The Impact of Canal Construction on the Hydro-Morphodynamic Processes in Coastal Tidal Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
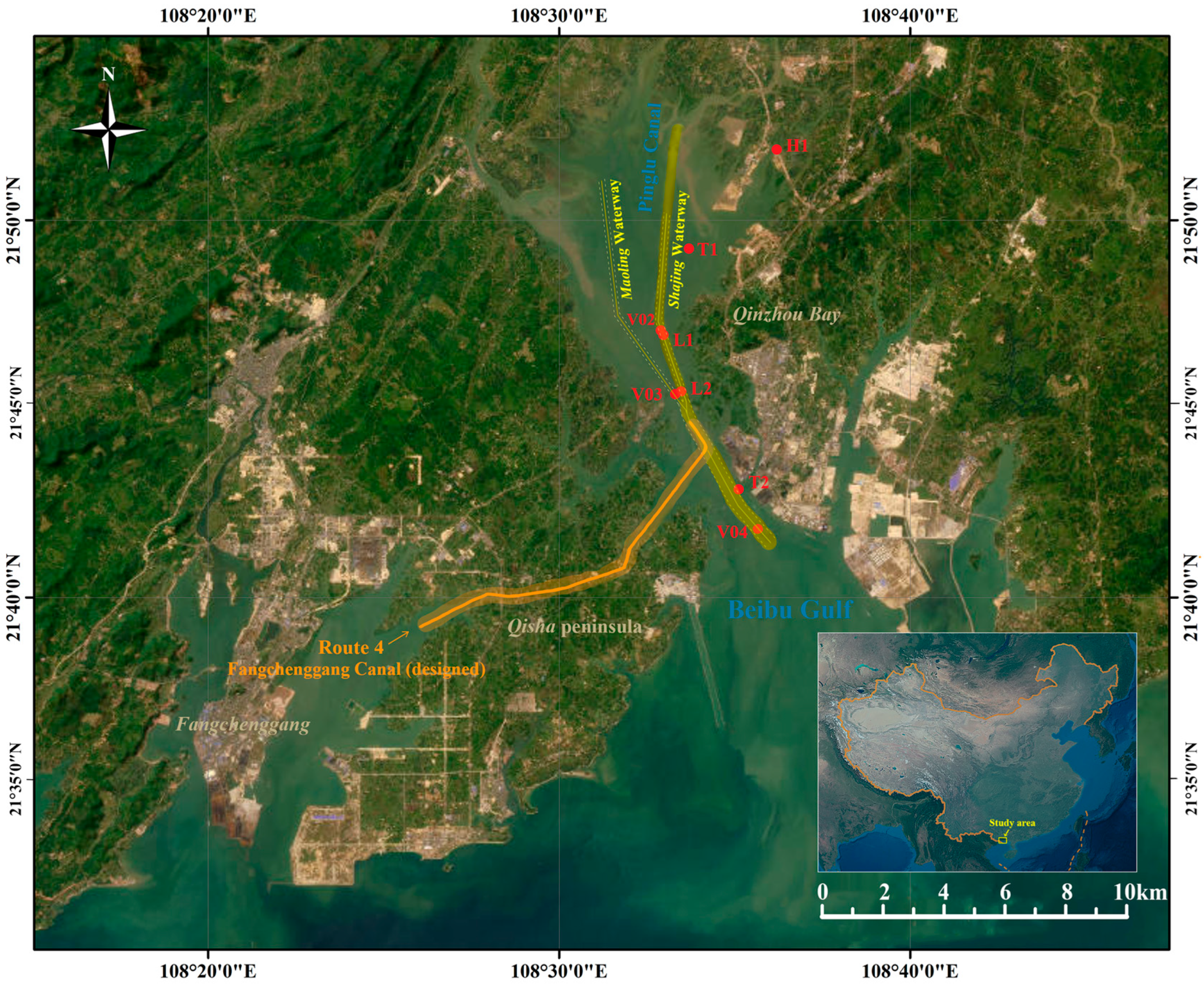
2.1. Description of the Research Domain
2.2. Methods
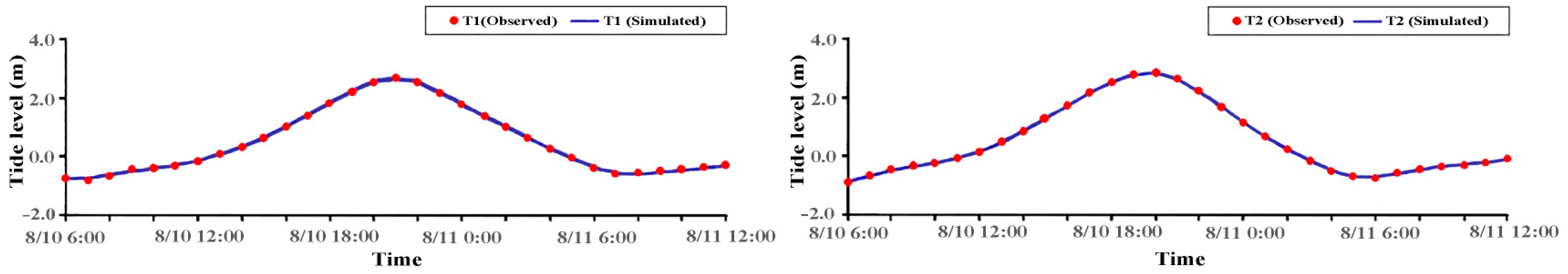
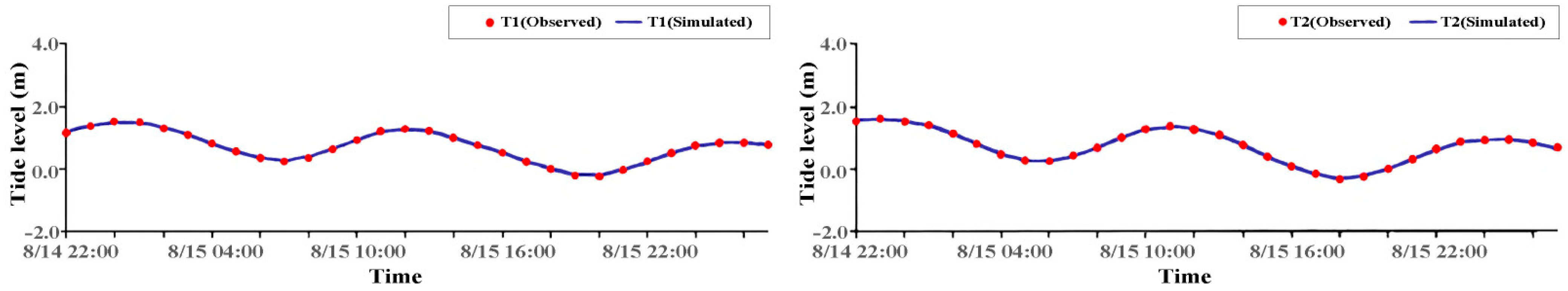
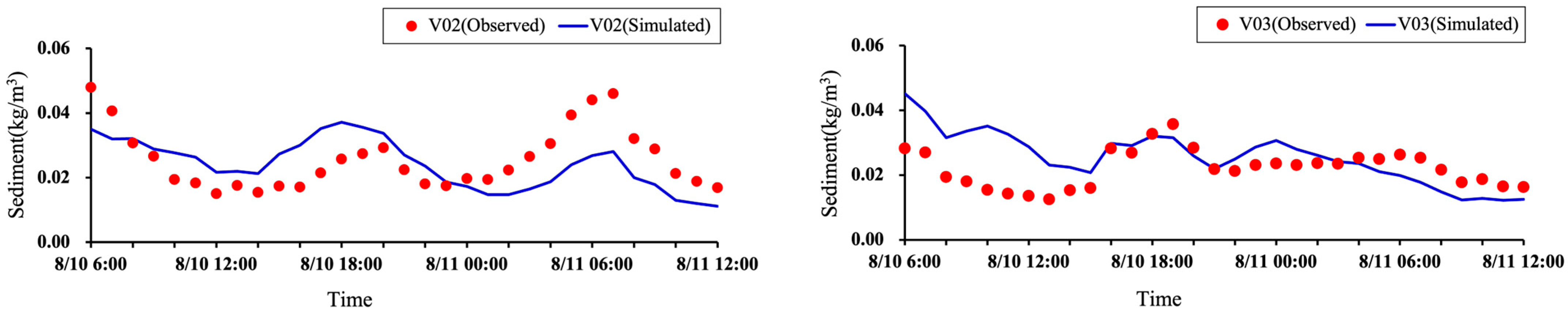
2.3. Model Validation
3. Results
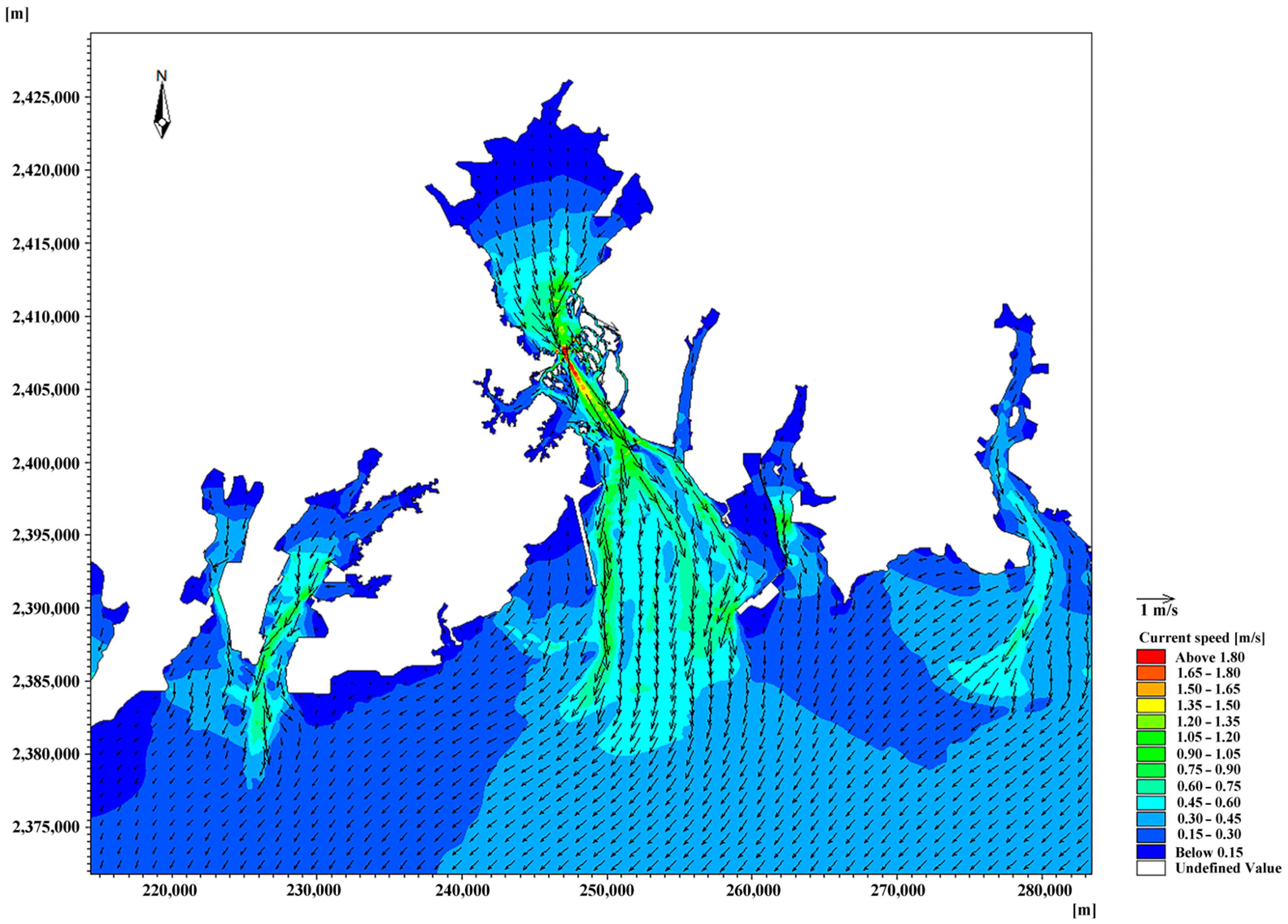
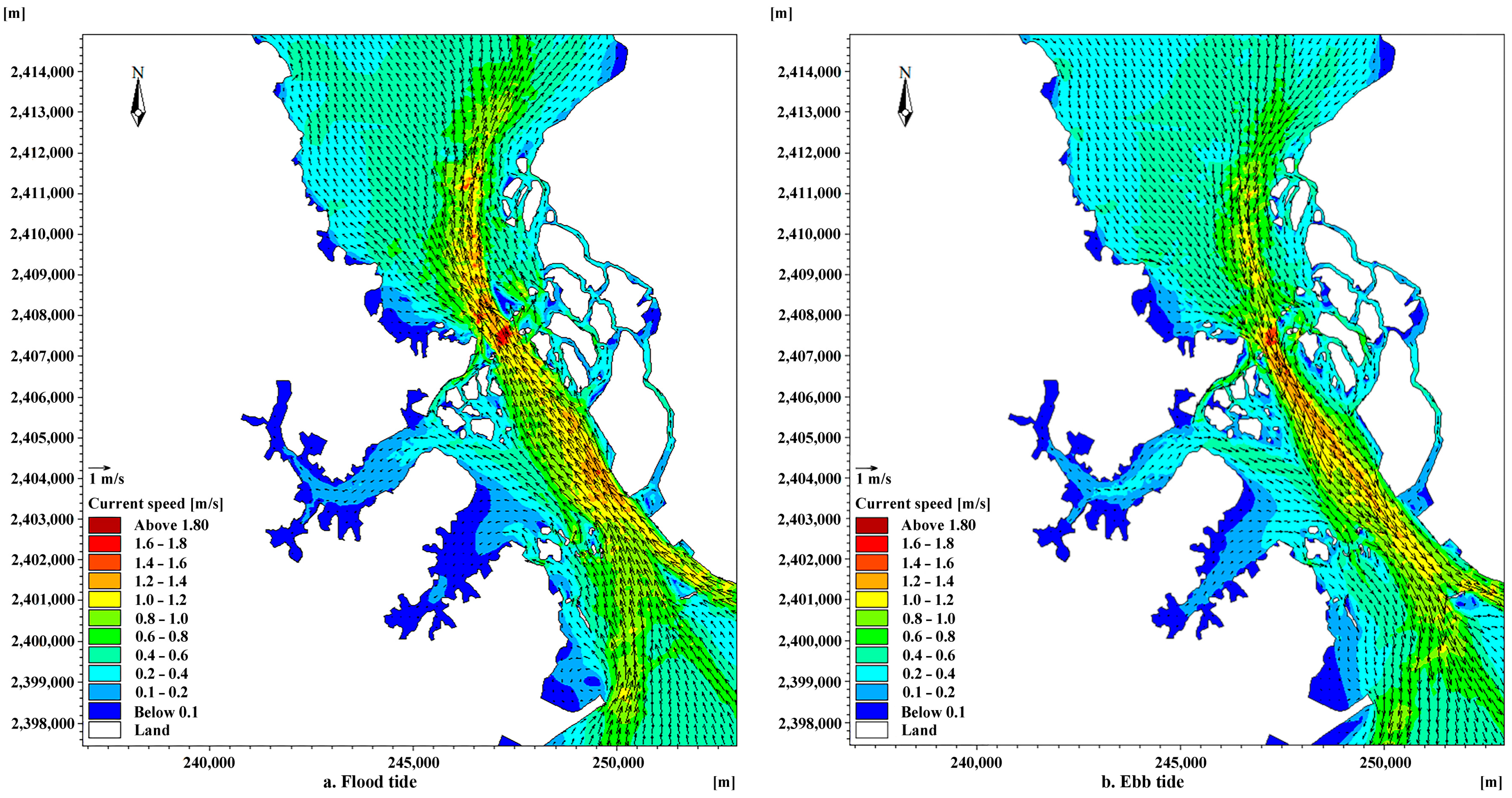
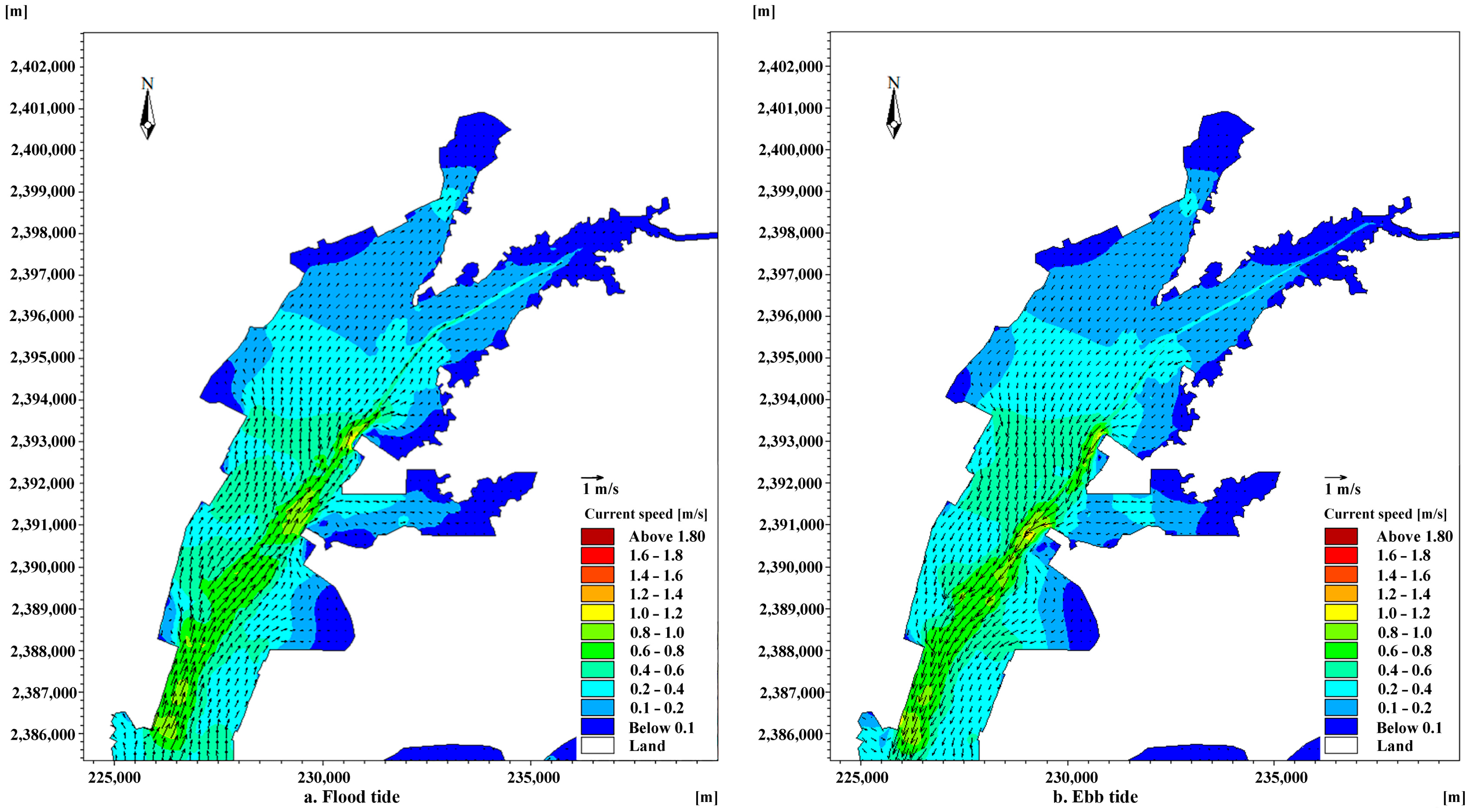
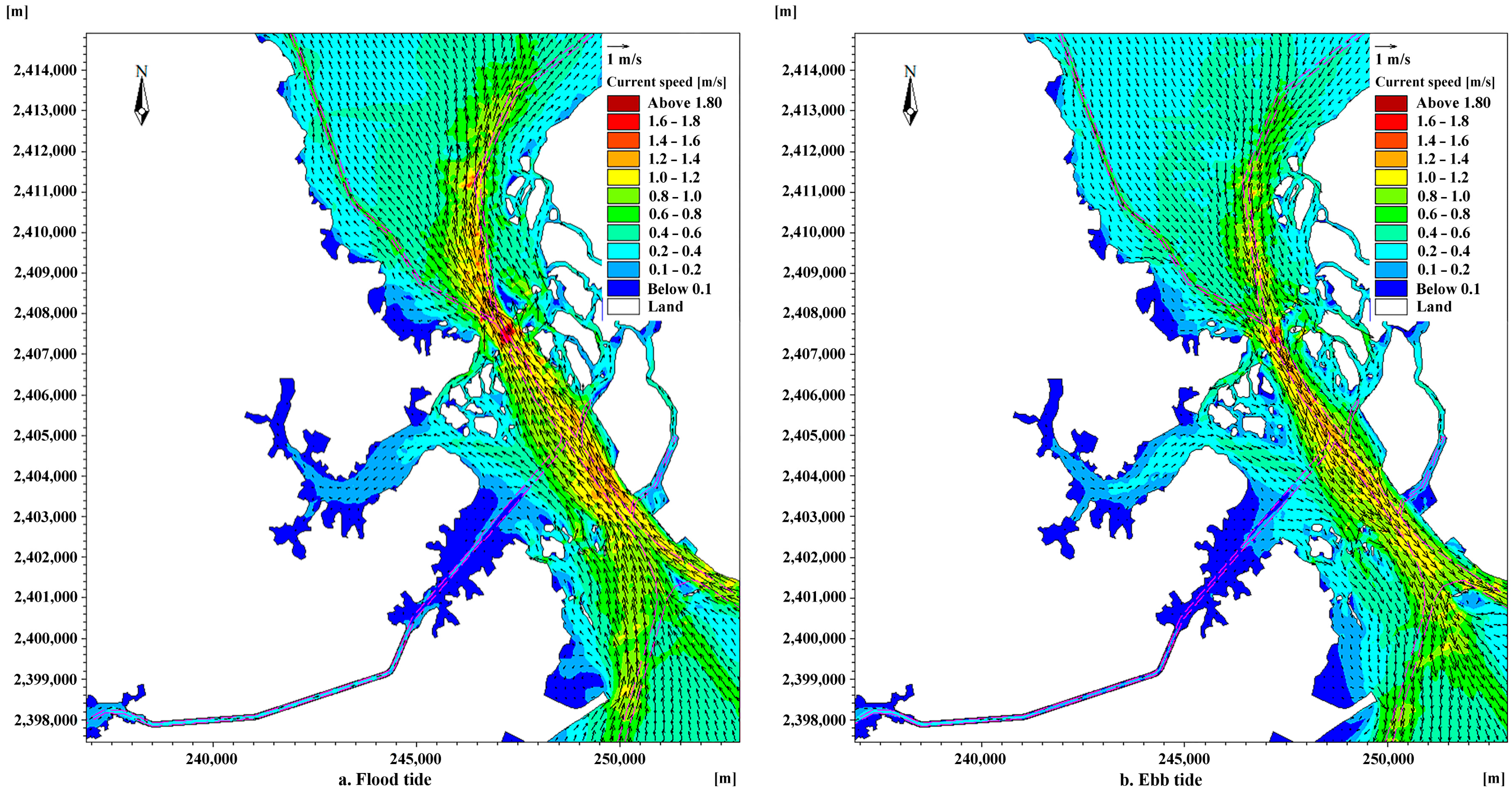
3.1. Tidal Currents in Coastal Channels
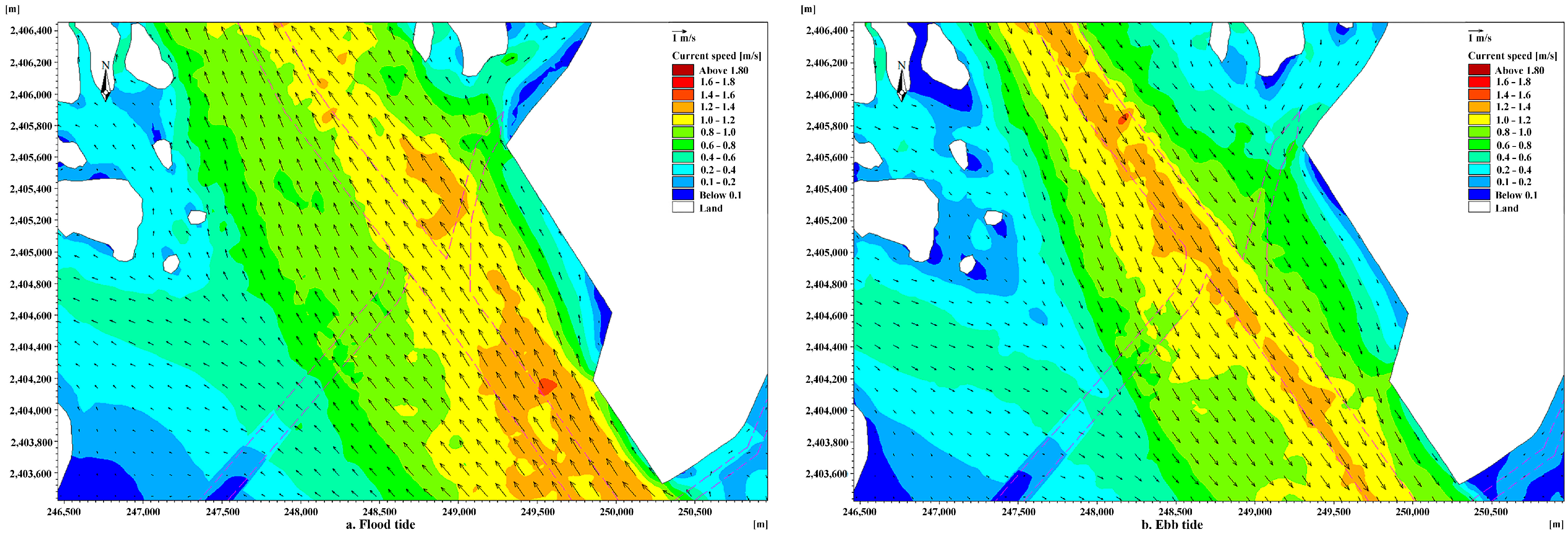
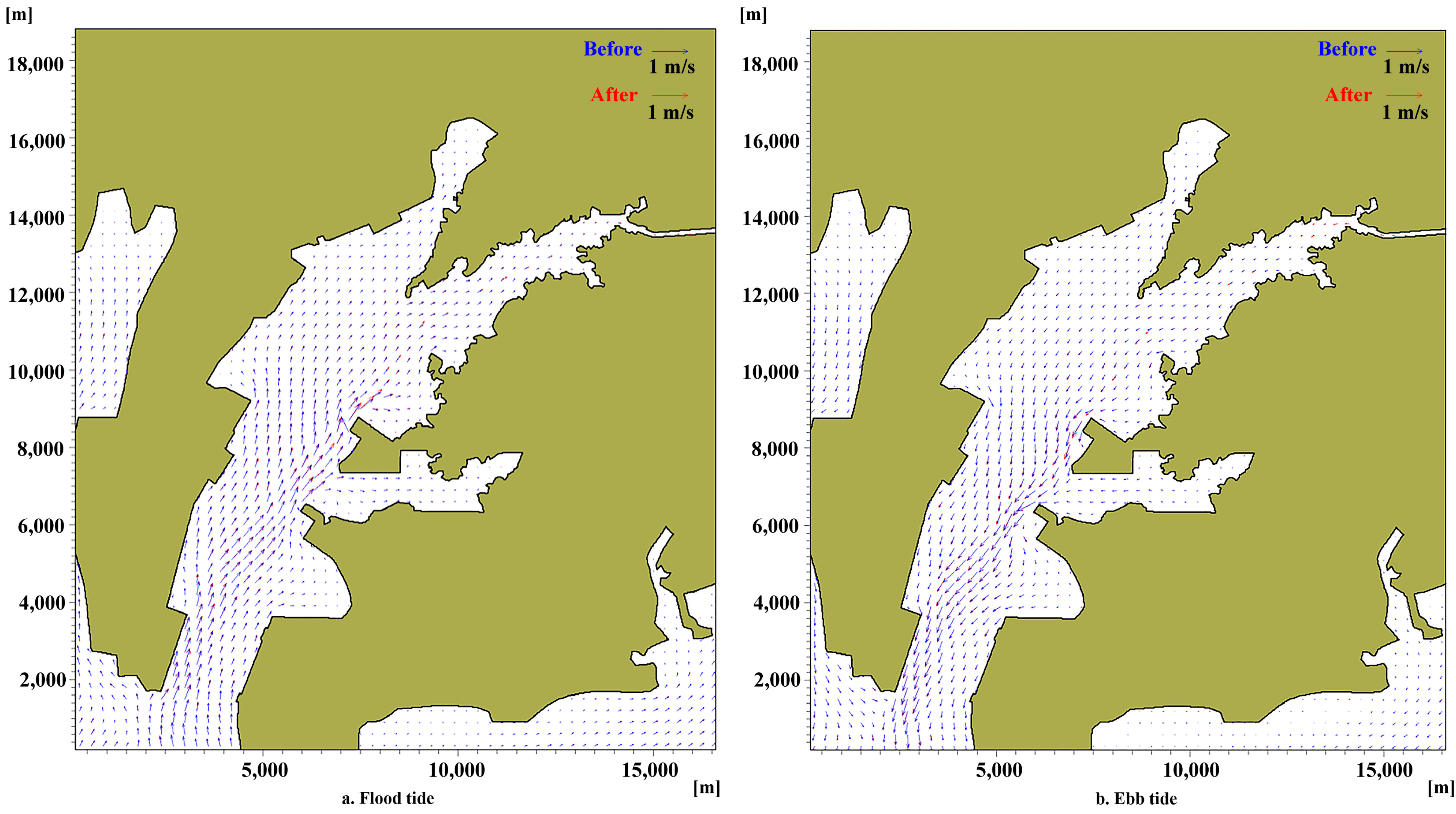
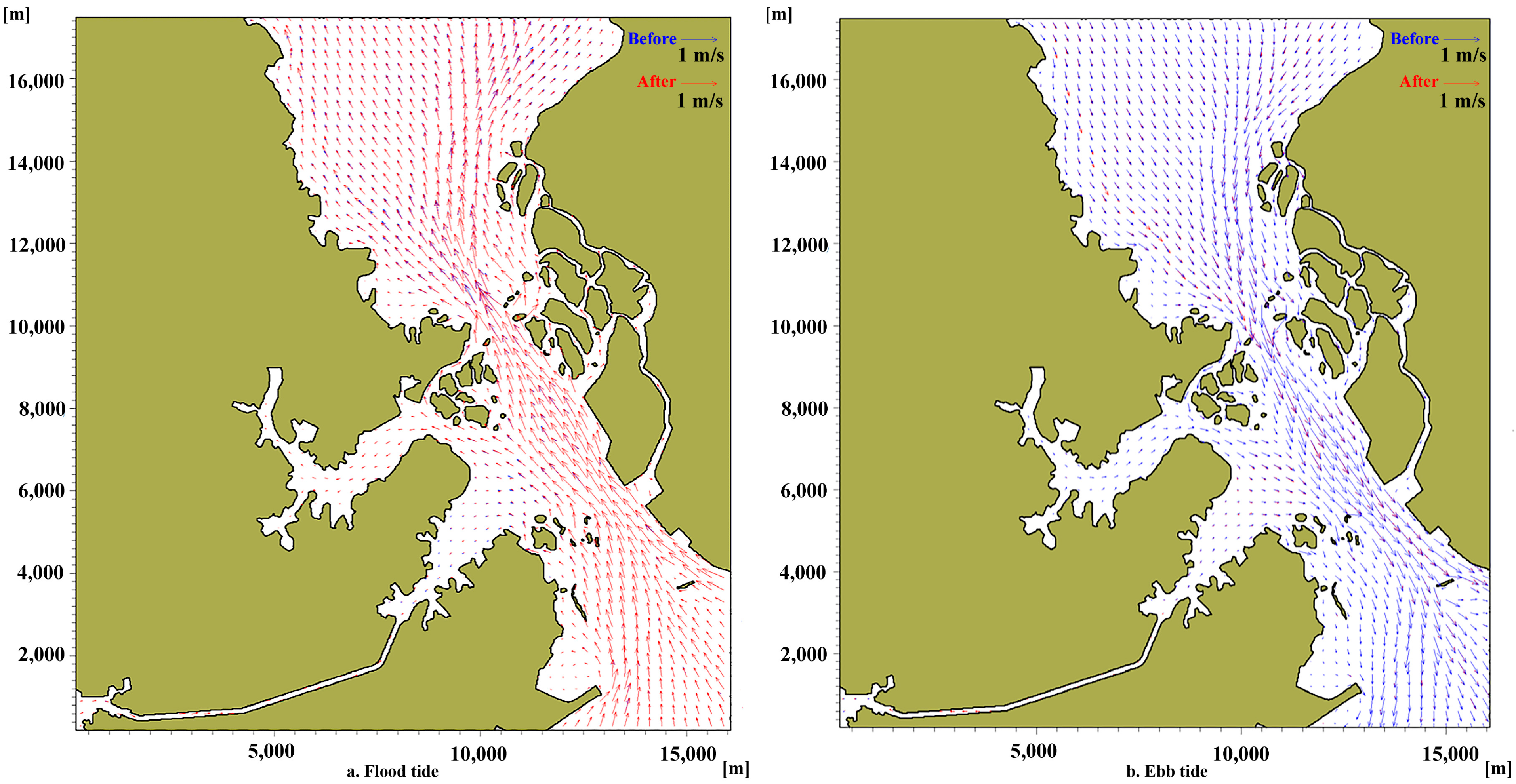
3.2. Variations in Hydrodynamic Conditions
3.3. Distribution of Maximum Flow Velocity
3.4. Comparison of Sedimentation Intensity
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in Hydrodynamic Conditions Resulted by Canal Construction
4.2. Response Mechanism of Sediment Transport
4.3. Sustainability and Risk Management of Canal Construction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mutema, M.; Dhavu, K. Review of factors affecting canal water losses based on a meta-analysis of worldwide data. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yin, D.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, R.; Lin, G.; Jia, H. The Ecological Effect of Ship Canals on Wetlands. Water 2024, 16, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Wang, X.; Waseem, M.; Zaman, M.; Aziz, F.; Khan, R.Z.N.; Ashraf, M. Flood management, characterization and vulnerability analysis using an integrated RS-GIS and 2D hydrodynamic modelling approach: The