Probabilistic Noise Detection and Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based Noise Reduction Methods for Snapping Shrimp Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
- SPP is calculated for SSN detection, and the detection results are analyzed;
- NMF weighted by the SPP is proposed to reduce SSN effectively;
- The proposed SSN detection and reduction methods are integrated as a unified solution.
2. Related Works
2.1. SSN Detection
2.1.1. LP Analysis
2.1.2. Statistical Model Based LR
2.2. NMF-Based Source Separation Techniques
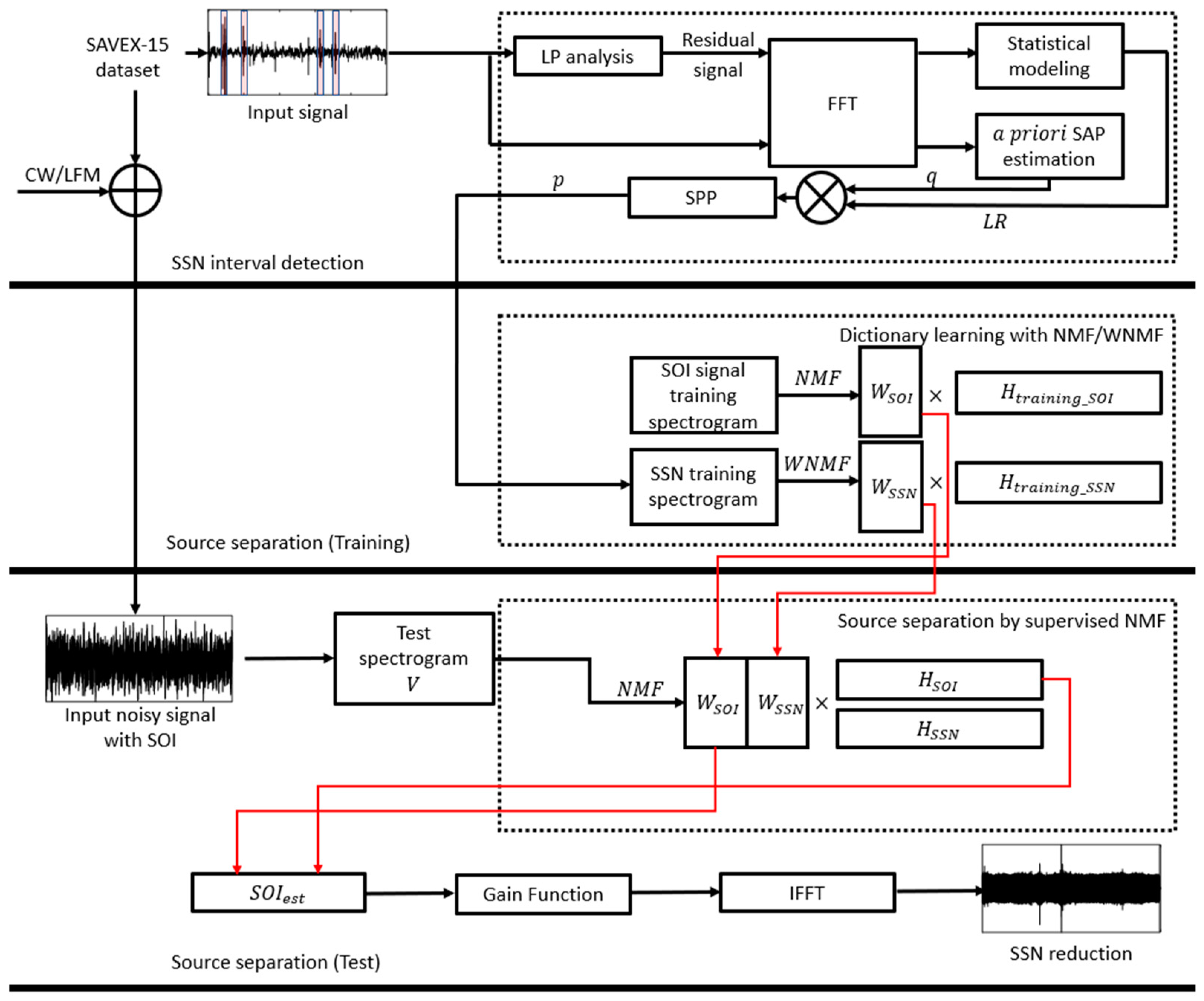
3. Proposed Approach
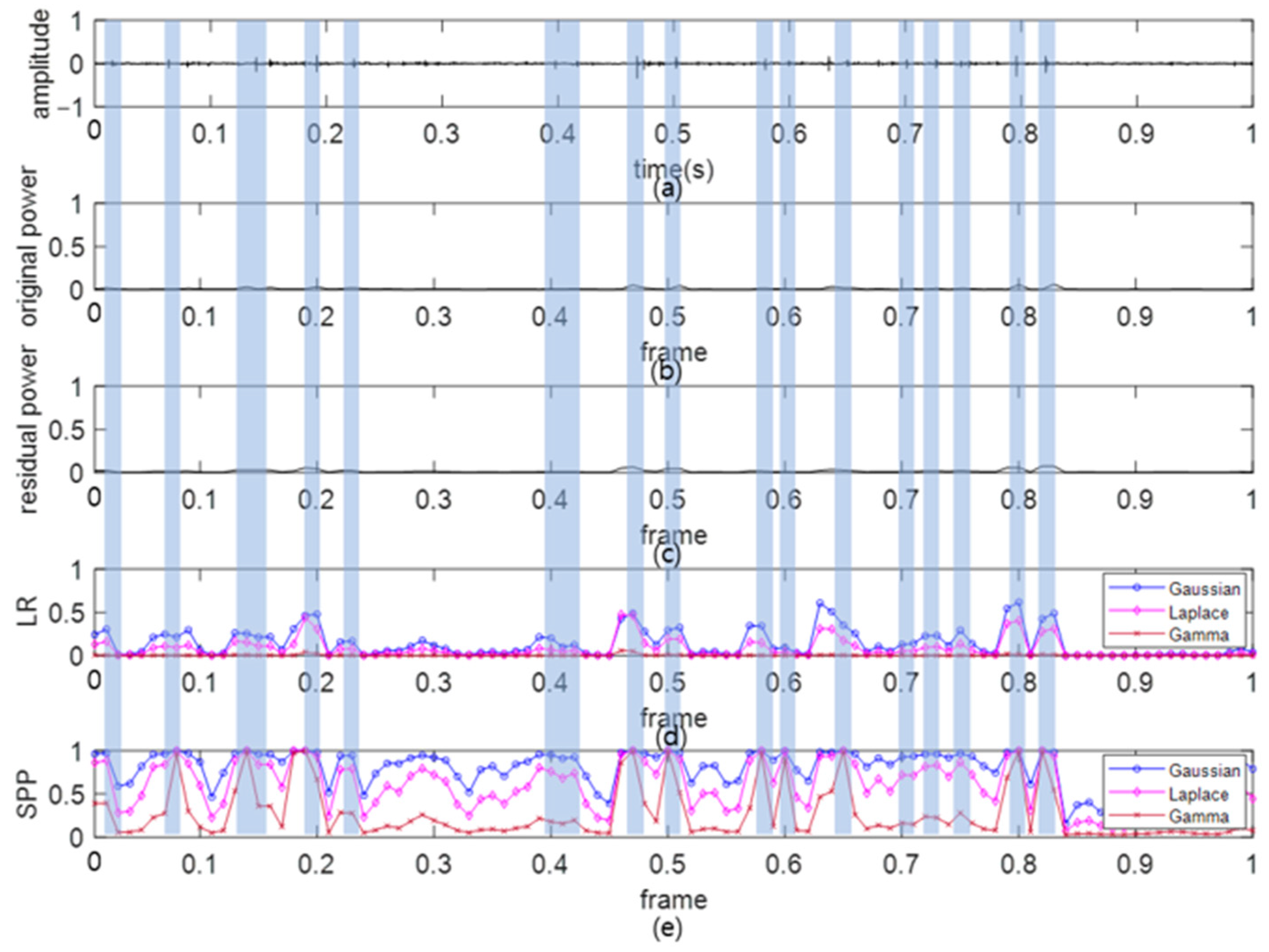
3.1. SPP Calculation for SSN Detection
3.2. SSN Reduction Using WNMF
4. Experiments
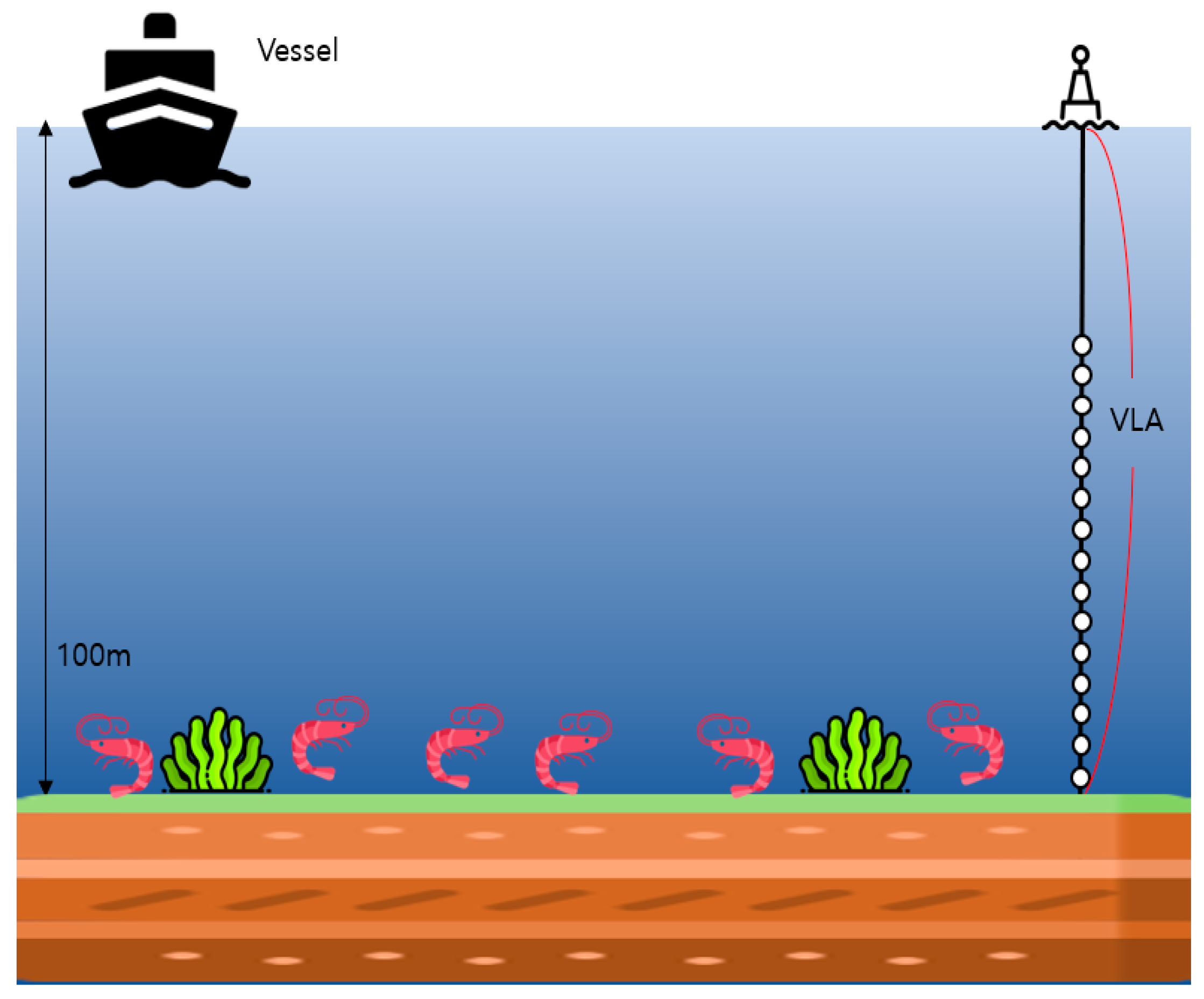
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Experimental Result
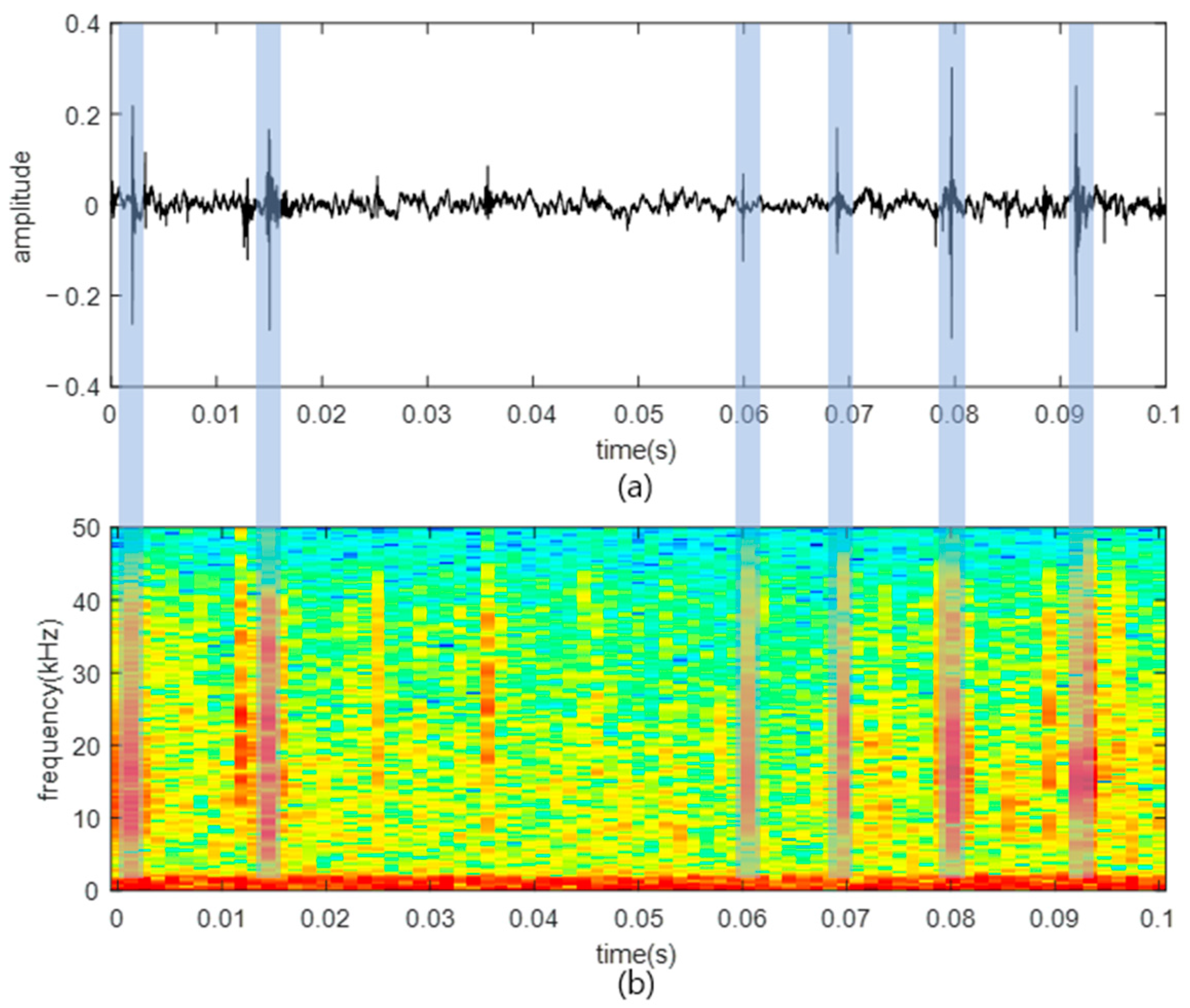
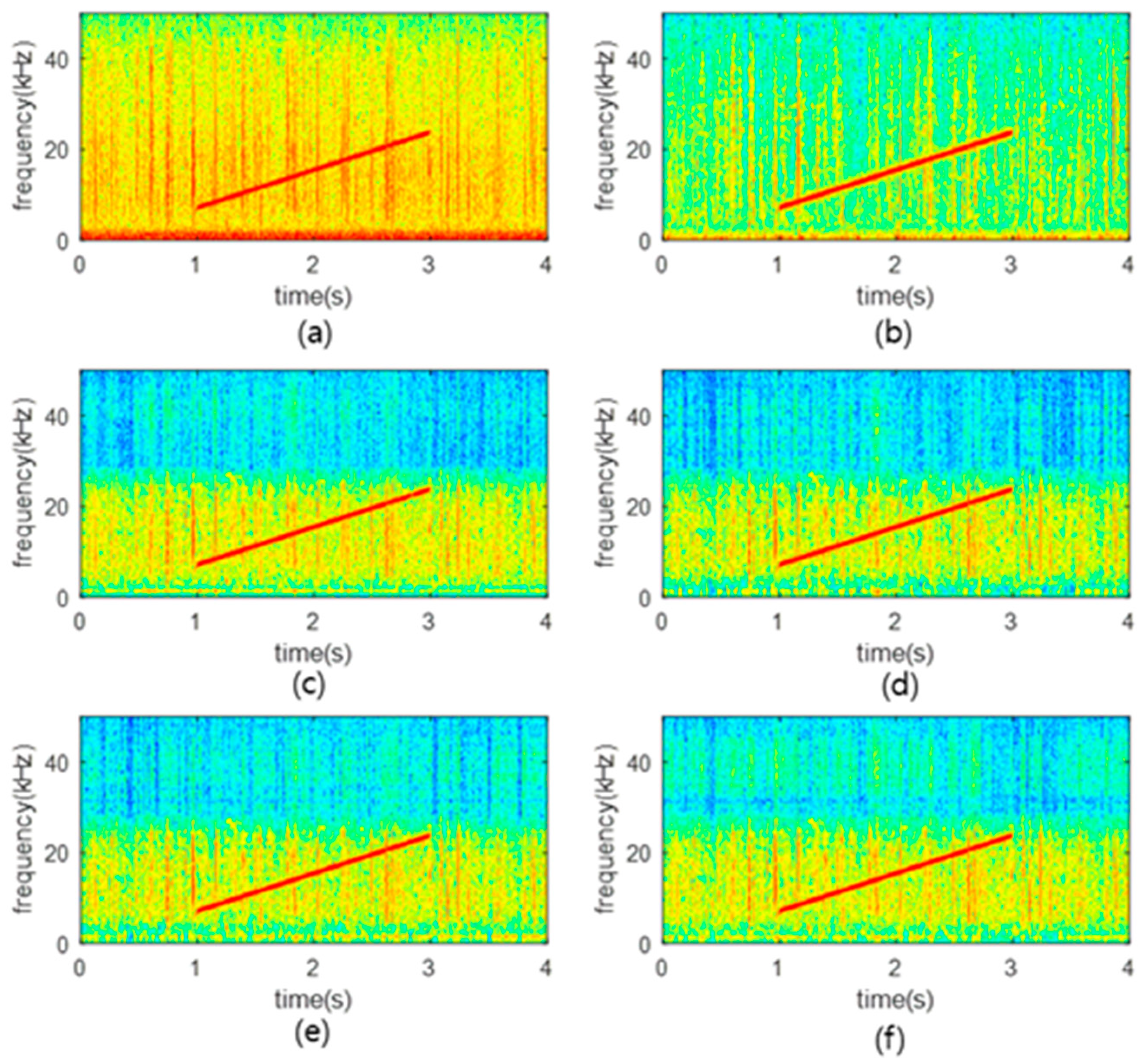
4.2.1. SSN Interval Detection
4.2.2. SSN Reduction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wicksten, M.K.; McClure, M.R. Snapping shrimps (Decapoda: Caridea: Alpheidae) from the Dampier Archipelago, western Australia. Rec. West. Aust. Mus. Suppl. 2007, 73, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Everest, F.A.; Young, R.W.; Johnson, M.W. Acoustical characteristics of noise produced by snapping shrimp. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1948, 20, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.; Hahn, J.; Cho, B.K.; Kim, B.C. Snapping shrimp sound measured under laboratory conditions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 07HG04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, M.; Schmitz, B.; Von der Heydt, A.; Lohse, D. How snapping shrimp snap: Through cavitating bubbles. Science 2000, 289, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.T.; Teck, T.E.; Chitre, M.; Potter, J.R. Estimating the spatial and temporal distribution of snapping shrimp using a portable, broadband 3-dimensional acoustic array. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2003, Celebrating the Past… Teaming toward the Future (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37492), San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 September 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2706–2713. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.W.; Everest, F.A.; Young, R.W. The role of snapping shrimp (Crangon and Synalpheus) in the production of underwater noise in the sea. Biol. Bull. 1947, 93, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Choi, J.W.; Shin, S.; Song, H.C. Temporal Variability in Acoustic Behavior of Snapping Shrimp in the East China Sea and Its Correlation With Ocean Environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 779283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Tong, F. Orthogonal Projection and Distributed Compressed Sensing Based Impulsive Noise Estimation for Underwater Acoustic OSDM Communication. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 22279–22293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, Z.; Niu, K.; Chen, P.; Rong, Y. New results on joint channel and impulsive noise estimation and tracking in underwater acoustic OFDM systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loye, D.P.; Proudfoot, D.A. Underwater Noise to Marine Life. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 18, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, B.C.; Jung, S.K.; Park, Y.; Lee, Y.K. Seawater temperature and wind speeds dependences and diurnal variation of ambient noise at the snapping shrimp colony. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2012 Oceans, Yeosu, Republic of Korea, 21–24 May 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.D.; Doherty, J.F. A steganographic app-roach to sonar tracking. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 44, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hong, J. Snapping shrimp noise detection methods based on linear prediction analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 24, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.C.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, B.N.; Nam, S. Shallow-water acoustic variability experiment 2015 (SAVEX15) in the northern East China Sea. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Seok, J.; Hong, J. Snapping Shrimp Noise Detection Based on Statistical Model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, T. Monaural Sound Source Separation by Perceptually Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization; Tampere University of Technology Tech. Rep.; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Seung, H. Algorithms for non-negative matrix factorization. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2000, 13, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Seung, H. Learning the parts of objects by nonnegative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozerov, A.; Févotte, C. Multichannel nonnegative matrix factorization in convolutive mixtures for audio source separation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I. Optimal speech enhancement under signal presence uncertainty using log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirszhorn, A.; Dov, D.; Talmon, R.; Cohen, I. Transient interference suppression in speech signals based on the OM-LSA algorithm. In Proceedings of the IWAENC 2012, International Workshop on Acoustic Signal Enhancement, Aachen, Germany, 4–6 September 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, J.; Wisdom, S.; Erdogan, H.; Hershey, J. SDR–half-baked or well done? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, A.; Markel, J. Distance measures for speech processing. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1976, 24, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoul, J. Linear prediction: A tutorial review. Proc. IEEE. 1975, 63, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Kim, N.S.; Mitra, S.K. Voice activity detection based on multiple statistical models. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Min, G.; Sun, M.; Zheng, Y. Speech Enhancement Combining NMF Weighted by Speech Presence Probability and Statistical Model. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2015, E98-A(12), 2701–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.; Berdugo, B. Noise estimation by minima controlled recursive averaging for robust speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P. Subjective evaluation and comparison of speech enhancement algorithms. Speech Commun. 2007, 49, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

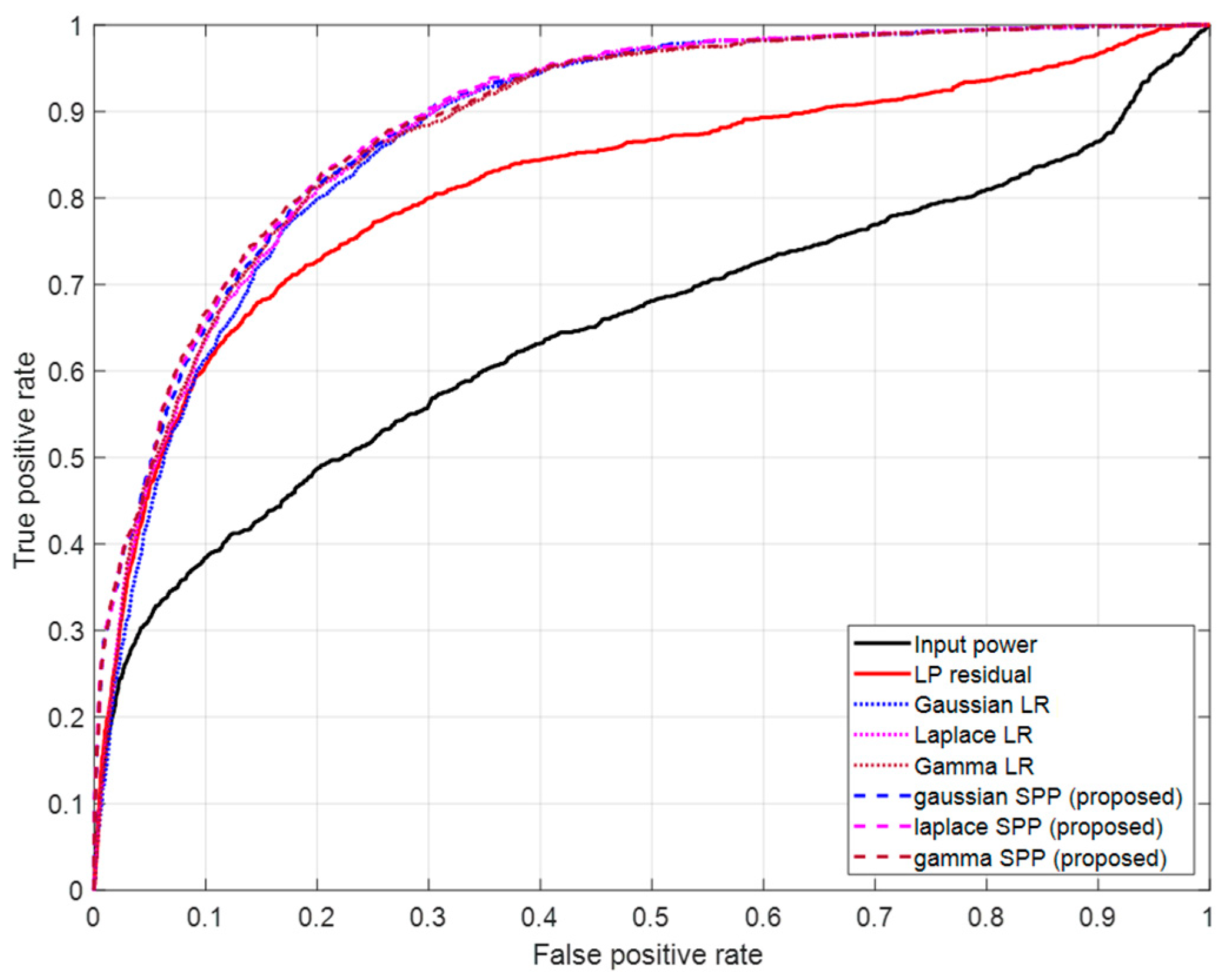
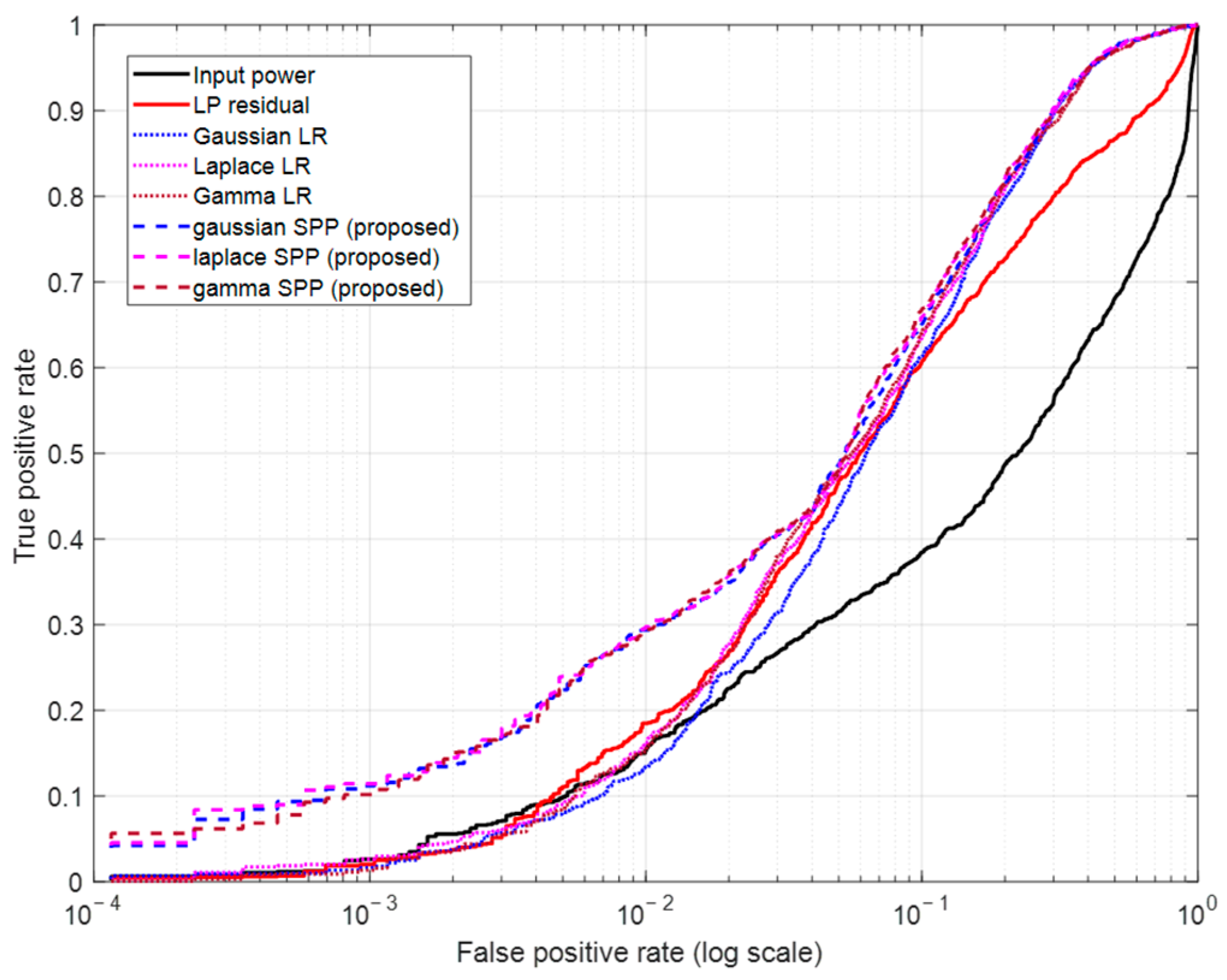

| AUC | Gaussian | Laplace | Gamma |
|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 0.8802 | 0.8857 | 0.8844 |
| SPP | 0.8941 | 0.8935 | 0.8920 |
| CW | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | ||
| −10 | 0.12 | 5.94 | 7.38 | 7.36 | 7.73 | 5.49 | 5.90 | 5.88 | 6.49 | |
| −5 | 6.15 | 9.18 | 11.14 | 11.17 | 11.48 | 8.96 | 10.15 | 10.17 | 10.66 | |
| 0 | 10.03 | 12.87 | 15.33 | 15.43 | 15.68 | 12.77 | 14.62 | 14.68 | 15.08 | |
| 5 | 12.56 | 17.04 | 19.81 | 19.91 | 20.13 | 16.98 | 19.26 | 19.31 | 19.65 | |
| 10 | 13.79 | 21.18 | 24.11 | 24.17 | 24.31 | 21.15 | 23.71 | 23.73 | 23.97 | |
| LFM | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | ||
| −10 | 1.32 | 3.46 | 3.84 | 3.74 | 4.13 | 2.13 | 2.71 | 2.51 | 2.46 | |
