Assessment of the Offshore Migration of Mussel Production Based on an Aquaculture Similarity Index (ASI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Databases
3.1.1. Thermohaline Variables
3.1.2. Hydrodynamic Variables
3.1.3. Biogeochemical Variables
3.1.4. Topographic Variables
3.1.5. Administrative Limitations
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Reducing Data to a Common Grid
3.2.2. Normalizing Variables
3.2.3. Weighing the Different Contributions (Delphi)
3.2.4. Sensitivity Analysis of the ASI
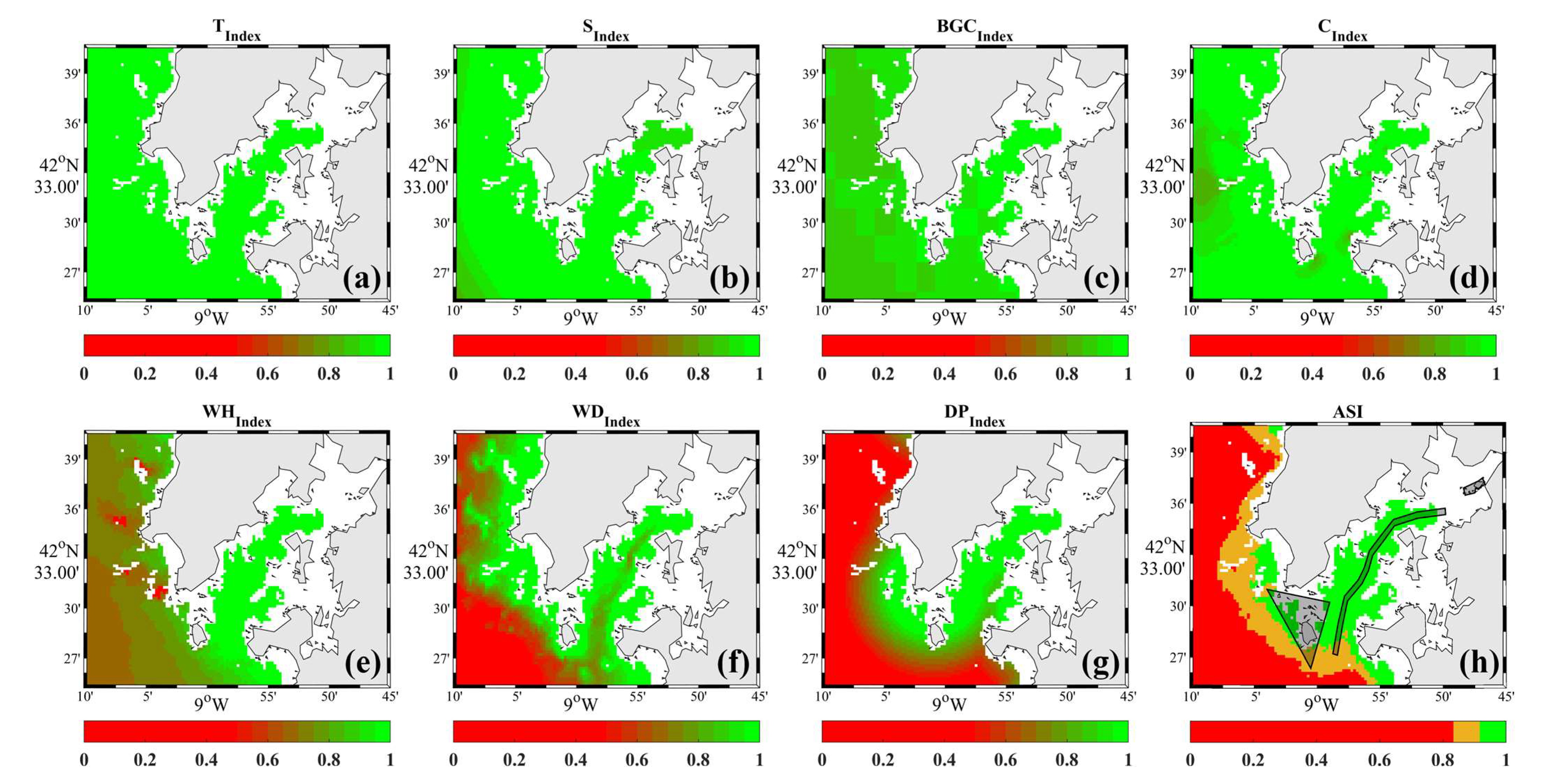
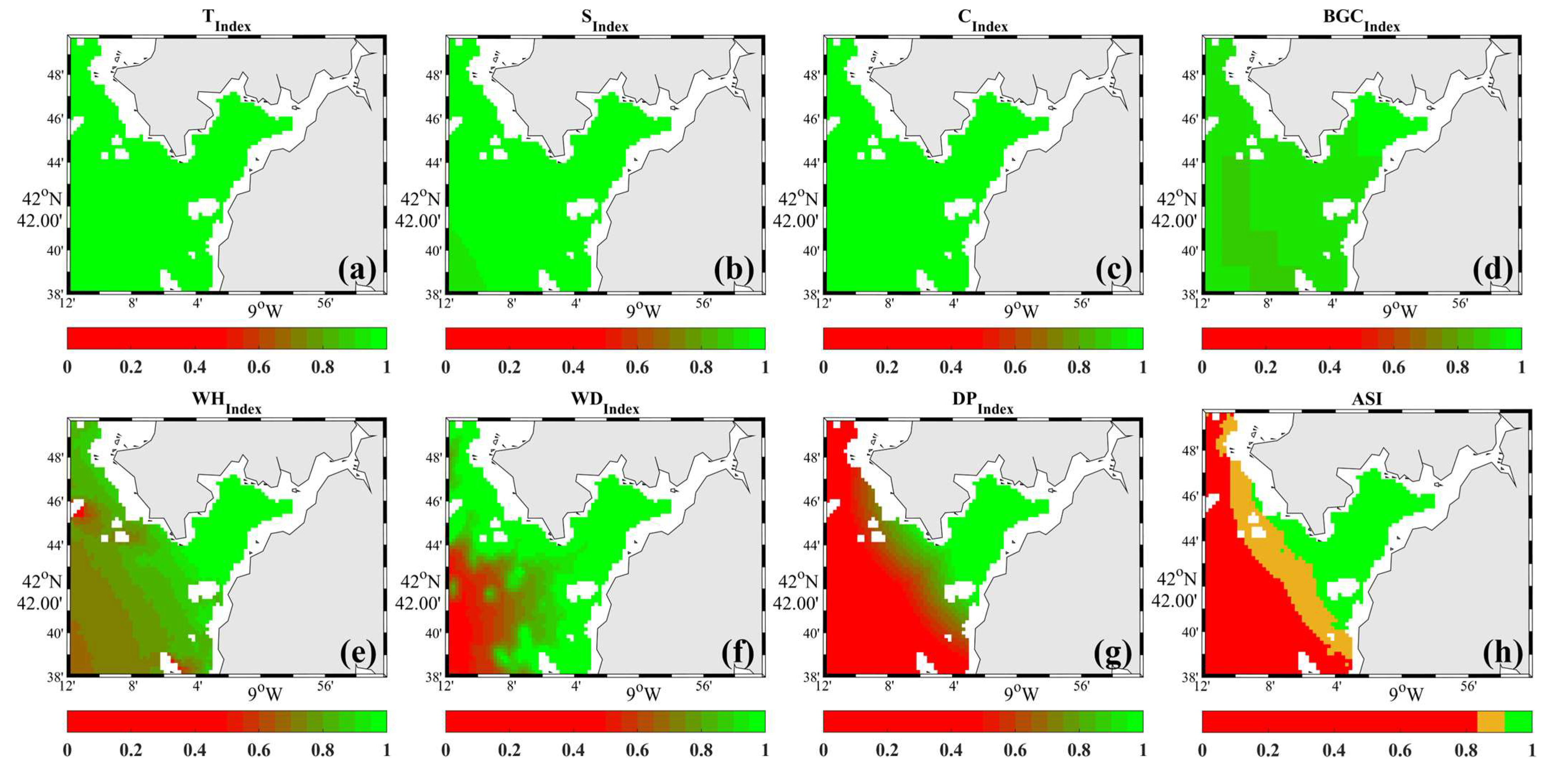
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FishStat: Global Aquaculture Production 1950–2022. 2025. Available online: www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics/software/fishstatj (accessed on 22 September 2025).
