Formation Mechanism of NW-Trending Faults and Their Significance on Basin Evolution in Zhu III Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, SE China
Abstract
1. Introduction
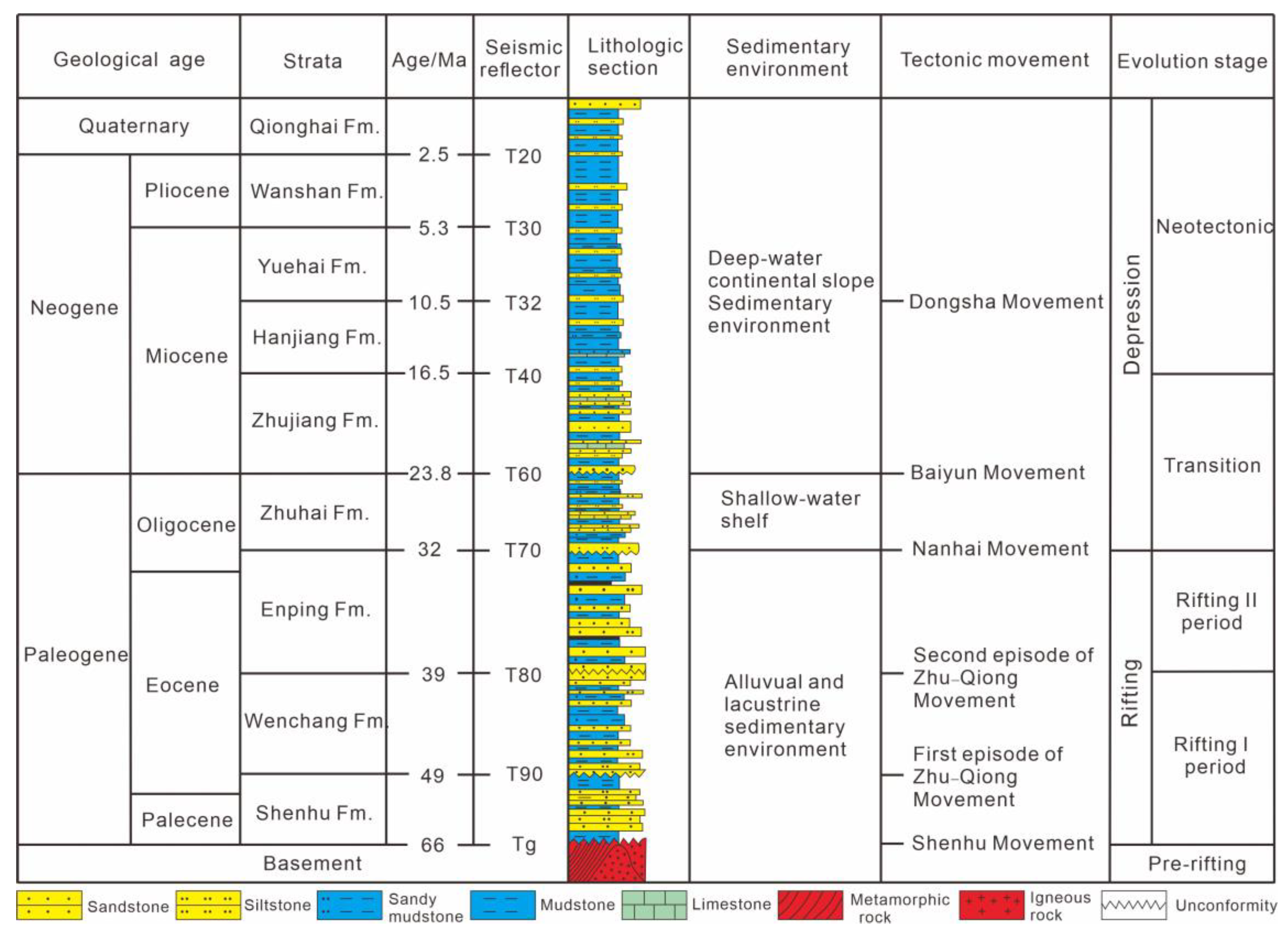
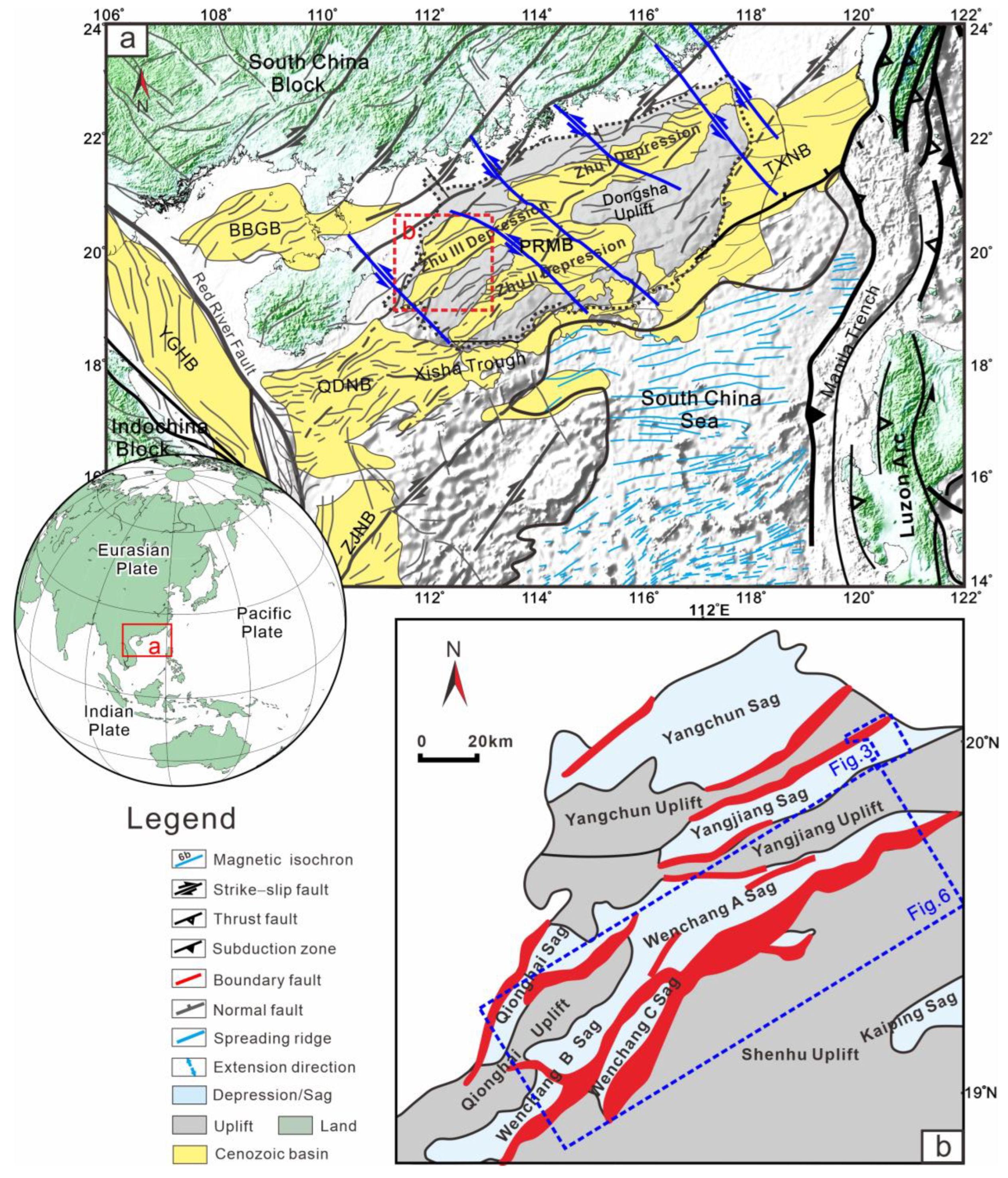
2. Geological Setting
3. Data and Methods
4. Results
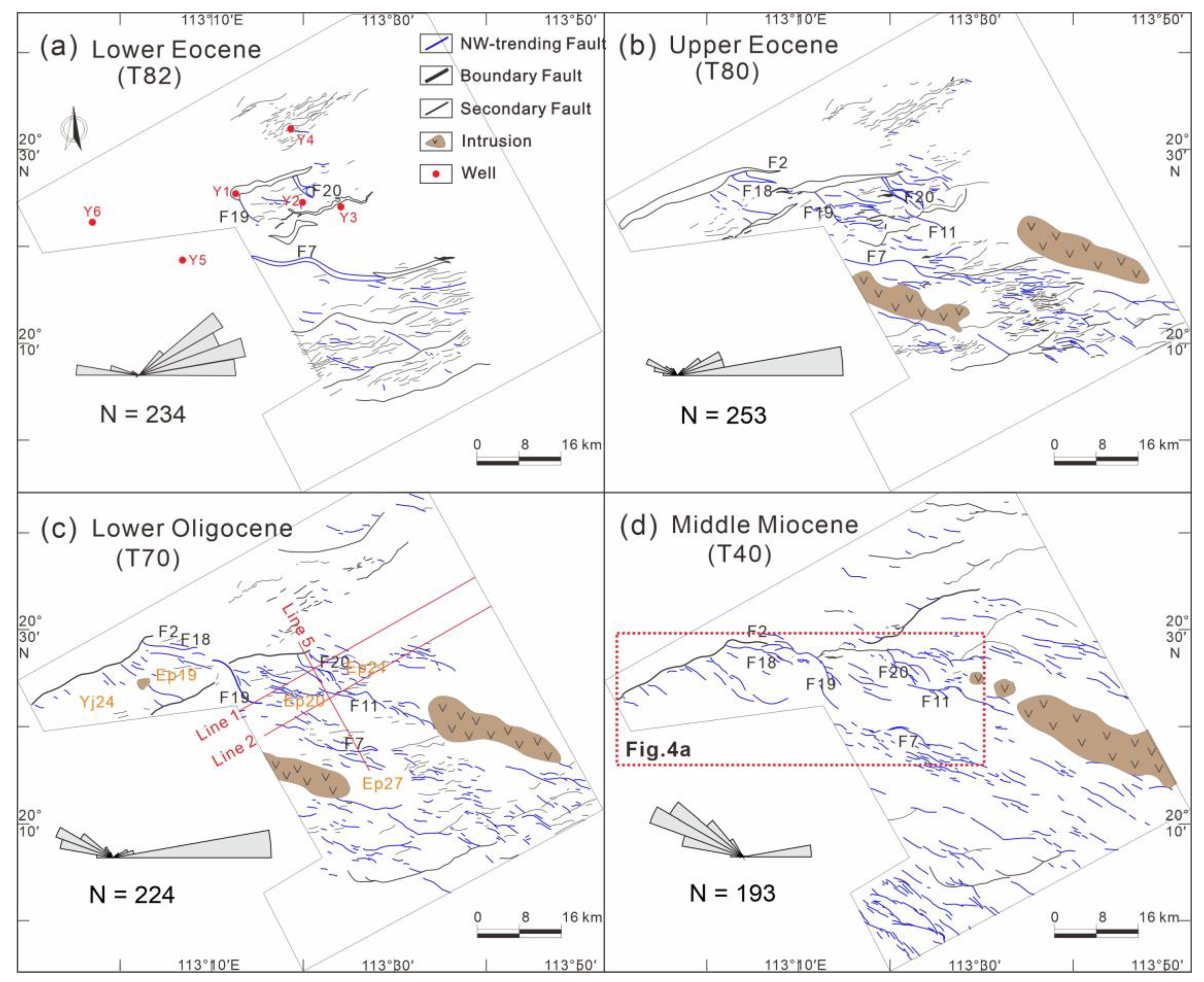
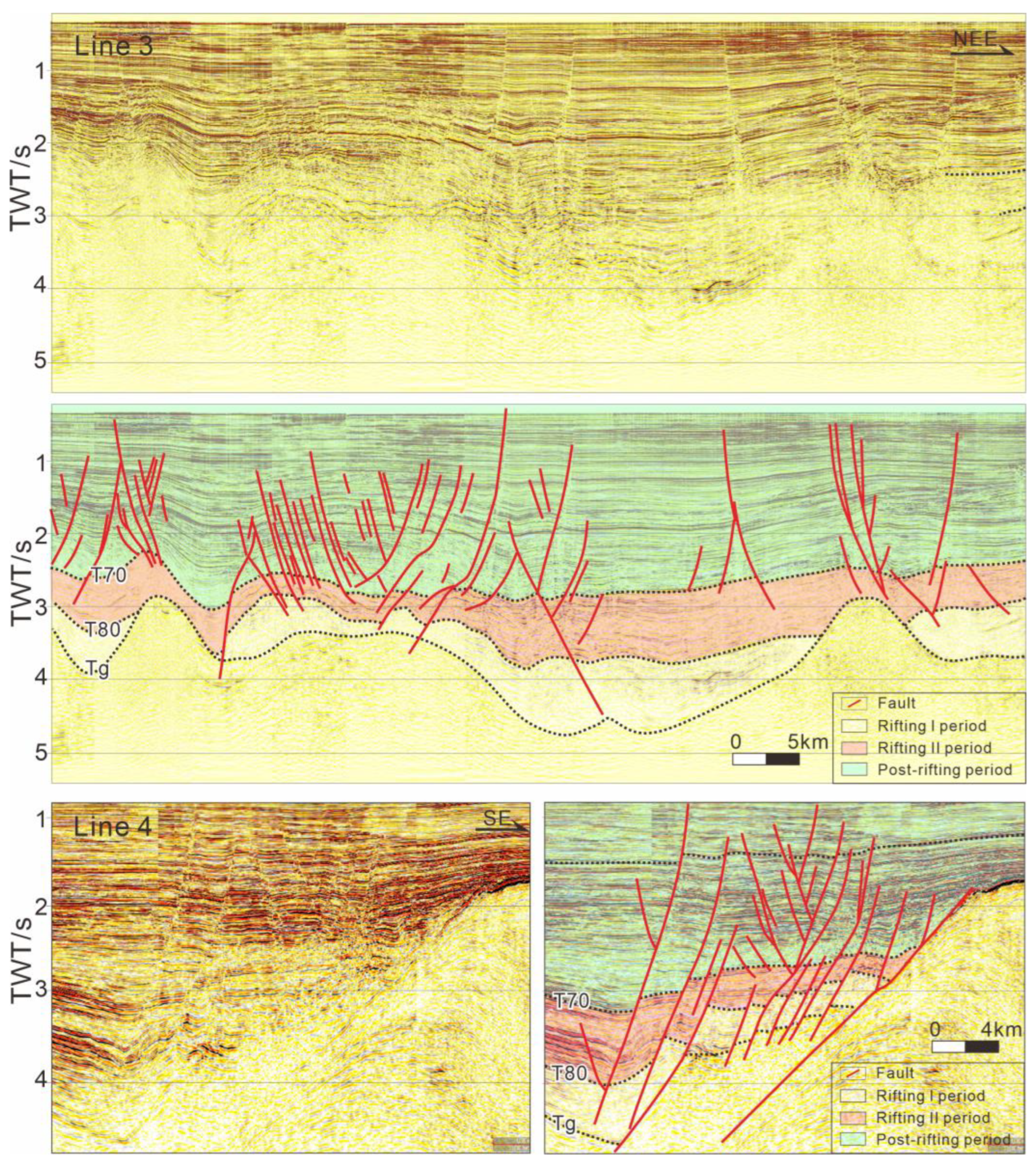
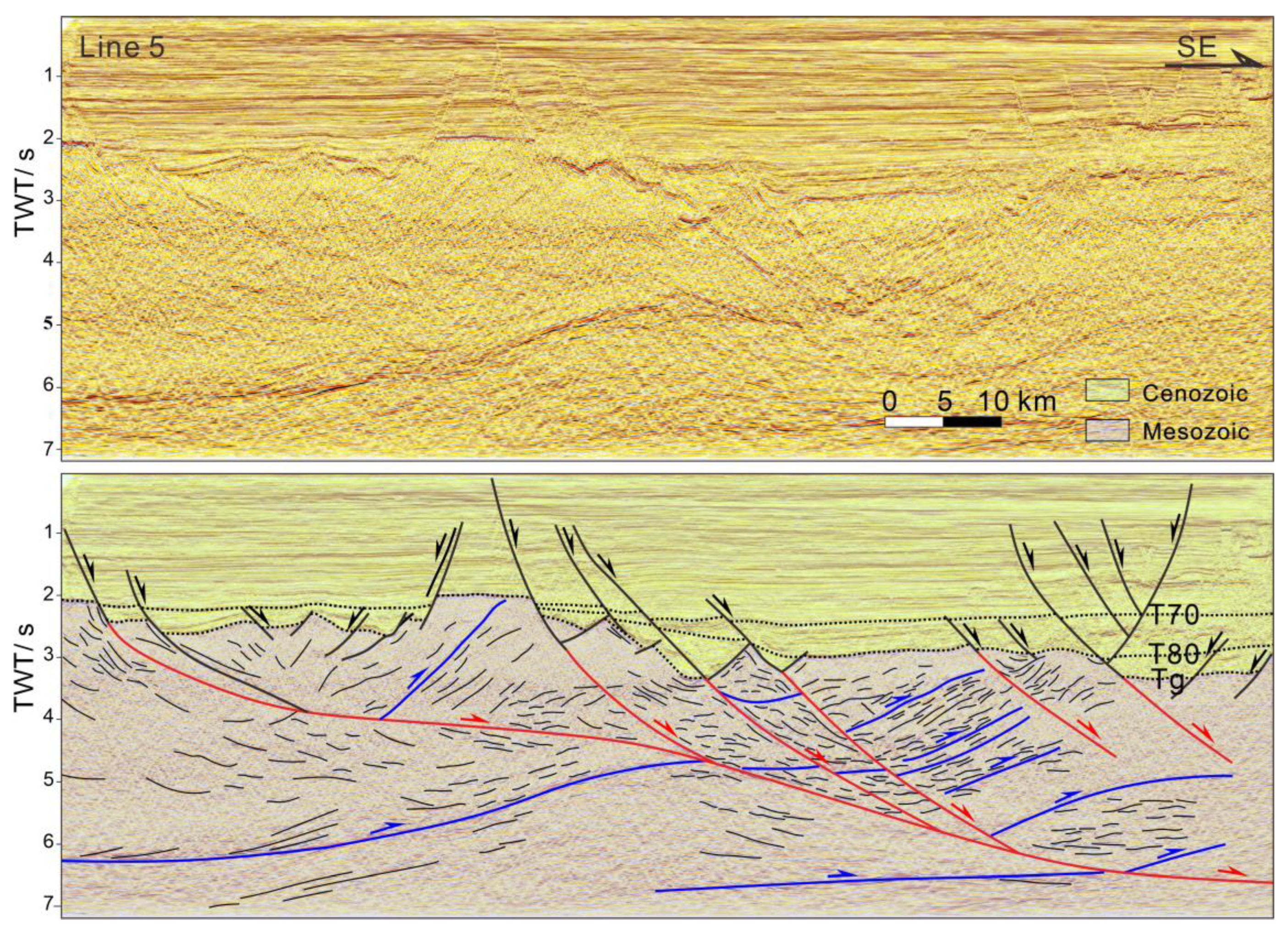
4.1. Fault Patterns of the Yangjiang Sag
4.2. Fault Patterns of the Wenchang Sag
5. Discussion
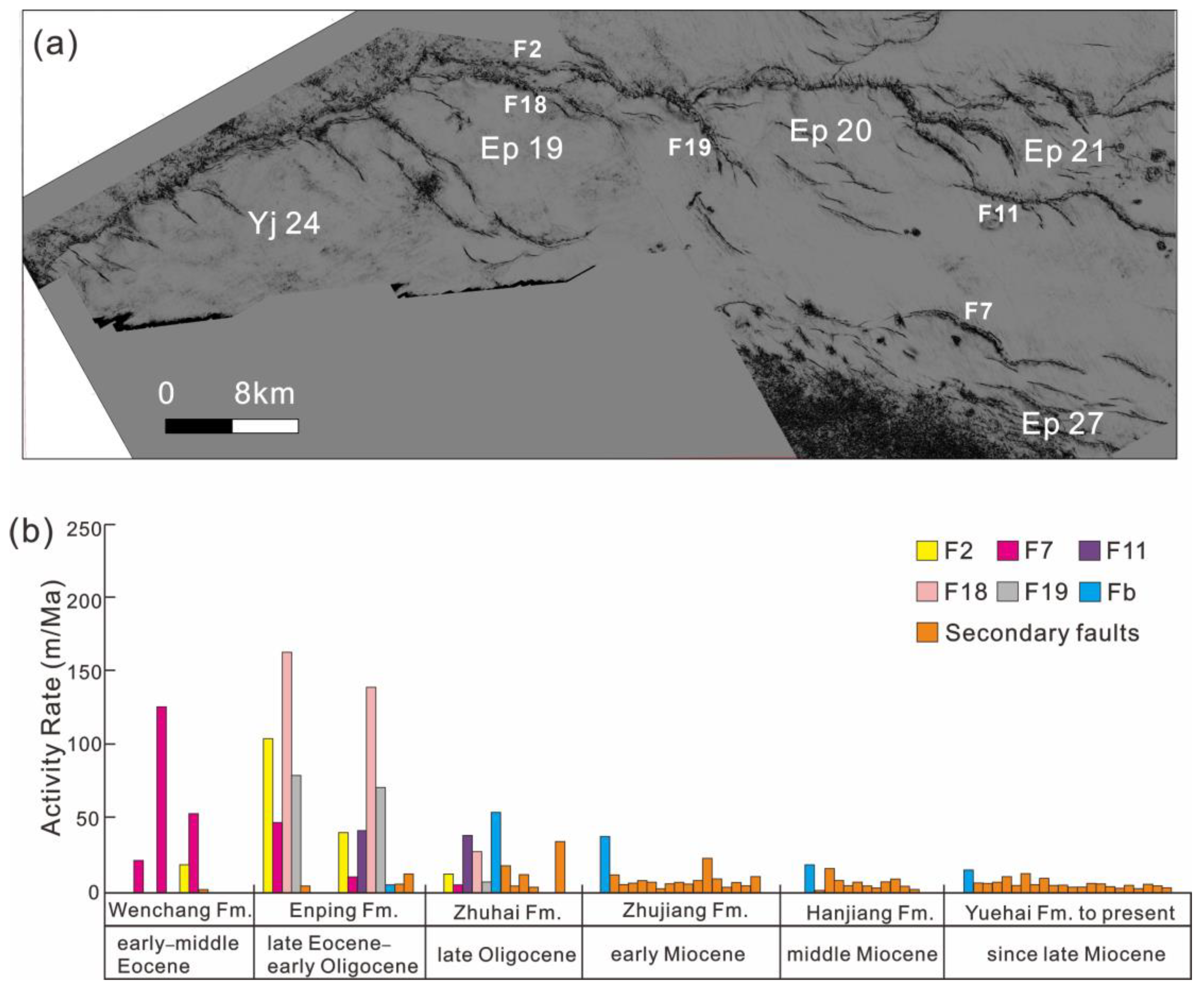
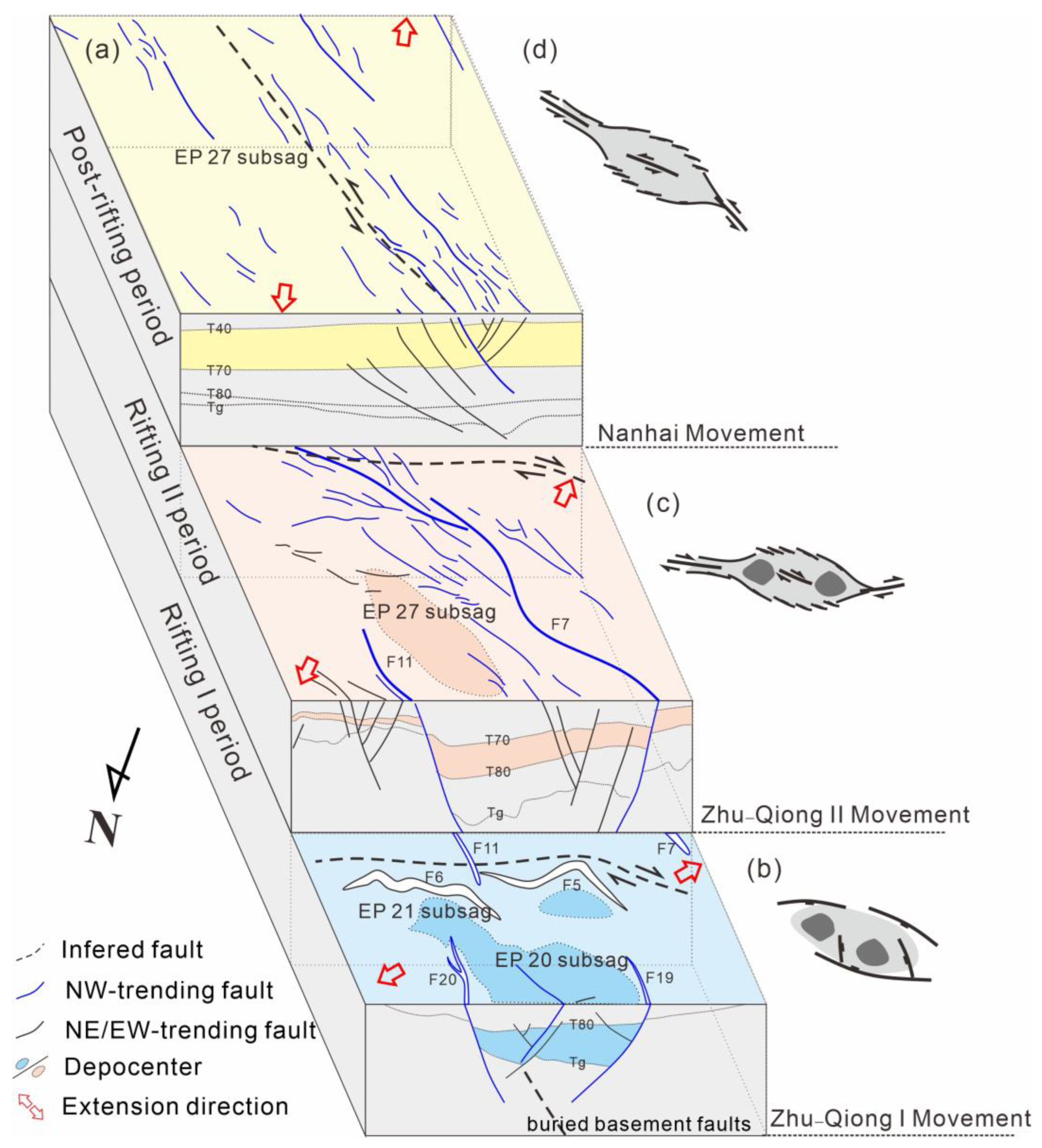
5.1. Development Stages of NW-Trending Faults
5.2. Genetic Types and Formation Mechanism
5.3. Geodynamic Process
5.4. Significance on Basin Evolution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.P.; Li, W.; Ren, C.J.; Li, C.S. Basin Evolution in the Mesozoic and Superposition of Cenozoic Basin in the area of the Jiyang Depression. Acta Geol. Sin. 2003, 77, 280–286, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Y.B.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhao, D.J.; Hao, F.; Wang, Z.F.; Tian, J.Q. The origin and distribution of crude oil in Zhu III sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 732–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Lou, R.; Wang, Q. Fault reactivation in No.4 structural zone and its control on oil and gas accumulation in Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgaier, F.; Busch, B.; Hilgers, C. Fault leakage and reservoir charging in the Upper Rhine Graben, Germany—Assessment of the Leopoldshafen fault bend. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 156, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, H.; Moustafa, A.R. Impact of structural geometry of tilted fault blocks on hydrocarbon entrapment and deposition of syn–rift clastic reservoirs: Belayim Marine field (Gulf of Suez rift). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmagh, N.M.; Lin, W.R.; Radwan, A.E.; Manshad, A.K. Comprehensive analysis of stress magnitude and orientations and natural fractures in complex structural regimes oil reservoir: Implications for tectonic and oil field development in the Zagros suture zone. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhong, Z.H.; Keep, M.; Zhou, D.; Cai, D.S.; Li, X.S.; Wu, S.M. 3D analogue modeling of the South China Sea: A discussion on breakup pattern. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Suo, Y.H.; Peng, G.R.; Li, S.Z.; Du, X.D.; Chao, X.Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G.Z.; Santosh, M.; Jiang, S.H.; et al. Three-stage extension in the Cenozoic Pearl River Mouth Basin triggering onset of the South China Sea spreading. Gondwana Res. 2023, 120, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Carter, A.; Hoang, L.V.; Fox, M.; Pham, S.N.; Vinh, H.B. Evolution of the continental margin of South to Central Vietnam and its relationship to opening of the South China Sea (East Vietnam Sea). Tectonics 2022, 41, e2021TC006971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.H.; Zheng, Q.G.; Li, J.