Numerical Study on the Keying of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with Chain Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modeling
2.1. CEL Method
2.2. CEL Model
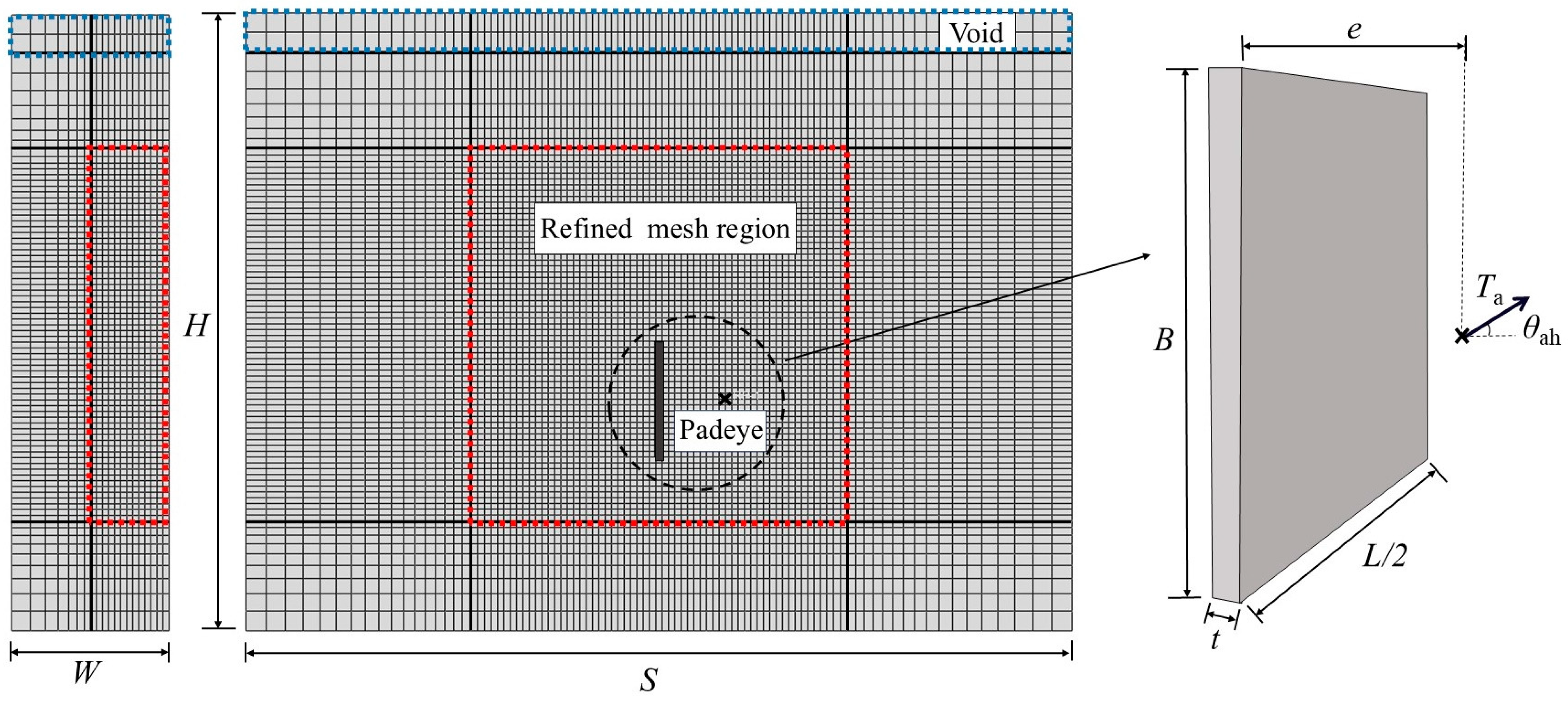
2.2.1. Model Establishment
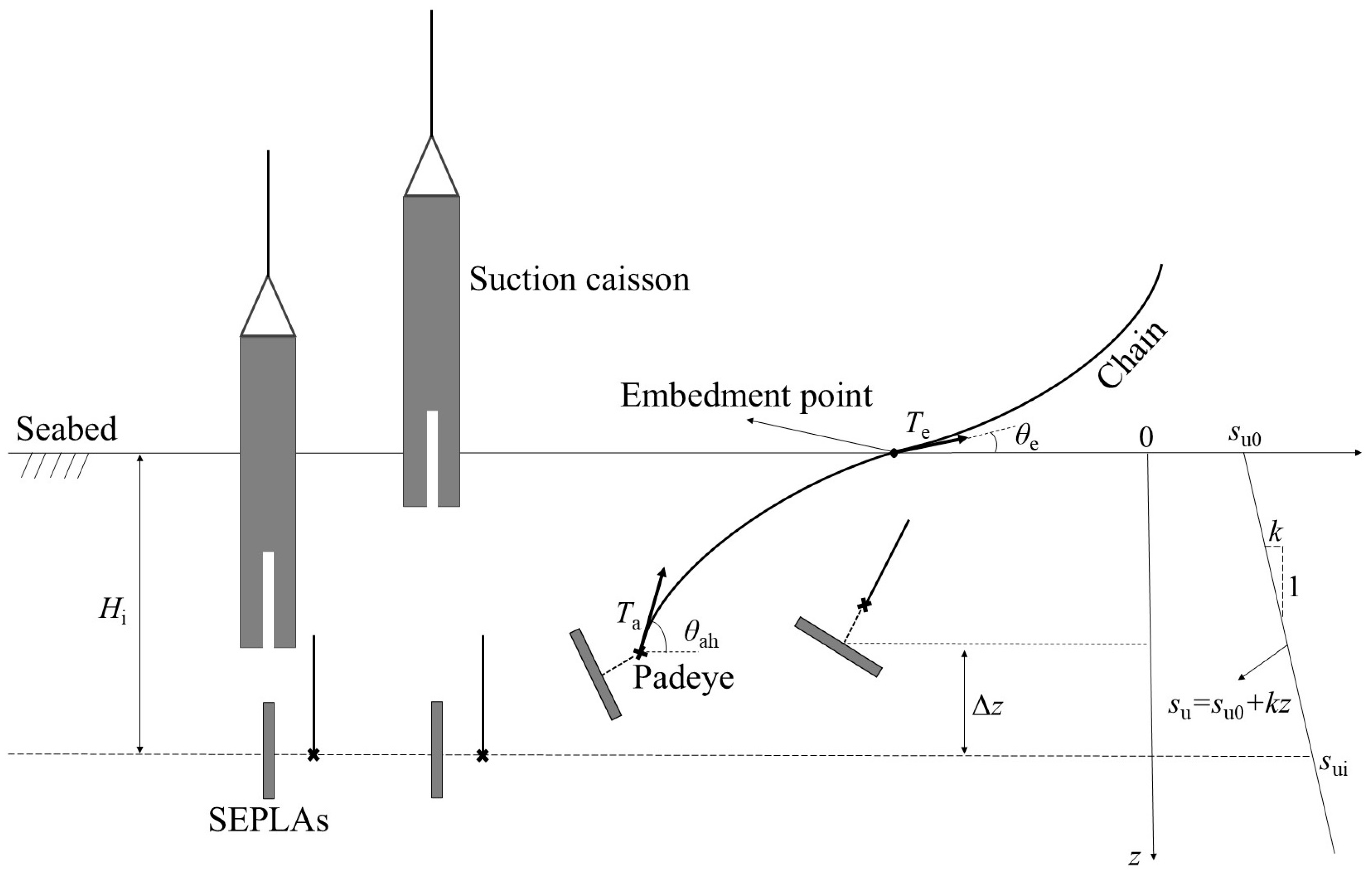
2.2.2. Incorporating Chain Effects into the CEL Model
- Give the initial values of Ta and θah at the padeye, i.e., Ta = Ta0 and θah = θah0.
- Calculate Tax = Tacosθah and Taz = Tasinθah acted on the padeye, and conduct an incremental CEL analysis.
