Abstract
As the global demand for seaweed products increases, resource managers, conservation groups, and other stakeholders strive to protect wild seaweed populations and the ecosystem services they provide from the damaging effects of over-harvesting. Ascophyllum nodosum (rockweed) is a slow-growing, intertidal brown alga of the North Atlantic that is commercially harvested for crop biostimulants, soil conditioners, and other products. Rockweed is considered a foundation species due to its high abundance, tall canopy, habitat characteristics, and role in detrital food webs. Rockweed shoots survive after harvesting if the holdfast remains intact, but rates of canopy and biomass recovery depend on the intensity of harvesting. In Maine, USA, and eastern Canada, little is known about how harvesting rockweed at various intensities affects recovery rates of algal height or biomass. Herein, we evaluate published studies and suggest improved experimental designs. Most experimental studies focus on a single harvest event, often with incomplete data on control plots, amount of biomass removed, or previous harvesting history at study sites. Much has been learned from previous work, but more rigorous studies are needed to develop harvest recommendations that address both commercial and conservation-related goals. Importantly, experimental studies of the effects of repeated harvesting on rockweed beds are lacking.
1. Introduction
Brown seaweeds such as kelp and rockweed (Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis) are canopy-forming foundation species that provide a range of ecosystem functions and services—for example, as primary producers, nursery and foraging habitats for fish and wildlife, and serving as a buffer against coastal erosion [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Ascophyllum nodosum, hereafter rockweed, is a dominant and extremely abundant intertidal seaweed that is harvested commercially in Maine, eastern Canada, Iceland, Ireland, and elsewhere in northern Europe to supply an expanding global market [3,5,7,8].
Rockweed is a slow-growing perennial that often reaches >1–2 m in height. It is highly clonal and comprises a long-lived holdfast (>50 years) from which numerous erect fronds develop with a lifespan often greater than 10–15 years [9,10]. This species serves as a habitat for many species of invertebrates, shorebirds, waterfowl, and at least 30 species of fish [2,11,12,13,14]. It is also the host of a complex symbiosis involving at least five other species: an epiphytic red alga, Vertebrata lanosa, with its obligate red algal parasite Choreocolax polysiphoniae, a facultative brown algal epiphyte Elachista fucicola, with its abundant insect associate Halocladius variabilis, and the obligate, mutualistic ascomycete, Mycophycias ascophylli [15,16]. Mycophycias ascophylli may enhance the desiccation tolerance of rockweed [17].
Growing apically from a basal holdfast, rockweed has dichotomously branching fronds with air bladders that lift the thallus with the rise of the tide (Figure 1 and Figure 2). At high tide, juvenile fish such as pollock, cod, and herring find food and protection from predators in rockweed beds [2,18,19]. Young eiders (Somateria mollisima) also forage in the floating canopy [20]. At low tide, a thick layer of overlapping rockweed fronds protects invertebrates from heat and desiccation and serves as a foraging habitat for shorebirds and seabirds [3,21].
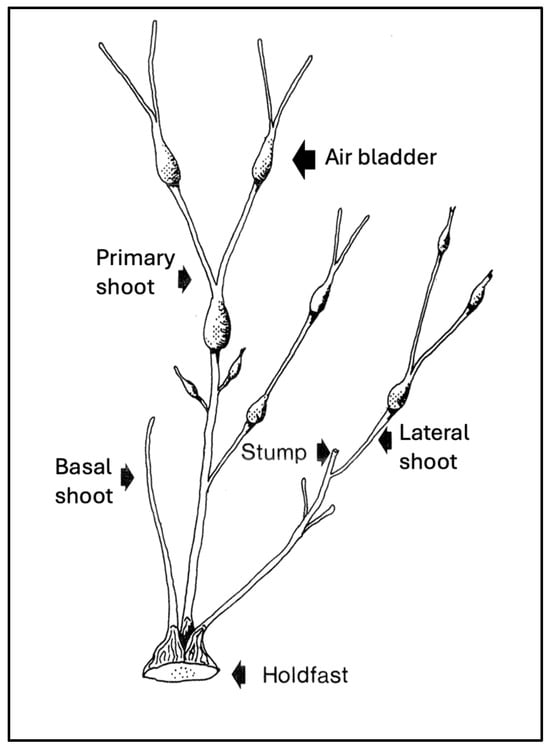
Figure 1.
Morphology of shoots on a small, non-reproductive rockweed clump [22]. For each shoot section, one air bladder is produced per year.
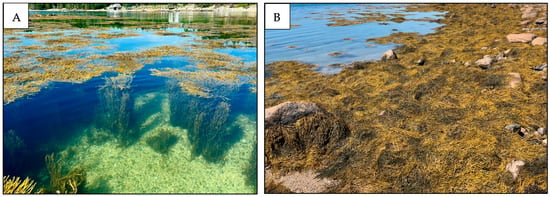
Figure 2.
Rockweed beds at (A) high tide and (B) low tide in Penobscot Bay, Maine.
The distribution, biomass, and vertical structure of rockweed beds are influenced by many factors, including wave exposure, ice scouring, tidal amplitude, current flow, and rates of recruitment on available substrates [13]. Sexual reproduction in Maine and eastern Canada occurs mostly in May–June, when receptacles on each male or female individual release nutrient-rich sperm and eggs into the water column [3,9,23]. Recruitment of rockweed germlings on rocky substrates can be severely constrained by periwinkle grazing (Littorina spp.) and wave action [24,25]. Rockweed often co-occurs with a smaller brown alga, Fucus vesiculosus (bladder wrack), which tolerates wave exposure better and recruits more quickly, but is typically shaded out by overarching rockweed fronds over time [6]. Natural breakage of rockweed fronds is common, releasing vast amounts of decomposing biomass into coastal ecosystems [13]. In Cobscook Bay, Maine, for example, more than half of rockweed’s annual productivity enters detrital food webs via breakage, dehisced reproductive structures, and epidermal shedding, benefitting filter feeders like scallops, mussels, and clams [13,26].
