The Effects of Controlling Gas Escape and Bottom Current Activity on the Evolution of Pockmarks in the Northwest of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
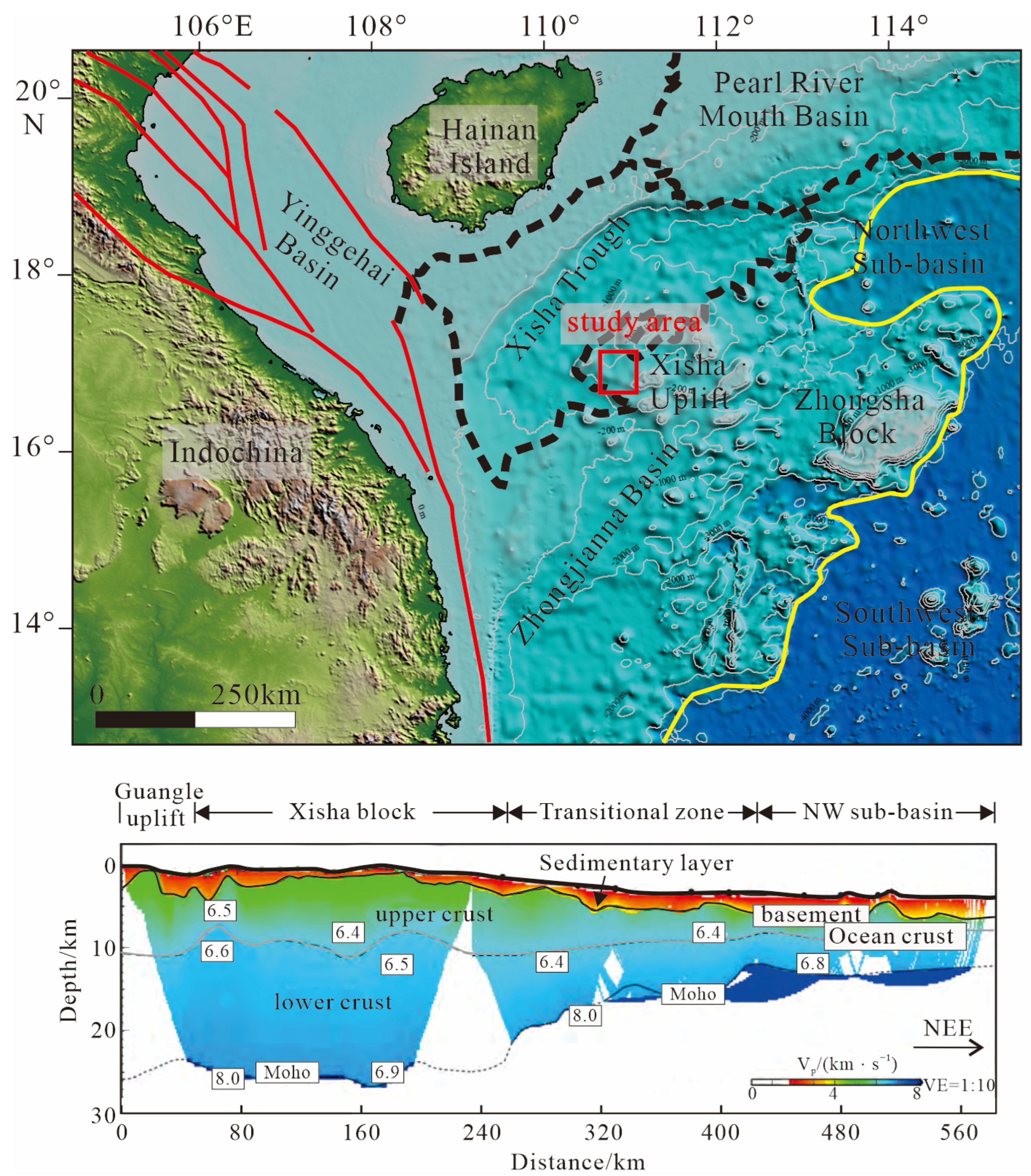
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
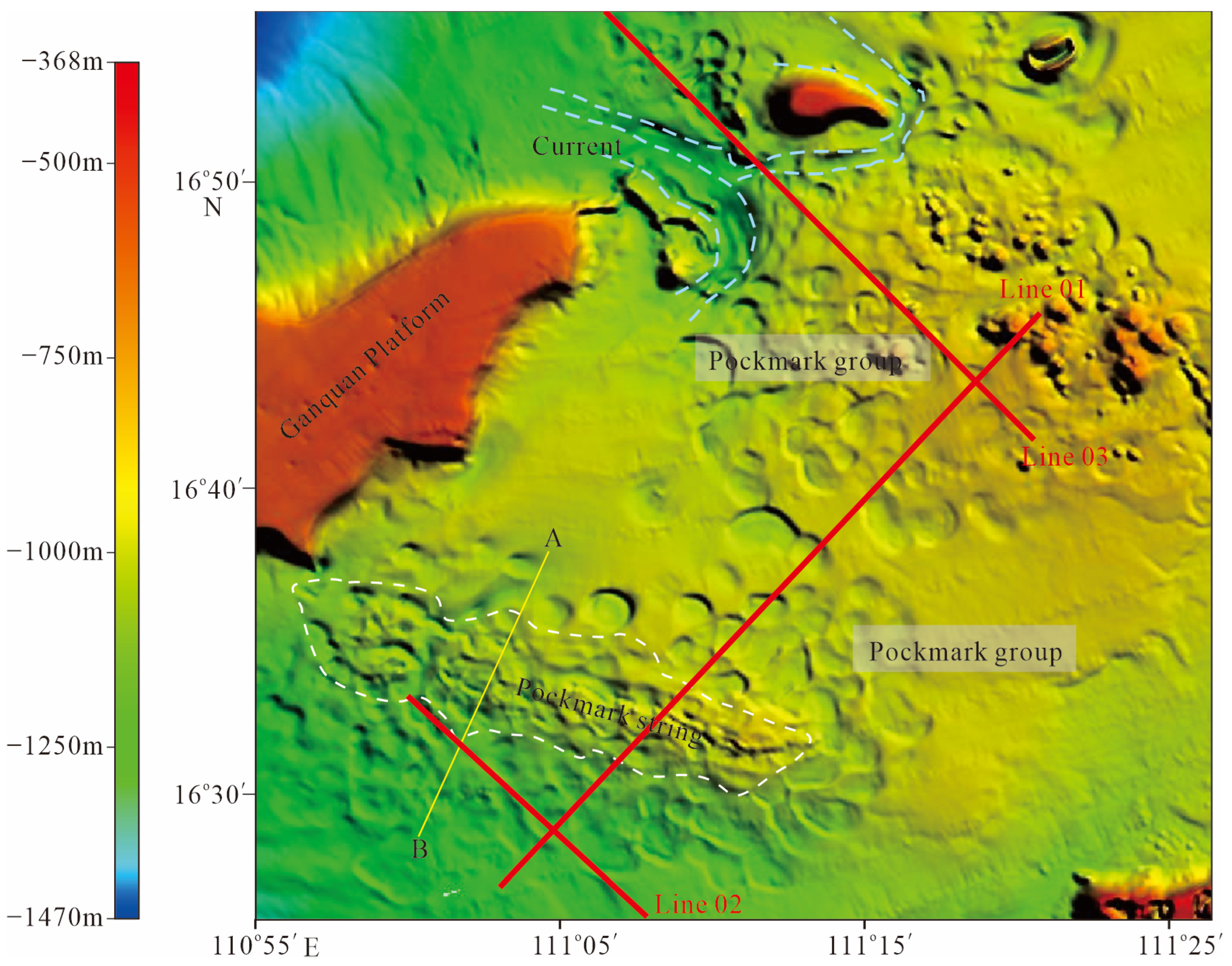
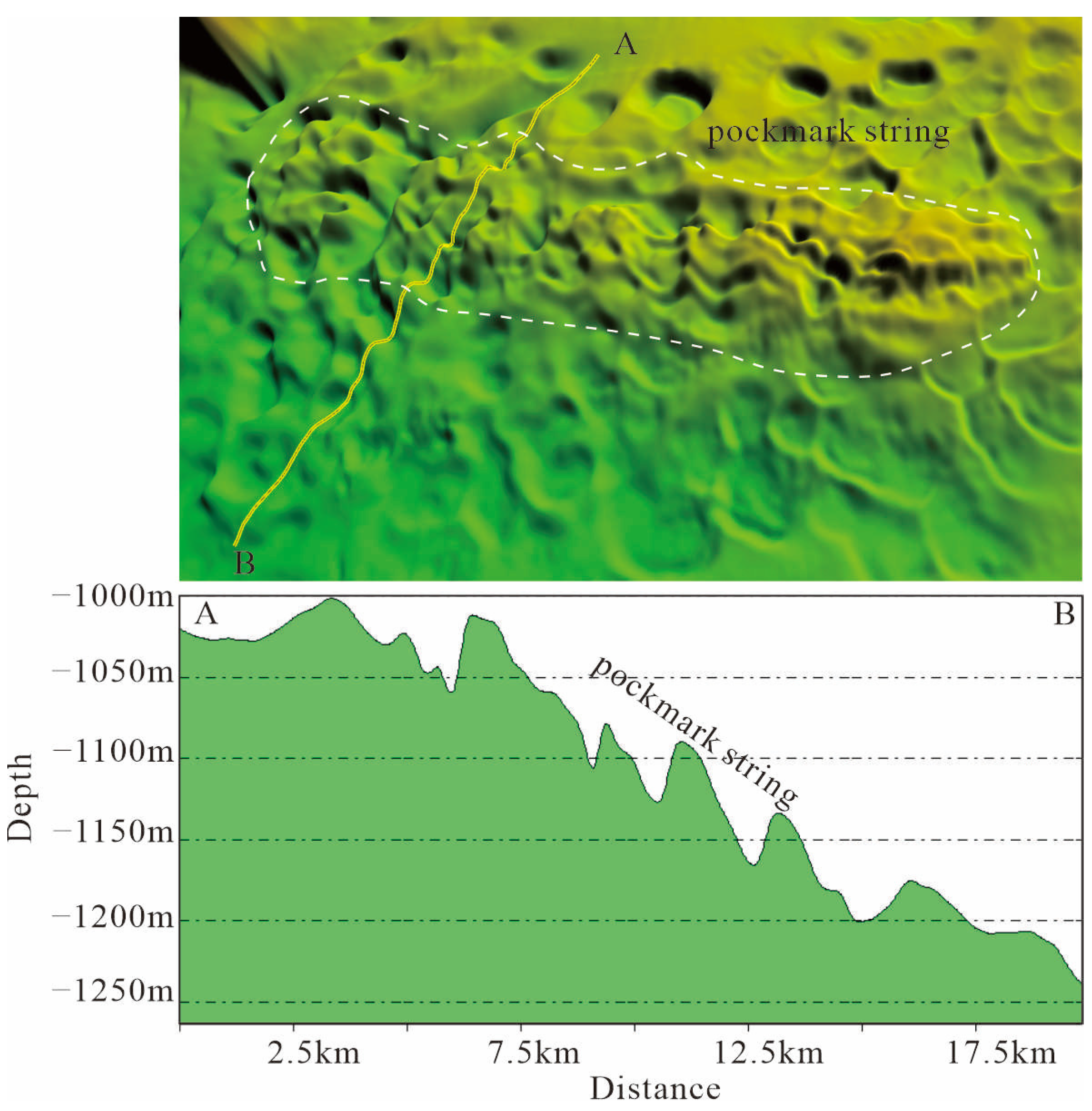