- If the time interval Δt is equal or greater than the control time interval tc, update the padeye location (xa, za) and calculate the average rotational velocity urave = Δur/Δt. ur is the rotation angle of the anchor. If Δt < tc, execute step b.
- Compare the values of urave and the control rotational angular velocity urc. If urave > urc, apply a new drag force Ta = Ta − ΔT, otherwise Ta= Ta + ΔT, where ΔT is a load increment.
- Update the value θah via Equation (1), with the updated Ta and za.
- Repeat steps b–e until the predefined inclination of the SEPLA is achieved.
2.3. Sensitivity of FE Parameters
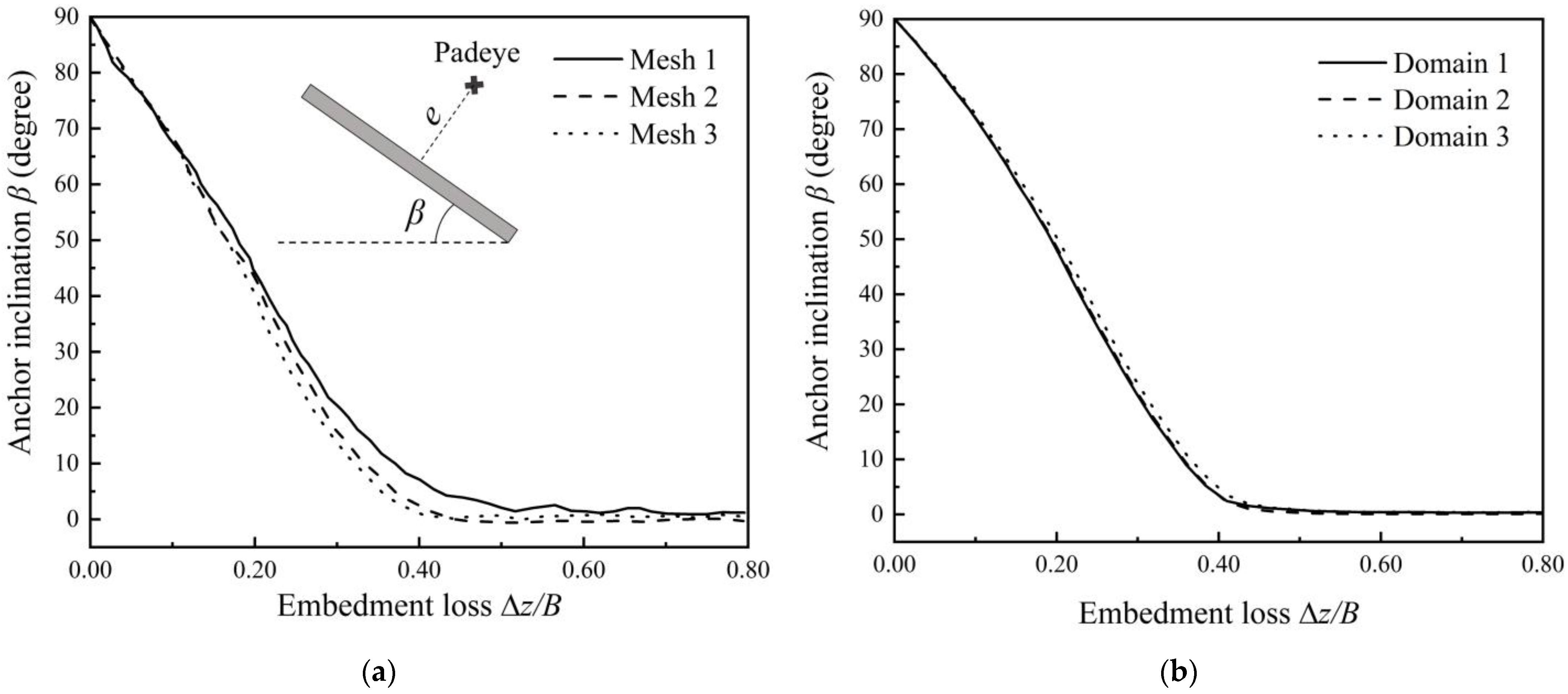
2.3.1. Sensitivity of Mesh and Domain Sizes
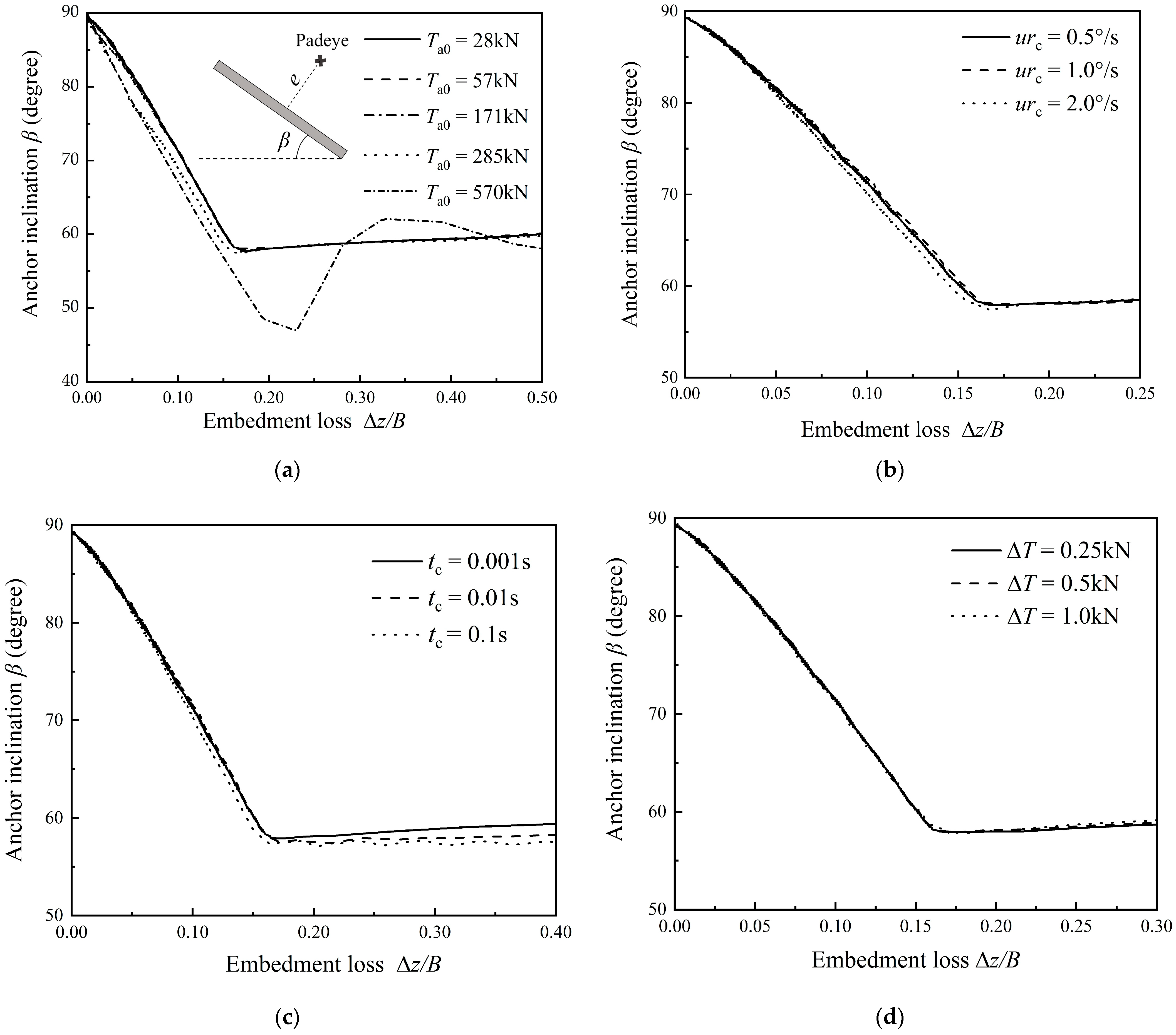
2.3.2. Sensitivity of Parameters of VUAMP
2.4. Validation of the CEL Model
3. Parametric Study
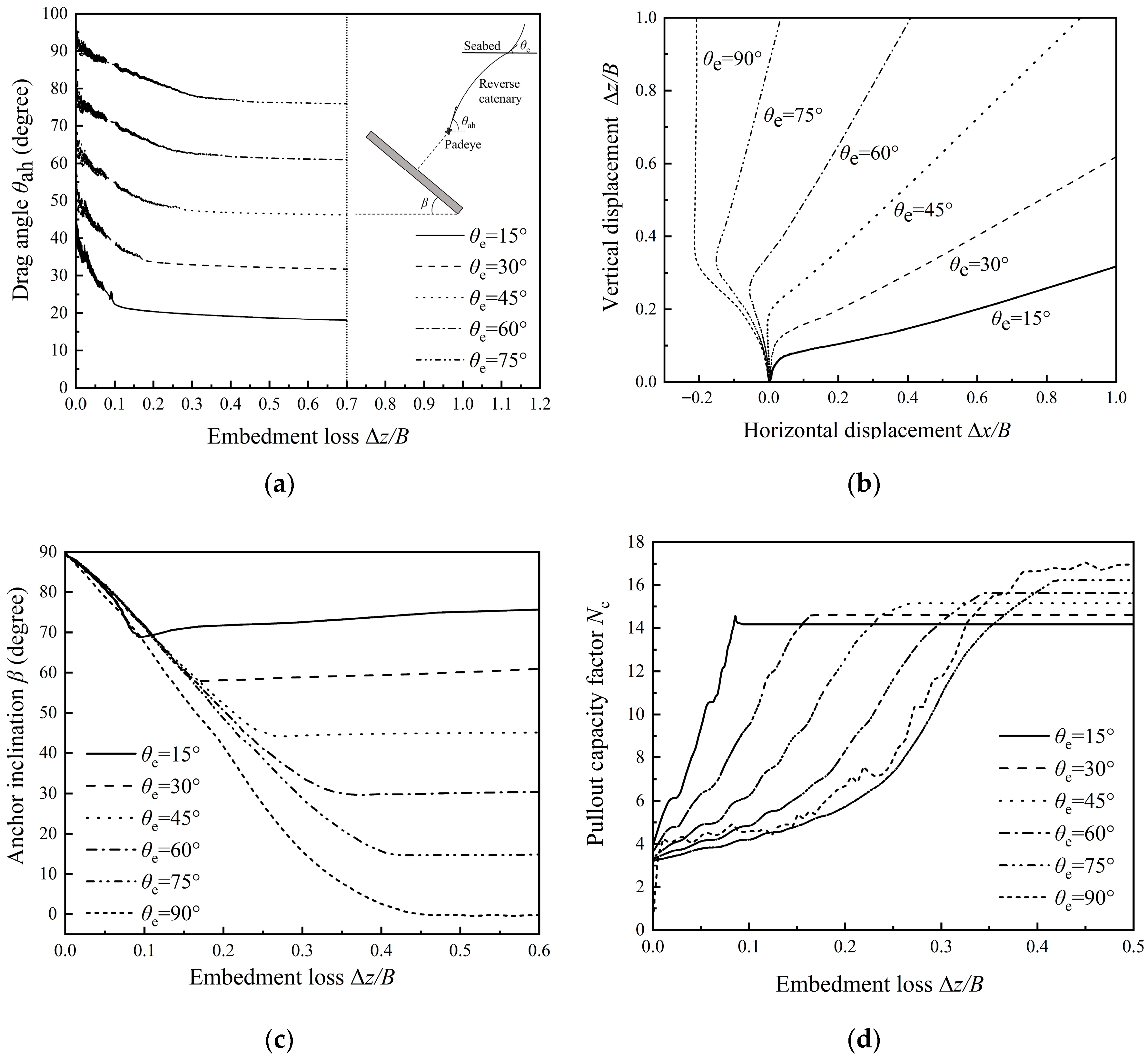
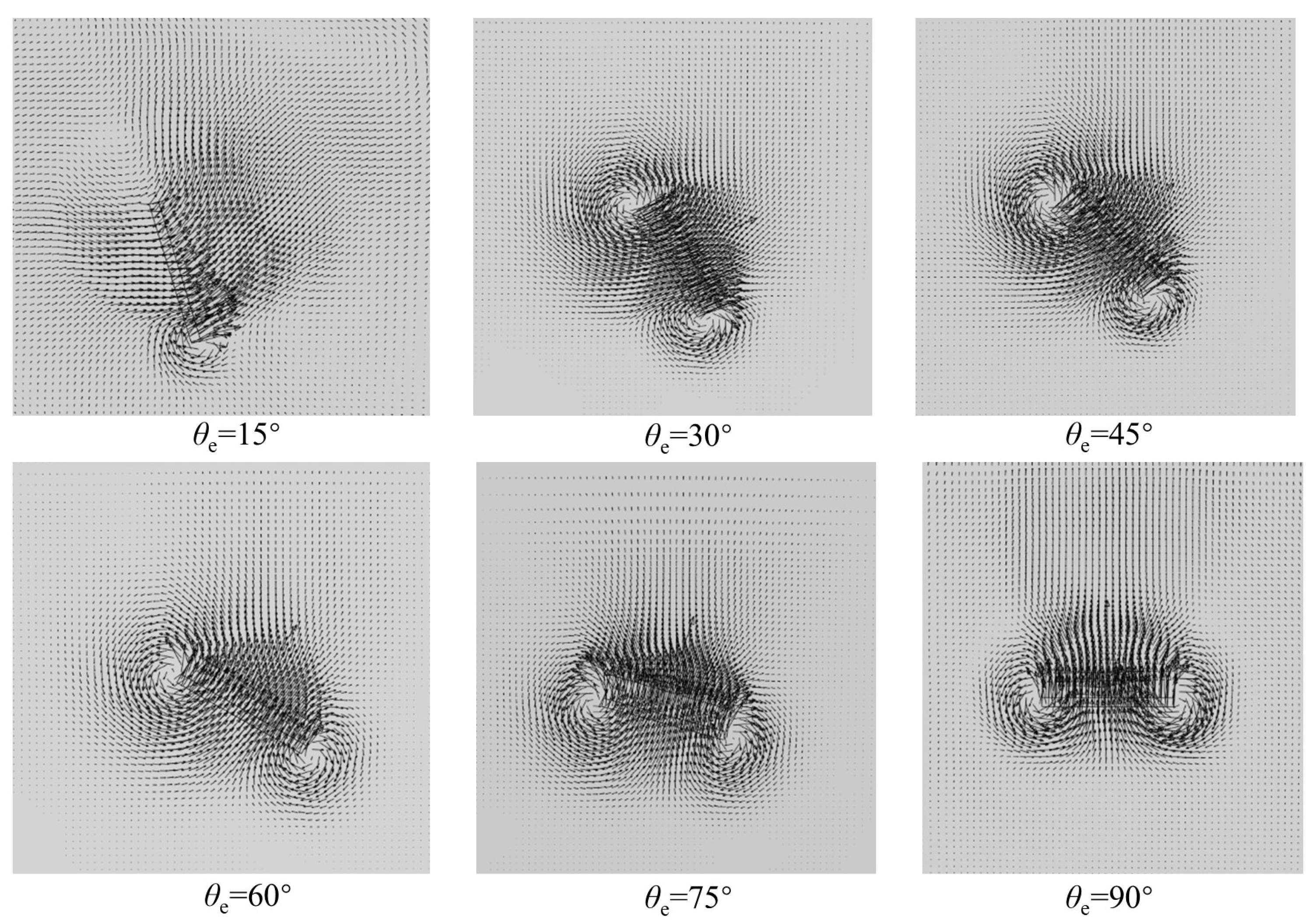
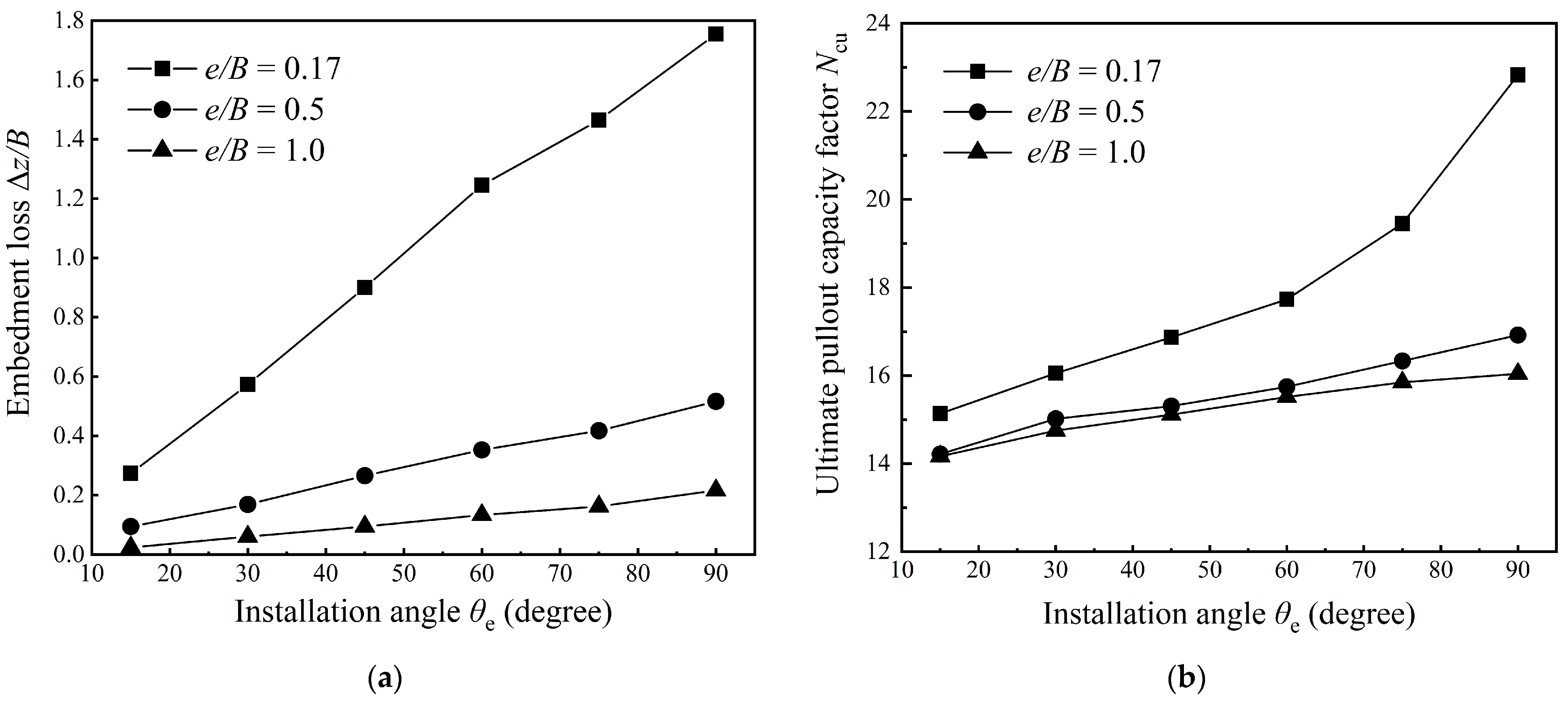
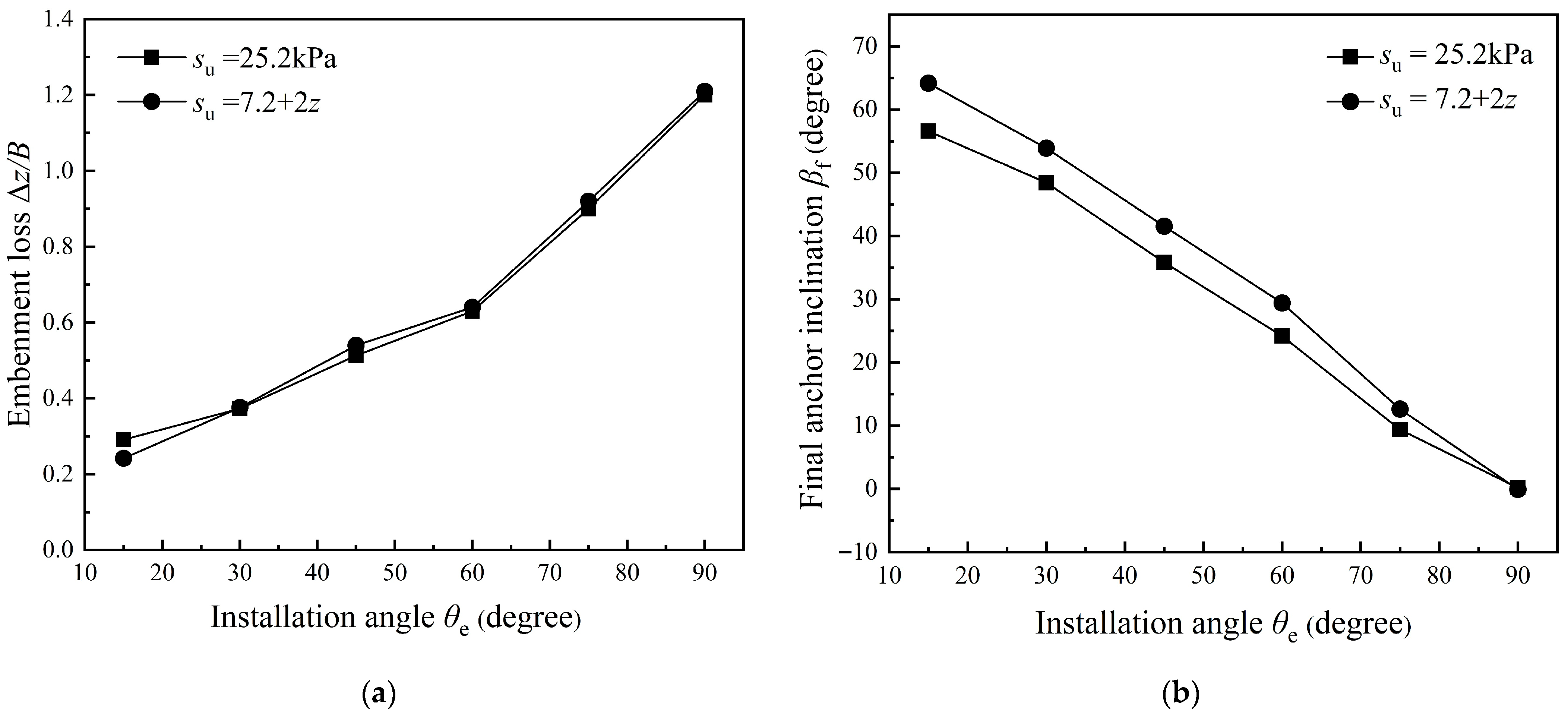
3.1. Installation Angle
3.2. Load Eccentricity
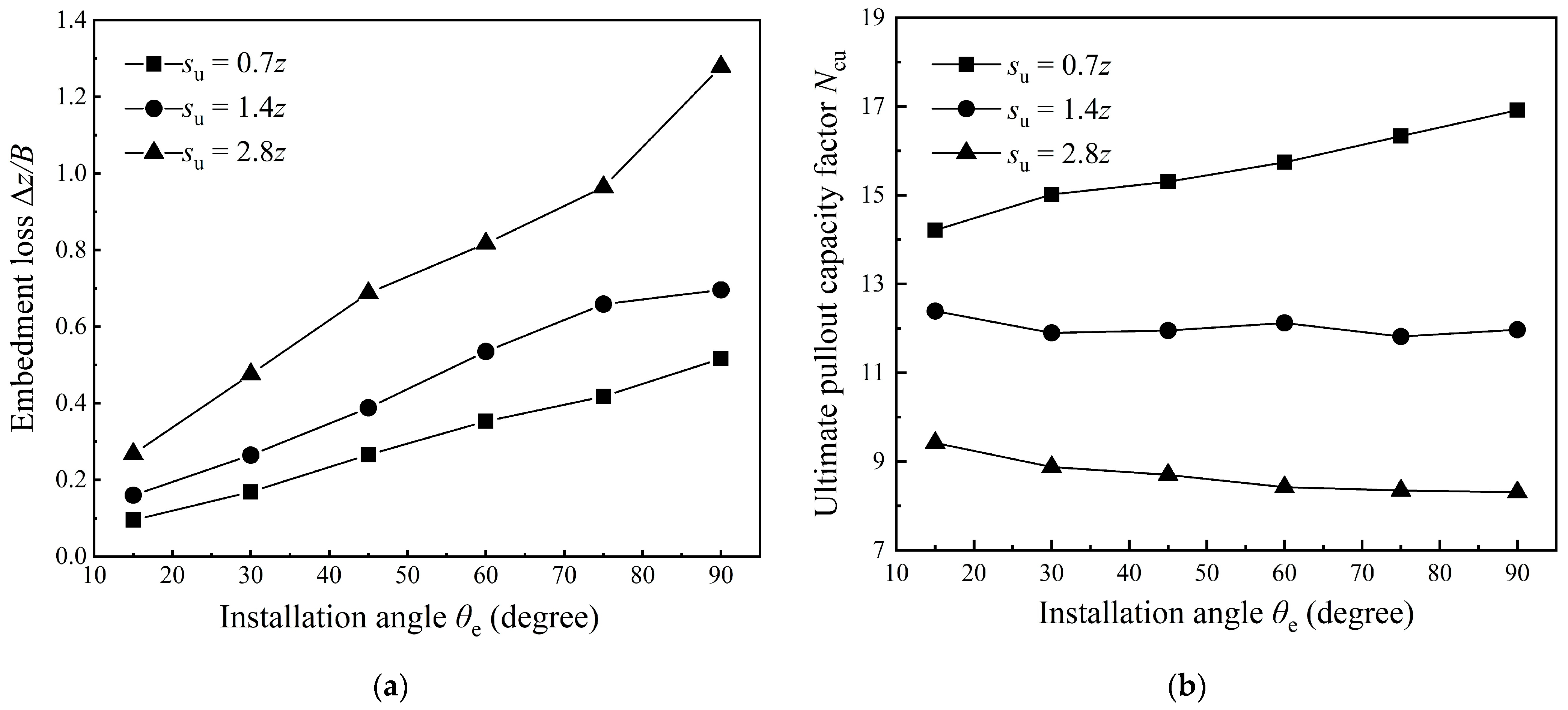
3.3. Soil Strength
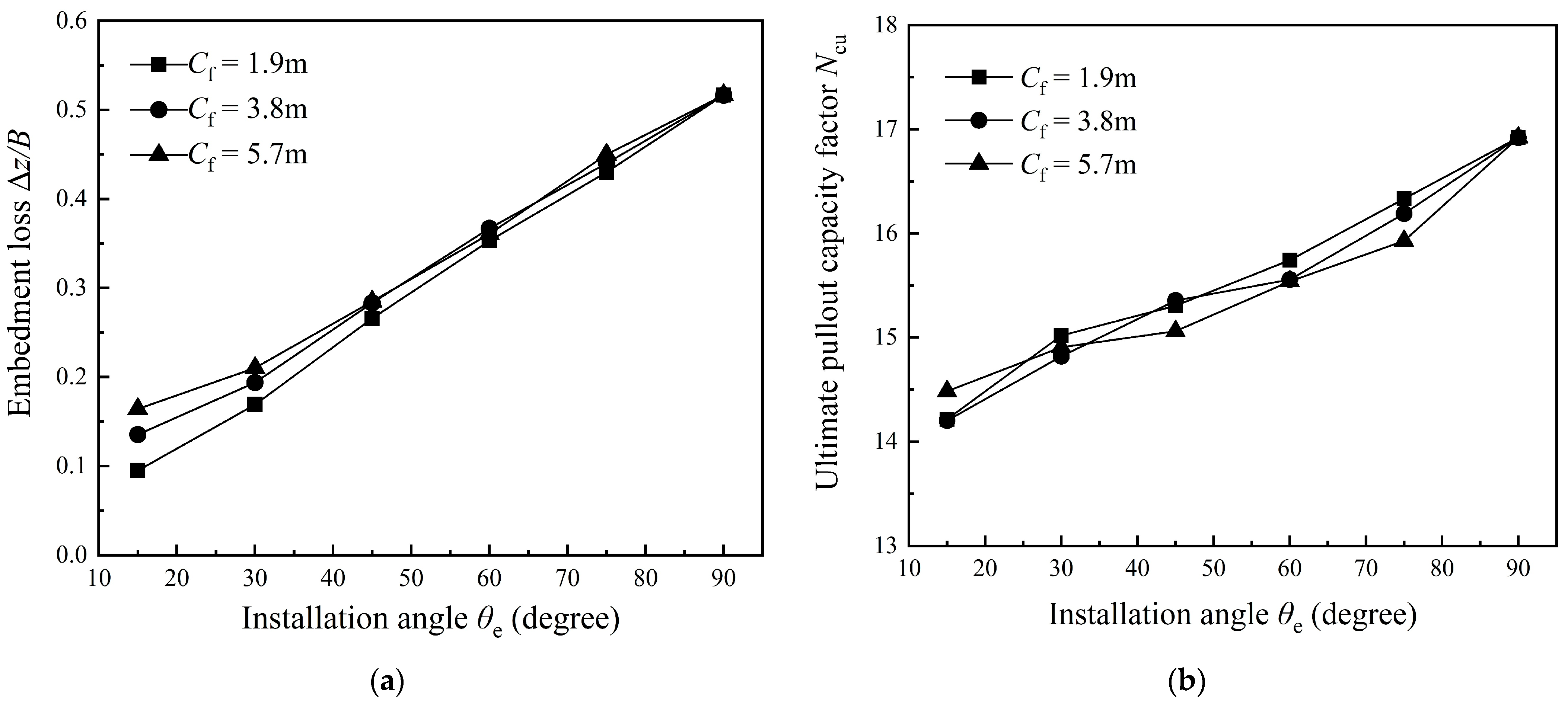
3.4. Mechanical Parameters of the Chain
4. Empirical Formulae
4.1. Embedment Loss
4.2. Ultimate Pullout Capacity Factor
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CASPA | Chain and Suction Embedded Plate Anchor Plasticity Analysis |
| CEL | Coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian |
| FE | Finite Element |
| LDFE | Large Deformation Finite Element |
| RITSS | Remeshing and Interpolation Technique with Small Strain |
| SEPLAs | Suction Embedded Plate Anchors |
| VUAMP | Vectorized User Amplitude |
| A | fluke area |
| B | anchor width |
| Cf | combination parameter which denotes the product of d, Ncl and En |
| d | chain diameter |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| En * | multiplier to give the effective width in the normal direction |
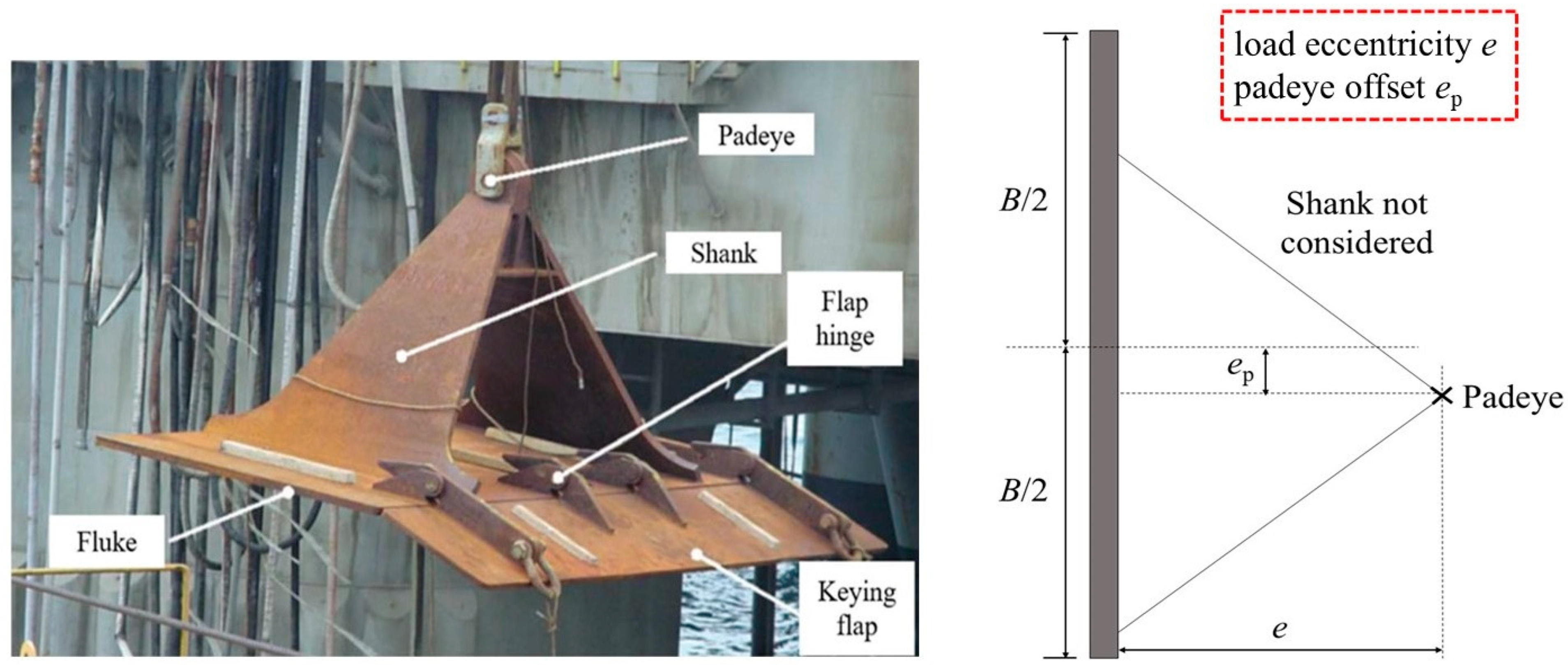
| e | load eccentricity |
| ep | padeye offset |
| H | soil height |
| Hi | initial embedment depth of the anchor |
| k | soil strength gradient |
| L | anchor length |
| Nc * | pullout capacity factor for the anchor |
| Ncl * | pullout capacity factor for the chain |