Because macroalgae like rockweed provide unique intertidal habitats as well as other ecosystem functions and services, conservation biologists recommend an ecosystem-based management approach rather than a single-species focus for sustainable harvesting practices [4,5,27]. A broad multi-species view of rockweed management acknowledges the ecological benefits of maintaining tall, reproductive canopies and mitigating the consequences of wide-scale biomass removal from commercial harvesting. In contrast, rockweed harvesters and government regulatory agencies often focus primarily on commercially viable rates of biomass extraction [3,8,28], rather than recognizing rockweed as being part of a complex ecosystem.
2. Harvesting Methods and Regulations
Commercial cutting methods for rockweed typically use mechanical vessels (“suction cutters”, Figure 3) or hand-cutting using rakes and skiffs [29,30]. Mechanical vessels were used in Nova Scotia, Canada, from 1985 until 1994, after which they were discontinued in favor of hand-raking with skiffs [29].
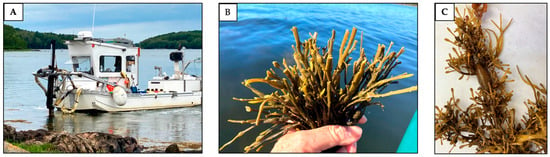
Figure 3.
Examples of (A) a mechanical harvesting vessel operating at high tide; (B) rockweed shoots recently cut by a mechanical harvesting vessel; and (C) an older cut shoot with a large air bladder, many reproductive structures, several small side shoots, and a small epiphyte (Fucus vesiculosus, top center).
Prior to the 1990s, a lack of regulation led to devastating effects of overharvesting on rockweed beds in southwest Nova Scotia, including heavy mortality due to holdfast removal, as noted by Vandermeulen in 2013 [31]:
“Historically then, from the first rake harvests through to mechanization, the management regime routinely allowed an intense harvest of Ascophyllum on many shores in southwest Nova Scotia which took years to recover. The evidence strongly indicates that this took place at bay-wide scales, suggesting that an undesirable level of habitat loss had occurred at a landscape scale”(see Appendix A for details).
By the early 1990s, the coast of southwest and southern Nova Scotia was divided into sectors that were allocated to specific companies [28] (Table 1). Assigned sectors were also established in New Brunswick when commercial rake-harvesting was first allowed in 1995 [29]. By 2000, nearly all sectors in both provinces were assigned to Acadian Seaplants LLC (Dartmouth, NS, Canada), an international company that processes rockweed for soil conditioners, crop biostimulants, and animal fodder [28].

Table 1.
Comparison of key rockweed harvesting regulations and laws in Maine, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia [2,27,28,29,32,33]. In New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, commercially harvested areas are leased and are under provincial jurisdiction, as shown here.
Current regulations for commercial rockweed harvesting differ in Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Maine (Table 1). The minimum cutting height in Canada is shorter than in Maine (12.7 cm vs. 41 cm). Canadian provinces have quotas on how much rockweed can be removed with its holdfasts attached (10% in New Brunswick, 15% in Nova Scotia) and how much biomass can be harvested from assigned sectors (17% in New Brunswick, 20–25% in Nova Scotia). While mechanical harvesting is not allowed in New Brunswick, it can be permitted in Nova Scotia. In 2023, the Nova Scotia Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture implemented a new policy under which mechanical suction-cutter vessels can be approved for rockweed leases. This rarely used policy requires biomass assessments, delineating sectors for use, reporting planned harvest amounts, and submission of GPS tracking logs (personal comm. to A. Snow from Wendy Vissers, [33]).
In Maine, the Cobscook Bay Management Area has harvesting requirements that are similar to those in New Brunswick, but there are no restrictions on mechanical harvesting throughout Maine (Table 1). The Maine Department of Marine Resources (DMR) published a draft rockweed fishery management plan in 2014 that was never implemented [3,27]. Harvest reporting sectors have been designated for the entire coast of Maine, but these sectors are not assigned to specific harvesters except in the Cobscook Bay Management Area (Table 1). In Canada, private property does not extend to intertidal areas, in contrast to the situation in Maine. In 2019, the Maine Supreme Judicial Court ruled that ownership of intertidal lands, in effect since the 1600s, includes ownership of rockweed [34]. However, rockweed beds that occur on substrates that are not connected to upland property at low tide, such as offshore ledges, are considered public property and are freely available to harvesters.
3. Assessing Recovery of Rockweed After Harvesting
A scientific understanding of recovery rates is essential for making decisions about rockweed harvest management and conservation. The goals of this review are to evaluate the scientific rigor of previous research on how known intensities and frequencies of harvesting affect recovery rates for rockweed height and biomass, and to suggest improved protocols for future studies. As used here, harvest “intensity” refers to the combined effects of inadvertent holdfast removal, the heights at which cutting occurs, and the percent of total rockweed biomass removed per m2 during each harvest event. Shoot height is a key component of recovery from harvesting because it reflects the quality of the habitat and canopy height for other species [1,2,13].
Recovery of rockweed biomass can be interpreted in several ways—first, as recovery to a level that is sufficiently profitable to allow re-harvesting; second, as recovery to match baseline conditions at each site (which may have been harvested in the past); and third, as recovery to match the biomass of naturally occurring rockweed beds that have not been harvested previously. To document recovery, some studies simply measure “before and after” changes in height and biomass at sites that have been harvested (e.g., [24,35]). However, because of year-to-year variation in growing conditions [36], it is important to include an unharvested control treatment for statistical comparisons with harvest treatments. It is also critical that seasonal changes in biomass are reflected in the time of sampling and re-sampling. This is because the biomass of large fronds can vary by at least 30% based on the presence of receptacles reaching maturity in late spring to early summer vs. post-dehiscence of receptacles in mid-summer to early fall [37,38]. Thus, changes in sampling time by a few weeks to a month can dramatically alter biomass assessments.
Field experiments with rockweed are inherently difficult due to logistical constraints such as having sufficient time, personnel, intertidal access, and funding to carry out well-designed studies. A major challenge for designing rigorous field experiments is accounting for variability in percent rockweed cover, shoot density, biomass, height, and size class distributions, both within and among study sites. Moreover, commercial harvesting that occurs unexpectedly at a research site can compromise planned harvest vs. control treatments [39]. In Maine, a further challenge is obtaining permission from upland property owners to conduct research at selected intertidal sites.