case of Deg Nullah, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gan, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Horton, D.E. Urbanization enhances channel and surface runoff: A quantitative analysis using both physical and empirical models over the Yangtze River basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cai, L.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, Y. Numerical simulation of the impact of an integrated renovation project on the Maowei Sea hydrodynamic environment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemes, R.W.A.; Duong, T.M.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Morphological response of a highly engineered estuary to altering channel depth and restoring wetlands. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, M.O.; Fernandes, E.H.; Siegle, E. Impacts of coastal structures on hydro-morphodynamic patterns and guidelines towards sustainable coastal development: A case studies review. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, O.; El-Geziry, T.M.; Khedr, A.; Alam El-Din, K. Impacts of recent development processes on the temporal and spatial sea-level variations along the Suez Canal. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 66, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Gan, M.; Xu, T.; Wei, Z. A century of tidal evolution around the Panama Canal. Cont. Shelf Res. 2024, 283, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J. Wave influence in the construction, shaping and destruction of river deltas: A review. Mar. Geol. 2015, 361, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Cooke, S.J.; Wolter, C.; Young, N.; Bennett, J.R. On the conservation value of historic canals for aquatic ecosystems. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 251, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel, R.A.; Viero, D.P.; Carniello, L.; D’alpaos, L. Multipurpose use of artificial channel networks for flood risk reduction: The case of the waterway Padova–Venice (Italy). Water 2020, 12, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortegón, E.; Moreno-Andrés, J. Anthropogenic modifications to estuaries facilitate the invasion of non-native species. Processes 2021, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, V.M.; Kim, W.; López, J.L.; Edmonds, D.; Geleynse, N.; Olariu, C.; Steel, R.J.; Hiatt, M.; Passalacqua, P. Impact of tidal currents on delta-channel deepening, stratigraphic architecture, and sediment bypass beyond the shoreline. Geology 2016, 44, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Talke, S.; Geyer, W.R.; Al-Zubaidi, H.A.M.; Sommerfield, C.K. Bigger tides, less flooding: Effects of dredging on barotropic dynamics in a highly modified estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Llanes, G.; López-Ruiz, A. On the assessment of channel deepening impacts in micro-meso tidal estuaries: A systematic analysis. Ocean Model. 2025, 196, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Y. Influence of change in river discharge and tides on stagnation points in the Yangtze River estuary. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, R.L.; Hale, R.P.; Goodbred, S.L. Flow reorganization in an anthropogenically modified tidal channel network: An example from the southwestern ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 