Spatio-Temporal Variability of Key Habitat Drivers in China’s Coastal Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Satellite Data
2.2.2. In Situ Data for SDD Calibration/Validation
2.2.3. Pre-Processing Pipeline
2.3. Remote-Sensing Algorithm for Water Transparency
2.4. Spatio-Temporal Analysis
2.4.1. Trend Detection
2.4.2. Seasonal Cycle Extraction
3. Results
3.1. The Annual Mean Spatial Distribution of Environmental Factor in China Sea
3.2. Seasonal Variations in Environmental Factors in China Sea
3.3. Long-Term Trends of Environmental Factors in China Sea
| Zsd Trends | Extent |
|---|---|
| Very significantly reduced | |
| Significantly reduced | |
| Not significantly reduced | |
| Not significantly increased | |
| Significantly increased | |
| Very significantly increased |
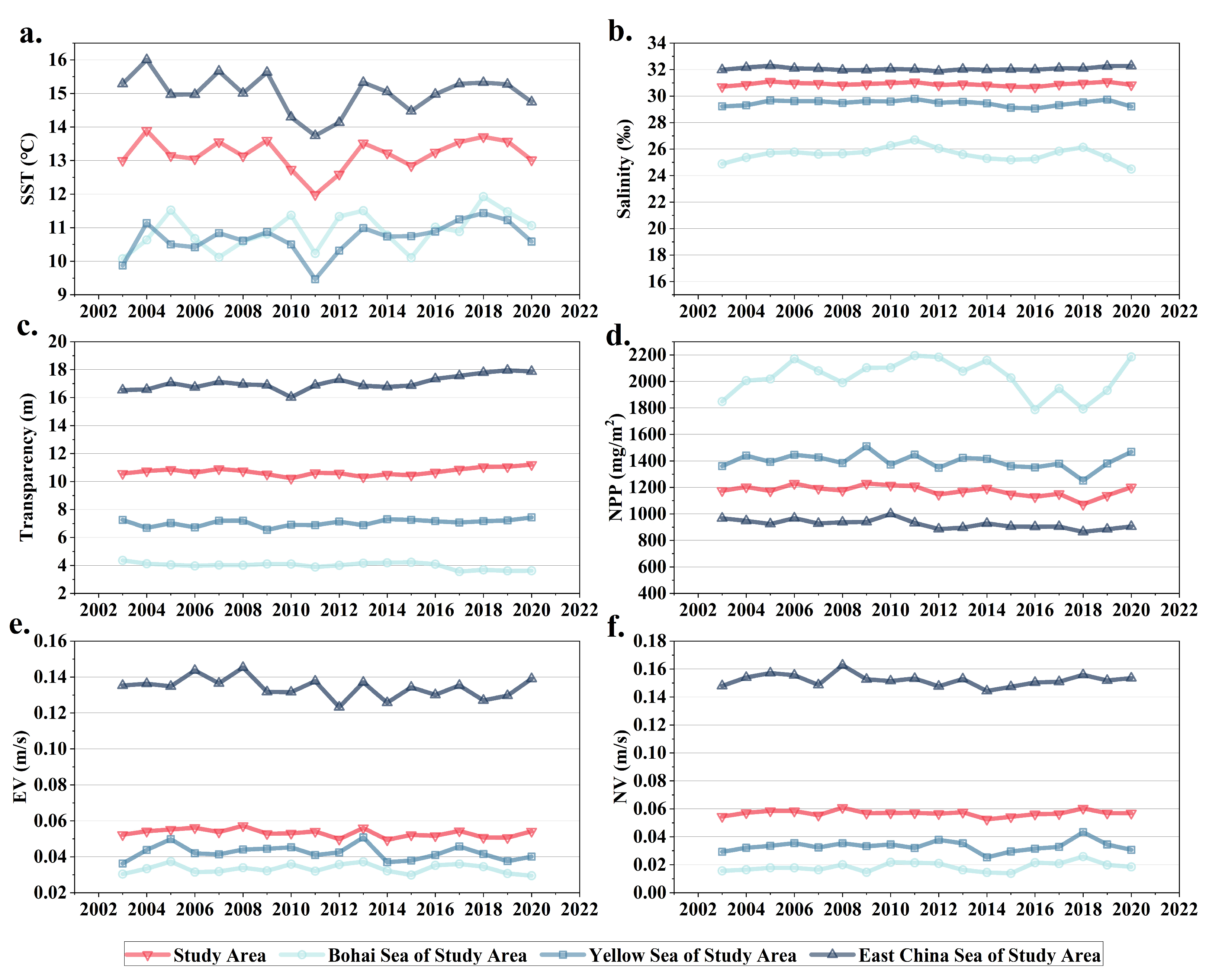
3.4. Interannual Variations in Environmental Factors in China Sea
3.5. Correlation Among Coastal Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Key Findings in Relation to Previous Studies
4.2. Implications for Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management and Policy
4.3. Limitations and Uncertainties
4.4. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; McCauley, D.J.; Altieri, A.H.; Silliman, B.R.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; He, Q. A wide megafauna gap undermines China’s expanding coastal ecosystem conservation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashion, T.; Le Manach, F.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Most fish destined for fishmeal production are food-grade fish. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegorelli, C.; De Andres, M.; Garcia-Onetti, J.; Rayo, S.; Garcia-Sanabria, J. Marine protected areas as socio-economic systems: A method for defining socio-economic criteria in marine planning. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1358950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, L.E.; Bohmann, K.; Craig, O.E.; Orton, D.; Pedersen, M.W.; Olsen, M.T.; Thurstan, R.H.; Scourse, J. Shifting seas: Understanding deep-time human impacts on marine ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2025, 380, 20240026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, R. The state of world fisheries and aquaculture (Sofia) 2020 report. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2020, 16, 800–801. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q. Conservation of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) based on its life history: Dilemma and breakthrough. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 1297–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pan, H.; Cao, R.; Wang, J.; Lv, X. Multiple Timescale Variations in Water Transparency in the Eastern China Seas over the Period 1997–2019. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2023, 128, e2022JC019170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mi, T.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yao, Q. Upwelling of cold water in the South Yellow Sea alleviates phosphorus and silicon limitations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2025, 70, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Nutrient Structure of the Taiwan Warm Current and Estimation of Vertical Nutrient Fluxes in Upwelling Areas in the East China Sea in Summer. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2014, 13, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Xiao, F.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Luo, J.; Du, Y. Inversion and analysis of transparency changes in the eastern coastal waters of China from 2003 to 2023 by an improved QAA-based method. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1503177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Dang, Y.; Ban, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, F. Integrating Remote Sensing and Ecological Modeling to Assess Marine Habitat Suitability for Endangered Chinese Sturgeon. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhuang, P. Migration and feeding habits of juvenile Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis Gray 1835) in the Yangtze Estuary: Implications for conservation. Aquat. Conserv.-Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W. First Insights into the Migration Route and Spatial Distribution of the Endangered Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) in the Yangtze River Estuary. Fishes 2024, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J. Large and Small Yellow Croakers Feeding and Living Together Make Large Yellow Croaker Population Recovery Difficult: A Guild Perspective. Biology 2024, 13, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Jiang, R.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Cui, G. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of Larimichthys polyactis in Zhoushan fishing ground and the adjacent waters based on two-stage GAM. J. Fish. Sci. China 2022, 29, 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Chen, Q.; Fu, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Sun, R.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y. Daily growth of young-of-the-year largehead hairtail (Trichiurus japonicus) in relation to environmental variables in the East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 201, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Lin, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, X. Analysis on responses of hairtail catches to fishing and climate factors in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, China. J. Fish. Sci. China 2012, 19, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, T.; Sun, G.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Weng, N. A Comprehensive Ensemble Model for Marine Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Prediction in Meteorologically Sparse and Complex Regions: A Case Study in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Ban, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z. An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM plus and OLI Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akritas, M.G.; Murphy, S.A.; Lavalley, M.P. The Theil-Sen estimator with doubly censored data and applications to astronomy. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.A.; Liu, C.T.; Chuang, W.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Shiah, F.K.; Tang, T.Y.; Chung, S.W. Enhanced buoyancy and hence upwelling of subsurface Kuroshio waters after a typhoon in the southern East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 42, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Bilal, M. Variations of transparency derived from GOCI in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 12191–12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.; Wu, L. Possible origins of the western pacific warm pool decadal variability. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Geng, X.; Stuecker, M.F.; Jin, F.-F. Modulation of tropical cyclones in the southeastern part of western North Pacific by tropical Pacific decadal variability. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4475–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienert, F.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. Decadal prediction of interannual tropical and North Pacific sea surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 5913–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Kusakabe, M.; Southon, J.R. 10 Be profiles in the East China Sea and the Okinawa Trough. Deep.-Sea Res. Part II-Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Wen, T.; Zhang, C.; Han, X. Distribution of dissolved inorganic nitrogen over the continental slope of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shen, X.; Jiang, M. Change characteristics of DSi and nutrition structure at the Yangtze River Estuary after Three Gorges Project impounding and their ecological effect. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2017, 43, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, F.-T.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Ge, J.-Z.; Deng, B.; Du, J.-Z.; Zhang, J. Reconstruction of the main phytoplankton population off the Changjiang Estuary in the East China Sea and its assemblage shift in recent decades: From observations to simulation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Lin, L.S.; Cheng, J.H. Distribution characteristic of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis Bleeker) and its relationship with bottom water temperature and salinity in the northern East China Sea in autumn. J. Fish. Sci. China 2009, 16, 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Cheng, J. An Analysis of the Current Situation of Fishery Biology of Small Yellow Croaker in the East China Sea. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2004, 34, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Q.; Delu, P.; Zhihua, M. Water transparency (Secchi depth) monitoring in the China Sea with the SeaWiFS satellite sensor. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems and Hydrology VI, Maspalomas, Canary Islands, Spain, 26 October 2004; pp. 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Zhou, B.; Xing, Q.; Fan, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, X. Monitoring Secchi depth of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using a semi-analytical algorithm. In Proceedings of the Conference on Ocean Remote Sensing and Monitoring from Space, Beijing, China, 18 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, D.; Pohlmann, T. The influence of the Three-Gorges Dam on hydrographic and hydrodynamic conditions of the East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2011, 30, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhu, C.; Wu, L.; Huang, L. Problems caused by the Three Gorges Dam construction in the Yangtze River basin: A review. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Song, J.; Vigier, N. Progressive Evolution of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Sediment Weathering Intensity Since the Three Gorges Dam Operation. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Pan, Y.Q.; Jin, X.L.; Du, H.Y.; Li, M.C.; Jiang, P.H. The delineation of ecological redline area for catchment sustainable management from the perspective of ecosystem services and social needs: A case study of the Xiangjiang watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, X.M.; Liu, T.; Yang, G.; Liu, S.J.; Lyu, J.X.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, H.; Gao, J.H. Recent warming of the Kuroshio Current has promoted offshore sediment transport in the Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2024, 9, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Xie, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, L. A novel spectro-temporal index NDTeI combined with machine learning algorithm for Sentinel-2 cloud detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 4023–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, D.; Zhou, T. Impact of Turbidity on Satellite-Derived Bathymetry: Comparative Analysis Across Seven Ports in the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| SST | Salinity | Transparency | NPP | EV | NV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | 1 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.56 |
| Salinity | 0.95 | 1 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.49 |
| Transparency | 0.76 | 0.71 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.65 | 0.58 |
| NPP | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.07 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| EV | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 1 | 0.76 |
| NV | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.76 | 1 |
| SST | Salinity | Transparency | NPP | EV | NV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | 1 | −0.26 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| Salinity | −0.26 | 1 | 0.2 | −0.36 | −0.13 | 0 |
| Transparency | 0.17 | 0.2 | 1 | −0.6 | −0.05 | −0.07 |
| NPP | 0.05 | −0.36 | −0.6 | 1 | −0.09 | 0.04 |
| EV | 0.12 | −0.13 | −0.05 | −0.09 | 1 | 0.16 |
| NV | 0.08 | 0 | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, S.; Dang, Y.; Ban, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, F. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Key Habitat Drivers in China’s Coastal Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101874
Cao S, Dang Y, Ban X, Zhou Y, Luo J, Zhu J, Xiao F. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Key Habitat Drivers in China’s Coastal Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101874
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Shuhui, Yingchao Dang, Xuan Ban, Yadong Zhou, Jiahuan Luo, Jiazhi Zhu, and Fei Xiao. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Variability of Key Habitat Drivers in China’s Coastal Waters" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101874
APA StyleCao, S., Dang, Y., Ban, X., Zhou, Y., Luo, J., Zhu, J., & Xiao, F. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Variability of Key Habitat Drivers in China’s Coastal Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101874







