Salinity Prediction Based on Improved LSTM Model in the Qiantang Estuary, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Methods
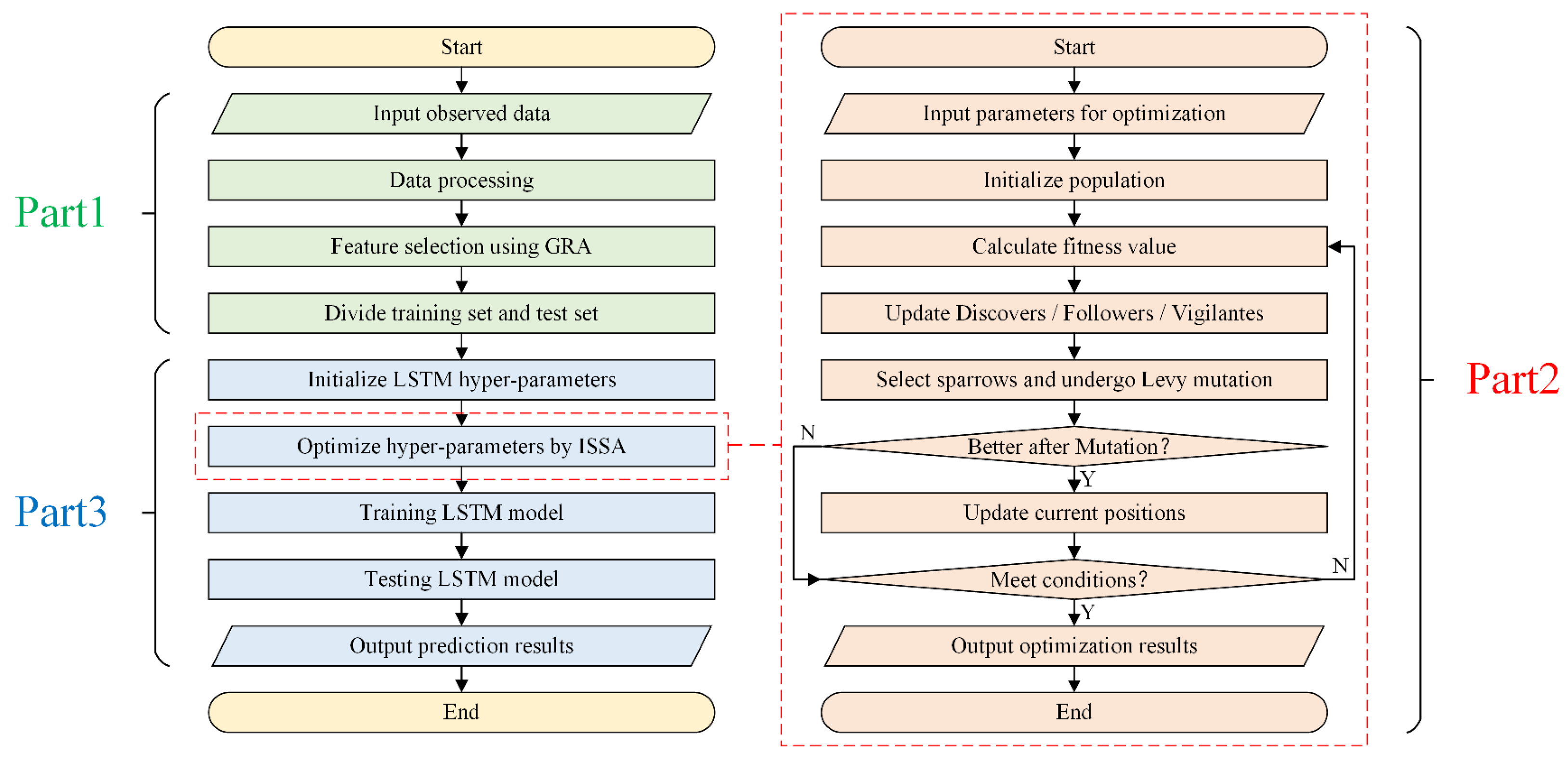
