Prediction Analysis on the Sediment Erosion and Energy Dissipation Inside a Three-Stage Centrifugal Pump
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical Model
2.1. Mathematical Method Settings
2.1.1. Governing Equation
2.1.2. Particle Track Model and Erosion Model
2.2. Numerical Simulation Setup
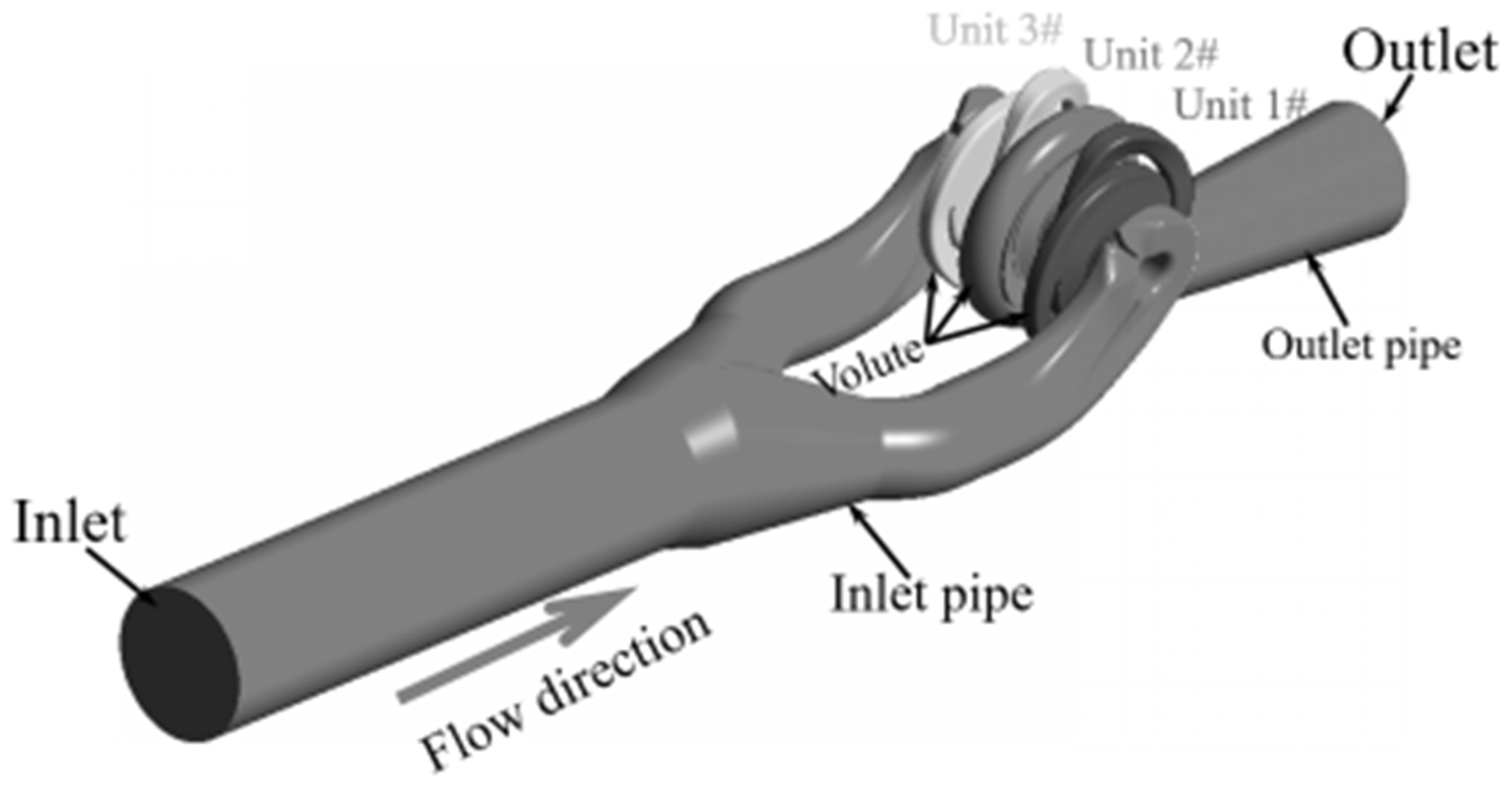
2.2.1. Geometric Model
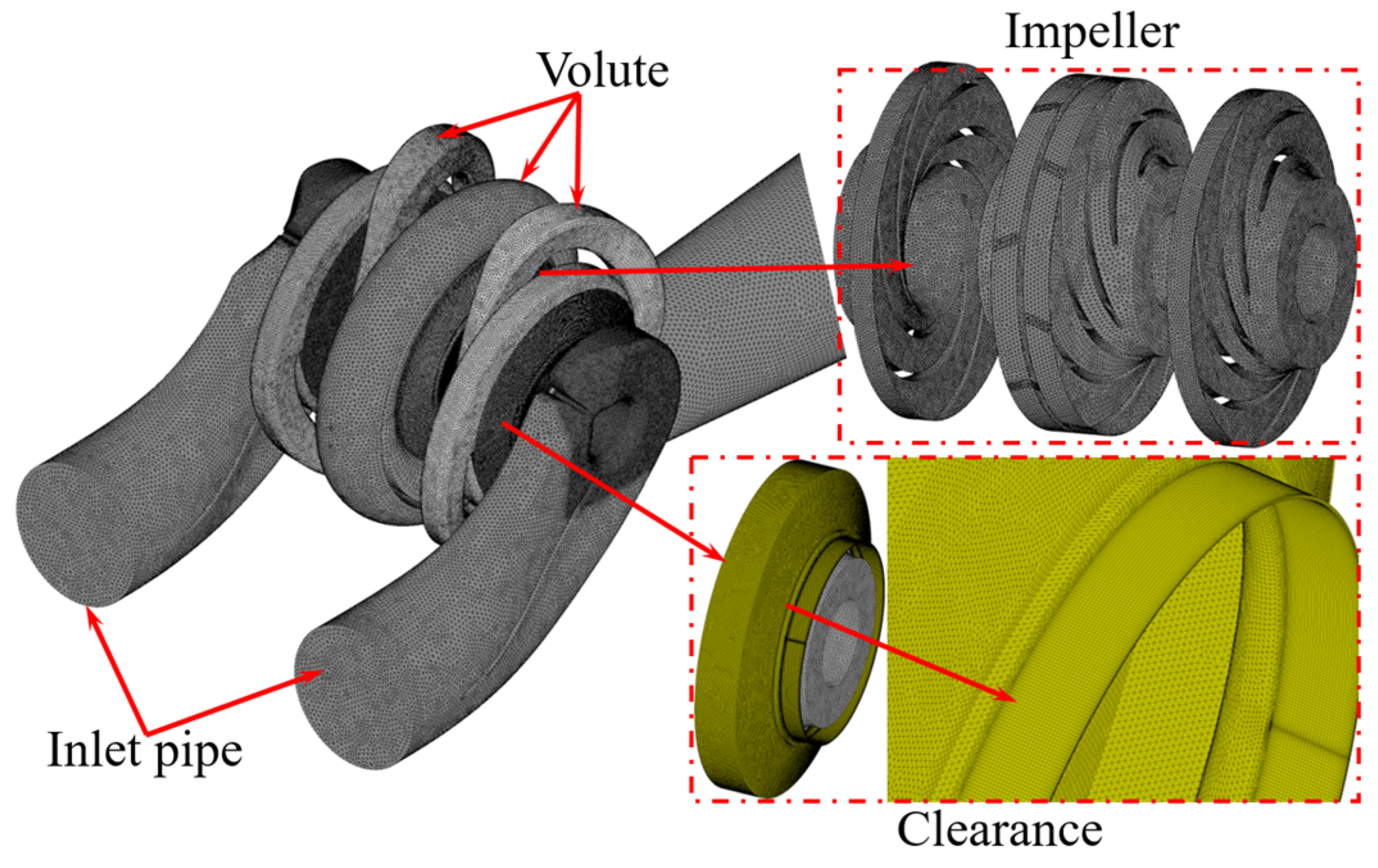
2.2.2. Boundary and Parameter
2.2.3. Research Proposal
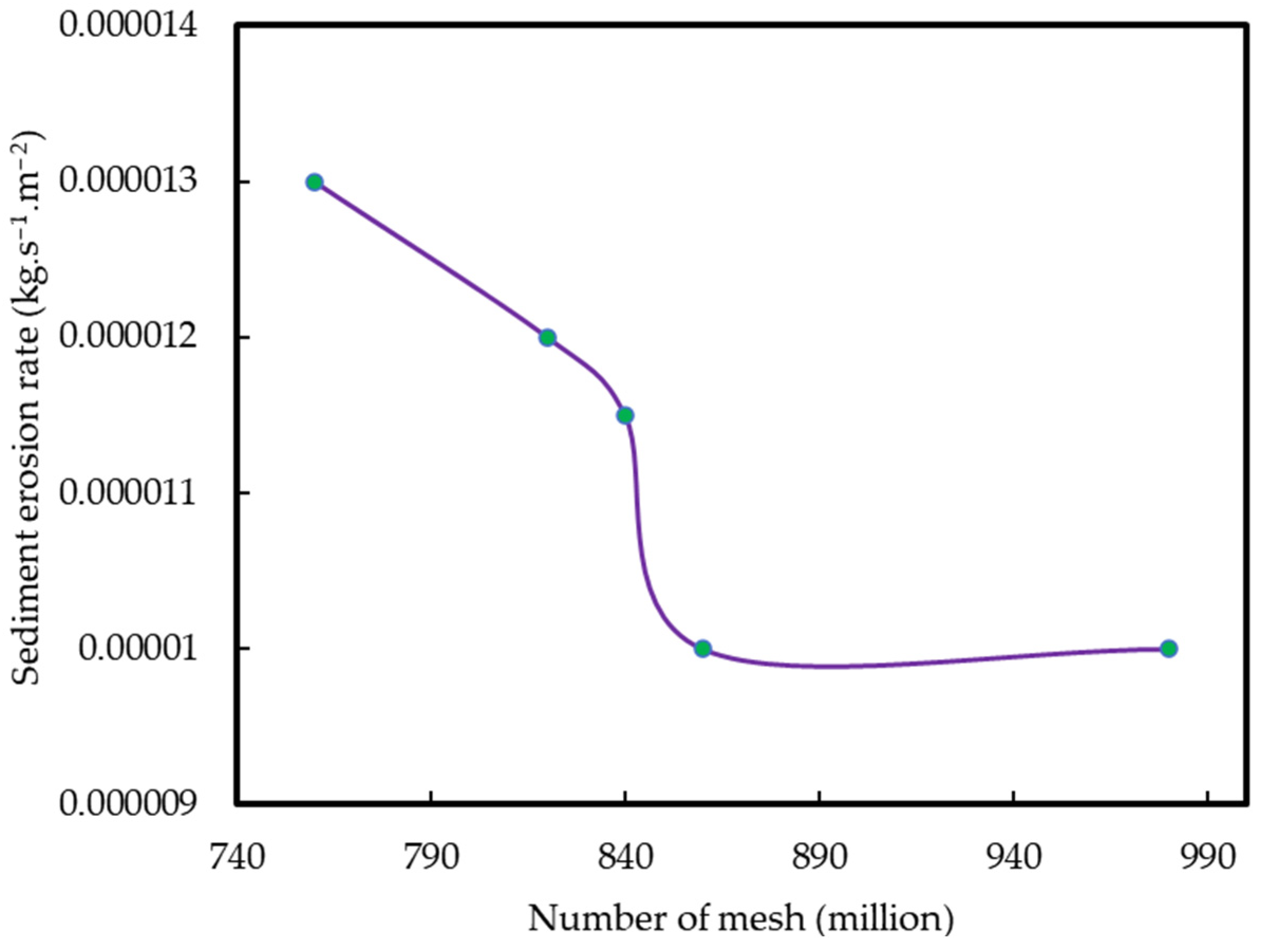
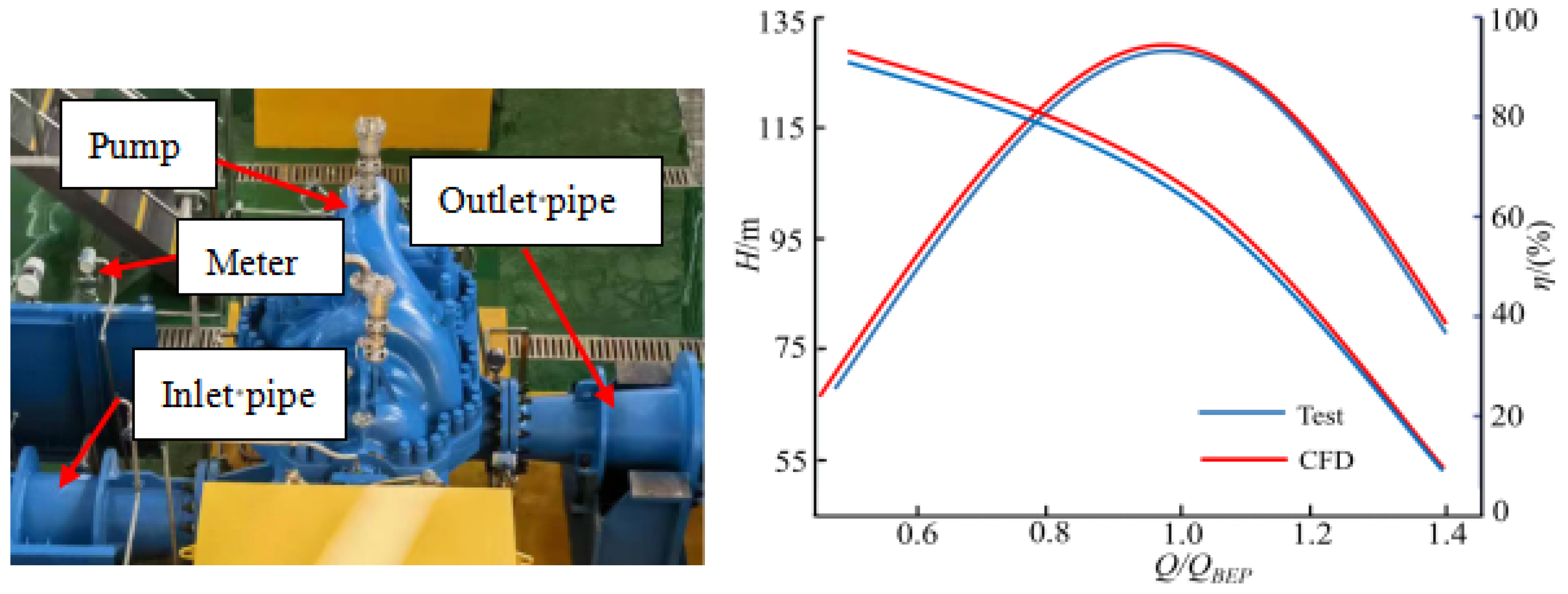
2.3. Reliability Verification
2.4. Entropy Production Theory
3. Results and Discussions
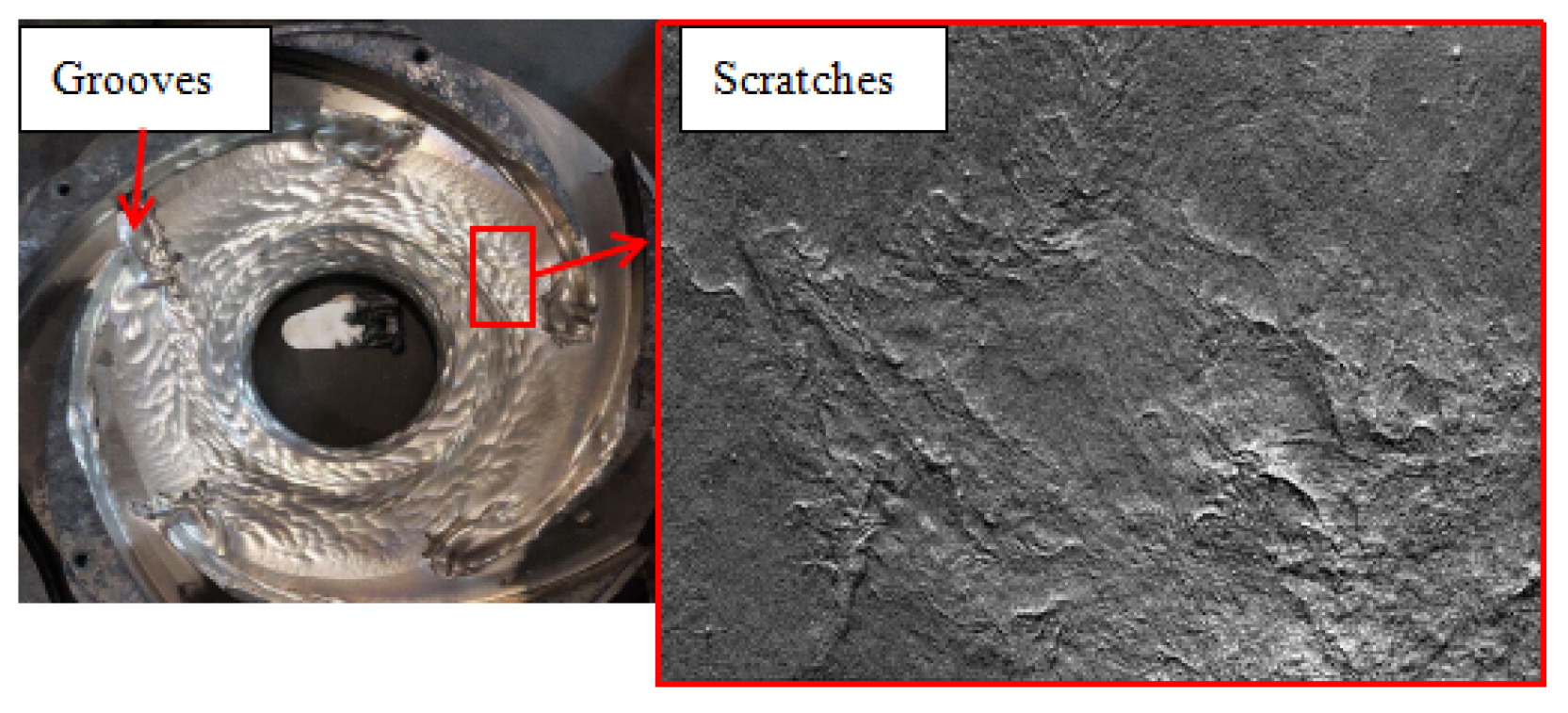
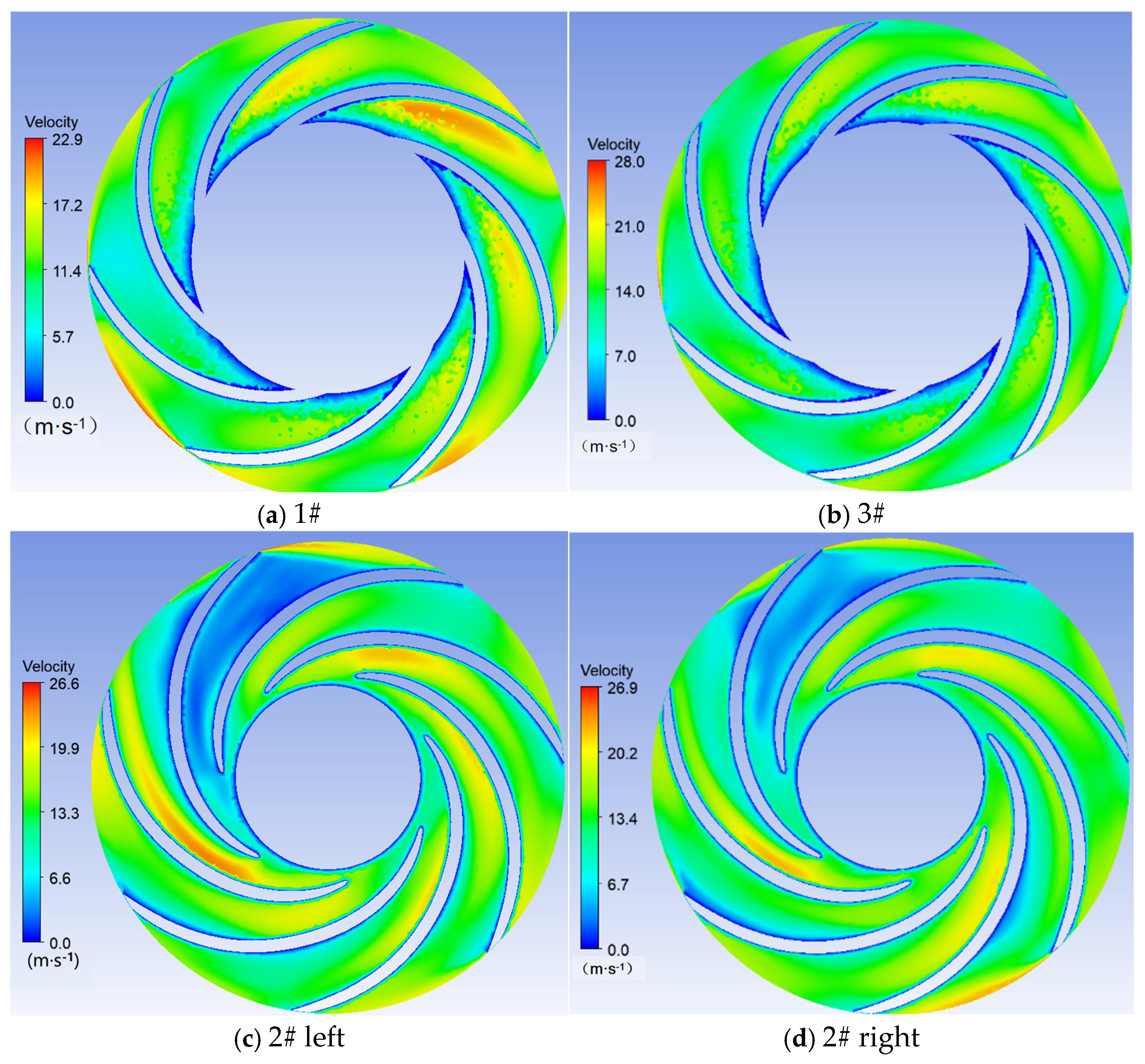
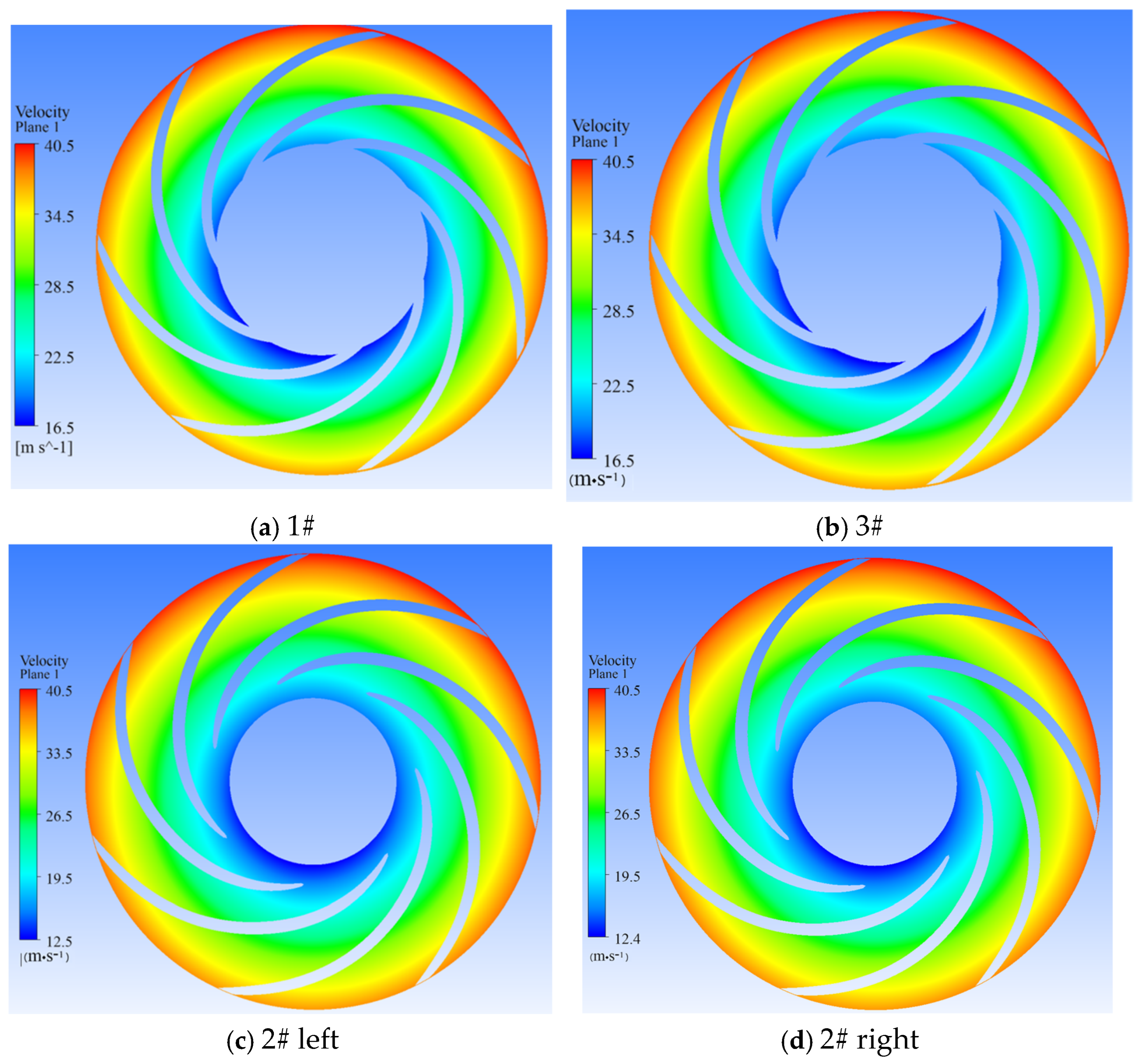
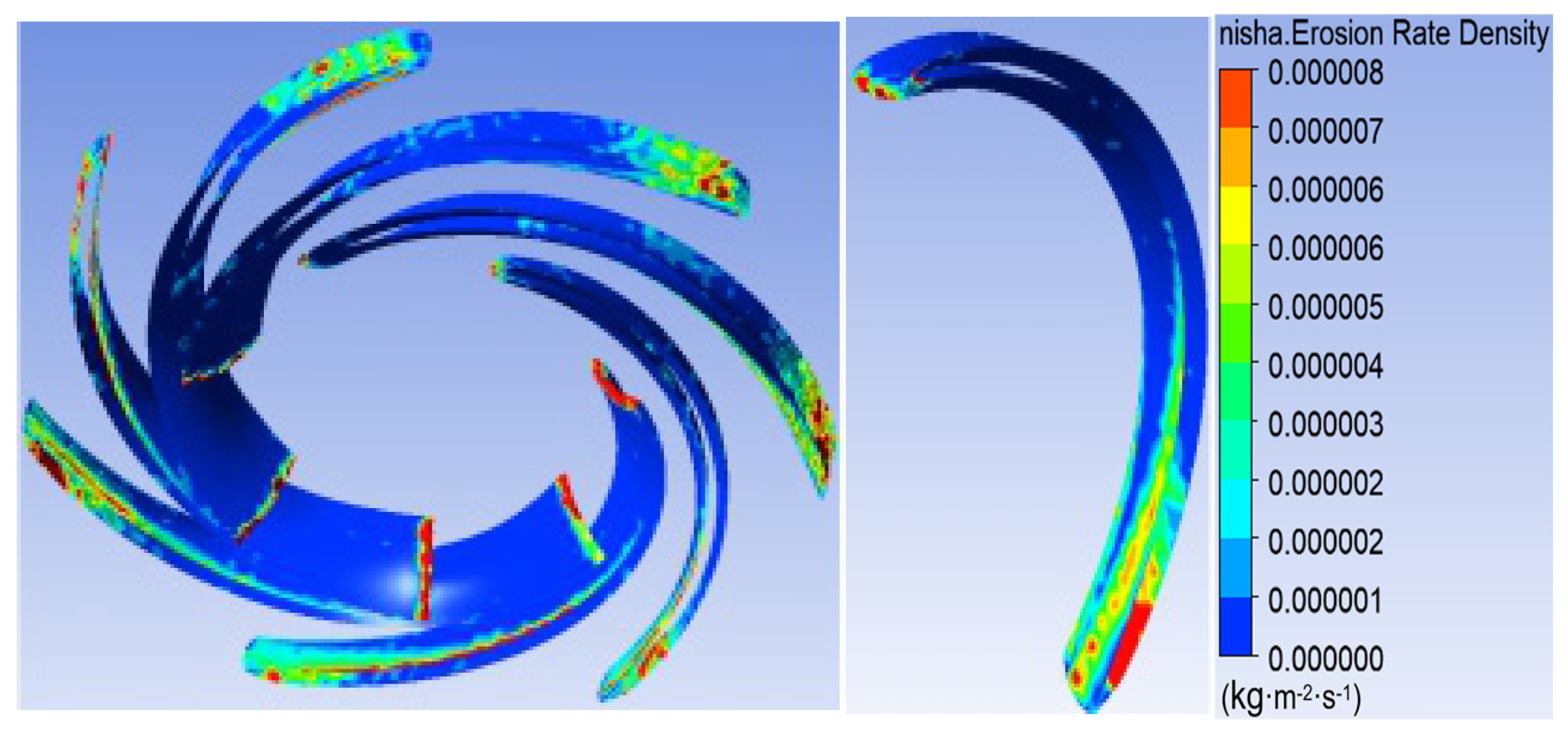
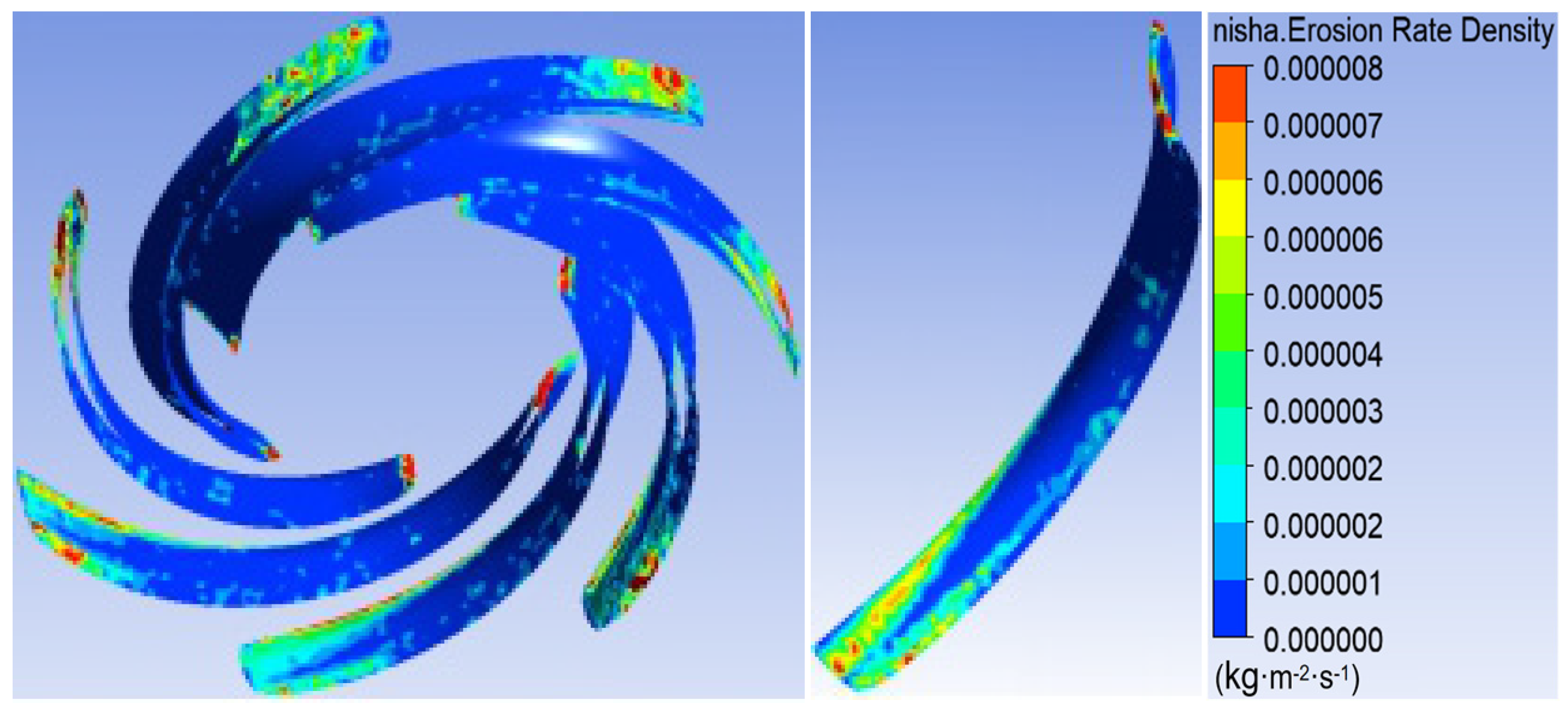
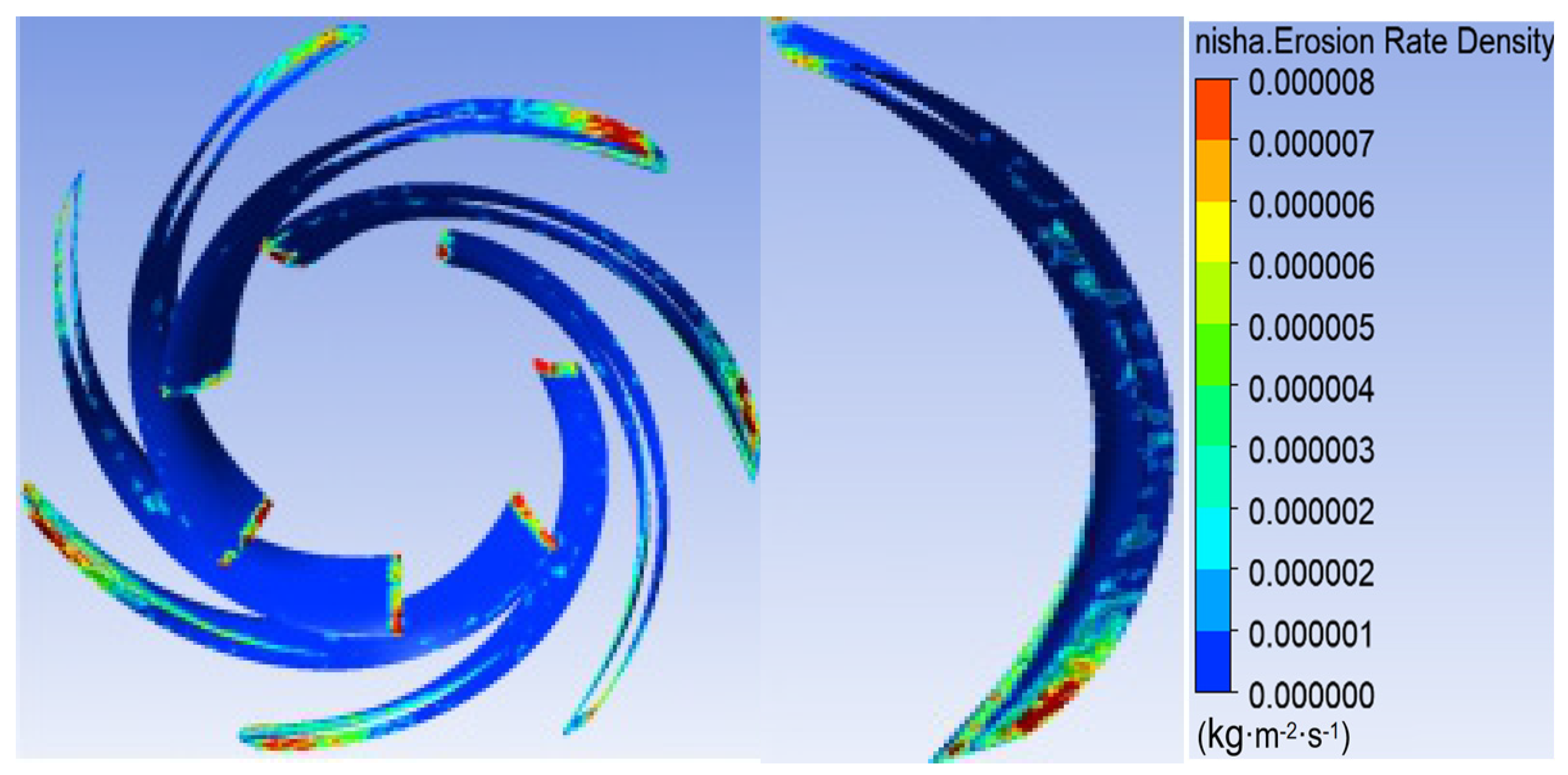
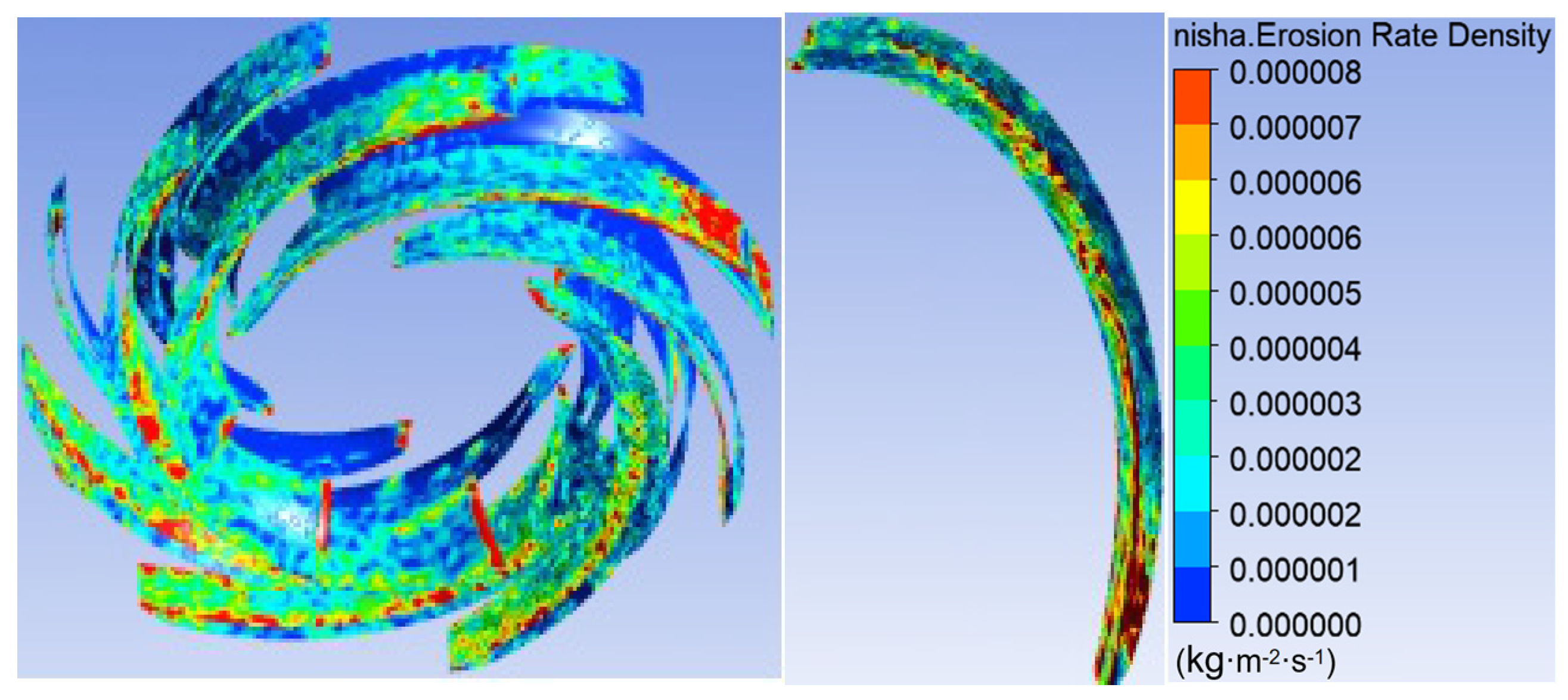
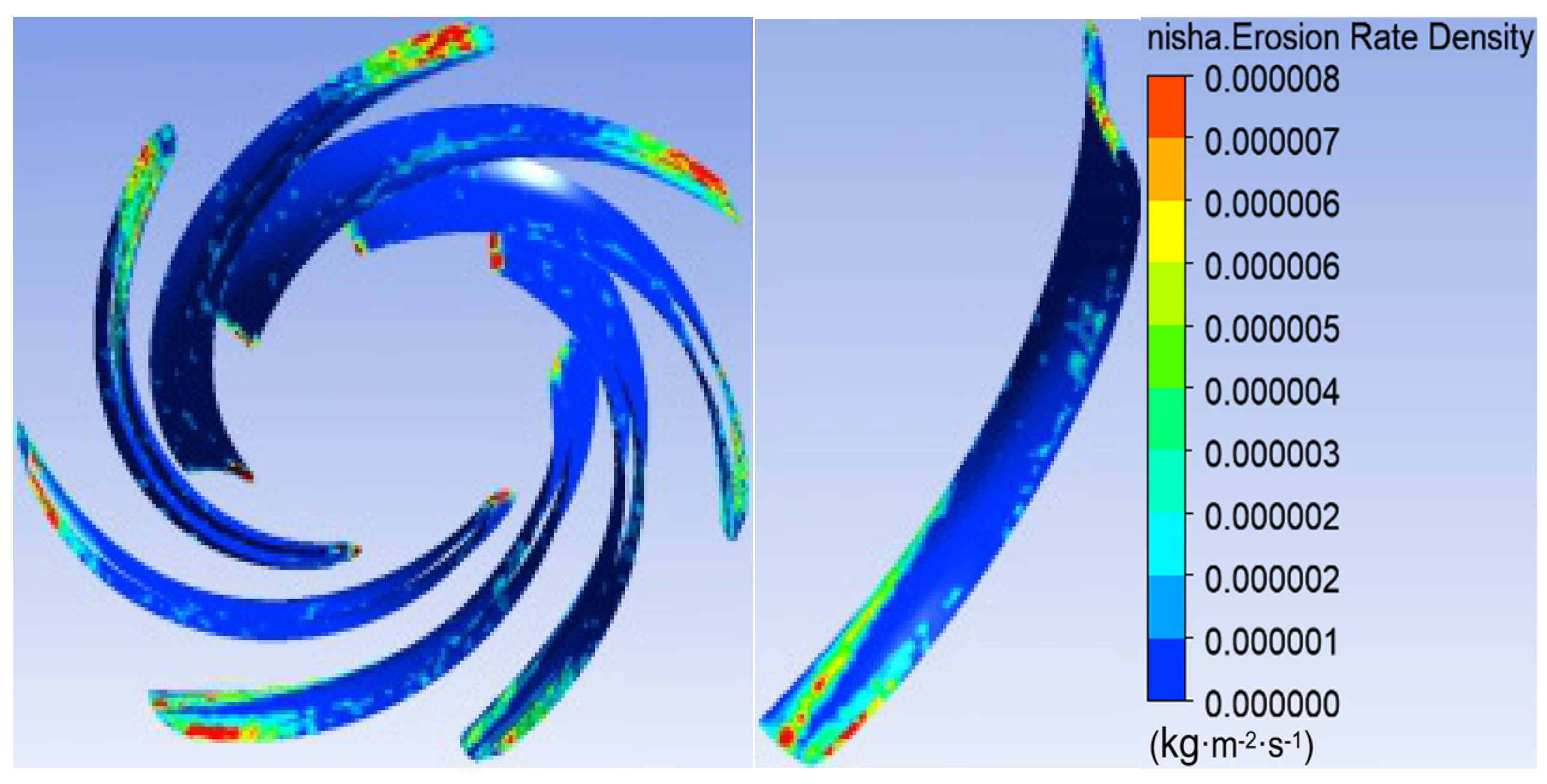
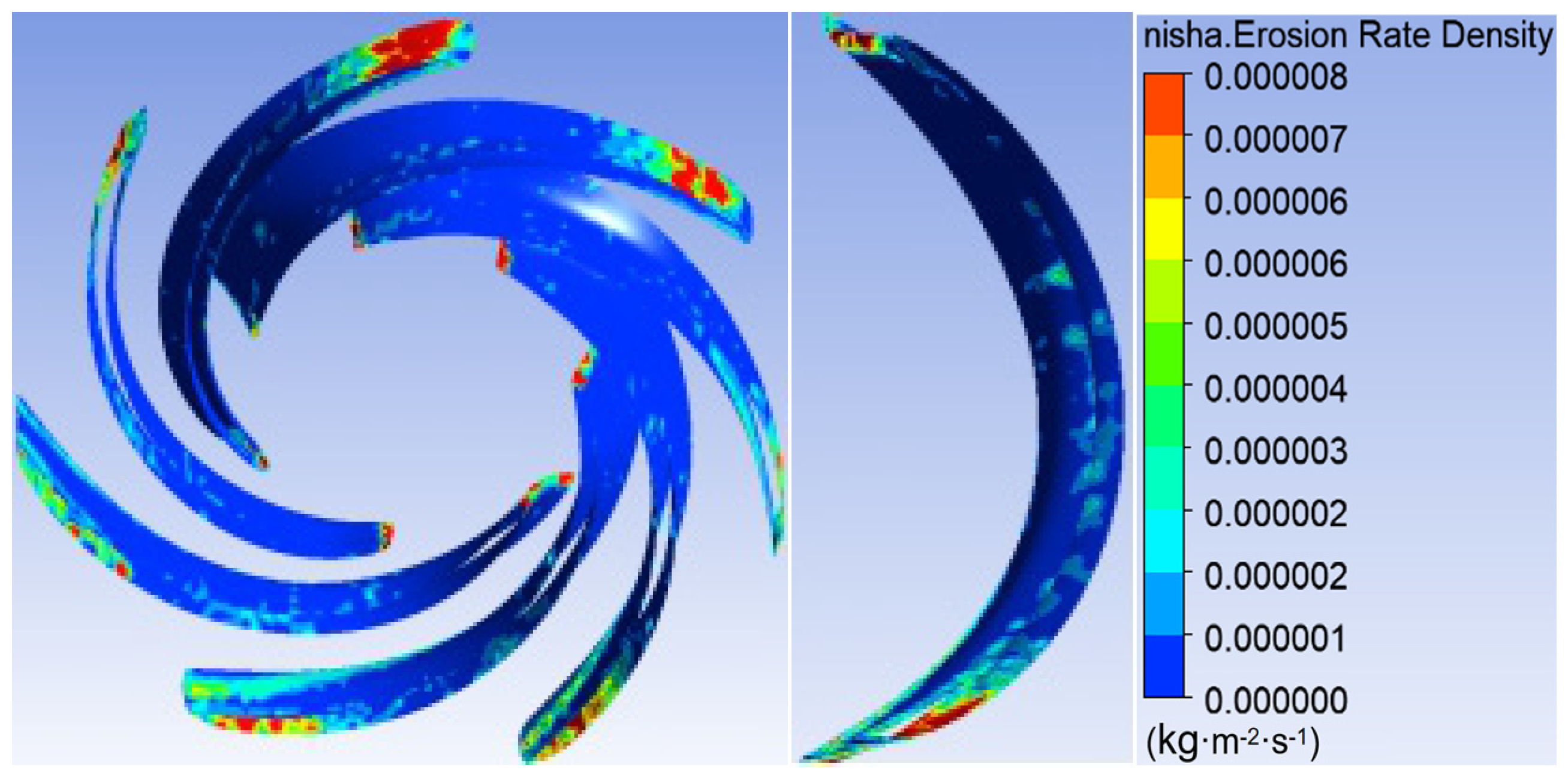
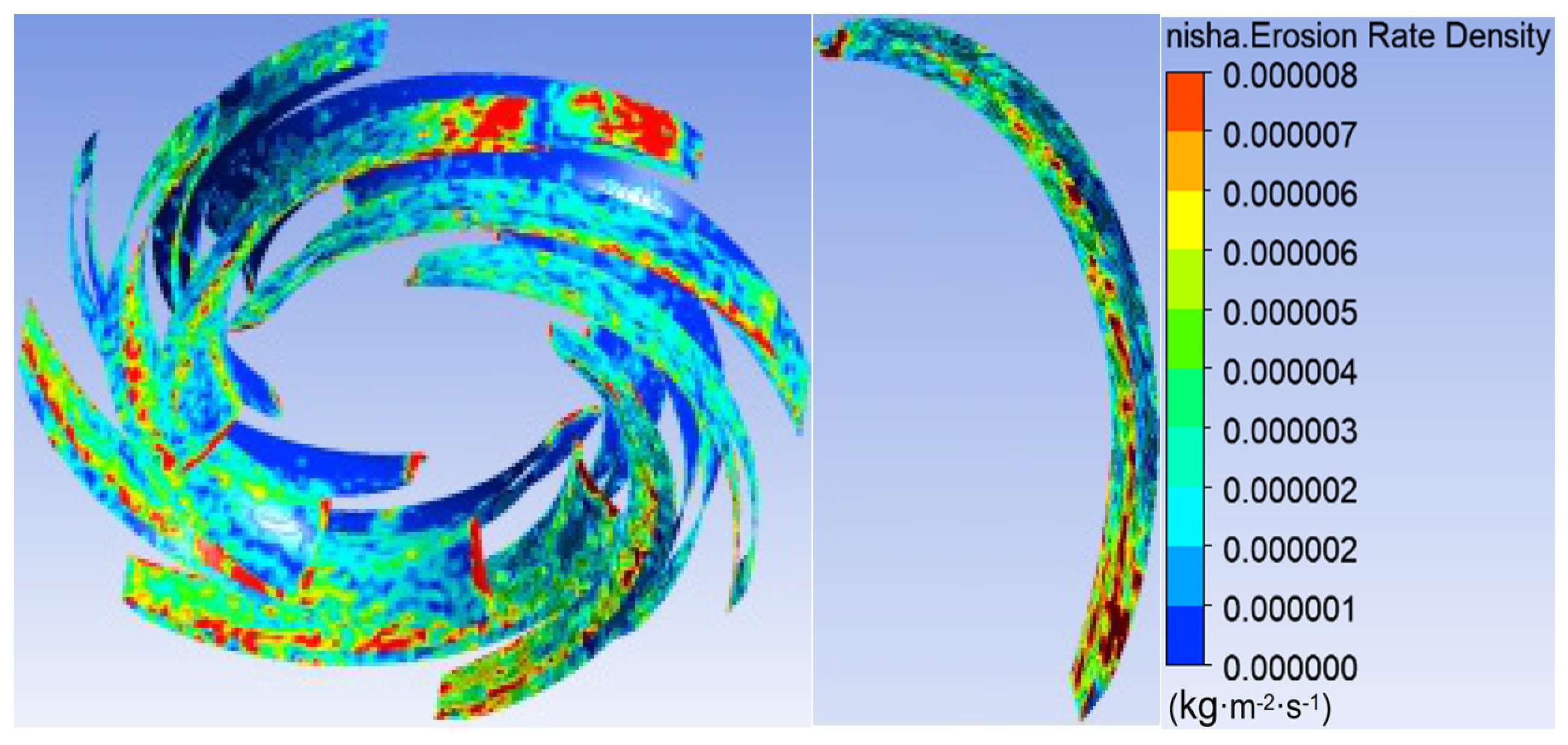
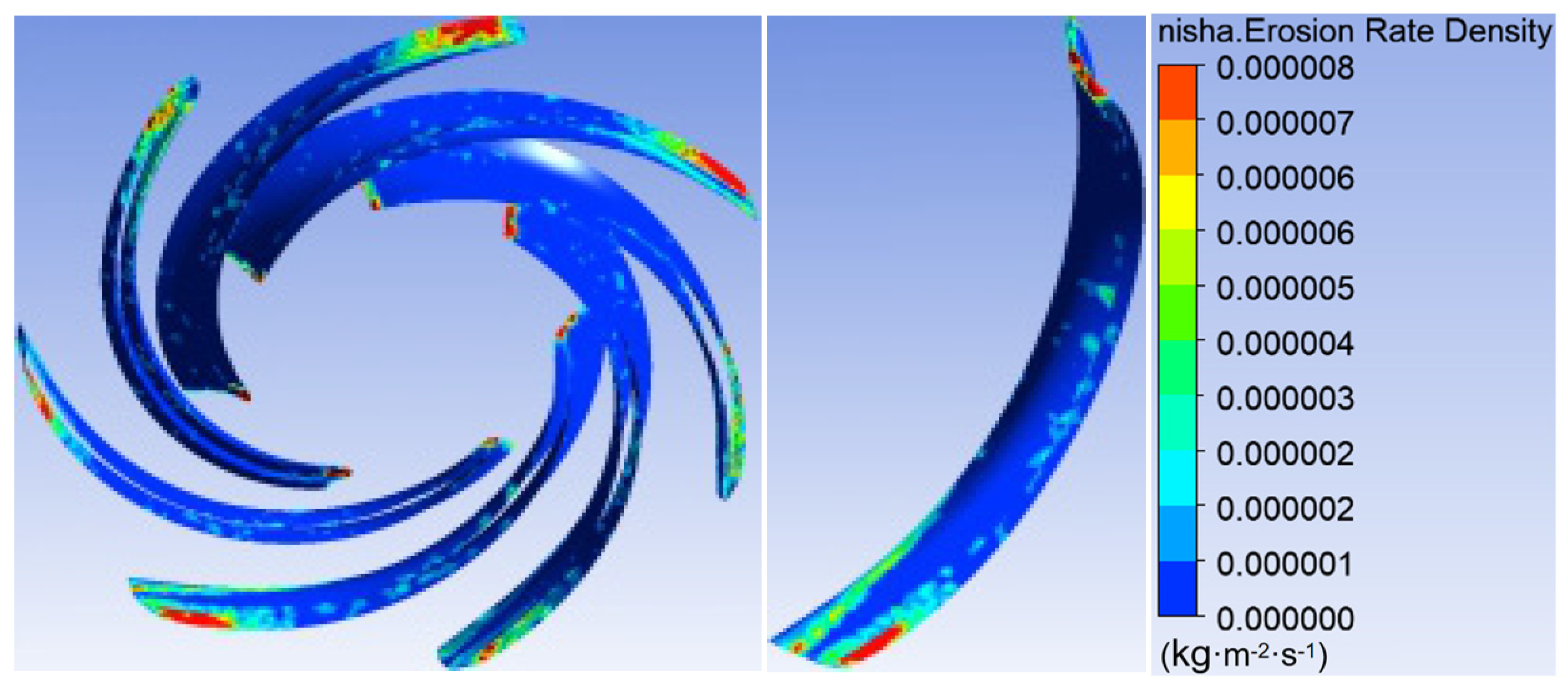
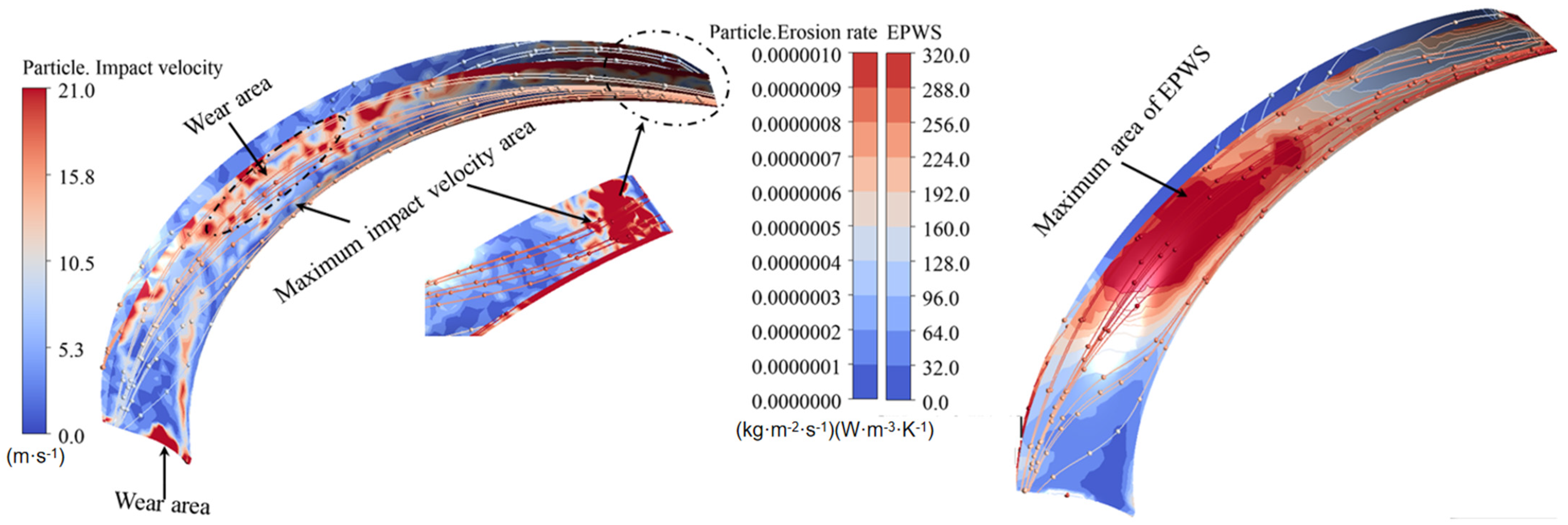
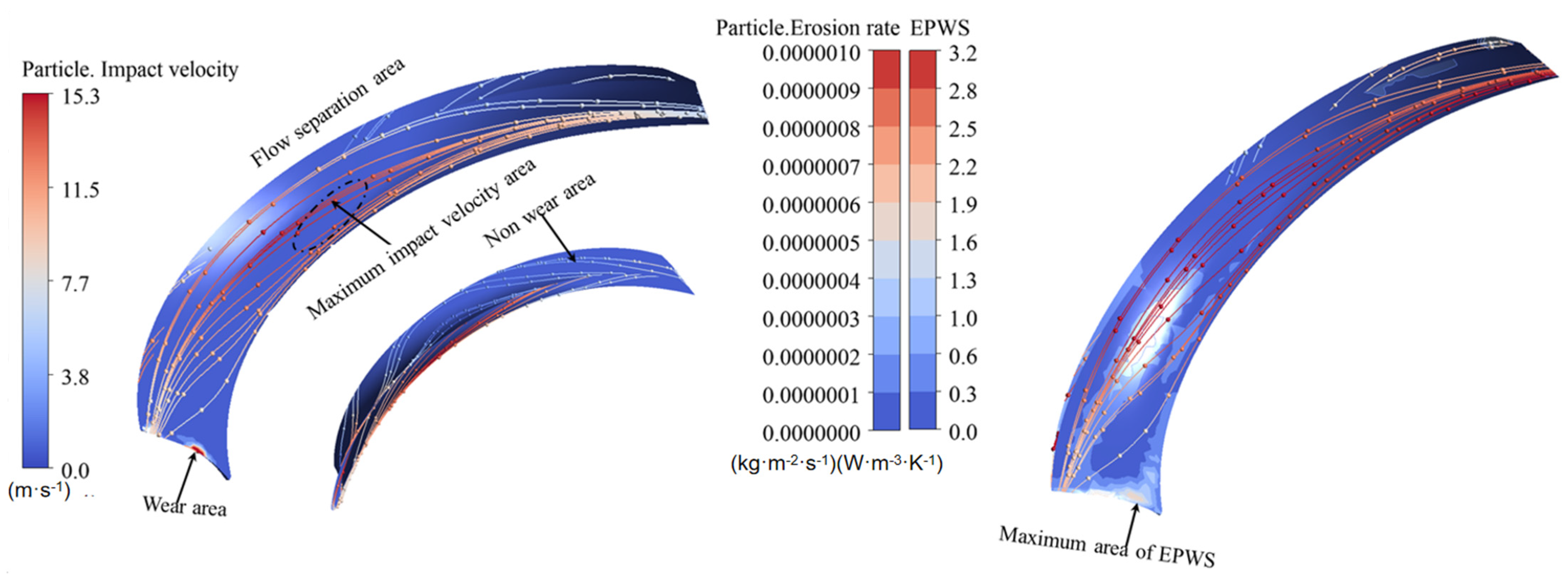
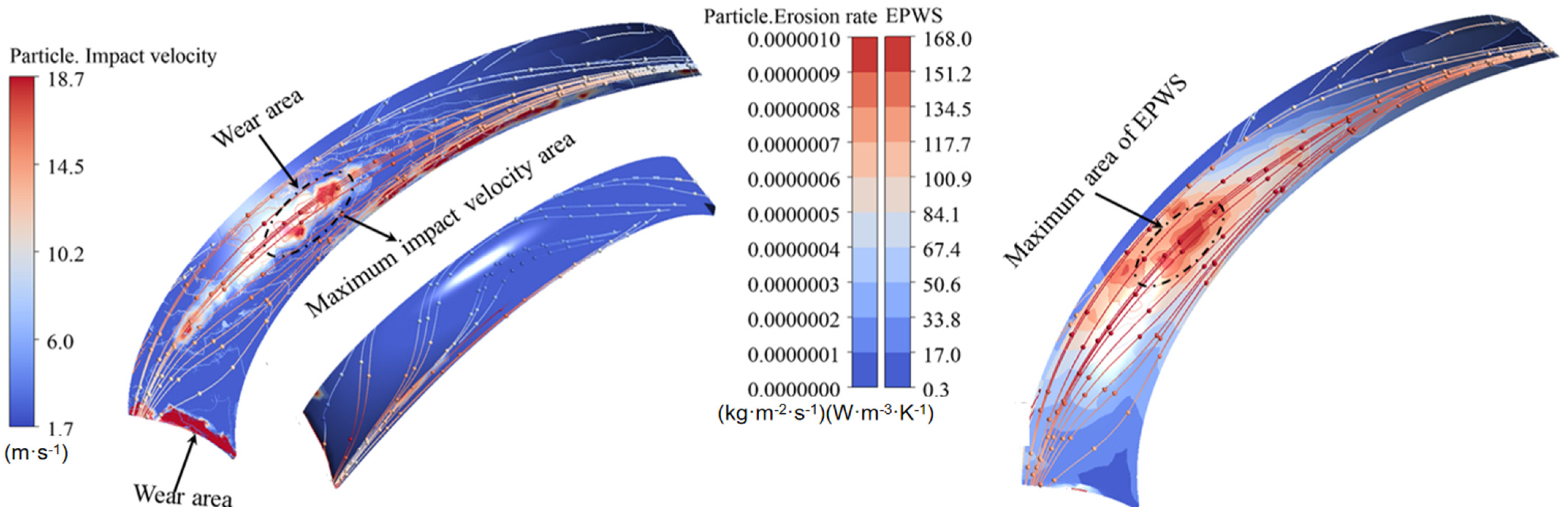
3.1. Sediment Erosion of Water Pump
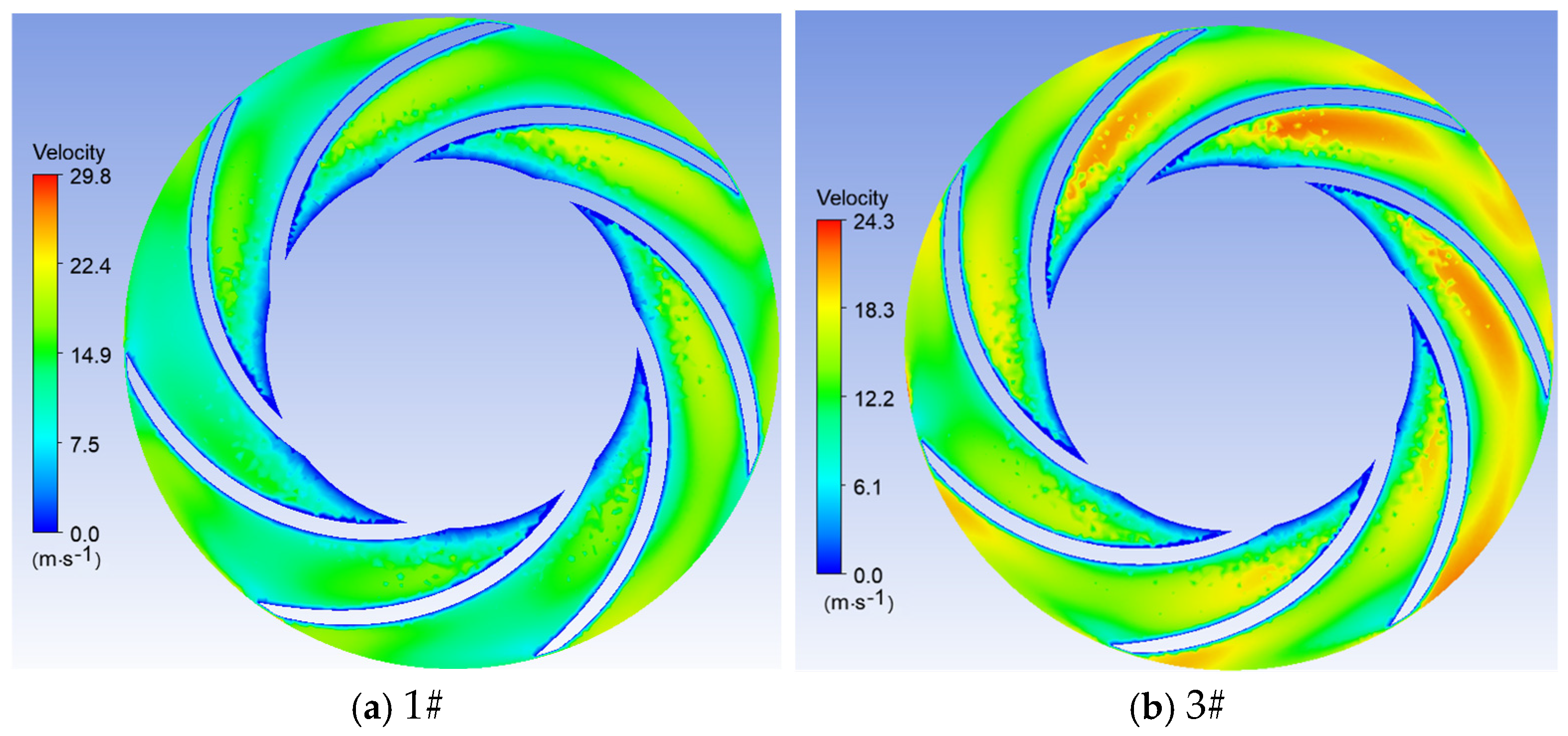
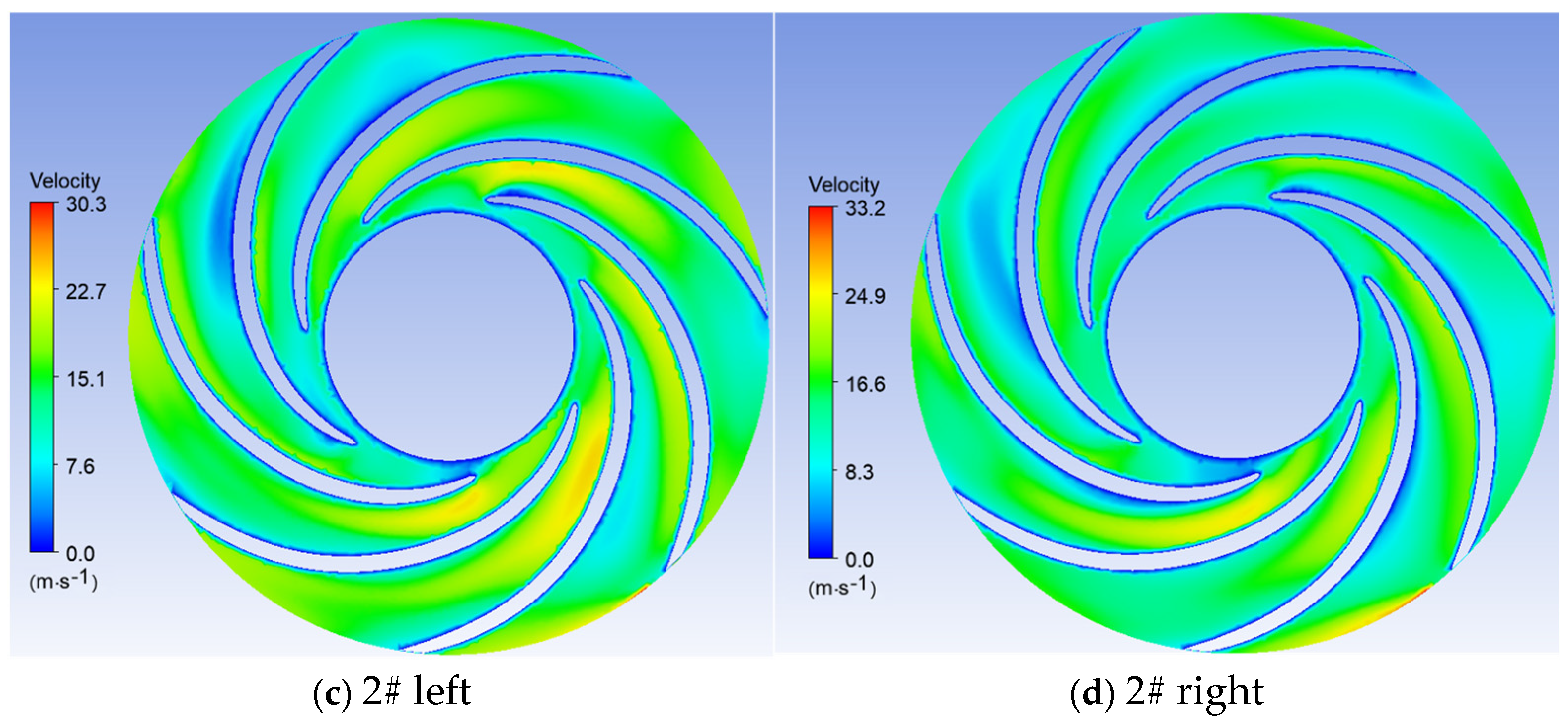
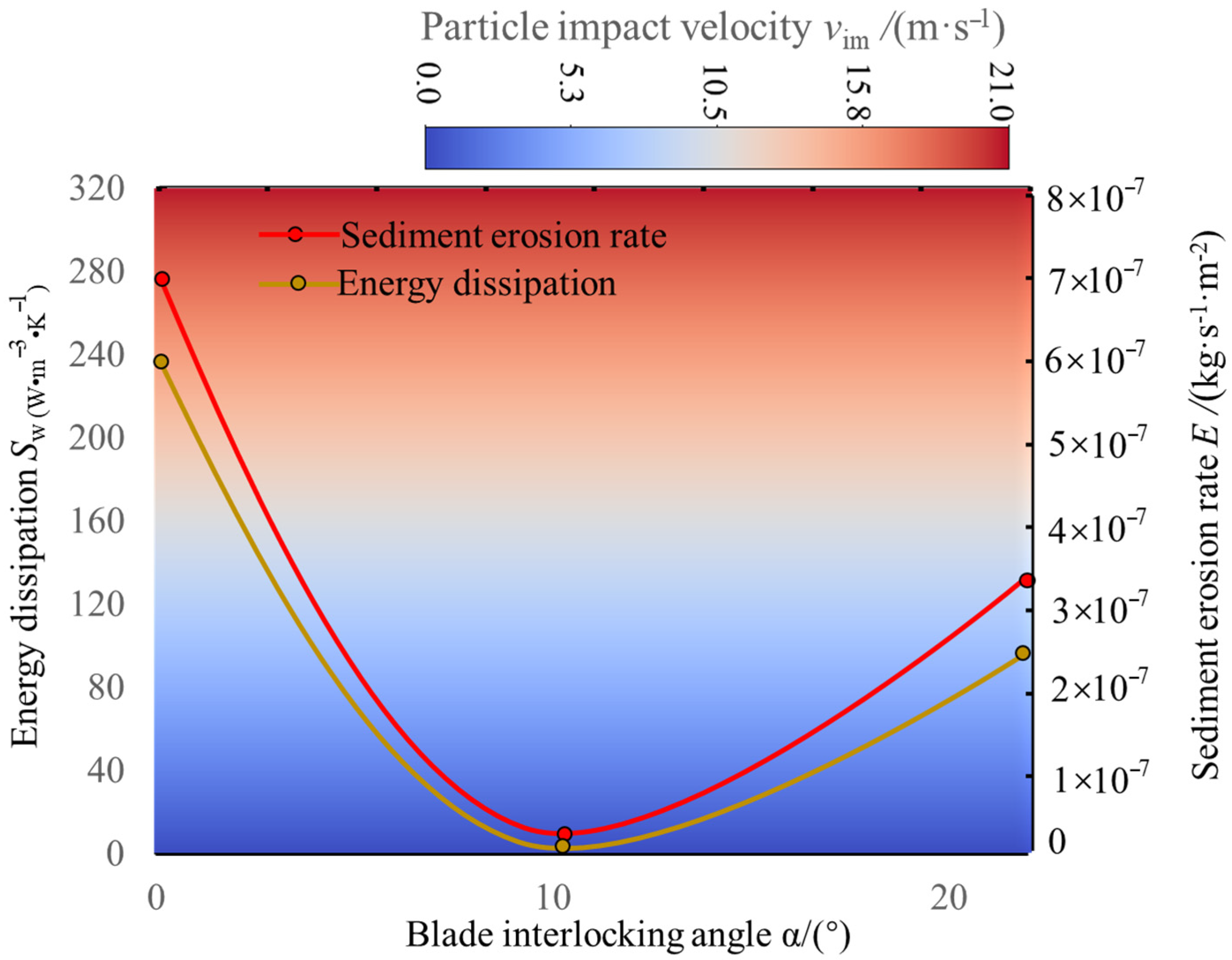
3.2. Impact of Blade Interlocking Angle on Unit Performance
3.3. Effect of Blade Symmetry Angle on Sediment Erosion
