Mechanisms of Freak Wave Generation from Random Wave Evolution in 3D Island-Reef Topography
Abstract
1. Introduction
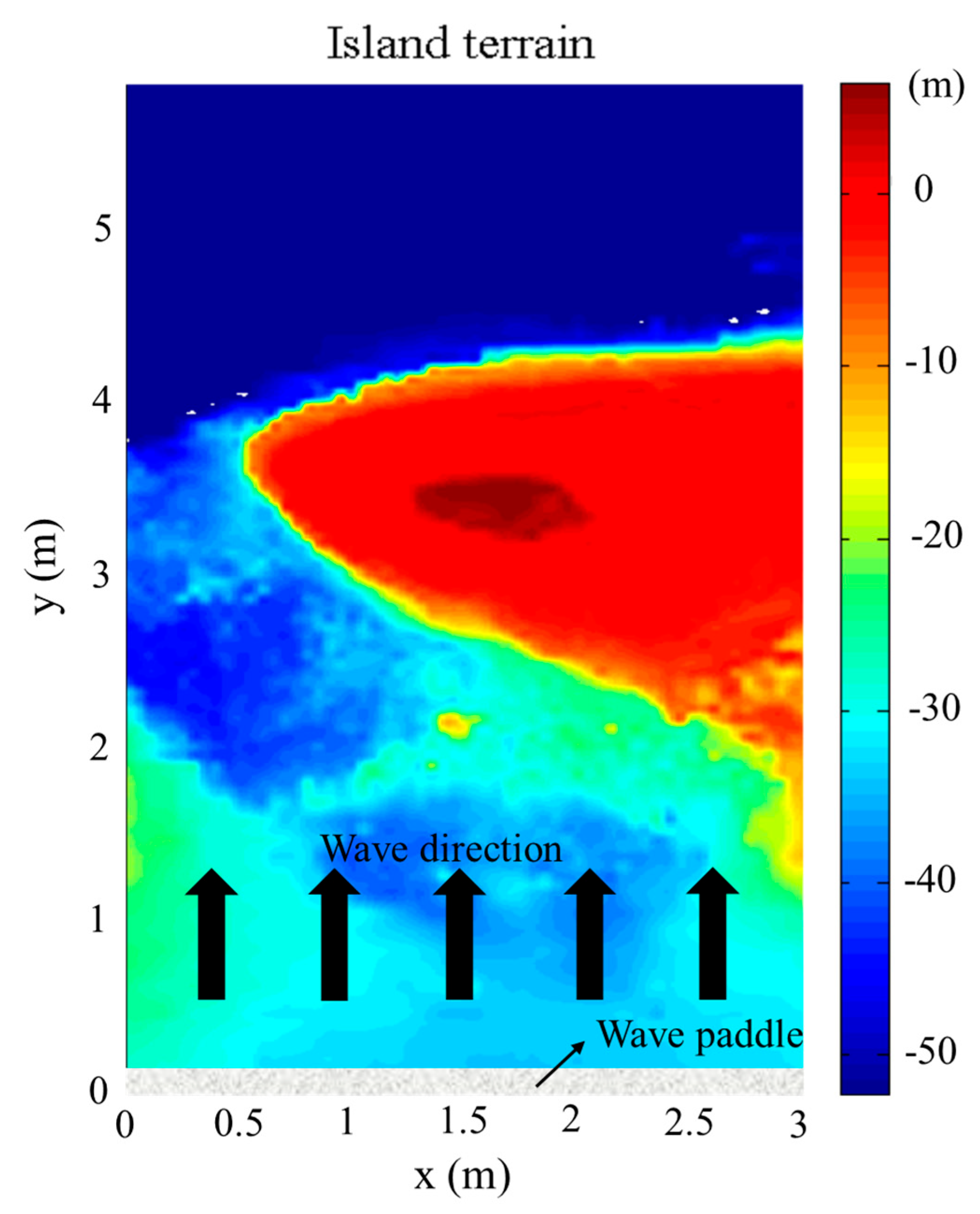
2. Experimental Setup
3. Wavelet Transform
| Case | Hfr/Hs | Hcr/Hs | Hcr/Hfr | Tfr (s) | Ts (s) | H (cm) | kh | Type | Names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.40 | 1.53 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 37.80 | 3.96 | Type 1 | Huge single crest |
| 2 | 2.28 | 1.45 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 0.77 | 24.50 | 1.66 | ||
| 3 | 2.01 | 1.17 | 0.58 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 16.00 | 1.18 | ||
| 4 | 2.08 | 1.31 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 37.41 | 2.41 | ||
| 5 | 2.01 | 1.20 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 28.00 | 2.51 | ||
| 6 | 2.16 | 1.28 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 33.64 | 2.93 | ||
| 7 | 2.07 | 1.27 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 26.33 | 1.74 | ||
| 8 | 2.10 | 1.23 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 37.80 | 2.44 | ||
| 9 | 2.03 | 1.25 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.85 | 27.71 | 1.54 | ||
| 10 | 2.04 | 1.32 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 44.48 | 2.66 | ||
| 11 | 2.09 | 1.29 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 36.20 | 2.59 | ||
| 12 | 2.08 | 1.32 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 24.80 | 1.49 | ||
| 13 | 2.01 | 1.46 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 32.82 | 1.87 | ||
| 14 | 2.00 | 1.35 | 0.68 | 0.8 | 1.08 | 39.87 | 1.38 | ||
| 15 | 2.20 | 1.25 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 29.35 | 2.10 | ||
| 16 | 2.20 | 1.38 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 18.20 | 1.27 | Type 2 | Freak wave group |
| 17 | 2.01 | 1.26 | 0.62 | 1.06 | 1.14 | 2.09 | 0.06 | ||
| 18 | 2.06 | 1.10 | 0.53 | 0.94 | 1.02 | 27.71 | 1.07 | Type 3 | Vertical symmetrical freak wave |
| 19 | 2.00 | −1.07 | −0.54 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 36.20 | 2.40 | Type 4 | “Hole in the sea” |
| 20 | 2.03 | −1.04 | −0.51 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 29.35 | 1.80 | ||