Recommended Protocols
In this section, we summarize optimal research protocols for field studies of recovery rates after harvesting. It is seldom possible to follow all of these guidelines. Therefore, the limitations of each published study should be stated explicitly when communicating results, especially in the context of applying the study’s findings to management decisions.
- Quantify biomass and height as the dependent variables for documenting recovery.
- Biomass is typically recorded as wet kg per square meter and can be measured destructively or non-destructively, typically within random or haphazardly placed quadrats [30,40].
- Biomass sampling should be carried out when fronds are at the same reproductive state in each year of the study.
- Unharvested rockweed beds often have a skewed or bimodal distribution of size classes, with a small proportion of very large fronds that cast shade on subcanopy and basal shoots [40,41]. Because most biomass is present in the tallest fronds, data on how size class distributions are affected by harvesting are useful (as in [36,40,41]).
- Height should be measured for the tallest fronds per quadrat as an index of canopy height. If only the average height per quadrat is reported, the height of the canopy may be underestimated due to the skewed or bimodal size distributions cited above.
- Choose study sites where rockweed biomass and height are representative of commercially targeted areas, such as sheltered coves and bays or moderately exposed areas where rockweed is a minimum of ~1 m tall.
- Ideally, these should be sites that were not harvested previously or within the past decade. If the sites have been harvested recently or if their harvest history is unknown, this caveat should be explained in the paper’s abstract and conclusions.
- Site locations with GPS coordinates should be published to allow follow-up studies.
- To test for recovery of biomass and height from a single harvest event, compare harvested sites or plots with unharvested sites or plots.
- As noted above, an unharvested control treatment is essential because biomass and height can vary among years [36], confounding the effects of harvesting on recovery rates over time.
- For both treatments (control vs. harvested), obtain data on biomass and height immediately before the time of harvesting as well as immediately after harvesting, followed by repeated sampling in the same month over several years. This is often referred to as a BACI design, for Before-After and Control-Impact, where “impact” refers to experimental harvesting [30].
- Report how much biomass was removed from the site or experimental plot at the time of harvesting and explain the harvesting method at each site (e.g., hand-cut, rake-cut, or type of mechanical vessel).
- Use replicated treatments that take existing variability into account, ideally by performing power tests [39,42,43].
- The experimental design should allow inferential statistics and avoid pseudo-replication [44].
- For each experimental treatment (control vs. harvested), replication should be sufficient to ensure that biologically important differences between treatments (should they occur) are statistically significant.
- Use permanently marked plots, transects, and quadrats for documenting year to year changes at the same location.
- Inability to re-sample the same exact location adds to variability in the data, as occurred in [30].
- For long-term studies, include a treatment with repeated harvest events, such as every two or three years.
4. Review of Key Papers
4.1. Choice of Studies
To identify peer-reviewed studies about recovery of rockweed beds after harvesting, we used Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com, accessed on 15 November 2025), Web of Science (https://clarivate.com, accessed on 15 November 2025), and references in relevant publications. Our search was limited to studies in Maine, USA, and eastern Canada based on the assumption that rockweed beds in Northern Europe have different ecological and harvesting conditions. With the exception of one PhD dissertation, Fegley (2001) [36], we selected only publications that appeared in a peer-reviewed scientific journal. Fegley [36] was included because this is one of the most thorough and rigorous studies we encountered.
We found a total of nine relevant publications, which fall into three groups: (1) experiments with hand-cutting at a local scale, (2) experiments with commercial-type cutting by rake or mechanical vessel, and (3) comparative studies (Table 2, Figure 4). Surprisingly, only three experimental studies reported the effects of harvesting on both biomass and height—Fegley (2001) [36], Ugarte et al. (2006) [40], and Johnston et al. (2023) [30]—all of which involved a single harvest event. We included the two comparative (non-experimental) studies in Table 2 because they have been cited by others as evidence for recovery after harvesting. For each of the nine studies, key findings and caveats related to the recovery of biomass and height are summarized below, in chronological order within each group. We do not describe results that were tangential to the primary goal of this review, which is to assess the scientific rigor of research on how rockweed harvesting affects recovery rates of biomass and height.

Table 2.
Summary of selected studies of rockweed biomass and height recovery after harvesting. Asterisks indicate the three most relevant studies, which report data on both biomass and height. NA indicates “not applicable”.
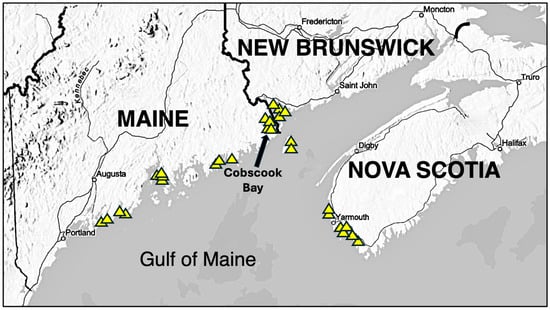
Figure 4.
Map of the coast of Maine, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia. Triangles indicate study site areas from publications in Table 2.
4.2. Experiments with Hand-Cutting
4.2.1. Keser et al. (1981)—“Regrowth of Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus Under Various Harvesting Regimes in Maine, USA” [24]
Hand-cutting experiments are not representative of bed-scale commercial harvesting, which removes biomass more variably across a rockweed bed [30,40], but this approach can show how quickly rockweed biomass and height recover at a very local scale. Keser et al. [24] reported biomass recovery three years after hand-cutting at 0 cm (scraped at the holdfast), 15 cm, or 25 cm above the holdfast, with a single cutting vs. annual cutting at eight sites in Maine. No unharvested control plots were used. As noted above, current regulations in Canada and Maine stipulate that harvesting should not occur below 12.7 cm or 41 cm, respectively, to allow re-growth from lower side shoots (Table 1). Therefore, the treatments used by Keser et al. [24] were more severe than what is currently allowed in Maine. Their study sites ranged from sheltered coves to wave-exposed rocky headlands, and initial rockweed biomass per m2 differed as much as 4-fold among the 8 sites. Rockweed individuals at exposed sites were smaller and had fewer annually produced air bladders than those at more sheltered sites. Annual cutting led to strong declines in biomass, as did scraping at 0 cm. Their findings for single cutting events at 15 or 25 cm varied among sites, making it difficult to draw general conclusions about recovery. Also, sample sizes for their experimental treatments at each site were not clear and they did not report recovery of shoot height. We conclude that Keser et al. [24] is not very helpful for the goals of this review because of the limitations listed here.
