Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Drivers of Wetland Change on Chongming Island (2000–2020) Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
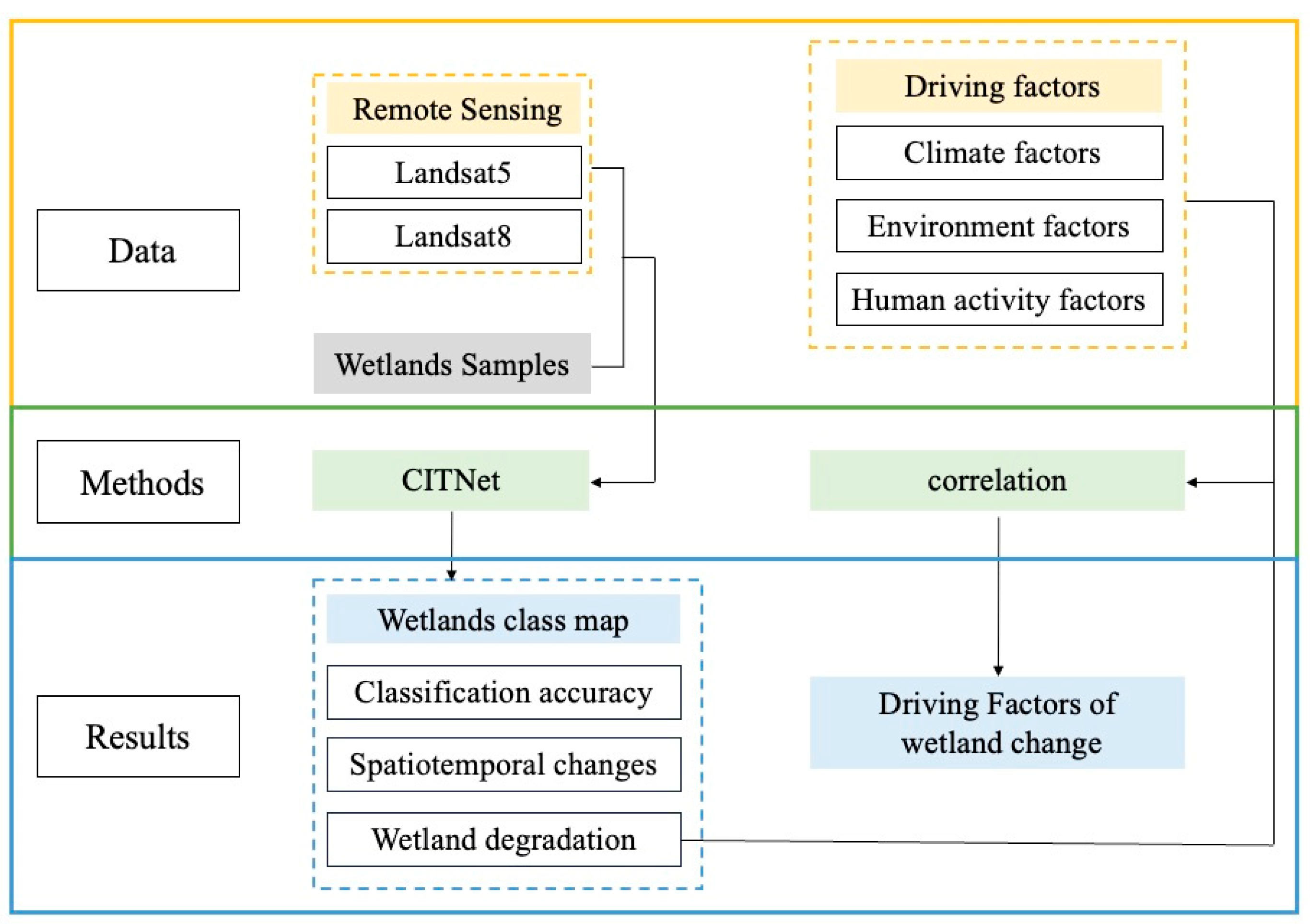
2. Materials and Methods
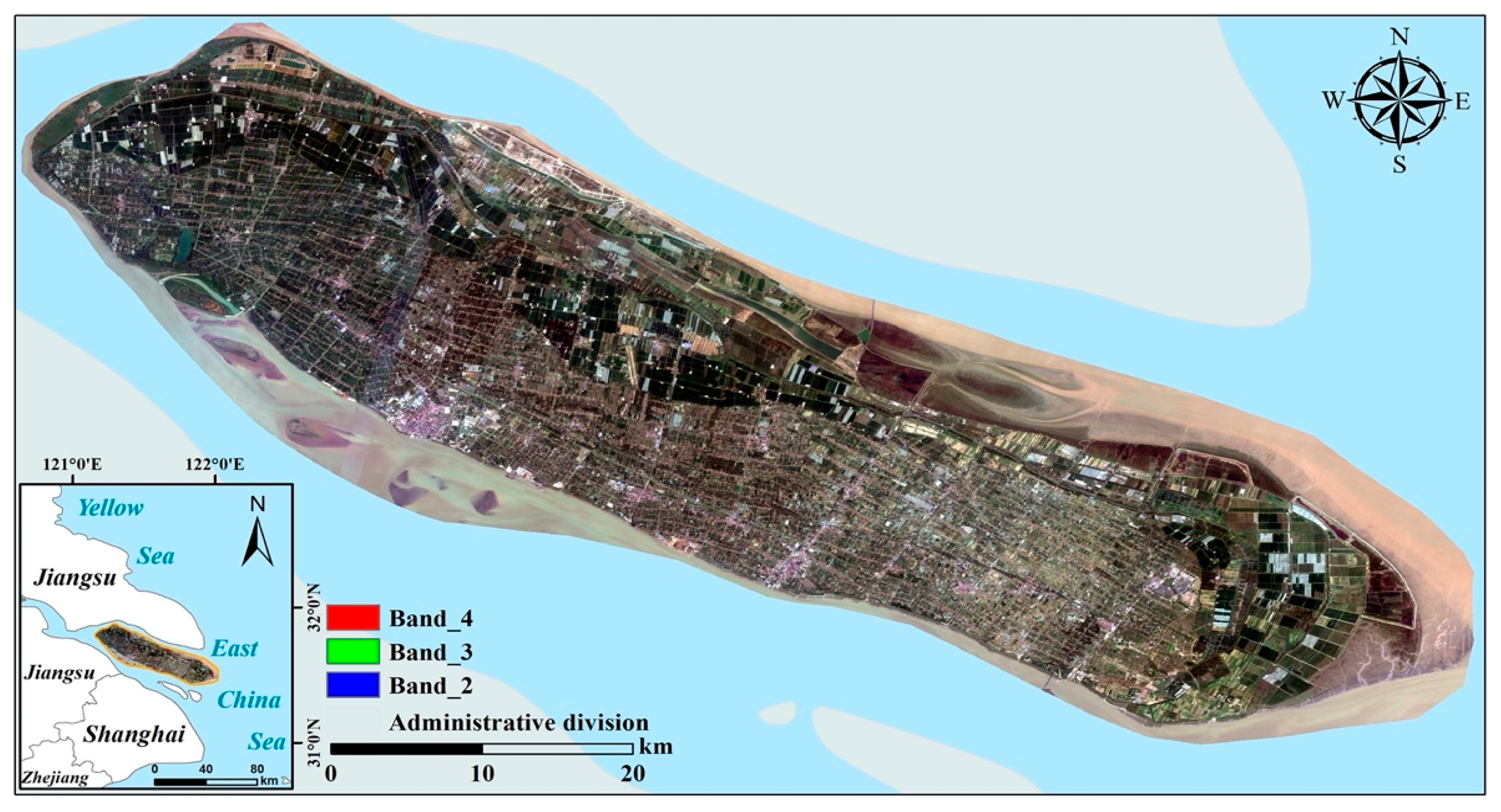
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Remote Sensing Data and Driving Factors
2.3. Classification Method
3. Results
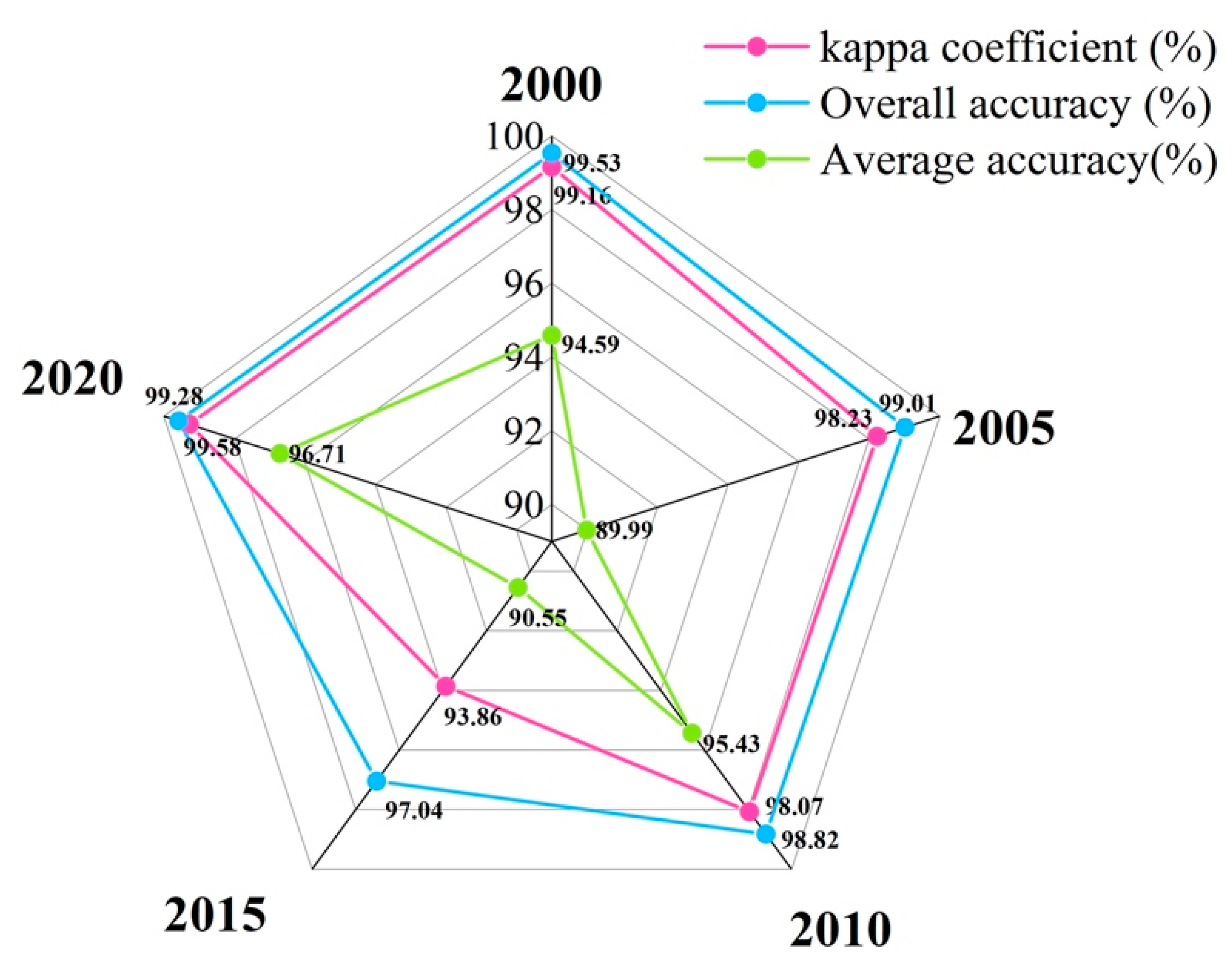
3.1. Classification Accuracy
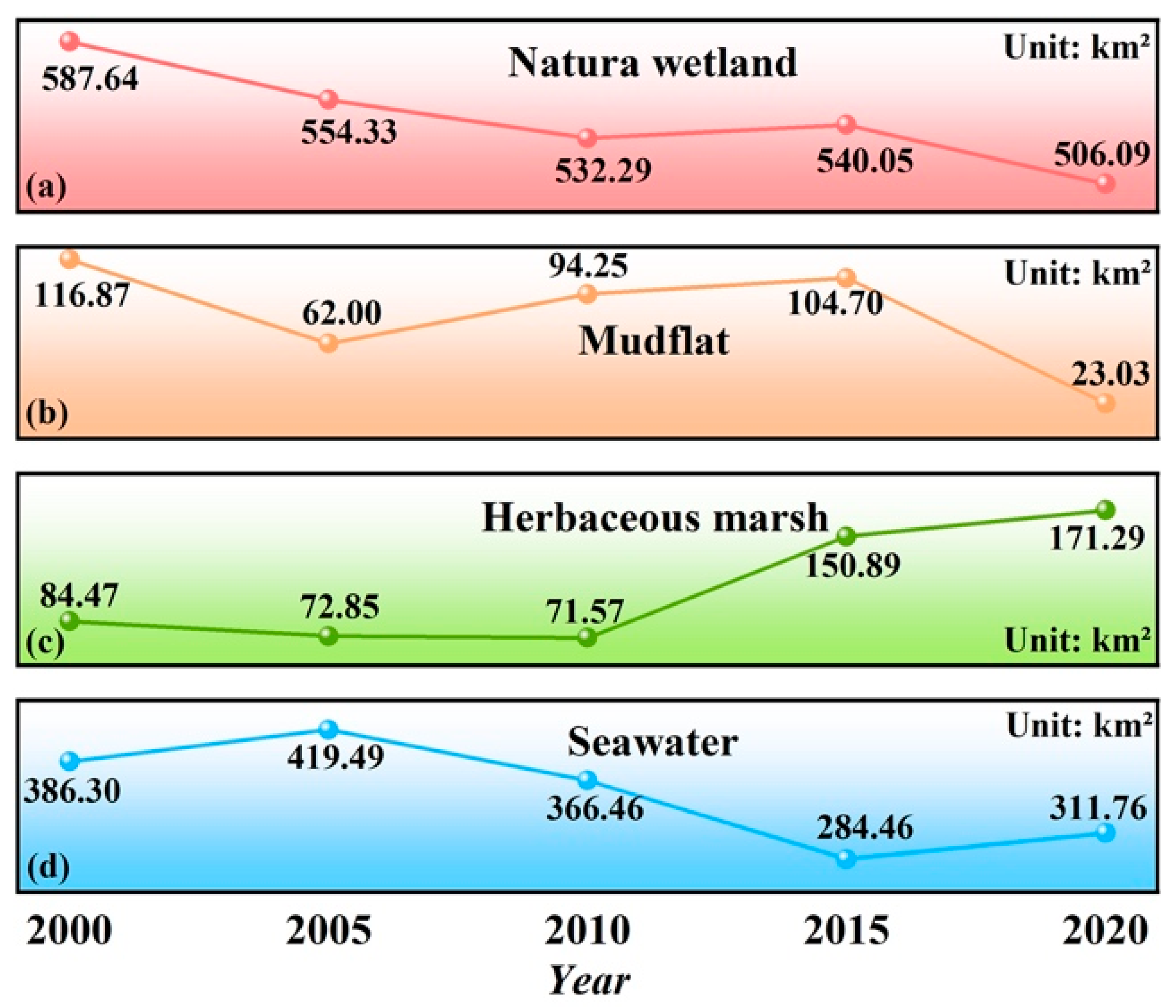
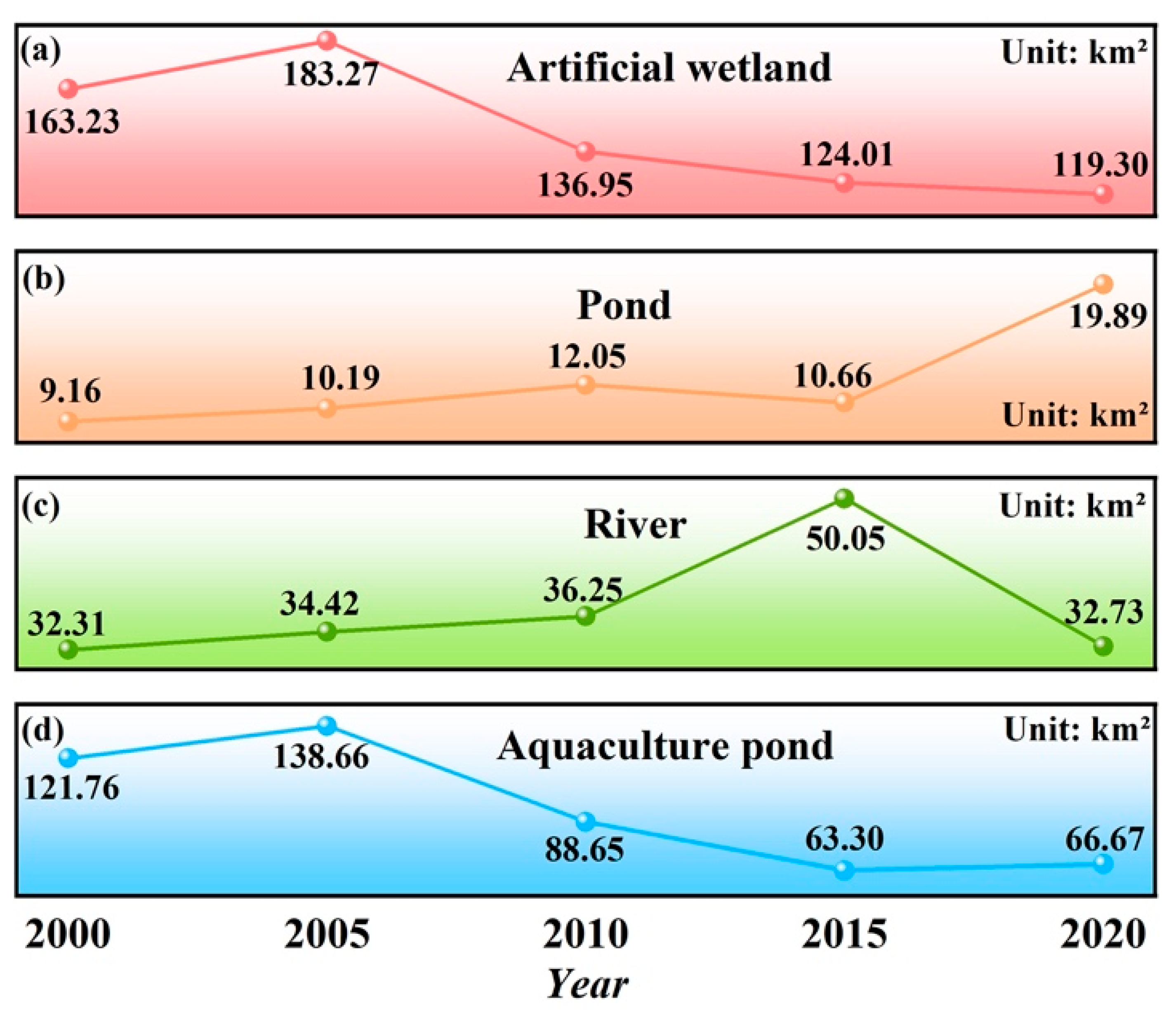
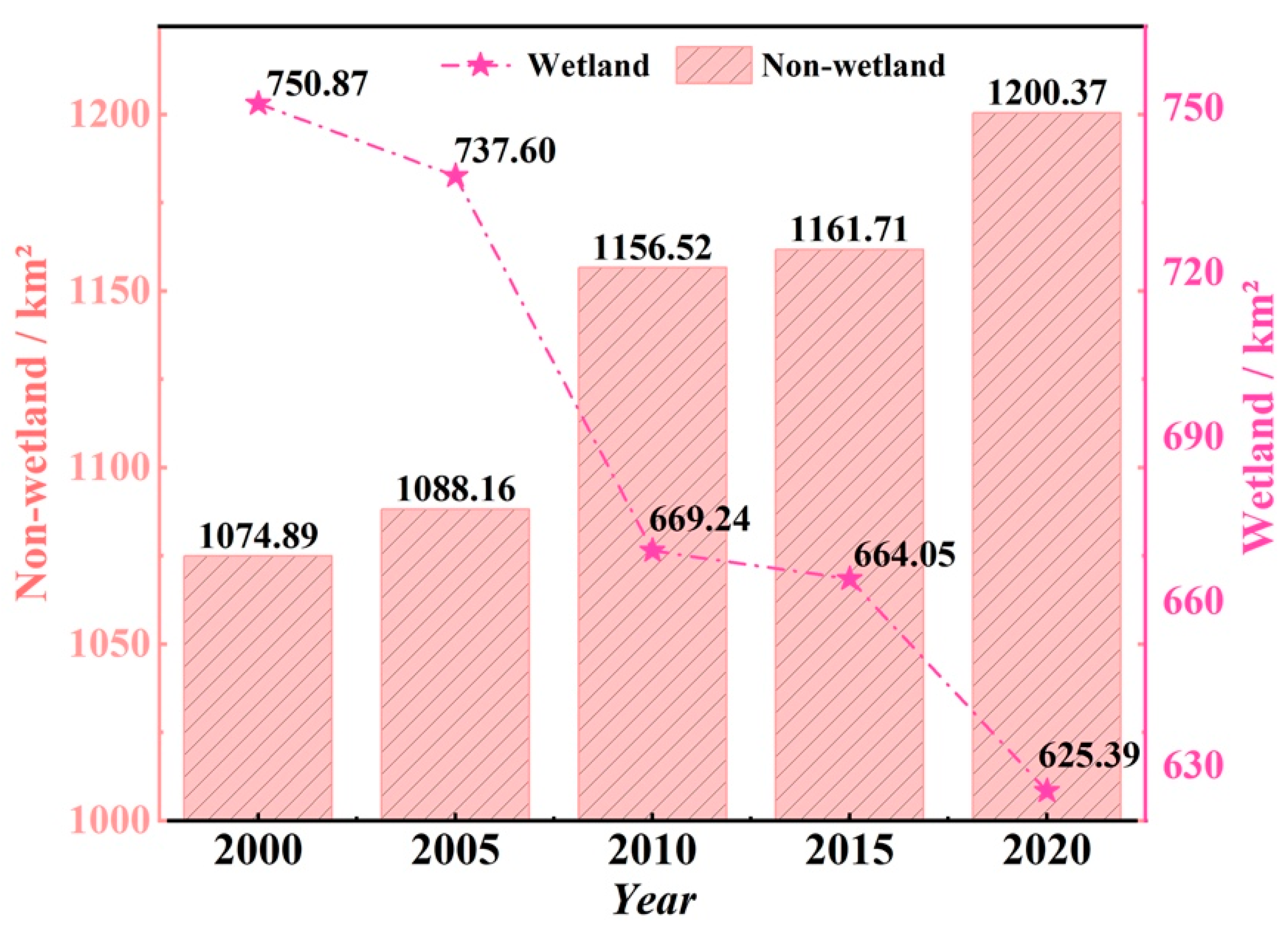
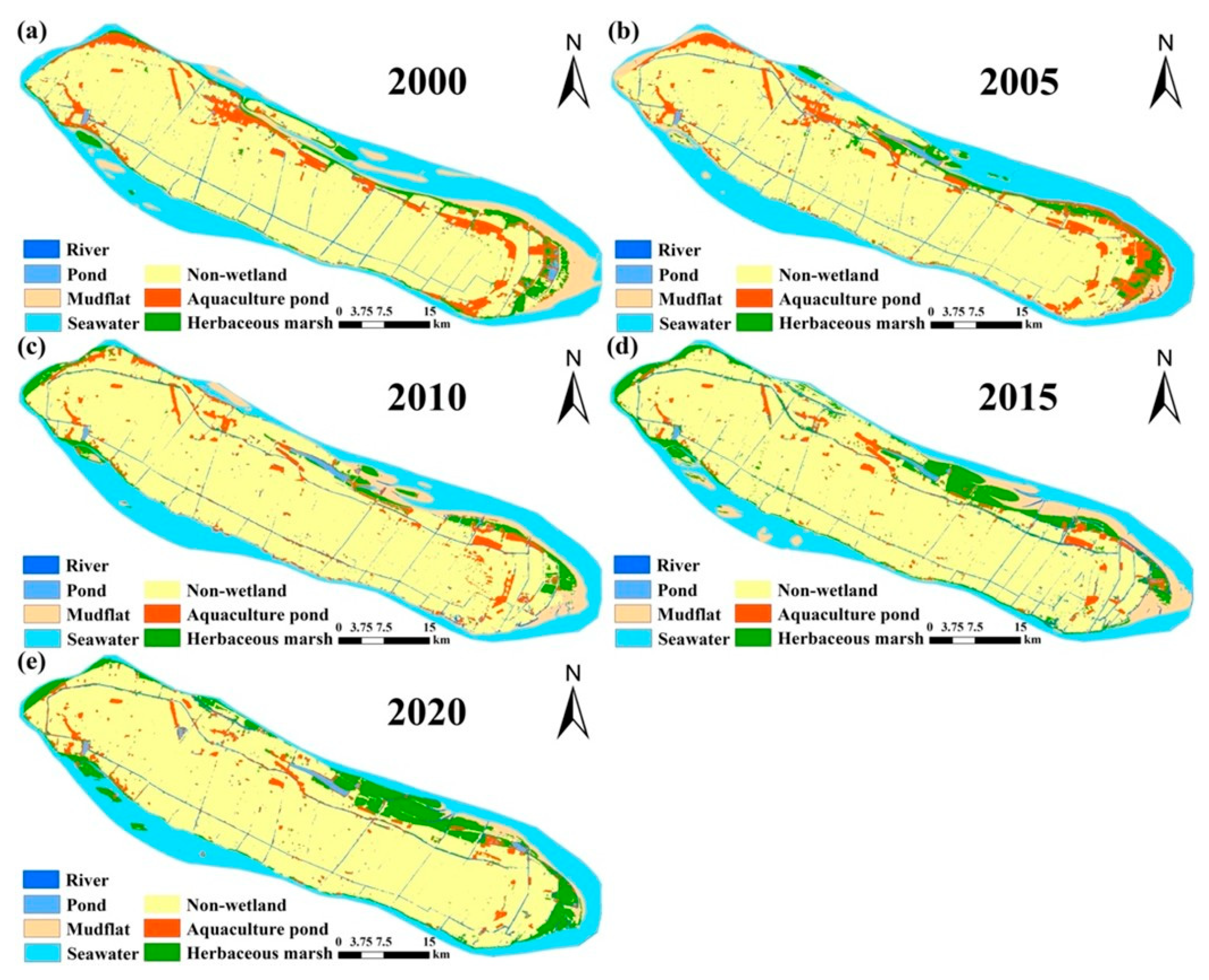
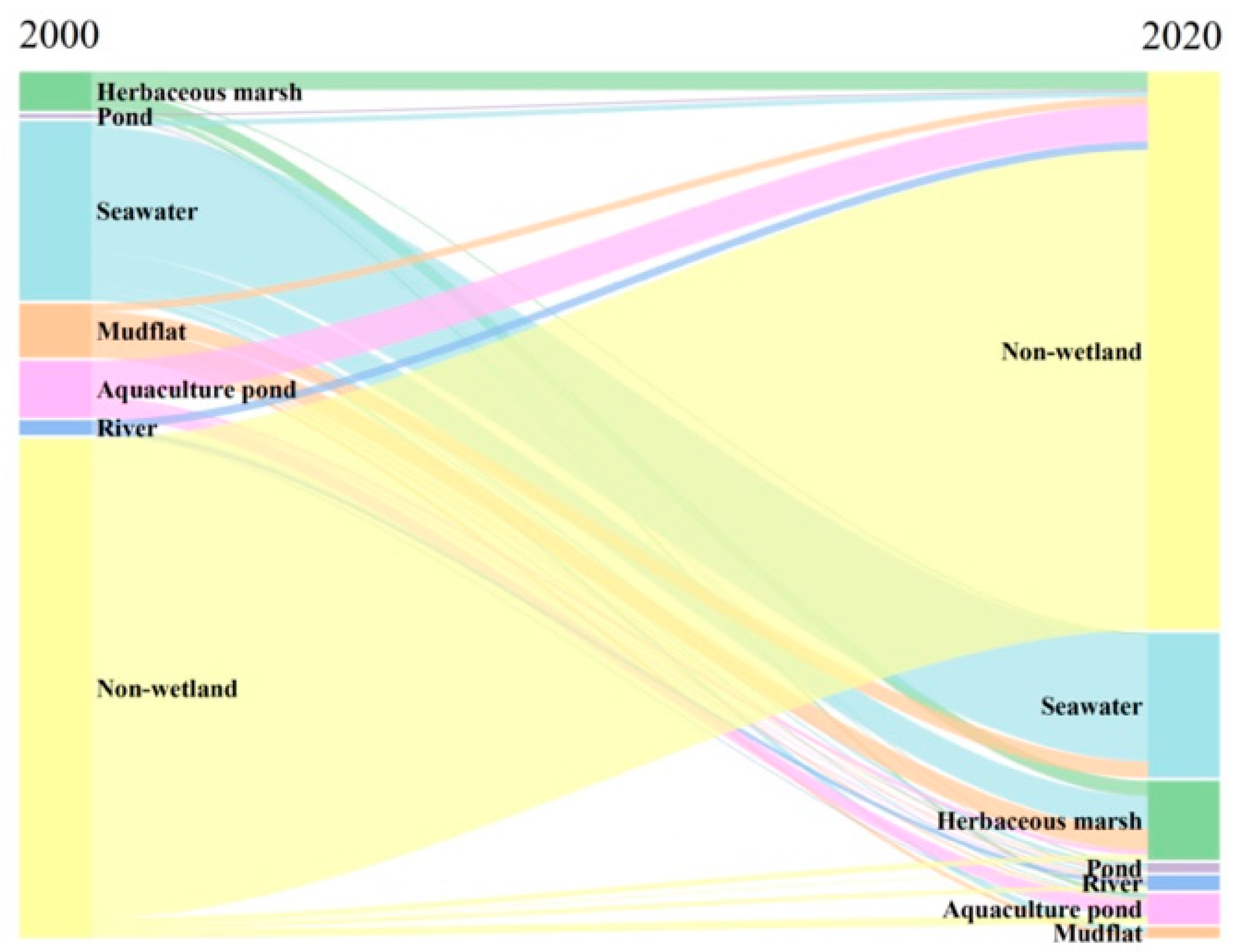
3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in Wetlands on Chongming Island
3.2.1. Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Area
3.2.2. Spatial Dynamics of Wetland Distribution
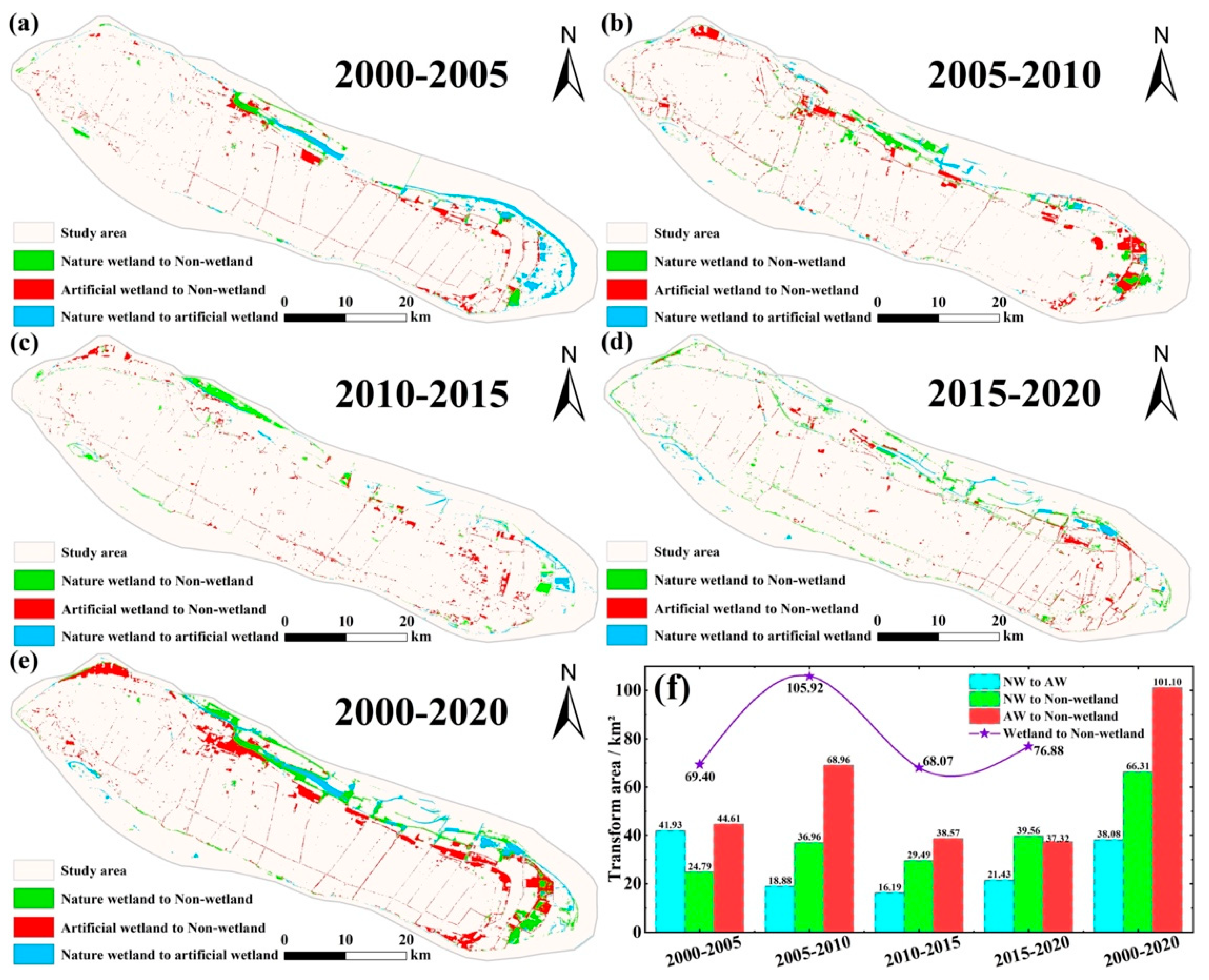
3.3. Patterns and Processes of Wetland Landscape Transformation
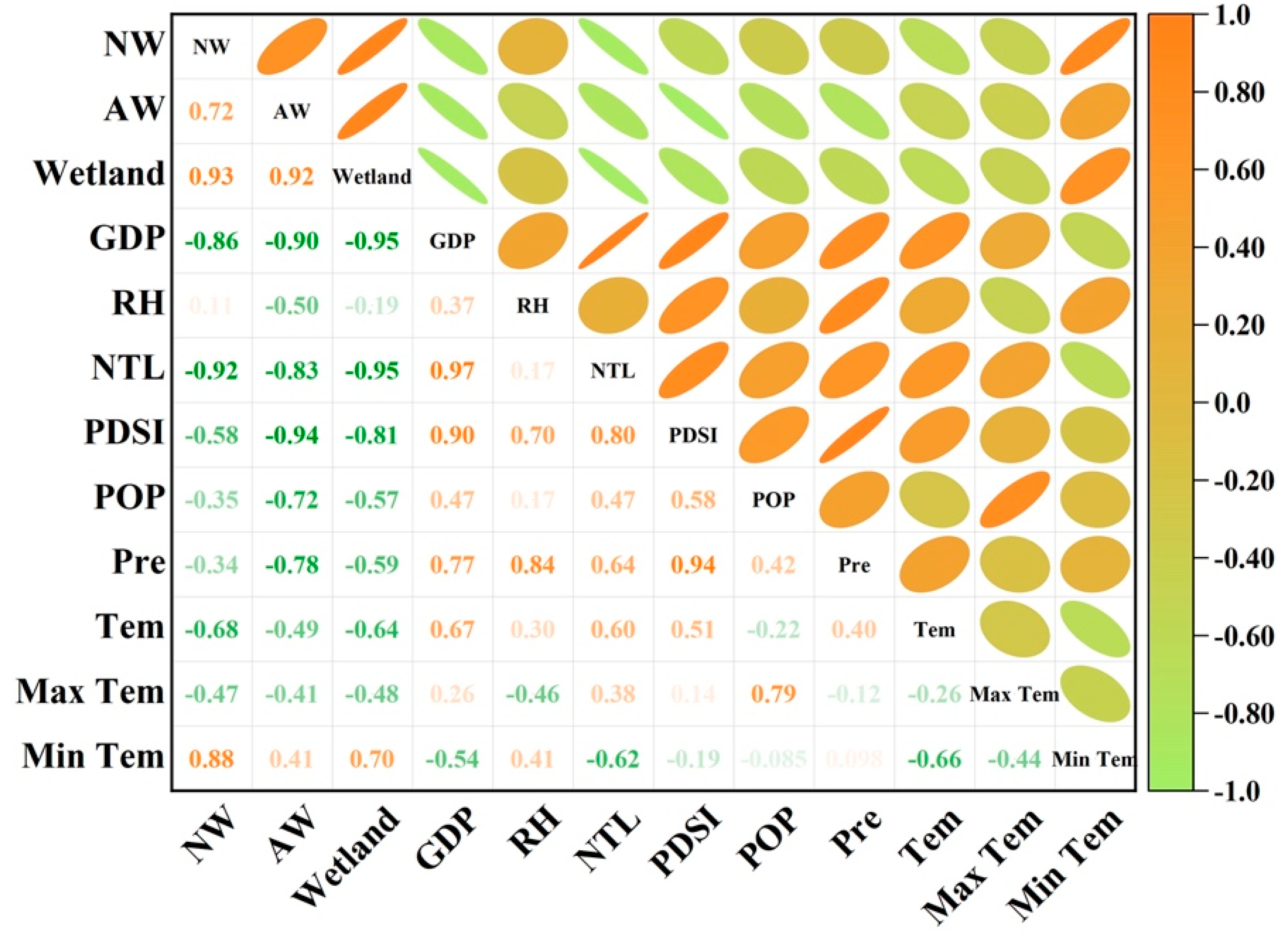
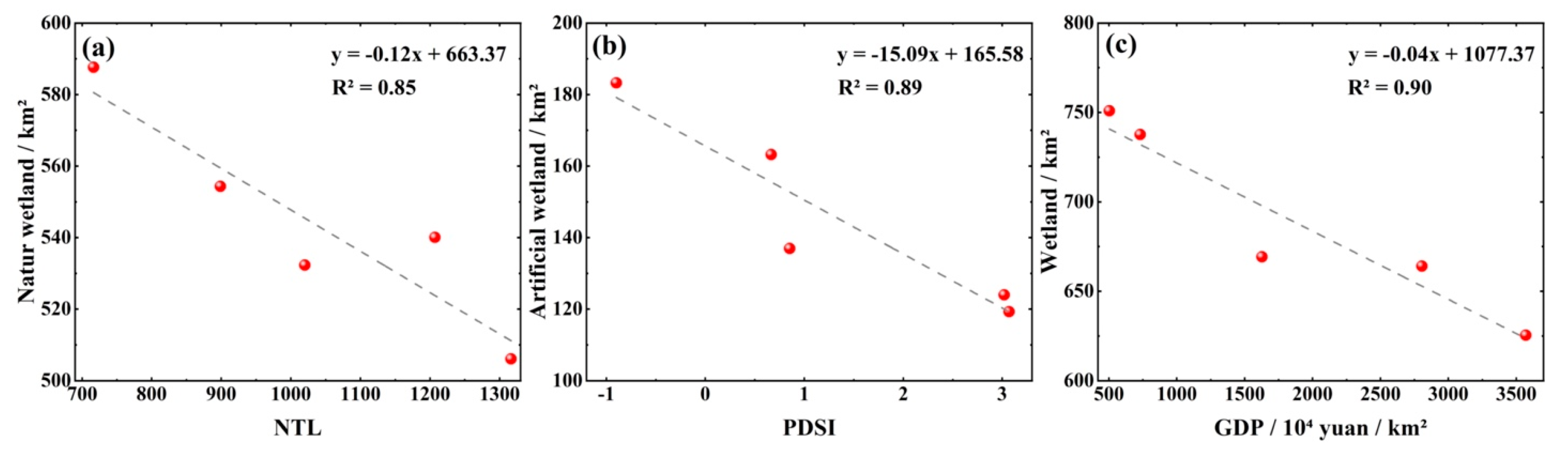
3.4. Driving Factors of Wetland Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Natural Wetland Dynamics Under Anthropogenic and Ecological Pressures
4.2. Policy-Driven Trajectories of Artificial Wetland Change
4.3. Comparison with Previous Studies and Integrated Driving Mechanisms
4.4. Synthesis and Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, N. Wetland losses and the status of wetland-dependent species. In The Wetland Book II: Distribution, Description, and Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S.; Na, X. Comparison of land use/land cover change and landscape patterns in Honghe National Nature Reserve and the surrounding Jiansanjiang region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandra, T.V.; Rajinikanth, R.; Ranjini, V.G. Economic valuation of wetlands. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 439. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhong, Y. CITNet: Convolution interaction transformer network for hyperspectral and LiDAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5535918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Tang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ge, Z.; Gao, J. Variations in tidal flats of the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during 1950s–2010s: Future crisis and policy implication. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 108, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Gao, S. Long-term reclamation of tidal flats of Chongming Island and ecological security of Yangtze estuary, China. Reg. Environ. Change 2024, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, L.; Huang, H. Coastal wetlands in the Changjiang estuary. In Ecological Continuum from the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Watersheds to the East China Sea Continental Margin; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 137–159. [Google Scholar]
- Deegan, L.A.; Johnson, D.S.; Warren, R.S.; Peterson, B.J.; Fleeger, J.W.; Fagherazzi, S.; Wollheim, W.M. Coastal eutrophication as a driver of salt marsh loss. Nature 2012, 490, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Hoozemans, F.M.J.; Marchand, M. Increasing flood risk and wetland losses due to global sea-level rise: Regional and global analyses. Glob. Environ. Change 1999, 9, S69–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Niu, Y.; Zeng, Z. Driving forces of changes in China’s wetland area from the first (1999–2001) to second (2009–2011) National Inventory of Wetland Resources. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; He, M.; Hu, B.; Mo, X.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. Status of wetlands in China: A review of extent, degradation, issues and recommendations for improvement. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2017, 146, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.B.; Zhou, D.M.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.N.; Huang, H.B.; Li, C.C.; et al. Mapping wetland changes in China between 1978 and 2008. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Melillo, J.M.; Zhang, Z. China’s changing landscape during the 1990s: Large-scale land transformations estimated with satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Gao, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, G. Changes of the wetland landscape in Shenzhen City from 1988 to 2007 and the driving force analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 2706–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Du, J.; Liu, L.; Zeng, L.; Ren, C. Wetland degradation: Its driving forces and environmental impacts in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Fu, B. Wetland loss under the impact of agricultural development in the Sanjiang Plain, NE China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 166, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, W.; Wu, N.; Shi, R.