| 21 | 2.15 | −1.13 | −0.53 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 32.69 | 2.28 |
4. Results and Discussion
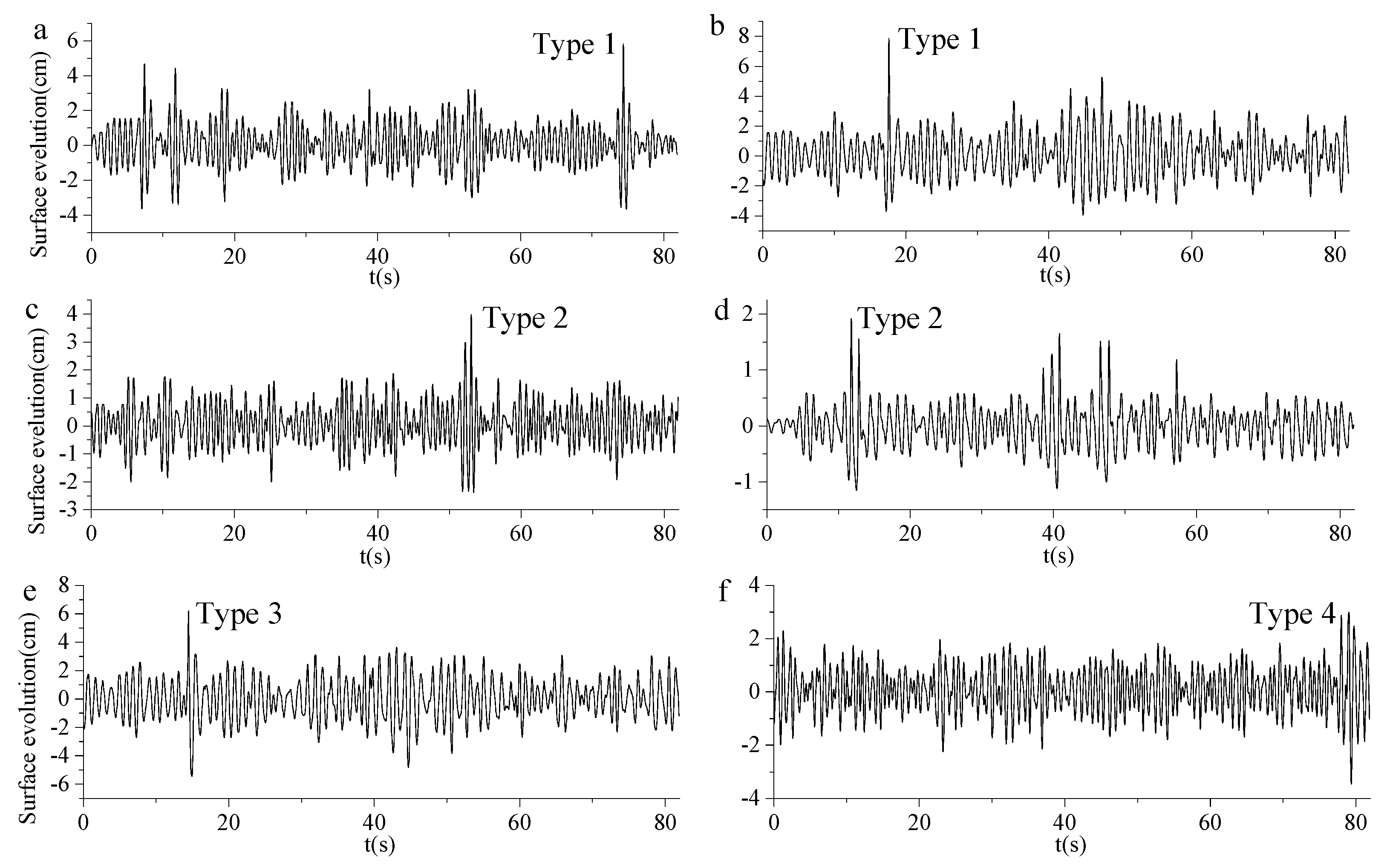
4.1. Freak Wave Events in the Experiment
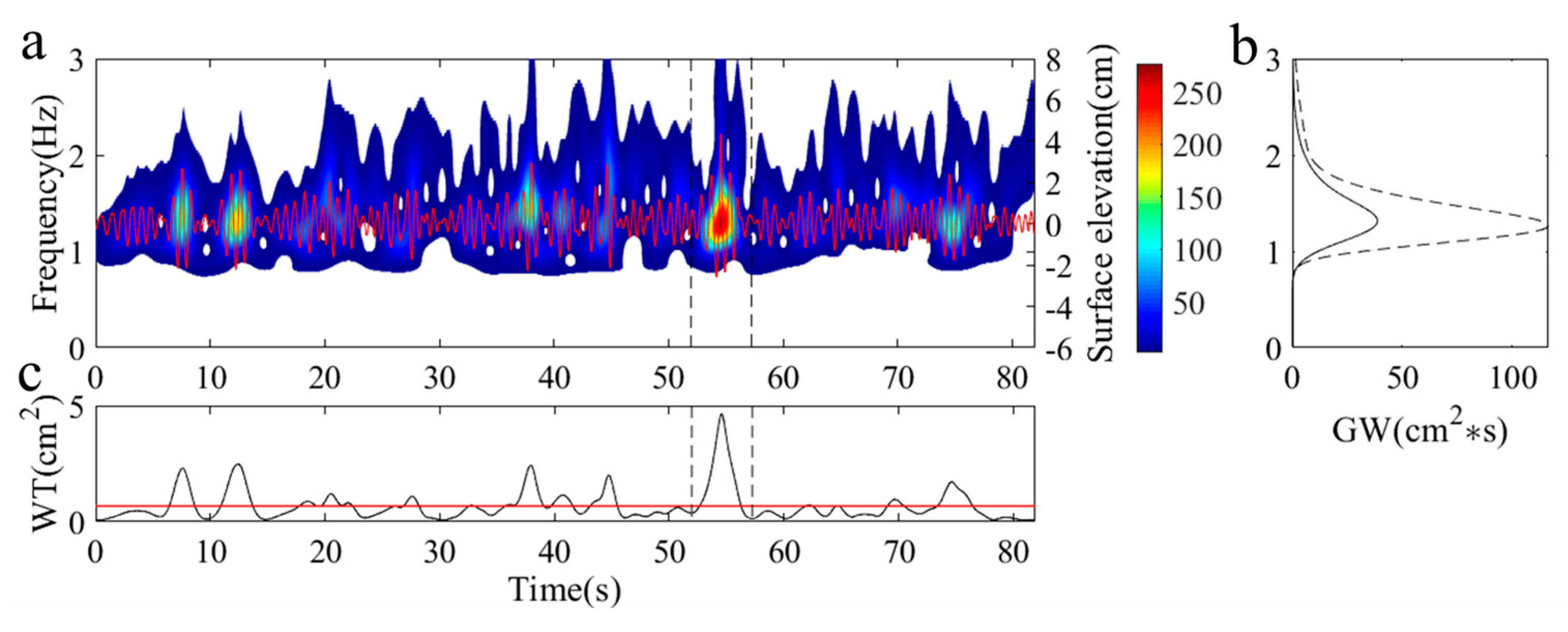
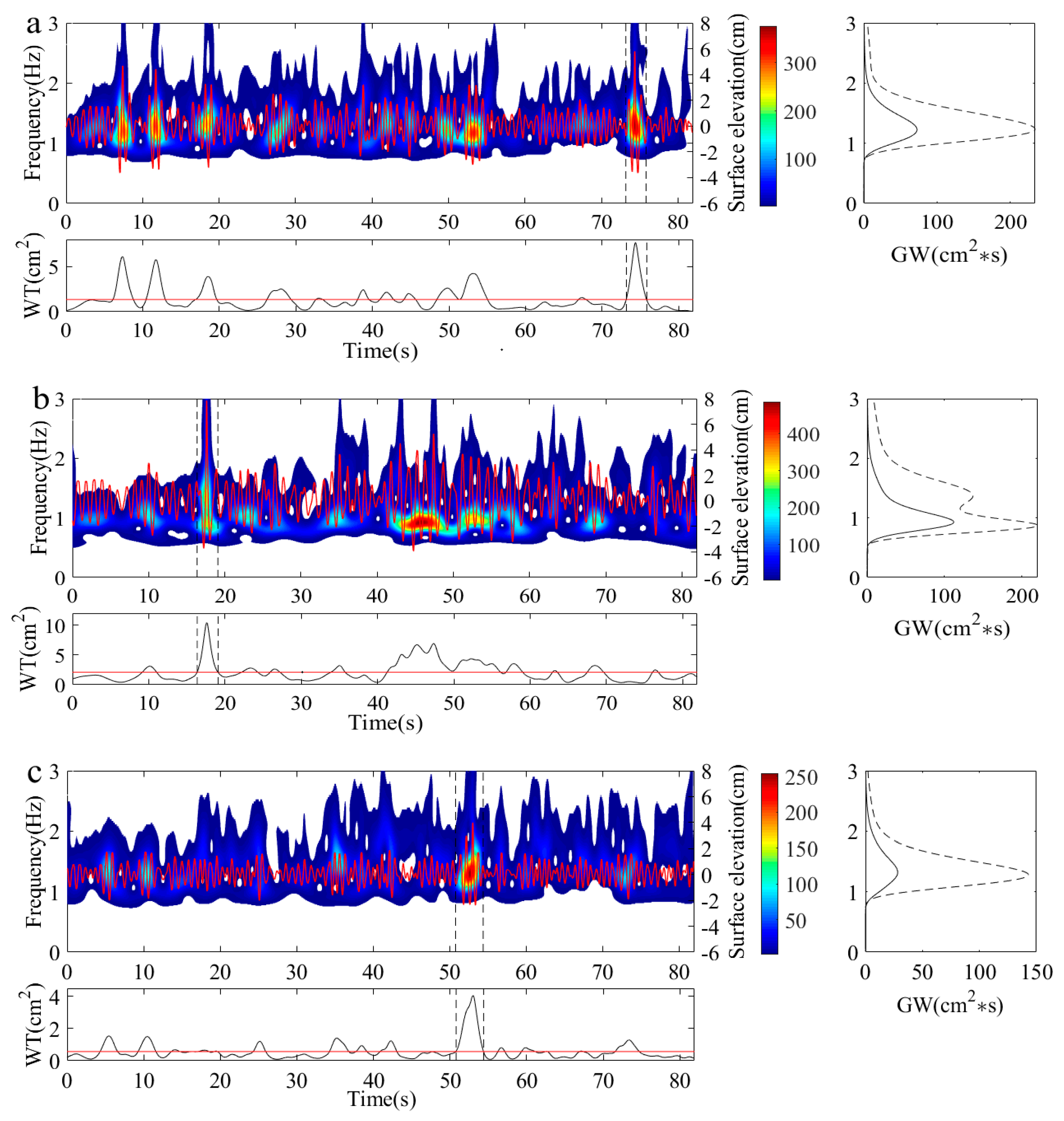
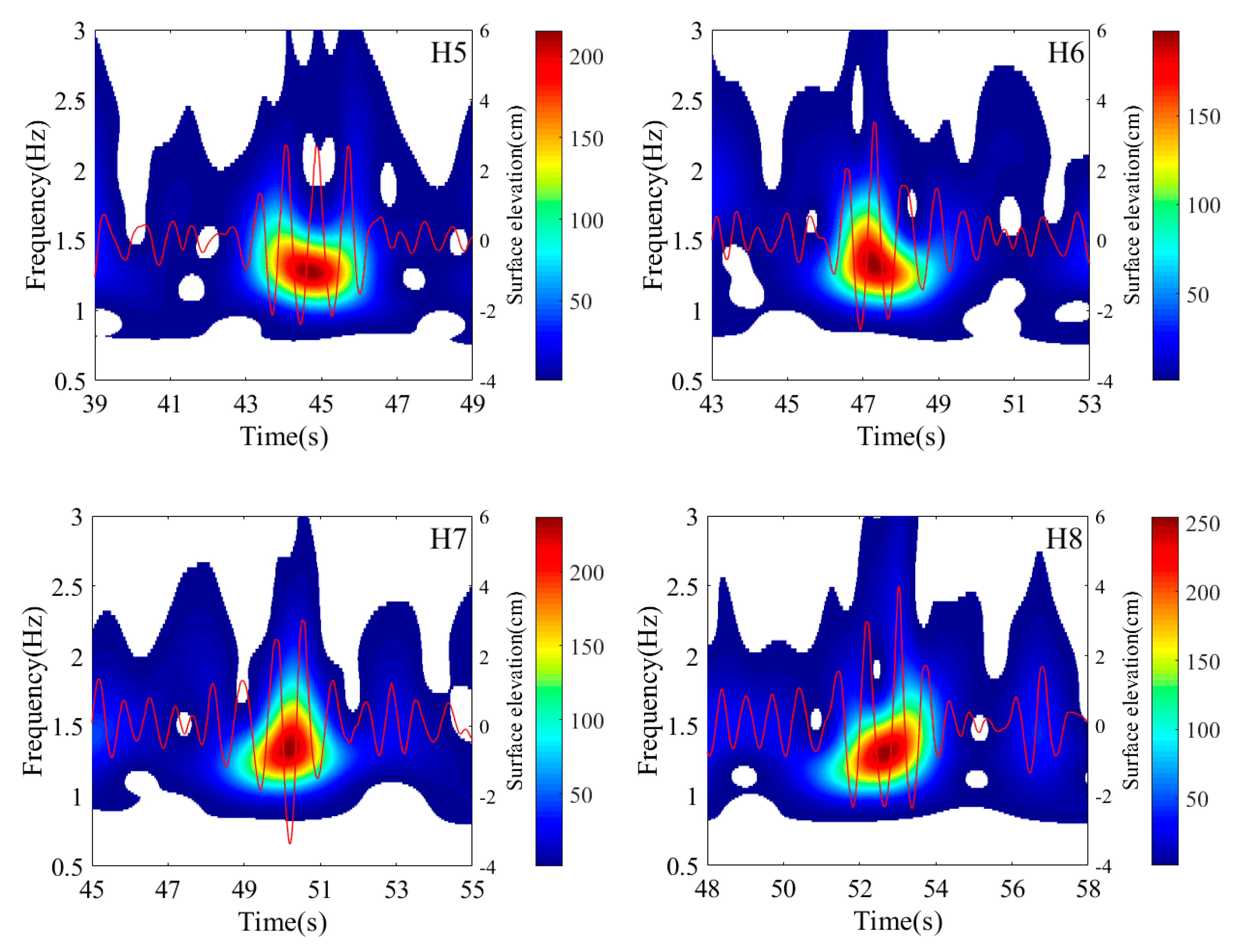
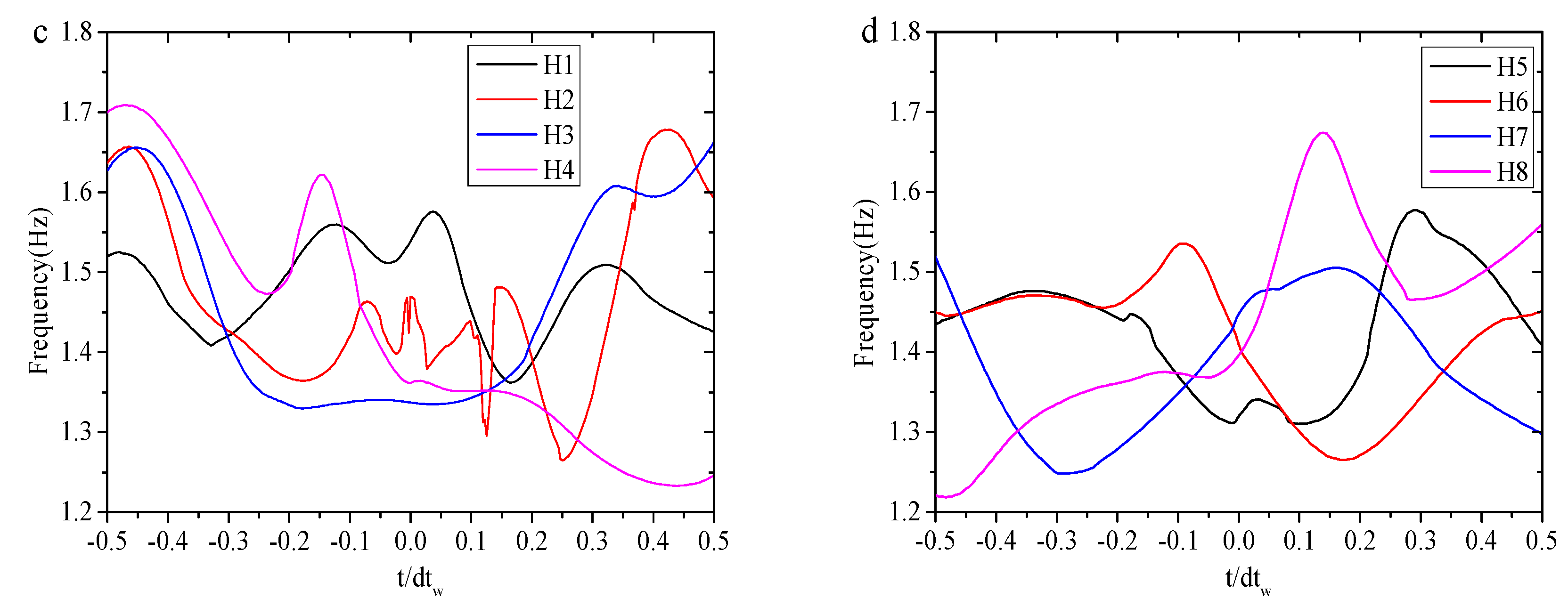
4.2. Wavelet Analysis of Different Types of Freak Waves
4.3. The Wavelet Energy Variation in the Freak Waves Evolution Process
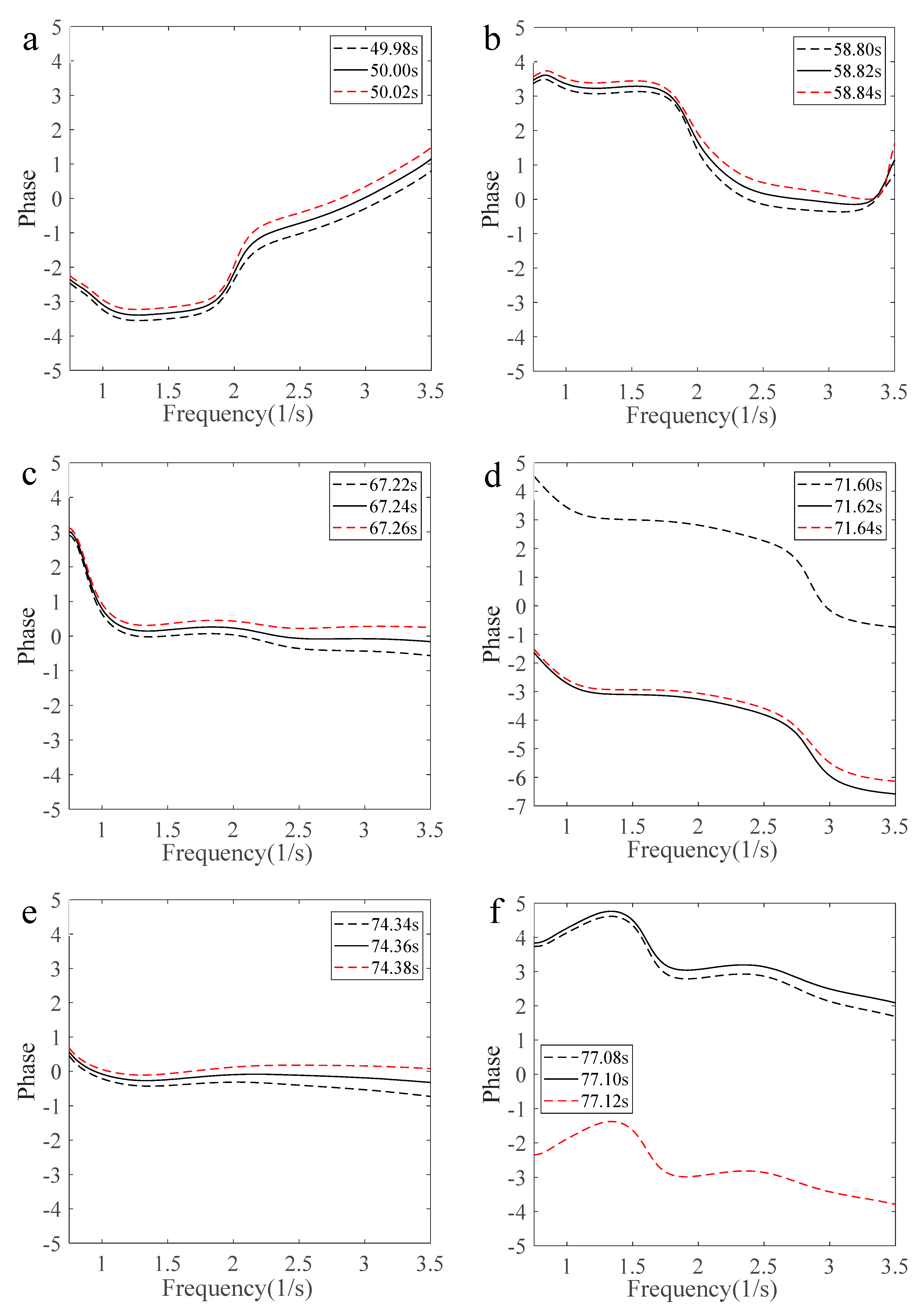
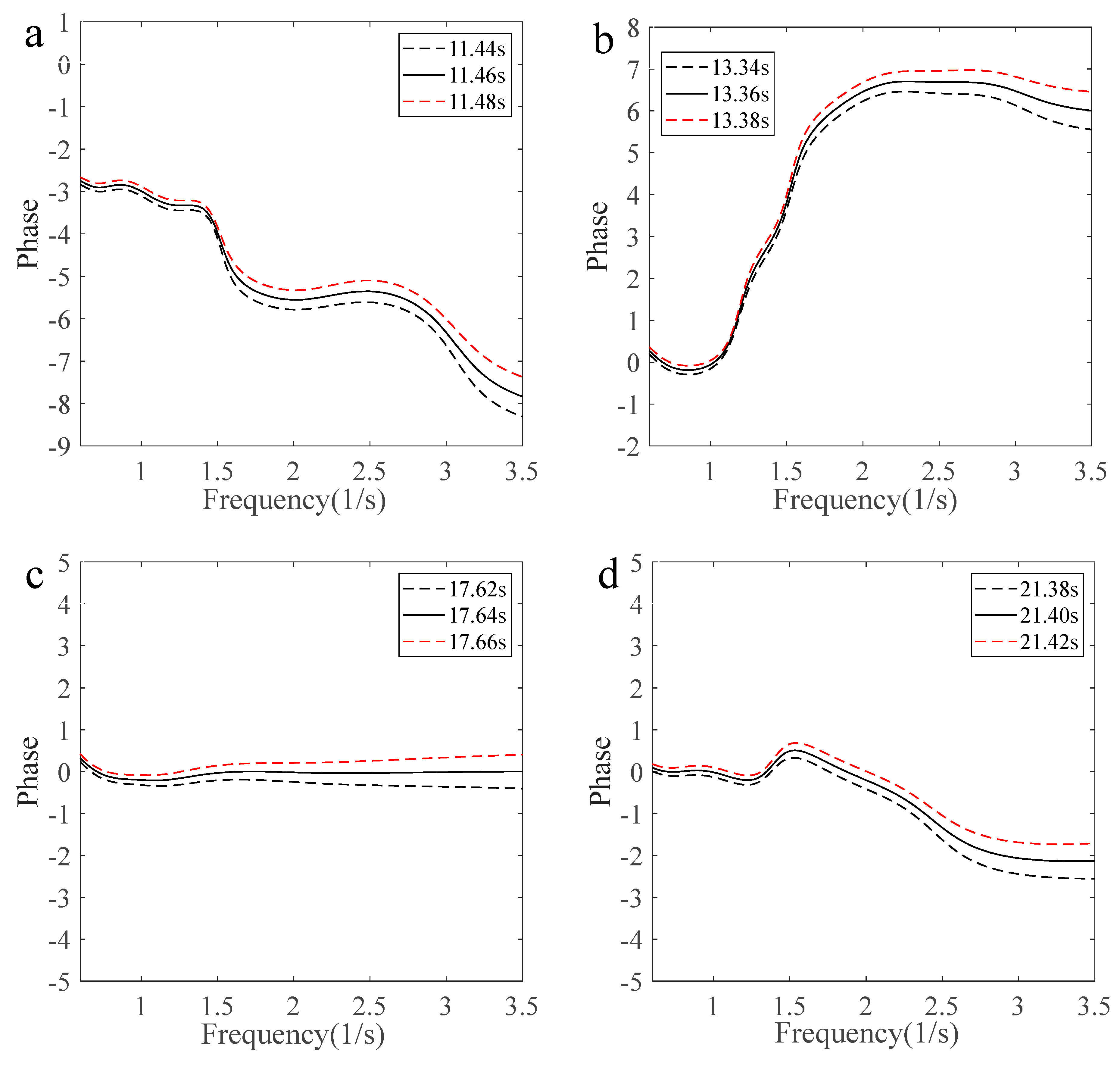
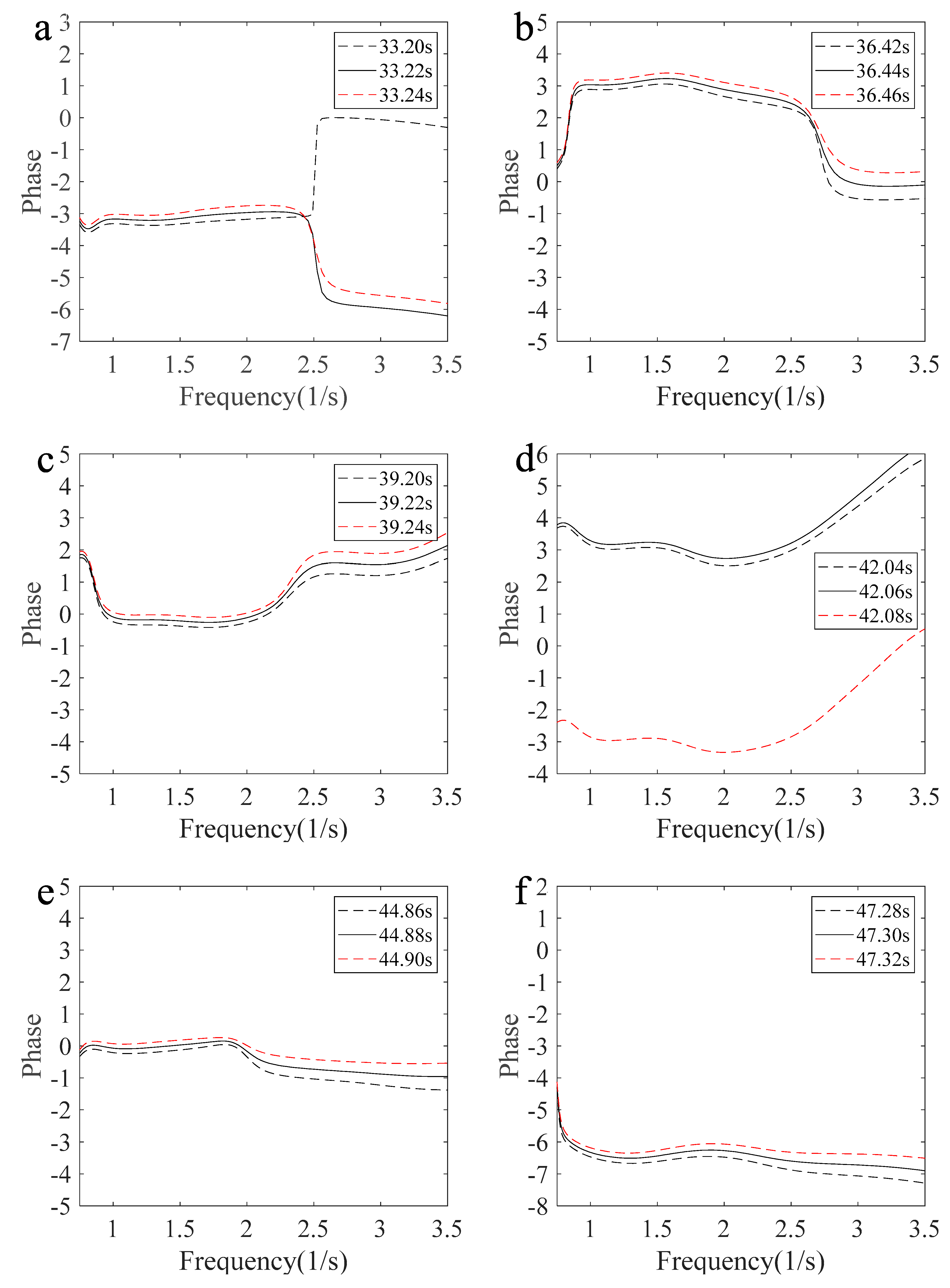
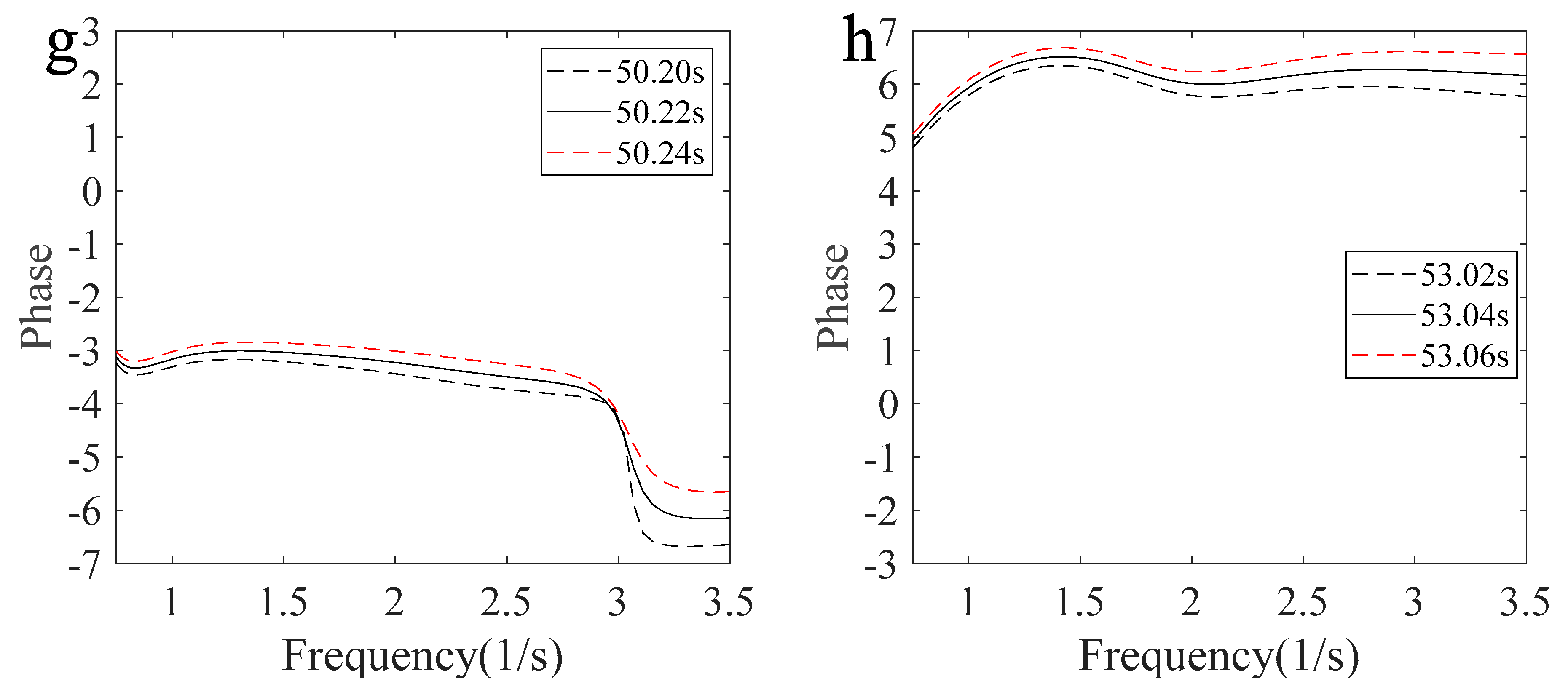
4.4. Phase Variation Characteristics with Freak Wave Evolution
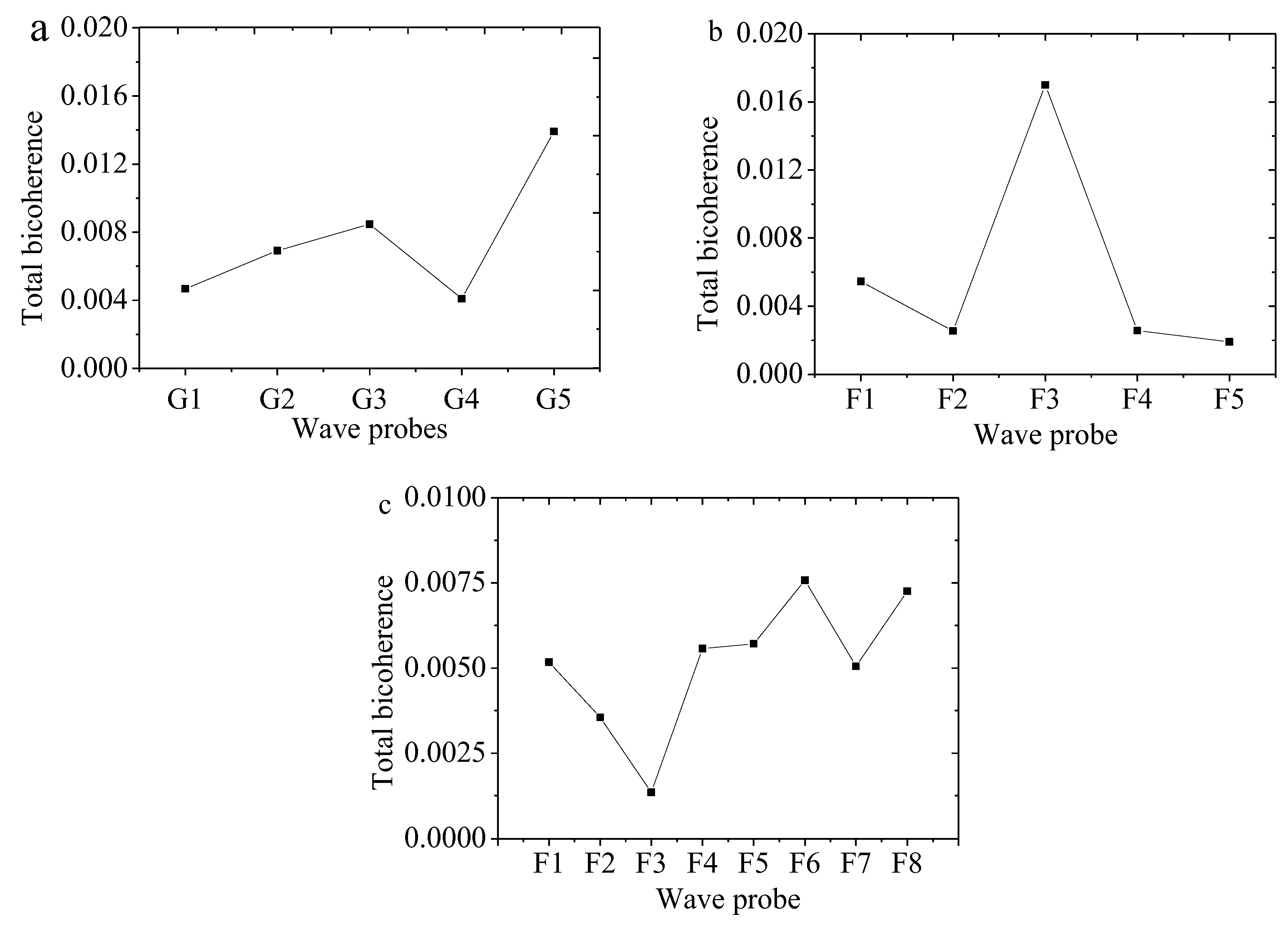
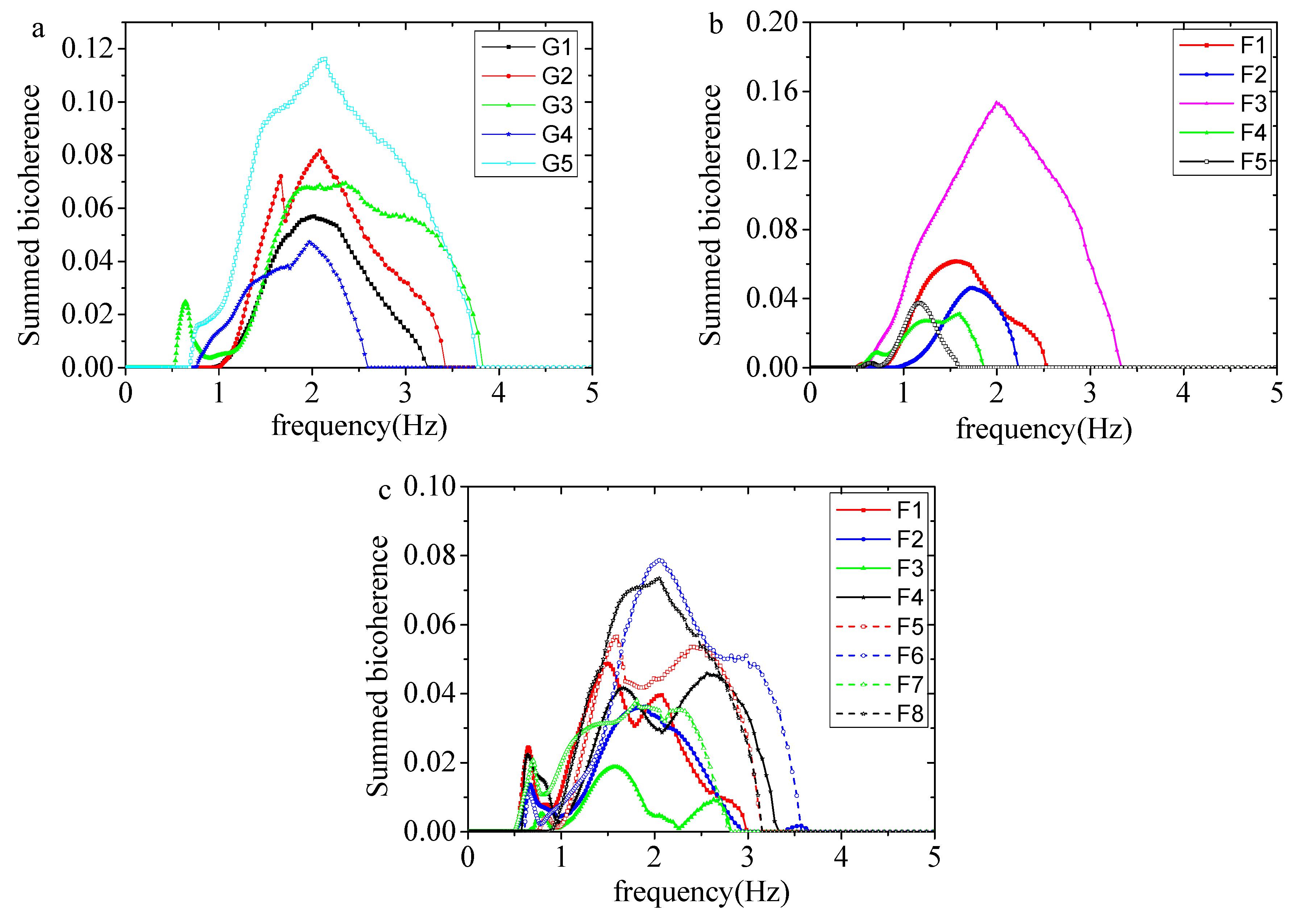
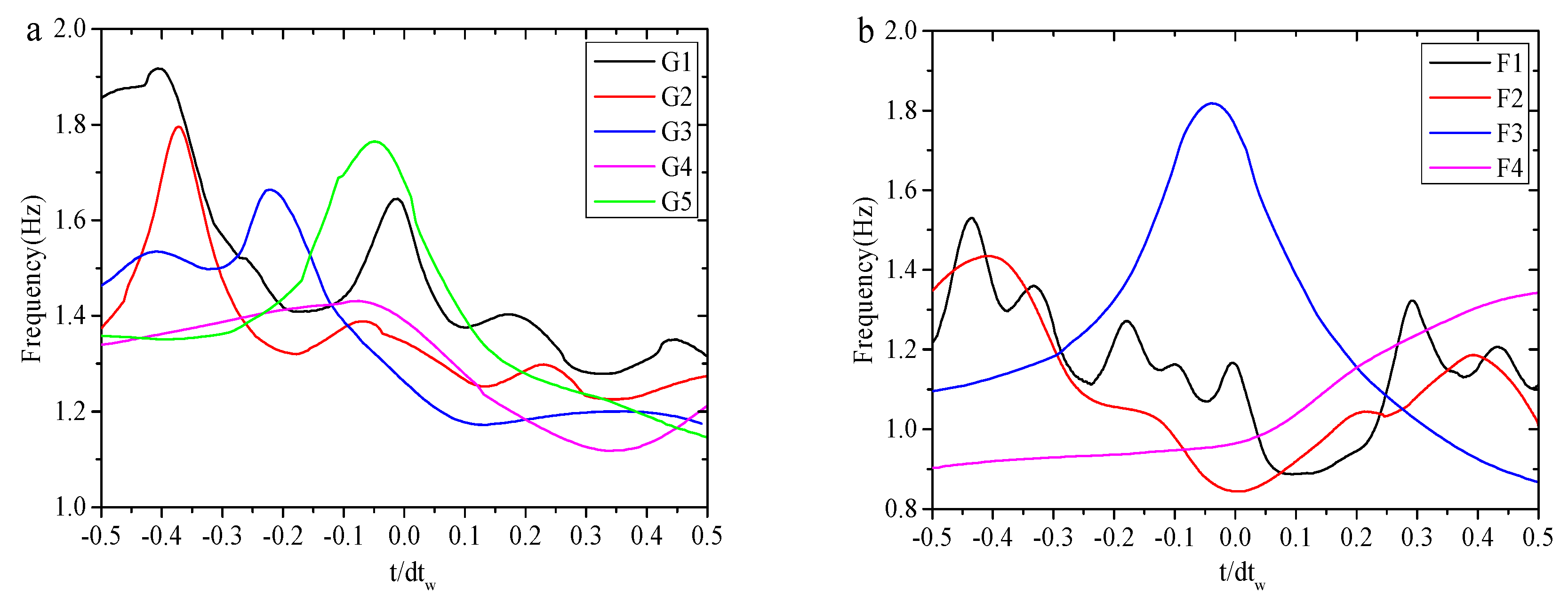
4.5. Nonlinear Interactions with Freak Wave Evolution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sand, S.E.; Ottesen-Hansen, N.E.; Klinting, P.; Gudmestad, O.T.; Sterndorff, M.J. Freak wave kinematics. In Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Water Wave Kinematics, Molde, Norway, 22–25 May 1989; pp. 535–550. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.G. Freak waves: A possible explanation. In Water Wave Kinematics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.G.; Cherneva, Z.; Antão, E.M. Characteristics of abnormal waves in North Sea storm sea states. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2003, 25, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharif, C.; Pelinovsky, E.; Slunyaev, A. Rogue Waves in the Ocean; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Xu, G.; Xie, W.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Z. Characteristics of freak wave and its interaction with marine structures: A review. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 287, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acanfora, M.; Coppola, T.; Fasano, E. Estimation of rogue wave loads on ship structures by exploiting linear wave theory. In Developments in the Analysis and Design of Marine Structures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Koh, C.G.; Lee, W.X.; Lin, P.Z.; Reeve, D.C. Experimental study of freak wave impacts on a tension-leg platform. Mar. Struct. 