4.2.2. Fegley (2001)—“Ecological Implications of Rockweed, Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis, Harvesting” [36]
Fegley [36] carried out a well-designed factorial experiment in the Penobscot Bay region of Maine to document the effects of cutting on the recovery of rockweed biomass and height. This study involved 36 plots (each 25 m2), and included 4 similar sites, 3 treatments per site, 3 plots per treatment, and replicated quadrats in each plot. The experimental treatments were controls, hand-cut either once at 18 cm or once at 36 cm. Data from adjacent, unharvested areas at each site showed that rockweed biomass per m2 varied among years and was greatest in the last year of the experiment. This makes it essential that results from the unharvested control treatment be available for comparison.
Two years after cutting at 18 or 36 cm, fewer shoots were >50 cm tall, shoots in this size class were shorter, and more shoots were present in the smallest size class (<25 cm) because of new growth of basal shoots and lateral branches. Removal of apical dominance and greater light penetration after cutting likely contributed to the release of suppressed shoots in the subcanopy, as hypothesized by others [47,48,49]. After two years, mean biomass values were 67% and 88% of control plots for the 18 cm-cut and 36 cm-cut treatments, respectively, but these effects were not statistically significant because of variability within and among sites. For both cutting treatments, Fegley [36] concluded that the cut plots did not return to baseline conditions after two years because shoots were shorter and biomass per m2 was less than control plots.
4.2.3. Gendron et al. (2018)—“Managing Disturbance: The Response of a Dominant Intertidal Seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis to Different Frequencies and Intensities of Harvesting” [45]
Gendron et al. [45] has been cited as a study of recovery, but this example is not useful for our purposes because the treatments were not replicated. This study was carried out at a single site in the St. Lawrence River estuary in the Province of Quebec and was published as a descriptive 28-year data set. The authors described how rockweed biomass recovered at individual 25 m2 plots, each of which was subjected to a different intensity and frequency of harvesting (no control plots were used). The authors acknowledged that the lack of replication made it impossible to test for treatment effects on biomass recovery in their study.
4.3. Experiments with Commercial Cutting
4.3.1. Ang et al. (1993)—“Changes in the Population Structure of Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis Due to Mechanical Harvesting” [41]
Ang et al. [41] documented the immediate effects of a single harvest by a Norwegian suction cutter boat on rockweed density and height, but they did not study rates of recovery. At a site in southwest Nova Scotia with no previous harvesting history, they established 10 permanently marked quadrats (0.25 m2) in each of 4 harvested transects vs. 2 unharvested transects. The harvester moved the cutter head over the harvested transects for an average of 18 min and removed an estimated 80% of the available biomass. This effort was considered to mimic harvesting in heavily cut patches of rockweed. Rockweed clump density and shoot height of previously tagged individuals were recorded immediately after the experimental harvest (a clump is made up of basal shoots from the same holdfast).
Ang et al. [41] found that mechanical harvesting caused 20–36% mortality of the rockweed clumps. Control quadrats had a bimodal distribution of size classes and ~13% were >100 cm tall. Immediately after harvesting, more than 95% of shoots that initially were >50 cm tall at these transects had been cut or removed by the machine, and hardly any were >70 cm tall. As expected, the mechanical harvest removed primarily the longest shoots at this previously unharvested site.
4.3.2. Lazo and Chapman (1996)—“Effects of Harvesting on Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. (Fucales, Phaeophyta): A Demographic Approach” [39]
To document the effects of different cutting intensities by a Norwegian suction cutter boat on rockweed height and biomass, these investigators conducted a factorial design experiment. They established three harvested and three unharvested plots at a site in Nova Scotia that was likely harvested two years earlier. However, an unplanned cut by a local contractor prevented the researchers from measuring the recovery of height and biomass at the end of this two-year study. Instead, they reported effects of the cutting treatments on survival, height (net change in growth and breakage), and reproductive status for tagged shoots in four size classes. The mean cutting height at the experimentally harvested plots was estimated to be about 20 cm. Canopy removal was associated with enhanced growth in the smaller size classes, but the authors stated that “assessment of the time required for a stand to recover to biomass levels prior to the harvest was not an objective”.
4.3.3. Ugarte et al. (2006)—“Changes in the Brown Seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. Plant Morphology and Biomass Produced by Cutter Rake Harvests in Southern New Brunswick, Canada” [40]
Ugarte et al. [40] documented the effects of rake harvesting on average clump biomass and length at a site in New Brunswick that had not been harvested previously. They established three harvested plots and two control plots, each 8 m × 8 m. Although they intended to remove 50% of the biomass at each harvested plot, the actual amounts removed were 33%, 34%, and 51%. Nearly all cutting occurred at ≥60 cm above the holdfast. Most of the harvested biomass came from clumps that were >90 cm tall, thereby removing much of the canopy. Compensatory growth of suppressed shoots contributed to biomass recovery after the experimental harvest, as in Fegley [36]. Suppressed shoots that initially were 21–60 cm long grew more in the two years after harvesting than suppressed shoots of similar size in the two control plots, such that the average clump biomass generally recovered within a year. However, based on their data, we assume that harvesting also resulted in a lower canopy than was present initially. This study of a single ‘light’ rake-harvest is often cited as evidence that rockweed biomass recovers fully within a year and that growth of suppressed shoots can be stimulated by harvesting.
4.3.4. Johnston et al. (2023)—“Bed-Scale Impact and Recovery of a Commercially Important Intertidal Seaweed” [30]
Johnston et al. [30] tested for bed-scale effects of unreported amounts of harvesting on biomass and height recovery one year later. This study was intended to provide a snapshot of how ‘typical’ harvesting by three commercial companies affected rockweed recovery along the coast of Maine. Focusing on bed-scale effects of harvesting at many experimental sites is a worthy goal, but this study suffered from several limitations noted below.