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, B.; Liu, P. Assessing the impacts of reclamation and invasion on ecological dynamics of coastal wetland vegetation in the Yangtze Estuary from 1985 to 2019: A case study of Chongming Island, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Smith, J.P.; Dai, S.B.; Gao, A.; Li, P. Impact of dams on Yangtze River sediment supply to the sea and delta intertidal wetland response. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F03006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, W.; Gao, S. Typhoon and flooding occurrences on Chongming Island, Changjiang Estuary, as revealed by a newly acquired sedimentary record. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1366676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Guo, Y.; Dong, W. Future changes and uncertainties in temperature and precipitation over China based on CMIP5 models. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Tendency of land reclamation in coastal areas of Shanghai from 1998 to 2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Megonigal, J.P. Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Ibrahim, A.N.; Wang, Z.; Ma, C.; Gong, J. Spatial–temporal land-use/land-cover dynamics and their impacts on surface temperature in Chongming Island of Shanghai, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4037–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E. Evolution of an estuarine Island in the anthropocene: Complex dynamics of Chongming Island, Shanghai, PR China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Pu, Y.; Luan, Z. Shoreline dynamics of Chongming Island and driving factor analysis based on landsat images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Ibrahim Abdoul, N.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gong, J. Remote sensing of urban growth and landscape pattern changes in response to the expansion of Chongming Island in Shanghai, China. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Sarris, A.; Huang, X. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis of expansion characteristics of Chongming Island in Shanghai, China. In Proceedings of the 2013 Second International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–16 August 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Li, B. Quantifying expansion and removal of Spartina alterniflora on Chongming island, China, using time series Landsat images during 1995–2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Gao, S. Wetland utilization and adaptation practice of a coastal megacity: A case study of Chongming Island, Shanghai, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 627963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Long, X.; Song, Y.; Lu, F.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Han, G. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of coastal aquaculture ponds in China from 1985 to 2023. Ying yong sheng tai xue bao. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Gao, W.; Gao, Z.; Shi, R.H.; Zhang, C. Phenology-based Spartina alterniflora mapping in coastal wetland of the Yangtze Estuary using time series of GaoFen satellite no. 1 wide field of view imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 026020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y. Rapid invasion of Spartina alterniflora in the coastal zone of mainland China: New observations from Landsat OLI images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z. The range expansion patterns of Spartina alterniflora on salt marshes in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. A high-performance and in-season classification system of field-level crop types using time-series landsat data and a machine learning approach. Remote Sens. 2018, 210, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Man, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; He, J.; Tian, D. Leaf area index inversion of Spartina alterniflora using UAV hyperspectral data based on multiple optimized machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.; Siqueira, J.V.; Sales, M.H.; Fonseca, A.V.; Ribeiro, J.G.; Numata, I.; Cochrane, M.A.; Barber, C.P.; Roberts, D.A.; Barlow, J. Ten-year landsat classification of deforestation and forest degradation in the Brazilian Amazon. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5493–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 35643-2017; Land Use Classification Standard. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Marjani, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Gill, E.W. CVTNet: A fusion of convolutional neural networks and vision transformer for wetland mapping using sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 satellite data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Lu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, C. Enhanced hyperspectral image classification for coastal wetlands using a hybrid CNN-transformer approach with cross-attention mechanism. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1613565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yu, S. Losses of natural coastal wetlands by land conversion and ecological degradation in the urbanizing Chinese coast. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, M.; Salehi, B.; Mahdavi, S.; Granger, J. Spectral Analysis of wetlands in Newfoundland using Sentinel 2A and Landsat 8 imagery. In Proceedings of the Imaging and Geospatial Technology Forum, Baltimore, MD, USA, 12–16 March 2017; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Mi, J.; Liu, W. GWL_FCS30: Global 30 m wetland map with fine classification system using multi-sourced and time-series remote sensing imagery in 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2023, 15, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Type | Secondary Type | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural wetland | Mudflat | Intertidal zone between high and low tide levels. |  |
| Herbaceous marsh | Marsh wetlands dominated by herbaceous plants and adjacent shallow water areas. |  | |
| Seawater Zone | Shallow marine waters covered by seawater. |  | |
| Artificial wetland | Pond | Artificial surface water bodies, including reservoirs, ponds, and storage pools. |  |
| Aquaculture pond | Artificial water bodies for fish, shrimp and crab farming. |  | |
| River | Narrow, naturally of flowing water bodies. |  |
| Optical Image | Spectral Feature | Parameter Variable | Define or Describe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat8 OLI | Spectral band | B1 | Coastal aerosol |
| B2 | Blue band | ||
| B3 | Green band | ||
| B4 | Red band | ||
| B5 | NIR band | ||
| B6 | SWIR 1 band | ||
| B7 | SWIR 2 band | ||
| Landsat5 TM | Spectral band | B1 | Blue band |
| B2 | Green band | ||
| B3 | Red band | ||
| B4 | NIR band | ||
| B5 | SWIR 1 band | ||
| B7 | SWIR 2 band |
