Abstract
This study develops a YOLO (You Only Look Once)-based 3D perception algorithm for UVMS (Underwater Vehicle-Manipulator Systems) for precise object detection and localization, crucial for enhanced grasping tasks. The object detection algorithm, YOLOv5s-CS, integrates an enhanced YOLOv5s model with C3SE attention and SPPFCSPC feature fusion, optimized for precise detection and two-dimensional localization in underwater environments with sparse features. Distance measurement is further improved by refining the SGBM (Semi-Global Block Matching) algorithm with Census transform and subpixel interpolation. Ablation studies highlight the YOLOv5s-CS model’s enhanced performance, with a 3.5% increase in mAP and a 6.4% rise in F1 score over the base YOLOv5s, and a 2.1% mAP improvement with 15% faster execution than YOLOv8s. Implemented on a UVMS, the algorithm successfully conducted pool grasping experiments, proving its applicability for autonomous underwater robotics.
1. Introduction
In the maritime sector, the strategic shift towards automation, particularly emphasized in the context of harvesting high-value seafood, holds paramount significance. The deployment of Underwater Vehicle-Manipulator Systems (UVMS) in these contexts not only yields significant economic benefits but also substantially mitigates operational risks [1]. Central to the operational efficacy of UVMS in autonomous fishing is the advancement of underwater sensing technology. The optimization of perception performance and the broadening of its applicative spectrum stand as essential factors for the strategic realization and effectiveness of UVMS [2].
For UVMS to perform autonomous grasping, obtaining target orientation and distance for 3D detection is crucial, yet the adoption of autonomous detection in underwater robotics faces challenges: (1) Low contrast and texture differentiation in turbid underwater environments hinder accurate detection [3,4]; (2) Above-water distance sensors perform poorly underwater, thereby failing to provide essential distance information for grasping [5]; (3) The difficulty in achieving a balance between detection accuracy and real-time processing for computationally limited UVMS platforms. Therefore, the development of a 3D perception framework tailored for autonomous marine biota grasping tasks by UVMS represents a significant research imperative, aiming to overcome the aforementioned obstacles. This endeavor necessitates innovative approaches to enable small-target recognition within complex scenes featuring weak textures, adapt distance sensing technologies for underwater applications, and refine detection algorithms to achieve an optimal balance between precision and computational efficiency.
Three-dimensional perception of underwater targets is categorically divided into two sub-tasks: object detection and distance measurement [6]. Deep learning has significantly advanced object detection, with YOLOv5 standing out for its efficiency and speed, making it ideal for UVMS. Its architectural improvements ensure a balanced performance in accuracy and processing speed [7], proving effective in underwater scenarios and outperforming other algorithms in both speed and accuracy [8]. Recent studies have introduced modifications to enhance YOLOv5’s capabilities: Zhai et al. [9] refined the feature extraction network of YOLOv5 and incorporated an attention mechanism, significantly improving the model’s feature extraction capability in fish recognition scenarios; Yu et al. [10] proposed the TR-YOLOv5s model, which integrates a transformer module, demonstrating effective detection of targets in underwater sonar images; Xuan et al. [11] embedded an extensive feature extraction layer within the YOLOv5 architecture, enhancing the detection of small-scale targets in sea cucumber detection tasks, outperforming existing models; Moreover, Zhang et al. [12] employed the EfficientNetv2-S network as the backbone for the YOLOv5 algorithm, effectively recognizing benthic marine organisms while reducing the model’s parameter count. Despite theoretical accuracy gains, these improved algorithms still require real-world validation in robotic systems and lack the provision of essential distance data for effective UVMS autonomous grasping.
UVMS typically rely on two-dimensional image data for autonomous grasping perception [13,14], but the distance information is crucial for enhancing grasp success [15]. In comparison to costly acoustic sensors, stereo vision systems offer a more feasible solution for proximal underwater environmental sensing due to their flexibility and lower cost [16]. Zhou et al. [17] introduced a stereo vision-based underwater object measurement paradigm, demonstrating the precision of stereo measurement algorithms in the underwater environment. Kong et al. [18] treated the calibration of underwater stereo vision distance measurements as a multi-objective optimization problem, employing the NSGA-II algorithm for resolution. Jiang et al. [19] proposed an improved ORB stereo-matching algorithm with adaptive thresholding and non-maximum suppression, reducing feature point clustering and matching time. These methodologies lay a foundational framework for distance perception in UVMS grasping tasks. Nonetheless, when deploying these algorithms on actual robotic systems, further optimizations of speed and accuracy are imperative to achieve operational efficacy.
To the best of our knowledge, there exists a scarcity of work addressing the autonomous grasping of UVMS with 3D perception. This paper introduces a novel framework for UVMS grasping perception, leveraging YOLO-based object detection and stereo vision distance measurement algorithms. The principal contributions of this work are delineated as follows:
(1) We propose a YOLO-based perception algorithm for UVMS grasping, integrating object detection with stereo vision distance measurement to achieve target detection with 3D coordinate information;
(2) We introduce the YOLOv5s-CS object detection algorithm, an enhancement over the standard YOLOv5s algorithm, featuring improved attention and feature fusion modules. This advancement bolsters the detection capabilities for weakly textured targets within complex underwater environments;
(3) We optimized the SGBM (Semi-Global Block Matching) algorithm for stereo distance measurement by incorporating Census transform and subpixel fitting. The effectiveness of this enhanced 3D perception algorithm was validated through distance measurement experiments and real-world grasping tests.