In 2018, Johnston et al. [30] established 19 control sites and 19 ‘impact’ (i.e., harvested) sites using an unbalanced design (not paired) across four regions of the state, which were designated as Mid-Coast, Penobscot, Jonesport, and Cobscook. Each site was at least 100 m long and a few sites that were assigned to the same treatment were adjacent to each other [50,51], which is not ideal. Prior to the study, the researchers did not know how recently the sites had been harvested commercially, but employees of the three collaborating companies estimated at least three years. Thirteen of the impact sites were harvested using mechanical vessels and six were harvested by hand-raking. Data from both methods were combined for analyses.
At each site, the researchers recorded mean biomass and mean canopy height using 10 quadrats (0.25 m2) one year before harvesting, soon after harvesting, and one year after harvesting. Additional details about their methods and analyses can be found in the original paper and other papers by Johnston et al. [43,51].
Small sample sizes at each site (N = 10 quadrats), a lack of permanently marked quadrats, and highly variable biomass and height within and among rockweed beds detracted from the statistical rigor of this study [42]. Pre-harvest measurements were made one year before harvesting instead of immediately beforehand, adding another source of variation due to the net effects of growth vs. natural breakage over the time between measurements. Effects of harvesting based on pre- and post-harvest measurements at each impact site were barely detectable, presumably because of the variation previously noted, as well as inherently patchy levels of harvesting intensity within sites. The authors noted that: “there were several impact sites that increased in mean height (N = 5) and biomass (N = 8) between the pre-harvest and harvested time periods. This is likely due to a lack of spatial overlap between transects and harvest at these sites.”
A statistically significant effect of harvesting was found at only one of the four regions, Mid-Coast, where six sites were machine-harvested and four sites served as controls. Standardized effect sizes comparing the effects of harvesting for biomass and height were −0.78 and −0.28, respectively, for the Mid-Coast region, compared to only −0.28 and −0.11 for data from all four regions combined. These results suggest that harvesting intensity was highly variable across the 19 replicates for the impact treatment. An important finding of Johnston et al. [30] was that “sites that experienced higher intensities of harvest were less likely to fully recover height or biomass one year post-harvest.” However, the authors summarized their data from all four regions by stating that rapid recovery from harvesting occurred within a year, even though an initial impact of harvesting was not detected at three of the four regions. Many of the limitations listed above also apply to companion papers, theses, and PhD dissertations based on this BACI study [43,50,51,52,53,54].
4.4. Comparative Studies
4.4.1. Lauzon-Guay et al. (2021)—“Biomass and Height of Ascophyllum nodosum After Two Decades of Continuous Commercial Harvesting in Eastern Canada” [35]
Lauzon-Guay et al. [35] asked whether cumulative effects of harvesting by Acadian Seaplants over two decades led to detrimental effects on rockweed biomass or height. They compared company data from stock assessments in 1996-1998 with similar assessments conducted in 2016–2020 for sectors that had been “continuously harvested” in Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. Unfortunately, the frequency, intensity, or patchiness of “continuous” harvesting were not explained.
Between the two time periods, average height increased by 14 cm in New Brunswick and decreased by 8 cm in Nova Scotia, while differences in biomass were negligible. Although two decades of harvesting did not appear to have harmed rockweed biomass or height, this study lacked unharvested controls for the two time periods. Therefore, it is somewhat misleading to state that long-term harvesting had “no effect” on rockweed biomass or height (for example, as cited by Lauzon-Guay et al., 2023 [46]). The take-home message from this study is that the company’s harvesting methods (which were not presented), did not appear to cause cumulative changes in standing stocks over time, with the caveat that the study lacked appropriate unharvested controls.
4.4.2. Lauzon-Guay et al. (2023)—“Morphology of Ascophyllum nodosum in Relation to Commercial Harvesting in New Brunswick, Canada” [46]
Lauzon-Guay et al. [46] sought to determine whether repeated rake-cutting of rockweed clumps caused the clumps to become shorter or “bushier” due to inherently slow apical growth (often ~8–12 cm per year [3]) and increased lateral branching. In New Brunswick, they measured morphological characteristics of rockweed clumps from one transect at each of three rockweed beds in areas that were closed to harvesting vs. three beds in areas that were harvested commercially. Transects in the three harvested areas were located where no harvesting was evident in the year of the study. The commercial beds had been harvested on a “near continual basis for over 20 years,” but no details were provided about how often or how intensively each sampled rockweed bed had been harvested.
Few differences were found in average clump size or morphology in comparisons between closed areas vs. harvested areas. “No effect” may be a valid interpretation of their results, but it is also possible that the lack of differences resulted from small sample sizes, variability in the data, and/or variability in past harvesting intensities. In any case, this comparative study does not address our main question about how quickly rockweed beds recover from known frequencies and intensities of harvesting.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
At the scale of small plots, Fegley [36] showed that rockweed biomass and height did not recover from hand-cutting at 18 cm and 36 cm within two years, as expected for this 1–2 m tall, slow-growing alga. For larger-scale plots, we found only two studies that tested for the effects of commercial-type rake or mechanical harvesting on the recovery of rockweed biomass and height one or two years later, both from a single harvest event (Ugarte et al. [40], Johnston et al. [30]). Ugarte et al. [40] showed that previously unharvested rockweed clumps in New Brunswick recovered their initial biomass and much of their average height within two years after a low-intensity, experimental rake-harvest (33–50% biomass removal, with at least 60 cm of shoot height remaining after the harvest). Results from Johnston et al. [30] are more difficult to interpret, primarily because they did not detect changes in biomass or height after harvesting in three of the four regions of the coast (a result that could be attributable to small sample sizes). Across all regions, these authors concluded that “One year post-harvest, mean rockweed biomass fully recovered at impact sites relative to control sites, while mean height remained lower at impact sites.” Because of several limitations of this study, their conclusion that rockweed biomass “fully recovered” within a year after commercial harvesting is questionable.