| Ncu * | ultimate pullout capacity factor for the anchor |
| R2 * | correlation coefficient for the fitted curve |
| S | soil length |
| su | undrained shear strength of the soil |
| suc | soil strength of the anchor center during the keying |
| sui | soil strength at the initial embedment depth |
| Ta | drag force at the padeye |
| Ta0 | initial value of Ta |
| Te | drag force at the embedment point |
| t | anchor thickness |
| tc | control time interval |
| ur | rotational angular velocity |
| urc | control rotational angular velocity |
| urave | average rotational velocity |
| W | soil width |
| (xa, za) | padeye location |
| β | anchor inclination to the horizontal |
| βf | final anchor inclination to the horizontal |
| ΔT | load increment |
| Δx/B * | normalized horizontal displacement of the anchor |
| Δz/B * | normalized embedment loss |
| γ′anchor | submerged unit weight of the anchor |
| γ′soil | submerged unit weight of the soil |
| θah | drag angle at the padeye |
| θah0 | initial value of θah |
| θe | drag angle at the embedment point which is also called the installation angle |
| μ | frictional coefficient between soil and chain |
| μc | frictional coefficient between soil and anchor |
| * Dimensionless parameters | |
References
- Tomassi, A.; de Franco, R.; Trippetta, F. High-resolution synthetic seismic modelling: Elucidating facies heterogeneity in carbonate ramp systems. Pet. Geosci. 2025, 31, petgeo2024-047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Ye, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Tang, H.; Han, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, S. Load-Bearing Performance of SEPLAs in Spatially Variable Clay. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. A 2025, 11, 04025029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Lin, H.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, W.; Ding, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Q. A large deformation finite element investigation of SEPLA: Failure mechanism and bearing capacities when loaded differently. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 143, 103864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerfontaine, B.; White, D.; Kwa, K.; Gourvenec, S.; Knappett, J.; Brown, M. Anchor geotechnics for floating offshore wind: Current technologies and future innovations. Ocean Eng. 2023, 279, 114327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, B.; Treu, H.; Fulton, T. Field Testing of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Stavanger, Norway, 17–22 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y. Effects of soil remoulding on keying behaviours of strip plate anchors with padeye offset. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 141, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, C.; Lowmass, A.; Gaudin, C.; Randolph, M. Physical modelling to assess keying characteristics of plate anchors. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Physical Modelling in Geotechnics, London, UK, 20 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Hu, Y. Three-dimensional numerical analysis of the keying of vertically installed plate anchors in clay. Comput. Geotech. 2009, 36, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Cassidy, M.; Gaudin, C. The influence of padeye offset on plate anchor re-embedding behaviour. Geotech. Lett. 2014, 4, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gaudin, C.; Randolph, M.; Cassidy, M. Influence of padeye offset on the bearing capacity of three dimensional plate anchors. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Randolph, M.; Cassidy, M. Analytical solution for ultimate embedment depth and potential holding capacity of plate anchors. Geotechnique 2015, 65, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gaudin, C.; Cassidy, M.; Randolph, M. Considerations on the design of keying flap of plate anchors. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Gaudin, C.; Cassidy, M. Improving plate anchor design with a keying flap. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gaudin, C.; Randolph, M. Large deformation finite element analysis investigating the performance of anchor keying flap. Ocean Eng. 2013, 59, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Yu, L. Keying behavior of suction embedded plate anchors with flap in clay. Ocean Eng. 2017, 131, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, C.; Simkin, M.; White, D.J.; O’Loughlin, C. Experimental investigation into the