2. Methodology
In the context of UVMS grasping scenarios [20], this study presents a novel target perception algorithm that synergizes advanced YOLO-based object detection with stereo distance measurement techniques, as shown in Figure 1. Utilizing the YOLOv5s-CS object detection network, this algorithm accurately determines the positions of targets within input images. Subsequently, it employs a stereo-matching algorithm to assess the distances to these targets, thereby deriving the 3D coordinates essential for UVMS grasping operations, as shown in Figure 2. This methodology enables precise and efficient target localization in complex underwater environments, facilitating the development of advanced autonomous grasping capabilities in UVMS platforms.
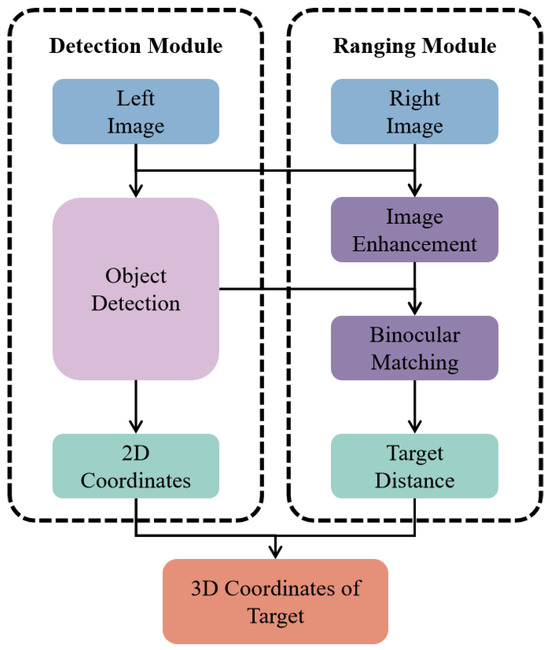
Figure 1.
Underwater 3D object perception framework.
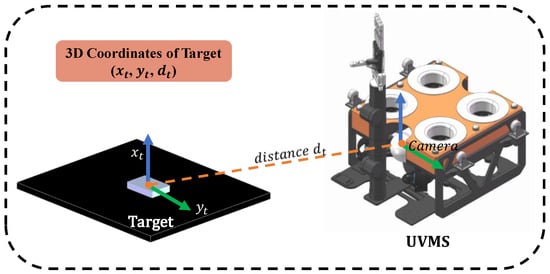
Figure 2.
Detection of target coordinates.
2.1. YOLOv5s-CS Object Detection Algorithm
Within the realm of UVMS for grasping applications, the accuracy and real-time performance of object detection algorithms are of paramount importance [21]. YOLOv5 stands out as a quintessential algorithm in this domain, characterized by its swift detection capabilities and elevated accuracy rates [22]. This research adopts the YOLOv5s model, a more streamlined version, as the foundational object detection framework. To further enhance its accuracy and efficiency, this study incorporates the Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) network [23] into the backbone network, thereby improving the robustness of target recognition in UVMS grasping scenarios and optimizing computational speed. Furthermore, this study integrates the Connected Spatial Pyramid Convolution (CSPC) approach to refine the feature fusion network within YOLOv5s, augmenting the model’s capability to represent target features more effectively. The network architecture of YOLOv5s-CS is detailed in Figure 3, illustrating the strategic enhancements made to facilitate superior performance in complex underwater object detection tasks.
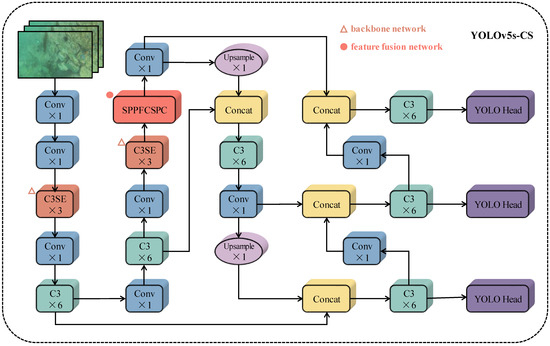
Figure 3.
Optimized network structure of YOLOv5s-CS.
In the YOLOv5s-CS model architecture, the incorporation of the Path Aggregation Network (PAN) [24] within the neck network structure facilitates a more effective fusion of high-level semantic information with low-level detail information. This enhancement is achieved by up-sampling the feature maps derived from the backbone at scales of 8x, 16x, and 32x to a consistent size prior to their concatenation. The up-sampling procedure is further refined through the inclusion of bottleneck modules and residual structures, facilitating the recognition of targets across multiple scales.
Within the head prediction network, the newly fused feature layers from the neck are segregated into three grid scales: 80 × 80, 40 × 40, and 20 × 20. The system employs anchor boxes of varying aspect ratios to detect objects within these grids. It adjusts the aspect ratio of the prior boxes based on positional information and generates accurate bounding boxes at the locations of image targets. This process decodes the positional category information within the boxes, allowing for precise detection of targets, as shown in Figure 4.
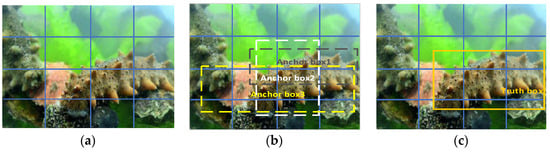
Figure 4.
Object detection process: (a) Grid size partitioning. (b) Anchor box adjustment. (c) Ground truth box detection.