4.1. Interpretation of Multibeam Bathymetry Data
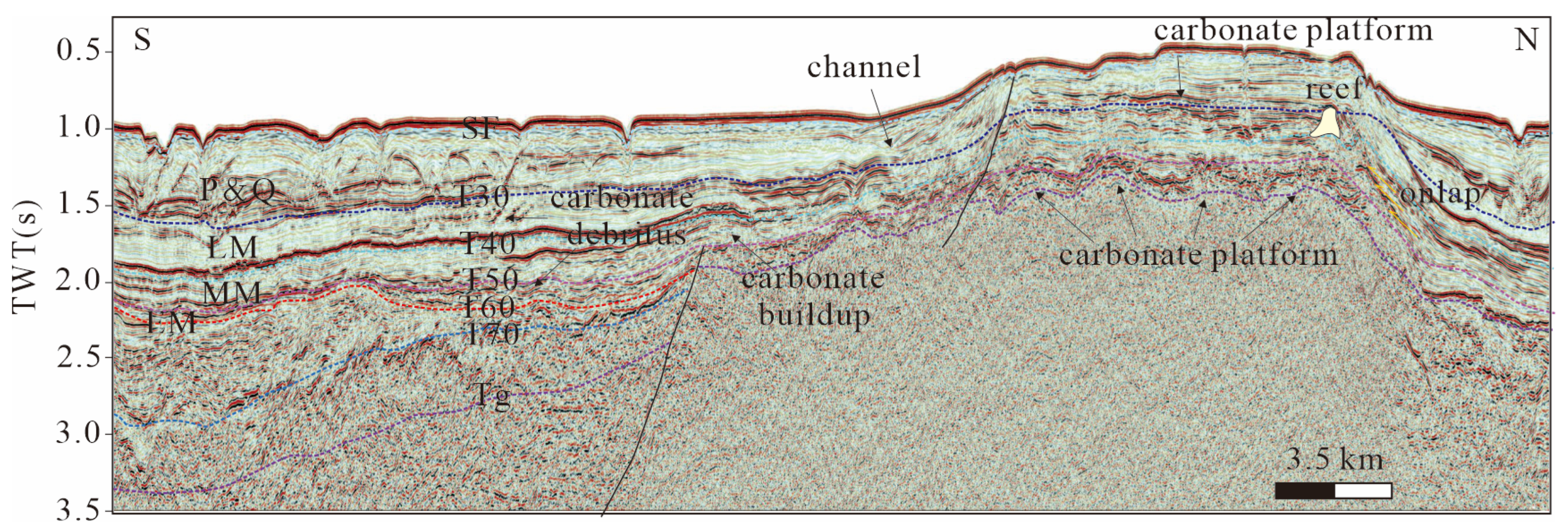
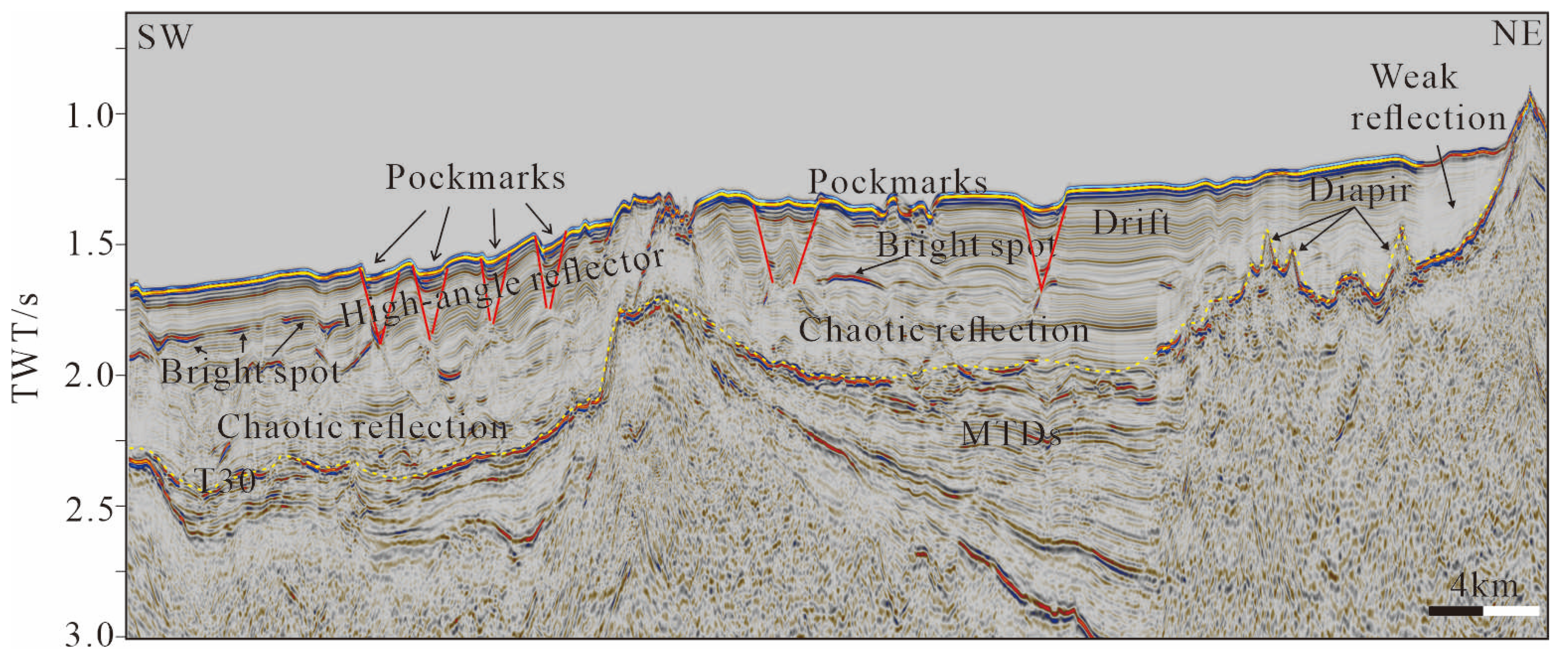
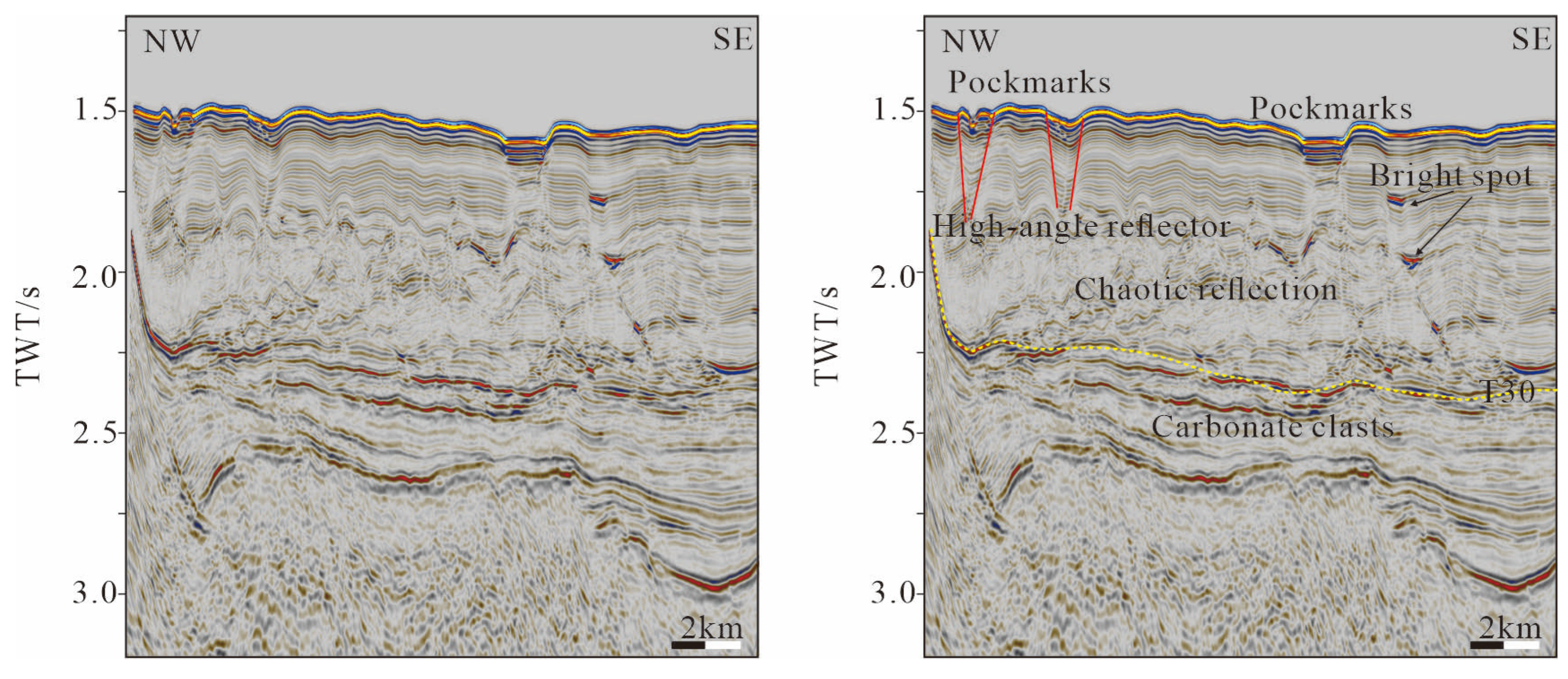
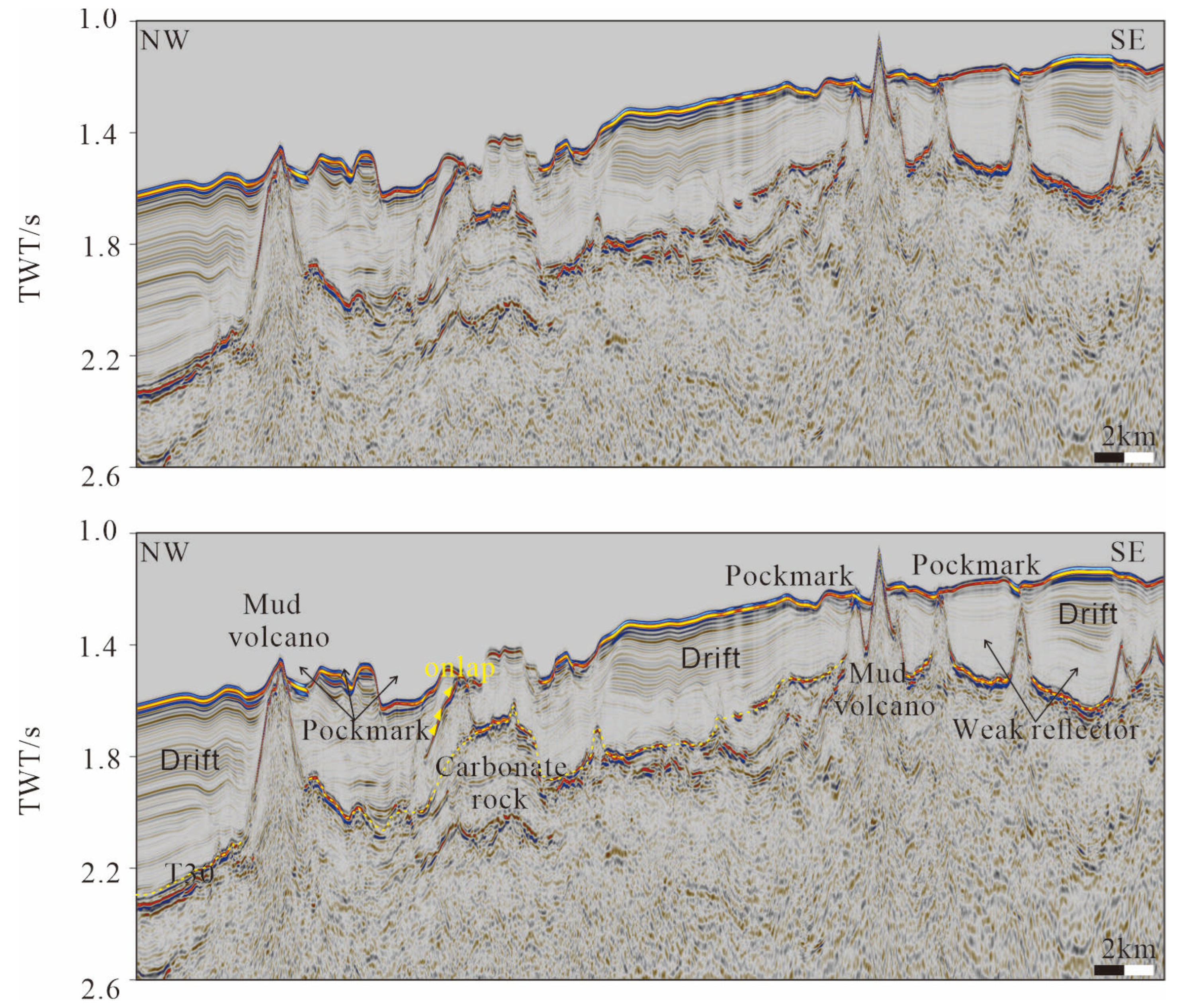
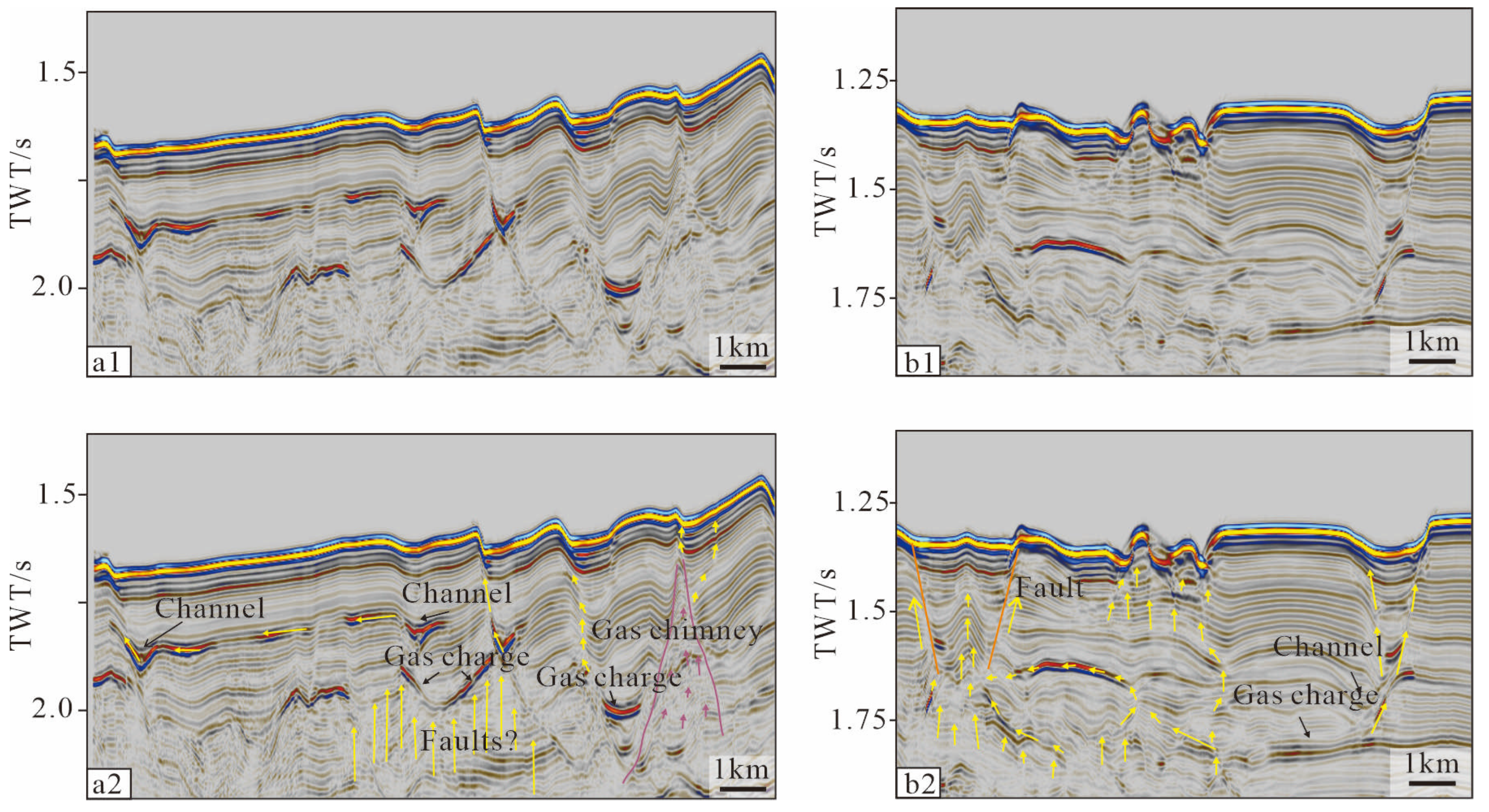
4.2. Interpretation of 2D Seismic Data
4.2.1. Seismic Facies in the Southern Part of the Study Area