2020, 74, 102821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, J. Dynamic response and mooring fracture performance analysis of a semi-submersible floating offshore wind turbine under freak waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; He, M.; Cui, C. Experimental Study on Hydrodynamic Characteristics of a Submerged Floating Tunnel under Freak Waves (I: Time-Domain Study). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Mi, C.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y. Transient gap resonance between two closely-spaced boxes triggered by nonlinear focused wave groups. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 305, 117938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, G. Monsters of the deep. New Sci. 2001, 170, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Haver, S. A possible freak wave event measured at the Draupner jacket January 1 1995. In Rogue Waves 2004: Proceedings of a Workshop Organized; Ifremer: Brest, France, 2004; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Veltcheva, A.D.; Soares, C.G. Analysis of abnormal wave groups in Hurricane Camille by the Hilbert Huang Transform method. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 42, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherneva, Z.; Soares, C.G. Time–frequency analysis of the sea state with the Andrea freak wave. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 3143–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didenkulova, E.; Didenkulova, I.; Medvedev, I. Freak wave events in 2005-2021: Statistics and analysis of favourable wave and wind conditions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2023, 23, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner-Gregersen, E.M.; Gramstad, O.; Trulsen, K.; Magnusson, A.K.; Støle-Hentschel, S.; Aarnes, O.J.; Breivik, Ø. Rogue waves: Results of the exwamar project. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 292, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Waseda, T.; Chabchoub, A. (Eds.) Science and Engineering of Freak Waves; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Onorato, M.; Osborne, A.R.; Serio, M.; Cavaleri, L.; Brandini, C.; Stansberg, C.T. Extreme waves, modulational instability and second order theory: Wave flume experiments on irregular waves. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 2006, 25, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S. Observations of freak waves in random wave field in 2D experimental wave flume. China Ocean. Eng. 2013, 27, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, A.; Waseda, T.; Houtani, H.; Cavaleri, L.; Greaves, D.; Onorato, M. Rogue waves in opposing currents: An experimental study on deterministic and stochastic wave trains. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 769, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Wang, X.J.; Shi, H.D.; Guedes Soares, C. Investigation on abnormal wave dynamics in regular and irregular sea states. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 222, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelinovsky, E.; Talipova., T.; Kharif., C. Nonlinear-dispersive mechanism of the freak wave formation in shallow water. Phys. D 2000, 147, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; Swan, C. The evolution of large ocean waves: The role of local and rapid spectral changes. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 2007, 463, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fochesato, C.; Grilli, S.; Dias, F. Numerical modeling of extreme rogue waves generated by directional energy focusing. Wave Motion 2007, 44, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Gao, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y. Hydrodynamic wave forces on two side-by-side barges subjected to nonlinear focused wave groups. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 317, 120056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yu, Y. An efficient focusing model for generation of freak waves. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.L.; Draycott, S.; Adcock, T.A.A.; Taylor, P.H.; van den Bremer, T. Laboratory recreation of the Draupner wave and the role of breaking in crossing seas. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 860, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabchoub, A. Tracking breather dynamics in irregular sea state conditions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 144103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Ji, X. Wave groupiness analysis of the process of 2D freak wave generation in random wave trains. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 104, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Kao, C.C.; Doong, D.J. An analysis of the characteristics of freak waves using the wavelet transform. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2011, 22, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christou, M.; Ewans, K. Field measurements of rogue water waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltcheva, A.; Soares, C.G. Wavelet analysis of non-stationary sea waves during Hurricane Camille. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 95, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slunyaev, A.; Pelinovsky, E.; Soares, C.G. Modeling freak waves from the North Sea. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2005, 27, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmediev, N.; Ankiewicz, A.; Soto-Crespo, J.M.; Dudley, J. Rogue wave early warning through spectral measurements. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 375, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Ma, Y.; Perlin, M.; Ma, X.; Yu, B.; Xu, J. Experimental study of wave–wave nonlinear interactions using the wavelet-based bicoherence. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abroug, I.; Abcha, N.; Jarno, A.; Marin, F. Laboratory study of non-linear wave–wave interactions of extreme focused waves in the nearshore zone. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 3279–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lian, J.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Ma, B. Wavelet bispectral analysis and nonlinear characteristics in waves generated by submerged jets. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 264, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tai, B.; Dong, G.; Fu, R.; Perlin, M. An experiment on reconstruction and analyses of in-situ measured freak waves. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 244, 110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, J.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, L. An experimental study on deterministic freak waves: Generation, propagation and local energy. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 118, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, M.; Ewans, K.; Buchner, B.; Swan, C. Spectral characteristics of an extreme crest measured in a laboratory basin. Proc. Rogue Waves 2008, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fedele, F.; Brennan, J.; de León, S.P.; Dudley, J.; Dias, F. Real world ocean rogue waves explained without the modulational instability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D. Research on the statistical characteristic of freak waves based on observed wave data. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 243, 110323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, T.T.; Herbers, T.H. Nonlinear wave statistics in a focal zone. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 1948–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Benoit, M. Wave–bottom interaction and extreme wave statistics due to shoaling and de-shoaling of irregular long-crested wave trains over steep seabed changes. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 912, A28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trulsen, K.; Zeng, H.; Gramstad, O. Laboratory evidence of freak waves provoked by non-uniform bathymetry. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 097101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trulsen, K.; Raustøl, A.; Jorde, S.; Bæverfjord Rye, L. Extreme wave statistics of long-crested irregular waves over a shoal. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 882, 067102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; He, D.; Dong, G. Experimental investigation on the hydrodynamic characteristics of extreme wave groups over unidirectional sloping bathymetry. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 282, 114982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, A.; Cavaleri, L.; Babanin, A.V.; Benoit, M.; Bitner-Gregersen, E.M.; Monbaliu, J.; Onorato, M.; Osborne, A.R.; Stansberg, C.T. Occurrence of extreme waves in three-dimensional mechanically generated wave fields propagating over an oblique current. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, A.; Proment, D.; Salman, H.; Monbaliu, J.; Frascoli, F.; Dafilis, M.; Stramignoni, E.; Forza, R.; Manfrin, M.; Onorato, M. Wind generated rogue waves in an annular wave flume. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 144503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, T.B.; Feir, J.E. The disintegration of wave trains on deep water Part 1. Theory. J. Fluid Mech. 1967, 27, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tao, A.; Fan, J.; Yang, Z.; Lv. T.; Wang, G.; Zheng, J. Long time evolution of modulated wave trains. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 311, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysthe, K.; Krogstad, H.E.; Müller, P. Oceanic rogue waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2008, 40, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slunyaev, A.; Didenkulova, I.; Pelinovsky, E. Rogue waters. Contemp. Phys. 2011, 52, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabchoub, A.; Onorato, M.; Akhmediev, N. Hydrodynamic envelope solitons and breathers. In Rogue and Shock Waves in Nonlinear Dispersive Media; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 55–87. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, Y. A comparative review on the functional forms of directional wave spectrum. Coast. Eng. J. 1999, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Liu, P.C.; Yasuda, T. Analysis of freak wave measurements in the Sea of Japan. Ocean. Eng. 2002, 29, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Pan, G.; Wan, D. Analysis of statistical characteristics of freak waves based on high order spectral coupled with cfd method. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 323, 120615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ma, X.; Zang, J.; Dong, G.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L. Numerical investigation of harbor oscillations induced by focused transient wave groups. Coast. Eng. 2020, 158, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Benoit, M.; Kimmoun, O.; Chabchoub, A.; Hsu, H.