- Soliño, M.; Figueras, A. The vulnerability of mussel aquaculture: Understanding environmental threats and future directions. Aquaculture 2025, 599, 742196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.D.G.; Hughes, A.R.; Hultgren, K.M.; Miner, B.G.; Sorte, C.J.; Thornber, C.S.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Tomanek, L.; Williams, S.L. The impacts of climate change in coastal marine systems. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Duffy, J.M.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Marine Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Escalera, L.; Reguera, B.; Nogueira, E.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Bode, A.; Rey, V.; Fraga, S. Red tides in the Galician rías: Historical overview, ecological impact, and future monitoring strategies. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2024, 26, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M.; deCastro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, L.; Sousa, M.C. How can ocean warming at the NW Iberian Peninsula affect mussel aquaculture? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, S.; Vázquez, E.; Román, M.; Viejo, R.M.; Weidberg, N.; Troncoso, J.S.; Woodin, S.A.; Wethey, D.S.; Olabarria, C. Understanding the effects of recent atmospheric heatwaves on seagrass-inhabited intertidal shellfish beds: A mesocosm experiment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 212, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Des, M.; Fernandez-Novoa, D.; deCastro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, J.L.; Sousa, M.C.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Modeling salinity drop in estuarine areas under extreme precipitation events within a context of climate change: Effect on bivalve mortality in Galician Rías Baixas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Olivares, A.; Des, M.; Olabarria, C.; deCastro, M.; Vázquez, E.; Sousa, M.C.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Does global warming threaten small-scale bivalve fisheries in NW Spain? Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 180, 105707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, J.L.; deCastro, M.; Iglesias, D.; Sousa, M.C.; ElSerafy, G.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Historical and Future Naturalization of Magallana Gigas in the Galician Coast in a Context of Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Olivares, A.; Des, M.; deCastro, M.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Assessing the Vulnerability of Commercial Bivalves to Intensifying Atmospheric Heatwaves in Coastal Ecosystems. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 209, 107210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Sustainable Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Soto, D.; Brummett, R. Aquaculture Zoning, Site Selection and Area Management under the Ecosystem Approach to Aquaculture; Report ACS18071; FAO; World Bank: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, E.; Woodin, S.A.; Wethey, D.S.; Peteiro, L.G.; Olabarria, C. Reproduction Under Stress: Acute Effect of Low Salinities and Heat Waves on Reproductive Cycle of Four Ecologically and Commercially Important Bivalves. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 685282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Olabarría, C.; Vázquez, E. Assessment of Risks Associated with Extreme Climate Events in Small-Scale Bivalve Fisheries: Conceptual Maps for Decision-Making Based on a Review of Recent Studies. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.; Prego, R. Rias, estuaries and incised valleys: Is a ria an estuary? Mar. Geol. 2003, 196, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gil, S. A natural laboratory for shallow gas: The Rías Baixas (NW Spain). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2003, 23, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartelle, V.; García-Moreiras, I.; Martínez-Carreño, N.; Sobrino, C.M.; García-Gil, S. The role of antecedent morphology and changing sediment sources in the postglacial palaeogeographical evolution of an incised valley: The sedimentary record of the Ría de Arousa (NW Iberia). Glob. Planet. Change 2022, 208, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; deCastro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M.; Prego, R. Inter-and intra-annual analysis of the salinity and temperature evolution in the Galician Rías Baixas–ocean boundary (northwest Spain). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2005, 110, C04008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, J.J.; Prego, R.; Ruiz-Villarreal, M.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Montero, P.; Santos, A.P.; Pérez-Villar, V. Evaluation of the seasonal variations in the residual circulation in the Ría of Vigo (NW Spain) by means of a 3D baroclinic model. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 47, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, F. Upwelling off the Galician coast, northwest Spain. Coast. Upwelling 1981, 1, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Rosón, G.; Pérez, F.F.; Pazos, Y. Hydrographic variability off the Rías Baixas (NW Spain) during the upwelling season. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1993, 98, 14447–14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Moreira, C.; Alvarez, I.; deCastro, M. Ekman transport along the Galician coast (northwest Spain) calculated from forecasted winds. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, C10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, E.D.; Largier, J.L.; Torres, R.; Sheridan, M.; Trasviña, A.; Souza, A.; Pazos, Y.; Valle-Levinson, A. Coastal upwelling and downwelling forcing of circulation in a semi-enclosed bay: Ria de Vigo. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, J.O.; Tenore, K.R.; Castillejo, F.; Atkinson, L.P.; Schwing, F.B.; Lavin, A. The relationship of upwelling to mussel production in the Rias on the western coast of Spain. J. Mar. Res. 1987, 452, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedracoba, S.; Alvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Rosón, G.; Herrera, J.L. Short-timescale thermohaline variability and residual circulation in the central segment of the coastal upwelling system of the Ría de Vigo (northwest Spain) during four contrasting periods. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2005, 110, C03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.F.; Alvarez Salgado, X.; Rosón, G.; Ríos, A.F. Carbonic-calcium system, nutrients and total organic nitrogen in continental runoff to the Galician Rias Baixas, NW Spain. Oceanol. Acta 1992, 15, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Doval, M.D.; López, A.; Madriñán, M. Temporal variation and trends of inorganic nutrients in the coastal upwelling of the NW Spain (Atlantic Galician rías). J. Sea Res. 2016, 108, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, F.G.; Labarta, U.; Reiriz, M.J. Coastal upwelling, primary production and mussel growth in the Rías Baixas of Galicia. In Sustainable Increase of Marine Harvesting: Fundamental Mechanisms and New Concepts; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Pérez, F.F.; Ríos, A.F. Seasonal patterns and long-term trends in an estuarine upwelling ecosystem (Ría de Vigo, NW Spain). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Alberti, A. Xeografia de Galicia; Instituto Geológico y Minero de España: Madrid, Spain, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, L. Oceanography of the Ria de Arosa (NW Spain). In Konik, Meteor International Medelingen en Verlan; Staatsuitgeverij: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 96, p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, M.N.; Taboada, J.J. Influences of atmospheric variability on freshwater input in Galician Rias in winter. J. Atmos. Ocean Sci. 2005, 10, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeáns Rodríguez, M.; Suárez Rey, R.; Arean Varela, N.; Suárez Bilbao, M.; Carracedo García, P.; Gómez Hombre, B. Atlas de Oleaje de Galicia. In Caracterización Del Oleaje Costero Con Alta Resolución; MeteoGalicia: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2014; Available online: https://www.meteogalicia.gal/datosred/infoweb/meteo/proxectos/energymare/Atlas_Ondas_Galicia.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2025).
- Arguilé-Pérez, B.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Costoya, X.; deCastro, M.; Carracedo, P.; Dias, J.M.; Rusu, L.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Harnessing of different WECs to harvest wave energy along the Galician Coast (NW Spain). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, R.; Sotillo, M.G.; Cailleau, S.; Lorente, P.; Levier, B.; Amo-Baladrón, A.; Reffray, G.; Alvarez Fanjul, E. Strengths and weaknesses of the CMEMS forecasted and reanalyzed solutions for the Iberia-Biscay-Ireland (IBI) waters. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 159, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutknecht, E.; Reffray, G.; Mignot, A.; Dabrowski, T.; Sotillo, M.G. Modelling the marine ecosystem of Iberia-Biscay-Ireland (IBI) European waters for CMEMS operational applications. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 1489–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOG. Decree 406/1996, of November 7, Which Approves the Regulation for Marine Culture Nurseries in the Waters of Galicia. 1996. Available online: https://www.xunta.gal/dog/Publicados/1996/19961121/AnuncioBB56_gl.html (accessed on 22 September 2025).