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.R. Formation and evolution of Zhu-3 south fault and its control on the depocenter shift in Zhu-3 depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 33, 807–813, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Gan, J.; Lu, J.; Zhan, Z.P. The style distribution and hydrocarbon accumulation of inverted structures in Zhu-3 depression. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2014, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Y.B.; Liu, J.Z.; Hao, F.; Bao, X.H.; Xu, S.; Teng, C.Y.; Wang, Z.F. Geochemical characteristics and origins of natural gas in the Zhu III sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 101, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, N.; Haszeldine, R.S.; Shu, Y.T.; Stewart, R.J.; Scott, V.; Wilkinson, M. CO2 sequestration with limited sealing capability: A new injection and storage strategy in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (China). Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2018, 68, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Chen, S.J.; You, J.J.; Li, H.; Lei, M.Z. Geochemical characteristics and sources of crude oil in the Wenchang B depression and the Western Qionghai uplift of the Zhu-3 sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 219, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.G.; Li, J.L.; Lei, B.H.; Song, P.; Li, Q.; Shi, D.F.; Liu, H.; Lin, C.S. Differential tectonic evolution and formation mechanism of three subsags in Wenchang Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.W.; Dong, Y.L.; Tan, M.X.; Chen, H.H.; Sun, L.P.; Shun, L.P.; Li, S.L.; Zhao, X.M. Tecono-stratigraphy of Paleogene Zhu-3 depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea: Implications for syn-rift architecture in multiphase rifts. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Pang, X.; Tang, D.Q.; Liu, B.J.; Xu, D.H. Transtensional tectonism and its effects on the distribution of sandbodies in the Paleogene Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2013, 34, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ye, Q.; Mei, L.F.; Shi, H.S.; Camanni, G.; Shu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, L.; Deng, P.; Li, G. The Late Cretaceous tectonic evolution of the South China Sea area, An overview, and new perspectives from 3D seismic reflection data. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 187, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.H.; Li, S.Z.; Peng, G.R.; Du, X.D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, G.Z.; Somerville, I.; Diao, Y.X.; Liu, Z.Q.; et al. Cenozoic basement-involved rifting of the northern South China Sea margin. Gondwana Res. 2022, 120, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Mei, L.F.; Pang, X.; Zheng, J.Y.; Ye, Q.; Hao, S.H. Magmatism within the northern margin of the South China Sea during the post-rift stage: An overview, and new insights into the geodynamics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 225, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.L.; Peng, G.R.; Zhu, D.W.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Zhan, H.W.; Zhao, L.T. Structure and formation mechanism of the Pearl River Mouth basin: Insights from multi-phase strike-slip motions in the Yangjiang Sag, SE China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 226, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Li, W.; Fan, C.W.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Meng, M.F. Control of the Cenozoic transformation in regional extension direction on the development and evolution of fault system in Zhusan Depression. Mar. Geol. Front. 2023, 39, 52–65, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.D.; Peng, G.R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Xu, X.M.; Zhu, D.W. Faults and Its Impacts on Petroleum Accumulation in Eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 2020, 41, 414–421, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Peng, G.R.; Zhu, D.W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Du, X.D.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H. Fault-controlled Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Eastern Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2021, 45, 123–130, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Gan, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, B.; Deng, G.J.; Zheng, R.F.; Wu, Y.Y.; Cao, Z. Strike-slip deformation mechanism and its petroleum geology significance along south fault in Zhu III depression under extensional tectonic setting. China Offshore Oil Gas 2013, 25, 9–15, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.F.; Zhou, J.X.; Yang, X.B.; You, J.J.; Li, S.S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. The different extension and strike-slip mechanism and its accumulation controlling effect in Wenchang B sag. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 2422–2432, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, H.W.; Wang, G.Z.; Peng, G.R.; Suo, Y.H.; Wang, P.C.; Du, X.D.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.Z.; Zhu, D.W. Cenozoic evolution of the Yangjiang-Yitong’ansha fault zone in the northern South China Sea: Evidence from 3D seismic data. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1070004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, P.; Lin, J. Preferential mantle lithospheric extension under the South China margin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2001, 18, 929–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.N.; Ren, J.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, X.S.; Lei, C. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Barckhausen, U.; Engels, M.; Franke, D.; Ladage, S.; Pubellier, M. Reply to chang et al. 2014, evolution of the South China Sea: Revised ages for breakup and seafloor spreading. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.L.; Li, C.F.; Wang, L.J.; Liu, Y.T.; Peng, X.; Yao, Z.W.; Yao, Y.J. The onset of seafloor spreading at the northeastern continent-ocean boundary of the South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 133, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Hu, L.; Wang, S.C.; Lei, M.Z.; Li, M.; Hu, Q.M.; Liu, K. Structural characteristics and reservoir-control mechanism of Wenchang 9-7 transfer slope zone in Zhu III Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2023, 28, 83–93, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, P.; Tapponnier, P. Relation of the tectonics of eastern China to the India-Eurasia collision: Application of slip-line field theory to large-scale continental tectonics. Geology 1977, 5, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: A preliminary synthesis. Tectonophysics 2010, 488, 293–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Ben-Avraham, Z.; Kelty, T.; Yu, H.S. Origin of marginal basins of the NW Pacific and their plate tectonic reconstructions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 130, 154–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Faccenna, C.; Becker, T.; Tesauro, M.; Sternai, P.; Bouilhol, P. Mantle Flow and Deforming Continents: From India-Asia Convergence to Pacific Subduction. Tectonics 2018, 37, 2887–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.C.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Guo, L.L.; Santosh, M.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, G.Z.; Jiang, Z.X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, J.; et al. Structural and kinematic analysis of Cenozoic rift basins in South China Sea: A synthesis. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton-Johnson, A.; Cullen, A.B. Continental rifting in the South China Sea through extension and high heat flow: An extended history. Gondwana Res. 2023, 120, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, S.M. Meso-Cenozoic tectonothermal pattern of the Pearl River Mouth Basin: Constraints from zircon and apatite fission track data. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Wu, J.S.; Chen, B.; Zhong, H.Z.; Hao, H.J.; Li, P.L.; Su, N.E. Integrated geophysical researches on base texture of Zhujiang River Mouth Basin. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2002, 21, 13–22, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Z.; Wu, X.J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, W.Y.; He, H.J. Meso-Cenozoic faults in Zhujiang River Mouth Basin and their geodynamics background. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2005, 24, 52–61, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zhou, D.; Sun, L.T.; Chen, C.M.; Pang, X.; Jiang, J.Q.; Fan, H. Dynamic Analysis on Rifting Stage of Pearl River Mouth Basin through Analogue Modeling. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 21, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.L. Cenozoic tectonic movement in the Pearl River Mouth Basin. China Offshore Oil Gas 1993, 7, 11–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.R.; Liu, W.L.; Wan, Z.F.; Guo, F. Determination of Cenozoic tectonic movement in the northern South China Sea and the relationship between oil-gas reservoir and tectonic movement. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2010, 29, 161–165, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Xiao, J.; Chen, S.P.; Lin, Z.L. Control of Paleomorphology to Sedimentary Filling in Marginal Sea Basin—By Taking Zhu III Depression for Example. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2008, 30, 10–16, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Lin, C.S.; Zhang, Z.T.; Zhang, B.; Shu, L.F.; Feng, X.; Hong, F.H.; Xing, Z.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Su, E.Y. Breakup unconformities at the end of the early Oligocene in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea: Significance for the evolution of basin dynamics and tectonic geography during rift-drift transition. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2019, 40, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C.K. Major unconformities/termination of extension events and associated surfaces in the South China Seas: Review and implications for tectonic development. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 120, 62–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuet, J.; Yeh, Y.; Lee, C. Geodynamics of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2016, 692, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.C.; Liu, G.D.; Ge, J.W.; Zhang, X.T.; Cao, Z.; Lei, Y.C.; Yuan, A.; Zhang, M.Y. Geochemical characteristics and depositional environment of Paleogene lacustrine source rocks in the Lufeng sag, Pearl River Mouth basin, South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 171, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.R.; Zhang, X.T.; Xu, X.M.; Bai, H.J.; Cai, G.F.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.W. Important discoveries and understandings of oil and gas exploration in Yangjiang sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. China Pet. Explor. 