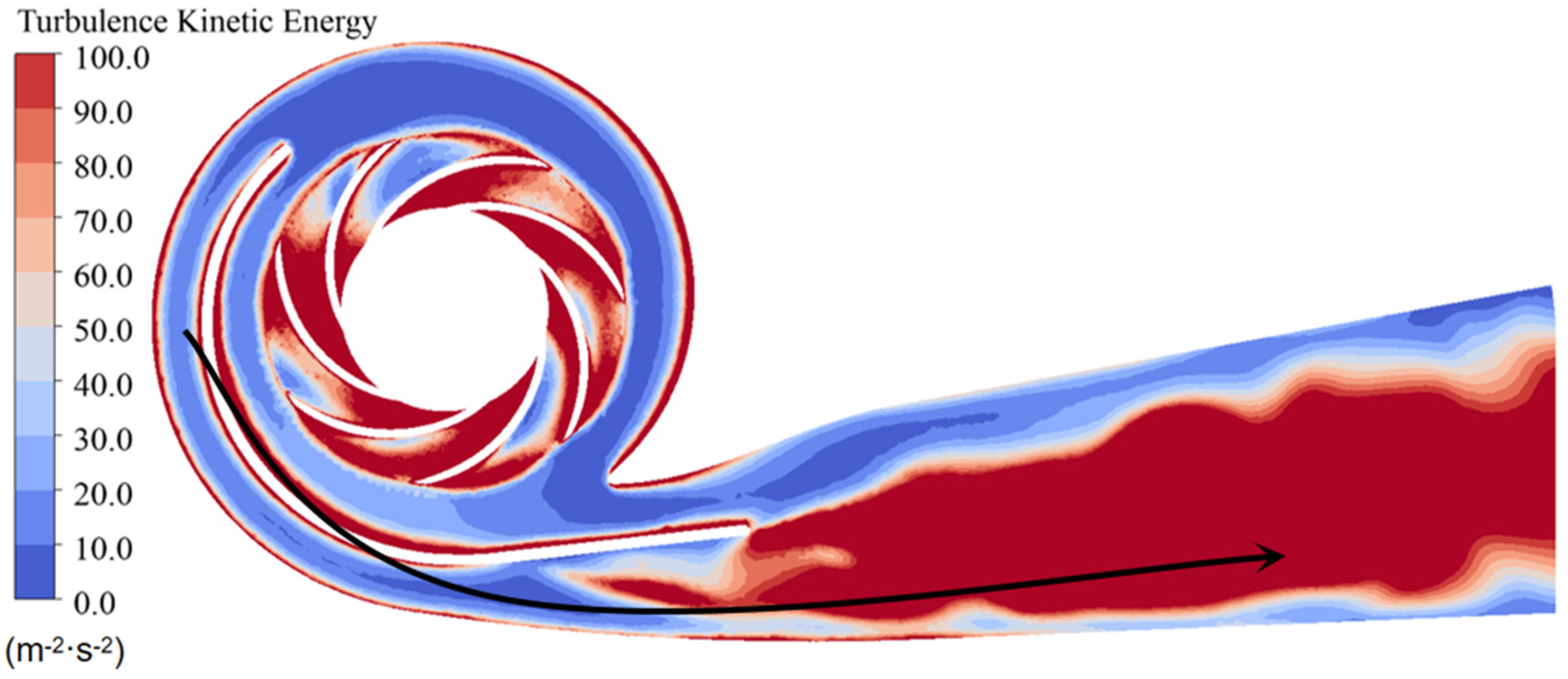
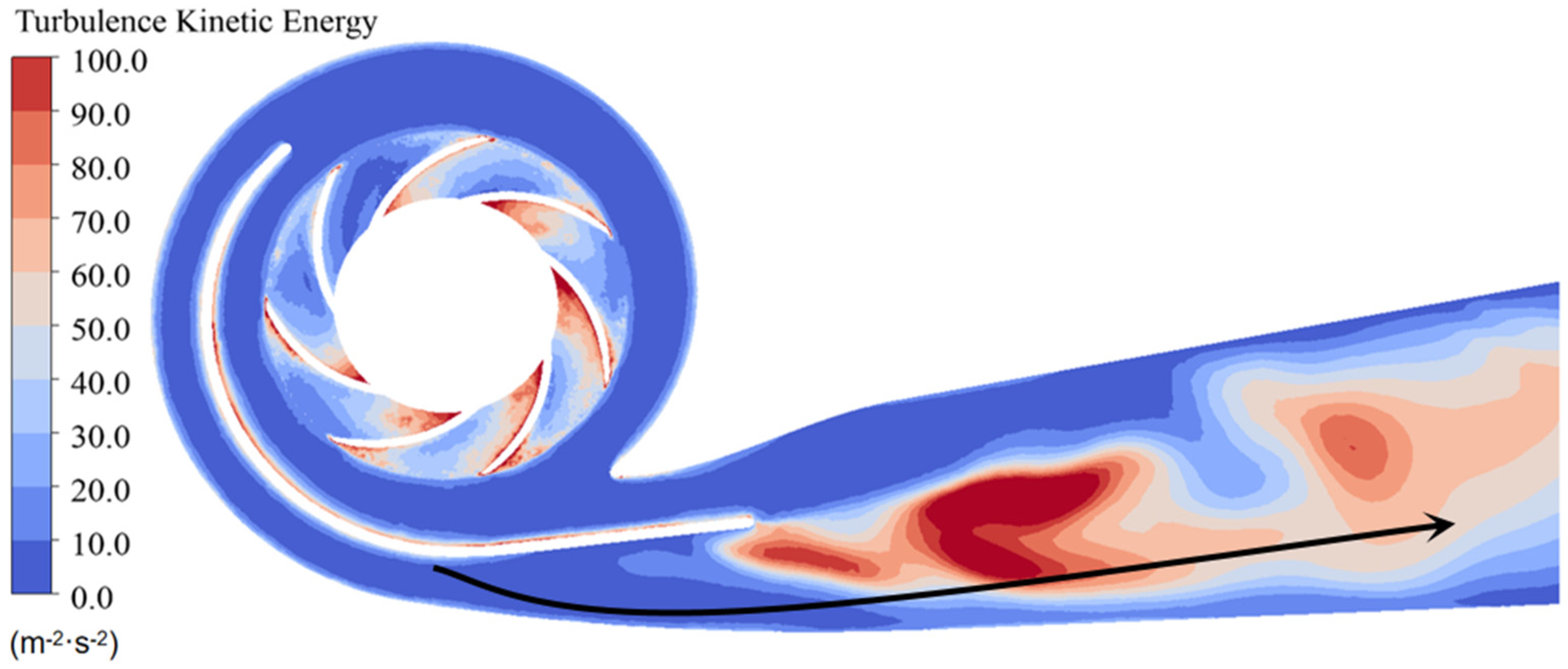
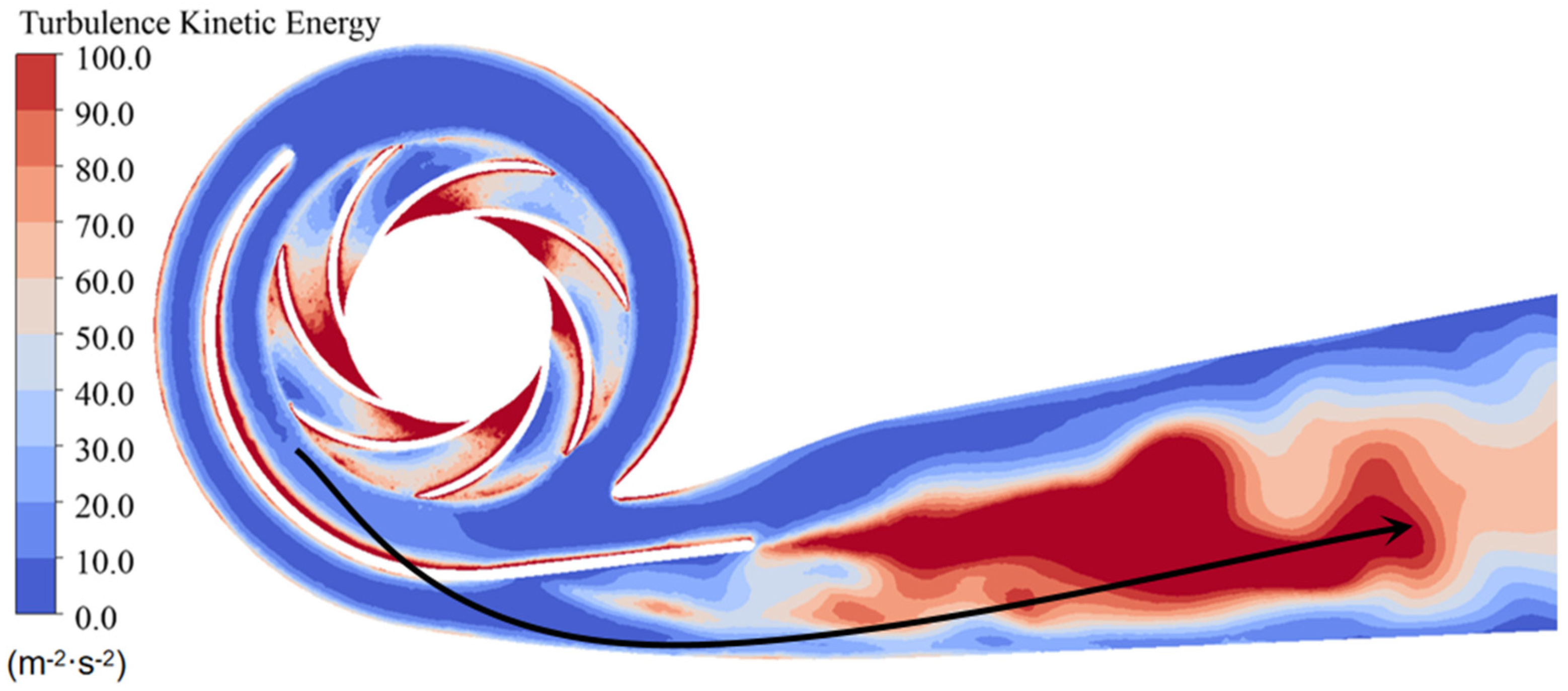
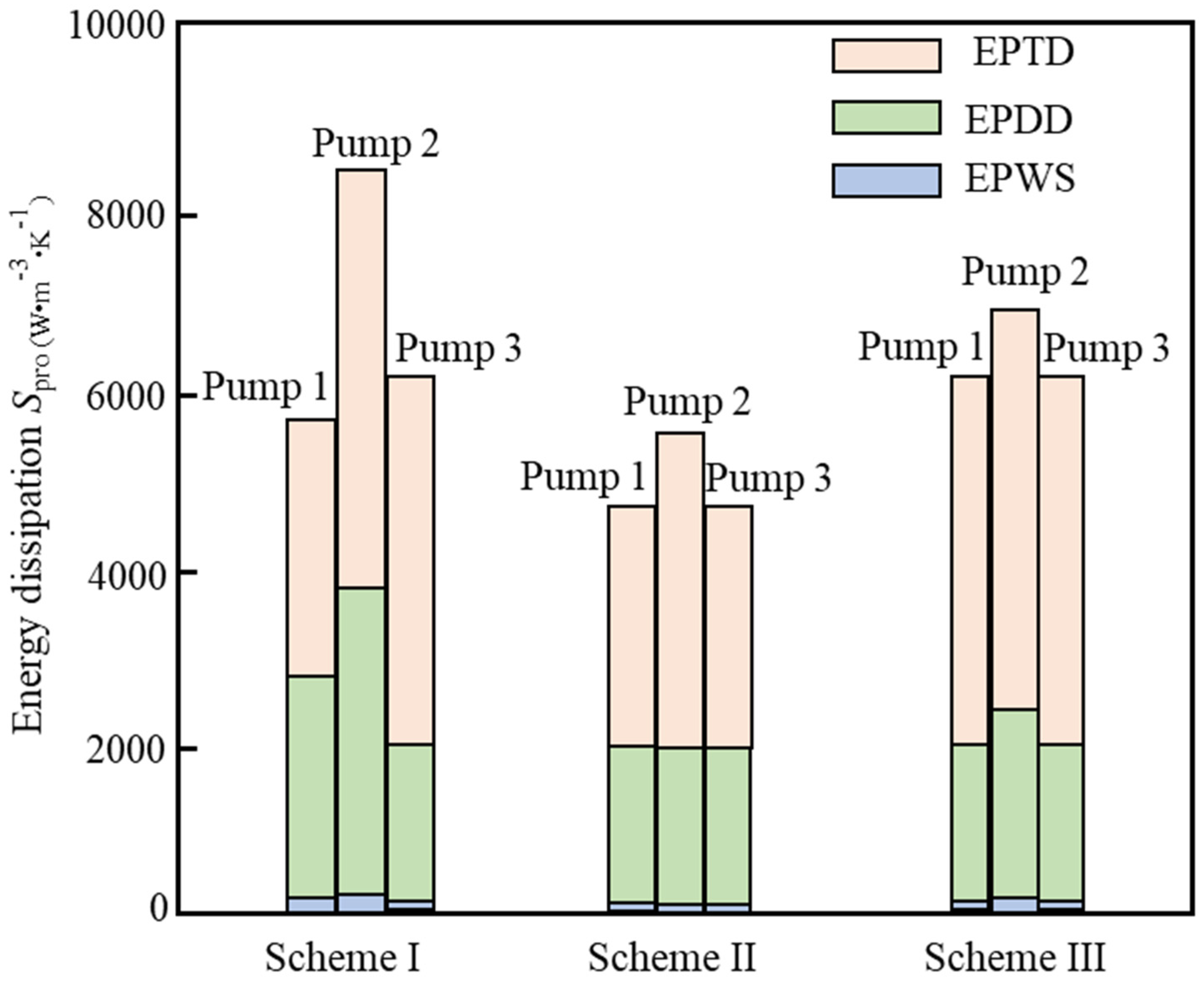
3.4. Energy Dissipation Analysis in Water Pump
4. Discussion Between Erosion and Energy Dissipation
5. Conclusions
- The study reveals an evolutionary pattern in flow velocity distribution across the stages of a three-stage centrifugal pump: the first-stage impeller inlet exhibits high but uneven velocity, prone to local high-speed jets; the second stage shows more uniform distribution due to improved inflow, yet with a strengthened velocity gradient in the impeller passage; the final stage develops high-speed zones induced by secondary flows and separation vortices near the blade pressure side trailing edge and the tongue region. This progression from disorder to order and then to complex structures directly influences particle trajectories and energy transfer efficiency.
- The study reveals how blade angles affect wear and energy loss by altering flow patterns and particle impacts. In Scheme I, particles slide along the pressure surface, causing banded wear and increased turbulence. Scheme II’s symmetrical blade arrangement localizes wear to the trailing edge and reduces energy loss through improved flow attachment. Scheme III’s staggered angles lead to direct suction surface impacts, creating pit-shaped erosion and significantly higher turbulence dissipation.
