within level ‘A’ of factor ‘Season’ | |||||||
| Groups | t | P(perm) | Groups | t | P(perm) | |||
| 1, 2 | 2.1448 | 0.002 * | 1, 2 | 1.5019 | 0.021 * | |||
| 1, 3 | 2.5799 | 0.001 *** | 1, 3 | 1.8861 | 0.011 * | |||
| 1, 4 | 2.573 | 0.005 * | 1, 4 | 1.7998 | 0.004 * | |||
| 2, 3 | 1.0671 | 0.344 | 2, 3 | 1.5535 | 0.031 * | |||
| 2, 4 | 1.4874 | 0.062 | 2, 4 | 1.3564 | 0.099 | |||
| 3, 4 | 0.8655 | 0.631 | 3, 4 | 1.8211 | 0.012 * | |||
| FGs PERMANOVA Distance × Season × Year | ||||||||
| Source | df | MS | P (perm) | |||||
| Distance | 3 | 1224.6 | 0.0003 ** | |||||
| Season | 1 | 2669.5 | 0.0001 *** | |||||
| Year | 1 | 1607.9 | 0.0011 ** | |||||
| Distance × Season | 3 | 455.73 | 0.2177 | |||||
| Distance × Year | 3 | 812.43 | 0.0065 ** | |||||
| Season × Year | 1 | 1198.3 | 0.0091 ** | |||||
| Distance × Season × Year | 3 | 711.17 | 0.0154 * | |||||
| Pairwise t-tests for pairs of levels of factor Season | ||||||||
| Within level ‘1’ of factor ‘Distance’ | Within level ‘2’ of factor ‘Distance’ | |||||||
| Groups | t | P (perm) | Groups | t | P (perm) | |||
| S, A | 1.3225 | 0.1419 | S, A | 1.8668 | 0.035 * | |||
| Within level ‘3’ of factor ‘Distance’ | Within level ‘4’ of factor ‘Distance’ | |||||||
| Groups | t | P(perm) | Groups | t | P(perm) | |||
| S, A | 1.5871 | 0.0554 | S, A | 2.2406 | 0.003 ** | |||
| FGs DISTLM Marginal Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Pseudo-F | p | R2 |
| # Ligula (Adult leaves) | 1.7235 | 0.142 | 0.036115 |
| W Rhizome | 3.1256 | 0.006 * | 0.063625 |
| W Epiphytes | 3.8116 | 0.001 ** | 0.076521 |
| Surface Temp | 3.8092 | 0.003 * | 0.076476 |
| Salinity Surf | 4.2628 | 0.002 * | 0.084809 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marrone, A.; Rinaldi, A.; Montalto, V.; Gauci, A.; Ape, F.; Ringeard, H.; Spoto, M.; Martinez, M.; La Marca, E.C.; Mirto, S.; et al. Surviving in a Warmer Marine World: A Study on the Impact of Thermal Effluent on Posidonia oceanica Meadows and Associated Fish Assemblages in the Maltese Islands. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030475
Marrone A, Rinaldi A, Montalto V, Gauci A, Ape F, Ringeard H, Spoto M, Martinez M, La Marca EC, Mirto S, et al. Surviving in a Warmer Marine World: A Study on the Impact of Thermal Effluent on Posidonia oceanica Meadows and Associated Fish Assemblages in the Maltese Islands. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(3):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030475
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarrone, Alessio, Alessandro Rinaldi, Valeria Montalto, Adam Gauci, Francesca Ape, Henri Ringeard, Marco Spoto, Marco Martinez, Emanuela Claudia La Marca, Simone Mirto, and et al. 2025. "Surviving in a Warmer Marine World: A Study on the Impact of Thermal Effluent on Posidonia oceanica Meadows and Associated Fish Assemblages in the Maltese Islands" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 3: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030475
APA StyleMarrone, A., Rinaldi, A., Montalto, V., Gauci, A., Ape, F., Ringeard, H., Spoto, M., Martinez, M., La Marca, E. C., Mirto, S., & Deidun, A. (2025). Surviving in a Warmer Marine World: A Study on the Impact of Thermal Effluent on Posidonia oceanica Meadows and Associated Fish Assemblages in the Maltese Islands. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(3), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030475