2141–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Shen, F.; He, Q.; Cao, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, M. Changes in suspended sediments in the Yangtze River Estuary from 1984 to 2020: Responses to basin and estuarine engineering constructions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 805, 150381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Jin, Z.; Chu, X.; Wang, W.; Yao, H. Route Selection for the Extension Line of Pinglu Canal: A Comparative Study. Land 2025, 14, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB50139-2014; Standards for Inland Waterway Navigation. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, P.; Chen, F.; He, Z. Evolutions of hydrodynamics and sediment transport pattern in the Qiantang Estuary (China) in response to multidecadal embankment constructions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 309, 108965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.; Grasmeijer, B.; Perk, L. Effect of channel deepening on tidal flow and sediment transport: Part I—Sandy channels. Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 1457–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitink, A.J.F.; Jay, D.A. Tidal river dynamics: Implications for deltas. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 240–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkol, A.; Schwenk, J.; Katifori, E.; Shaw, J.B. Interplay of river and tidal forcings promotes loops in coastal channel networks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; de Swart, H.E.; Valle-Levinson, A. Role of asymmetric tidal mixing in the subtidal dynamics of narrow estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 2623–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Sun, T.; Fagherazzi, S. Effect of tides on mouth bar morphology and hydrodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 4169–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Edmonds, D.A.; Nardin, W.; Leonardi, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Falcini, F.; Jerolmack, D.J.; Mariotti, G.; Rowland, J.C.; Slingerland, R.L. Dynamics of river mouth deposits. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 642–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.A.; Meselhe, E.A. The use of large water and sediment diversions in the lower Mississippi River (Louisiana) for coastal restoration. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. The fluid dynamics of river dunes: A review and some future research directions. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; van der Wegen, M.; Roelvink, J.A.; He, Q. The role of river flow and tidal asymmetry on 1-D estuarine morphodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 2315–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Analysis of the impact of Suez Canal blockage on the global shipping network. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Meire, P.; Bouma, T.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Ysebaert, T.; De Vriend, H.J. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change. Nature 2013, 504, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, D. A model and algorithm for vessel scheduling through a two-way tidal channel. Marit. Policy Manag. 2019, 47, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, J.T.; Thaxton, R.D.; Rathburn, S.L.; Friedman, J.M.; Mueller, E.R.; Scott, M.L. Sediment-ecological connectivity in a large river network. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 47, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carse, A.; Lewis, J.A. Toward a political ecology of infrastructure standards: Or, how to think about ships, waterways, sediment, and communities together. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2016, 49, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





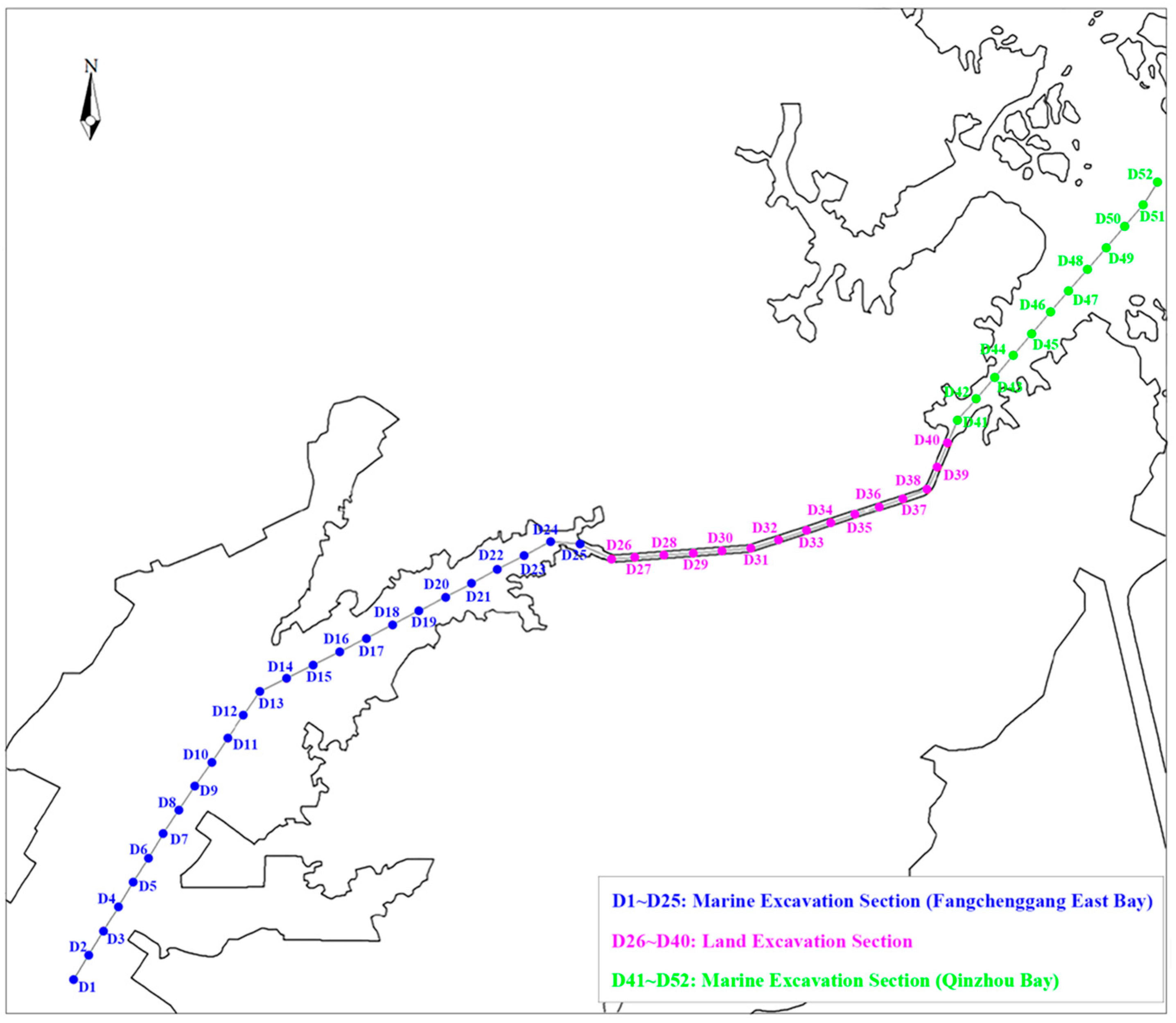
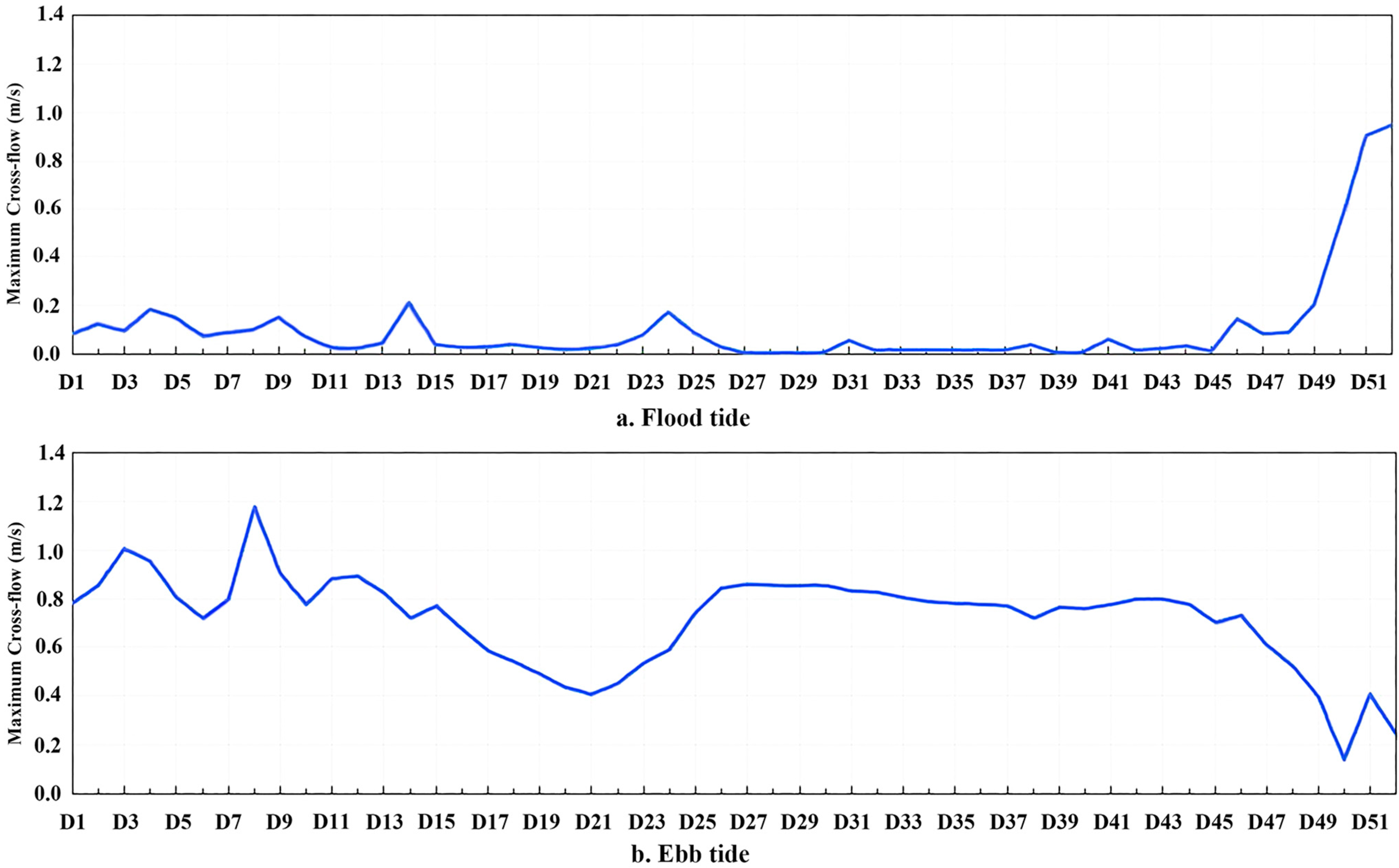
| Point | Maximum Flood Tide | Maximum Ebb Tide | Average Flow Velocity (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | ||
| D26 | 0.76 | 101 | 0.84 | 281 | 0.35 |
| D27 | 0.77 | 85 | 0.86 | 265 | 0.36 |
| D28 | 0.77 | 85 | 0.86 | 265 | 0.36 |
| D29 | 0.77 | 85 | 0.85 | 265 | 0.36 |
| D30 | 0.79 | 85 | 0.86 | 265 | 0.37 |
| D31 | 0.80 | 75 | 0.84 | 254 | 0.37 |
| D32 | 0.80 | 71 | 0.83 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D33 | 0.78 | 71 | 0.80 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D34 | 0.77 | 71 | 0.79 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D35 | 0.77 | 71 | 0.78 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D36 | 0.77 | 71 | 0.78 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D37 | 0.77 | 71 | 0.77 | 251 | 0.37 |
| D38 | 0.72 | 46 | 0.732 | 225 | 0.35 |
| D39 | 0.76 | 22 | 0.76 | 202 | 0.38 |
| D40 | 0.76 | 22 | 0.76 | 202 | 0.38 |
| Point | Maximum Flood Tide | Maximum Ebb Tide | Average Flow Velocity (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | ||
| D1 | 0.63 | 37 | 0.84 | 216 | 0.47 |
| D2 | 0.57 | 36 | 0.91 | 210 | 0.46 |