The YOLOv5s-CS model features an optimized backbone network structure and feature fusion network, finely tuned to strike an enhanced balance between accuracy and real-time performance. Such design refinements bolster the model’s proficiency in processing and analyzing underwater imagery for object detection tasks. This ensures efficient operation in dynamic environments, maintaining high detection precision without sacrificing performance speed.
2.1.1. Optimization of Backbone Networks
In the domain of underwater object detection, especially for grasping tasks, distinguishing small targets from the background poses a significant challenge. This challenge arises from the significant variability in spatial features within underwater scenes, influenced by factors such as water conditions, equipment variations, and meteorological changes. Addressing this challenge necessitates the enhancement of the backbone network through the integration of attention mechanisms, with a specific emphasis on channel attention mechanisms to accommodate the aforementioned variability.
This study incorporates the SE channel attention mechanism module into the optimized residual network structure, referred to as the SE bottleneck, to enhance feature representation and focus. The process begins with the input feature map X, which undergoes convolution operations to generate a new feature map U. This feature map comprises C two-dimensional feature channels of dimensions H × W, represented as: where . The output of this convolution operation is formulated as:
where vc denotes the cth parameter within the convolution kernel , , , .
Subsequently, a compression operation is applied through global average pooling to generate weights that signify the importance of each feature channel, expressed as:
where .
The model’s generalization capability is enhanced with two fully connected layers, incorporating a dimensionality reduction layer with a ratio r (reducing the output size to ), a ReLU activation function layer, and a dimensionality increasing layer (restoring the output size to ). Finally, a recalibration function applies these weights to the previous features channel-wise through scaling, with the SE block’s output defined as:
where and represents the multiplication of scalar sc with the feature map channel .
The SE bottleneck is synergistically integrated with the C3 module of the YOLOv5s network architecture to create the C3SE module (Figure 5). This optimized module enhances the detection network’s ability to emphasize critical information and suppress background noise, thereby increasing the confidence in target detection. Additionally, the compression process reduces dependency on channel-specific features, which in turn improves the model’s computational speed, making it a robust solution for real-time underwater object detection tasks.
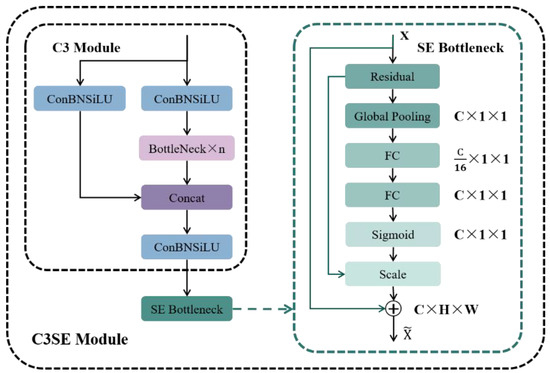
Figure 5.
Integration of the C3SE module with SE bottleneck. (The C3SE module integrates the SE bottleneck into the C3 module by introducing a squeeze-and-excitation mechanism. This mechanism improves the network’s ability to model channel interdependencies and enhances the discriminative power of the network. The diagram shows how the C3 module (consisting of ConBNSiLU, Bottleneck n, Concat, and ConBNSiLU) is extended with an SE bottleneck to form the C3SE module. This integration allows for better feature recalibration and more robust feature representations in the YOLOv5s network architecture).
2.1.2. Optimization of Feature Fusion Networks
The foundational YOLOv5s object detection model employs the Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) method for feature fusion. The SPP module uses 5 × 5, 9 × 9, and 13 × 13 convolution kernels, which concatenate the output in the depth direction after the convolution operation is completed. However, due to its simple structure, its feature expression ability is limited, and there is some optimization space for the size of the three convolution kernels. In this work, we enhance the SPP structure to develop an improved feature fusion network named SPPFCSPC, as depicted in Figure 6.
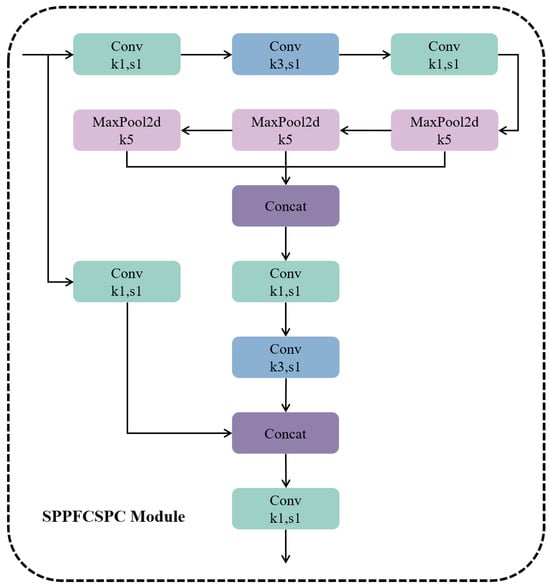
Figure 6.
SPPFCSPC module architecture. (k1, s1, etc., represent the relevant parameters of the convolution; for example, k1 indicates that the size of the convolution kernel is 1, and s1 indicates that the step size of the convolution kernel is 1.).
In this optimized architecture, the SPPF module operates in a sequential manner, employing a single CBS convolution followed by pooling operations through three 5 × 5 pooling layers. This modification optimizes the algorithm’s speed while ensuring consistency in the results. The CSPC module further processes the feature map output from the SPPF module through convolution operations, incorporating multiple convolutional kernels to capture information across different scales of targets and scenes. This enhancement significantly improves the network’s feature representation capability, thereby facilitating a more robust and efficient detection mechanism in object detection tasks.