| −5 | 6.01 | 5.82 | 7.22 | 7.05 | 7.39 | 6.72 | 7.42 | 7.24 | 7.20 | |
| 0 | 9.73 | 7.82 | 10.58 | 10.33 | 10.61 | 11.17 | 12.15 | 11.98 | 11.96 | |
| 5 | 12.39 | 9.73 | 14.08 | 13.75 | 13.99 | 15.38 | 16.92 | 16.75 | 16.76 | |
| 10 | 13.71 | 11.64 | 17.78 | 17.41 | 17.63 | 19.11 | 21.71 | 21.55 | 21.58 | |
| CW | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | −9.09 | 2.33 | 7.02 | 9.01 | 8.94 | 9.40 | 6.63 | 7.84 | 7.72 | 8.32 | |
| −5 | −4.55 | 9.19 | 11.05 | 13.51 | 13.45 | 13.91 | 10.79 | 12.51 | 12.41 | 12.99 | |
| 0 | 0.43 | 11.69 | 15.54 | 18.28 | 18.24 | 18.70 | 15.33 | 17.36 | 17.27 | 17.84 | |
| 5 | 5.43 | 13.20 | 20.29 | 23.16 | 23.12 | 23.58 | 20.10 | 22.28 | 22.18 | 22.74 | |
| 10 | 10.42 | 13.96 | 25.12 | 28.01 | 27.96 | 28.41 | 24.94 | 27.16 | 27.06 | 27.61 | |
| LFM | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | −9.09 | 4.60 | 4.55 | 5.42 | 5.22 | 5.52 | 5.06 | 6.31 | 5.97 | 5.85 | |
| −5 | −4.55 | 8.64 | 7.28 | 8.86 | 8.62 | 8.94 | 9.63 | 10.93 | 10.62 | 10.54 | |
| 0 | 0.42 | 11.30 | 10.13 | 12.55 | 12.26 | 12.58 | 14.22 | 15.61 | 15.31 | 15.27 | |
| 5 | 5.42 | 13.03 | 13.23 | 16.52 | 16.19 | 16.51 | 18.85 | 20.36 | 20.07 | 20.05 | |
| 10 | 10.42 | 13.89 | 16.62 | 20.73 | 20.36 | 20.68 | 23.51 | 25.14 | 24.86 | 24.87 | |
| CW | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | −10.06 | −3.26 | 5.94 | 7.38 | 7.36 | 7.73 | 5.49 | 5.90 | 5.88 | 6.49 | |
| −5 | −5.03 | 5.95 | 9.18 | 11.14 | 11.17 | 11.49 | 8.96 | 10.15 | 10.16 | 10.66 | |