Taken together, previous studies suggest that the intensity of commercial harvesting can be highly variable, ranging from 20–36% mortality from machine-harvesting reported by Ang et al. [41] and an average machine-cutting height of only 20 cm (Lazo and Chapman [39]), to more of a thinning and trimming effect from the study of rake-harvesting by Ugarte et al. [40] and the largely undetected effects of both types of harvesting reported by Johnston et al. [30]. Compared to rake-harvesting, mechanical vessels can harvest rockweed more quickly and can operate over a longer harvest season [28,33]. Further research is needed to determine the effects of the range of harvesting intensities that occur with both methods on rockweed biomass and height, especially in the context of repeated harvest events separated by fallow periods of ~2–3 years. Carefully designed studies should also include natural, unharvested plots as a baseline.
We suspect that there are many cases when a single harvest event leaves behind a healthy subcanopy of previously suppressed fronds that are capable of enhanced growth after harvesting, as documented by Fegley [36] and Ugarte et al. [40]. However, we have also observed inactive “stumps” of older shoots that were decapitated by harvesting, lacked lateral branches or basal shoots, and may be inhibited by epiphyte colonization on wounded branches (A. Snow and D. Porter, personal observation). Likewise, others described a lack of functional growing points on older portions of the thallus [39,55,56,57]. When older shoots are truncated by harvesting that removes the subcanopy over a large area, bed-scale recovery may depend on the growth of basal shoots arising directly from holdfasts, as well as new recruitment from germlings and the growth of any remaining rockweed fronds that still have lateral branches.
In summary, ecosystem-based management requires understanding the effects of various intensities and frequencies of harvesting on rockweed canopies and productivity. Ultimately, it is important to consider the cumulative effects of prolonged harvesting on rockweed and its role in coastal ecosystems. We recommend that further discussion of the effects of commercial harvesting on rockweed biomass and height acknowledge the complex and largely unknown effects of various cutting heights, amounts of biomass removal, and cutting frequencies on recovery rates. Also important is distinguishing between the goals of: (1) biomass recovery that is sufficient for commercial re-harvesting vs. (2) full recovery of natural rockweed habitats and their associated ecosystem functions and services. Addressing these goals also needs to be put into the context of climate change and the changing distribution of Fucus serratus, a non-native species that sometimes occupies the lower intertidal zone in Nova Scotia [58].
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, A.A.S.; review and editing, A.A.S., D.P., D.J.G. and H.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We thank Nancy Prentiss, Robin Hadlock Seeley, Sarah Hardy, and several anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the paper. We also thank Wendy Vissers, Marine Plant Advisor, Nova Scotia Dept. of Fisheries and Aquaculture, and Kristin Dinning, New Brunswick Department of Agriculture, Aquaculture, and Fisheries, for current information about harvesting requirements in Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
From the 2013 report by Canada’s Department of Fisheries and Oceans.
Vandermeulen, H. 2013 [31]. Information to Support Assessment of Stock Status of Commercially Harvested Species of Marine Plants in Nova Scotia: Irish Moss, Rockweed and Kelp. DFO Can. Sci. Advis. Sec. Res. Doc. 2013/042. vi + 50 p.
https://waves-vagues.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/library-bibliotheque/349705.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2025)
Excerpts from this report—
“Upon application of the habitat protection objective described at the beginning of this report, the Nova Scotian harvest of Ascophyllum has been found to have the potential for undesirable habitat impacts at a landscape scale. Moreover, in some years in some bays the gear type and intensity of harvest may have been harmful to the resource itself. There is a pressing need to overhaul the harvest of Ascophyllum in Nova Scotia, particularly if these populations may be sensitive to climate change as indicated in the literature.”
“There is strong evidence indicating that Ascophyllum has been routinely heavily harvested in southwest Nova Scotia at bay wide scales, even well before the purported beginning of the harvest in 1959. As early as 1952, MacFarlane (1952) [59] noted that Fucus vesiculosus would invade overharvested areas in Nova Scotia, and that “under present harvesting conditions it requires at least three years before full recovery of a harvested Ascophyllum area”. In other words, from the very beginning of the Ascophyllum harvest in Nova Scotia, harvesters were employing the old European style of harvest for Ascophyllum—completely denuding an area and then waiting three years (or more) for it to grow back (Canadian Atlantic Fisheries Scientific Advisory Committee 1993) [60]. Chopin (1998) [61] states that a triennial harvest pattern, 50% removal and then a three year fallow period, was firmly established in Nova Scotia in the 1990s. All of this evidence indicates an undesirable level of habitat loss at a landscape scale.”
“In a consultant’s report to the then Nova Scotia Department of Fisheries, Cunningham (1990) [62] describes the results of field observations in southwest Nova Scotia in the summer of 1990. He describes numerous instances of overharvesting Ascophyllum at a bay wide scale—all indicating an undesirable level of habitat loss at a landscape scale. Here are some examples:
- Goat Island and Vicinity—“...recently harvested and there was no weed left.”
- Thornes Cove—“The beds at this cove and nearby were completely depleted.”
- Bear Island—“Examining several beds in the Deep Brook area we found them all harvested with the exception of a few small patches. Very little biomass is left behind, perhaps less than 2%”.
- Pinkney’s Point—“At present it would be very difficult to harvest any Asco in an economical manner.”
- Inner Spectacle Island—“...has been really overharvested.”
- Murder Island—“...has been severely harvested...”
- East side of Goose Bay—“...very heavily harvested...”
- Tusket River, western shore—“The whole area has been heavily harvested during the past several years...”
- The Tittle—“Most of the usual places were so harvested that the weed was too short to bother with.”
- Rocko Point and Abram’s River—“There is little of value to count as available weed at this point.”
- Etoile Island—“The island has been heavily harvested...”
- Pubnico Harbour western shore—“Very little Asco available.”
- Goodwins Island, Solomons Island, Egg Island, Vigneau Island—“The harvest has been heavy and complete...”
- Port Latour—“...heavily harvested...”