The SPPFCSPC module is designed to process an input image of dimensions H × W × 3 by initially segmenting it into blocks, wherein each 3 × 3 group of adjacent pixels is partitioned into a separate branch module. This is followed by a flattening operation along the channel direction. Subsequently, the image undergoes transformation through a convolution module, altering its dimensions from H × W × 3 to H/4 × W/4 × 48. This transformation is achieved via a MaxPool2d layer that applies a linear transformation to each pixel’s channels, changing the output image dimensions to H/4 × W/4 × C. A concatenation operation then amalgamates these features to produce the output feature map for the subsequent task network.
Within this architecture, the SPPF module utilizes a serial arrangement, employing a single CBS convolution followed by three 5 × 5 pooling layers for pooling operations. This approach, utilizing three 5 × 5 pools, incurs a significantly lower computational cost than the original SPP structure’s 5 × 5, 9 × 9, and 13 × 13 convolution kernels. Moreover, serially executing two 5 × 5 maximum pooling operations is equivalent to one 9 × 9 maximum pooling operation, thereby optimizing algorithm speed while ensuring consistency in outcomes. The CSPC module continues to process the feature map output from the SPPF module through convolution operations, incorporating multiple convolution kernels of varying scales. This allows for the capture of target and scene information across different scales, further enhancing the module’s capability for feature representation.
SPPFCSPC draws on the characteristics of SPPF, which reduces the complexity of pooling operations and speeds up computation to achieve more efficient computation compared to SPP; On the basis of SPPF, the combination of the CSPC module further enhances the feature fusion ability of the network and improves the gradient flow and feature expression ability of the network, which makes SPPFCSPC have a certain increase in FLOPs compared to SPPF (from 16.5 to 21.7). However, the addition of the CSPC module makes SPPFCSPC have higher accuracy in underwater small target scene recognition and good real-time performance.
2.2. Stereo Distance Measurement of Underwater Targets
2.2.1. Underwater Image Enhancement
During stereo distance measurements, the attenuation and scattering of light in underwater environments necessitate image enhancement to meet the requirements of stereo-matching algorithms. However, the classical Retinex method has limitations, including a risk of over-enhancement and the need for manual parameter tuning, which can lead to inconsistent outcomes. This study optimizes the Retinex method within a Bayesian inference framework, aiming to maximize posterior distribution for consistent image enhancement. The enhanced image obtained is expressed mathematically as:
where R(x, y) denotes the reflectance component, bounded within [0, 1], and I(x, y) signifies the incident light image component, with values ranging from [0, 255]. These components jointly determine the image L(x, y). To solve the maximum a posteriori problem, it is reformulated as a minimum energy problem, expressed as:
Here, E represents the energy function, and denote the and norms, respectively, is the gradient operator, represents the Laplace operator, and , , , and are the regularization term weight coefficients. The condition ensures that remains within the [0, 1] range. Introducing two auxiliary variables and , along with two deviation variables and , and initializing , , , the iteration expression at step k is given by:
where , , and denote the horizontal and vertical first-order differential operators, respectively. The solution for using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is derived as:
where , , , . denotes the FFT operator and and represent the conjugate transpose and inverse of the FFT operator, respectively. The and variables are updated using the method of alternating direction multipliers, as follows:
The incident light component is similarly derived using FFT:
Given the efficiency of FFT and shrink operations, the estimation of incident light component I and reflectance component can be effectively achieved within a few iterations. The iterative process of the algorithm is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Iterative process of underwater image enhancement algorithm.
The enhanced underwater image is converted from HSV to RGB space, showing improved feature details and a more uniform histogram compared to the original, as illustrated in Figure 7. This improvement in image quality enhances the feature point-matching performance of stereo distance measurement algorithms.

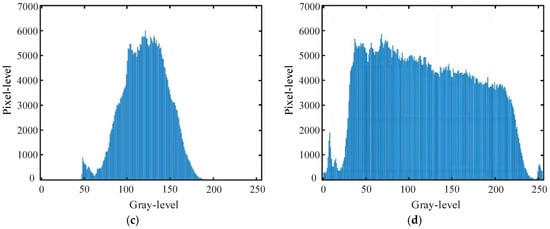
Figure 7.
Underwater image enhancement effect. (a) Original image; (b) enhanced image; (c) histogram; (d) and histogram.
2.2.2. Optimization of Stereo Vision-Matching Algorithms
Upon identifying the two-dimensional position of targets in the output image from the object detection network, acquiring accurate distance information becomes imperative for the precise execution of grasping tasks by UVMS. The efficacy of stereo distance measurement algorithms, pivotal in matching objects across left and right camera images, is crucial, as it directly impacts the 3D perception capabilities of UVMS. This study adapts the SGBM algorithm, renowned for its applicability in scenarios with weak textures, for stereo image-matching. The algorithm is further refined with the integration of Census transform and subpixel interpolation methods, enhancing the SGBM framework’s accuracy and processing speed, as illustrated in Figure 8. These modifications aim to refine the algorithm’s accuracy and speed, thus bolstering the 3D sensing proficiency of UVMS in complex underwater environments.