influence of a keying flap on the keying behaviour of plate anchors. In Proceedings of the Twentieth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Beijing, China, 20–25 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Cassidy, M.; Tian, Y.; Gaudin, C. Incorporating shank resistance into prediction of the keying behavior of suction embedded plate anchors. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; O’Loughlin, C. Pullout capacity and rotational behaviour of square anchors. In Pullout Capacity and Rotational Behaviour of Square Anchors; Taylor & Francis: Hong Kong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Hu, Y.; Randolph, M. Keying of rectangular plate anchors in normally consolidated clays. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tho, K.; Chen, Z.; Leung, C.; Chow, Y. Pullout behaviour of plate anchor in clay with linearly increasing strength. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, B.; Chatterjee, S. Effect of keying-induced soil remolding on the ultimate pull-out capacity and embedment loss of strip anchors in clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Yin, Z. Numerical investigations into the drainage effects on the behaviors of plate anchors under unidirectional and combined loadings. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 188, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, C.; Tham, K.; Ouahsine, S. Keying of plate anchors in NC clay under inclined loading. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2009, 19, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy, M.; Gaudin, C.; Randolph, M.; Wong, P.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y. A plasticity model to assess the keying of plate anchors. Geotechnique 2012, 62, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Aubeny, C.P.; Murff, J.D. Behavior of suction embedded plate anchors during keying process. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2012, 138, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, K.; Peng, J.; Xiao, Z. A unified explicit formula for calculating the maximum embedment loss of deepwater anchors in clay. Ocean Eng. 2021, 236, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hu, Y.; O’Loughlin, C.; Randolph, M. Loss in anchor embedment during plate anchor keying in clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H. Numerical implementation of the installation/mooring line and application to analyzing comprehensive anchor behaviors. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 54, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P. An efficient approach to incorporate anchor line effects into the coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian analysis of comprehensive anchor behaviors. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 59, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tho, K.; Leung, C.; Chow, Y. Large deformation numerical analysis of plate anchor keying process. In Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics III, Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics (ISFOG 2015), London, UK, 10–12 June 2015; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Xu, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, F. Finite—Element Analysis of Keying Process of Plate Anchors in Three—Layer Soft—Stiff—Soft Clay Deposits. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 7835379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zong, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, J. Ultimate pullout capacity of a square plate anchor in clay with an interbedded stiff layer. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8867678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, K.; Zhao, Y. Numerical investigation on the penetration of gravity installed anchors by a coupled Eulerian–Lagrangian approach. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 60, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, S.; Yin, J. Analysis of the drag anchor behaviour at shallow depths. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 160, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Tian, Y.; Cassidy, M. Investigation of the installation process of drag-in plate anchors from LDFE modelling. Geotechnique 2022, 74, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chow, Y.; Leung, C. Effect of Fluke Inclination on Behavior of Drag Anchor in Uniform Clay Under Unidirectional and Combined Loading. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2019, 141, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, R. Evaluation of undrained breakout capacity of shallowly buried plate anchors in cohesive soils using a tension-truncated Tresca strength criterion. Ocean Eng. 2025, 338, 122042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubecker, S.; Randolph, M. Profile and frictional capacity of embedded anchors chains. Int. J. Geoenviron. Eng. 1995, 21, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


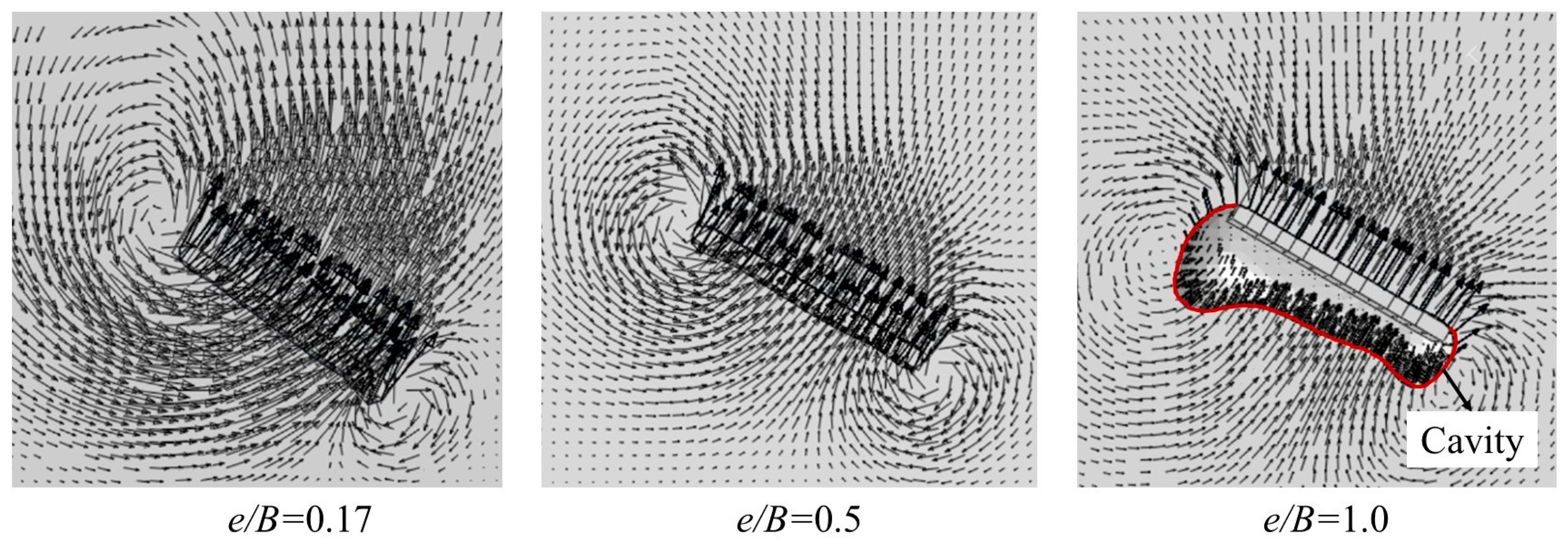

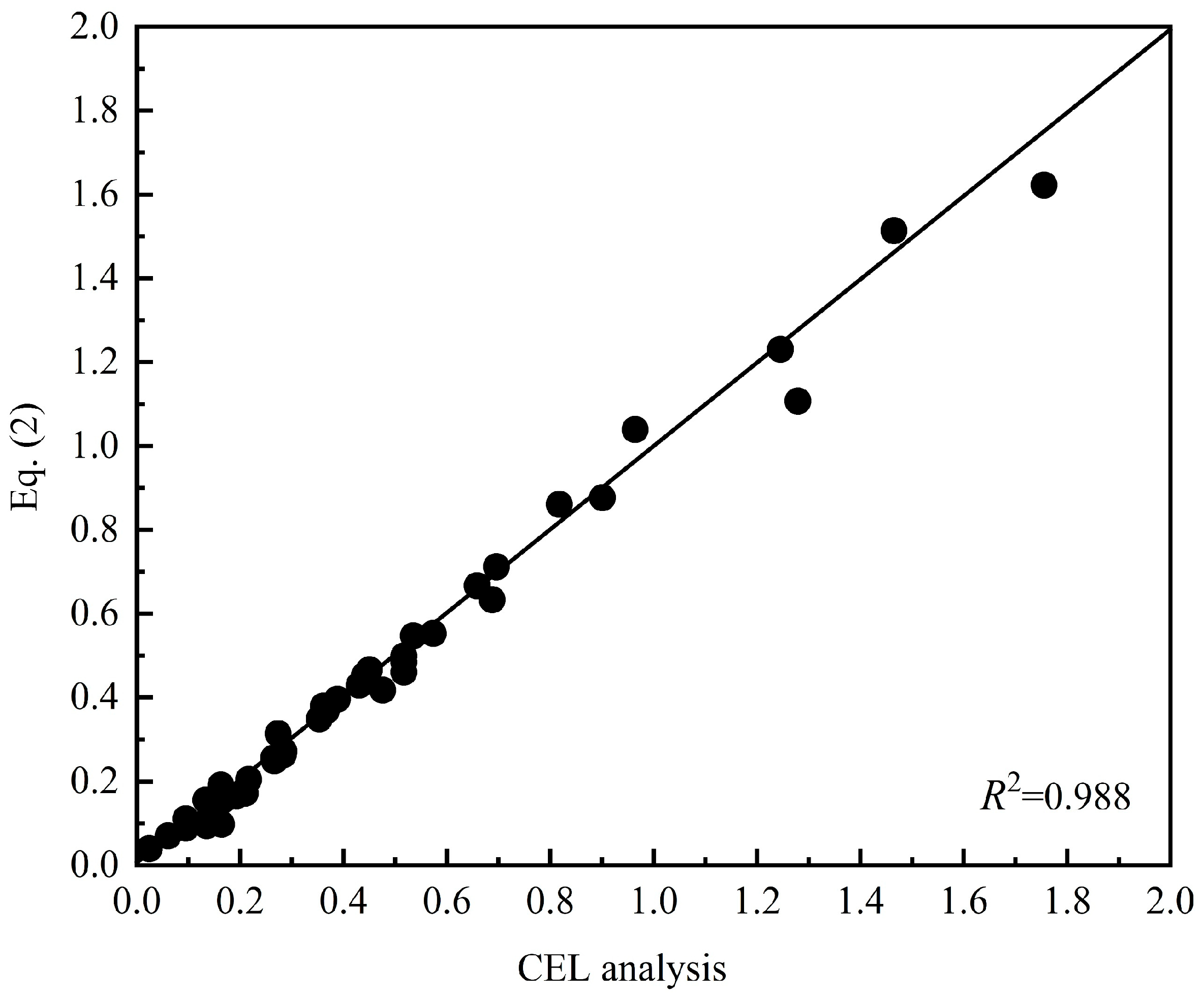
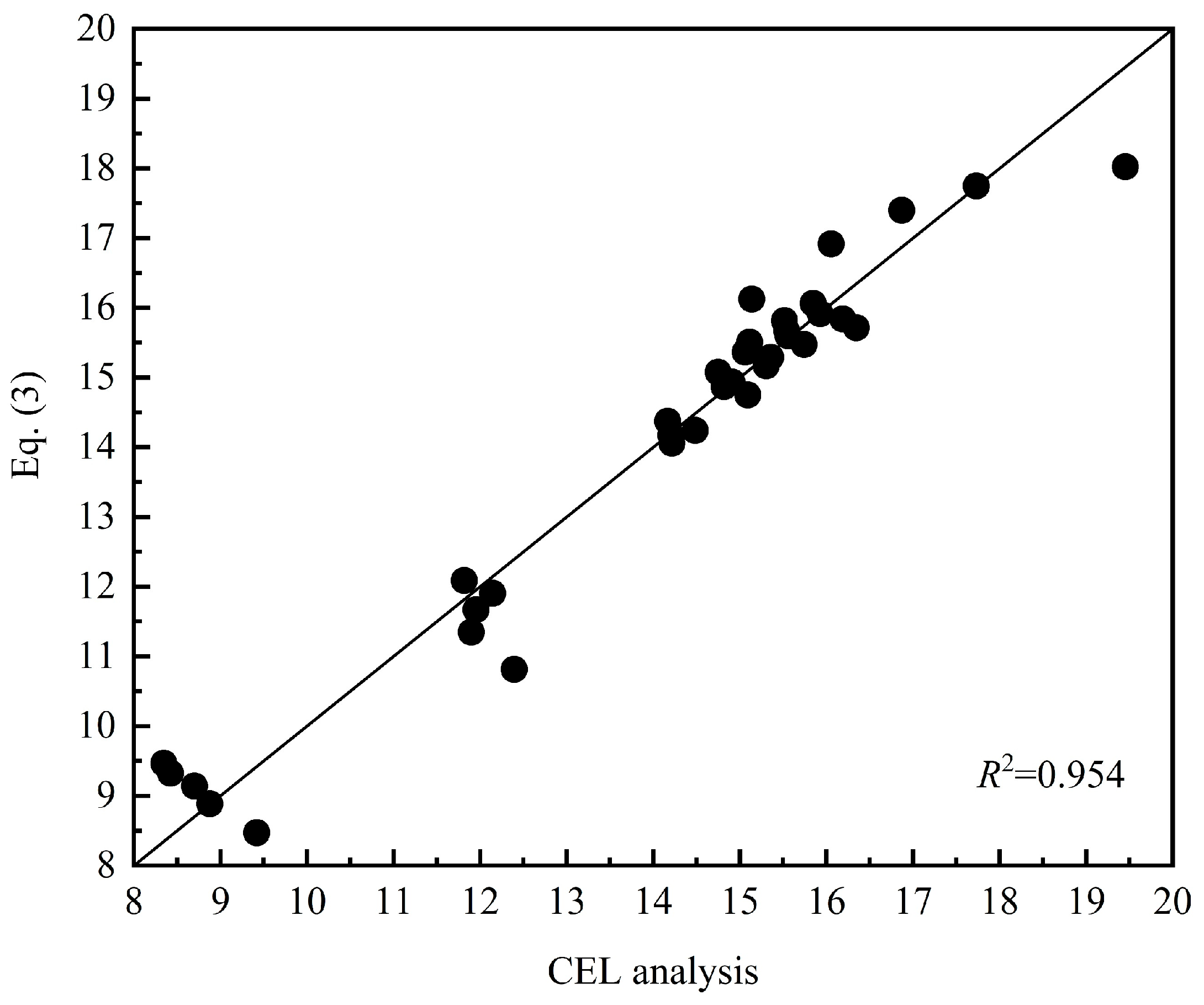
| Type | Model Parameters | RITSS [19] | CASPA [17] | Centrifuge Test [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | S (m) | 19.7 | 27.8 | 25.8 |
| W (m) | 4 | 7.9 | 4 | |
| H (m) | 16 | 25.9 | 16 | |
| su (kPa) | 0.7z | 1 + 1.25z | 18 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | |
| γ′soil (kN/m3) | 6.5 | 6.5 | 9.2 | |
| E/su | 500 | 500 | 500 | |
| Anchor | L (m) | 3 | 7.92 | 4 |
| B (m) | 3 | 4.64 | 4 | |
| t (m) | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.2 | |
| e/B | 0.17, 0.5 *, **, 1.0 | 0.558 | 0.625 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| γ’anchor (kN/m3) | 67 | 65 | 67.8 | |
| Hi/B | 3 | 4.47 | 3 | |
| Chain | Ncl, En, μ | 7.6, 1, 0.1 | 7.6, 1, 0.1 | 7.6, 1, 0.1 |
| d (m) | 0.1 | 0.41 | 0.1 | |
| θe (°) | 30 **, 45, 60, 75, 90 * | 40 | 60 |
| Case | Minimum Mesh Size | Length of Soil Domain (m) | Number of Elements | Embedment Loss Δz/B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh 1 | B/10 | 19.7 | 32,256 | 0.58 |
| Mesh 2 | B/20 | 19.7 | 152,520 | 0.51 |
| Mesh 3 | B/30 | 19.7 | 406,000 | 0.49 |
| Domain 1 | B/20 | 10.7 | 83,640 | 0.51 |
| Domain 2 | B/20 | 19.7 | 152,520 | 0.51 |
| Domain 3 | B/20 | 37.7 | 250,920 | 0.52 |
| Cases | Ta0 (kN) | urc (°/s) | tc (s) | ΔT (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 57 171 285 570 | 1.0 | 0.001 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 114 | 0.5 1.0 2.0 | 0.001 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 114 | 1.0 | 0.1 0.01 0.001 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 114 | 1.0 | 0.001 | 0.25 0.5 1.0 |