4.2.2. Seismic Facies in the Northern Part of the Study Area
5. Discussion
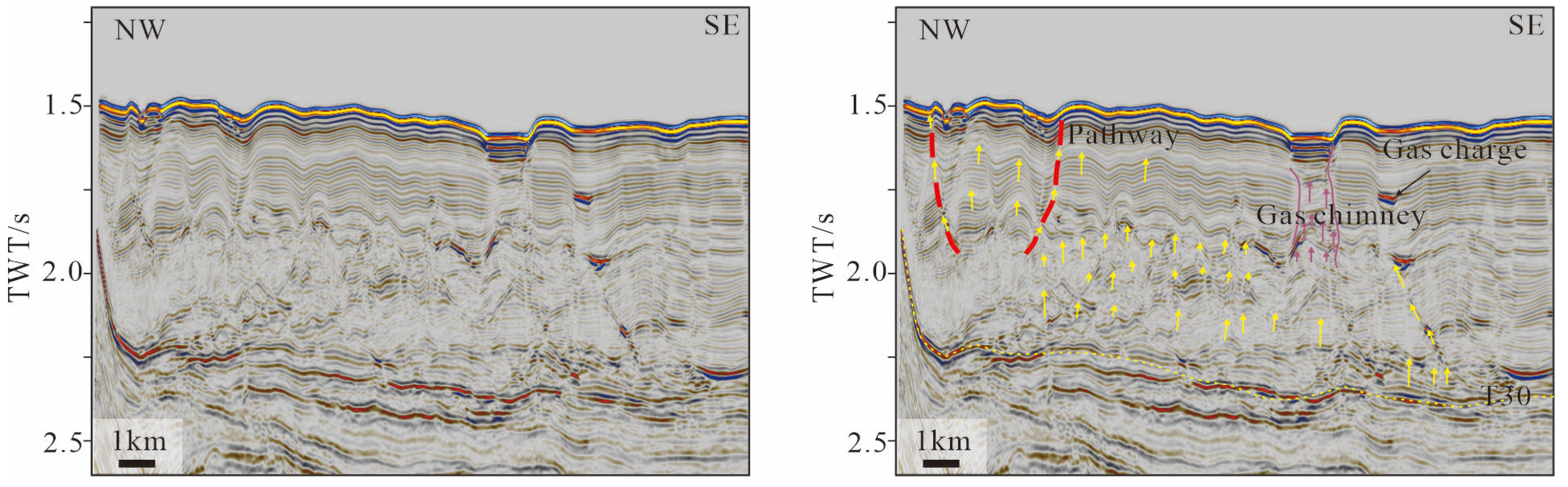
5.1. Gas Migration in the Southern Part of the Study Area
5.2. The Genesis of Pockmarks in the Study Area Is Primarily Attributed to Gas Escape
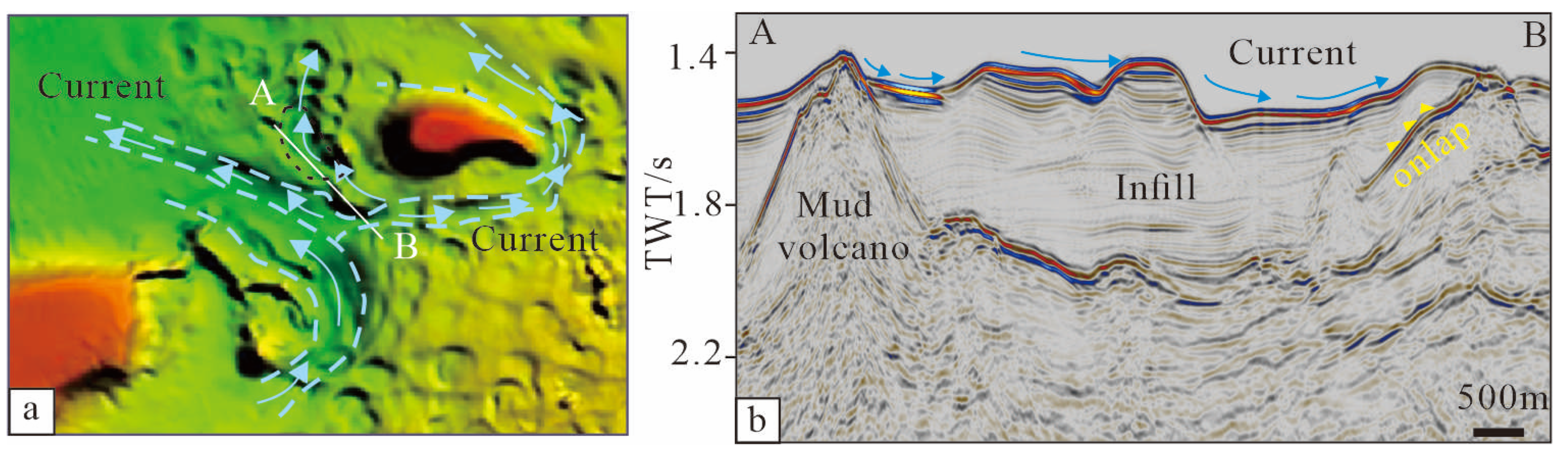
5.3. The Impact of Bottom Currents on Pockmarks in the Xisha Uplift
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on multibeam bathymetric data and 2D seismic profiles, 261 seabed pockmarks have been identified near the Ganquan Platform. Among them, there are 69 circular pockmarks, 19 elliptical pockmarks, 40 irregular-shaped pockmarks, 28 crescent-shaped pockmarks, 27 elongated pockmarks, and 18 ring-shaped pockmarks. The diameters of these pockmarks range from 0.21 to 4.96 km, with maximum depths reaching up to 30.882 m. A large number of small-scale pockmarks arranged in strings have been discovered in the southern part of the study area.
- (2)
- The genesis of pockmarks on the Xisha Uplift is primarily associated with the escape of gas. There are various types of escape pathways on the Xisha Uplift, such as faults, fractures, and gas chimneys. Based on the formation mechanism, pockmarks on the Xisha Uplift can be classified into four types: pockmarks formed by gas escape leading to strata collapse, pockmarks formed by gas escape causing strata deformation, pockmarks related to gas chimneys, and pockmarks related to diapirs.