3.1. Framework of ISSA-LSTM Model
3.2. Feature Selection Based on GRA
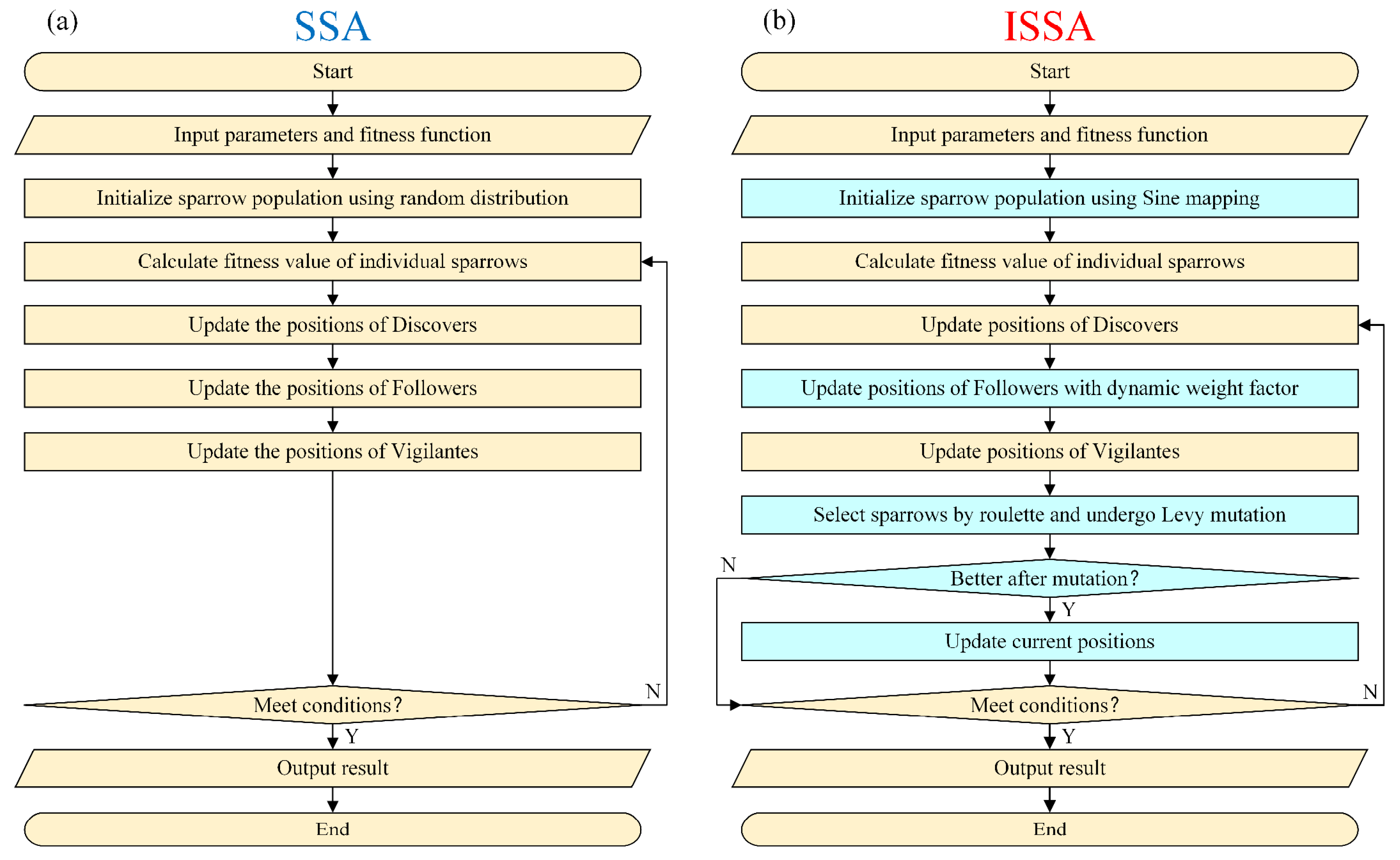
3.3. Hyperparameter Optimization Using ISSA
- Initial population optimization
- 2.