- Sediment erosion and energy dissipation in multistage centrifugal pumps are coupled through flow irreversibility. High-erosion regions spatially coincide with high entropy production zones. Particle impacts increase wall roughness, inducing flow separation and turbulence, thereby raising viscous dissipation by 15–25%. Flow disturbances from particles amplify turbulent dissipation, with fluctuating entropy production exceeding 35% in later stages. Optimizing blade angles simultaneously reduces both erosion and entropy production, demonstrating feasible synergistic improvement through flow control.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Z.; Chu, W.; Li, X.; Dong, W. Sediment erosion in the impeller of a double-suction centrifugal pump—A case study of the Jingtai Yellow River Irrigation Project, China. Wear 2019, 422–423, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Li, R.; Han, W.; Quan, H.; Guo, R. Erosion Wear on Impeller of Double-Suction Centrifugal Pump due to Sediment Flow. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2020, 13, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, S.; Banka, J.; Kumar, A.; Rai, A.K. Effects of sediment properties on abrasive erosion of a centrifugal pump. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 277, 118873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, M.A.; Zhou, L.; Yasser, E.; Bai, L.; Shi, W. Computational Methods of Erosion Wear in Centrifugal Pump: A State-of-the-Art Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 3789–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetrati, M.; Pak, A. Numerical simulation of sanding using a coupled hydro-mechanical sand erosion model. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Acharya, N.; Lama, R.; Chitrakar, S.; Neopane, H.P.; Zhu, B.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Numerical and experimental investigation of erosive wear in Francis runner blade optimized for sediment laden hydropower projects in Nepal. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 51, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Neopane, H.P.; Acharya, N.; Chitrakar, S.; Thapa, B.S.; Zhu, B. Sediment erosion in low specific speed francis turbines: A case study on effects and causes. Wear 2020, 442–443, 203152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Kang, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, G.; Li, L.; Su, M. Erosion estimation of guide vane end clearance in hydraulic turbines with sediment water flow. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 32, 1850100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, G. Trajectories of coarse granular sediment particles in a simplified centrifugal dredge pump model. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016680143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Guo, P.C.; Zheng, X.B.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, X.Q. Numerical simulation of flow in centrifugal pump under cavitation and sediment condition. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 15, 032056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yao, R.; Shen, Y.; Bi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, Z. Numerical Prediction of Erosion Based on the Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in a Double-Suction Centrifugal Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, Z. Study on sediment erosion of high head Francis turbine runner in Minjiang River basin. Renew. Energy 2022, 192, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, R.; Teran, L.; Grande, J.; Coronado, J.; Ladino, J.; Larrahondo, F.; Rodríguez, S. Minimizing erosive wear through a CFD multi-objective optimization methodology for different operating points of a Francis turbine. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 2217–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Su, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, B.; Dong, J. Experimental investigation of sediment erosion in a double-suction centrifugal pump in sandy rivers. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 774, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamazhonov, M.; Shakirov, B.; Matyakubov, B.; Makhmudov, A. Polymer materials used to reduce waterjet sediment erosion of pump parts. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2176, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, R.O.P.; Santos, L.P.; Viana, E.M.d.F.; Pinto, M.A.; Martinez, C.B. Case study: Effects of sediment concentration on the wear of fluvial water pump impellers on Brazil’s Acre River. Wear 2018, 408–409, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Xiong, W. An experimental insight into dynamic characteristics and wear of centrifugal pump handling multi-size particulate slurry. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.; Tao, R.; Zhu, D.; Xiao, R. FED evaluation in a small double-suction reversible pump turbine considering sediment erosion. J. Energy Storage 2024, 76, 109549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Research on the Relationship between Sediment Concentration and Centrifugal Pump Performance Parameters Based on CFD Mixture Model. Energies 2022, 15, 7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, B.; Ahn, S.-H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, G.; Li, Y. Slurry Flow and Erosion Prediction in a Centrifugal Pump after Long-Term Operation. Energies 2019, 12, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.X.; Dong, F.D.; Cheng, X.R. Numerical investigation of sediment erosion to the impeller in a double-suction centrifugal pump. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 062004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, G. Numerical investigation on the transient characteristics of sediment-laden two-phase flow in a centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, Z. Numerical prediction of the effect of free surface vortex air-entrainment on sediment erosion in a pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2022, 236, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Luo, Y.; Presas, A.