- (3)
- Bottom current activity has a significant impact on already formed pockmarks. Crescent-shaped and elongated pockmarks on the Xisha Uplift are largely the result of bottom current modifications of pre-existing pockmarks. Crescent-shaped pockmarks form due to uneven sedimentation rates within the pockmark caused by bottom currents, while elongated pockmarks result from strong erosion by bottom currents connecting multiple pockmarks together.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judd, A.; Hovland, M. Seabed Fluid Flow: The Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pilcher, R.; Argent, J. Mega-Pockmarks and Linear Pockmark Trains on the West African Continental Margin. Mar. Geol. 2007, 244, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboulot, V.; Cattaneo, A.; Sultan, N.; Garziglia, S.; Ker, S.; Imbert, P.; Voisset, M. Sea-Level Change and Free Gas Occurrence Influencing a Submarine Landslide and Pockmark Formation and Distribution in Deepwater Nigeria. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 375, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Cheng, C.; Kuang, Z.; Ren, J.; Liang, J.; Lai, H.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Fang, X.; Jiang, T. Sedimentary Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of the Giant Ancient Pockmarks in the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.H.; MacLean, B. Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1970, 81, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.; Thor, D.; Sandstrom, M.W.; Kvenvolden, K.A. Modern Biogenic Gas-Generated Craters (Sea-Floor “Pockmarks”) on the Bering Shelf, Alaska. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1979, 90, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M. Characteristics of Pockmarks in the Norwegian Trench. Mar. Geol. 1981, 39, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Talbot, M.R.; Qvale, H.; Olaussen, S.; Aasberg, L. Methane-Related Carbonate Cements in Pockmarks of the North Sea. J. Sediment. Res. 1987, 57, 881–892. [Google Scholar]
- Bussmann, I.; Suess, E. Groundwater Seepage in Eckernförde Bay (Western Baltic Sea): Effect on Methane and Salinity Distribution of the Water Column. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çifçi, G.; Dondurur, D.; Ergün, M. Deep and Shallow Structures of Large Pockmarks in the Turkish Shelf, Eastern Black Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2003, 23, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, P.Y.G.; Yoshinaga, M.Y.; Madureira, L.A.S.-P.; Hovland, M. Seabed Pockmarks Associated with Deepwater Corals off SE Brazilian Continental Slope, Santos Basin. Mar. Geol. 2004, 207, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandapath, S.; Chakraborty, B.; Karisiddaiah, S.M.; Menezes, A.; Ranade, G.; Fernandes, W.; Naik, D.K.; Raju, K.P. Morphology of Pockmarks along the Western Continental Margin of India: Employing Multibeam Bathymetry and Backscatter Data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.; Leifer, I.; Sassen, R.; Stine, P.; Mitchell, R.; Guinasso, N., Jr. Transfer of Hydrocarbons from Natural Seeps to the Water Column and Atmosphere. Geofluids 2002, 2, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, S.; Hovland, M.; Luo, P.; Lu, Y.; Qu, T. The Morphologies and Genesis of Mega-Pockmarks near the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, G.; Xing, J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, N. Research Progress of Seafloor Pockmarks in Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Classification. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.B.; Dossantos, R.F.; Schattner, U.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Bícego, M.C.; Lobo, F.J.; de Mahiques, M.M. Deep Pockmarks as Natural Sediment Traps: A Case Study from Southern Santos Basin (SW Atlantic Upper Slope). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2020, 40, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guan, Y.; Song, H.; Fan, W.; Li, H.; Kuang, Y.; Geng, M. A Preliminary Study on Morphology and Genesis of Giant and Mega Pockmarks near Andu Seamount, Nansha Region (South China Sea). Mar. Geophys. Res. 2020, 41, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Webb, K.E.; Depreiter, D. Numerical Simulation of Upwelling Currents in Pockmarks, and Data from the Inner Oslofjord, Norway. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Hsu, S.K.; Tsai, C.H.; Ku, C.Y.; Yeh, Y.C.; Wang, Y. Gas Seepage, Pockmarks and Mud Volcanoes in the near Shore of SW Taiwan. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2010, 31, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, P.; Huang, H.; Huang, B.; He, J.; Chen, D. Seabed Pockmark Formation Associated with Mud Diapir Development and Fluid Activities in the Yinggehai Basin of the South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2012, 31, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Zhu, J.T.; Zhou, H.T.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z.P.; Zhang, H. Seismic Characteristics and Mechanism of Fluid Flow Structures in the Central Depression of Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern Margin of South China Sea. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 62, 1108–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, H.; Guan, Y.; Yang, S.; Pinheiro, L.M.; Bai, Y.; Liu, B.; Geng, M. Morphologies, Classification and Genesis of Pockmarks, Mud Volcanoes and Associated Fluid Escape Features in the Northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 122, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.R.; Zhang, M.H.; Huang, H.B.; Qiu, X.L.; Zhang, J.Z. Crustal Structure of Xisha Block and Its Tectonic Attributes. Chin. J. Geophys. 2016, 59, 288–300. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.; Hayes, D.E. Origin and History of the South China Sea Basin. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1983, 27, 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhi, P.; Ding, R.; Zhao, L.; Gong, W.; Li, Z.; Ge, J. Differences in Thermo-Rheological Structure between Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the Extension Model in the Northwestern Margin of the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Müller, R.D.; Williams, S.E.; Zahirovic, S.; Dong, D. Full-Fit Reconstruction of the South China Sea Conjugate Margins. Tectonophysics 2015, 661, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Alves, T.M.; Ren, J.; Tong, C. Rift Structure and Sediment Infill of Hyperextended Continental Crust: Insights from 3D Seismic and Well Data (Xisha Trough, South China Sea). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.Q. A Preliminary Study on Foraminiferal Assemblages of Well 1, Xiyong, Xisha Islands and Their Coral Reef Formation. Trop. Oceanol./Redai Haiyang 1987, 6, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Fan, C.; Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Zhao, F.; Wan, K. Characteristics of Late Cenozoic Magmatic Activities on the Northern Margin of South China Sea and Their Tectonic Implications. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. Chin. 2017, 37, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Cao, L.; Shao, L. New Insights on the Origin of the Basement of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Sci. China (Earth Sci.) 2017, 60, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X. Development of the Miocene Guangle Carbonate Platform in the South China Sea: Architecture and Controlling Factors. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Yi, L. Magnetic Properties and Initiation of Biogenic Reefs in Xisha Islands, South China Sea, at the Oligo–Miocene Boundary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lu, F.; Lüdmann, T.; Fulthorpe, C.; Wang, B. Architecture, Development and Geological Control of the Xisha Carbonate Platforms, Northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 350, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pu, R.; Chen, Y.; Qu, H.; Shen, H. Seismic Analysis of Early-Mid Miocene Carbonate Platform in the Southern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Qin, Z.; Spence, G.; Lü, F. Seismic Characteristics of the Huaguang Mass Transport Deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications for Regional Tectonic Activity. Mar. Geol. 2013, 346, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.B.; Wu, S.G.; Lv, F.L.; Dong, D.D.; Gu, M.F. Seismic Characteristics and Development of the Xisha Carbonate Platforms, Northern Margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 770–783. [Google Scholar]