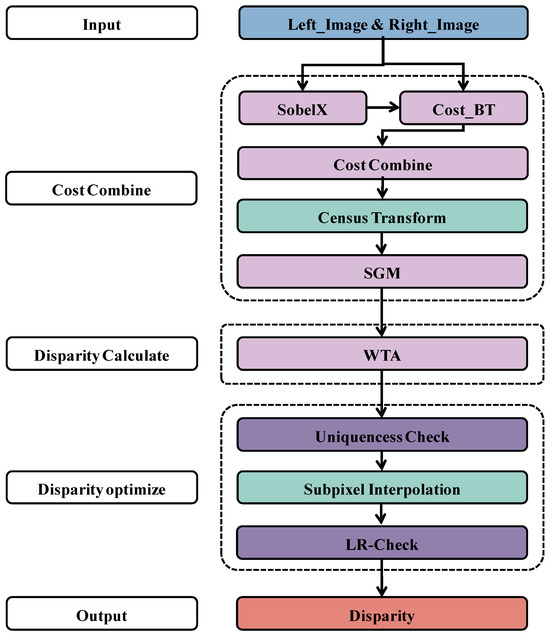
Figure 8.
Optimized framework of the SGBM.
Initially, image processing is conducted using the Sobel operator to incorporate spatial locality information for each pixel, denoted as:
resulting in a new image, denoted as:
where represents the pixel value of the new image, denotes the pixel value of the original image, and is a constant parameter. We utilize the Birchfield-Tomasi (BT) metric to compute the cost mapping for each pixel when matching left and right camera images, articulated as follows:
where denotes the range of within , with representing the subpixel coordinates, represents the grayscale intensity, and indicates the grayscale gradient at that position. The BT method exploits subpixel grayscale information, facilitating precise localization of depth discontinuities. Our methodology incorporates the Census transform at the initial stage of cost computation, iterating over pixel points to compute the Hamming distance:
where represents the Hamming distance between two corresponding windows in the left and right images, and denote the bit strings obtained through the Census transform of the two images, respectively, and signifies the number of pixels within the window, thereby representing the similarity between corresponding points in the left and right images. This iterative process ascertains the matching cost for the entire image, culminating in the computation of the total cost . Cost aggregation is performed through a dynamic programming approach, employing the global energy optimization strategy outlined in the Semi-Global Matching (SGM) algorithm [25], as follows:
where denotes the energy function for the disparity map and represents the sum of matching costs computed across the global disparity map, while and are penalty coefficients for different disparity interpolations, aimed at smoothing the resultant disparity map.
Subsequent to cost aggregation, the computation of disparity is conducted, with the ultimate disparity being ascertained via the Winner Takes All (WTA) algorithm. This paper utilizes a subpixel fitting approach for the post-processing of the disparity map. By interpolating a quadratic curve through the three points with the lowest matching costs, optimal pixel precision for the target point is achieved. The disparity corresponding to the extremum of this curve represents the new subpixel disparity (Figure 9) value for the target point. This method enhances the accuracy of the disparity estimation, facilitating a more precise 3D perception capability for underwater robotic operations.
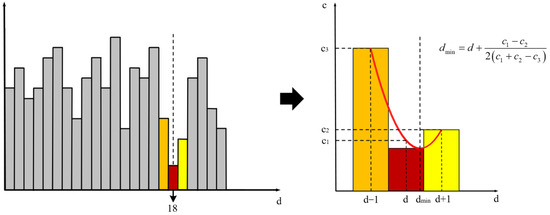
Figure 9.
Subpixel fitting approach.
3. Experiments and Result Analysis
3.1. Ablation Experiments
To evaluate the effectiveness of the attention and feature fusion module optimizations within the YOLOv5s-CS model, this paper conducted ablation experiments to demonstrate the enhancements in the performance metrics of the improved object detection model. To ensure the fairness of the experiments, identical initial settings for training were adopted. The experimental training environment and the hyperparameters are listed in Table 2. This methodological approach enables a rigorous assessment of the model’s improvements, attributing specific performance gains to the integrated attention mechanisms and feature fusion strategies.

Table 2.
Training environment and hyperparameter settings.
The dataset employed in this study is sourced from the China Underwater Robot Professional Contest (CUROC) and supplemented by additional open-source resources, totaling 3654 images. The dataset was partitioned into training, validation, and testing sets with an 8:1:1 distribution ratio. Image training incorporated the Mosaic data augmentation technique, which entails the random selection of four images from the dataset for subsequent rotation, scaling, and cropping, thereby creating a singular, augmented image [26]. This methodology not only enriches the dataset but also simulates a variety of underwater environmental conditions, thereby improving the robustness and generalizability of the proposed object detection model.
In the process of model training, it is customary to assess a model’s performance based on the loss observed in the training and validation datasets [27]. This paper conducts a comparative analysis of the training performance of the baseline YOLOv5s model, the YOLOv5s-C model with an individually enhanced attention module, the YOLOv5s-S model with an individually enhanced feature fusion module, and the comprehensive YOLOv5s-CS model developed in this study. As depicted in Figure 10, throughout 50 epochs of training, all models demonstrated satisfactory levels of fit without evident signs of overfitting or underfitting. Notably, the YOLOv5s-CS model achieved superior convergence and exhibited a more stable range of loss fluctuation compared to the other models, displaying enhanced detection performance and reduced loss values across both training and validation datasets.
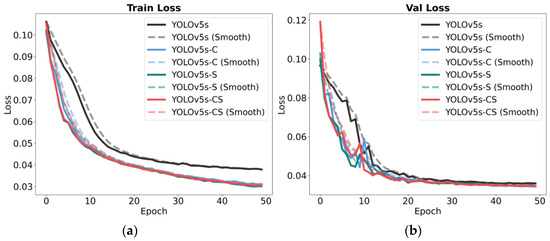
Figure 10.