| 0 | −0.02 | 9.97 | 12.87 | 15.33 | 15.43 | 15.68 | 12.77 | 14.62 | 14.68 | 15.08 | |
| 5 | 4.99 | 12.53 | 17.04 | 19.81 | 19.91 | 20.13 | 16.98 | 19.26 | 19.31 | 19.65 | |
| 10 | 9.99 | 13.78 | 21.18 | 24.11 | 24.17 | 24.31 | 21.15 | 23.71 | 23.73 | 23.97 | |
| LFM | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | −10.00 | 0.42 | 3.46 | 3.84 | 3.74 | 4.13 | 2.13 | 2.71 | 2.51 | 2.46 | |
| −5 | −5.00 | 5.89 | 5.82 | 7.22 | 7.05 | 7.39 | 6.72 | 7.42 | 7.24 | 7.20 | |
| 0 | 0.00 | 9.69 | 7.82 | 10.58 | 10.33 | 10.61 | 11.17 | 12.15 | 11.98 | 11.96 | |
| 5 | 5.00 | 12.36 | 9.73 | 14.08 | 13.75 | 13.99 | 15.38 | 16.92 | 16.75 | 16.76 | |
| 10 | 10.00 | 13.70 | 11.64 | 17.78 | 17.41 | 17.63 | 19.11 | 21.71 | 21.55 | 21.58 | |
| CW | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | 14.11 | 12.91 | 12.04 | 11.84 | 12.01 | 11.90 | 13.28 | 13.15 | 13.25 | 13.24 | |
| −5 | 14.11 | 12.43 | 11.42 | 11.25 | 11.41 | 11.30 | 12.67 | 12.59 | 12.69 | 12.67 | |
| 0 | 13.85 | 11.88 | 10.73 | 10.59 | 10.75 | 10.65 | 11.95 | 11.92 | 12.01 | 11.99 | |
| 5 | 13.56 | 11.42 | 10.23 | 10.10 | 10.25 | 10.17 | 11.40 | 11.39 | 11.48 | 11.47 | |
| 10 | 13.14 | 10.96 | 9.77 | 9.64 | 9.78 | 9.70 | 10.87 | 10.87 | 10.96 | 10.94 | |
| LFM | Noisy Input | OM-LSA | Basis Matrix Size: (128:32) | Basis Matrix Size: (128:64) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | NMF | NMF(G) | NMF(L) | NMF(A) | |||
| −10 | 4.36 | 3.11 | 3.08 | 2.86 | 2.99 | 3.11 | 3.08 | 2.84 | 2.96 | 3.10 | |