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Z. Numerical analysis on the modal characteristics of a pumped storage unit runner in cavitating flow. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qi, D.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Numerical Simulation Prediction of Erosion Characteristics in a Double-Suction Centrifugal Pump. Processes 2021, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Yang, Z.; Lyu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, L. Numerical study of turbulent flow past a rotating axial-flow pump based on a level-set immersed boundary method. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Muhirwa, A.; Maxime, B. Energy loss mechanisms of transition from pump mode to turbine mode of an axial-flow pump under bidirectional conditions. Energy 2022, 257, 124630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Han, L.; Wei, X.; Qin, D. Entropy production analysis of hysteresis characteristic of a pump-turbine model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 149, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gong, R.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Wei, X.; Qin, D. Analysis of vorticity dynamics for hump characteristics of a pump turbine model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 3641–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.; Siedlecki, C.A.; Jhun, C.; Weiss, W.J.; Manning, K.; Deutsch, S.; Pierce, W. Acquired Von Willebrand Syndrome and Blood Pump Design. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Flow rate Q (m3/h) | Head H (m) | Rotation Speed N (r/min) | Efficiency ƞ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 137 | 100 | 94.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Liang, H.; Lu, M.; Song, X.; Xi, B. Prediction Analysis on the Sediment Erosion and Energy Dissipation Inside a Three-Stage Centrifugal Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122248
Zhang B, Liang H, Lu M, Song X, Xi B. Prediction Analysis on the Sediment Erosion and Energy Dissipation Inside a Three-Stage Centrifugal Pump. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(12):2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122248
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bowen, Haojie Liang, Meining Lu, Xijie Song, and Bin Xi. 2025. "Prediction Analysis on the Sediment Erosion and Energy Dissipation Inside a Three-Stage Centrifugal Pump" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 12: 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122248
APA StyleZhang, B., Liang, H., Lu, M., Song, X., & Xi, B. (2025). Prediction Analysis on the Sediment Erosion and Energy Dissipation Inside a Three-Stage Centrifugal Pump. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(12), 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122248