Train and validation loss curves for various models. (a) Train loss. (b) Val loss.
This study validates the enhanced performance of the YOLOv5s-CS model using key metrics: accuracy, recall, and mean Average Precision (mAP), facilitating a thorough assessment of the YOLOv5s, YOLOv5s-C, YOLOv5s-S, and YOLOv5s-CS models. As depicted in Figure 11, the evaluation metrics for the algorithms show a rapid improvement within the initial 30 epochs, stabilizing gradually by the 50th epoch. The results reveal that the targeted optimizations of the attention and feature fusion modules, and their integrative enhancement within the YOLOv5s-CS framework, outperform the original YOLOv5s model’s capabilities. Due to the structural optimizations implemented, the enhanced models demonstrate more rapid improvements in performance metrics during the initial epochs compared to the YOLOv5s model. Notably, the YOLOv5s-CS model outperforms the YOLOv5s-C in training efficiency and exceeds the YOLOv5s-S in accuracy upon model convergence, affirming the efficacy of the SPPFCSPC module in boosting processing speed and the C3SE module in augmenting recognition precision.
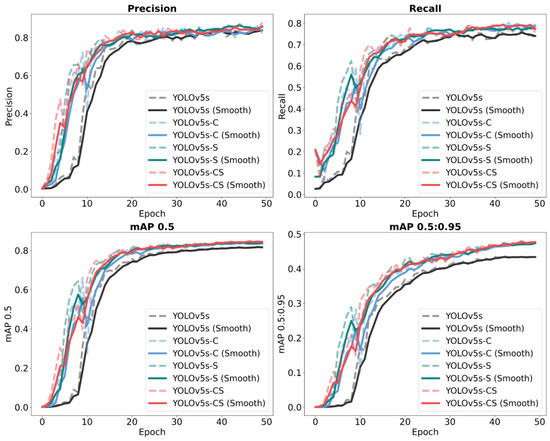
Figure 11.
Performance metrics curves for various models.
The proposed YOLOv5s-CS model exhibits significant advantages across various metrics, as illustrated in Figure 12. Specifically, compared to the baseline YOLOv5s model, the YOLOv5s-CS algorithm achieves a 3.8% increase in mAP@0.5 to 85%, a 10.1% rise in mAP@0.95 to 48.1%, and a 3.9% enhancement in the F1 score to 0.836. These comprehensive metrics indicate the effective optimization of the attention mechanism and feature fusion modules, rendering the YOLOv5s-CS model effective in scenarios involving small targets (Figure 13) and complex background conditions (Figure 14).
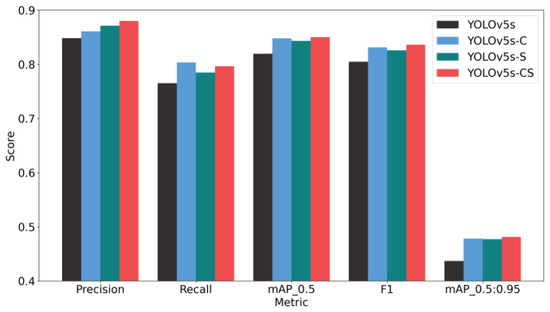
Figure 12.
Performance comparison of different models.

Figure 13.
Detection performance on small-object experiments.

Figure 14.
Detection performance in complex background experiments.
To substantiate the equilibrium between the lightweight architecture and precision performance of the YOLOv5s-CS model, this research undertook comparative analyses with four leading object detection algorithms: YOLOv6, YOLOv7, YOLOv8, and the newly introduced YOLOv9. As delineated in Table 3, after training for 50 epochs, the YOLOv5s-CS model outperforms the YOLOv6s, YOLOv7, and YOLOv9c models in terms of detection accuracy, whilst concurrently achieving a reduction in parameter count. For instance, compared to the YOLOv7 model, which has the highest accuracy among the compared models but a larger parameter count, the YOLOv5s-CS model increased the Frames Per Second (FPS) by 70% while reducing the parameter count by 63.2% and maintaining comparable accuracy. Relative to the YOLOv8s, a model of similar parameter scale but designed for lightweight applications, the YOLOv5s-CS model exhibited a 2.1% improvement in mAP and a 15% increase in FPS. These results corroborate the efficacy of the YOLOv5s-CS improvements, making it exceptionally suitable for applications in UVMS grasping where computational resources are limited and high precision and real-time performance are essential.

Table 3.
Comparative experiments with mainstream algorithms.
3.2. Stereo Distance Measurement Experiment
To evaluate the efficacy of the underwater target distance measurement algorithm developed in this study, based on binocular stereo vision, a streamlined measurement platform was established, as depicted in Figure 15. A calibration board was selected as the planar target object to conduct distance measurements utilizing the binocular stereo vision algorithm within a reasonable range of the grasping perception scenario. The results, illustrated in Figure 16 and Table 4, indicate that the designed underwater distance measurement algorithm exhibits high accuracy within the range of 500 mm to 1000 mm. It was observed that the measurement error increases slightly as the distance between the target object and the camera extends. Given the limited target distances typically involved in underwater UVMS grasping operations, the algorithm is expected to deliver optimal measurement outcomes within the operational scope, demonstrating its applicability and reliability for underwater robotic applications.
