Variation in the Occurrence of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages in the Northeastern East China Sea from 2019 to 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
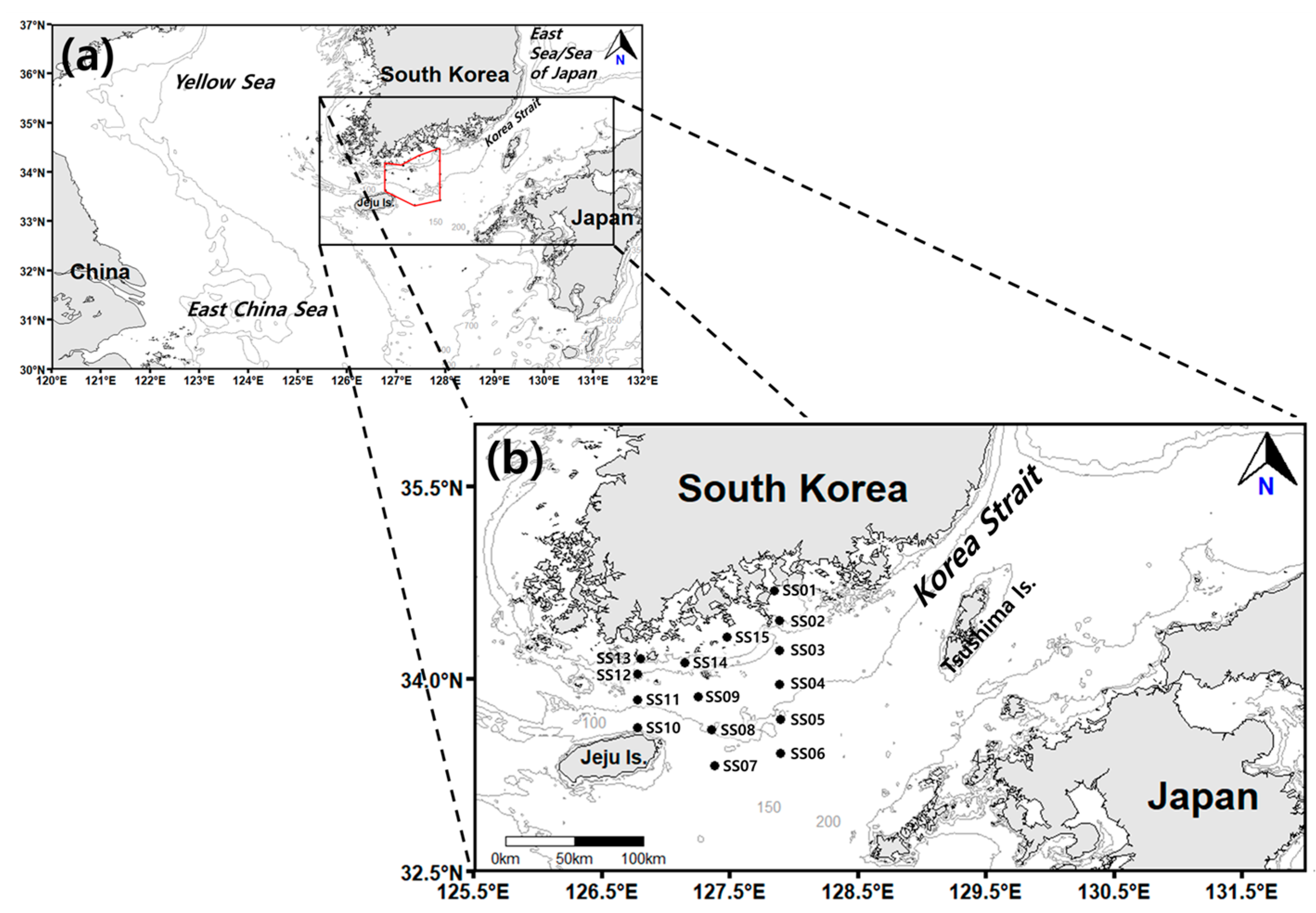
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Environmental Factors
2.2. Zooplankton Sample Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
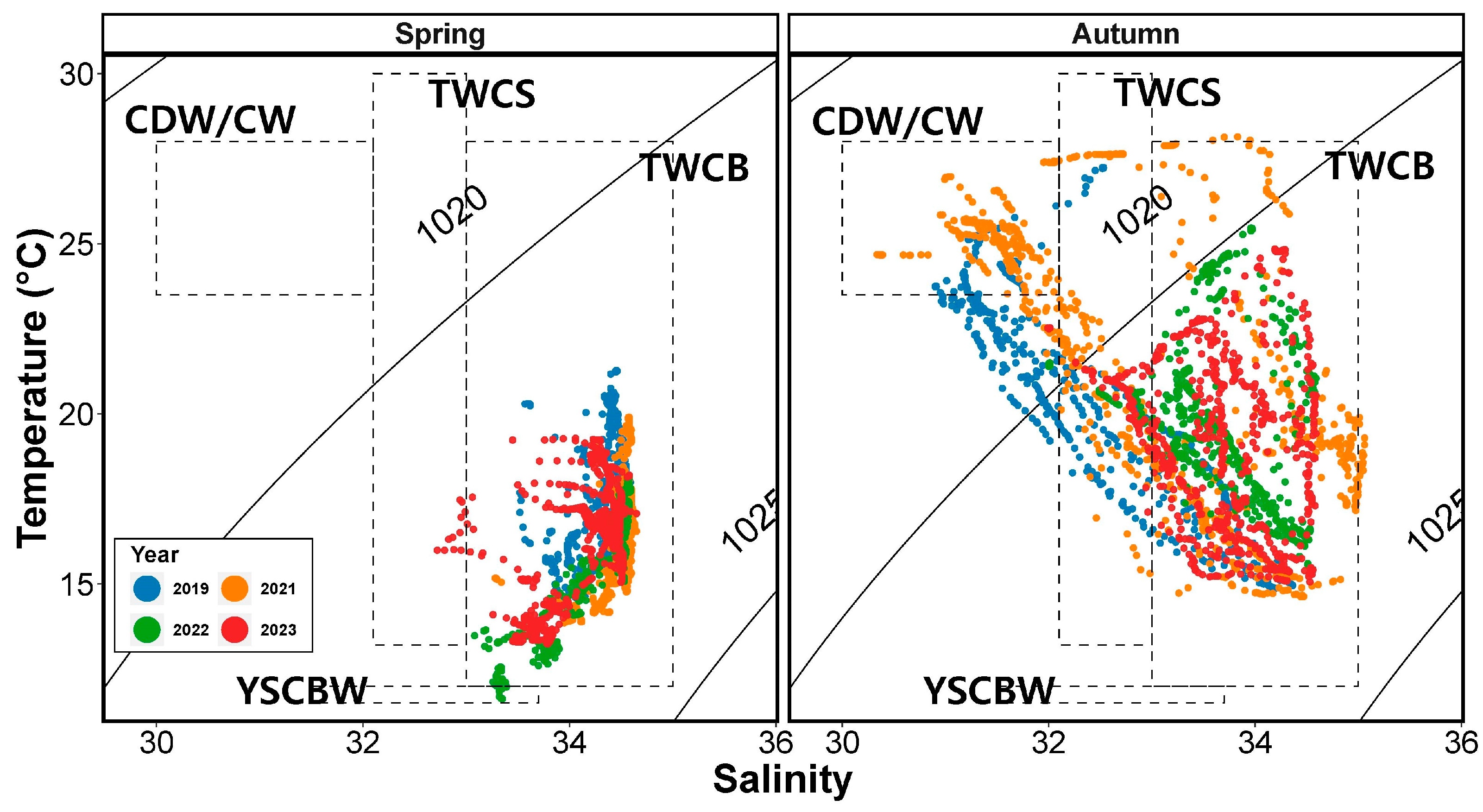
3.1. Seasonal Variation in the Environmental Factors
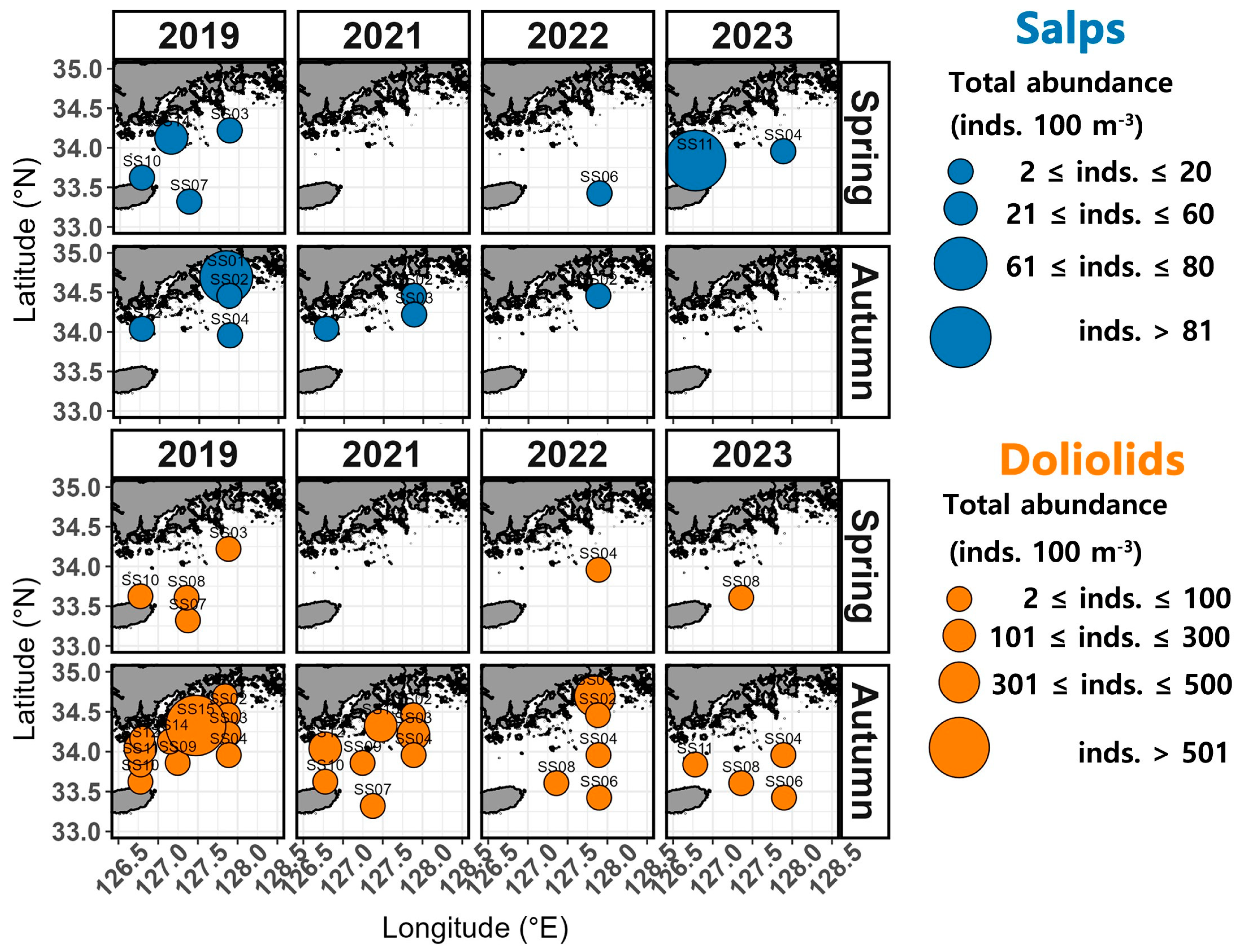
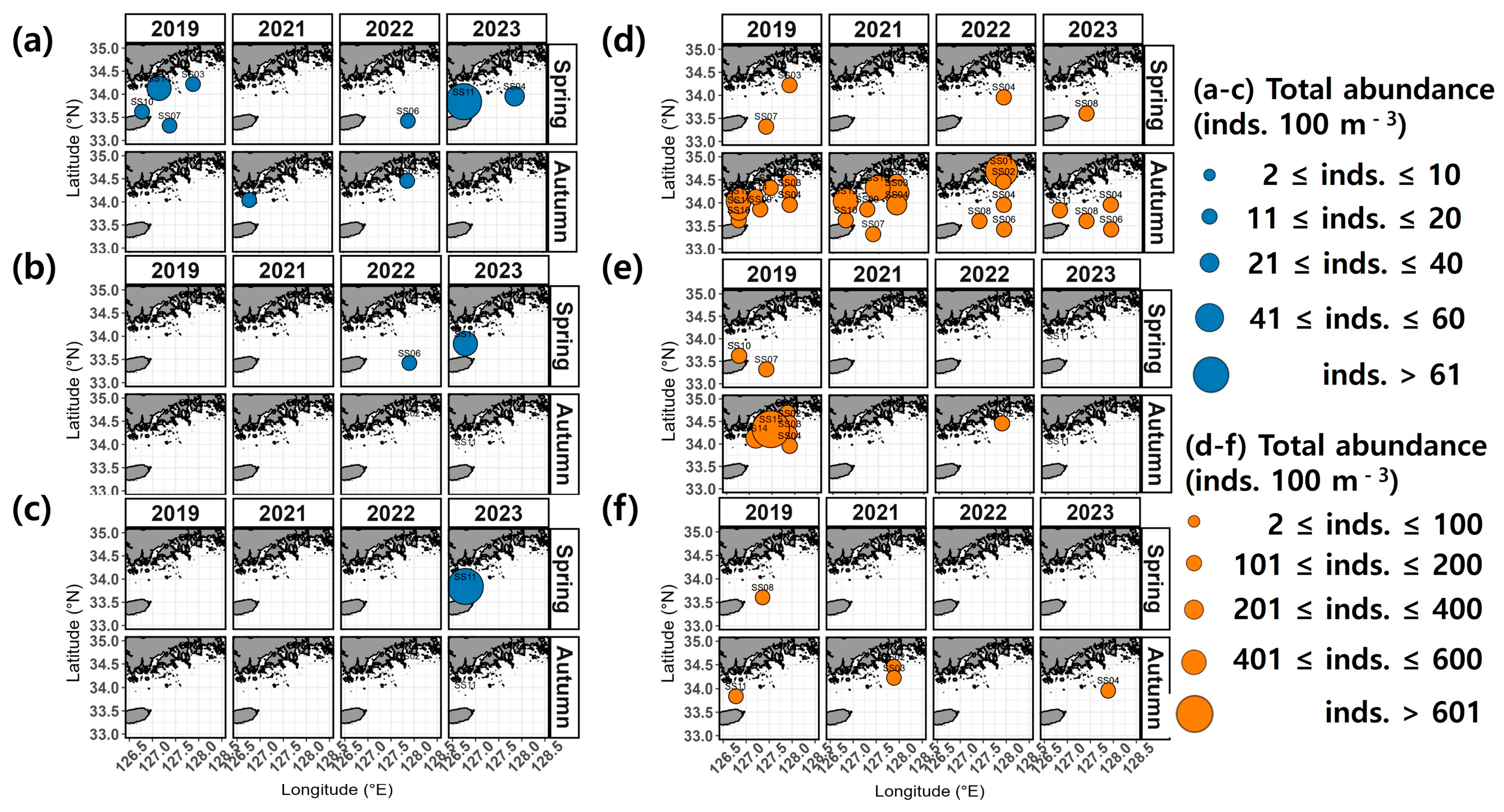
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages
3.3. Seasonal Variation in Salp and Doliolid Assemblages
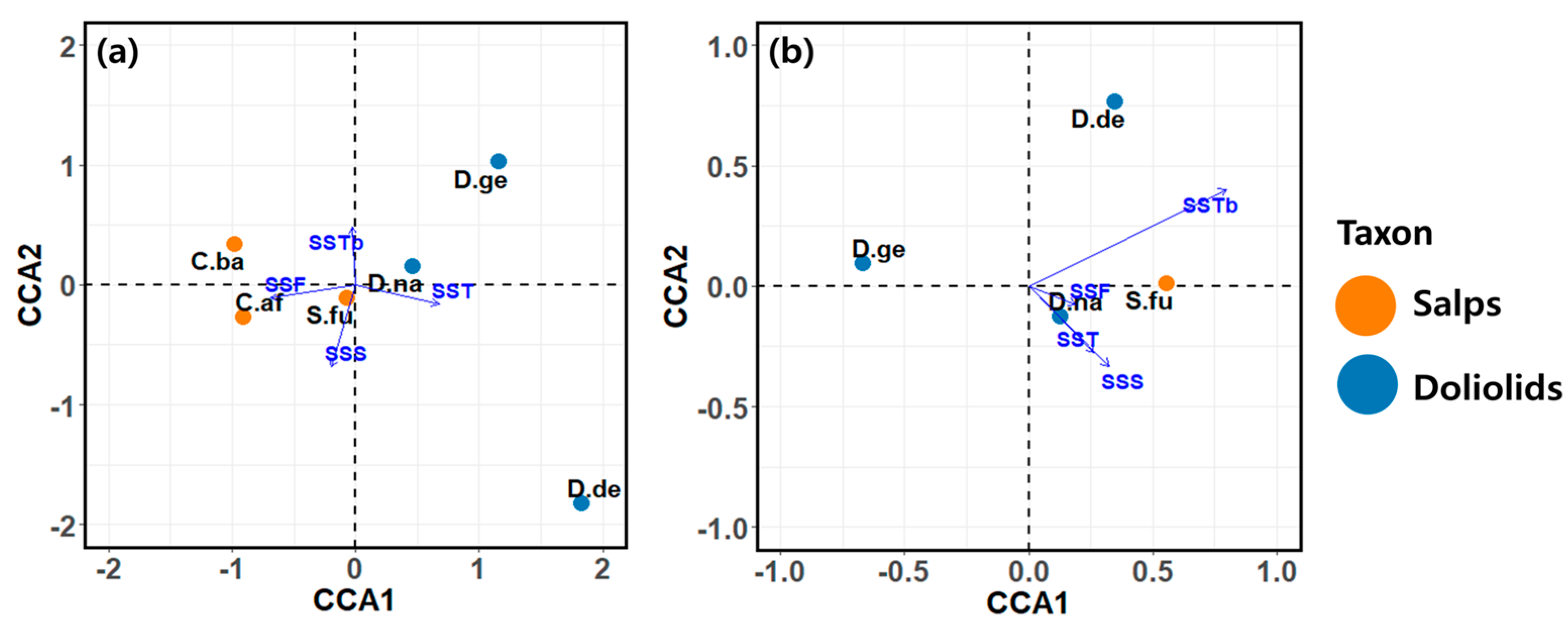
3.4. Environmental Envelopes for Salps and Doliolids
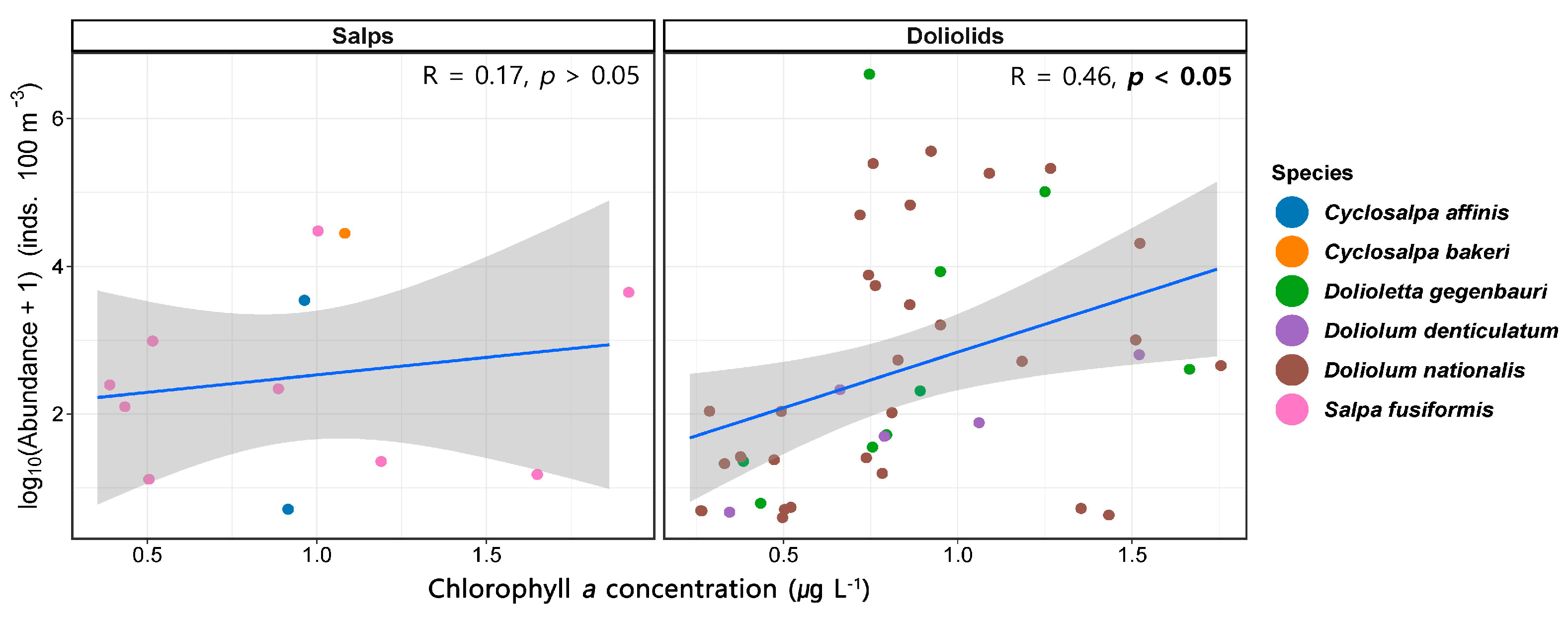
3.5. Relationship between Chlorophyll a Concentrations and the Abundance of Salps and Doliolids
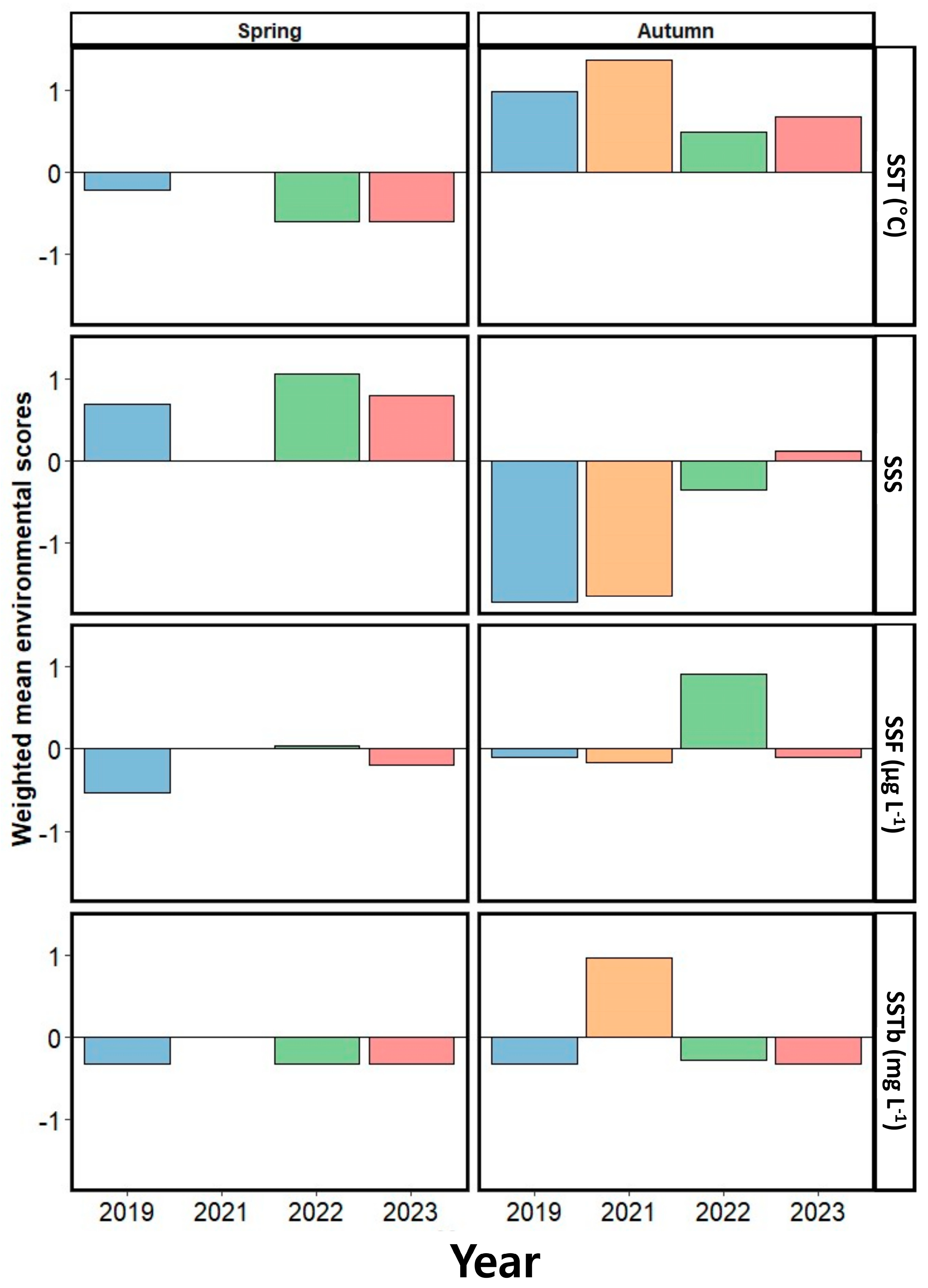
3.6. Factors Determining the Year-to-Year Variation in Dominant Species in Spring and Autumn
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bone, Q.; Braconnot, J.C.; Carré, C.; Ryan, K.P. On the Filter-Feeding of Doliolum (Tunicata: Thaliacea). J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 1997, 214, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereu, C.M.; Lavaniegos, B.E.; Goericke, R. Grazing Impact of Salp (Tunicata, Thaliacea) Assemblages in the Eastern Tropical North Pacific. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.H.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Lo, W.T. Influence of Monsoon-Driven Hydrographic Features on Thaliacean Distribution in Waters around Taiwan, Western North Pacific Ocean. Zool. Stud. 2013, 52, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, V.J.; Santora, J.A. Population Dynamics of Salpa thompsoni near the Antarctic Peninsula: Growth Rates and Interannual Variations in Reproductive Activity (1993–2009). Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 96, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschke, N.; Everett, J.D.; Richardson, A.J.; Suthers, I.M. Rethinking the Role of Salps in the Ocean. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, N.C.; Flintrop, C.M.; Konrad, C.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Swoboda, S.; Koch, F.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Brierley, A.S.; Bernasconi, M.; et al. Krill and Salp Faecal Pellets Contribute Equally to the Carbon Flux at the Antarctic Peninsula. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.K.; Stamieszkin, K.; Maas, A.E.; Durkin, C.A.; Passow, U.; Estapa, M.L.; Omand, M.M.; McDonnell, A.M.P.; Karp-Boss, L.; Galbraith, M.; et al. The Outsized Role of Salps in Carbon Export in the Subarctic Northeast Pacific Ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37, e2022GB007523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, A.I.; Batten, S.D.; Strasburger, W.W. Doliolid (Tunicata, Thaliacea) Blooms in the Southeastern Gulf of Alaska as a Result of the Recent Marine Heat Wave of 2014–2016. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 625486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, K.S.; Lo, W.T. Distribution of Thaliacea in SW Taiwan Coastal Water in 1997, with Special Reference to Doliolum denticulatum, Thalia democratica and T. orientalis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 292, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mianzan, H.; Pájaro, M.; Alvarez Colombo, G.; Madirolas, A. Feeding on Survival-Food: Gelatinous Plankton as a Source of Food for Anchovies. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Siegel, V.; Litvinov, F.; Loeb, V.; Watkins, J. Salp Distribution and Size Composition in the Atlantic Sector of the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part 2 Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüskow, F.; Galbraith, M.D.; Kwong, L.E.; Pakhomov, E.A. Biology and Distribution of Salps in the Subarctic Northeast Pacific. Mar. Biol. 2022, 169, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, C.K.; Décima, M.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; Selph, K.E.; Yingling, N.; Stukel, M.R. Prey Size Spectra and Predator to Prey Size Ratios of Southern Ocean Salps. Mar. Biol. 2023, 170, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Won, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.B. A New Record of Ihlea punctata and Redescription of Salpa fusiformis (Salpida: Salpidae) in Korean Waters. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 2010, 26, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, N.H.A.; Tadokoro, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Kakehi, S.; Suyama, S.; Takahashi, K. Distribution, Biomass, and Species Composition of Salps and Doliolids in the Oyashio–Kuroshio Transitional Region: Potential Impact of Massive Bloom on the Pelagic Food Web. J. Oceanogr. 2020, 76, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, N.H.A.; Motoki, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Fuji, T.; Taniuchi, Y.; Kakehi, S.; Kuroda, H.; Setou, T.; Takahashi, K. Basin-Scale Distribution of Salps and Doliolids in the Transition Region of the North Pacific Ocean in Summer: Drivers of Bloom Occurrence and Effect on the Pelagic Ecosystem. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 204, 102793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Choi, H.W.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.H. Distribution of a Pelagic Tunicate, Salpa fusiformis in Warm Surface Current of the Eastern Korean Waters and Its Impingement on Cooling Water Intakes of Uljin Nuclear Power Plant. J. Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch-Belmar, M.; Milisenda, G.; Basso, L.; Doyle, T.K.; Leone, A.; Piraino, S. Jellyfish Impacts on Marine Aquaculture and Fisheries. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.; Choi, B.-J.; Yoo, H.; Kim, B.; Bok, Y.; Chae, J. Unusual Mass Appearance of Salpa fusiformis (Thaliacea: Salpida) in Early Spring at a Nuclear Power Plant at Mid-Western Boundary of the East Sea. Ocean Sci. J. 2022, 57, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, K.A.; Haberlin, D.; Stantic, B.; Doyle, T.K. Mitigating and Managing the Impacts of Gelatinous Zooplankton on Finfish Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Jo, Y.J.; Go, W.; Kim, S.S.; Jeon, K.A.; Oh, H.J. Swarm of Salps (Tunicata: Thaliaca) and Its Impact on Marine Ecosystem in the South Sea of Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2000, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.K.; Kim, G.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, M.; Noh, J.H. Mass Occurrence of the Salp Salpa fusiformis during Spring 2017 in the Southern Waters of Korea and the Northern East China Sea. Ocean Polar Res. 2019, 41, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.B. The Movements of the Waters off the South Coast of Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 1976, 11, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, H.J. A Note on Water Masses and General Circulation in the Yellow Sea (Hwanghae). J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 1984, 19, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, H.B.; Jacobs, G.A.; Teague, W.J. Monthly Variations of Water Masses in the Yellow and East China Seas, November 6, 1998. J. Oceanogr. 1999, 55, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y. The Characteristics of Yellow Sea Bottom Cold Water in September, 2006. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Mar. Edu. 2011, 23, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Lim, Y.K. Variation in Phytoplankton Community Due to an Autumn Typhoon and Winter Water Turbulence in Southern Korean Coastal Waters. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2020, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.Y.; Kwon, K.Y.; Lee, W.C.; Kwak, J.H. Seasonal Variations in Primary Productivity and Biomass of Phytoplankton in Geoje-Hansan Bay on the Southern Coast of Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2019, 54, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Baek, S.H. Occurrence Characteristics of Harmful and Non-Harmful Algal Species Related to Coastal Environments in the Southern Sea of Korea. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.O.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, J.H. Phytoplankton Composition Associated with Physical and Chemical Variables during Summer in the Southern Sea of Korea: Implication of the Succession of the Two Toxic Dinoflagellates Cochlodinium (a.k.a. Margalefidinium) polykrikoides and Alexandrium affine. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2019, 516, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lee, D.H. Coastal Warming Heightens Direct Impacts of Seawater Temperature on Nutrients near Aquaculture Farms in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihara, M.; Murano, M. An Illustrated Guide to Marine Plankton in Japan; Tokai University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1997; p. 1574. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Apablaza, P.; Palma, S. First Record of Dolioletta gegenbauri (Uljanin, 1884) and Doliolum nationalis Borgert, 1893 for Chilean Waters (Tunicata, Doliolida). Investig. Mar. 2005, 33, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Won, J.-H.; Kim, C.-B. Report for Eight Species of Salpinae (Thaliacea: Salpida: Salpidae) from Korean Waters. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2017, 10, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, N.H.B.A.; Adam, N.A.B.; Kassim, Z. A Taxonomic Revision of the Genus Thalia Blumenbach, 1798; Weelia Yount, 1954; Brooksia Metcalf, 1918 (Salpida: Salpidae) from East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Zootaxa 2018, 4422, 451–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WoRMS Editorial Board WoRMS Editorial Board. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Won, J.H. Two New Records of Thaliacea (Chordata: Tunicata) in Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Diversity 2023, 39, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team, R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.; Cho, Y.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.; Xu, Z.; Chang, T. A Comprehensive Investigation of Coastal and Shelf Sediment Sources in the South Sea of Korea: A Marginal Sea of the Northwestern Pacific. Ocean Sci. J. 2023, 58, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Park, J.G.; Jeong, D.H.; Lim, D. Seasonal Changes in Water Masses and Phytoplankton Communities in the Western Part of South Coastal Waters, Korea. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 30, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.H. Characteristics on Spatial Distributions of Phytoplankton Communities in Relation to Water Masses in the Western South Sea, Korea in Early Autumn 2021. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2021, 39, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Pang, I.C.; Yoon, J.H. Response of the Changjiang Diluted Water around Jeju Island to External Forcings: A Modeling Study of 2002 and 2006. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; Dahms, H.U.; Lo, W.T.; Hwang, J.-S. Pelagic Tunicates in the China Seas. J. Nat. Hist. 2017, 51, 917–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Lin, M.; Zhang, J. Changes in Dominant Species of Thaliacea in the East China Sea. Acta Zool. Sin. 2006, 52, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.W.; Won, J.H.; Kim, C.B. Taxonomic Study of the Genus Thalia (Thaliacea: Salpida: Salpidae) from Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 2011, 27, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, K.; Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lian, S.; Liu, C. Distribution and Abundance of Thaliaceans in the Northwest Continental Shelf of South China Sea, with Response to Environmental Factors Driven by Monsoon. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; Chen, H.; Liu, G. Distribution and Abundance of Pelagic Tunicates in the North Yellow Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, N.A.; Ishak, N.H.A. Distribution and Diversity of Gelatinous Zooplankton in the Southern South China Sea. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 944, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daponte, M.C.; Capitanio, F.L.; Esnal, G.B. A Mechanism for Swarming in the Tunicate Salpa thompsoni (Foxton, 1961). Antarct. Sci. 2001, 13, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.M.; Paffenhöfer, G.A. Asexual Reproduction of the Doliolid, Dolioletta gegenbauri Uljanin (Tunicata, Thaliacea). J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibel, D.; Paffenhöfer, G.A. Predictability of Patches of Neritic Salps and Doliolids (Tunicata, Thaliacea). J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldis, J.R.; Davis, C.S.; James, M.R.; Ballara, S.L.; Booth, W.E.; Chang, F.H. Salp Grazing: Effects on Phytoplankton Abundance, Vertical Distribution and Taxonomic Composition in a Coastal Habitat. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 126, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G. Seasonal Variation in Abundance, Diel Vertical Migration and Body Size of Pelagic Tunicate Salpa fusiformis in the Southern Yellow Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wan, A.; Zhang, G.; Sun, S. Northward Expansion of a Warm-Water Doliolid Dolioletta gegenbauri (Uljanin, 1884) into a Temperate Bay, China. Water 2022, 14, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Schoeman, D.S. Climate Impact on Plankton Ecosystems in the Northeast Atlantic. Science 2004, 305, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Choo, S.; Soh, H.Y. Influence of Rainfall Events on Zooplankton Community Characteristics and Feeding Habits in Estuarine–Coastal Environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 950695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.; Kwak, M.T.; Cho, Y.K.; Yoon, Y.H.; Soh, H.Y. Effects of Water Masses on the Zooplankton Community Structure in the Northern East China Sea during the East Asian Summer Monsoon in 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station | Latitude (° N) | Longitude (° E) | Season | Spring | Autumn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||||
| Month | May | - | Apr. | Apr. | May | Sep. | - | Sep. | Oct. | Oct. | ||||
| Depth | ||||||||||||||
| SS01 | 34°41.5757′ | 127°50.4593′ | 15 | ○ | N/S | ○ | ○ | ○ | N/S | ○ | ○ | |||
| SS02 | 34°27.4718′ | 127°52.8835′ | 32 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| SS03 | 34°13.2107′ | 127°53.0974′ | 71 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||
| SS04 | 33°57.4283′ | 127°53.2937′ | 85 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| SS05 | 33°41.2990′ | 127°53.3781′ | 109 | ○ | ||||||||||
| SS06 | 33°25.4615′ | 127°53.7604′ | 126 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| SS07 | 33°18.7283′ | 127°21.8809′ | 100 | ○ | ○ | |||||||||
| SS08 | 33°36.3427′ | 127°21.4562′ | 100 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| SS09 | 33°51.5500′ | 127°14.7300′ | 84 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| SS10 | 33°37.4316′ | 126°46.5685′ | 139 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||
| SS11 | 33°50.3540′ | 126°46.7298′ | 46 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| SS12 | 34°02.4341′ | 126°46.5442′ | 46 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||