“Severe overharvesting was noted in Annapolis Basin between 1988 and 1991—about 80 to 90% harvest rate, or more (Sharp and Semple 1991) [63], prompting a full closure of the basin in 1995 (DFO 1998) [64]. The closure is further evidence that an undesirable level of habitat loss had occurred at a landscape scale.”
“Historically then, from the first rake harvests through to mechanization, the management regime routinely allowed an intense harvest of Ascophyllum on many shores in southwest Nova Scotia which took years to recover. The evidence strongly indicates that this took place at bay-wide scales, suggesting that an undesirable level of habitat loss had occurred at a landscape scale.”
References
- Schmidt, A.L.; Coll, M.; Romanuk, T.N.; Lotze, H.K. Ecosystem structure and services in eelgrass Zostera marina and rockweed Ascophyllum nodosum habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 437, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, R.H.; Schlesinger, W.H. Sustainable seaweed cutting? The rockweed (Ascophyllum nodosum) industry of Maine and the Maritime Provinces. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2012, 1249, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maine Dept of Marine Resources (Department of Marine Resources, Rockweed Plan Development Team). Fishery Management Plan for Rockweed (Ascophyllum nodosum). 2014. Available online: https://www.maine.gov/dmr/sites/maine.gov.dmr/files/docs/DMRRockweedFMPJan2014.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Kay, L.M.; Eddy, T.D.; Schmidt, A.L.; Lotze, H.K. Regional differences and linkage between canopy structure and community composition of rockweed habitats in Atlantic Canada. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Milewski, I.; Fast, J.; Kay, L.; Worm, B. Ecosystem-based management of seaweed harvesting. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, S.R.; Petraitis, P.S. Experimental evidence for resilience of rockweeds on rocky shores in the Gulf of Maine, USA. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 67, S211–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Morrison, L. The sustainable harvesting of Ascophyllum nodosum (Fucaceae, Phaeophyceae) in Ireland, with notes on the collection and use of some other brown algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvanneid, A.J.; Sundnes, F. Nature’s values in marine resource governance: An ethnographic case study of rockweed in Norway. Socio-Ecol. Practice Res. 2024, 6, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baardseth, E. Synopsis of Biological Data on Knobbed Wrack Ascophyllum nodosum (Linnaeus) Le Jolis; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1970; p. 56. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/b0672e (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Åberg, P. Size-based demography of the seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum in stochastic environments. Ecology 1992, 73, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A. Predation intensity in a rocky intertidal community. Effects of an algal canopy, wave action, and desiccation on predator feeding rates. Oecologia 1978, 34, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.C.; Scheibling, R.E. Structure and dynamics of epifaunal assemblages on intertidal macroalgae Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 27, 209–227. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24824696 (accessed on 15 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Vadas, R.L.; Wright, W.A.; Beal, B.F. Biomass and productivity of intertidal rockweeds (Ascophyllum nodosum LeJolis) in Cobscook Bay. Northeastern Nat. 2004, 11, 123–142. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/60225652 (accessed on 15 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Vercaemer, B.; Wong, M.C.; Bravo, M.A. Fish assemblages in rockweed (Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis) beds on the Atlantic Coast of Nova Scotia, Canada. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 3249, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Garbary, D.J.; Jamieson, M.M.; Taylor, B.R. Population ecology of the marine insect Halocladius variabilis (Diptera: Chironomidae) in the rocky intertidal zone of Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 376, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbary, D.J.; Brown, N.E.; MacDonell, H.J.; Toxopeus, J. Ascophyllum and its symbionts—A complex symbiotic community on North Atlantic shores. In Algal and Cyanobacterial Symbioses; Grube, M., Seckbach, J., Muggia, L., Eds.; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 547–572. [Google Scholar]
- Garbary, D.J.; London, J. The Ascophyllum/Polysiphonia/Mycosphaerella symbiosis. V. Mycosphaerella protects A. nodosum from desiccation. Bot. Mar. 1995, 38, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangeley, R.W.; Kramer, D.L. Tidal effects on habitat selection and aggregation by juvenile pollock Pollachius virens in the rocky intertidal zone. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series 1995, 126, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangeley, R.W.; Kramer, D.L. Use of rocky habitats by juvenile pollock Pollachius virens. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series 1995, 126, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.J. Feeding behavior of common Eider ducklings in relation to availability of rockweed habitat and duckling age. Waterbirds 2021, 24, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.; Klemmer, A.; Blomberg, E.; Baron, A.; Watson, V.; Tudor, L.; Welch, L.; Olsen, B. Macroalgae composition alters occupancy of multiple bird guilds in rocky intertidal communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 659, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, G.J. An Assessment of Ascophyllum nodosum Harvesting Methods in Southwestern Nova Scotia; Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Invertebrates and Marine Plants Division: St. Andrews, NB, Canada, 1981; p. 1012.