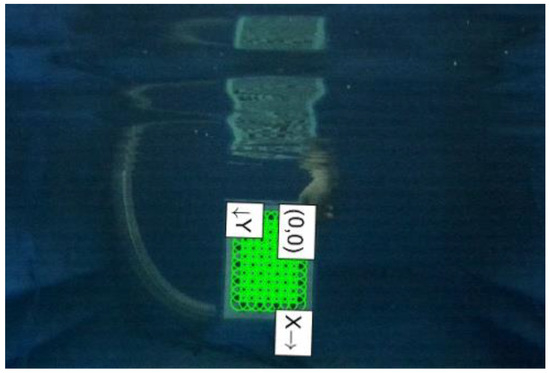
Figure 15.
Underwater binocular distance measurement experiment.
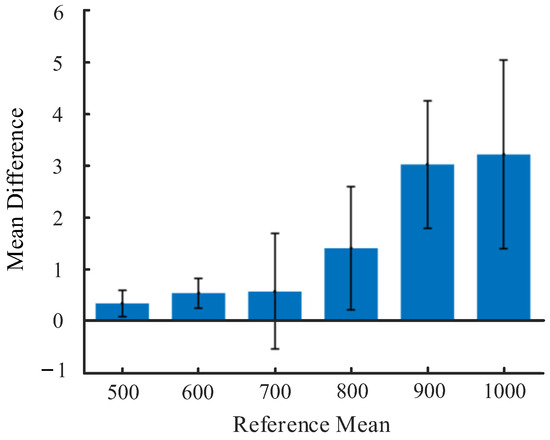
Figure 16.
Mean difference and standard deviation of distance measurement.

Table 4.
Experimental results of stereo distance measurement.
3.3. Real-World UVMS Grasping Experiment
This research is centered around grasping tasks within shallow underwater settings, conducting experiments by simulating sea cucumber grasping activities in a laboratory pool, as depicted in Figure 17.
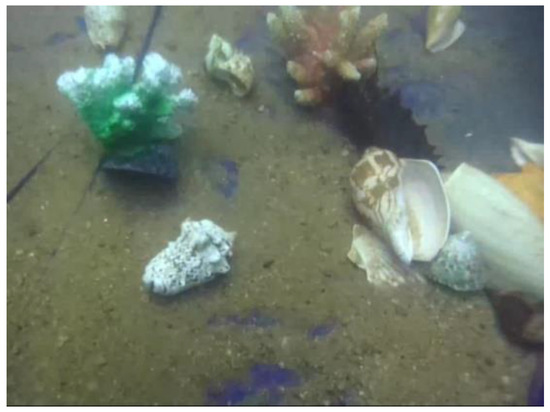

Figure 17.
Experimental environment for UVMS grasping.
The proposed 3D perception algorithm for UVMS grasping was deployed on our laboratory-developed UVMS (Figure 18) for experimental validation. This algorithm employs the YOLOv5-CS model to determine the two-dimensional coordinates of the target (sea cucumber), while the improved SGBM algorithm is utilized to match the target area and output distance information. The integration of these data yields the 3D coordinates and orientation of the sea cucumber’s center point. Subsequently, the UVMS, guided by control algorithms that process the target’s 3D information, navigates towards the predetermined location to execute the grasping operation, as demonstrated in Figure 19.
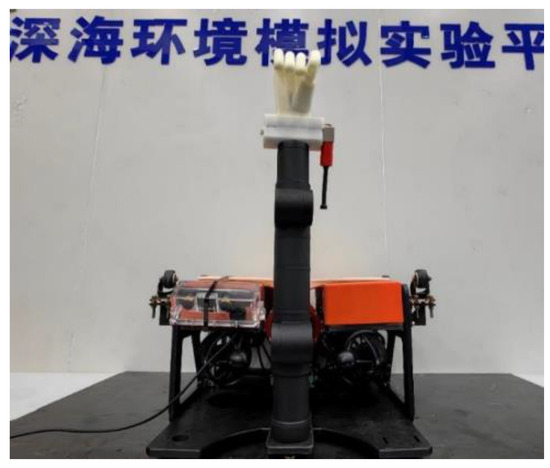
Figure 18.
The UVMS.

Figure 19.
UVMS grasping process. (a) Third-person perspective. (b) First-person perspective.
In this study, eight consecutive grasping trials were conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed UVMS grasping visual perception framework. Table 5 details the 3D coordinates output by the framework alongside the actual grasping outcomes, while Figure 20 depicts the variation in distance between the robotic arm and the target object during the grasping process. The experiments yielded a sea cucumber grasping success rate of 75%, which indirectly validates the effectiveness of the designed visual system.

Table 5.
UVMS grasping experimental results.
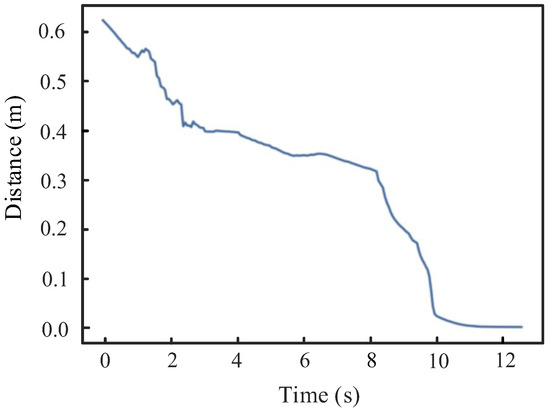
Figure 20.