| D3 | 0.81 | 27 | 1.08 | 215 | 0.58 |
| D4 | 0.96 | 36 | 0.90 | 222 | 0.59 |
| D5 | 0.82 | 40 | 0.59 | 218 | 0.47 |
| D6 | 0.72 | 35 | 0.50 | 211 | 0.42 |
| D7 | 0.80 | 27 | 0.66 | 202 | 0.52 |
| D8 | 1.18 | 32 | 1.01 | 208 | 0.78 |
| D9 | 0.91 | 42 | 0.70 | 222 | 0.54 |
| D10 | 0.78 | 33 | 0.55 | 215 | 0.42 |
| D11 | 0.92 | 34 | 0.48 | 213 | 0.40 |
| D12 | 0.89 | 35 | 0.48 | 214 | 0.39 |
| D13 | 0.83 | 36 | 0.41 | 216 | 0.36 |
| D14 | 0.75 | 46 | 0.41 | 234 | 0.31 |
| D15 | 0.77 | 60 | 0.38 | 241 | 0.30 |
| D16 | 0.68 | 60 | 0.34 | 241 | 0.27 |
| D17 | 0.59 | 60 | 0.31 | 239 | 0.25 |
| D18 | 0.54 | 60 | 0.35 | 237 | 0.22 |
| D19 | 0.49 | 59 | 0.39 | 238 | 0.19 |
| D20 | 0.43 | 60 | 0.39 | 241 | 0.18 |
| D21 | 0.41 | 60 | 0.40 | 240 | 0.17 |
| D22 | 0.45 | 59 | 0.43 | 241 | 0.19 |
| D23 | 0.54 | 60 | 0.48 | 233 | 0.21 |
| D24 | 0.60 | 72 | 0.61 | 258 | 0.25 |
| D25 | 0.74 | 107 | 0.71 | 290 | 0.31 |
| Point | Maximum Flood Tide | Maximum Ebb Tide | Average Flow Velocity (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | Flow Velocity (m/s) | Flow Direction (Degree) | ||
| D41 | 0.78 | 28 | 0.62 | 28 | 0.35 |
| D42 | 0.80 | 40 | 0.64 | 39 | 0.36 |
| D43 | 0.80 | 40 | 0.69 | 40 | 0.36 |
| D44 | 0.78 | 40 | 0.65 | 40 | 0.32 |
| D45 | 0.70 | 40 | 0.65 | 41 | 0.30 |
| D46 | 0.66 | 32 | 0.73 | 41 | 0.25 |
| D47 | 0.46 | 221 | 0.61 | 39 | 0.25 |
| D48 | 0.47 | 219 | 0.52 | 40 | 0.23 |
| D49 | 0.28 | 35 | 0.40 | 49 | 0.19 |
| D50 | 0.54 | 315 | 0.49 | 145 | 0.31 |
| D51 | 0.83 | 328 | 0.99 | 154 | 0.50 |
| D52 | 0.96 | 324 | 1.12 | 142 | 0.57 |
| Point | Sedimentation Intensity (m/a) | Point | Sedimentation Intensity (m/a) | Point | Sedimentation Intensity (m/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.28 | D26 | 0.07 | D41 | 0.10 |