| −5 | 4.38 | 2.81 | 2.71 | 2.51 | 2.63 | 2.72 | 2.80 | 2.56 | 2.68 | 2.80 | |
| 0 | 4.25 | 2.44 | 2.28 | 2.11 | 2.21 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 2.20 | 2.31 | 2.42 | |
| 5 | 3.93 | 2.04 | 1.87 | 1.74 | 1.81 | 1.87 | 2.05 | 1.85 | 1.93 | 2.03 | |
| 10 | 3.50 | 1.68 | 1.51 | 1.41 | 1.47 | 1.51 | 1.69 | 1.52 | 1.59 | 1.66 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Seok, J.; Hong, J. Probabilistic Noise Detection and Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based Noise Reduction Methods for Snapping Shrimp Noise. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010096
Park S, Seok J, Hong J. Probabilistic Noise Detection and Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based Noise Reduction Methods for Snapping Shrimp Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010096
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Suhyeon, Jongwon Seok, and Jungpyo Hong. 2025. "Probabilistic Noise Detection and Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based Noise Reduction Methods for Snapping Shrimp Noise" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 1: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010096
APA StylePark, S., Seok, J., & Hong, J. (2025). Probabilistic Noise Detection and Weighted Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based Noise Reduction Methods for Snapping Shrimp Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(1), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13010096