- MacFarlane, C. Observations on the annual growth of Ascophyllum nodosum. Trans. Nova Scotian Inst. Sci. 1932, 18, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Keser, M.; Vadas, R.L.; Larson, B.R. Regrowth of Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus under various harvesting regimes in Maine, USA. Bot. Mar. 1981, 24, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, R.L.; Wright, W.A.; Miller, S.L. Recruitment of Ascophyllum nodosum: Wave action as a source of mortality. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halat, L.; Galway, M.E.; Gitto, S.; Garbary, D.J. Epidermal shedding in Ascophyllum nodosum (Phaeophyceae): Seasonality, productivity and relationship to harvesting. Phycologia 2015, 54, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, H.M.; Claesson, S.; Erhart, S.; Schmitt, C.V.; Muhlin, J.F. Maine’s potential to be a global leader in sustainable seaweed harvesting and management. Maine Policy Rev. 2023, 32, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, R.A.; Sharp, G. Management and production of the brown algae Ascophyllum nodosum in the Canadian maritimes. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, R.A.; Sharp, G. A new approach to seaweed management in eastern Canada: The case of Ascophyllum nodosum. Can. Biol. Mar. 2001, 42, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, E.M.; Mittlestadt, H.N.; Braun, L.A.; Muhlin, J.F.; Olsen, B.J.; Webber, H.M.; Klemmer, A.J. Bed-scale impact and recovery of a commercially important intertidal seaweed. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2023, 561, 151869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, H. Information to support assessment of stock status of commercially harvested species of marine plants in Nova Scotia: Irish moss, rockweed, and kelp. DFO Can. Sci. Advis. Sec. Res. Doc. 2013, 42, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Fass, M.P. The current rockweed, Ascophyllum nodosum, harvesting regime on the shores of Nova Scotia–A review. Proc. Nova Scotian Inst. Sci. 2021, 51, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, G.J.; Sharp, J.T. Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis harvesting impacts and management options using GPS tracking of mechanical harvesters in Nova Scotia, Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 36, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, S.M.; Post, D.; Wedding, L.; Strong, A. The future of the public trust: The muddied waters of rockweed management in Maine. Ocean Coastal Law J. 2020, 25, 235. [Google Scholar]
- Lauzon-Guay, J.-S.; Ugarte, R.A.; Morse, B.L.; Robertson, C.A. Biomass and height of Ascophyllum nodosum after two decades of continuous commercial harvesting in eastern Canada. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 33, 1695–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegley, J. Ecological Implications of Rockweed, Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis, Harvesting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2001. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/etd/397/ (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Cousens, R. Quantitative reproduction and reproductive effort by stands of the brown alga Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis in southeastern Canada. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1985, 22, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, C.; Olesen, B.; Marbà, N.; Krause-Jensen, D. Reproductive allocation of the habitat-forming intertidal macroalga Ascophyllum nodosum decreases at its northern distribution edge. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e72141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, L.; Chapman, A.R.O. Effects of harvesting on Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. (Fucales, Phaeophyta): A demographic approach. J. Appl. Phycol. 1996, 8, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, R.A.; Sharp, G.; Moore, B. Changes in the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. plant morphology and biomass produced by cutter rake harvests in southern New Brunswick, Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 2006, 18, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, P.O.; Sharp, G.J.; Semple, R.E. Changes in the population structure of Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis due to mechanical harvesting. Hydrobiologia 1993, 260, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, R.H.; Hardy, S.; Prentiss, N.K.; Adey, W.H. Comment: A reexamination of bed-scale impact and recovery of a commercially important intertidal seaweed. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2024, 574, 151984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.M.; Mittlestadt, H.N.; Braun, L.A.; Muhlin, J.F.; Olsen, B.J.; Webber, H.M.; Klemmer, A.J. Bed-scale rockweed harvest findings are not altered by study critiques, a response to Seeley et al. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2024, 578, 152039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S. Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 1984, 54, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, L.; Merzouk, A.; Bergeron, P.; Johnson, L.E. Managing disturbance: The response of a dominant intertidal seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis to different frequencies and intensities of harvesting. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzon-Guay, J.-S.; Feibel, A.I.; Morse, B.L.; Ugarte, R.A. Morphology of Ascophyllum nodosum in relation to commercial harvesting in New Brunswick, Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.L. Meristems and growth control in Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol. New Phytol. 1970, 69, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousens, R. Frond size distributions and the effects of algal canopy on the behaviour of Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jolis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 92, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, R.L.; Wright, W.A. Recruitment, growth and management of Ascophyllum nodosum. Actas II Congr. Algas Mar. Chilenas 1986, 2, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, L. Understanding the Impacts of Anthropogenic Effects and Habitat Variability Interactions on Maine’s Rocky Intertidal Ecosystem. Master’s Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2022. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/etd/3709 (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Johnston, E.M.; Klemmer, A.J.; Braun, L.A.; Mittelstaedt, H.N.; Muhlin, J.F.; Webber, H.M.; Olsen, B.J. Evaluating bottom-up forcing of a rocky intertidal resource harvest on a high trophic- level consumer group. Estuar. Coastal Shelf Sci. 2024, 298, 10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstaedt, H.N. Untangling Influences of Community Dynamics at the Coastal Interface. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2023. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/etd/3860 (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Webber, H.M. The Foundation Roles of Rockweed, Ascophyllum nodosum (Linneaus) Le Jolis, in Maine’s Rocky Intertidal Zone. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2024. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/etd/3954 (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Johnston, E.M. Cross-Trophic-Level Dynamics in Aquatic Ecosystems and Their Application Across Ecological Contexts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2023. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/etd/3764 (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- David, H.M. Studies in the autecology of Ascophyllum nodosum Le Jol. J. Ecol. 1943, 31, 178–198. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2256547 (accessed on 15 November 2025). [CrossRef]
- Printz, H. Recuperation and recolonization in Ascophyllum. Int. Seaweed Symp. 1956, 2, 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Printz, H. Investigations of the failure of recuperation and repopulation in cropped Ascophyllum nodosum. Norske Vidensk. Akad. K. Mat. Nat. Kl. 1959, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Garbary, D.J.; Fass, M.P.; Vandermeulen, H. Invasive Fucus serratus (Fucaceae, Phaeophyceae) responds to climate change along the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia. Bot. Mar. 2021, 64, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, C. A survey of certain seaweeds of commercial importance in southwest Nova Scotia. Can. J. Bot. 1952, 30, 8–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Atlantic Fisheries Scientific Advisory Committee. Rockweed in Southwestern New Brunswick; Canadian Atlantic Fisheries Scientific Advisory Committee: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 1993.
- Chopin, T. The seaweed resources of eastern Canada. In Seaweed Resources of the World; Critchley, A., Ohno, M., Eds.; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Yokosuka, Japan, 1998; pp. 273–302. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, W. An assessment of Ascophyllum nodosum Resources in Selected Areas of Annapolis, Digby, Yarmouth and Shelburne Counties from a Commercial Perspective. Consultant Report to Nova Scotia Department of Fisheries. 1990. Available online: https://publications.gc.ca/pub?id=9.577630&sl=0 (accessed on 15 November 2025).
- Sharp, G.; Semple, R. An Assessment of Ascophyllum nodosum Resources in Scotia/Fundy 1990; Canadian Atlantic Fisheries Scientific Advisory Committee: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 1991.
- DFO (Department of Fisheries and Oceans). Rockweed in the Maritimes; DFO Science Stock Status Report; DFO: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1998.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).