Ecological Suitability Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in Coastal Waters of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea Based on MaxEnt Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
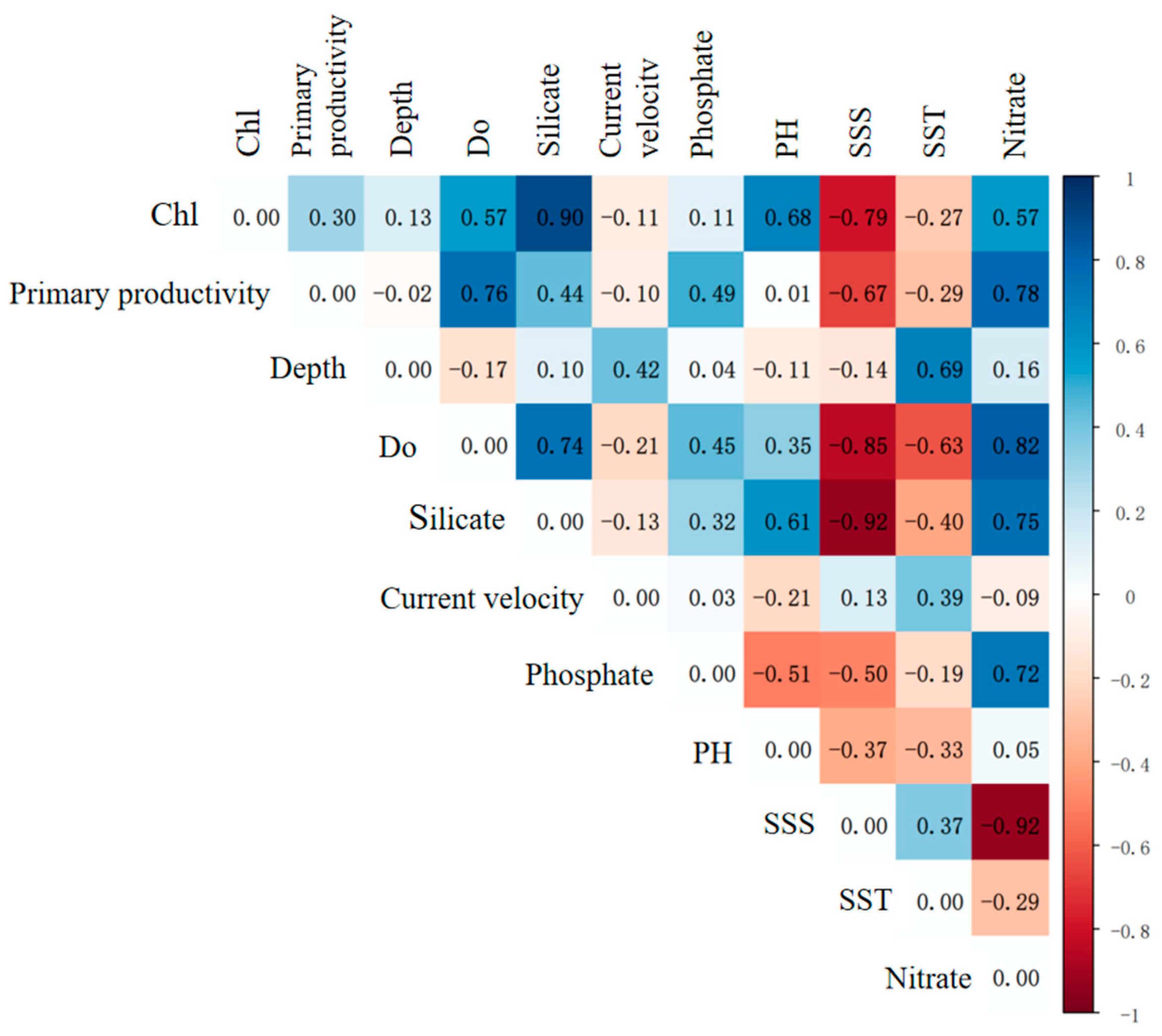
2.2. Collection and Processing of Environmental Factor Data
2.3. Further Screening of Environmental Factors
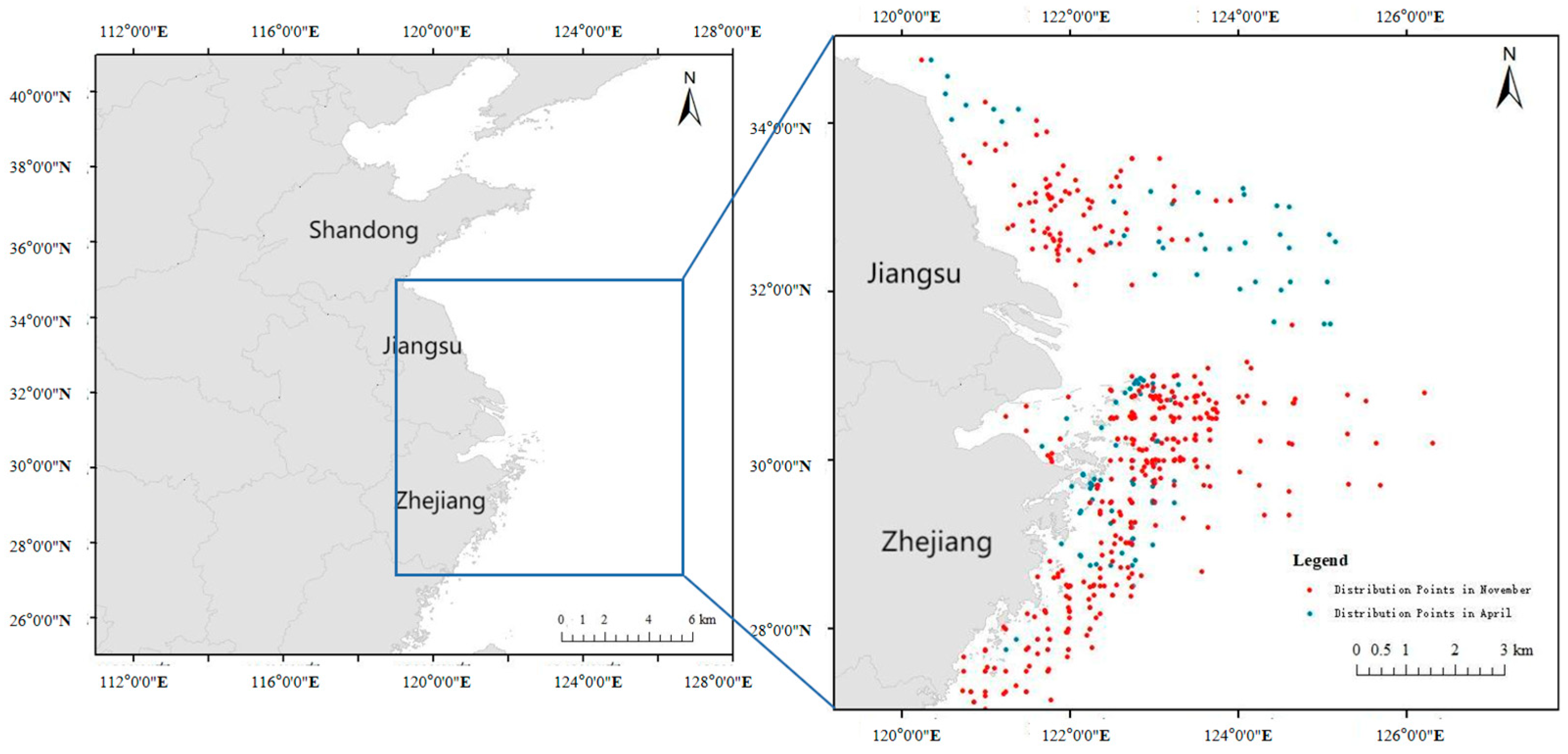
2.4. Species Distribution Data Collection and Processing
2.5. Map Data Collection
2.6. Optimization of the MaxEnt Model
2.7. MaxEnt Modeling
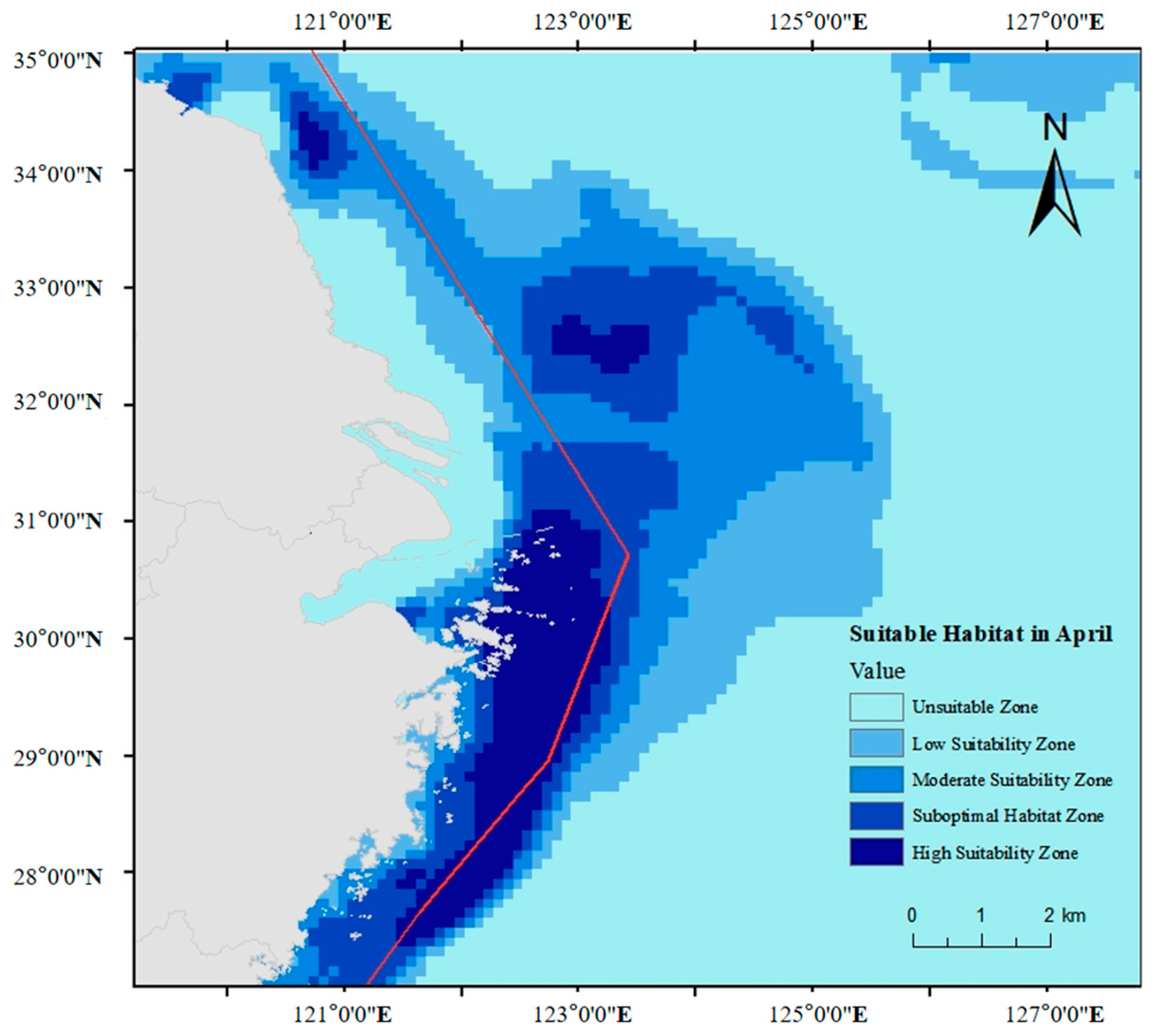
2.8. Mapping of Suitable Areas
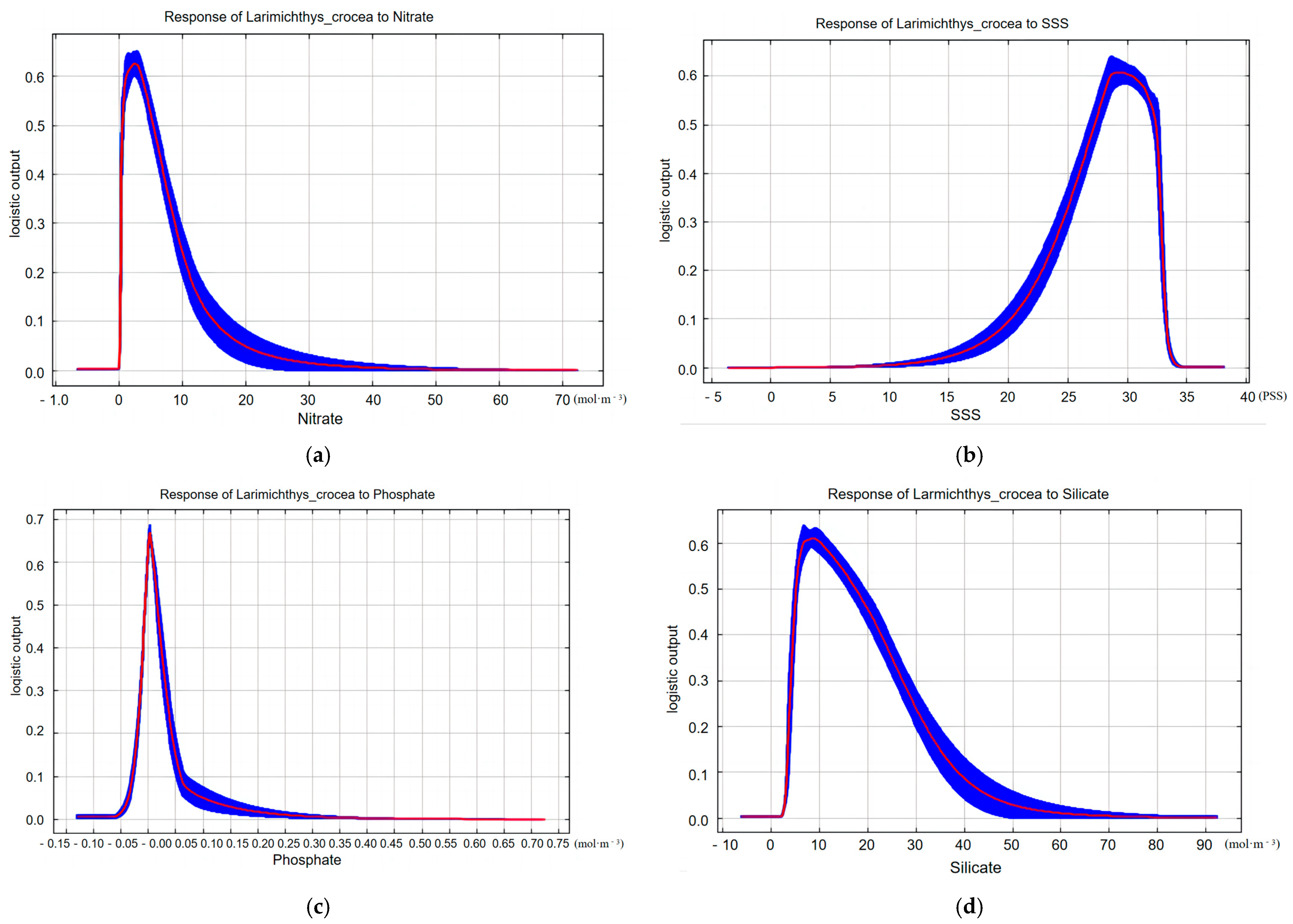
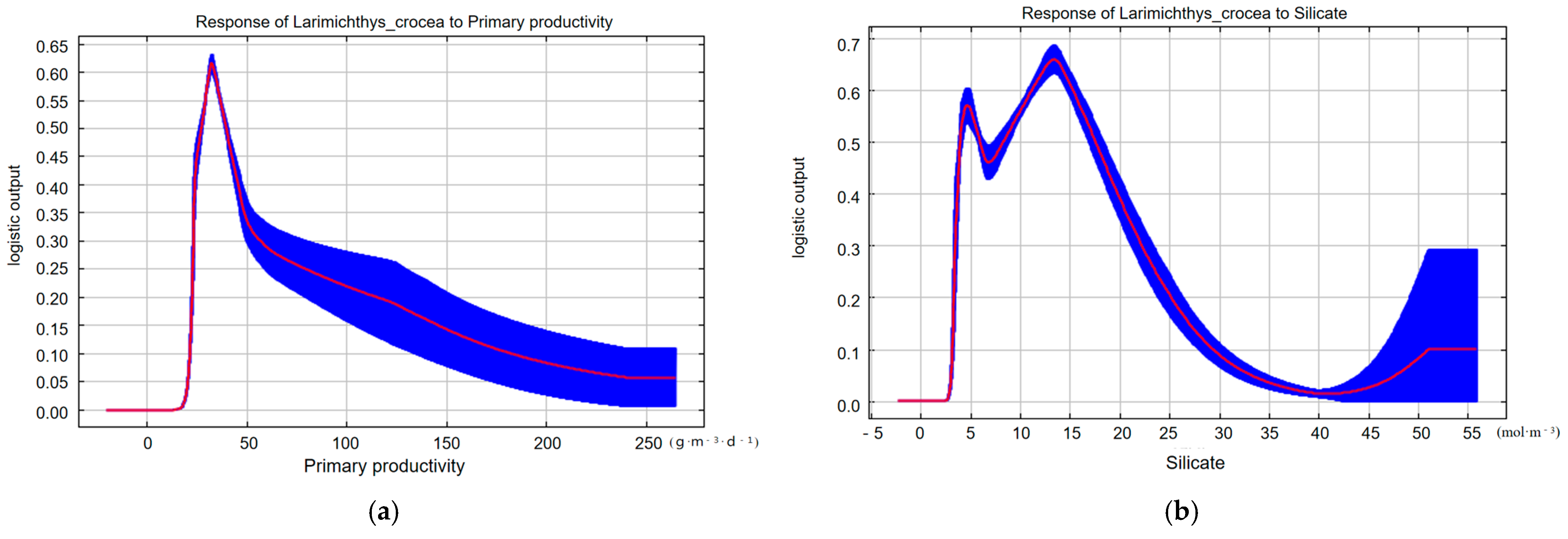
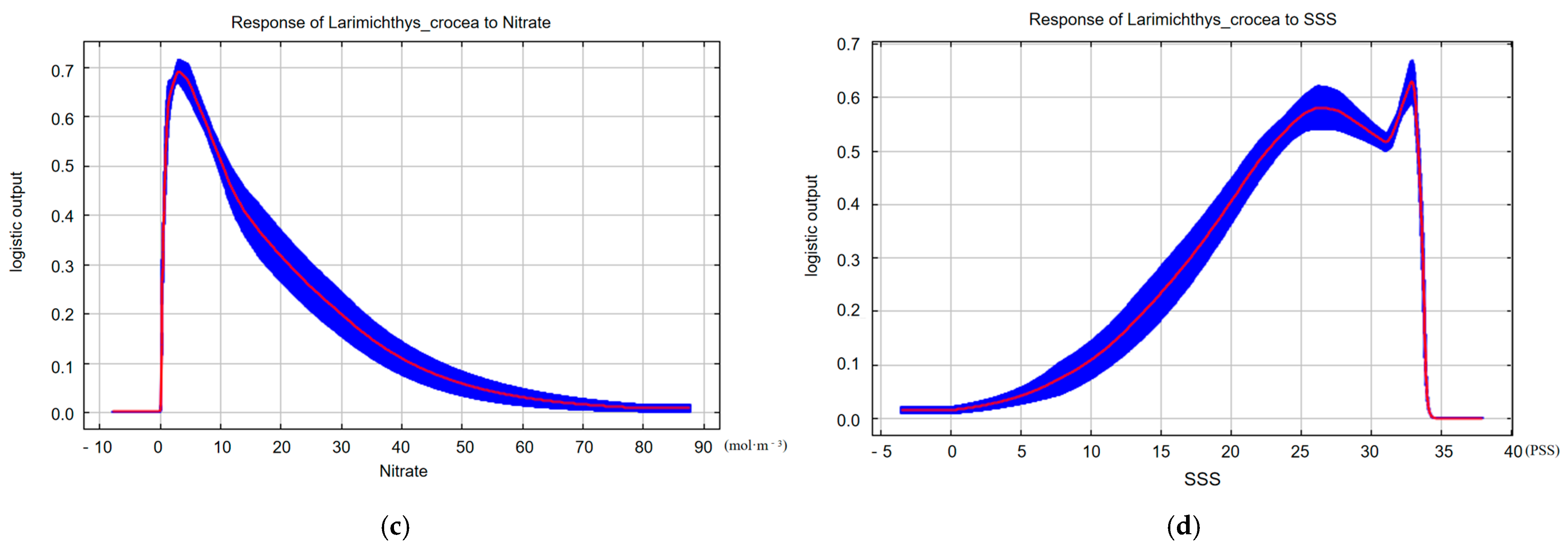
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, S. Atlas of the Main Economic Categories in the East China Sea: Three Fields, One Channel and Protected Areas, 1st ed.; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Xu, G.; Yu, R. Geographical variation of morphological characters and geographical population of Larimichthys crocea pseudosciaena crocea. Stud. Mar. Sin. 1962, 2, 79–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, F. Large Yellow Ceoaker—The first of the four marine products in China. Fortune Life 2018, 17, 30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, G.; Chen, B.; Zhang, C. Resource status of Larimichthys crocea overwintering in eastern and central Fujian fishing grounds. J. Fish. Res. 1983, 4, 12–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Liu, Z. The current stock of Larimichthys crocea Pseudosciaena crocea in the East China sea with respects of its stock decline. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2007, 22, 392–396. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.S.; Smith, B.A. What can community ecologists learn from species distribution models? Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, H.; Peng, S. The development and evaluation of species distribution models. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 557–567. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, M.; Zhong, Y. Application of maximum entropy model in the prediction of marine biological suitable areas. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 698–707. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.P. Maximum entropy (MaxEnt) modeling of species geographic distributions based on presence-only occurrence data. N. Y. Acad. Sci. Ann. 2012, 1260, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Miroslav Dudík, M. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, E.T. Information Theory and Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhou, G.; Sui, X.; He, Q.; Li, R. Dominant climatic factors of Quercus mongolica geographical distribution and their thresholds. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 103–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J. Study on the Spatio-Temporal Changes of Eutrophication in Zhejiang Coastal Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, D. Economic Status Quo and Industry Development of Marine Fishery in Jiangsu. J. Huaihai Inst. Technol. 2009, 7, 60–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Assessment of several fishing gear management strategies on economic species yield and biocommunity in Zhoushan fishing ground from the perspective of mixed fisheries. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2025, 49, 042514. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of Larimichthys polyactis in Zhoushan fishing ground and the adjacent waters based on two-stage GAM. J. Fish. Sci. China 2022, 29, 633–641. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Xia, L.; Li, R. The past, present and future of Zhoushan’s fisheries. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2015, 32, 44–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Potential risks, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in Zhoushan fishing ground, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Tang, J. Seasonal variation of fish community composition and diversity in Jiangsu coastal waters. Mar. Fish. 2017, 39, 9–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, B.; Wan, F. Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 15, 365–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.X.; Wang, H. Potential geographical distribution of Populus euphratica in China under future climate change scenarios based on MaxEnt model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6552–6563. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, M. Pharmaceutical Botany, 14th ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–345. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Hu, W.; Chen, B.; Tan, H. The potential distribution of main Sciaenidae species in coastal China based on MaxEnt model. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 41, 1825–1834. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Cause analysis of resources change and reconstruction strategy of Larimichthys crocea Daiqu group in the East China Sea. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 616–625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, Y. Feeding habits and seasonal variation of the food contents of the large yellow ceoaker, pseudosciaena crocea, pseudosciaena crocea (richardson), off chekiang and kiandsu. Stud. Mar. Sin. 1962, 2, 14–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Tian, F. Summer diet composition and feeding ecology of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in Guanjing Yang. J. Fish. Sci. China 2012, 19, 94–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, J. Feeding habits of Larimichthys crocea larvae, Juveniles and juveniles in Zhejiang coastal waters. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1965, 4, 355–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary Production of the Biosphere: Integrating Terrestrial and Oceanic Components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Han, X. Research on the particle size distribution and distribution and it’s effect on the physiology of marine phytoplankton. Mar. Sci. 2003, 11, 5–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Song, J.; Li, X. Seasonal change of PH in the waters off Changjiang river estuary and its impact factors. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 1033–1042. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, B. Effects and mechanisms of CO2-driven ocean acidification on marine fish behavior: A review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 5389–5403. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Bert, T.; Tweedale, W. The effects of temperature and salinity on survival and development of early life stage Florida stone crabs Menippe mercenaria (Say). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 157, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, J.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Botella-Cruz, M.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; Arribas, P.; Carbonell, J.A.; Millán, A.; Pallarés, S. Effects of salinity changes on aquatic organisms in a multiple stressor context. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Somero, G.N. The impact of ocean warming on marine organisms. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 805–816. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mo, S.; Hu, X.; Deng, T. Prediction of potential suitable areas of endangered plant Abies ziyuanensis based on MaxEnt and ArcGIS. Chin. J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 533–541. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Shen, J.; He, C. Analysis of Habitat Suitability and Conservation Gap of the Yunnan Snub-nosed Monkey Based on MaxEnt Model. Chin. J. Wildl. 2025, 46, 14–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Chen, X. Analysis of habitat distribution of Argentine shortfin squid (Illex argentinus) in the southwest Atlantic Ocean using maximum entropy model. J. Fish. China 2016, 40, 893–902. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; He, C. Comparison of habitat suitability of fiddler crab (Uca arcuata) based on habitat suitability index model and maximum entropy model. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2023, 38, 819–827. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, F. Simulation of spatio-temporal distribution of swordfish habitat in the western Indian Ocean based on maximum entropy model. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 44, 100–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, R.; Huang, Z. Effects of sample size and study range on accuracy of MaxEnt in predicting species distribution: A case study of the black-and-white snub-nosed monkey. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2019, 39, 126–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, W.; Gui, F. Study of suitable habitats for Sepiella maindroni in Zhoushan sea areas based on MaxEnt model. S. China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 22–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, K.; Agnalt, A.; Blankenship, H. Evolving Context and Maturing Science: Aquaculture-Based Enhancement and Restoration Enter the Marine Fisheries Management Toolbox. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Q. Reproductive Dynamics of the Large Yellow Croaker Larimichthys crocea (Sciaenidae), A Commercially Important Fishery Species in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 868580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, K. Understanding and managing enhancements: Why fisheries scientists should care. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 85, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, L.; Lenfant, P.; Clarke, L. Examining current best-practices for the use of wild post-larvae capture, culture, and release for fisheries enhancement. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1058497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




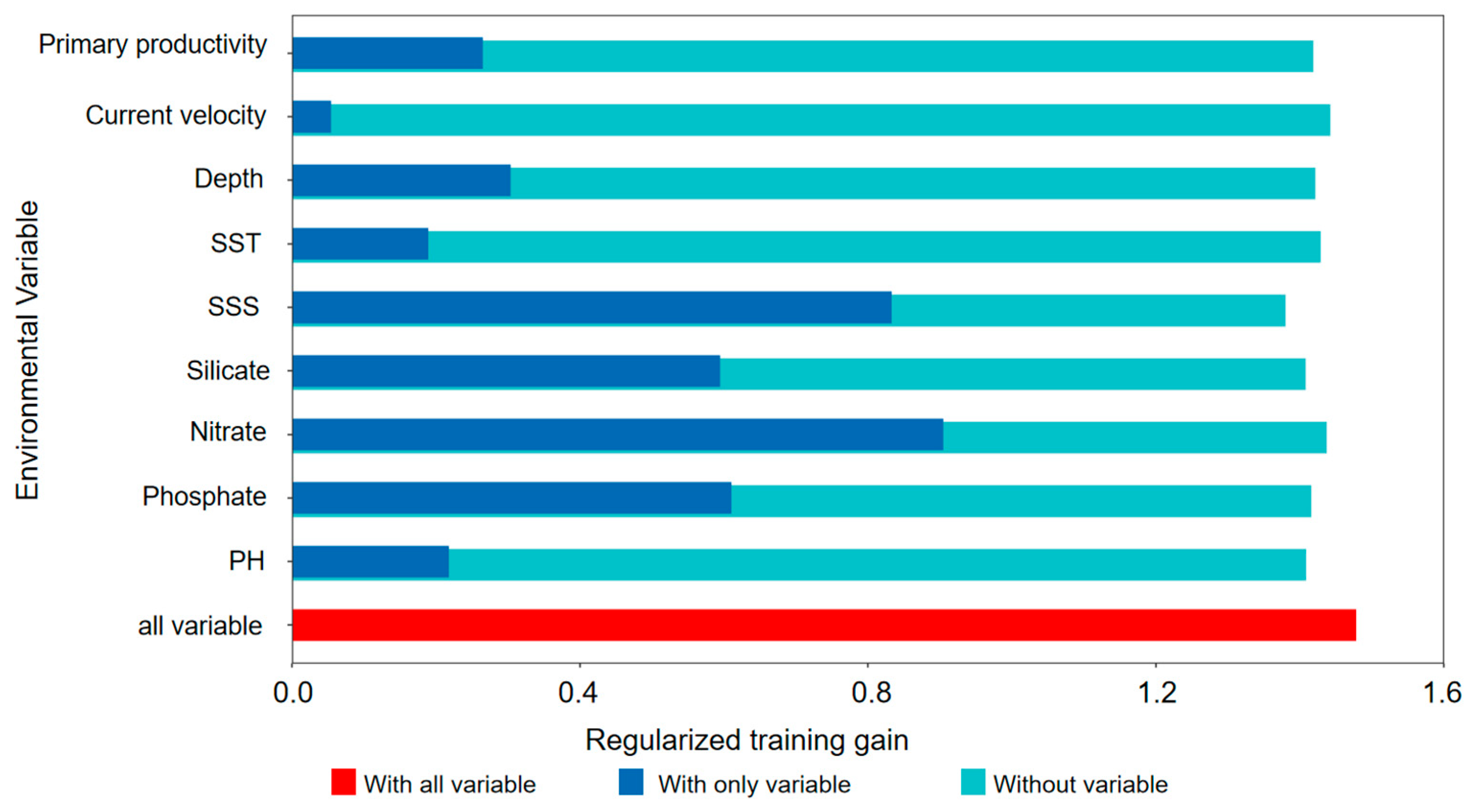
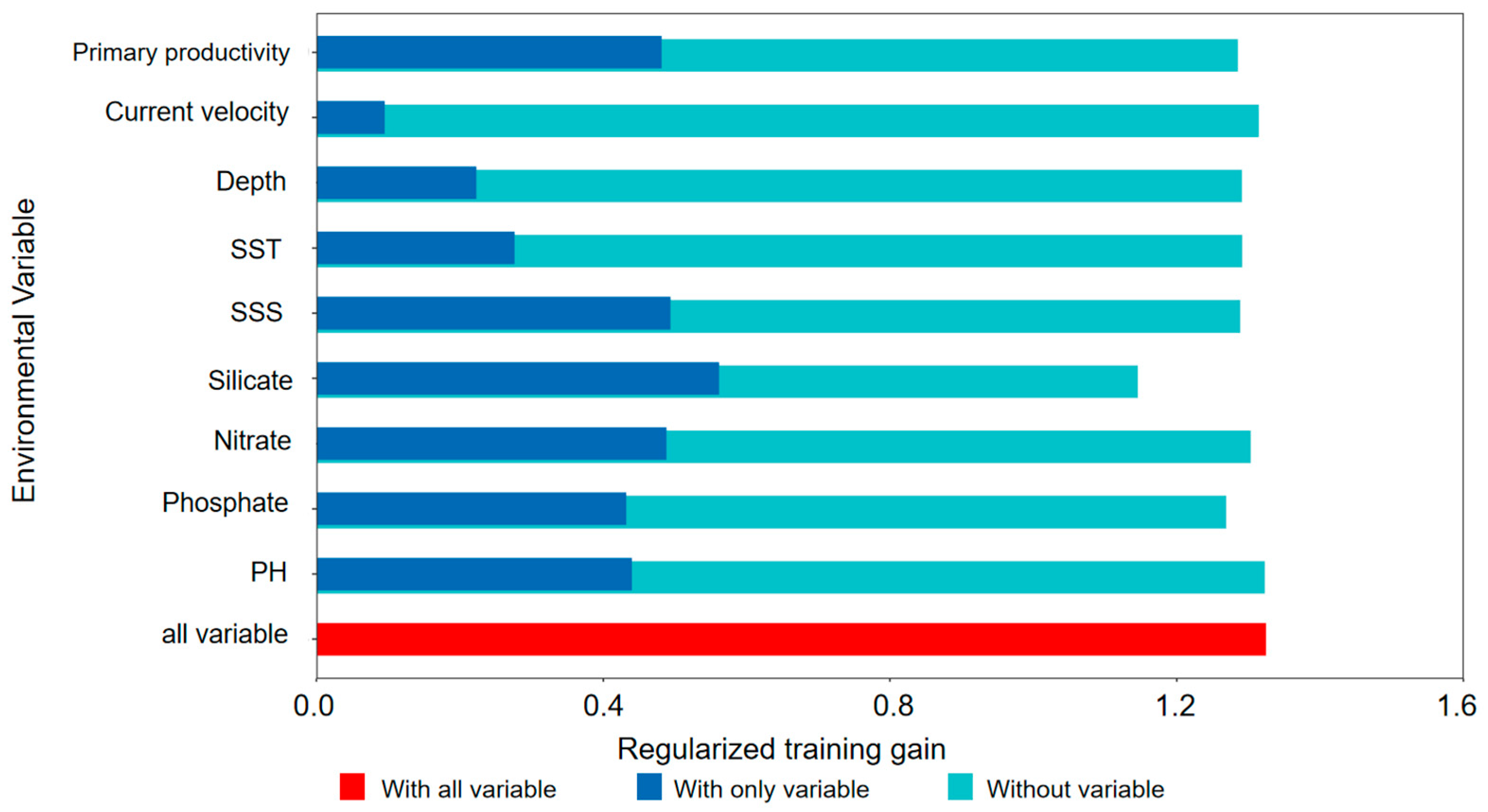


| Variable | Percent Contribution |
|---|---|
| Nitrate | 37 |
| SSS | 29.6 |
| Silicate | 8.3 |
| SST | 7.9 |
| pH | 5.7 |
| Depth | 3.8 |
| Chl | 2.5 |
| Do | 2.4 |
| Flow velocity | 1.4 |
| Primary productivity | 1 |
| Phosphate | 0.4 |
| Variable | Percent Contribution |
|---|---|
| Silicate | 23 |
| Chl | 19.1 |
| Phosphate | 15.6 |
| Depth | 14.9 |
| Nitrate | 10.9 |
| Primary productivity | 6.4 |
| SST | 5.8 |
| SSS | 2.8 |
| pH | 1.1 |
| Do | 0.3 |
| Flow velocity | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Meng, W.; Zhang, H.; Ge, H.; Wu, L.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Ecological Suitability Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in Coastal Waters of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea Based on MaxEnt Modeling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101945
Yu S, Meng W, Zhang H, Ge H, Wu L, Qu Y, Zhang Q, Zhou Y. Ecological Suitability Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in Coastal Waters of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea Based on MaxEnt Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101945
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shuwen, Wei Meng, Hongliang Zhang, Hui Ge, Lei Wu, Yao Qu, Qiuhong Zhang, and Yongdong Zhou. 2025. "Ecological Suitability Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in Coastal Waters of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea Based on MaxEnt Modeling" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101945
APA StyleYu, S., Meng, W., Zhang, H., Ge, H., Wu, L., Qu, Y., Zhang, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Ecological Suitability Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in Coastal Waters of the East China Sea and Yellow Sea Based on MaxEnt Modeling. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101945