- Hovland, M.; Gardner, J.V.; Judd, A. The Significance of Pockmarks to Understanding Fluid Flow Processes and Geohazards. Geofluids 2002, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.S. Seismic Bright Spots in the Gulf of Oman. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1977, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroot, B.M.; Schüttenhelm, R.T. Shallow Gas and Gas Seepage: Expressions on Seismic and Otheracoustic Data from the Netherlands North Sea. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 78, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, D.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Hu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.H. A Comprehensive Stratigraphic Study of Well XK-1 in the Xisha Area. J. Stratigr. 2018, 42, 485–498. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, N.; Marsset, B.; Ker, S.; Marsset, T.; Voisset, M.; Vernant, A.-M.; Bayon, G.; Cauquil, E.; Adamy, J.; Colliat, J. Hydrate Dissolution as a Potential Mechanism for Pockmark Formation in the Niger Delta. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B08101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboulot, V.; Thomas, Y.; Berné, S.; Jouet, G.; Cattaneo, A. Control of Quaternary Sea-level Changes on Gas Seeps. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4970–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dando, P.R.; Hara, S.C.M.; Schuster, U. Gas seepage from a carbonate-cemented sandstone reef on the Kattegat coast of Denmark. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1994, 11, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serié, C.; Huuse, M.; Schødt, N.H. Gas Hydrate Pingoes: Deep Seafloor Evidence of Focused Fluid Flow on Continental Margins. Geology 2012, 40, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustoft, S.; Mienert, J.; Bünz, S.; Nouzé, H. High-Resolution 3D-Seismic Data Indicate Focussed Fluid Migration Pathways above Polygonal Fault Systems of the Mid-Norwegian Margin. Mar. Geol. 2007, 245, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, D.; Jackson, C.; Lunn, R.; Schlische, R.; Shipton, Z.; Wibberley, C.; Withjack, M. A Review of Recent Developments Concerning the Structure, Mechanics and Fluid Flow Properties of Fault Zones. J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1557–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Gao, H. Sequence Characteristics of Cenozoic Stratigraphy in Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea. Geotecton. Metallog. 2005, 29, 403–409. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.J.; Li, W.L.; Chang, M. Gas Chimney and Hydrocarbon Exploration. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2006, 27, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Lu, F.; Wang, B.; Fan, G.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z. Geophysical Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of the Gas Chimney in Deepwater Area of Southern Qiongdongnan Basin. Prog. Geophys. 2013, 28, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Dillon, W.P.; Nealon, J.W.; Taylor, M.H.; Lee, M.W.; Drury, R.M.; Anton, C.H. Seafloor Collapse and Methane Venting Associated with Gas Hydrate on the Blake Ridge: Causes and Implications to Seafloor Stability and Methanerelease. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 2001, 124, 211–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, J.; Long, D. Images of the Seabed in the Faroe-Shetland Channel from Commercial 3D Seismic Data. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2001, 22, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzler, C.; Lindhorst, S.; Hübscher, C.; Lüdmann, T.; Fürstenau, J.; Reijmer, J. Giant Pockmarks in a Carbonate Platform (Maldives, Indian Ocean). Mar. Geol. 2011, 289, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, C.; Ussler Iii, W.; Borowski, W. Freshwater Ice Rafting: An Additional Mechanism for the Formation of Some High-Latitude Submarine Pockmarks. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1999, 19, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovland, M.; Jensen, S.; Indreiten, T. Unit Pockmarks Associated with Lophelia Coral Reefs off Mid-Norway: More Evidence of Control by ‘Fertilizing’ Bottom Currents. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2012, 32, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, G.; Dupré, S.; Baltzer, A.; Ehrhold, A.; Imbert, P.; Pitel, M.; Loubrieu, B.; Scalabrin, C.; Lazure, P.; Marié, L. Pockmarks on the South Aquitaine Margin Continental Slope: The Seabed Expression of Past Fluid Circulation and Former Bottom Currents. Comptes Rendus. Géosci. 2017, 349, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Liu, Z.; Hui, C.R. A Three-Layer Alternating Spinning Circulation in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. Focused Fluid-Flow Escape System and Sediments Deformation in Deep-Water Basins of Northern South China Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology), Qingdao, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Bian, M.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D. Study on the Wind and Wave Environmental Conditions of the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Shape | Long Axis Diameter/km | Short Axis Diameter/km | Depth/m | Number |
| Circular | 0.28–2.59 | 0.23–2.43 | 10.334–30.882 | 69 |
| Elliptical | 0.34–4.62 | 0.21–2.98 | 9.228–28.166 | 79 |
| Crescent-shaped | 0.51–3.83 | 0.31–1.98 | 9.235–26.731 | 28 |
| Elongated | 0.75–4.96 | 0.25–2.21 | 8.965–26.556 | 27 |
| Annular | 0.66–2.62 | 0.51–2.33 | 11.564–25.776 | 18 |
| Irregular | 0.35–2.63 | 0.29–2.33 | 10.528–31.002 | 40 |
| Shape | Volume/106 m3 | Surface Area/km2 | Perimeter/km | Orientation/° |
| Circular | 0.5–73.16 | 0.05–4.91 | 0.79–7.85 | 6.3–351.8 |
| Elliptical | 0.62–80.43 | 0.05–10.88 | 0.91–12.69 | 5.7–349.5 |
| Crescent-shaped | 0.39–65.04 | 0.02–6.39 | 0.83–9.57 | 12.3–355.2 |
| Elongated | 0.34–38.76 | 0.03–6.24 | 0.93–11.76 | 20.5–324.9 |
| Annular | 0.38–54.26 | 0.28–5.41 | 1.81–8.22 | 4.6–358.2 |
| Irregular | 0.65–75.48 | 0.06–10.76 | 1.12–9.72 | 7.1–342.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Guo, X.; Tian, F.; Fang, X. The Effects of Controlling Gas Escape and Bottom Current Activity on the Evolution of Pockmarks in the Northwest of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091505
Li X, Guo X, Tian F, Fang X. The Effects of Controlling Gas Escape and Bottom Current Activity on the Evolution of Pockmarks in the Northwest of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(9):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091505
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuelin, Xudong Guo, Fei Tian, and Xiaochen Fang. 2024. "The Effects of Controlling Gas Escape and Bottom Current Activity on the Evolution of Pockmarks in the Northwest of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 9: 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091505
APA StyleLi, X., Guo, X., Tian, F., & Fang, X. (2024). The Effects of Controlling Gas Escape and Bottom Current Activity on the Evolution of Pockmarks in the Northwest of the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(9), 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12091505