| SS13 | 34°09.7528′ | 126°47.9587′ | 43 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| SS14 | 34°07.6790′ | 127°08.7964′ | 39 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| SS15 | 34°19.5614′ | 127°28.4323′ | 18 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| Species | Form | Spring | Autumn | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| Cyclosalpa affinis | Aggregate zooid | N/S | * | * | N/S | ||||||
| Cyclosalpa bakeri | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Dolioletta gegenbauri | Gonozooid | * | *** | * | |||||||
| Dolioletta tritonis | Gonozooid | * | |||||||||
| Doliolum denticulatum | Gonozooid | * | * | * | * | ||||||
| Doliolum nationalis | Gonozooid | * | * | * | *** | *** | *** | * | |||
| Salpa fusiformis | Aggregate zooid | * | * | * | * | * | |||||
| Salpa fusiformis | Solitary zooid | * | * | * | |||||||
| Soestia zonaria | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Thalia cicar | Solitary zooid | * | |||||||||
| Thalia cicar | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Thalia orientalis | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Thalia rhomboides | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Thalia sibogae | Aggregate zooid | * | |||||||||
| Species | Temperature (°C) | ΔTemperature | Salinity | ΔSalinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolioletta gegenbauri | 16.9–24.4 | 7.5 | 31.41–34.35 | 2.94 |
| Doliolum denticulatum | 17.4–23.8 | 6.4 | 31.56–34.43 | 2.87 |
| Doliolum nationalis | 14.2–24.7 | 10.5 | 31.41–34.37 | 2.96 |
| Salpa fusiformis | 15.5–22.4 | 6.9 | 32.24–34.54 | 2.30 |
| Spring | Autumn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA1 | CCA2 | CCA1 | CCA2 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.4502 | 0.2276 | 0.1196 | 0.06398 |
| Proportion (%) | 60.4 | 30.5 | 59.1 | 31.6 |
| Cumulative Proportion (%) | 60.4 | 90.9 | 59.1 | 90.7 |
| Reference | Liao et al. (2013) [3] | Franco et al. (2017) [43] | Xu et al. (2006) [44] | Li et al. (2011) [46] | Ishak et al. (2020) [15] | Ishak et al. (2022) [16] | Kim et al. (2011) [45] | This Study | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Taiwan | China | Japan | South Korea | South Korea | ||||
| Region | Around Taiwan | East China Sea | South China Sea | North Pacific Ocean | Neighboring Waters of South Korea | Southern Sea of South Korea | |||
| Season | Summer, Winter | - | Summer, Winter | Summer | - | Spring | Autumn | ||
| Brooksia rostrata | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Cyclosalpa affinis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Cyclosalpa bakeri | ● | ● | |||||||
| Cyclosalpa floridana | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Cyclosalpa pinnata | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Cyclosalpa polae | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Cyclosalpa quadriluminis | ● | ● | |||||||