Variation curve of distance to target object.
Analysis of the instances where grasping was unsuccessful highlighted two primary causes:
(1) The operational range of the underwater robotic arm is limited, with several joint constraints, making some computationally identified target points inaccessible, resulting in ineffective attempts;
(2) Occasional slippage or displacement of sea cucumbers during the grasping attempt led to failures in securing the target, despite the target detection outputting substantially accurate location points on the individual sea cucumbers.
The experimental outcomes demonstrate that the underwater visual system designed in this work meets the requirements for real-time operation and feasibility. It is capable of being applied to UVMS, specifically fulfilling the demands for sea cucumber grasping tasks based on visual cues, thereby accomplishing visually guided sea cucumber grasping operations.
4. Conclusions
This paper introduces a deep learning perception algorithm for UVMS grasping, combining object detection with binocular stereo vision for underwater 3D perception. The developed YOLOv5s-CS algorithm, featuring an optimized attention mechanism and feature fusion, along with an improved SGBM for distance measurement, is tailored for complex underwater environments. Ablation experiments show that the improved measures proposed in this paper can improve the network performance, enhance the feature extraction ability and reduce the calculation time, improve the false detection and missed detection, and meet the requirements of accuracy and real-time. The algorithm’s effectiveness and feasibility for UVMS applications are validated through distance measurement experiments and real-world grasping tests.
Future work will extend towards a comprehensive visual grasping framework that includes the UVMS’s position and orientation for improved reliability and will seek to enrich the training dataset to cover a wider range of grasping scenarios, thereby enhancing system adaptability and precision.
Author Contributions
Y.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing—Review and Editing. F.Z.: Software, Validation, Data Curation. Y.L.: Software, Investigation, Resources. S.Z.: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing—Original Draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52375032), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFC2800202), and the Ningbo Science and Technology Innovation 2025 Major Special Project (2021Z079).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jin, W.; Tian, Y. Toward in situ zooplankton detection with a densely connected YOLOV3 model. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 114, 102783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Bian, X.; Cai, F.; Li, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, C. A review on visual servoing for underwater vehicle manipulation systems automatic control and case study. Ocean Eng. 2022, 260, 112065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, G. (Ed.) Modelling of Underwater Robots. In Underwater Robots; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Mei, H.; He, Q.; Liotta, A. A systematic review and analysis of deep learning-based underwater object detection. Neurocomputing 2023, 527, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, B.; Yuan, H.; Tan, Y. Ranging precision for underwater laser proximity pulsed laser target detection. Opt. Commun. 2019, 431, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, D.Q.; Sadjoli, N.; Azam, A.B.; Elhadidi, B.; Cai, Y.; Seet, G. Object perception in underwater environments: A survey on sensors and sensing methodologies. Ocean Eng. 2023, 267, 113202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Tang, F.; Li, S. Underwater Target Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv5. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Fang, S.; Li, N.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Tang, P.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Martínez Ortega, J.-F. Performance Comparison of Sea Cucumber Detection by the Yolov5 and DETR Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Wei, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, M. Multi-target tracking algorithm in aquaculture monitoring based on deep learning. Ocean Eng. 2023, 289, 116005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gong, Q.; Huang, C.; Zheng, G.; Ma, J. Real-Time Underwater Maritime Object Detection in Side-Scan Sonar Images Based on Transformer-YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, K.; Deng, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, J. SO-YOLOv5: Small object recognition algorithm for sea cucumber in complex seabed environment. Fish. Res. 2023, 264, 106710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, J.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Xing, B.; Xu, J. Marine zoobenthos recognition algorithm based on improved lightweight YOLOv5. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huo, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, J. Underwater object tracker: UOS Track for marine organism grasping of underwater vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2023, 285, 115449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Wang, R.; Tan, M. Development and Control of an Underwater Vehicle–Manipulator System Propelled by Flexible Flippers for Grasping Marine Organisms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3898–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Duo, Y.; Chen, B.; Kong, S.; Shao, Z.; Gong, Z.; et al. An Underwater Robotic System with a Soft Continuum Manipulator for Autonomous Aquatic Grasping. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 29, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, Z.; Kong, S.; Yu, J. An Underwater Micro Cable-Driven Pan-Tilt Binocular Vision System with Spherical Refraction Calibration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.; Ye, Q.; Yu, D.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y. A binocular vision-based underwater object size measurement paradigm: Calibration-Detection-Measurement (C-D-M). Measurement 2023, 216, 112997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Fang, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J. A NSGA-II-Based Calibration Algorithm for Underwater Binocular Vision Measurement System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Qin, H.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X. Binocular Vision-Based Non-Singular Fast Terminal Control for the UVMS Small Target Grasp. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, Q.; Tan, M.; Zhou, C.; Yu, J. Development of an Underwater Manipulator and Its Free-Floating Autonomous Operation. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Ren, Y.; Tan, M. Grasping Marine Products with Hybrid-Driven Underwater Vehicle-Manipulator System. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ni, X.; Yu, P. Real-time ship detection system for wave glider based on YOLOv5s-lite-CBAM model. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 144, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Paisley, J. PanNet: A deep network architecture for pan-sharpening. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmueller, H. Stereo processing by Semiglobal Matching and Mutual Information. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, H.; Guo, X. Real-Time Vehicle Detection Based on Improved YOLO v5. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Kang, L.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, M.-H.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. Lightweight Deep Neural Network for Joint Learning of Underwater Object Detection and Color Conversion. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6129–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).