- Followers strategy optimization
- 3.
- Population mutation
3.4. Model Setting and Evaluation Index
4. Results
4.1. Result of Feature Selection
4.2. Results of Hyperparameters Optimization
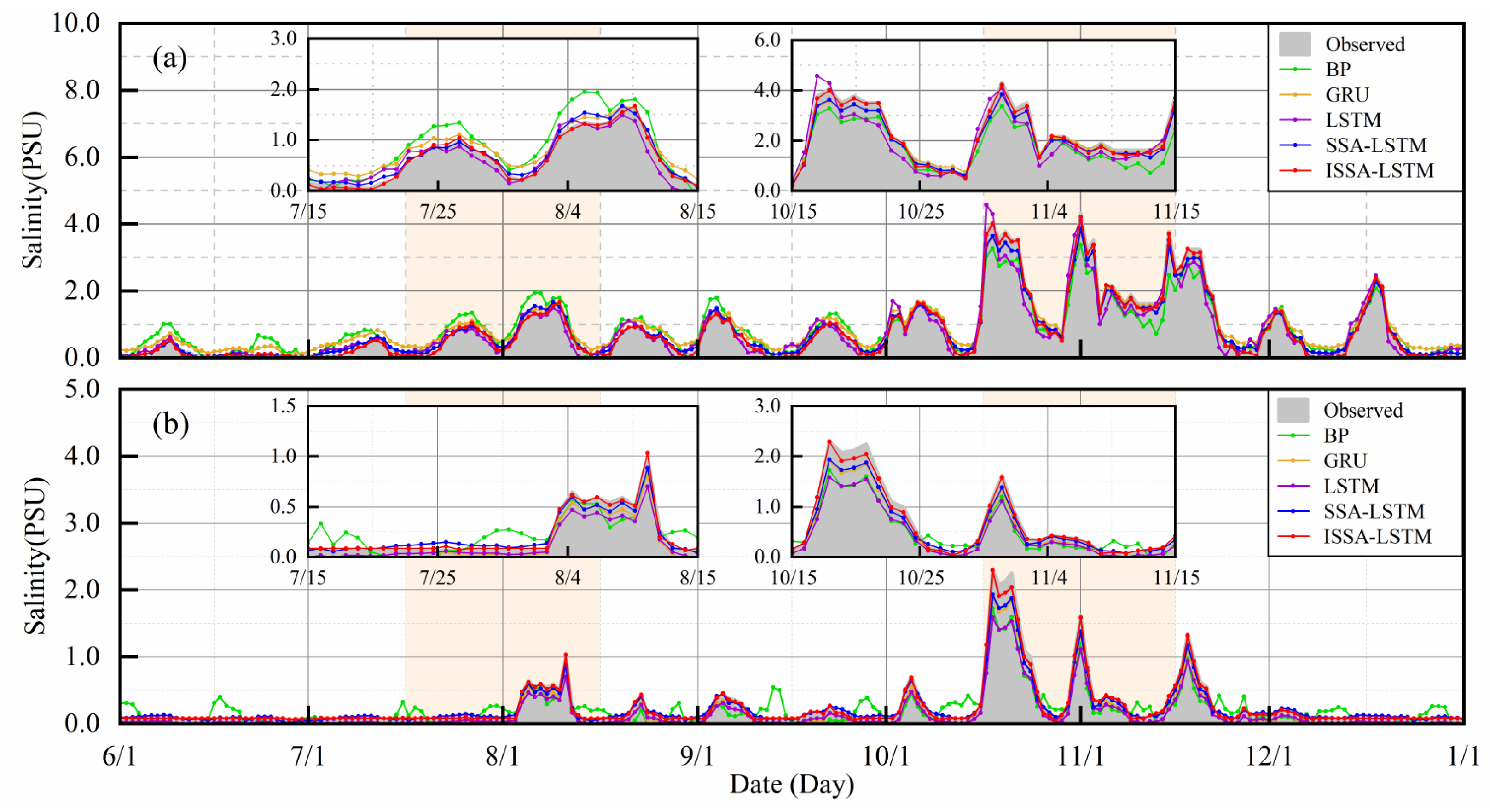
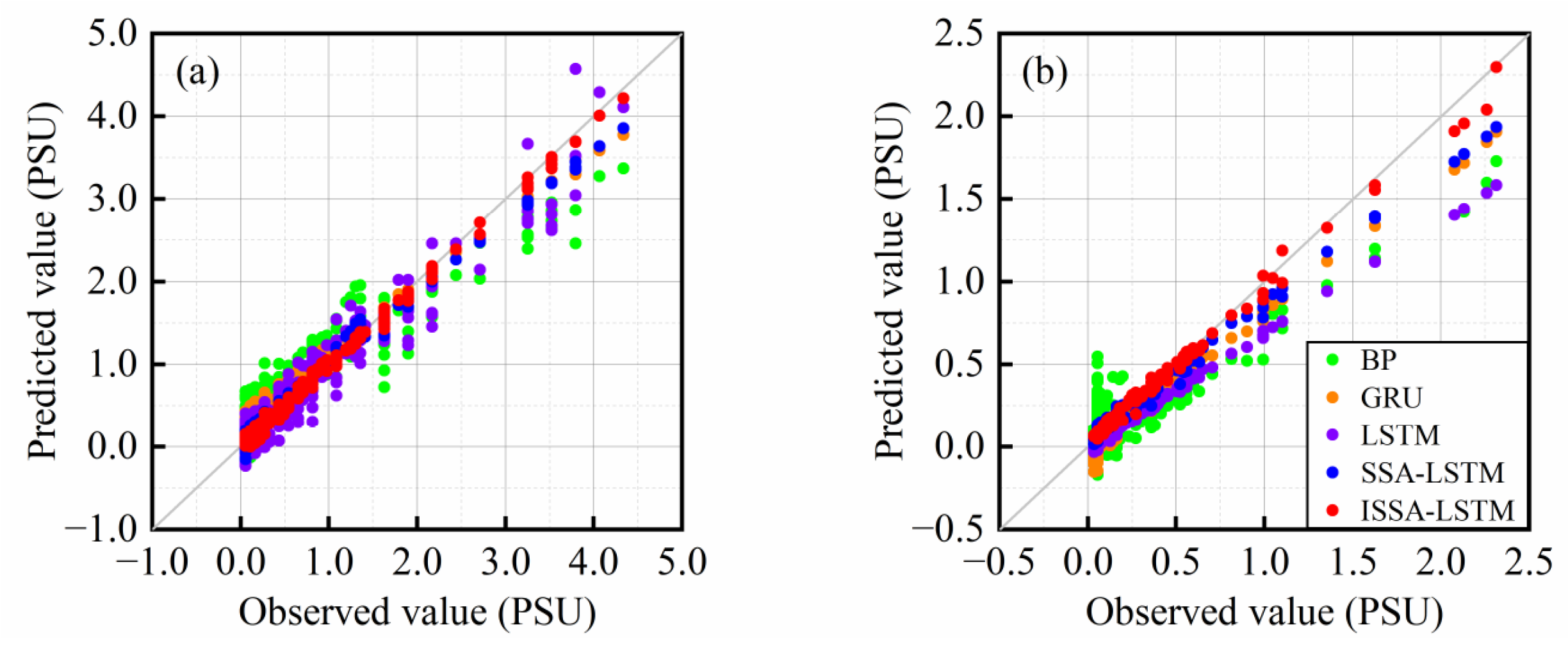
4.3. Results of Different Prediction Models
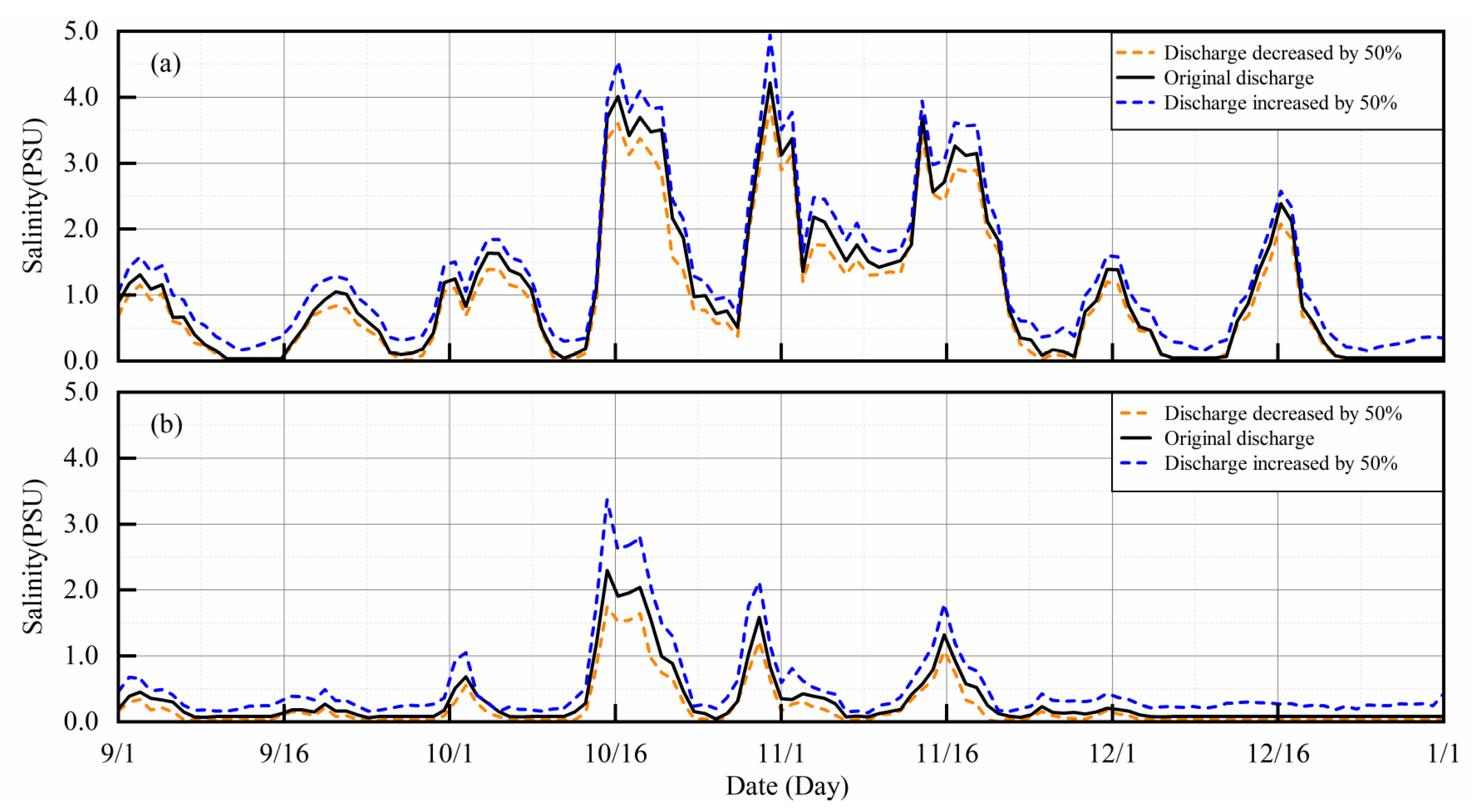
4.4. Further Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslami, S.; Hoekstra, P.; Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Trung, N.N.; Hoch, J.M.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Dung, D.D.; Tho, T.Q.; Voepel, H.E.; Woillez, M.-N.; et al. Projections of Salt Intrusion in a Mega-Delta under Climatic and Anthropogenic Stressors. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, D.; Ferrarin, C.; Maicu, F.; Manfè, G.; Lorenzetti, G.; Umgiesser, G.; Zaggia, L.; Levinson, A.V. Saltwater Intrusion in a Mediterranean Delta Under a Changing Climate. J. Geophys. Res. 2021, 126, e2020JC016437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, H.; Yang, J.; Liang, J.; Ji, X. Assessing the Influence of Typhoons on Salt Intrusion in the Modaomen Estuary within the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudaryanto; Naily, W. Ratio of Major Ions in Groundwater to Determine Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Areas. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hetland, R.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Sun, N. Response of Salt Intrusion in a Tidal Estuary to Regional Climatic Forcing. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 074019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tu, X.; Chen, X.; Vijay, P.S.; Leonardo, A.; Lin, K.; Liu, Z.; Lai, R. A Framework for Water Supply Regulation in Coastal Areas by Avoiding Saltwater Withdrawal Considering Upstream Streamflow Distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, B.; Duan, K. Coupling Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network for Forecasting Estuarine Salinity. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Peng, S. Forecasting Salinity Time Series Using RF and ELM Approaches Coupled with Decomposition Techniques. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundara, N.C.; Asce, M.; Seneviratne, S.A.; Reyes, E.; Chung, F.I. Artificial Neural Network for Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta Flow–Salinity Relationship for CalSim 3.0. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zou, H.; Gong, W. Salt Intrusion Dynamics in a Well-Mixed Sub-Estuary Connected to a Partially to Well-Mixed Main Estuary. Ocean. Sci. 2024, 20, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Klingbeil, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Burchard, H. Salinity Mixing in a Tidal Multi-Branched Estuary with Huge and Variable Runoff. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-B.; Tak, Y.-J.; Cho, Y.-K.; Na, H. Fortnightly Variability of Horizontal Salinity Gradient Affects Exchange Flow in the Sumjin River Estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1077004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bang, D.P.; Phan, N.V.; Guillou, S.; Nguyen, K.D. A 3D Numerical Study on the Tidal Asymmetry, Residual Circulation and Saline Intrusion in the Gironde Estuary (France). Water 2023, 15, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Lu, P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Yu, X.; Lan, T.; Chen, X. Modeling Saltwater Intrusion Using an Integrated Bayesian Model Averaging Method in the Pearl River Delta. J. Hydroinformatics 2019, 21, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, R.; Chen, X.; Cong, P. Impact of Upstream Runoff and Tidal Level on the Chlorinity of an Estuary in a River Network: A Case Study of Modaomen Estuary in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydroinformatics 2019, 21, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Kong, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Lin, K.; Xu, C.; Lan, T.; Liu, Z.; He, Y. An Integrated Framework of Input Determination for Ensemble Forecasts of Monthly Estuarine Saltwater Intrusion. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zou, R.; Chen, X.; Ren, T.; Su, H.; Liu, Y. Simulate the Forecast Capacity of a Complicated Water Quality Model Using the Long Short-Term Memory Approach. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and a Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network for Surface Water Quality Prediction of the Xiaofu River, China. Water 2023, 15, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayneh, A.; Adamowski, J.; Khalil, B.; Ozga-Zielinski, B. Long-Term SPI Drought Forecasting in the Awash River Basin in Ethiopia Using Wavelet Neural Network and Wavelet Support Vector Regression Models. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Chen, L. A Nonlinear Hybrid Wind Speed Forecasting Model Using LSTM Network, Hysteretic ELM and Differential Evolution Algorithm. Energy Conv. Manag. 2018, 173, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasimehr, H.; Shabani, M.; Yousefi, M. An Optimized Model Using LSTM Network for Demand Forecasting. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 143, 106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, T. A Novel Hybrid Model for Water Quality Prediction Based on VMD and IGOA Optimized for LSTM. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; He, M.; Bai, Z.; Ding, Z.; Sandhu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Namadi, P.; Tom, B.; Hoang, R.; Anderson, J. Multi-Location Emulation of a Process-Based Salinity Model Using Machine Learning. Water 2022, 14, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Pham, N.H.; Pham, Q.B.; Pham, T.L.; Ngo, X.Q.; Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen, P.N.; Veettil, B.K. Performances of Different Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Saltwater Intrusion in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta Using Limited Input Data: A Study from Ham Luong River. Water Resour. 2022, 49, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.S. Prediction of Salinity of Nakdong River Estuary Using Deep Learning Algorithm (LSTM) for Time Series Analysis. J. Korean Soc. Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 34, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z. Air Quality Prediction Model Based on mRMR–RF Feature Selection and ISSA–LSTM. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, N.-S. Estuary Salinity Prediction Using a Coupled GA-SVM Model: A Case Study of the Min River Estuary, China. Water Supply 2017, 17, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Cao, L.; Lu, D.; Hu, Z.; Yue, Y. Application of Swarm Intelligence Optimization Algorithms in Image Processing: A Comprehensive Review of Analysis, Synthesis, and Optimization. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. Research and Application of a Novel Swarm Intelligence Optimization Technique: Sparrow Search Algorithm. Donghua Univ. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Jin, A.; Nie, W.