| Driving Factor | Feature | Data Name | Unit | Data Source | Data Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climatic Factor | Pre | Precipitation | mm | https://em.cams.cma.cn (accessed on 11 October 2024) | 2000–2020 1 km spatial resolution |
| Temp | Temperature | °C | |||
| Max Temp | Max Temperature | °C | |||
| Min Temp | Min Temperature | °C | |||
| RH | Relative humidity | % | |||
| Environmental Index | PDSI | Palmer Drought Severity Index | - | Figshare https://figshare.com (accessed on 15 September 2021) | |
| Human Activity | POP | Population Density | people/km2 | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 15 January 2023) | |
| GDP | Gross National Product | Ten thousand yuan/km2 | |||
| NTL | Night Light | - | Data sharing and Service Portal https://data.casearth.cn (accessed on 9 October 2023) | 2000–2020 80 m spatial resolution |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, A.; Yu, Y.; Fang, H.; Feng, J.; Ji, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Drivers of Wetland Change on Chongming Island (2000–2020) Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101837
Yi A, Yu Y, Fang H, Feng J, Ji J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Drivers of Wetland Change on Chongming Island (2000–2020) Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101837
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, An, Yang Yu, Hua Fang, Jiajun Feng, and Jinlin Ji. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Drivers of Wetland Change on Chongming Island (2000–2020) Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101837
APA StyleYi, A., Yu, Y., Fang, H., Feng, J., & Ji, J. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Drivers of Wetland Change on Chongming Island (2000–2020) Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101837