2019, 24, 267–279, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nanni, U.; Pubellier, M.; Chan, L.S.; Senell, R.J. Rifting and reactivation of a Cretaceous structural belt at the northern margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 136, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yu, Y.X.; Zhang, X.T.; Peng, G.R.; Niu, S.L.; Qiu, X.W.; Lu, M.S.; He, Y.B. Multiphase faults activation in the southwest Huizhou Sag, Pearl River Mouth basin: Insights from 3D seismic data. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 152, 106257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Cao, X.Z.; Wang, G.Z.; Liu, B.; Li, X.Y.; Suo, Y.H.; Jiang, Z.X.; Guo, L.L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.C.; et al. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and plate reconstruction of the Pacific Plate. J. Geomech. 2019, 25, 642–677, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, H.W.; Cai, G.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, Y.W.; Suo, Y.H.; Wang, P.C.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, B.; Guo, L.L.; et al. Paleogene fault activity and basin controlling characteristics in the northern South China Sea margin—A case study of the eastern Yangjiang sag. Geotecton. Metallog. 2021, 45, 20–39, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Lei, B.H.; Zheng, Q.G.; Duan, L.; Yan, Y. Stress Field Evolution and its Controls on Oil Accumulation in the Wenchang Sag. Geotecton. Metallog. 2015, 39, 601–609, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.D.; Cao, X.Z.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, F.K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. NE-Trending transtensional faulting in the Pearl River Mouth basin of the northern South China Sea margin. Gondwana Res. 2022, 120, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalán, P.V. Identification of strike-slip faults in seismic sections. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1987; pp. 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.P.; Liu, W.H.; Xu, L.G.; Zheng, L.H. Identification of strike-slip fault and its petroleum geology significance. Pet. Geol. 2007, 1, 17–23, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.J.; Chen, D.X.; Chang, L.; Li, J.H.; Yin, Z.J. Migration and accumulation of crude oils in the Qionghai Uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin, Offshore South China Sea. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Alves, T.M.; Xia, S.H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Mi, L.J.; Wu, S.G.; Cao, J.H.; Fan, C.Y. Along-strike segmentation of the South China Sea margin imposed by inherited pre-rift basement structures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 530, 115862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Bai, Z.Z.