- Amidror, I. Scattered data interpolation methods for electronic imaging systems: A survey. J. Electron. Imaging 2002, 11, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, S.E.; Pitman, A.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; McAneney, J. Evaluation of the AR4 climate models’ simulated daily maximum temperature, minimum temperature, and precipitation over Australia using probability density functions. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4356–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.; Linstone, H.A.; Turoff, M. The Delphi method: Techniques and applications. J. Mark. Res. 1976, 13, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Xiao, Z.N.; Peng, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Du, Z.B. Rezoning global offshore wind energy resources. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, L.; Sousa, M.C.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Dias, J.M. A habitat suitability model for aquaculture site selection: Ria de Aveiro and Rias Baixas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; de Castro, M.; Costoya, X.; Rusu, L.; Dias, J.M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. A Delphi method to classify wave energy resource for the 21st century: Application to the NW Iberian Peninsula. Energy 2021, 235, 121396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalos, M.H.; Whitlock, P.A. Monte Carlo Methods; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-527-40760-6. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, E.C.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Darmaraki, S.; Donat, M.G.; Hobday, A.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; Schlegel, R.W.; Sen Gupta, A. Marine heatwaves. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2021, 13, 313–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des, M.; Castro-Olivares, A.; deCastro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Analysis of estuarine marine heatwaves in an upwelling system: The Ría de Arousa as a case study. Glob. Planet. Change 2025, 249, 104776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarria, C.; Gestoso, I.; Lima, F.P.; Vázquez, E.; Comeau, L.A.; Gomes, F.; Seabra, R.; Babarro, J.M. Response of Two Mytilids to a Heatwave: The Complex Interplay of Physiology, Behaviour and Ecological Interactions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, C.; Glaser, D.; Canu, M.; Pastres, R. Coupling habitat-specific temperature scenarios with tolerance landscape to predict the impacts of climate change on farmed bivalves. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 188, 106038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longdill, P.C.; Healy, T.R.; Black, K.P. An integrated GIS approach for sustainable aquaculture management area site selection. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radiarta, I.N.; Saito, K.; Ito, Y. GIS-based multicriteria evaluation models for identifying suitable sites for Japanese scallop farming in Funka Bay, Hokkaido, Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Karakassis, I.; Massa, F.; Fezzard, D.; Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Soto, D.; Chapela, R.; Avila, P.; Macias, J.C.; Tomassetti, P.; et al. Aquaculture’s Struggle for Space: The Need for Coastal Spatial Planning and the Potential Benefits of Allocated Zones for Aquaculture (AZAs) to Avoid Conflict and Promote Sustainability. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Souto, D.; Martínez-Mariño, V.; Morán, P.; Olabarria, C.; Vázquez, E. Hiding from heat: The transcriptomic response of two clam species is modulated by behaviour and habitat. J. Therm. Biol. 2024, 119, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, D.; Castro, C.G.; Aguiar, E.; Labarta, U.; Figueiras, F.G.; Fernández-Reiriz, M.J. Biodeposit contribution to natural sedimentation in a suspended Mytilus Galloprovincialis Lmk mussel farm in a Galician Ría (NW Iberian Peninsula). Aquaculture 2014, 432, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froján, M.; Castro, C.G.; Zúñiga, D.; Arbones, B.; Alonso-Pérez, F.; Figueiras, F.G. Mussel farming impact on pelagic production and respiration rates in a coastal upwelling embayment (Ría de Vigo, NW Spain). Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; López-Pérez, A.E.; León, I. Impact of sediment mobilization on trace elements release in Galician Rías (NW Iberian Peninsula): Insights into aquaculture. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedracoba, S.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Labarta, U.; Fernández-Reiriz, M.J.; Gómez, B.; Balseiro, C. Water flows through mussel rafts and their relationship with wind speed in a coastal embayment (Ría de Ares-Betanzos, NW Spain). Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Swift, M.R.; Dewhurst, T.; Tsukrov, I.; Celikkol, B.; Newell, C. Dynamics of submersible mussel rafts in waves and current. China Ocean Eng. 2015, 28, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, E.; Piedracoba, S.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Labarta, U. Circulation of water through a mussel raft: Clearance area vs. idealized linear flows. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 9, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, T.; Hallowell, S.T.; Newell, C. Dynamics of an array of submersible mussel rafts in waves and current. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering–OMAE, Glasgow, UK, 9–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Landmann, J.; Flack, C.; Kowalsky, U.; Hildebrandt, A.; Goseberg, N. Hydrodynamic coefficients of mussel dropper lines derived from large-scale experiments and structural dynamics. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Ener. 2024, 10, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, J.; Frohlinga, L.; Gieschenb, R.; Buckc, B.H.; Heasmane, K.; Scotte, N.; Smeatone, M.; Goseberg, N.; Hildebrandt, A. Drag and inertia coefficients of live and surrogate shellfish dropper lines under steady and oscillatory flow. Ocean Eng. 2021, 235, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, J.; Ongsiek, T.; Goseberg, N.; Heasmane, K.; Buckc, B.H.; Paffenholz, J.A.; Hildebrandt, A. Physical Modelling of Blue Mussel Dropper Lines for the Development of Surrogates and Hydrodynamic Coefficients. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