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Research on SSA-LSTM-Based Slope Monitoring and Early Warning Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Cao, L.; Lu, D.; Hu, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Ding, H. Review and Empirical Analysis of Sparrow Search Algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10867–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.J.; Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. Input Determination for Neural Network Models in Water Resources Applications. Part 2. Case Study: Forecasting Salinity in a River. J. Hydrol. 2005, 301, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Wan, M.; Han, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, C. A Filter Feature Selection Method Based on the Maximal Information Coefficient and Gram-Schmidt Orthogonalization for Biomedical Data Mining. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Huang, S.; Zheng, R. Influence of Tide and Runoff on Saltwater Intrusion in the Qiantang River Estuary, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 691, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, C.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Storm Surge-Induced Salinity Augmentation in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Sustainbility 2024, 16, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongbloed, H.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Dijkstra, Y.M.; Donkers, P.B.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Influence of Wind on Subtidal Salt Intrusion and Stratification in Well-Mixed and Partially Stratified Estuaries. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 3139–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Sun, Z.L.; Pan, D. Neural Network Modeling of Salinity in Qiantang Estuary. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. Ed. 2011, 38, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.H.; Sun, Z.L.; Hu, S.X. Prediction of Salinity in Qiantang Estuary Based on Wavelet Neural Network Optimized by Particle Swarm Optimization. AMM 2013, 353–356, 2683–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, R. Salinity Time Series Prediction Based on LSTMs Neual Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT), Guilin, China, 26–28 April 2019; pp. 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Gao, L.; Pan, C.; Pang, Y. Detecting the Mechanisms of Longitudinal Salt Transport during Spring Tides in Qiantang Estuary. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2019, 16, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, P.; Thilagavathi, K. Data Reduction Techniques of Hyperspectral Images: A Comparative Study; IEEE: Chennai, India, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J. Control Problems of Grey Systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.J.; Lu, I.J.; Lewis, C. Grey Relation Performance Correlations among Economics, Energy Use and Carbon Dioxide Emission in Taiwan. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Xie, W.; Li, X. An Improved Henry Gas Solubility Optimization Algorithm Based on Lévy Flight and Brown Motion. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 12584–12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data | Station | Unit | Sampling Frequency | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water level | GP | m | hourly | 17,544 |
| Discharge | FCJ | m3/s | daily | 731 |
| Salinity | CQ/QB/GP | PSU | at least 2 times per day | 1759/1584/2103 |
| Wind | HZ | m/s | hourly | 17,544 |
| No. | Function Expression | Range | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 2 | [−10, 10] | 0 | |
| 3 | [−100, 100] | 0 | |
| 4 | [−30, 130] | 0 | |
| 5 | [−5.12, −5.12] | 0 |
| Function | Mean | Variance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA | ISSA | SSA | ISSA | |
| F1 | 1.15 × 10−34 | 1.04 × 10−75 | 3.64 × 10−34 | 3.14 × 10−75 |
| F2 | 9.12 × 10−22 | 1.20 × 10−37 | 3.20 × 10−21 | 3.52 × 10−37 |
| F3 | 2.19 × 10−21 | 7.36 × 10−50 | 3.20 × 10−21 | 2.32 × 10−49 |
| F4 | 3.15 × 10−14 | 8.91 × 10−23 | 9.56 × 10−14 | 2.82 × 10−22 |
| F5 | 5.15 × 10−06 | 4.64 × 10−10 | 1.12 × 10−05 | 7.45 × 10−10 |
| Type | Abbreviation | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Salinity related | St | Maximum daily salinity at the CQ and QB station (Target) |
| S0 | Maximum daily salinity at the GP station | |
| S1 | Maximum daily salinity of 1 day ago at the GP station | |
| S2 | Maximum daily salinity of 2 days ago before at the GP station | |
| Tidal range related | TR0 | Daily tidal rage at the GP station |
| TR1 | Daily tidal rage of 1 day ago at the GP station | |
| TR2 | Daily tidal rage of 2 days ago at the GP station | |
| Runoff related | Q0 | Daily runoff discharge |
| Q1 | Daily runoff discharge of 1 day ago | |
| Q2 | Daily runoff discharge of 2 days ago | |
| Wind related | WWE | West-East component of daily surface wind speed |
| WNS | North-South component of daily surface wind speed |