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, L.Z.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; He, T.; Ma, R.Y. Tectonic framework research in Zhujiang River Mouth Basin based on gravity and magnetic data. Haiyang Xuebao 2023, 45, 25–43, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.Y. Genesis of Cenozoic basins in northwest Pacific margin (2): Linked dextral pull-apart basin system. Oil Gas Geol. 2000, 21, 185–190, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Bukhari, S.W.H.; Ding, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Cheng, H.; Somerville, I. Evolution of pull-apart basins with overlapping NE-trending strike-slip fault systems in the northern South China Sea margin: Insight from numerical modeling. Tectonophysics 2023, 846, 229679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Sun, L.T.; Pang, X.; Yan, C.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Zhao, Z.X.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, C.M. The mechanism of post-rift fault activities in Baiyun sag, Pearl River Mouth basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 89, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.F.; Zhang, X.T.; Peng, G.R.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.J.; Bai, H.J.; Li, Z.S.; Ma, X.N.; Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H. Neogene volcanism and tectonics along the Yangjiang-Yitong’ansha Fault Zone in the Northern South China Sea margin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2021, 45, 40–52, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.C.; Qu, H.J.; Jia, Q.J.; Zhang, L.G.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; Ji, M.; Sun, R.; Guan, L.M.; Hayat, K. Passive continental margin segmentation of the marginal seas and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of the northern continental margin in South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 123, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.W.; Xu, C.G.; Wang, D.Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Xiao, S.G.; Zhou, X. Superimposed characteristics and genetic mechanism of strike–slip faults in the Bohai Sea, China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 254–267, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-based reconstructions and animations. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 20, 353–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; Stock, J.M. Slowing of India’s convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics. Tectonics 2009, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, A.; Avouac, J.-P.; Royer, J.