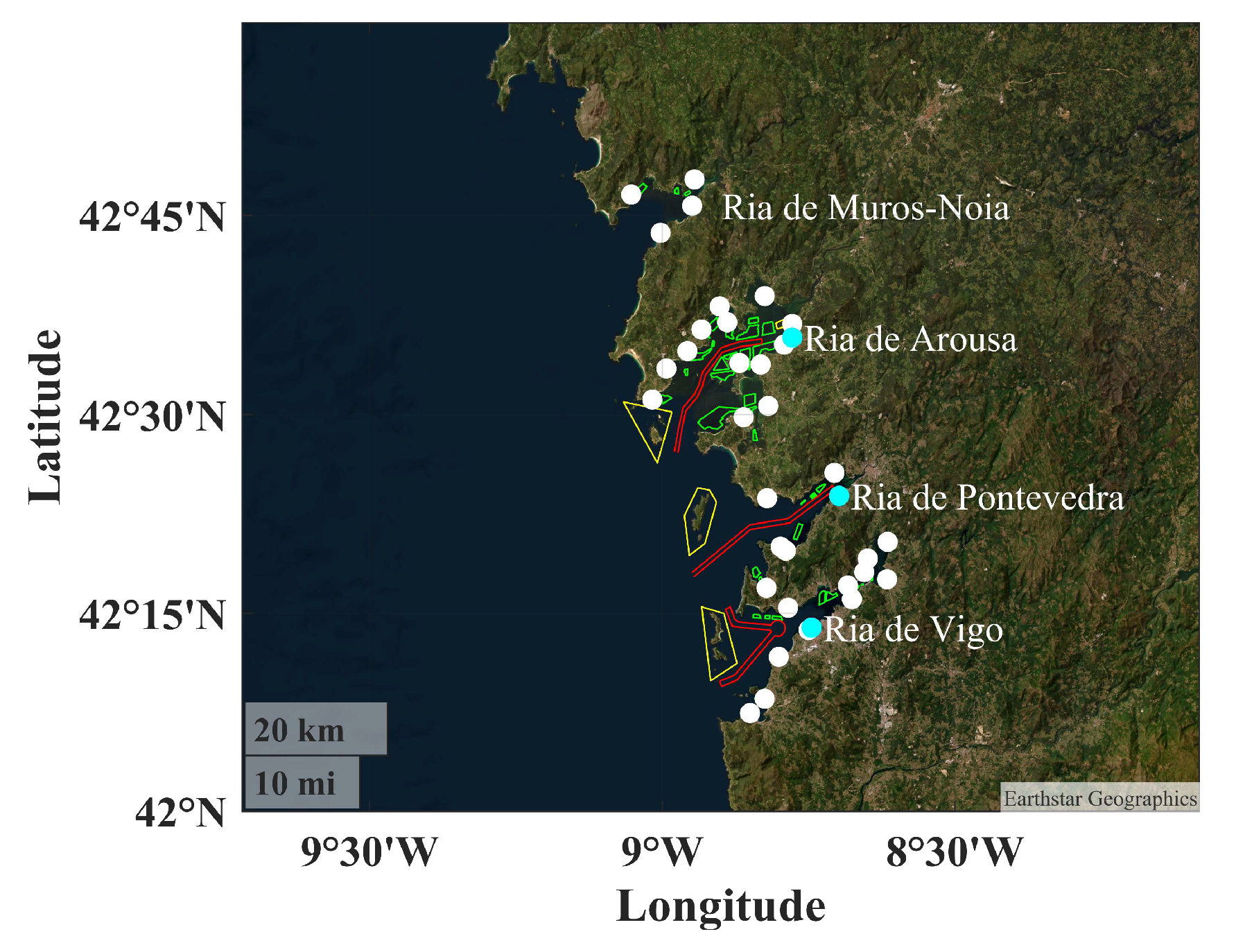


| Ría | Volume (km3) | Surface (km2) | Length (m) | Mean Mouth Depth (m) | Farming Zones (n) | Aquaculture Area (km2) | Main River (s) | Mean River Discharge (m−3 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vigo | 3.2 | 176 | 31 | 50 (S), 25 (N) | 11 | 5.6 | Verdugo-Oitaven | 17 |
| Pontevedra | 3.5 | 141 | 22 | 60 (S), 15 (N) | 11 | 4.1 | Lérez | 25.6 |
| Arousa | 5.4 | 230 | 25 | 55 (S), 5 (N) | 23 | 37.4 | Ulla & Umia | 79.3 & 16.3 |
| Muros-Noia | 2.1 | 125 | 13 | 50 | 3 | 1.9 | Tambre | 54.1 |
| Normalized Value | (%) (for S, T or C) |
|---|---|
| 0 | <50 |
| 0.5 | (55, 50] |
| 0.55 | (60, 55] |
| 0.6 | (65, 60] |
| 0.65 | (70, 65] |
| 0.75 | (75,70] |
| 0.8 | (80, 75] |
| 0.85 | (85, 80] |
| 0.9 | (90, 85] |
| 0.95 | (95, 90] |
| 1 | ≥95 |
| Normalized Value () | (p = 50, 90 or 99) |
|---|---|
| 0 | >2 |
| 0.5 | (1.9, 2] |
| 0.55 | (1.8, 1.9] |
| 0.6 | (1.7, 1.8] |
| 0.65 | (1.6, 1.7] |
| 0.7 | (1.5, 1.6] |
| 0.75 | (1.4, 1.5] |
| 0.8 | (1.3, 1.4] |
| 0.85 | (1.2, 1.3] |
| 0.9 | (1.1, 1.2] |
| 0.95 | (1, 1.1] |
| 1 | ≤1 |
| Normalized Value () | Water Depth (m) |
|---|---|
| 0 | >100 |
| 0.5 | (85, 90] |
| 0.55 | (80, 85] |
| 0.6 | (75, 80] |
| 0.65 | (70, 75] |
| 0.7 | (65, 70] |
| 0.75 | (60, 65] |
| 0.8 | (55, 60] |
| 0.85 | (50, 55] |
| 0.9 | (45, 50] |
| 0.95 | (40, 45] |
| 1 | ≤40 |
| Normalized Value () | Distance to the Nearest Port (km) |
|---|---|
| 0 | >10 |
| 0.5 | (9.5, 10] |
| 0.55 | (9, 9.5] |
| 0.6 | (8.5, 9] |
| 0.65 | (8, 8.5] |
| 0.7 | (7.5, 8] |
| 0.75 | (7, 7.5] |
| 0.8 | (6.5, 7] |
| 0.85 | (6, 6.5] |
| 0.9 | (5.5, 6] |
| 0.95 | (5, 5.5] |
| 1 | ≤5.0 |
| Index | |
|---|---|
| TIndex | 0.151 ± 0.047 |
| SIndex | 0.124 ± 0.057 |
| BGQIndex | 0.164 ± 0.034 |
| CIndex | 0.134 ± 0.044 |
| WHIndex | 0.166 ± 0.034 |
| WDIndex | 0.138 ± 0.045 |
| DPIndex | 0.124 ± 0.052 |
| Categorization of Suitability | ASI |
|---|---|
| Unsuitable | <0.8 |
| Marginal | [0.8–0.9) |
| Optimal | [0.9–1.0] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
deCastro, N.G.; deCastro, M.; Des, M.; Costoya, X.; Gómez-Gesteira, M. Assessment of the Offshore Migration of Mussel Production Based on an Aquaculture Similarity Index (ASI). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101869
deCastro NG, deCastro M, Des M, Costoya X, Gómez-Gesteira M. Assessment of the Offshore Migration of Mussel Production Based on an Aquaculture Similarity Index (ASI). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101869
Chicago/Turabian StyledeCastro, Nicolás G., Maite deCastro, Marisela Des, Xurxo Costoya, and Moncho Gómez-Gesteira. 2025. "Assessment of the Offshore Migration of Mussel Production Based on an Aquaculture Similarity Index (ASI)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101869
APA StyledeCastro, N. G., deCastro, M., Des, M., Costoya, X., & Gómez-Gesteira, M. (2025). Assessment of the Offshore Migration of Mussel Production Based on an Aquaculture Similarity Index (ASI). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101869