| Cyclosalpa sewelli | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Dolioletta gegenbauri | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Dolioletta tritonis | ● | ||||||||
| Doliolina mulleri | ● | ● | |||||||
| Doliolum denticulatum | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Doliolum nationalis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Iasis cylindrica | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Ihlea punctata | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Pegea confoederata | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Ritteriella amboinensis | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Ritteriella picteti | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Salpa aspera | ● | ||||||||
| Salpa fusiformis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Salpa maxima | ● | ● | |||||||
| Salpa younti | ● | ||||||||
| Soestia zonaria | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| Thalia cicar | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Thalia democratica | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Thalia orientalis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Thalia rhomboides | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Thalia sibogae | ● | ● | |||||||
| Traustedtia multitentaculata | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-U.; Jeong, Y.S.; Choo, S.; Soh, H.Y. Variation in the Occurrence of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages in the Northeastern East China Sea from 2019 to 2023. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060862
Choi H-U, Jeong YS, Choo S, Soh HY. Variation in the Occurrence of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages in the Northeastern East China Sea from 2019 to 2023. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(6):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060862
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyung-Uk, Young Seok Jeong, Seohwi Choo, and Ho Young Soh. 2024. "Variation in the Occurrence of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages in the Northeastern East China Sea from 2019 to 2023" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 6: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060862
APA StyleChoi, H.-U., Jeong, Y. S., Choo, S., & Soh, H. Y. (2024). Variation in the Occurrence of Salp and Doliolid Assemblages in the Northeastern East China Sea from 2019 to 2023. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(6), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060862