-Y. India-Asia collision and the Cenozoic slowdown of the Indian plate: Implications for the forces driving plate motions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhu, R.W.; Liu, H.L.; Qiu, X.L.; Huang, H.B. The Cenozoic activities of Yangjiang-Yitongdong Fault: Insights from analysis of the tectonic characteristics and evolution processes in western Zhujiang (Pearl) River Mouth Basin. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, C.J.; Royden, L.H.; Burchfiel, B.C. Motion of the Pacific Plate relative to Eurasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extension along the eastern margin of Eurasia. Geology 1995, 23, 719–722. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.D.; Seton, M.; Zahirovic, S.; Williams, S.E.; Cannon, J. Ocean Basin Evolution and Global-Scale Plate Reorganization Events Since Pangea Breakup. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 44, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Tamaki, K.; Li, S.T.; Zhang, J.X. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in Eastern China and adjacent areas. Tectonophysics 2002, 344, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Suo, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Cao, X.Z.; Wang, P.C.; Guo, L.L.; Yu, S.Y.; Lan, H.Y.; Li, S.J.; et al. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1550–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Shi, H.S.; Mei, L.F.; Shu, Y.; Liu, H.L.; Wei, T.; Yan, H. Post-Rift Faulting Migration, Transition and Dynamics in Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Sci. 2017, 42, 105–118, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Mu, D.; Chen, Y.; Rong, P. Formation Mechanism of NW-Trending Faults and Their Significance on Basin Evolution in Zhu III Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, SE China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060858
Zhu P, Zhao L, Zhang J, Mu D, Chen Y, Rong P. Formation Mechanism of NW-Trending Faults and Their Significance on Basin Evolution in Zhu III Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, SE China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(6):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060858
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Pengfei, Lintao Zhao, Jiantai Zhang, Dunling Mu, Yichun Chen, and Pengfei Rong. 2024. "Formation Mechanism of NW-Trending Faults and Their Significance on Basin Evolution in Zhu III Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, SE China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 6: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060858
APA StyleZhu, P., Zhao, L., Zhang, J., Mu, D., Chen, Y., & Rong, P. (2024). Formation Mechanism of NW-Trending Faults and Their Significance on Basin Evolution in Zhu III Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, SE China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(6), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060858