| D2 | 0.27 | D27 | 0.07 | D42 | 0.12 |
| D3 | 0.33 | D28 | 0.07 | D43 | 0.13 |
| D4 | 0.32 | D29 | 0.06 | D44 | 0.09 |
| D5 | 0.28 | D30 | 0.06 | D45 | 0.09 |
| D6 | 0.23 | D31 | 0.06 | D46 | 0.13 |
| D7 | 0.28 | D32 | 0.05 | D47 | 0.13 |
| D8 | 0.29 | D33 | 0.05 | D48 | 0.18 |
| D9 | 0.29 | D34 | 0.05 | D49 | 0.20 |
| D10 | 0.20 | D35 | 0.04 | D50 | 0.16 |
| D11 | 0.15 | D36 | 0.05 | D51 | 0.13 |
| D12 | 0.14 | D37 | 0.06 | D52 | 0.05 |
| D13 | 0.14 | D38 | 0.07 | ||
| D14 | 0.14 | D39 | 0.08 | ||
| D15 | 0.13 | D40 | 0.09 | ||
| D16 | 0.12 | ||||
| D17 | 0.12 | ||||
| D18 | 0.12 | ||||
| D19 | 0.12 | ||||
| D20 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, H.; Chu, X.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, Z. The Impact of Canal Construction on the Hydro-Morphodynamic Processes in Coastal Tidal Channels. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112048
Feng H, Chu X, Zhao P, Jiang Z, Jin Z. The Impact of Canal Construction on the Hydro-Morphodynamic Processes in Coastal Tidal Channels. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112048
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Honglin, Xiao Chu, Peng Zhao, Zhonglian Jiang, and Zhefei Jin. 2025. "The Impact of Canal Construction on the Hydro-Morphodynamic Processes in Coastal Tidal Channels" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112048
APA StyleFeng, H., Chu, X., Zhao, P., Jiang, Z., & Jin, Z. (2025). The Impact of Canal Construction on the Hydro-Morphodynamic Processes in Coastal Tidal Channels. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112048