| Station | Impact Factors | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | S1 | S2 | TR0 | TR1 | TR2 | Q0 | Q1 | Q2 | WWE | WNS | |
| CQ | 0.863 | 0.864 | 0.865 | 0.826 | 0.825 | 0.825 | 0.743 | 0.741 | 0.739 | 0.530 | 0.455 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| GP | 0.841 | 0.841 | 0.842 | 0.812 | 0.812 | 0.811 | 0.766 | 0.763 | 0.761 | 0.536 | 0.457 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| Hyperparameters | Range | CQ Station | QB Station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSA-LSTM | ISSA-LSTM | SSA-LSTM | ISSA-LSTM | ||
| L1 | 1–100 | 51 | 21 | 67 | 52 |
| L2 | 1–100 | 47 | 4 | 35 | 9 |
| B | 16–64 | 52 | 29 | 39 | 27 |
| K | 10–100 | 92 | 62 | 49 | 96 |
| lr | 0.001–0.01 | 0.00549 | 0.00246 | 0.00502 | 0.00906 |
| Models | Evaluation Indexes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAPE | RMSE | NSE | |
| BP | 0.341 | 1.869 | 0.475 | 0.753 |
| GRU | 0.325 | 1.665 | 0.452 | 0.779 |
| LSTM | 0.346 | 1.444 | 0.480 | 0.768 |
| SSA-LSTM | 0.257 | 0.798 | 0.426 | 0.801 |
| ISSA-LSTM | 0.223 | 0.681 | 0.381 | 0.842 |
| Models | Evaluation Indexes | Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAPE | RMSE | NSE | |
| BP | 0.150 | 1.442 | 0.263 | 0.609 |
| GRU | 0.127 | 1.013 | 0.197 | 0.730 |
| LSTM | 0.102 | 0.770 | 0.210 | 0.704 |
| SSA-LSTM | 0.096 | 0.573 | 0.192 | 0.761 |
| ISSA-LSTM | 0.081 | 0.479 | 0.168 | 0.806 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, R.; Sun, Z.; Jiao, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, L. Salinity Prediction Based on Improved LSTM Model in the Qiantang Estuary, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081339
Zheng R, Sun Z, Jiao J, Ma Q, Zhao L. Salinity Prediction Based on Improved LSTM Model in the Qiantang Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(8):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081339
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Rong, Zhilin Sun, Jiange Jiao, Qianqian Ma, and Liqin Zhao. 2024. "Salinity Prediction Based on Improved LSTM Model in the Qiantang Estuary, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 8: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081339
APA StyleZheng, R., Sun, Z., Jiao, J., Ma, Q., & Zhao, L. (2024). Salinity Prediction Based on Improved LSTM Model in the Qiantang Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(8), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12081339