| Case | Cf (m) | e/B | su (kPa) | θe (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.9 | 0.17 | 0.7z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 2 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.7z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 3 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 1.4z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 4 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 2.8z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 5 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 0.7z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 6 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 0.7z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| 7 | 5.7 | 0.5 | 0.7z | 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90 |
| θe (°) | e/B | su (kPa) | Cf (m) | CEL Analysis | Equation (2) | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20° | 0.3 | 1.0z | 2.85 | 0.300 | 0.272 | 9.33% |
| 40° | 0.6 | 2.0z | 4.05 | 0.375 | 0.391 | 4.27% |
| 90° | 0.3 | 1.0z | 2.85 | 1.041 | 1.105 | 6.15% |
| 90° | 0.6 | 2.0z | 4.05 | 0.783 | 0.785 | 0.26% |
| θe (°) | e/B | su (kPa) | Cf | CEL Analysis | Equation (3) | Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20° | 0.3 | 1.0z | 2.85 | 14.279 | 13.865 | 13.640 | 1.63% |
| 40° | 0.6 | 2.0z | 4.05 | 9.89 | 10.278 | 10.666 | 3.78% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, Y. Numerical Study on the Keying of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with Chain Effects. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112056
Li X, Yan W, Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Lang Y. Numerical Study on the Keying of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with Chain Effects. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xue, Wei Yan, Yanbing Zhao, Yongye Li, Yan Zhang, and Yun Lang. 2025. "Numerical Study on the Keying of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with Chain Effects" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112056
APA StyleLi, X., Yan, W., Zhao, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., & Lang, Y. (2025). Numerical Study on the Keying of Suction Embedded Plate Anchors with Chain Effects. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112056