-C. Statistics of Extreme Waves in Coastal Waters: Large Scale Experiments and Advanced Numerical Simulations. Fluids 2019, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, R.; Abcha, N.; Abroug, I.; Lecoq, N.; Turki, E.-I. A Multi-Approach Analysis forMonitoring Wave Energy Driven by Coastal Extremes. Water 2024, 16, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Ma, Y.; Dong, G.; Perlin, M. A wavelet-based wave group detector and predictor of extreme events over unidirectional sloping bathymetry. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 229, 108936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glejin, J.; Kumar, V.S.; Nair, T.M.B.; Singh, J. Freak waves off Ratnagiri, west coast of India. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
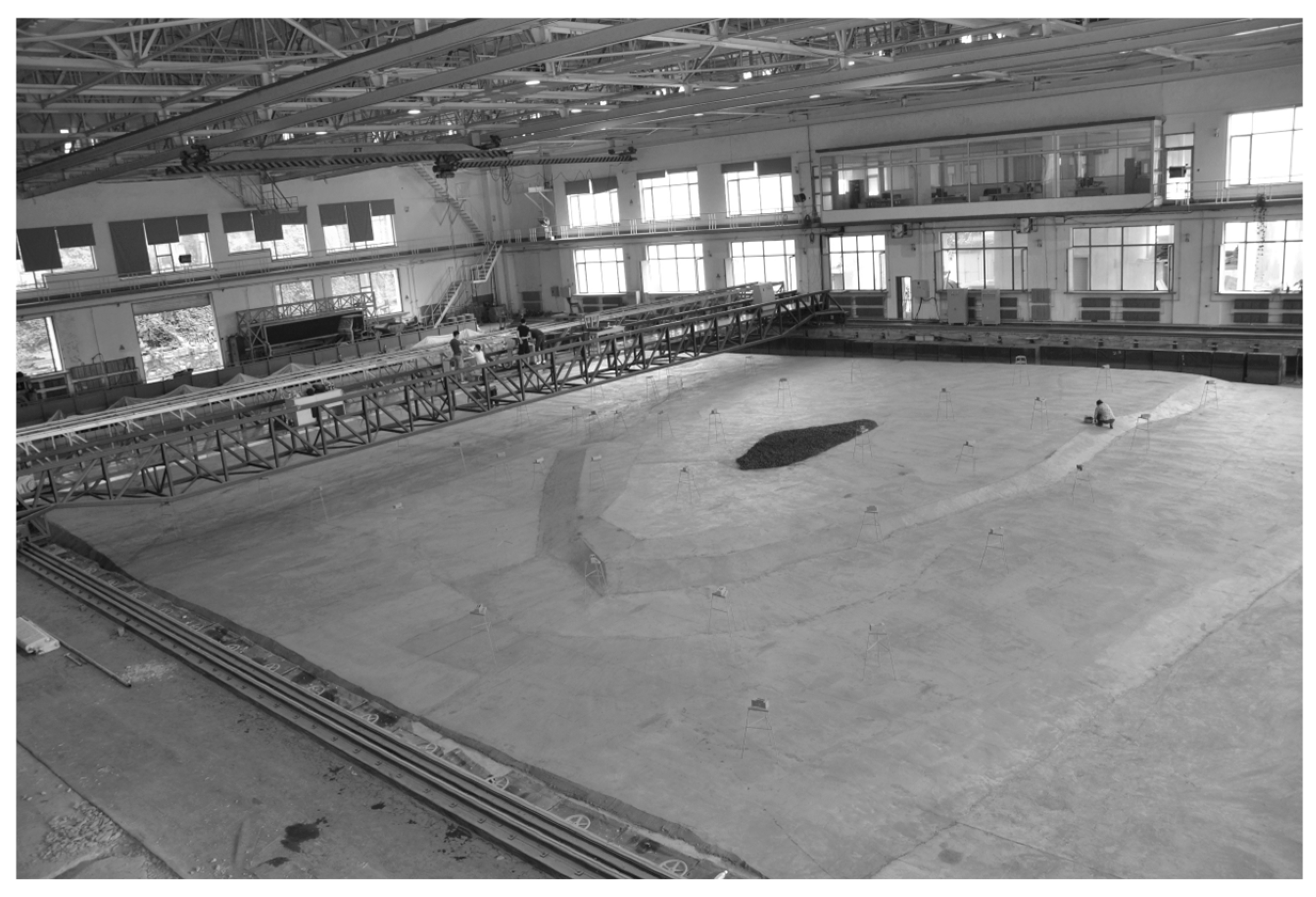


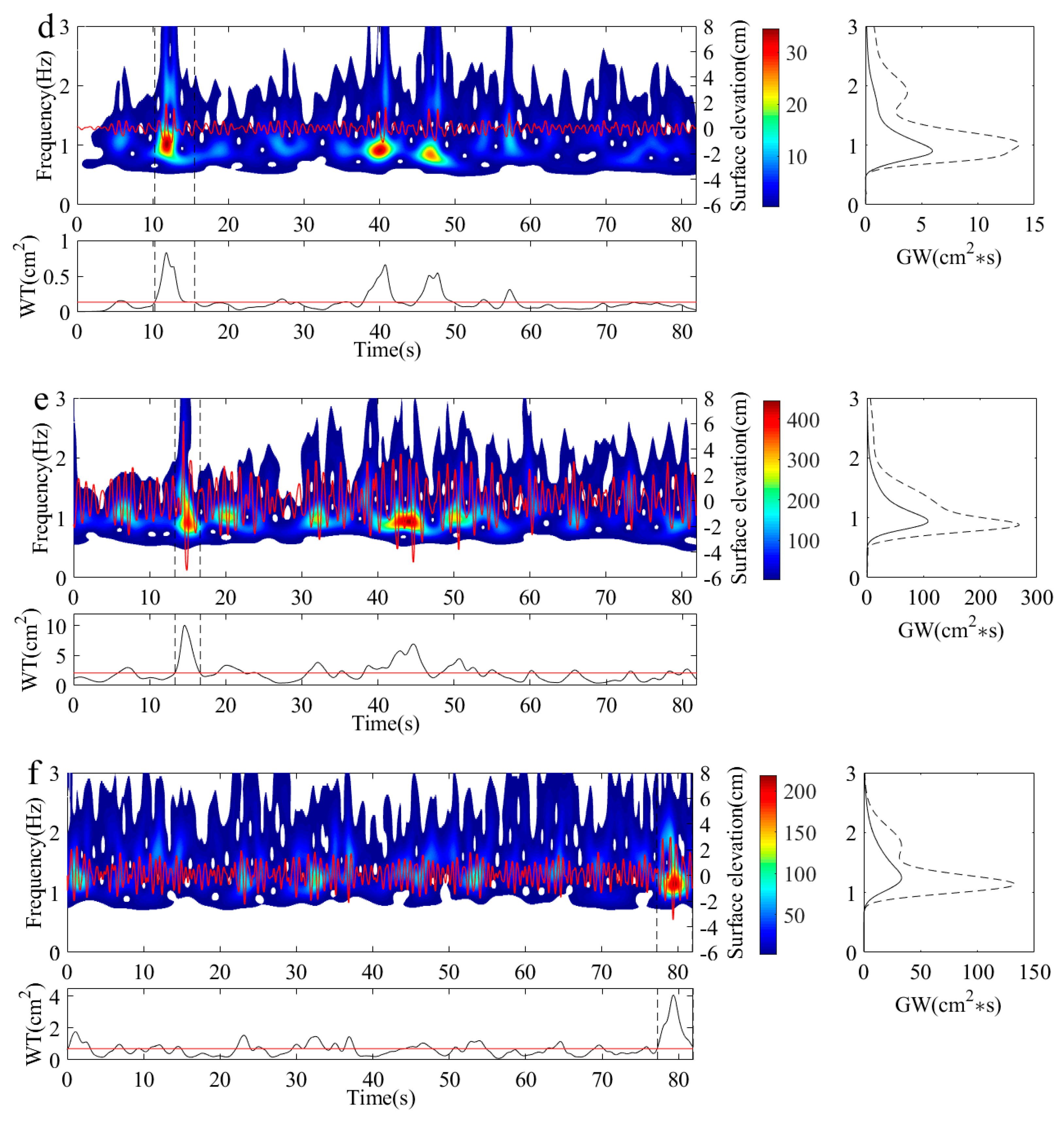
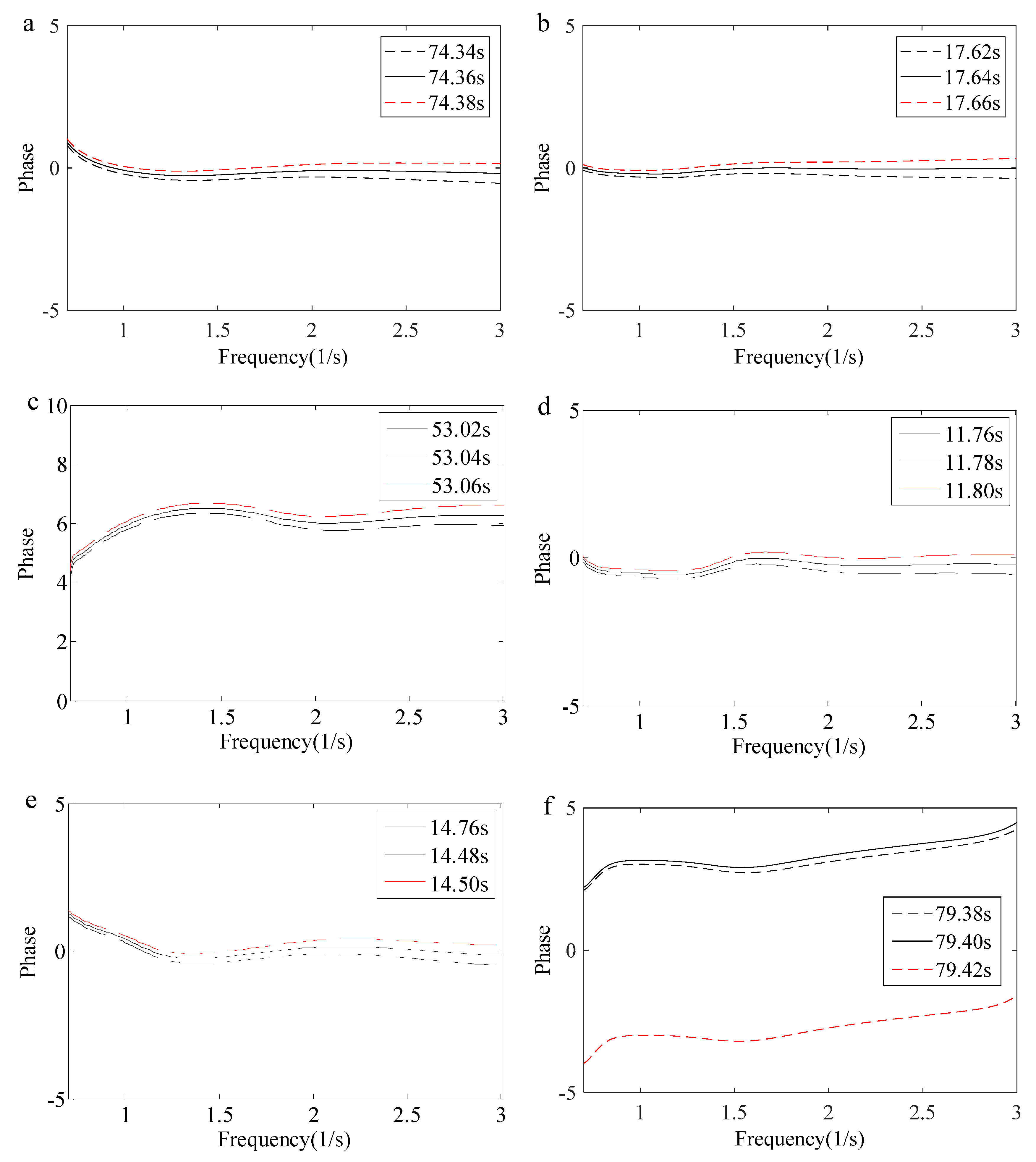

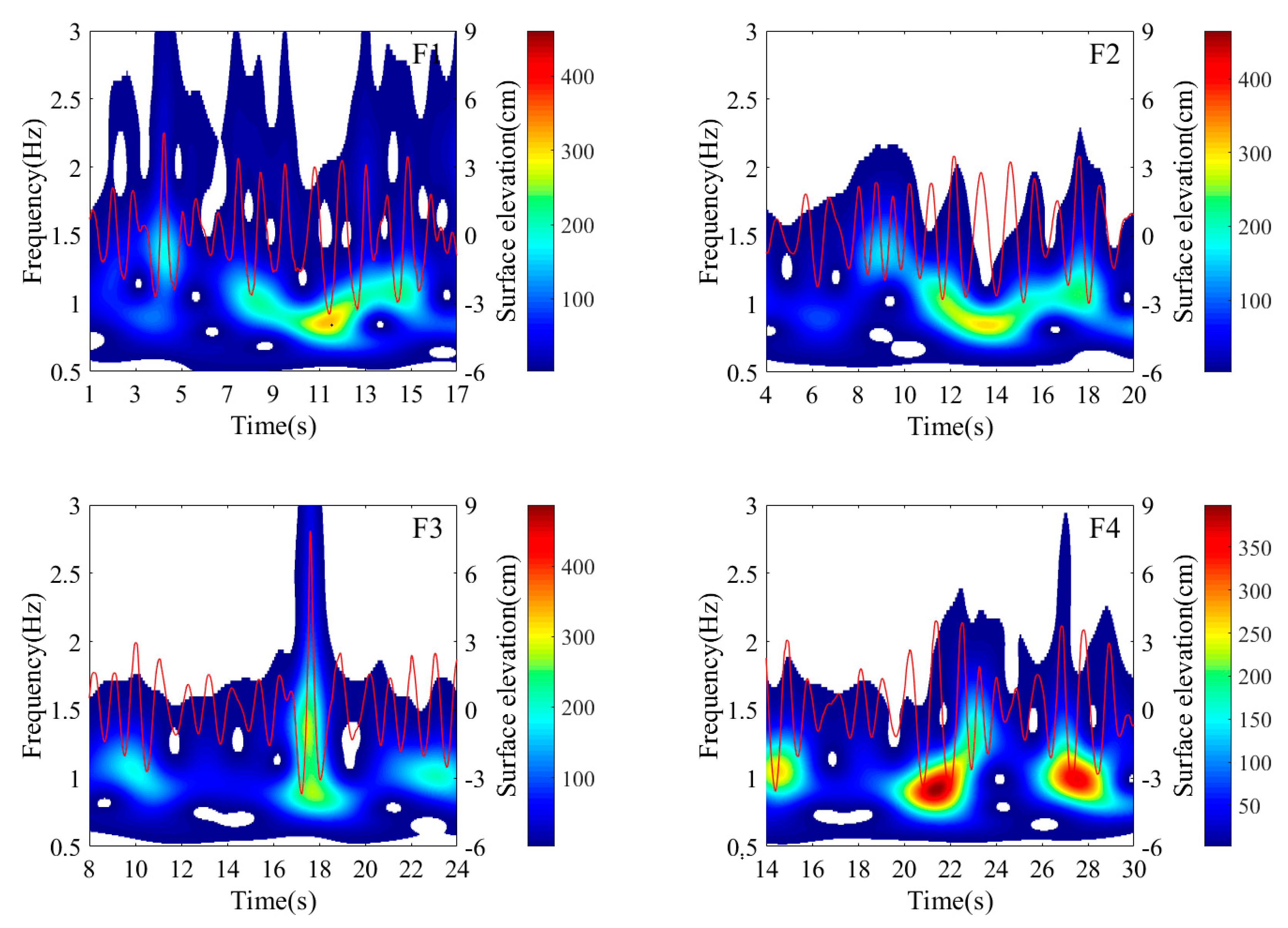
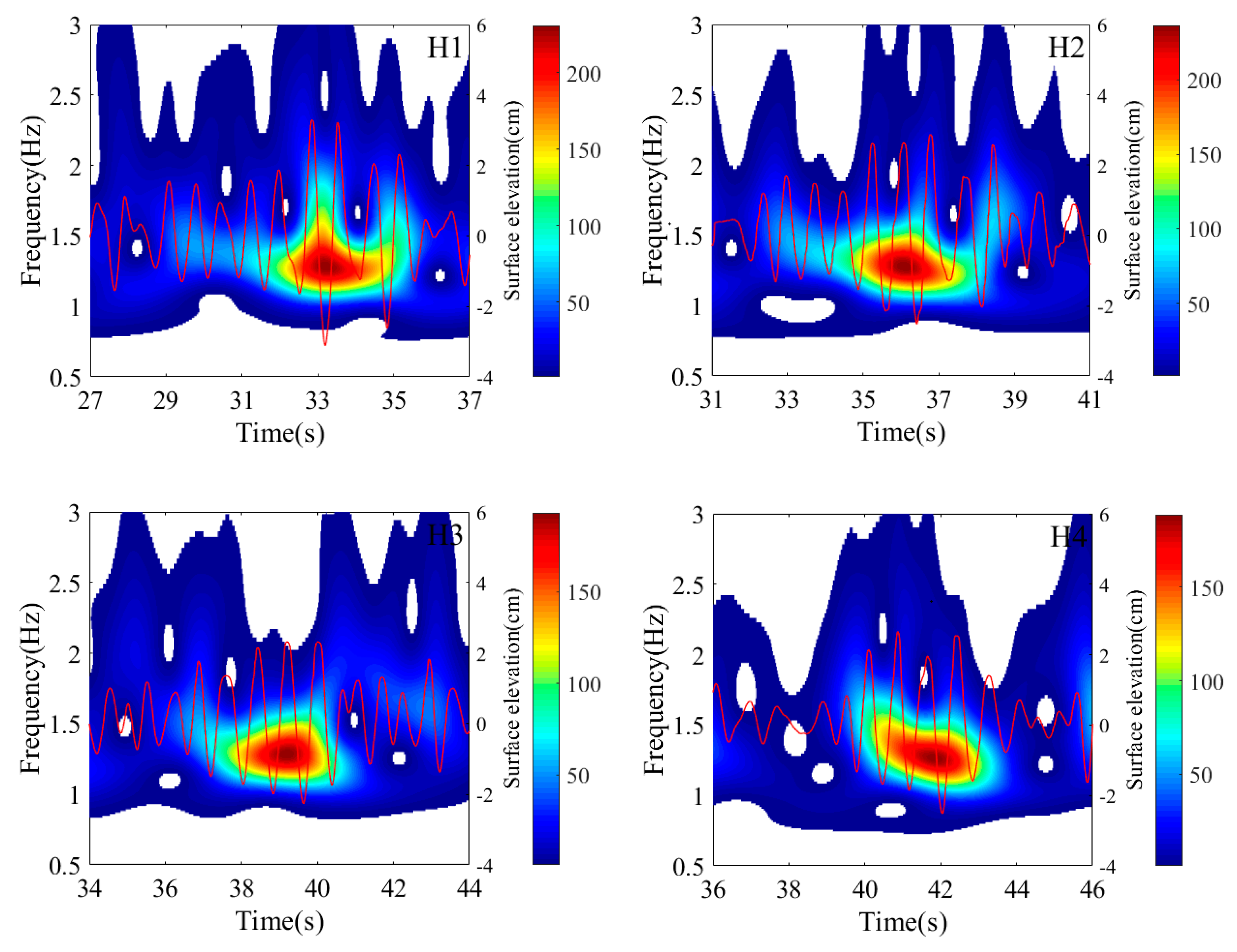
| Case | /cm | /s |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1.61 | 0.67, 0.73, 0.8, 0.87, 0.93, 1, 1.07, 1.21 |
| A2 | 3.59 | 0.67, 0.73, 0.8, 0.87, 0.93, 1, 1.07, 1.14 |
| A3 | 6.35 | 0.8, 0.87, 0.93, 1, 1.07, 1.14, 1.21 |
| A4 | 8.05 | 0.8, 0.87, 0.93, 1, 1.07, 1.14, 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, A.; Zhou, T.; Ding, D.; Ma, X.; Zou, L. Mechanisms of Freak Wave Generation from Random Wave Evolution in 3D Island-Reef Topography. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101926
Wang A, Zhou T, Ding D, Ma X, Zou L. Mechanisms of Freak Wave Generation from Random Wave Evolution in 3D Island-Reef Topography. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101926
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Aimin, Tao Zhou, Dietao Ding, Xinyu Ma, and Li Zou. 2025. "Mechanisms of Freak Wave Generation from Random Wave Evolution in 3D Island-Reef Topography" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101926
APA StyleWang, A., Zhou, T., Ding, D., Ma, X., & Zou, L. (2025). Mechanisms of Freak Wave Generation from Random Wave Evolution in 3D Island-Reef Topography. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101926






